Deck 7: Solids, Liquids, and Phase Changes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/58
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Solids, Liquids, and Phase Changes
1
Which has the highest surface tension at room temperature?
A)CH4
B)CF4
C)CCl4
D)CBr4
E)CI4
A)CH4
B)CF4
C)CCl4
D)CBr4
E)CI4
CI4
2
Ammonia's unusually high melting point is the result of
A)dipole-dipole forces.
B)London dispersion forces.
C)hydrogen bonding.
D)covalent bonding.
E)ionic bonding.
A)dipole-dipole forces.
B)London dispersion forces.
C)hydrogen bonding.
D)covalent bonding.
E)ionic bonding.
hydrogen bonding.
3
Place the substances in order of increasing melting point. CS2 KCl NF3
A)CS2 < NF3 < KCl
B)KCl < NF3 < CS2
C)NF3 < CS2 < KCl
D)CS2 < KCl < NF3
E)NF3 < KCl < CS2
A)CS2 < NF3 < KCl
B)KCl < NF3 < CS2
C)NF3 < CS2 < KCl
D)CS2 < KCl < NF3
E)NF3 < KCl < CS2
CS2 < NF3 < KCl
4
What is determined by the magnitude of intermolecular forces in a liquid and is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow?
A)Surface tension
B)Adhesion
C)Polarity
D)Viscosity
E)Cohesion
A)Surface tension
B)Adhesion
C)Polarity
D)Viscosity
E)Cohesion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which one of the following crystallizes in a metallic lattice?
A)C
B)NaMnO4
C)K
D)LiClO4
E)K2Cr2O7
A)C
B)NaMnO4
C)K
D)LiClO4
E)K2Cr2O7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Place the substances in order of increasing viscosity. CH3OH C2H6 HO-CH2CH2-OH
A)C2H6 < HO-CH2CH2-OH < CH3OH
B)CH3OH< C2H6 < HO-CH2CH2-OH
C)HO-CH2CH2-OH< C2H6 < CH3OH
D)CH3OH < HO-CH2CH2-OH < C2H6
E)C2H6 < CH3OH < HO-CH2CH2-OH
A)C2H6 < HO-CH2CH2-OH < CH3OH
B)CH3OH< C2H6 < HO-CH2CH2-OH
C)HO-CH2CH2-OH< C2H6 < CH3OH
D)CH3OH < HO-CH2CH2-OH < C2H6
E)C2H6 < CH3OH < HO-CH2CH2-OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
For the solid forms of the following elements, which one is most likely to be of the molecular type?
A)Cs
B)C
C)Pb
D)S
E)Cr
A)Cs
B)C
C)Pb
D)S
E)Cr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which state of matter is described as having a definite shape and volume?
A)solid
B)liquid
C)gas
D)solution
E)mixture
A)solid
B)liquid
C)gas
D)solution
E)mixture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the substances would form an ionic solid?
A)NCl3
B)NH4Cl
C)Ag
D)He
E)OF2
A)NCl3
B)NH4Cl
C)Ag
D)He
E)OF2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The energy required to increase the surface of a liquid per unit area is called the
A)capillary action.
B)surface tension.
C)viscosity.
D)cohesion.
E)specific elasticity.
A)capillary action.
B)surface tension.
C)viscosity.
D)cohesion.
E)specific elasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following lacks a regular three-dimensional arrangement of atoms?
A)crystalline solids
B)ionic crystals
C)solids
D)amorphous solids
E)molecular solids
A)crystalline solids
B)ionic crystals
C)solids
D)amorphous solids
E)molecular solids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If liquid bromine is cooled to form a solid, which type of solid does it form?
A)atomic
B)metallic
C)molecular
D)ionic
E)covalent
A)atomic
B)metallic
C)molecular
D)ionic
E)covalent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which state of matter is described as taking on the shape and volume of its container?
A)solid
B)liquid
C)gas
D)solution
E)mixture
A)solid
B)liquid
C)gas
D)solution
E)mixture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which state of matter is described as taking on the shape of its container, but having a specific volume?
A)solid
B)liquid
C)gas
D)solution
E)mixture
A)solid
B)liquid
C)gas
D)solution
E)mixture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Place the substances in order of increasing melting point. CO2 CH4 OF2
A)OF2 < CO2 < CH4
B)CH4 < CO2 < OF2
C)OF2 < CH4 < CO2
D)CO2 < CH4 < OF2
E)CO2 < OF2 < CH4
A)OF2 < CO2 < CH4
B)CH4 < CO2 < OF2
C)OF2 < CH4 < CO2
D)CO2 < CH4 < OF2
E)CO2 < OF2 < CH4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements is ?
A)The higher the viscosity, the faster a liquid flows.
B)The viscosity increases with increasing temperature.
C)The stronger the intermolecular forces, the higher the viscosity.
D)Hydrogen bonding in water gives rise to its unusually low viscosity.
E)The viscosity of gases is larger than the viscosity of liquids.
A)The higher the viscosity, the faster a liquid flows.
B)The viscosity increases with increasing temperature.
C)The stronger the intermolecular forces, the higher the viscosity.
D)Hydrogen bonding in water gives rise to its unusually low viscosity.
E)The viscosity of gases is larger than the viscosity of liquids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Ethanol (C2H5-OH) will have a greater viscosity than ethylene glycol (HO-CH2CH2-OH) at the same temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the substances would form a metallic solid?
A)NCl3
B)KCl
C)Ni
D)Ar
E)MgF2
A)NCl3
B)KCl
C)Ni
D)Ar
E)MgF2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Place the substances in order of increasing melting point. CH4
C3H8
C2H4
A)C3H8 < C2H4 < CH4
B)C2H4 < CH4 < C3H8
C)C3H8 < CH4 < C2H4
D)CH4 < C2H4 < C3H8
E)C2H4 < C3H8 < CH4
C3H8
C2H4
A)C3H8 < C2H4 < CH4
B)C2H4 < CH4 < C3H8
C)C3H8 < CH4 < C2H4
D)CH4 < C2H4 < C3H8
E)C2H4 < C3H8 < CH4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following terms refers to the resistance of a liquid to flow?
A)Surface tension
B)Capillary action
C)Viscosity
D)Adhesion
E)Cohesion
A)Surface tension
B)Capillary action
C)Viscosity
D)Adhesion
E)Cohesion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the process in which molecules undergo a phase change from the gas phase to the liquid phase?
A)vaporization
B)condensation
C)freezing
D)melting
E)sublimation
A)vaporization
B)condensation
C)freezing
D)melting
E)sublimation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the process in which molecules undergo a phase change from the solid phase to the liquid phase?
A)vaporization
B)condensation
C)freezing
D)melting
E)sublimation
A)vaporization
B)condensation
C)freezing
D)melting
E)sublimation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Place the substances in order of decreasing boiling point. BeCl2 CBr4 BeBr2
A)BeCl2 > CBr4 > BeBr2
B)BeCl2 > BeBr2 > CBr4
C)CBr4 > BeBr2 > BeCl2
D)BeBr2 > BeCl2 > CBr4
A)BeCl2 > CBr4 > BeBr2
B)BeCl2 > BeBr2 > CBr4
C)CBr4 > BeBr2 > BeCl2
D)BeBr2 > BeCl2 > CBr4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is q if 28.6 g of water is heated from 22.0°C to 78.3°C? The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g·°C.
A)2.60 J
B)2.63 kJ
C)6.74 kJ
D)9.37 kJ
E)3.94×104 kJ
A)2.60 J
B)2.63 kJ
C)6.74 kJ
D)9.37 kJ
E)3.94×104 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the process in which molecules undergo a phase change from the liquid phase to the gas phase?
A)vaporization
B)condensation
C)freezing
D)melting
E)sublimation
A)vaporization
B)condensation
C)freezing
D)melting
E)sublimation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The specific heat (capacity) is
A)amount of energy needed to change 1 g of a substance by 1°C.
B)amount of energy needed to change 1 mol of a substance by 1°C
C)amount of energy required to melt 1 g of substance.
D)amount of substance that is heated by 1°C.
E)the temperature increase, in K, associated with heating 1 g of a substance for 1 minute.
A)amount of energy needed to change 1 g of a substance by 1°C.
B)amount of energy needed to change 1 mol of a substance by 1°C
C)amount of energy required to melt 1 g of substance.
D)amount of substance that is heated by 1°C.
E)the temperature increase, in K, associated with heating 1 g of a substance for 1 minute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following properties indicates the presence of strong intermolecular forces in a liquid?
A)a low heat of vaporization
B)a low critical temperature
C)a low vapor pressure
D)a low boiling point
E)a low melting point
A)a low heat of vaporization
B)a low critical temperature
C)a low vapor pressure
D)a low boiling point
E)a low melting point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which corresponds to the temperature-dependent partial pressure above the surface of a liquid?
A)Surface tension
B)Vapor pressure
C)Boiling point
D)Viscosity
E)Capillary action
A)Surface tension
B)Vapor pressure
C)Boiling point
D)Viscosity
E)Capillary action

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which substance has the highest vapor pressure at room temperature?
A)HF
B)HCl
C)HBr
D)HI
E)All of these substances have the same vapor pressure at room temperature.
A)HF
B)HCl
C)HBr
D)HI
E)All of these substances have the same vapor pressure at room temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the process in which molecules undergo a phase change from the liquid phase to the solid phase?
A)vaporization
B)condensation
C)freezing
D)melting
E)sublimation
A)vaporization
B)condensation
C)freezing
D)melting
E)sublimation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Select the pair of substances in which the one with the lower vapor pressure at a given temperature is listed first.
A)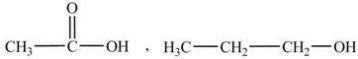
B)PH3, NH3
C) CF4, CBr4
D)C3H8,C4H10
E)F2, Cl2
A)
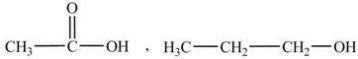
B)PH3, NH3
C) CF4, CBr4
D)C3H8,C4H10
E)F2, Cl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which statement concerning the vapor pressures of water and methanol (CH3OH) is ?
A)At 25ºC, methanol has a higher vapor pressure than water because methanol has a lower normal boiling point than water.
B)At 25ºC, methanol has a higher vapor pressure than water because methanol is a poorer solvent than water.
C)At 25ºC, methanol has a higher vapor pressure than water because methanol is a less viscous liquid than water.
D)At 25ºC, methanol has a higher vapor pressure than water because the density of methanol is less than the density of water.
E)At 25ºC, methanol has a higher vapor pressure than water because methanol has weaker intermolecular forces than water.
A)At 25ºC, methanol has a higher vapor pressure than water because methanol has a lower normal boiling point than water.
B)At 25ºC, methanol has a higher vapor pressure than water because methanol is a poorer solvent than water.
C)At 25ºC, methanol has a higher vapor pressure than water because methanol is a less viscous liquid than water.
D)At 25ºC, methanol has a higher vapor pressure than water because the density of methanol is less than the density of water.
E)At 25ºC, methanol has a higher vapor pressure than water because methanol has weaker intermolecular forces than water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Place the substances in order of decreasing boiling point. CO2 CH4 OF2
A)OF2 > CO2 > CH4
B)CH4 > CO2 > OF2
C)OF2 > CH4 > CO2
D)CO2 > CH4 > OF2
E)CO2 > OF2 > CH4
A)OF2 > CO2 > CH4
B)CH4 > CO2 > OF2
C)OF2 > CH4 > CO2
D)CO2 > CH4 > OF2
E)CO2 > OF2 > CH4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the process in which molecules undergo a phase change directly from the gas phase to the solid phase?
A)deposition
B)sublimation
C)freezing
D)condensation
E)melting
A)deposition
B)sublimation
C)freezing
D)condensation
E)melting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which substance has the lowest vapor pressure at room temperature?
A)HF
B)HCl
C)HBr
D)HI
E)H2
A)HF
B)HCl
C)HBr
D)HI
E)H2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Place the substances in order of increasing viscosity. CH3CH2CH2CH3 H2NCH2CH2NH2 CH3CH2CH2NH2
A)CH3CH2CH2CH3 < CH3CH2CH2NH2 < H2NCH2CH2NH2
B)H2NCH2CH2NH2 < CH3CH2CH2NH2 < CH3CH2CH2CH3
C)H2NCH2CH2NH2 < CH3CH2CH2CH3 < CH3CH2CH2NH2
D)CH3CH2CH2CH3 < H2NCH2CH2NH2 < CH3CH2CH2NH2
E)CH3CH2CH2NH2 < H2NCH2CH2NH2 < CH3CH2CH2CH3
A)CH3CH2CH2CH3 < CH3CH2CH2NH2 < H2NCH2CH2NH2
B)H2NCH2CH2NH2 < CH3CH2CH2NH2 < CH3CH2CH2CH3
C)H2NCH2CH2NH2 < CH3CH2CH2CH3 < CH3CH2CH2NH2
D)CH3CH2CH2CH3 < H2NCH2CH2NH2 < CH3CH2CH2NH2
E)CH3CH2CH2NH2 < H2NCH2CH2NH2 < CH3CH2CH2CH3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Select the pair of substances in which the one with the higher vapor pressure at a given temperature is listed first.
A)C7H16, C5H12
B)CCl4, CBr4
C)H2O, H2S
D)CH3CH2OH, CH3-O-CH3
E)Xe, Kr
A)C7H16, C5H12
B)CCl4, CBr4
C)H2O, H2S
D)CH3CH2OH, CH3-O-CH3
E)Xe, Kr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Place the substances in order of increasing boiling point. BF3 NF3 BeF2
A)NF3 < BF3 < BeF2
B)BF3 < NF3 < BeF2
C)NF3 < BeF2 < BF3
D)BeF2 < NF3 < BF3
E)BeF2 < BF3 < NF3
A)NF3 < BF3 < BeF2
B)BF3 < NF3 < BeF2
C)NF3 < BeF2 < BF3
D)BeF2 < NF3 < BF3
E)BeF2 < BF3 < NF3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Place the substances in order of increasing boiling point. BeF2 SF2 Ar
A)BeF2 < SF2 < Ar
B)Ar < BeF2 < SF2
C)SF2 < Ar < BeF2
D)SF2 < BeF2 < Ar
E)Ar < SF2 < BeF2
A)BeF2 < SF2 < Ar
B)Ar < BeF2 < SF2
C)SF2 < Ar < BeF2
D)SF2 < BeF2 < Ar
E)Ar < SF2 < BeF2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the process in which molecules undergo a phase change directly from the solid phase to the gas phase?
A)deposition
B)sublimation
C)freezing
D)condensation
E)melting
A)deposition
B)sublimation
C)freezing
D)condensation
E)melting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 1500 g of water from 25°C to 52°C? The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g·°C.
A)1500 kJ
B)170 kJ
C)6.3 kJ
D)41 J
E)41 kJ
A)1500 kJ
B)170 kJ
C)6.3 kJ
D)41 J
E)41 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When Karl Kaveman adds chilled grog to his new granite mug, he removes 10.9 kJ of energy from the mug.If it has a mass of 625 g and was at 25°C, what is its new temperature? Specific heat capacity of granite = 0.79 J/g·°C.
A)3°C
B)14°C
C)22°C
D)47°C
E)None of these choices is correct.
A)3°C
B)14°C
C)22°C
D)47°C
E)None of these choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Benzene is a starting material in the synthesis of nylon fibers and polystyrene (styrofoam).Its specific heat capacity is 1.74 J/g·°C.If 16.7 kJ of energy is absorbed by a 225-g sample of benzene at 20.0°C, what is its final temperature?
A)−22.7°C
B)37.7°C
C)42.7°C
D)62.7°C
E)80.1°C
A)−22.7°C
B)37.7°C
C)42.7°C
D)62.7°C
E)80.1°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Ethylene glycol, used as a coolant in automotive engines, has a specific heat capacity of 2.42 J/g·°C.Calculate q when 3.65 kg of ethylene glycol is cooled from 132°C to 85°C.
A)−1900 kJ
B)−420 kJ
C)−99 kJ
D)−0.42 kJ
E)−4.2 × 10−6 kJ
A)−1900 kJ
B)−420 kJ
C)−99 kJ
D)−0.42 kJ
E)−4.2 × 10−6 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the energy in kJ/mol required to melt 1 mole of a solid?
A)molar heat of freezing
B)molar heat of fission
C)molar heat of vaporization
D)molar heat of fusion
E)molar heat of condensation
A)molar heat of freezing
B)molar heat of fission
C)molar heat of vaporization
D)molar heat of fusion
E)molar heat of condensation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If 325 g of water at 4.2°C absorbs 12.28 kJ, what is the final temperature of the water? The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g·°C.
A)4.21°C
B)4.8°C
C)9.0°C
D)13.2°C
E)2938°C
A)4.21°C
B)4.8°C
C)9.0°C
D)13.2°C
E)2938°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What mass of water would need to evaporate from your skin in order to dissipate 1.70 ×105 J of heat from the surface of your body? H2O(l) → H2O(g) ∆Hvap = 40.7 kJ/mol
A)2.26 g
B)4.18 g
C)75.2 g
D)4.18 ×103 g
E)4.07 × 104 g
A)2.26 g
B)4.18 g
C)75.2 g
D)4.18 ×103 g
E)4.07 × 104 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What amount of energy (heat) is required to warm a 73.5-g sample of liquid ethanol from 15.0ºC to 29.5ºC? The specific heat capacity of ethanol is 2.46 J/gºC.
A)0.485 J
B)433 J
C)2.62 × 103 J
D)5.33 × 103 J
E)238 J
A)0.485 J
B)433 J
C)2.62 × 103 J
D)5.33 × 103 J
E)238 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If, as a pioneer, you wished to warm your room by taking an object heated on top of a pot-bellied stove to it, which of the following 15-pound objects, each heated to 100°C, would be the best choice? The specific heat capacity (in J/g·°C) for each substance is given in parentheses.Iron (0.450), copper (0.387), granite (0.79), gold (0.129), water (4.184).
A)iron
B)copper
C)granite
D)gold
E)H2O
A)iron
B)copper
C)granite
D)gold
E)H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A piece of copper with a mass of 218 g has a heat capacity of 83.9 J/°C.What is the specific heat of copper?
A)0.385 J/g·°C
B)1.83 × 104 J/g·°C
C)2.60 J/g·°C
D)1.32 J/g·°C
E)24.5 J/g·°C
A)0.385 J/g·°C
B)1.83 × 104 J/g·°C
C)2.60 J/g·°C
D)1.32 J/g·°C
E)24.5 J/g·°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What quantity of heat is required to melt 2.00 kg of iron at its melting point (1809 K)? For iron, ∆Hfus = 13.80 kJ/mol.
A)0.385 kJ
B)6.90 kJ
C)27.6 kJ
D)494 kJ
E)771 kJ
A)0.385 kJ
B)6.90 kJ
C)27.6 kJ
D)494 kJ
E)771 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A 275-g sample of nickel at l00.0°C is placed in 100.0 g of water at 22.0°C.What is the final temperature of the water? Assume no heat transfer with the surroundings.The specific heat of nickel is 0.444 J/g·°C and the specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g·°C.
A)39.6°C
B)40.8°C
C)61.0°C
D)79.2°C
E)82.4°C
A)39.6°C
B)40.8°C
C)61.0°C
D)79.2°C
E)82.4°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 22.8 g of copper from 20.0°C to 875.0°C? The specific heat of copper is 0.385 J/g·°C.
A)14.4 J
B)176 J
C)7.51 kJ
D)7.68 kJ
E)9.90 kJ
A)14.4 J
B)176 J
C)7.51 kJ
D)7.68 kJ
E)9.90 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the change in temperature if a 25.0-g block of aluminum absorbs 10.0 kJ of heat? The specific heat of aluminum is 0.900 J/g·°C.
A)0.44°C
B)22.5°C
C)225°C
D)360°C
E)444°C
A)0.44°C
B)22.5°C
C)225°C
D)360°C
E)444°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 12.0 g of water from 15.4°C to 93.0°C? The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g·°C.
A)223 J
B)773 J
C)503 J
D)4.67 ×103 J
E)3.90 ×103 J
A)223 J
B)773 J
C)503 J
D)4.67 ×103 J
E)3.90 ×103 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If 75.4 J of energy is absorbed by 0.25 mol of CCl4 at constant pressure, what is the change in temperature? The specific heat of CCl4 is 0.861 J/g·°C.
A)17.8°C
B)21.9°C
C)2.3°C
D)9.1°C
E)44.6°C
A)17.8°C
B)21.9°C
C)2.3°C
D)9.1°C
E)44.6°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A glass containing 200.0 g of H2O at 20.0°C was placed in a refrigerator.The water loses 11.7 kJ as it cools to a constant temperature.What is its new temperature? The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g·°C.
A)0.0°C
B)4.0°C
C)6.0°C
D)14.0°C
E)34.0°C
A)0.0°C
B)4.0°C
C)6.0°C
D)14.0°C
E)34.0°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What amount of energy (heat) is required to warm a 65.0-g sample of liquid water from 25.0ºC to 96.5ºC? The specific heat capacity of water is 4.184 J/gºC.
A)4.60 J
B)1.11 × 103 J
C)2.62 × 104 J
D)1.94 ×104 J
E)1.61 J
A)4.60 J
B)1.11 × 103 J
C)2.62 × 104 J
D)1.94 ×104 J
E)1.61 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



