Deck 17: Electrochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Electrochemistry
1
What is the name given to the experimental apparatus for generating electricity through the use of a spontaneous reaction?
A)Electrolytic cell
B)Galvanic cell
C)Redox cell
D)Cathode
E)Anode
A)Electrolytic cell
B)Galvanic cell
C)Redox cell
D)Cathode
E)Anode
Galvanic cell
2
Which is not a redox reaction?
A)Al(OH)4−(aq) + 4H+(aq) → Al3+(aq) + 4H2O(l)
B)C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
C)Na6FeCl8(s) + 2Na(l) → 8NaCl(s) + Fe(s)
D)2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
E)CO2(g) + H2(g) → CO(g) + H2O(g)
A)Al(OH)4−(aq) + 4H+(aq) → Al3+(aq) + 4H2O(l)
B)C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
C)Na6FeCl8(s) + 2Na(l) → 8NaCl(s) + Fe(s)
D)2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
E)CO2(g) + H2(g) → CO(g) + H2O(g)
Al(OH)4−(aq) + 4H+(aq) → Al3+(aq) + 4H2O(l)
3
If a substance is reduced, it must undergo a
A)gain of electrons.
B)loss of oxygen.
C)gain of hydrogen.
D)loss of electrons.
E)gain of oxygen.
A)gain of electrons.
B)loss of oxygen.
C)gain of hydrogen.
D)loss of electrons.
E)gain of oxygen.
gain of electrons.
4
Complete and balance the following redox equation.Now sum the coefficients of all species in the balanced equation.(Remember to add the coefficients that are equal to one, and to add the coefficients of any species added to the equation.) The sum of the smallest whole number coefficients is Bi(OH)3 + SnO22− → Bi + SnO32− (basic solution)
A)32
B)25
C)16
D)13
E)4
A)32
B)25
C)16
D)13
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When the following redox equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient of Zn(s)? Zn(s) + ReO4−(aq) → Re(s) + Zn2+(aq) (acidic solution)
A)2
B)7
C)8
D)16
E)None of these choices is correct.
A)2
B)7
C)8
D)16
E)None of these choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When the following redox equation is balanced using the smallest whole-number coefficients, what is the coefficient of NO2? Sn + HNO3 → SnO2 + NO2 + H2O (acidic solution)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When the following redox equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient for nitrogen dioxide? I2(s) + HNO3(aq) → HIO3(aq) + NO2(g) + H2O(l)
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)5
E)10
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)5
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When the following redox equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient of Sn(OH)3−? Bi(OH)3(s) + Sn(OH)3-(aq) → Sn(OH)62−(aq) + Bi(s) (basic solution)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)6
E)12
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)6
E)12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the following balanced redox reaction. Mn2+(aq) + S2O82−(aq) + 2H2O(l) → MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42−(aq) Which of the following statements is ?
A)Mn2+(aq) is the oxidizing agent and is reduced.
B)Mn2+(aq) is the oxidizing agent and is oxidized.
C)Mn2+(aq) is the reducing agent and is oxidized.
D)Mn2+(aq) is the reducing agent and is reduced.
E)Manganese does not change its oxidation number in this reaction.
A)Mn2+(aq) is the oxidizing agent and is reduced.
B)Mn2+(aq) is the oxidizing agent and is oxidized.
C)Mn2+(aq) is the reducing agent and is oxidized.
D)Mn2+(aq) is the reducing agent and is reduced.
E)Manganese does not change its oxidation number in this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Complete and balance the following redox equation.When properly balanced using the smallest whole-number coefficients, the coefficient of S is H2S + HNO3 → S + NO + H2O (acidic solution)
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)5.
E)6.
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)5.
E)6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When the following redox equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients, the coefficient for the hydrogen sulfate ion will be ______. Al(s) + HSO4−(aq) + OH−(aq) → Al2O3(s) + S2−(aq) + H2O(l)
A)1
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)8
A)1
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When the following equation is balanced with the lowest whole number coefficients, the coefficients are:Cu(s) + H+(aq) + NO3−(aq) → NO(g) + H2O(l) + Cu2+(aq)
A)1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1
B)3, 2, 1, 1, 1, 3
C)3, 2, 4, 2, 4, 3
D)1, 8, 2, 2, 4, 1
E)3, 8, 2, 2, 4, 3
A)1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1
B)3, 2, 1, 1, 1, 3
C)3, 2, 4, 2, 4, 3
D)1, 8, 2, 2, 4, 1
E)3, 8, 2, 2, 4, 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When the following redox equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient of Sb3+(aq)? BrO3−(aq) + Sb3+(aq) → Br−(aq) + Sb5+(aq) (acidic solution)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Consider the reaction CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(l)
In this reaction, which substances are the oxidizing agent and reducing agent, respectively?
A)CuO and H2
B)H2 and CuO
C)CuO and Cu
D)H2O and H2
E)Cu and H2O
In this reaction, which substances are the oxidizing agent and reducing agent, respectively?
A)CuO and H2
B)H2 and CuO
C)CuO and Cu
D)H2O and H2
E)Cu and H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the oxidizing agent in the (unbalanced) reaction? Cu(s) + H+(aq) + NO3−(aq) → NO(g) + H2O(l) + Cu2+(aq)
A)Cu
B)H+
C)NO3−
D)NO
E)Cu2+
A)Cu
B)H+
C)NO3−
D)NO
E)Cu2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the following balanced redox reaction.3CuO(s) + 2NH3(aq) → N2(g) + 3H2O(l) + 3Cu(s) Which of the following statements is ?
A)CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and copper is reduced.
B)CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and copper is oxidized.
C)CuO(s) is the reducing agent and copper is oxidized.
D)CuO(s) is the reducing agent and copper is reduced.
E)CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and N2(g) is the reducing agent.
A)CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and copper is reduced.
B)CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and copper is oxidized.
C)CuO(s) is the reducing agent and copper is oxidized.
D)CuO(s) is the reducing agent and copper is reduced.
E)CuO(s) is the oxidizing agent and N2(g) is the reducing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Complete and balance the following redox equation using the set of smallest whole numbers coefficients.What is the sum of the coefficients? HI + HNO3 → I2 + NO (acidic solution)
A)5
B)7
C)14
D)17
E)None of these choices is correct.
A)5
B)7
C)14
D)17
E)None of these choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consider the following redox equation. Mn(OH)2(s) + MnO4−(aq) → MnO42−(aq) (basic solution)
When the equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient for OH−(aq) and on which side of the equation is OH−(aq) present?
A)4, reactant side
B)4, product side
C)6, reactant side
D)6, product side
E)8, reactant side
When the equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient for OH−(aq) and on which side of the equation is OH−(aq) present?
A)4, reactant side
B)4, product side
C)6, reactant side
D)6, product side
E)8, reactant side

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A certain electrochemical cell has for its cell reaction: Zn + HgO → ZnO + Hg
Which is the half-reaction occurring at the anode?
A)HgO + 2e− → Hg + O2−
B)Zn2++ 2e− → Zn
C)Zn → Zn2+ + 2e−
D)ZnO + 2e− → Zn
Which is the half-reaction occurring at the anode?
A)HgO + 2e− → Hg + O2−
B)Zn2++ 2e− → Zn
C)Zn → Zn2+ + 2e−
D)ZnO + 2e− → Zn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the purpose of a salt bridge in an electrochemical cell?
A)A salt bridge provides electrical contact between the electrodes that make up the cell.
B)A salt bridge carries electrons between the cathode and anode.
C)A salt bridge insulates the two electrodes.
D)A salt bridge allows the electrolyte solution to siphon from one side of the cell to the other so the levels remain
Equal.
E)A salt bridge allows electrolyte to flow from one half-cell to the other in order to maintain electroneutrality.
A)A salt bridge provides electrical contact between the electrodes that make up the cell.
B)A salt bridge carries electrons between the cathode and anode.
C)A salt bridge insulates the two electrodes.
D)A salt bridge allows the electrolyte solution to siphon from one side of the cell to the other so the levels remain
Equal.
E)A salt bridge allows electrolyte to flow from one half-cell to the other in order to maintain electroneutrality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Based on the following electrochemical cell, which statement is ? 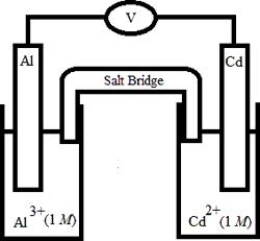 Half-Reaction E° (V) Al3+(aq) + 3e- →
Half-Reaction E° (V) Al3+(aq) + 3e- →
−1)66
Al(s)
Cd2+(aq) + 2e- →
−0)40
Cd(s)
A)Al(s) is oxidized and is the anode.
B)Al(s) is oxidized and is the cathode.
C)Cd(s) is oxidized and is the anode.
D)Cd(s) is oxidized and is the cathode.
E)No reaction occurs because E°cell < 0.
 Half-Reaction E° (V) Al3+(aq) + 3e- →
Half-Reaction E° (V) Al3+(aq) + 3e- →−1)66
Al(s)
Cd2+(aq) + 2e- →
−0)40
Cd(s)
A)Al(s) is oxidized and is the anode.
B)Al(s) is oxidized and is the cathode.
C)Cd(s) is oxidized and is the anode.
D)Cd(s) is oxidized and is the cathode.
E)No reaction occurs because E°cell < 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which element is associated with the term "galvanized"?
A)Ga
B)Zn
C)Cd
D)Hg
E)Pb
A)Ga
B)Zn
C)Cd
D)Hg
E)Pb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Aluminum does not corrode in the same manner as iron does, because
A)aluminum does not react with oxygen gas.
B)a protective layer of aluminum oxide forms on the metal surface.
C)aluminum is harder to oxidize than iron.
D)iron gives cathodic protection to aluminum.
E)the electrical circuit cannot be completed on an aluminum surface.
A)aluminum does not react with oxygen gas.
B)a protective layer of aluminum oxide forms on the metal surface.
C)aluminum is harder to oxidize than iron.
D)iron gives cathodic protection to aluminum.
E)the electrical circuit cannot be completed on an aluminum surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which is the half-reaction at the cathode in a lead storage battery?
A)Pb(s)+ PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42-(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
B)PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42−(aq) + 2e− → PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
C)Pb(s) + SO42−(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 2e−
D)Pb(s) → Pb(s) + 2e−
E)H2(g) → 2H+(aq) + 2e−
A)Pb(s)+ PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42-(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
B)PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42−(aq) + 2e− → PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
C)Pb(s) + SO42−(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 2e−
D)Pb(s) → Pb(s) + 2e−
E)H2(g) → 2H+(aq) + 2e−

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which is the half-reaction at the anode in a lead storage battery?
A)Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42−(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
B)PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42−(aq) + 2e− → PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
C)Pb(s) + SO42-(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 2e−
D)Pb(s) → Pb(s) + 2e−
E)H2(g) → 2H+(aq) + 2e−
A)Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42−(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
B)PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42−(aq) + 2e− → PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
C)Pb(s) + SO42-(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 2e−
D)Pb(s) → Pb(s) + 2e−
E)H2(g) → 2H+(aq) + 2e−

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Iron objects such as storage tanks and underground pipelines can be protected from corrosion by connecting them through a wire to a piece of
A)Pb.
B)Ag.
C)Sn.
D)Mg.
E)Cu.
A)Pb.
B)Ag.
C)Sn.
D)Mg.
E)Cu.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which is the correct cell notation for the following reaction? Au3+(aq) + Al(s) → Al3+(aq) + Au(s)
A)Al3+(aq)|Al(s)||Au3+(aq)|Au(s)
B)Al(s)|Al3+(aq)||Au3+(aq)|Au(s)
C)Al3+(aq)|Au3+(aq)||Al(s)|Au(s)
D)Al3+(aq)|Au(s)||Au3+(aq)|Al(s)
E)Au(s)|Al(s)||Au3+(aq)|Al3+(aq)
A)Al3+(aq)|Al(s)||Au3+(aq)|Au(s)
B)Al(s)|Al3+(aq)||Au3+(aq)|Au(s)
C)Al3+(aq)|Au3+(aq)||Al(s)|Au(s)
D)Al3+(aq)|Au(s)||Au3+(aq)|Al(s)
E)Au(s)|Al(s)||Au3+(aq)|Al3+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A voltaic cell prepared using aluminum and nickel has the following cell notation.Al(s) | Al3+(aq) || Ni2+(aq) | Ni(s) Which reaction occurs at the anode?
A)Al(s) → Al3+(aq) + 3e−
B)Al3+(aq) + 3e− → Al(s)
C)Ni(s) → Ni2+(aq) + 2e−
D)Ni2+(aq) + 2e− → Ni(s)
E)Ni(s) + Ni2+(aq) → Al(s) + Al3+(aq)
A)Al(s) → Al3+(aq) + 3e−
B)Al3+(aq) + 3e− → Al(s)
C)Ni(s) → Ni2+(aq) + 2e−
D)Ni2+(aq) + 2e− → Ni(s)
E)Ni(s) + Ni2+(aq) → Al(s) + Al3+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A voltaic cell is prepared using copper and silver.Its cell notation is shown below.Cu(s) | Cu2+(aq) || Ag+(aq) | Ag(s) Which reaction occurs at the cathode?
A)Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e−
B)Cu2+(aq) + 2e−→ Cu(s)
C)Ag(s) → Ag+(aq) + e−
D)Ag+(aq) + e− → Ag(s)
E)Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
A)Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e−
B)Cu2+(aq) + 2e−→ Cu(s)
C)Ag(s) → Ag+(aq) + e−
D)Ag+(aq) + e− → Ag(s)
E)Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which electrochemical cell pictured below corresponds to the following cell diagram?
Cr(s) | Cr3+(aq, 1.0 M) || Sn2+(aq, 1.0 M) | Sn(s)
A)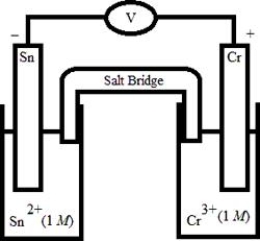
B)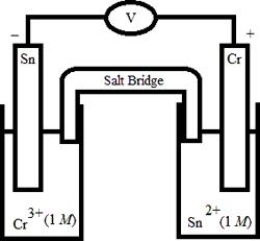
C)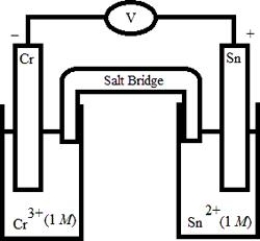
D)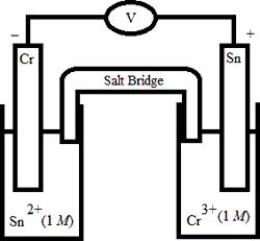
E)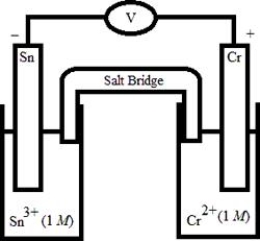
Cr(s) | Cr3+(aq, 1.0 M) || Sn2+(aq, 1.0 M) | Sn(s)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



