Deck 13: Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Equilibrium
1
Which is the correct equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2C6H6(g) + 15O2(g)  12CO₂(g) + 6H₂O(g)
12CO₂(g) + 6H₂O(g)
A)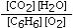
B)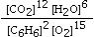
C)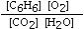
D)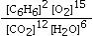
E)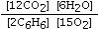
 12CO₂(g) + 6H₂O(g)
12CO₂(g) + 6H₂O(g)A)
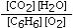
B)
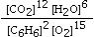
C)
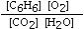
D)
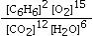
E)
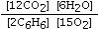
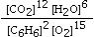
2
At 450°C, tert-butyl alcohol decomposes into water and isobutene.(CH3)3COH(g)  (CH3)2CCH2(g) + H2O(g) A reaction vessel contains these compounds at equilibrium.What will happen if the volume of the container is reduced by 50% at constant temperature?
(CH3)2CCH2(g) + H2O(g) A reaction vessel contains these compounds at equilibrium.What will happen if the volume of the container is reduced by 50% at constant temperature?
A)The forward reaction will proceed in order to reestablish equilibrium.
B)The reverse reaction will proceed in order to reestablish equilibrium.
C)No change occurs.
D)The equilibrium constant will increase.
E)The equilibrium constant will decrease.
 (CH3)2CCH2(g) + H2O(g) A reaction vessel contains these compounds at equilibrium.What will happen if the volume of the container is reduced by 50% at constant temperature?
(CH3)2CCH2(g) + H2O(g) A reaction vessel contains these compounds at equilibrium.What will happen if the volume of the container is reduced by 50% at constant temperature?A)The forward reaction will proceed in order to reestablish equilibrium.
B)The reverse reaction will proceed in order to reestablish equilibrium.
C)No change occurs.
D)The equilibrium constant will increase.
E)The equilibrium constant will decrease.
The reverse reaction will proceed in order to reestablish equilibrium.
3
Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction shown. 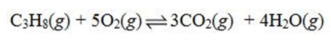
A)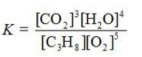
B)
C)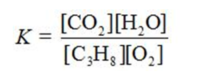
D)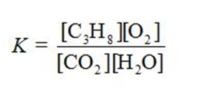
E)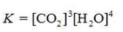
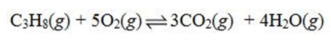
A)
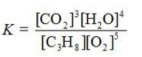
B)

C)
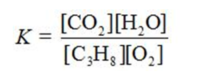
D)
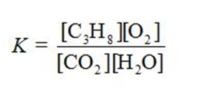
E)
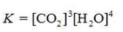
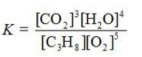
4
The reaction system POBr3(g)  POBr(g) + Br2(g) is at equilibrium.Which of the following statements describes the behavior of the system if POBr is added to the container?
POBr(g) + Br2(g) is at equilibrium.Which of the following statements describes the behavior of the system if POBr is added to the container?
A)POBr will be consumed in order to establish a new equilibrium.
B)The partial pressures of POBr3 and POBr will remain steady while the partial pressure of bromine increases.
C)The partial pressure of bromine will increase while the partial pressure of POBr decreases.
D)The partial pressure of bromine remains steady while the partial pressures of POBr3 and POBr increase.
E)The forward reaction will proceed to establish equilibrium.
 POBr(g) + Br2(g) is at equilibrium.Which of the following statements describes the behavior of the system if POBr is added to the container?
POBr(g) + Br2(g) is at equilibrium.Which of the following statements describes the behavior of the system if POBr is added to the container?A)POBr will be consumed in order to establish a new equilibrium.
B)The partial pressures of POBr3 and POBr will remain steady while the partial pressure of bromine increases.
C)The partial pressure of bromine will increase while the partial pressure of POBr decreases.
D)The partial pressure of bromine remains steady while the partial pressures of POBr3 and POBr increase.
E)The forward reaction will proceed to establish equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
For the reaction 2X(g) + Y(g)  2Z(g), K = 1.00 ×103 at 500 K.If at equilibrium the concentration of X is 0.20 M and the concentration of Y is 0.50 M, what is the equilibrium concentration of Z?
2Z(g), K = 1.00 ×103 at 500 K.If at equilibrium the concentration of X is 0.20 M and the concentration of Y is 0.50 M, what is the equilibrium concentration of Z?
A)2.2 M
B)3.2 M
C)3.5 M
D)4.5 M
E)7.1 M
 2Z(g), K = 1.00 ×103 at 500 K.If at equilibrium the concentration of X is 0.20 M and the concentration of Y is 0.50 M, what is the equilibrium concentration of Z?
2Z(g), K = 1.00 ×103 at 500 K.If at equilibrium the concentration of X is 0.20 M and the concentration of Y is 0.50 M, what is the equilibrium concentration of Z?A)2.2 M
B)3.2 M
C)3.5 M
D)4.5 M
E)7.1 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is defined as a fraction with equilibrium product concentrations in the numerator and equilibrium reactant concentrations in the denominator and each concentration raised to a power equal to the corresponding stoichiometric coefficient in the balanced chemical equation?
A)Reversibility expression
B)Reaction expression
C)Equilibrium expression
D)Product quotient
E)Mass action
A)Reversibility expression
B)Reaction expression
C)Equilibrium expression
D)Product quotient
E)Mass action

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction shown. 2NOCl(g) ⇌ 2NO(g) + Cl2(g)
A)
B)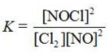
C)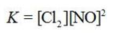
D)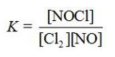
E)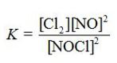
A)

B)
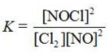
C)
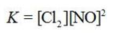
D)
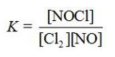
E)
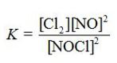

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
At equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Hydrogen peroxide may decompose to form water and oxygen gas according to the following reaction. 2H2O2(g)  2H2O(g) + O2(g)
2H2O(g) + O2(g)
In a particular experiment, 1.75 moles of H2O2 were placed in a 2.5-L reaction chamber at 307ºC.After equilibrium was reached, 1.20 moles of H2O2 remained.What is K for the reaction?
A)2.0 × 10−4
B)2.3 × 10−2
C)2.4 × 10-3
D)5.5 × 10−3
E)3.9 × 10−4
 2H2O(g) + O2(g)
2H2O(g) + O2(g)In a particular experiment, 1.75 moles of H2O2 were placed in a 2.5-L reaction chamber at 307ºC.After equilibrium was reached, 1.20 moles of H2O2 remained.What is K for the reaction?
A)2.0 × 10−4
B)2.3 × 10−2
C)2.4 × 10-3
D)5.5 × 10−3
E)3.9 × 10−4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
At 35ºC, the equilibrium constant for the reaction 2NOCl(g) ![<strong>At 35ºC, the equilibrium constant for the reaction 2NOCl(g) 2NO(g) + Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) is K = 1.6 × 10<sup>−5</sup>.An equilibrium mixture was found to have the following concentrations of Cl<sub>2</sub> and NOCl: [Cl<sub>2</sub>] = 1.2 × 10<sup>−2</sup> M; [NOCl] = 2.8 × 10<sup>−1</sup> M.Calculate the concentration of NO(g) at equilibrium.</strong> A)1.0 × 10<sup>−4</sup> M B)1.0 × 10<sup>−2</sup> M C)2.8 × 10<sup>−1</sup> M D)2.4 × 10<sup>−2</sup> M E)1.6 × 10<sup>−3</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9c_f81b_8379_d59077930e7e_TB1849_11.jpg) 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) is K = 1.6 × 10−5.An equilibrium mixture was found to have the following concentrations of Cl2 and NOCl: [Cl2] = 1.2 × 10−2 M; [NOCl] = 2.8 × 10−1 M.Calculate the concentration of NO(g) at equilibrium.
2NO(g) + Cl2(g) is K = 1.6 × 10−5.An equilibrium mixture was found to have the following concentrations of Cl2 and NOCl: [Cl2] = 1.2 × 10−2 M; [NOCl] = 2.8 × 10−1 M.Calculate the concentration of NO(g) at equilibrium.
A)1.0 × 10−4 M
B)1.0 × 10−2 M
C)2.8 × 10−1 M
D)2.4 × 10−2 M
E)1.6 × 10−3 M
![<strong>At 35ºC, the equilibrium constant for the reaction 2NOCl(g) 2NO(g) + Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) is K = 1.6 × 10<sup>−5</sup>.An equilibrium mixture was found to have the following concentrations of Cl<sub>2</sub> and NOCl: [Cl<sub>2</sub>] = 1.2 × 10<sup>−2</sup> M; [NOCl] = 2.8 × 10<sup>−1</sup> M.Calculate the concentration of NO(g) at equilibrium.</strong> A)1.0 × 10<sup>−4</sup> M B)1.0 × 10<sup>−2</sup> M C)2.8 × 10<sup>−1</sup> M D)2.4 × 10<sup>−2</sup> M E)1.6 × 10<sup>−3</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9c_f81b_8379_d59077930e7e_TB1849_11.jpg) 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) is K = 1.6 × 10−5.An equilibrium mixture was found to have the following concentrations of Cl2 and NOCl: [Cl2] = 1.2 × 10−2 M; [NOCl] = 2.8 × 10−1 M.Calculate the concentration of NO(g) at equilibrium.
2NO(g) + Cl2(g) is K = 1.6 × 10−5.An equilibrium mixture was found to have the following concentrations of Cl2 and NOCl: [Cl2] = 1.2 × 10−2 M; [NOCl] = 2.8 × 10−1 M.Calculate the concentration of NO(g) at equilibrium.A)1.0 × 10−4 M
B)1.0 × 10−2 M
C)2.8 × 10−1 M
D)2.4 × 10−2 M
E)1.6 × 10−3 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A mixture of 0.500 mole of carbon monoxide and 0.400 mole of bromine was placed into a rigid 1.00-L container and the system was allowed to come to equilibrium.The equilibrium concentration of COBr2 was 0.233 M.What is K for this reaction? CO(g) + Br2(g)  COBr2(g)
COBr2(g)
A)5.23
B)2.14
C)1.17
D)0.467
E)0.191
 COBr2(g)
COBr2(g)A)5.23
B)2.14
C)1.17
D)0.467
E)0.191

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Compounds A, B, and C react according to the following equation.3A(g) + 2B(g) ![<strong>Compounds A, B, and C react according to the following equation.3A(g) + 2B(g) 2C(g) At 100°C a mixture of these gases at equilibrium showed that [A] = 0.855 M, [B] = 1.23 M, and [C] = 1.75 M.What is the value of K for this reaction?</strong> A)0.309 B)0.601 C)1.66 D)2.25 E)3.24](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9c_82e4_8379_f5364b6c375c_TB1849_11.jpg) 2C(g) At 100°C a mixture of these gases at equilibrium showed that [A] = 0.855 M, [B] = 1.23 M, and [C] = 1.75 M.What is the value of K for this reaction?
2C(g) At 100°C a mixture of these gases at equilibrium showed that [A] = 0.855 M, [B] = 1.23 M, and [C] = 1.75 M.What is the value of K for this reaction?
A)0.309
B)0.601
C)1.66
D)2.25
E)3.24
![<strong>Compounds A, B, and C react according to the following equation.3A(g) + 2B(g) 2C(g) At 100°C a mixture of these gases at equilibrium showed that [A] = 0.855 M, [B] = 1.23 M, and [C] = 1.75 M.What is the value of K for this reaction?</strong> A)0.309 B)0.601 C)1.66 D)2.25 E)3.24](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9c_82e4_8379_f5364b6c375c_TB1849_11.jpg) 2C(g) At 100°C a mixture of these gases at equilibrium showed that [A] = 0.855 M, [B] = 1.23 M, and [C] = 1.75 M.What is the value of K for this reaction?
2C(g) At 100°C a mixture of these gases at equilibrium showed that [A] = 0.855 M, [B] = 1.23 M, and [C] = 1.75 M.What is the value of K for this reaction?A)0.309
B)0.601
C)1.66
D)2.25
E)3.24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A container was charged with hydrogen, nitrogen, and ammonia gases at 120°C and the system was allowed to reach equilibrium.What will happen if the volume of the container is increased at constant temperature? 3H2(g) + N2(g)  2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
A)There will be no effect.
B)More ammonia will be produced at the expense of hydrogen and nitrogen.
C)Hydrogen and nitrogen will be produced at the expense of ammonia.
D)The equilibrium constant will increase.
E)The equilibrium constant will decrease.
 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)A)There will be no effect.
B)More ammonia will be produced at the expense of hydrogen and nitrogen.
C)Hydrogen and nitrogen will be produced at the expense of ammonia.
D)The equilibrium constant will increase.
E)The equilibrium constant will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For the nitrogen fixation reaction, 3H2(g) + N2(g)  2NH3(g), K = 6.0 × 10−2 at 500°C.If 0.250 M H2 and 0.050 M NH3 are present at equilibrium, what is the equilibrium concentration of N2?
2NH3(g), K = 6.0 × 10−2 at 500°C.If 0.250 M H2 and 0.050 M NH3 are present at equilibrium, what is the equilibrium concentration of N2?
A)3.3 M
B)2.7 M
C)0.20 M
D)0.083 M
E)0.058 M
 2NH3(g), K = 6.0 × 10−2 at 500°C.If 0.250 M H2 and 0.050 M NH3 are present at equilibrium, what is the equilibrium concentration of N2?
2NH3(g), K = 6.0 × 10−2 at 500°C.If 0.250 M H2 and 0.050 M NH3 are present at equilibrium, what is the equilibrium concentration of N2?A)3.3 M
B)2.7 M
C)0.20 M
D)0.083 M
E)0.058 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
At elevated temperatures, hydrogen iodide may decompose to form hydrogen gas and iodine gas, as follows. 2HI(g) ![<strong>At elevated temperatures, hydrogen iodide may decompose to form hydrogen gas and iodine gas, as follows. 2HI(g) H<sub>2</sub>(g) + I<sub>2</sub>(g) In a particular experiment, the concentrations at equilibrium were measured to be [HI] = 0.85 mol/L, [I<sub>2</sub>] = 0.60 mol/L, and [H<sub>2</sub>] = 0.27 mol/L.What is K for the above reaction?</strong> A)5.3 B)0.22 C)4.5 D)0.19 E)1.6× 10<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9c_82e3_8379_812b10ac22ec_TB1849_11.jpg) H2(g) + I2(g)
H2(g) + I2(g)
In a particular experiment, the concentrations at equilibrium were measured to be [HI] = 0.85 mol/L, [I2] = 0.60 mol/L, and [H2] = 0.27 mol/L.What is K for the above reaction?
A)5.3
B)0.22
C)4.5
D)0.19
E)1.6× 102
![<strong>At elevated temperatures, hydrogen iodide may decompose to form hydrogen gas and iodine gas, as follows. 2HI(g) H<sub>2</sub>(g) + I<sub>2</sub>(g) In a particular experiment, the concentrations at equilibrium were measured to be [HI] = 0.85 mol/L, [I<sub>2</sub>] = 0.60 mol/L, and [H<sub>2</sub>] = 0.27 mol/L.What is K for the above reaction?</strong> A)5.3 B)0.22 C)4.5 D)0.19 E)1.6× 10<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9c_82e3_8379_812b10ac22ec_TB1849_11.jpg) H2(g) + I2(g)
H2(g) + I2(g)In a particular experiment, the concentrations at equilibrium were measured to be [HI] = 0.85 mol/L, [I2] = 0.60 mol/L, and [H2] = 0.27 mol/L.What is K for the above reaction?
A)5.3
B)0.22
C)4.5
D)0.19
E)1.6× 102

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If, in a particular process, reactants are able to form products, and products are also able to form reactants, then this process may be described as
A)a reversible process.
B)an elementary process.
C)at equilibrium.
D)forbidden.
E)a forward process.
A)a reversible process.
B)an elementary process.
C)at equilibrium.
D)forbidden.
E)a forward process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
During a chemical reaction, what defines when the concentrations of the reactants and products reach a constant level?
A)Elementary process
B)Reversible reaction
C)Rate law
D)Rate constant
E)Equilibrium
A)Elementary process
B)Reversible reaction
C)Rate law
D)Rate constant
E)Equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A 6.0-L vessel was found to contain 1.0 mol BrCl3, 2.0 mol Br2 and 6.0 mol Cl2.What is the equilibrium constant, K, for this equilibrium mixture for the reaction 2BrCl3(g)  Br2(g) + 3Cl2(g)?
Br2(g) + 3Cl2(g)?
A)0.014
B)108
C)18
D)12
E)432
 Br2(g) + 3Cl2(g)?
Br2(g) + 3Cl2(g)?A)0.014
B)108
C)18
D)12
E)432

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which substances are included in the equilibrium constant expression, Kc?
A)Only pure solids
B)Only pure liquids
C)Only pure solids and liquids
D)Only gases and dissolved substances
E)All participating substances
A)Only pure solids
B)Only pure liquids
C)Only pure solids and liquids
D)Only gases and dissolved substances
E)All participating substances

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which is the correct equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2BrCl3(g) ![<strong>Which is the correct equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2BrCl<sub>3</sub>(g) Br<sub>2</sub>(g) + 3Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) </strong> A) K<sub>c</sub> = [Br<sub>2</sub>] [Cl<sub>2</sub>]/[BrCl<sub>3</sub>] B) K<sub>c</sub> = [Br<sub>2</sub>] [Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup>/[BrCl<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup> C) K<sub>c</sub> = [Br<sub>2</sub>] [Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>/[BrCl<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup> D) K<sub>c</sub> = [BrCl<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>/([Br<sub>2</sub>] × [Cl<sub>2</sub>]3) E) K<sub>c</sub> = 2[BrCl<sub>3</sub>]<sup><sub>2</sub></sup>/([Br<sup>2</sup>] × 3[Cl2]<sup>3</sup>)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9c_0da6_8379_c52b0a42d726_TB1849_11.jpg) Br2(g) + 3Cl2(g)
Br2(g) + 3Cl2(g)
A) Kc = [Br2] [Cl2]/[BrCl3]
B) Kc = [Br2] [Cl2]5/[BrCl3]2
C) Kc = [Br2] [Cl2]3/[BrCl3]2
D) Kc = [BrCl3]2/([Br2] × [Cl2]3)
E) Kc = 2[BrCl3]2/([Br2] × 3[Cl2]3)
![<strong>Which is the correct equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2BrCl<sub>3</sub>(g) Br<sub>2</sub>(g) + 3Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) </strong> A) K<sub>c</sub> = [Br<sub>2</sub>] [Cl<sub>2</sub>]/[BrCl<sub>3</sub>] B) K<sub>c</sub> = [Br<sub>2</sub>] [Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup>/[BrCl<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup> C) K<sub>c</sub> = [Br<sub>2</sub>] [Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>/[BrCl<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup> D) K<sub>c</sub> = [BrCl<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>/([Br<sub>2</sub>] × [Cl<sub>2</sub>]3) E) K<sub>c</sub> = 2[BrCl<sub>3</sub>]<sup><sub>2</sub></sup>/([Br<sup>2</sup>] × 3[Cl2]<sup>3</sup>)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9c_0da6_8379_c52b0a42d726_TB1849_11.jpg) Br2(g) + 3Cl2(g)
Br2(g) + 3Cl2(g) A) Kc = [Br2] [Cl2]/[BrCl3]
B) Kc = [Br2] [Cl2]5/[BrCl3]2
C) Kc = [Br2] [Cl2]3/[BrCl3]2
D) Kc = [BrCl3]2/([Br2] × [Cl2]3)
E) Kc = 2[BrCl3]2/([Br2] × 3[Cl2]3)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When the following reaction is at equilibrium 2NOCl(g) ![When the following reaction is at equilibrium 2NOCl(g) 2NO(g) + Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) then [NO]<sup>2</sup> [Cl<sub>2</sub>] = K [NOCl]<sup>2</sup>.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9d_1f2c_8379_217481861122_TB1849_11.jpg) 2NO(g) + Cl2(g)
2NO(g) + Cl2(g)
then [NO]2 [Cl2] = K [NOCl]2.
![When the following reaction is at equilibrium 2NOCl(g) 2NO(g) + Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) then [NO]<sup>2</sup> [Cl<sub>2</sub>] = K [NOCl]<sup>2</sup>.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9d_1f2c_8379_217481861122_TB1849_11.jpg) 2NO(g) + Cl2(g)
2NO(g) + Cl2(g)then [NO]2 [Cl2] = K [NOCl]2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which reaction shown will have the highest concentration of products at equilibrium?
A)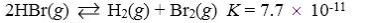
B)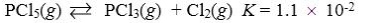
C)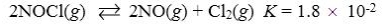
D)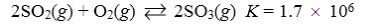
E)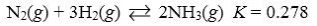
A)
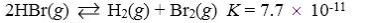
B)
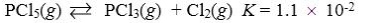
C)
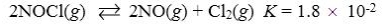
D)
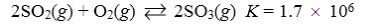
E)
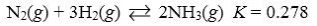

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Determine the balanced chemical equation that corresponds to the given equilibrium expression. 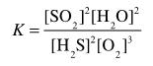
A)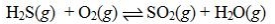
B)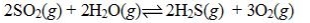
C)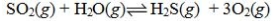
D)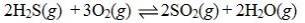
E)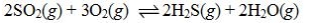
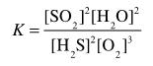
A)
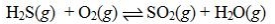
B)
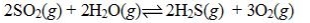
C)
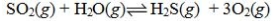
D)
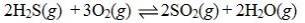
E)
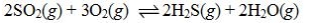

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the system 3H2(g) + N2(g)  2NH3(g) is at equilibrium and more N2 is added, a net reaction that consumes some of the added N2 will occur until a new equilibrium is reached.
2NH3(g) is at equilibrium and more N2 is added, a net reaction that consumes some of the added N2 will occur until a new equilibrium is reached.
 2NH3(g) is at equilibrium and more N2 is added, a net reaction that consumes some of the added N2 will occur until a new equilibrium is reached.
2NH3(g) is at equilibrium and more N2 is added, a net reaction that consumes some of the added N2 will occur until a new equilibrium is reached.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When a reaction system reaches equilibrium, the forward and reverse reactions stop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Determine the balanced chemical equation that corresponds to the given equilibrium expression. 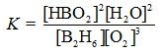
A)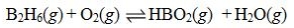
B)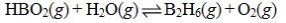
C)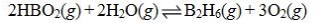
D)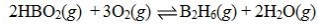
E)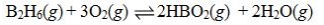
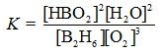
A)
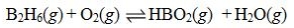
B)
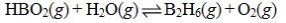
C)
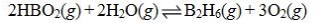
D)
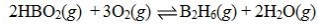
E)
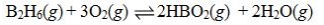

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction CuO(s) + H2(g) ![The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction CuO(s) + H<sub>2</sub>(g) Cu(s) + H<sub>2</sub>O(g) is K = [H<sub>2</sub>]/[H<sub>2</sub>O].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9d_1f2d_8379_31b5eef2f1c9_TB1849_11.jpg) Cu(s) + H2O(g) is K = [H2]/[H2O].
Cu(s) + H2O(g) is K = [H2]/[H2O].
![The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction CuO(s) + H<sub>2</sub>(g) Cu(s) + H<sub>2</sub>O(g) is K = [H<sub>2</sub>]/[H<sub>2</sub>O].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1849/11ea78cf_0f9d_1f2d_8379_31b5eef2f1c9_TB1849_11.jpg) Cu(s) + H2O(g) is K = [H2]/[H2O].
Cu(s) + H2O(g) is K = [H2]/[H2O].
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which reaction shown will have the highest concentration of reactants at equilibrium?
A)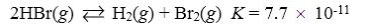
B)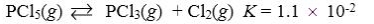
C)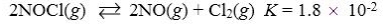
D)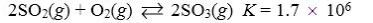
E)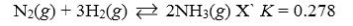
A)
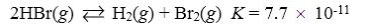
B)
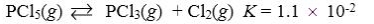
C)
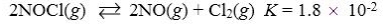
D)
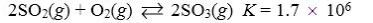
E)
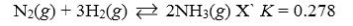

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which reaction shown will have the highest concentration of products at equilibrium?
A)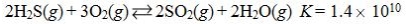
B)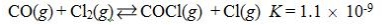
C)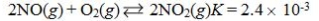
D)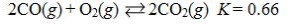
E)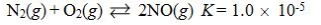
A)
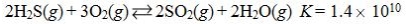
B)
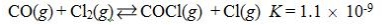
C)
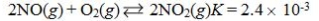
D)
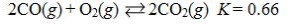
E)
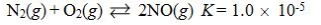

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which reaction shown will have the highest concentration of reactants at equilibrium?
A)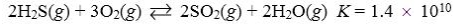
B)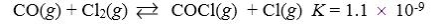
C)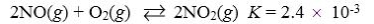
D)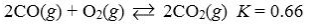
E)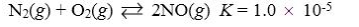
A)
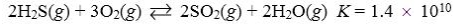
B)
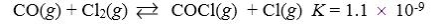
C)
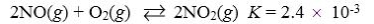
D)
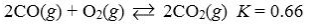
E)
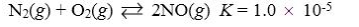

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



