Deck 15: Quantile Regression, Count Data, Sample Selection Bias, and Quasi-Experimental Methods
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/29
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Quantile Regression, Count Data, Sample Selection Bias, and Quasi-Experimental Methods
1
You can control for sample-selection bias by performing
A)two-stage least squares.
B)weighted least squares.
C)a Heckman selection correction.
D)difference-in-difference estimation.
A)two-stage least squares.
B)weighted least squares.
C)a Heckman selection correction.
D)difference-in-difference estimation.
C
2
Sample-selection bias occurs when
A)the researcher selects a bad sample.
B)the sample contains an independent variable that is correlated with the error term.
C)individuals randomly select the sample to which they belong.
D)individuals non-randomly select themselves into a given outcome of the dependent variable.
A)the researcher selects a bad sample.
B)the sample contains an independent variable that is correlated with the error term.
C)individuals randomly select the sample to which they belong.
D)individuals non-randomly select themselves into a given outcome of the dependent variable.
D
3
Sample-selection bias presents a problem because it
A)results in OLS coefficient estimates that are biased and inconsistent.
B)does not account for the correlation between the independent variable and the error term.
C)does not account for the time-invariant component of the error term.
D)does not account for the autoregressive structure of the error term.
A)results in OLS coefficient estimates that are biased and inconsistent.
B)does not account for the correlation between the independent variable and the error term.
C)does not account for the time-invariant component of the error term.
D)does not account for the autoregressive structure of the error term.
A
4
Non-negative count data occur when the dependent variable takes on
A)only positive values.
B)the values of 0 or 1.
C)integers that are greater than or equal to 0 and arise from counting.
D)integers that are strictly greater than 0 and arise from counting rather than ranking.
A)only positive values.
B)the values of 0 or 1.
C)integers that are greater than or equal to 0 and arise from counting.
D)integers that are strictly greater than 0 and arise from counting rather than ranking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When performing difference-in-difference estimation,the control group is the group
A)for which the policy shock occurred.
B)for which the policy shock did not occur.
C)of observation in the "before" sample.
D)of observation in the "after" sample.
A)for which the policy shock occurred.
B)for which the policy shock did not occur.
C)of observation in the "before" sample.
D)of observation in the "after" sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Quantile regression
A)estimates marginal effects at the mean values of the independent variables.
B)results in biased estimates for skewed distributions.
C)can be estimated in Excel.
D)results in estimates approximating either the median or other percentiles of the dependent variable.
A)estimates marginal effects at the mean values of the independent variables.
B)results in biased estimates for skewed distributions.
C)can be estimated in Excel.
D)results in estimates approximating either the median or other percentiles of the dependent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Quantile regression is different than OLS in that it
A)does not estimate marginal effects at the mean values of the dependent and independent variables.
B)only uses the data below the quantile where the quantile regression is being estimated.
C)estimates marginal effects at the mean values of the dependent and independent variables.
D)minimizes the sum of squared residuals to obtain the coefficient estimates.
A)does not estimate marginal effects at the mean values of the dependent and independent variables.
B)only uses the data below the quantile where the quantile regression is being estimated.
C)estimates marginal effects at the mean values of the dependent and independent variables.
D)minimizes the sum of squared residuals to obtain the coefficient estimates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The first-stage in the Heckman selection correction is estimating
A)the individual's self-selection decision and using those estimates to calculate predicted values of the self-selection decision.
B)estimating the regression model and calculating the residuals.
C)the individual's self-selection decision and using those estimates to calculate inverse Mill's ratios.
D)estimating the regression model and calculating the residuals and using those estimates to calculate predicted values of the dependent variable.
A)the individual's self-selection decision and using those estimates to calculate predicted values of the self-selection decision.
B)estimating the regression model and calculating the residuals.
C)the individual's self-selection decision and using those estimates to calculate inverse Mill's ratios.
D)estimating the regression model and calculating the residuals and using those estimates to calculate predicted values of the dependent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose you wish to determine factors affecting the number of surfers observed surfing at a given surf spot,an appropriate model to estimate the model would be
A)OLS.
B)the logit.
C)the ordered probit.
D)the Poisson model.
A)OLS.
B)the logit.
C)the ordered probit.
D)the Poisson model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In which of the following cases would you want to estimate a Negative Binomial model?
A)When individuals non-randomly select different outcomes of the dependent variable.
B)When you are attempting to replicate a randomized clinical trial.
C)When you are dealing with non-negative count data.
D)When you suspect that the marginal effects are different for different values of the dependent variable.
A)When individuals non-randomly select different outcomes of the dependent variable.
B)When you are attempting to replicate a randomized clinical trial.
C)When you are dealing with non-negative count data.
D)When you suspect that the marginal effects are different for different values of the dependent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Quasi-experimental methods attempt to
A)control for sample-selection bias.
B)estimate marginal effects at different points in the distribution of the dependent variable.
C)account for endogeneity of an independent variable.
D)replicate randomized clinical trials.
A)control for sample-selection bias.
B)estimate marginal effects at different points in the distribution of the dependent variable.
C)account for endogeneity of an independent variable.
D)replicate randomized clinical trials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
You can choose between the Poisson and the Negative Binomial models by performing a
A)test of over-dispersion.
B)Poisson choice test.
C)Negative Binomial test.
D)test of overall significance of the Poisson model.
A)test of over-dispersion.
B)Poisson choice test.
C)Negative Binomial test.
D)test of overall significance of the Poisson model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In which of the following cases would you want to estimate a Poisson model?
A)When individuals non-randomly select different outcomes of the dependent variable.
B)When you are attempting to replicate a randomized clinical trial.
C)When you are dealing with non-negative count data.
D)When you suspect that the marginal effects are different for different values of the dependent variable.
A)When individuals non-randomly select different outcomes of the dependent variable.
B)When you are attempting to replicate a randomized clinical trial.
C)When you are dealing with non-negative count data.
D)When you suspect that the marginal effects are different for different values of the dependent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Non-negative count data presents a challenge because OLS estimates
A)are biased.
B)cannot be calculated.
C)are heteroskedastic.
D)are the BLUE.
A)are biased.
B)cannot be calculated.
C)are heteroskedastic.
D)are the BLUE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The second-stage in the Heckman selection correction is including the _____ in the second-stage regression to control for the potential sample-selection bias.
A)estimated residuals
B)calculated inverse Mills ratios
C)predicted value of the dependent variable
D)predicted value of the self-selection variable
A)estimated residuals
B)calculated inverse Mills ratios
C)predicted value of the dependent variable
D)predicted value of the self-selection variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Difference-in-difference estimators attempt to
A)attempt to replicate randomized clinical trials by comparing treatment and control groups before and after a treatment is imposed to estimate the impact of a given policy intervention.
B)take differences of both the dependent and independent variables.
C)only difference the dependent variables and regress the differences on the independent variables.
D)obtain estimates at points in the distribution of the dependent variable aside from the mean.
A)attempt to replicate randomized clinical trials by comparing treatment and control groups before and after a treatment is imposed to estimate the impact of a given policy intervention.
B)take differences of both the dependent and independent variables.
C)only difference the dependent variables and regress the differences on the independent variables.
D)obtain estimates at points in the distribution of the dependent variable aside from the mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose you wish to explain the number of nights per week that individuals eat dinner at a restaurant,an appropriate model to estimate would be
A)Weighted Least Squares.
B)the negative binomial model.
C)OLS.
D)the probit.
A)Weighted Least Squares.
B)the negative binomial model.
C)OLS.
D)the probit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In which of the following cases would you want to use a Heckman selection correction model?
A)When individuals non-randomly select different outcomes of the dependent variable.
B)When you are attempting to replicate a randomized clinical trial.
C)When you are dealing with non-negative count data.
D)When you suspect that the marginal effects are different for different values of the dependent variable.
A)When individuals non-randomly select different outcomes of the dependent variable.
B)When you are attempting to replicate a randomized clinical trial.
C)When you are dealing with non-negative count data.
D)When you suspect that the marginal effects are different for different values of the dependent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When performing difference-in-difference estimation,the treatment group is the group
A)for which the policy shock occurred.
B)for which the policy shock did not occur.
C)of observation in the "before" sample.
D)of observation in the "after" sample.
A)for which the policy shock occurred.
B)for which the policy shock did not occur.
C)of observation in the "before" sample.
D)of observation in the "after" sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In which of the following cases would you want to use quantile regression?
A)When individuals non-randomly select different outcomes of the dependent variable.
B)When you are attempting to replicate a randomized clinical trial.
C)When you are dealing with non-negative count data.
D)When you suspect that the marginal effects are different for different values of the dependent variable.
A)When individuals non-randomly select different outcomes of the dependent variable.
B)When you are attempting to replicate a randomized clinical trial.
C)When you are dealing with non-negative count data.
D)When you suspect that the marginal effects are different for different values of the dependent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose you are interested in testing the claim that students who participate in band perform better on standardized tests but you are worried that the results might be biased because individuals are likely to self-select into joining the band.You only have test scores for those students that participate in band.Suppose that for a sample of 14,111 6th-grade students you estimate the Heckman selection model (marginal effects listed,standard errors in parentheses) 
a)Explain why OLS is inappropriate in this circumstance and how this model improves on OLS.
b)Which variable are you using to identify the model? Does this choice seem correct? Explain.
c)Discuss the results above.

a)Explain why OLS is inappropriate in this circumstance and how this model improves on OLS.
b)Which variable are you using to identify the model? Does this choice seem correct? Explain.
c)Discuss the results above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is quantile regression? When might it be preferred to OLS? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is non-negative count data? Why does it present a concern for OLS? How might you control for non-negative count data in the estimation process? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In which of the following cases would you want to use difference-in-difference estimation?
A)When individuals non-randomly select different outcomes of the dependent variable.
B)When you are attempting to replicate a randomized clinical trial.
C)When you are dealing with non-negative count data.
D)When you suspect that the marginal effects are different for different values of the dependent variable.
A)When individuals non-randomly select different outcomes of the dependent variable.
B)When you are attempting to replicate a randomized clinical trial.
C)When you are dealing with non-negative count data.
D)When you suspect that the marginal effects are different for different values of the dependent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose you are interested in explaining the number of surfers surfing at your favorite spot on a given day.After collecting data on the number of surfers,the height of the waves (in feet),the water temperature,and whether the day was a weekend on a sample of 92 days,you estimate the following marginal effects for the Poisson model 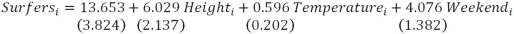
a)Why is OLS not appropriate in this circumstance? How does a Poisson model improve on OLS?
b)Discuss the results.
c)What assumption is necessary for Poisson to be the appropriate model? How would you test this assumption? If this assumption fails,what alternative model could you estimate?
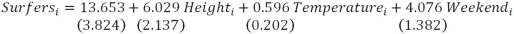
a)Why is OLS not appropriate in this circumstance? How does a Poisson model improve on OLS?
b)Discuss the results.
c)What assumption is necessary for Poisson to be the appropriate model? How would you test this assumption? If this assumption fails,what alternative model could you estimate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose you are interested in explaining the effect that family income (thousands)has on child birth weight and you are concerned that the true marginal effects differ for at different points in the birth weight distribution.In a sample of 22,365 live births,you estimate following 
a)What is quantile regression? Which variable is the quantile of?
b)In what circumstances would quantile regression be preferable to OLS?
c)Discuss the results presented above.

a)What is quantile regression? Which variable is the quantile of?
b)In what circumstances would quantile regression be preferable to OLS?
c)Discuss the results presented above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is sample-selection bias? Why does it present a problem for OLS? How can you control for its presence? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose you observe that several different communities in a large metropolitan area raised their sales tax by one percentage point in 2012 while several others did not.In an effort to determine how the increase affected car sales in the affected communities you estimate a difference-in-difference estimator for 2011 and 2013 car sales and get 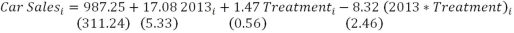
a)Why would you want to estimate a difference in difference model?
b)Draw a graph with the 4 means on it and explain where the difference in difference estimator is on the graph.
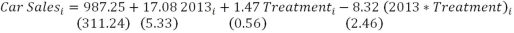
a)Why would you want to estimate a difference in difference model?
b)Draw a graph with the 4 means on it and explain where the difference in difference estimator is on the graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is a difference-in-difference estimator? When is it appropriate to use one? How do you do so? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



