Deck 15: Biochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Biochemistry
1
Which of the structures below corresponds to the dipeptide serylalanine? Note the following structures: 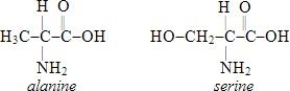
A)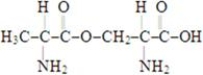
B)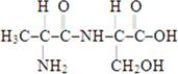
C)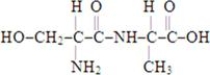
D)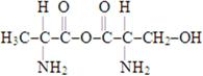
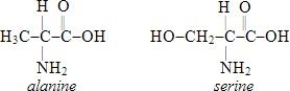
A)
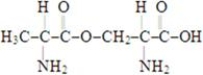
B)
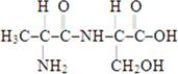
C)
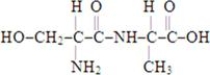
D)

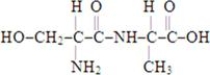
2
Phosphorus is an essential mineral element.It is an important atom in which one of the following?
A)Amino acids
B)Proteins
C)Polyethylene
D)Nylon
E)DNA
A)Amino acids
B)Proteins
C)Polyethylene
D)Nylon
E)DNA
DNA
3
Which of the following describes a lipid?
A)A group of molecules that contain both a carboxylic acid and amine functional group.
B)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
C)A group of small organic molecules that are insoluble in water.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A molecule that contains C, H, and N and exhibits Brønsted base behavior
A)A group of molecules that contain both a carboxylic acid and amine functional group.
B)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
C)A group of small organic molecules that are insoluble in water.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A molecule that contains C, H, and N and exhibits Brønsted base behavior
A group of small organic molecules that are insoluble in water.
4
Which of the following describes a fat?
A)A group of molecules that contain both a carboxylic acid and amine functional group.
B)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
C)A group of small organic molecules that are insoluble in water.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A tri-ester of glycerol where each of the hydroxyl-group hydrogen atoms in glycerol has been replaced by the alkyl group of a relatively long hydrocarbon chain carboxylic acid.
A)A group of molecules that contain both a carboxylic acid and amine functional group.
B)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
C)A group of small organic molecules that are insoluble in water.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A tri-ester of glycerol where each of the hydroxyl-group hydrogen atoms in glycerol has been replaced by the alkyl group of a relatively long hydrocarbon chain carboxylic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is not a protein?
A)hormones, such as oxytocin
B)structural substances, such as keratin
C)antibodies, such as immunoglobulin
D)transport facilitators, such as hemoglobin
E)saturated triglycerides, such as triolein
A)hormones, such as oxytocin
B)structural substances, such as keratin
C)antibodies, such as immunoglobulin
D)transport facilitators, such as hemoglobin
E)saturated triglycerides, such as triolein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following describes a triglyceride?
A)A molecules composed of three small sugar molecules.
B)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
C)A group of small organic molecules that are insoluble in water.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A tri-ester of glycerol where each of the hydroxyl-group hydrogen atoms in glycerol has been replaced by the alkyl group of a relatively long hydrocarbon chain carboxylic acid.
A)A molecules composed of three small sugar molecules.
B)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
C)A group of small organic molecules that are insoluble in water.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A tri-ester of glycerol where each of the hydroxyl-group hydrogen atoms in glycerol has been replaced by the alkyl group of a relatively long hydrocarbon chain carboxylic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of these elements is not found in proteins?
A)S
B)P
C)C
D)O
E)N
A)S
B)P
C)C
D)O
E)N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not a carbohydrate?
A)C6H12O6
B)C5H10O5
C)C10H18O9
D)C6H14O6
E)C12H22O11
A)C6H12O6
B)C5H10O5
C)C10H18O9
D)C6H14O6
E)C12H22O11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following describes a steroid?
A)A group of molecules that have a special grouping of 5- and 6-member rings in common.
B)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
C)A large biological polymer composed of amino acids.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A group of molecules that make up a lipid bilayer.
A)A group of molecules that have a special grouping of 5- and 6-member rings in common.
B)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
C)A large biological polymer composed of amino acids.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A group of molecules that make up a lipid bilayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The breaking apart of a dissacharide into its monosaccharide components involves the addition of a water molecule and is called _______.
A)condensation
B)peptide linkage
C)secondary structure
D)hydrolysis
E)transport
A)condensation
B)peptide linkage
C)secondary structure
D)hydrolysis
E)transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following describes a phospholipid?
A)A molecules composed of three small sugar molecules.
B)A diglyceride with an organic phosphate group in place of one of the fatty acids.
C)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A tri-ester of glycerol where each of the hydroxyl-group hydrogen atoms in glycerol has been replaced by the alkyl group of a relatively long hydrocarbon chain carboxylic acid.
A)A molecules composed of three small sugar molecules.
B)A diglyceride with an organic phosphate group in place of one of the fatty acids.
C)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A tri-ester of glycerol where each of the hydroxyl-group hydrogen atoms in glycerol has been replaced by the alkyl group of a relatively long hydrocarbon chain carboxylic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is a fatty acid?
A)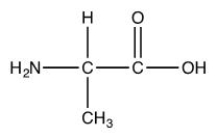
B)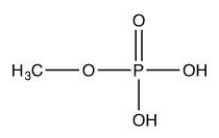
C)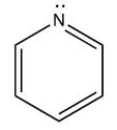
D)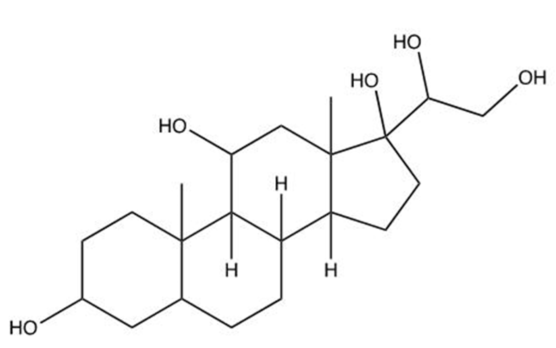
E)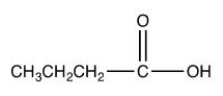
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the structures below corresponds to the dipeptide alanylserine? 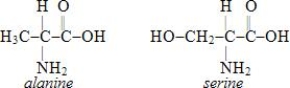
A)
B)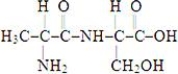
C)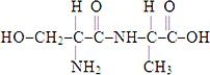
D)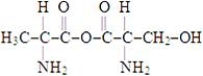
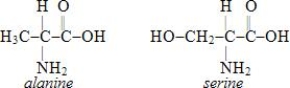
A)

B)
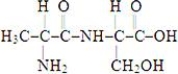
C)
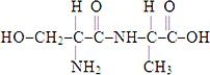
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following refers to a primary structure?
A)The shape the protein chain adopts as the result of hydrogen bonding.
B)The sequence of amino acids that make up a protein chain.
C)The folding of a protein into a characteristic shape.
D)The shape formed by two or more folded protein chains coming together.
E)None of the above.
A)The shape the protein chain adopts as the result of hydrogen bonding.
B)The sequence of amino acids that make up a protein chain.
C)The folding of a protein into a characteristic shape.
D)The shape formed by two or more folded protein chains coming together.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following describes a protein?
A)A molecules composed of three small sugar molecules.
B)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
C)A large biological polymer composed of amino acids.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A tri-ester of glycerol where each of the hydroxyl-group hydrogen atoms in glycerol has been replaced by the alkyl group of a relatively long hydrocarbon chain carboxylic acid.
A)A molecules composed of three small sugar molecules.
B)A relatively small, water-soluble molecule that contains either a ketone or an aldehyde functional group.
C)A large biological polymer composed of amino acids.
D)And ester of phosphoric acid where one or more of the ionizable hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an R group.
E)A tri-ester of glycerol where each of the hydroxyl-group hydrogen atoms in glycerol has been replaced by the alkyl group of a relatively long hydrocarbon chain carboxylic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A peptide bond (also called an amide bond) joins two amino acids together.What atoms are linked by this bond?
A)C - O
B)C - H
C)C - N
D)N - S
E)S - C
A)C - O
B)C - H
C)C - N
D)N - S
E)S - C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a steroid?
A)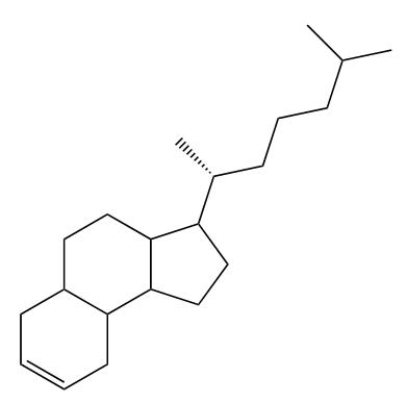
B)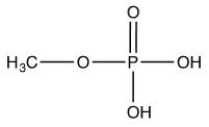
C)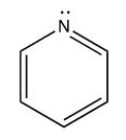
D)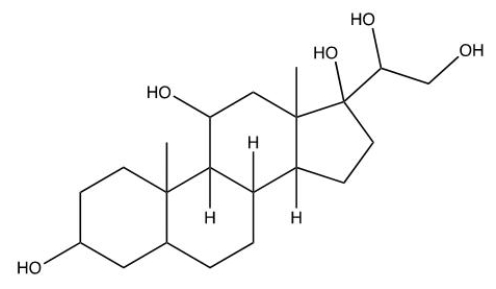
E)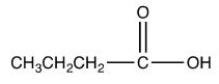
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An amino acid is a compound that contains at least
A)one amino group and one amide group.
B)two amino groups and one carboxylic acid group.
C)one hydroxyl group and one methyl group.
D)one carboxylic acid group and one amino group.
E)one methyl group and one amide group.
A)one amino group and one amide group.
B)two amino groups and one carboxylic acid group.
C)one hydroxyl group and one methyl group.
D)one carboxylic acid group and one amino group.
E)one methyl group and one amide group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following refers to a secondary structure?
A)The shape the protein chain adopts as the result of hydrogen bonding.
B)The sequence of amino acids that make up a protein chain.
C)The folding of a protein into a characteristic shape.
D)The shape formed by two or more folded protein chains coming together.
E)None of the above.
A)The shape the protein chain adopts as the result of hydrogen bonding.
B)The sequence of amino acids that make up a protein chain.
C)The folding of a protein into a characteristic shape.
D)The shape formed by two or more folded protein chains coming together.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The backbone of a strand of nucleic acid consists of
A)phosphate units only.
B)phosphate and sugar units.
C)polyester.
D)phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base units.
E)sugar units only.
A)phosphate units only.
B)phosphate and sugar units.
C)polyester.
D)phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base units.
E)sugar units only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



