Deck 11: Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/189
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
1
In a criminal trial,a Type I error is made when an innocent person is convicted.
True
2
The probability of a Type I error is denoted by:
A)β
B)1 − β
C)α
D)1 − α
A)β
B)1 − β
C)α
D)1 − α
α
3
A null hypothesis is a statement about the value of a population parameter.
True
4
A Type II error is committed if we make:
A)a correct decision when the null hypothesis is false.
B)a correct decision when the null hypothesis is true.
C)an incorrect decision when the null hypothesis is false.
D)an incorrect decision when the null hypothesis is true.
A)a correct decision when the null hypothesis is false.
B)a correct decision when the null hypothesis is true.
C)an incorrect decision when the null hypothesis is false.
D)an incorrect decision when the null hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A Type II error is represented by α; it is the probability of rejecting a true null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A Type II error is represented by 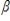 ; it is the probability of failing to reject a false null hypothesis.
; it is the probability of failing to reject a false null hypothesis.
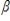 ; it is the probability of failing to reject a false null hypothesis.
; it is the probability of failing to reject a false null hypothesis.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The probability of making a Type I error and the level of significance are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Reducing the probability of a Type I error also reduces the probability of a Type II error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A Type I error is represented by 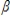 .
.
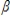 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In a criminal trial,a Type II error is made when an innocent person is acquitted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The hypothesis of most interest to the researcher is:
A)the alternative hypothesis.
B)the null hypothesis.
C)both hypotheses are of equal interest.
D)Neither hypothesis is of interest.
A)the alternative hypothesis.
B)the null hypothesis.
C)both hypotheses are of equal interest.
D)Neither hypothesis is of interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An alternative or research hypothesis is an assertion that holds if the null hypothesis is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The statement of the null hypothesis always includes an equals sign (=).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A professor of linguistics refutes the claim that the average student spends 3 hours studying for the midterm exam.She thinks they spend more time than that.Which hypotheses are used to test the claim?
A)H0: μ = 3 vs.H1: μ > 3
B)H0: μ = 3 vs.H1: μ ≠ 3
C)H0: μ ≠ 3 vs.H1: μ = 3
D)H0: μ = 3 vs.H1: μ < 3
A)H0: μ = 3 vs.H1: μ > 3
B)H0: μ = 3 vs.H1: μ ≠ 3
C)H0: μ ≠ 3 vs.H1: μ = 3
D)H0: μ = 3 vs.H1: μ < 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
It is possible to commit a Type I error and a Type II error at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
There is an inverse relationship between the probabilities of Type I and Type II errors; as one increases,the other decreases,and vice versa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In testing a hypothesis,statements for the null and alternative hypotheses as well as the selection of the level of significance should precede the collection and examination of the data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A Type I error is committed if we make:
A)a correct decision when the null hypothesis is false.
B)a correct decision when the null hypothesis is true.
C)an incorrect decision when the null hypothesis is false.
D)an incorrect decision when the null hypothesis is true.
A)a correct decision when the null hypothesis is false.
B)a correct decision when the null hypothesis is true.
C)an incorrect decision when the null hypothesis is false.
D)an incorrect decision when the null hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Increasing the probability of a Type I error will increase the probability of a Type II error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A Type I error is represented by α; it is the probability of rejecting a true null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
We cannot commit a Type I error when the:
A)null hypothesis is true.
B)level of significance is 0.10.
C)null hypothesis is false.
D)test is a two-tail test.
A)null hypothesis is true.
B)level of significance is 0.10.
C)null hypothesis is false.
D)test is a two-tail test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements is not true?
A)The probability of making a Type II error increases as the probability of making a Type I error decreases.
B)The probability of making a Type II error and the level of significance are the same.
C)The power of the test decreases as the level of significance decreases.
D)All of these choices are true.
A)The probability of making a Type II error increases as the probability of making a Type I error decreases.
B)The probability of making a Type II error and the level of significance are the same.
C)The power of the test decreases as the level of significance decreases.
D)All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The level of significance can be:
A)any number between −1.0 and 1.0.
B)any number greater than zero.
C)any number greater than 1.96 or less than −1.96.
D)None of these choices.
A)any number between −1.0 and 1.0.
B)any number greater than zero.
C)any number greater than 1.96 or less than −1.96.
D)None of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A Type II error is defined as:
A)rejecting a true null hypothesis.
B)rejecting a false null hypothesis.
C)not rejecting a true null hypothesis.
D)not rejecting a false null hypothesis.
A)rejecting a true null hypothesis.
B)rejecting a false null hypothesis.
C)not rejecting a true null hypothesis.
D)not rejecting a false null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A Type I error occurs when we:
A)reject a false null hypothesis.
B)reject a true null hypothesis.
C)don't reject a false null hypothesis.
D)don't reject a true null hypothesis.
A)reject a false null hypothesis.
B)reject a true null hypothesis.
C)don't reject a false null hypothesis.
D)don't reject a true null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a criminal trial,a Type I error is made when:
A)a guilty defendant is acquitted.
B)an innocent person is convicted.
C)a guilty defendant is convicted.
D)an innocent person is acquitted.
A)a guilty defendant is acquitted.
B)an innocent person is convicted.
C)a guilty defendant is convicted.
D)an innocent person is acquitted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is an appropriate null hypothesis?
A)The mean of a population is equal to 60.
B)The mean of a sample is equal to 60.
C)The mean of a population is not equal to 60.
D)All of these choices are true.
A)The mean of a population is equal to 60.
B)The mean of a sample is equal to 60.
C)The mean of a population is not equal to 60.
D)All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following would be an appropriate alternative hypothesis?
A)The mean of a population is equal to 70.
B)The mean of a sample is equal to 70.
C)The mean of a population is greater than 70.
D)The mean of a sample is greater than 70.
A)The mean of a population is equal to 70.
B)The mean of a sample is equal to 70.
C)The mean of a population is greater than 70.
D)The mean of a sample is greater than 70.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If a researcher rejects a true null hypothesis,she has made a(n)____________________ error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If a test of hypothesis has a Type I error probability of .05,this means that:
A)if the null hypothesis is true,we don't reject if 5% of the time.
B)if the null hypothesis is true,we reject it 5% of the time.
C)if the null hypothesis is false,we don't reject it 5% of the time.
D)if the null hypothesis is false,we reject it 5% of the time.
A)if the null hypothesis is true,we don't reject if 5% of the time.
B)if the null hypothesis is true,we reject it 5% of the time.
C)if the null hypothesis is false,we don't reject it 5% of the time.
D)if the null hypothesis is false,we reject it 5% of the time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If we reject the null hypothesis when it is false,then we have committed:
A)a Type II error.
B)a Type I error.
C)both a Type I error and a Type II error.
D)neither a Type I error nor a Type II error.
A)a Type II error.
B)a Type I error.
C)both a Type I error and a Type II error.
D)neither a Type I error nor a Type II error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The owner of a local Jazz Club has recently surveyed a random sample of n = 200 customers of the club.She would now like to determine whether or not the mean age of her customers is over 30.If so,she plans to alter the entertainment to appeal to an older crowd.If not,no entertainment changes will be made.The appropriate hypotheses to test are:
A)H0: μ = 30 vs.H1: μ < 30.
B)H0: μ = 30 vs.H1: μ > 30.
C)H0: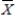 = 30 vs.H1:
= 30 vs.H1:
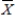 < 30.
< 30.
D)H0:
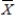
= 30 vs.H1:
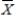
> 30.
A)H0: μ = 30 vs.H1: μ < 30.
B)H0: μ = 30 vs.H1: μ > 30.
C)H0:
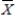 = 30 vs.H1:
= 30 vs.H1: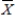 < 30.
< 30.D)H0:
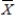
= 30 vs.H1:
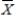
> 30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In a criminal trial,a Type II error is made when:
A)a guilty defendant is acquitted.
B)an innocent person is convicted.
C)a guilty defendant is convicted.
D)an innocent person is acquitted.
A)a guilty defendant is acquitted.
B)an innocent person is convicted.
C)a guilty defendant is convicted.
D)an innocent person is acquitted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The probability of a Type II error is denoted by:
A)α
B)β
C)1 − α
D)1 − β
A)α
B)β
C)1 − α
D)1 − β

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Researchers claim that 40 tissues is the average number of tissues a person uses during the course of a cold.The company who makes Puffs brand tissues thinks that fewer of their tissues are needed.What are their null and alternative hypotheses?
A)H0: μ = 40 vs.H1: μ > 40
B)H0: μ = 40 vs.H1: μ < 40
C)H0: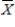 = 40 vs.H1:
= 40 vs.H1:
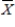 < 40
< 40
D)H0: μ < 40 vs.H1: μ = 40
A)H0: μ = 40 vs.H1: μ > 40
B)H0: μ = 40 vs.H1: μ < 40
C)H0:
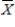 = 40 vs.H1:
= 40 vs.H1: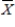 < 40
< 40D)H0: μ < 40 vs.H1: μ = 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If a researcher fails to reject a false null hypothesis he has made a(n)____________________ error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A spouse suspects that the average amount of money spent on Christmas gifts for immediate family members is above $1,200.The correct set of hypotheses is:
A)H0: μ = 1200 vs.H1: μ < 1200
B)H0: μ > 1200 vs.H1: μ = 1200
C)H0: μ = 1200 vs.H1: μ > 1200
D)H0: μ < 1200 vs.H1: μ = 1200
A)H0: μ = 1200 vs.H1: μ < 1200
B)H0: μ > 1200 vs.H1: μ = 1200
C)H0: μ = 1200 vs.H1: μ > 1200
D)H0: μ < 1200 vs.H1: μ = 1200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following probabilities is equal to the significance level α?
A)Probability of making a Type I error.
B)Probability of making a Type II error.
C)Probability of rejecting H0 when you are supposed to.
D)Probability of not rejecting H0 when you shouldn't.
A)Probability of making a Type I error.
B)Probability of making a Type II error.
C)Probability of rejecting H0 when you are supposed to.
D)Probability of not rejecting H0 when you shouldn't.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following conclusions is not an appropriate conclusion from a hypothesis test?
A)Reject H0.Sufficient evidence to support H1.
B)Fail to reject H0.Insufficient evidence to support H1.
C)Accept H0.Sufficient evidence to support H0.
D)All of these choices are true.
A)Reject H0.Sufficient evidence to support H1.
B)Fail to reject H0.Insufficient evidence to support H1.
C)Accept H0.Sufficient evidence to support H0.
D)All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose we wish to test H0: μ = 45 vs.H1: μ > 45.What will result if we conclude that the mean is greater than 45 when the actual mean is 50?
A)We have made a Type I error.
B)We have made a Type II error.
C)We have made both a Type I error and a Type II error.
D)We have made the correct decision.
A)We have made a Type I error.
B)We have made a Type II error.
C)We have made both a Type I error and a Type II error.
D)We have made the correct decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The p-value of a test is the probability of observing a test statistic at least as extreme as the one computed given that the null hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The p-value is the probability that the null hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Suppose an auto manufacturer states that their car goes from 0 to 60 miles per hour in 10 seconds on average,and you suspect that time is longer.
a.Set up the null and alternative hypotheses to test this claim.
b.Explain how you know which is the null hypothesis and which is the alternative hypothesis.
a.Set up the null and alternative hypotheses to test this claim.
b.Explain how you know which is the null hypothesis and which is the alternative hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
After you set up the hypotheses and collect your data,you calculate the statistic that serves as the criterion for making your decision.This number is called the ____________________ statistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
You cannot commit a(n)____________________ error when the null hypothesis is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The hypothesis testing procedure begins with the assumption that the null hypothesis is ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The probability of a Type I error is denoted by ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The p-value of a test is the smallest α at which the null hypothesis can be rejected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For each of the following pairs of null and alternative hypotheses,determine whether or not they are statistically correct to conduct a hypothesis test.
a.H0: μ = 25,H1: μ < 25
b.H0: μ = 30,H1: μ > 30
c.H0:
 = 35,H1:
= 35,H1:
 > 35
> 35
d.H0:
 = 40,H1:
= 40,H1:
 < 40
< 40
e.H0: μ ≠ 60,H1: μ = 60
a.H0: μ = 25,H1: μ < 25
b.H0: μ = 30,H1: μ > 30
c.H0:
 = 35,H1:
= 35,H1: > 35
> 35 d.H0:
 = 40,H1:
= 40,H1: < 40
< 40 e.H0: μ ≠ 60,H1: μ = 60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Formulate the null and alternative hypothesis in each case:
a.Ten years ago the average American drank 2.5 cups of coffee per day.You suspect that amount has changed since then.
b.A researcher at Ohio State University speculates that the average SAT score for entering freshmen is higher than the national average of 1,650.
c.The manager of the University of Iowa bookstore suspects the average amount of money a student spends on books is less than the reported $400.
a.Ten years ago the average American drank 2.5 cups of coffee per day.You suspect that amount has changed since then.
b.A researcher at Ohio State University speculates that the average SAT score for entering freshmen is higher than the national average of 1,650.
c.The manager of the University of Iowa bookstore suspects the average amount of money a student spends on books is less than the reported $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
You cannot commit a(n)____________________ error when the null hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose a pickup and delivery company states that their packages arrive within two days or less on average.You want to find out whether the actual average delivery time is longer than this.You conduct a hypothesis test.
a.Set up the null and alternative hypotheses.
b.Suppose you conclude wrongly that the company's statement about average delivery time is within two days.What type of error is being committed and what is the impact of that error?
c.Suppose you conclude wrongly that the delivery company's average time to delivery is in fact longer than two days.What type of error did you commit and what is the impact of this error?
d.Which error is worse from the company's standpoint,a Type I or a Type II error? Why?
e.Which error is worse from a consumer standpoint,a Type I or a Type II error? Why?
a.Set up the null and alternative hypotheses.
b.Suppose you conclude wrongly that the company's statement about average delivery time is within two days.What type of error is being committed and what is the impact of that error?
c.Suppose you conclude wrongly that the delivery company's average time to delivery is in fact longer than two days.What type of error did you commit and what is the impact of this error?
d.Which error is worse from the company's standpoint,a Type I or a Type II error? Why?
e.Which error is worse from a consumer standpoint,a Type I or a Type II error? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The probability of a Type II error is denoted by ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Explain why a Type I error and a Type II error have an inverse relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Explain the difference between accepting H0 and failing to reject H0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In order to determine the p-value,it is necessary to know the level of significance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A p-value is usually set at 0.05.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If a researcher rejects a false null hypothesis,she has made a(n)____________________ decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Think about a situation where you have a test for a virus.First,you are tested positive or negative.Second,you either really do have the virus or you don't.
a.If you actually have the virus but the test did not catch it,which error has been made and what is the impact of that error?
b.If you actually don't have the virus but the test says you did,which error is being made and what is the impact of this error?
c.Which error is the worst one to commit in this situation and why?
a.If you actually have the virus but the test did not catch it,which error has been made and what is the impact of that error?
b.If you actually don't have the virus but the test says you did,which error is being made and what is the impact of this error?
c.Which error is the worst one to commit in this situation and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If a researcher fails to reject a true null hypothesis,he has made a(n)____________________ decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A two-tail test for the population mean μ produces a test-statistic z = 1.89.The p-value associated with the test is 0.0588.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following p-values will lead us to reject the null hypothesis if the level of significance equals 0.05?
A)0.150
B)0.100
C)0.051
D)0.025
A)0.150
B)0.100
C)0.051
D)0.025

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A p-value is a probability,and must be between 0 and 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
For a given level of significance,if the sample size is increased,the probability of committing a Type I error will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A one-tail p-value is two times the size of a two-tail test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The critical values will bound the rejection and non-rejection regions for the null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In testing the hypotheses H0: μ = 50 vs.H1: μ ≠ 50,the following information is known: n = 64,  = 53.5,and σ = 10.The standardized test statistic z equals:
= 53.5,and σ = 10.The standardized test statistic z equals:
A)1.96
B)−2.80
C)2.80
D)−1.96
 = 53.5,and σ = 10.The standardized test statistic z equals:
= 53.5,and σ = 10.The standardized test statistic z equals:A)1.96
B)−2.80
C)2.80
D)−1.96

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
For a given level of significance,if the sample size is increased,the probability of committing a Type II error will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If we reject a null hypothesis at the 0.05 level of significance,then we must also reject it at the 0.10 level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In order to determine the p-value,which of the following is not needed?
A)The level of significance.
B)Whether the test is one-tail or two-tail.
C)The value of the test statistic.
D)All of these choices are true.
A)The level of significance.
B)Whether the test is one-tail or two-tail.
C)The value of the test statistic.
D)All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If your p-value is greater than 0.900 you should reject H0 at the 0.10 level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If a null hypothesis is rejected at the 0.05 level of significance,it must be rejected at the 0.025 level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In a one-tail test,the p-value is found to be equal to 0.054.If the test had been two-tail,then the p-value would have been 0.027.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The larger the p-value,the more likely one is to reject the null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A sample is used to obtain a 95% confidence interval for the mean of a population.The confidence interval goes from 10.89 to 13.21.If the same sample had been used to test H0: μ = 12 vs.H1: μ ≠ 12,H0 could not be rejected at the 0.05 level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If we reject the null hypothesis,we conclude that there is enough statistical evidence to infer that the alternative hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Using the confidence interval when conducting a two-tail test for the population mean μ,we do not reject the null hypothesis if the hypothesized value for μ falls between the lower and upper confidence limits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A one-tail test for the population mean μ produces a test-statistic z = −0.75.The p-value associated with the test is 0.7734.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If we do not reject the null hypothesis,we conclude that there is enough statistical evidence to infer that the null hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A sample is used to obtain a 95% confidence interval for the mean of a population.The confidence interval goes from 78.21 to 87.64.If the same sample had been used to test the null hypothesis that the mean of the population differs from 90,the null hypothesis could be rejected at a level of significance of 0.05.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



