Deck 13: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/166
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Chemical Equilibrium
1
A mixture of carbon monoxide,hydrogen,and methanol is at equilibrium.The balanced chemical equation is: CO(g)+ 2H2(g)⇌ CH3OH(g).At 250°C,the mixture contains 0.0960 M CO,0.191 M H2,and 0.150 M CH3OH.What is the value for Kc?
A)2)33 × 10-2
B)0)244
C)4)09
D)42.8
A)2)33 × 10-2
B)0)244
C)4)09
D)42.8
42.8
2
For the reaction: N2(g)+ 2 O2(g)⇌ 2 NO2(g),Kc = 8.3 × 10-10 at 25°C.What is the concentration of N2 gas at equilibrium when the concentration of NO2 is twice the concentration of O2 gas?
A)2)1 × 10-10 M
B)4)2 × 10-10 M
C)2)4 × 109 M
D)4)8 × 109 M
A)2)1 × 10-10 M
B)4)2 × 10-10 M
C)2)4 × 109 M
D)4)8 × 109 M
4)8 × 109 M
3
Given the reaction: 2 HI ⇌ H2 + I2.If Kc' for the reverse reaction is 1.85 × 10-2 at 425°C,what is Kc for the forward reaction at the same temperature?
A)-1.85 × 10-2
B)1)85 × 10-2
C)3)70 × 10-2
D)54.1
A)-1.85 × 10-2
B)1)85 × 10-2
C)3)70 × 10-2
D)54.1
54.1
4
Nitric oxide reacts with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide:
2 NO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 NO2(g)
What is Kc' for the reverse reaction if the equilibrium concentration of NO is 0.300 M,O2 is 0.200 M,and NO2 is 0.530 M at 25°C?
A)0)0340
B)0)0641
C)0)624
D)15.6
2 NO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 NO2(g)
What is Kc' for the reverse reaction if the equilibrium concentration of NO is 0.300 M,O2 is 0.200 M,and NO2 is 0.530 M at 25°C?
A)0)0340
B)0)0641
C)0)624
D)15.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which one of the following statements about the equilibrium constant,Kp,is false?
A)Δn is equal to the sum of the coefficients of the gaseous products minus the sum of the coefficients of the gaseous reactants.
B)The relationship between Kp and Kc is: Kp = Kc (RT)Δn
C)The units for Kp are usually omitted.
D)Total pressures are used in the equilibrium equation in place of molar concentrations.
A)Δn is equal to the sum of the coefficients of the gaseous products minus the sum of the coefficients of the gaseous reactants.
B)The relationship between Kp and Kc is: Kp = Kc (RT)Δn
C)The units for Kp are usually omitted.
D)Total pressures are used in the equilibrium equation in place of molar concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If Kc is the equilibrium constant for a forward reaction,2 A⇌ B,what is Kc´ for the reaction 4 A⇌ 2B?
A)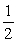 Kc
Kc
B)Kc
C)2 Kc
D)(Kc)2
A)
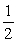 Kc
KcB)Kc
C)2 Kc
D)(Kc)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Nitric oxide reacts with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide:
2 NO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 NO2(g)
What is Kc for the forward reaction if the equilibrium concentration of NO is 0.200 M,O2 is 0.100 M,and NO2 is 0.250 M at 25°C?
A)8)00 × 10-2
B)6)41 × 10-2
C)12.5
D)15.6
2 NO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 NO2(g)
What is Kc for the forward reaction if the equilibrium concentration of NO is 0.200 M,O2 is 0.100 M,and NO2 is 0.250 M at 25°C?
A)8)00 × 10-2
B)6)41 × 10-2
C)12.5
D)15.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If Kc = 7.04 × 10-2 for the reaction: 2 HBr(g)⇌ H2(g)+ Br2(g),what is the value of Kc for the reaction: 1/2 H2(g)+ 1/2 Br2(g)== HBr(g)?
A)3)52 × 10-2
B)0)265
C)3)77
D)28.4
A)3)52 × 10-2
B)0)265
C)3)77
D)28.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Write the equilibrium equation for the forward reaction:
2 CH4 (g)+ 3 O2 (g)⇌ 2 CO (g)+ 4 H2O (g)
A)Kc =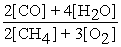
B)Kc =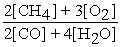
C)Kc =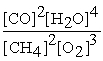
D)Kc =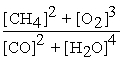
2 CH4 (g)+ 3 O2 (g)⇌ 2 CO (g)+ 4 H2O (g)
A)Kc =
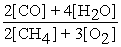
B)Kc =
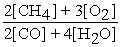
C)Kc =
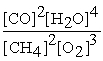
D)Kc =
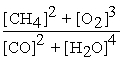

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Write the equilibrium equation for the reverse reaction:
2 CH4 (g)+ 3 O2 (g)⇌ 2 CO (g)+ 4 H2O (g)
A)Kc´ =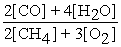
B)Kc´ =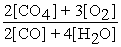
C)Kc´ =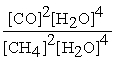
D)Kc´ =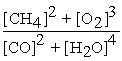
2 CH4 (g)+ 3 O2 (g)⇌ 2 CO (g)+ 4 H2O (g)
A)Kc´ =
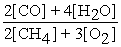
B)Kc´ =
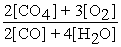
C)Kc´ =
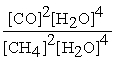
D)Kc´ =
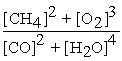

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If Kc is the equilibrium constant for a forward reaction what is Kc´ for the reverse reaction?
A)- Kc
B)Kc
C)(Kc)-1
D)none of these
A)- Kc
B)Kc
C)(Kc)-1
D)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the equilibrium equation for the reaction:
NH4NO3(s)⇌ N2O(g)+ 2 H2O(g)?
A)Kp = [N2O]
B)Kp = [N2O][H2O]
C)Kp = [N2O][H2O]2
D)Kp =![<strong>What is the equilibrium equation for the reaction: NH<sub>4</sub>NO<sub>3</sub>(s)⇌ N<sub>2</sub>O(g)+ 2 H<sub>2</sub>O(g)?</strong> A)K<sub>p</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>O] B)K<sub>p</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>O][H<sub>2</sub>O] C)K<sub>p</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>O][H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> D)K<sub>p</sub> =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4939/11ea7a38_c955_ec1e_aa4c_a5c0828c4e57_TB4939_11.jpg)
NH4NO3(s)⇌ N2O(g)+ 2 H2O(g)?
A)Kp = [N2O]
B)Kp = [N2O][H2O]
C)Kp = [N2O][H2O]2
D)Kp =
![<strong>What is the equilibrium equation for the reaction: NH<sub>4</sub>NO<sub>3</sub>(s)⇌ N<sub>2</sub>O(g)+ 2 H<sub>2</sub>O(g)?</strong> A)K<sub>p</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>O] B)K<sub>p</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>O][H<sub>2</sub>O] C)K<sub>p</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>O][H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> D)K<sub>p</sub> =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4939/11ea7a38_c955_ec1e_aa4c_a5c0828c4e57_TB4939_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The equilibrium equation is also known as the law of
A)coefficients.
B)constant concentration.
C)dynamic equilibrium.
D)mass action.
A)coefficients.
B)constant concentration.
C)dynamic equilibrium.
D)mass action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Write the equilibrium equation for the reverse reaction:
2 CH4(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 CO(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
A)Kp' =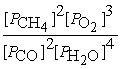
B)Kp' =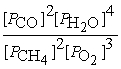
C)Kp' =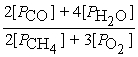
D)Kp' =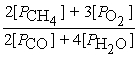
2 CH4(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 CO(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
A)Kp' =
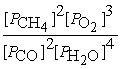
B)Kp' =
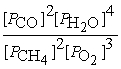
C)Kp' =
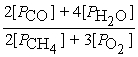
D)Kp' =
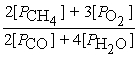

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is false regarding the equilibrium constant,Kc?
A)Kc for a reaction at a particular temperature always has the same value.
B)Kc for the reverse reaction is the negative of Kc for the forward reaction.
C)The numerical value of Kc depends on the form of the balanced equation.
D)When quoting Kc it is customary to omit units.
A)Kc for a reaction at a particular temperature always has the same value.
B)Kc for the reverse reaction is the negative of Kc for the forward reaction.
C)The numerical value of Kc depends on the form of the balanced equation.
D)When quoting Kc it is customary to omit units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If Kc equals 0.11 at 25°C for the reaction: N2O4(g)⇌ 2 NO2(g),what is Kc for the reaction: NO2(g)⇌ 1/2 N2O4(g)?
A)0)33
B)3)0
C)4)5
D)9)1
A)0)33
B)3)0
C)4)5
D)9)1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Write the equilibrium equation for the forward reaction:
2 CH4(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 CO(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
A)Kp =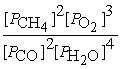
B)Kp=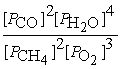
C)Kp =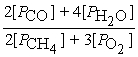
D)Kp =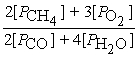
2 CH4(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 CO(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
A)Kp =
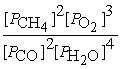
B)Kp=
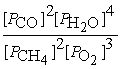
C)Kp =
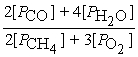
D)Kp =
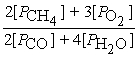

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which statement about the equilibrium constant is true? The value of Kc
A)changes as product concentration changes.
B)changes as reactant concentration changes.
C)changes as temperature changes.
D)never changes.
A)changes as product concentration changes.
B)changes as reactant concentration changes.
C)changes as temperature changes.
D)never changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Kp is related to Kc by the equation Kp = Kc (RT)n.What is the value of n for the reaction below? NH4NO3(s)⇌ N2O(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
A)-2
B)-1
C)+1
D)+2
A)-2
B)-1
C)+1
D)+2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which one of the following statements does not describe the equilibrium state?
A)Equilibrium is dynamic and there is no net conversion to reactants and products.
B)The concentration of the reactants is equal to the concentration of the products.
C)The concentration of the reactants and products reach a constant level.
D)The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
A)Equilibrium is dynamic and there is no net conversion to reactants and products.
B)The concentration of the reactants is equal to the concentration of the products.
C)The concentration of the reactants and products reach a constant level.
D)The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The oxidation of sulfur dioxide by oxygen to sulfur trioxide has been implicated as an important step in the formation of acid rain: 2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g).If the equilibrium partial pressures of SO2,O2,and SO3 are 0.564 atm,0.102 atm,and 0.333 atm respectively at 1000 K,what is Kp at that temperature?
A)0)292
B)3)42
C)5)79
D)8)11
A)0)292
B)3)42
C)5)79
D)8)11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the value for Kc for the following reaction:
PbCl2(s)⇌ Pb2+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq),
If PbCl2(s)= 1.50 grams,[Pb2+] = 1.6 × 10-2 M and [Cl-] = 3.2 × 10-2 M at equilibrium? (The molar mass of PbCl2(s)is 278 g/mol and its density is 5.85 g/cm3. )
A)7)6 × 10-7
B)1)6 × 10-5
C)6)2 × 104
D)1)3 × 106
PbCl2(s)⇌ Pb2+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq),
If PbCl2(s)= 1.50 grams,[Pb2+] = 1.6 × 10-2 M and [Cl-] = 3.2 × 10-2 M at equilibrium? (The molar mass of PbCl2(s)is 278 g/mol and its density is 5.85 g/cm3. )
A)7)6 × 10-7
B)1)6 × 10-5
C)6)2 × 104
D)1)3 × 106

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If Kc = 2.0 x 1033 at 25°C,for the following reaction: H2(g)+ Cl2(g)⇌ 2 HCl(g),then find Kp at the same temperature.
A)8)2 × 1031
B)9)7 × 1032
C)2)0 × 1033
D)4)9 × 1034
A)8)2 × 1031
B)9)7 × 1032
C)2)0 × 1033
D)4)9 × 1034

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the equilibrium equation for the following reaction?
C2H4 (g)+ 3 O2 (g)⇌ 2 CO2 (g)+ 2 H2O (l)
A)Kp =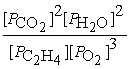
B)Kp =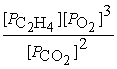
C)Kp =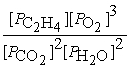
D)Kp =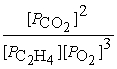
C2H4 (g)+ 3 O2 (g)⇌ 2 CO2 (g)+ 2 H2O (l)
A)Kp =
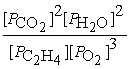
B)Kp =
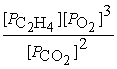
C)Kp =
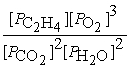
D)Kp =
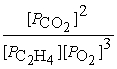

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the equilibrium equation for the following reaction?
FeS(s)+ 2 H3O+ (aq)⇌ Fe2+(aq)+ H2S (aq)+ 2 H2O (l)
A)Kc =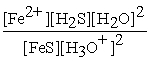
B)Kc =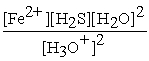
C)Kc =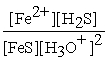
D)Kc =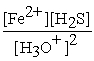
FeS(s)+ 2 H3O+ (aq)⇌ Fe2+(aq)+ H2S (aq)+ 2 H2O (l)
A)Kc =
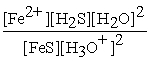
B)Kc =
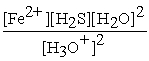
C)Kc =
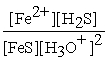
D)Kc =
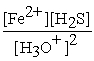

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The decomposition of ammonia is: 2 NH3(g)⇌ N2(g)+ 3 H2(g).If the pressure of ammonia is
1)0 × 10-3 atm,and the pressures of N2 and H2 are each 0.20 atm,what is the value for Kp' at 400°C for the reverse reaction?
A)-6.2 × 10-4
B)-1.6 × 103
C)6)2 × 10-4
D)1)6 × 103
1)0 × 10-3 atm,and the pressures of N2 and H2 are each 0.20 atm,what is the value for Kp' at 400°C for the reverse reaction?
A)-6.2 × 10-4
B)-1.6 × 103
C)6)2 × 10-4
D)1)6 × 103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Given the reaction at a certain temperature: 2 HI(g)⇌ H2(g)+ I2(g).At equilibrium,the partial pressure of HI is 1.8 × 10-3 atm,and the partial pressures for H2 and I2 are 0.10 atm each.Find Kp at that temperature.
A)3)2 × 10-4
B)5)6 × 101
C)3)1 × 103
D)3)1 × 104
A)3)2 × 10-4
B)5)6 × 101
C)3)1 × 103
D)3)1 × 104

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The decomposition of ammonia is: 2 NH3(g)= N2(g)+ 3 H2(g).If Kp is 1.5 × 103 at 400°C,what is the partial pressure of ammonia at equilibrium when N2 is 0.10 atm and H2 is 0.15 atm?
A)2)2 × 10-7 atm
B)4)7 × 10-4 atm
C)2)1 × 103 atm
D)4)4 × 106 atm
A)2)2 × 10-7 atm
B)4)7 × 10-4 atm
C)2)1 × 103 atm
D)4)4 × 106 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the equilibrium constant,Kc,for the reaction:
2 Hg(l)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 HgO(s)
If the amounts of reactants and products at equilibrium are: 1.00 g of HgO(s),2.00 mL of Hg(l),and 1.60 M O2(g)? (The molar mass and density of HgO(s)is 217 g/mol,and 1.10 g/cm3.The molar mass and density of Hg(l)is 201 g/mol,and 13.6 g/mL. )
A)6)85 × 10-4
B)4)66 × 10-2
C)0)625
D)1)46 × 103
2 Hg(l)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 HgO(s)
If the amounts of reactants and products at equilibrium are: 1.00 g of HgO(s),2.00 mL of Hg(l),and 1.60 M O2(g)? (The molar mass and density of HgO(s)is 217 g/mol,and 1.10 g/cm3.The molar mass and density of Hg(l)is 201 g/mol,and 13.6 g/mL. )
A)6)85 × 10-4
B)4)66 × 10-2
C)0)625
D)1)46 × 103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the equilibrium equation for the following reaction?
2 H2O (l)⇌ H3O+ (aq)+ OH- (aq)
A)Kc =![<strong>What is the equilibrium equation for the following reaction? 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup> (aq)</strong> A)K<sub>c </sub>= B)K<sub>c </sub>= C)K<sub>c </sub>= D)K<sub>c </sub>= [H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>] [OH<sup>-</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4939/11ea7a38_c957_e803_aa4c_7d892792f746_TB4939_11.jpg)
B)Kc =![<strong>What is the equilibrium equation for the following reaction? 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup> (aq)</strong> A)K<sub>c </sub>= B)K<sub>c </sub>= C)K<sub>c </sub>= D)K<sub>c </sub>= [H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>] [OH<sup>-</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4939/11ea7a38_c957_e804_aa4c_ed220492254a_TB4939_11.jpg)
C)Kc =![<strong>What is the equilibrium equation for the following reaction? 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup> (aq)</strong> A)K<sub>c </sub>= B)K<sub>c </sub>= C)K<sub>c </sub>= D)K<sub>c </sub>= [H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>] [OH<sup>-</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4939/11ea7a38_c957_e805_aa4c_3135f4d42781_TB4939_11.jpg)
D)Kc = [H3O+] [OH-]
2 H2O (l)⇌ H3O+ (aq)+ OH- (aq)
A)Kc =
![<strong>What is the equilibrium equation for the following reaction? 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup> (aq)</strong> A)K<sub>c </sub>= B)K<sub>c </sub>= C)K<sub>c </sub>= D)K<sub>c </sub>= [H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>] [OH<sup>-</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4939/11ea7a38_c957_e803_aa4c_7d892792f746_TB4939_11.jpg)
B)Kc =
![<strong>What is the equilibrium equation for the following reaction? 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup> (aq)</strong> A)K<sub>c </sub>= B)K<sub>c </sub>= C)K<sub>c </sub>= D)K<sub>c </sub>= [H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>] [OH<sup>-</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4939/11ea7a38_c957_e804_aa4c_ed220492254a_TB4939_11.jpg)
C)Kc =
![<strong>What is the equilibrium equation for the following reaction? 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup> (aq)</strong> A)K<sub>c </sub>= B)K<sub>c </sub>= C)K<sub>c </sub>= D)K<sub>c </sub>= [H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>] [OH<sup>-</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4939/11ea7a38_c957_e805_aa4c_3135f4d42781_TB4939_11.jpg)
D)Kc = [H3O+] [OH-]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the equilibrium equation for the dissociation of formic acid in water?
HCOOH (aq)+ H2O (l)⇌ H3O+ (aq)+ HCOO- (aq)
A)Kc =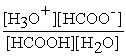
B)Kc =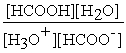
C)Kc =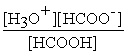
D)Kc =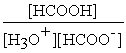
HCOOH (aq)+ H2O (l)⇌ H3O+ (aq)+ HCOO- (aq)
A)Kc =
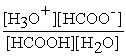
B)Kc =
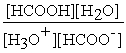
C)Kc =
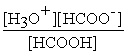
D)Kc =
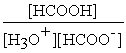

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If Kc = 0.900,and Kp = 538 for a hypothetical reaction,which of the equations below could represent the reaction at 25°C?
A)A(g)+ B(s)⇌ 3 C(g)
B)A(l)+ 2 B(g)⇌ 2 C(g)
C)B(g)⇌ C(l)+ D(l)
D)A(g)⇌ 2 C(s)+ D(g)
A)A(g)+ B(s)⇌ 3 C(g)
B)A(l)+ 2 B(g)⇌ 2 C(g)
C)B(g)⇌ C(l)+ D(l)
D)A(g)⇌ 2 C(s)+ D(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Phosphorus pentachloride decomposes to phosphorus trichloride and chlorine gas at elevated temperatures by the following reaction:
PCl5(g)⇌ PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g).If Kc = 1.8 at 250°C.
What is the value of Kp at the same temperature?
A)4)2 × 10-2
B)8)8 × 10-2
C)65
D)77
PCl5(g)⇌ PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g).If Kc = 1.8 at 250°C.
What is the value of Kp at the same temperature?
A)4)2 × 10-2
B)8)8 × 10-2
C)65
D)77

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
For which one of the following reactions will Kc = Kp?
A)CO(g)+ 2 H2(g)⇌ CH3OH(g)
B)ZnO(s)+ CO(g)⇌ Zn(s)+ CO2(g)
C)2 O3(g)⇌ 3 O2(g)
D)COCl2(g)⇌ CO(g)+ Cl2(g)
A)CO(g)+ 2 H2(g)⇌ CH3OH(g)
B)ZnO(s)+ CO(g)⇌ Zn(s)+ CO2(g)
C)2 O3(g)⇌ 3 O2(g)
D)COCl2(g)⇌ CO(g)+ Cl2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is true about the relationship of Kp and Kc for the reaction:
2 CH4(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 CO(g)+ 4 H2O(g)?
A)Kp < Kc
B)Kp = Kc
C)Kp > Kc
D)Kp and Kc are not related.
2 CH4(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 CO(g)+ 4 H2O(g)?
A)Kp < Kc
B)Kp = Kc
C)Kp > Kc
D)Kp and Kc are not related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The decomposition of ammonia is: 2 NH3(g)⇌ N2(g)+ 3 H2(g).If the partial pressure of ammonia is 1.6 × 10-3 atm and the partial pressures of N2 and H2 are each 0.25 atm at equilibrium,what is the value for Kc at 400°C for the forward reaction?
A)0)50
B)1)4
C)1)5 × 103
D)4)6 × 106
A)0)50
B)1)4
C)1)5 × 103
D)4)6 × 106

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Kp = 1.5 × 103 at 400°C for the reaction 2 NH3(g)⇌ N2(g)+ 3 H2(g).What is the value of Kp for the reaction:
2 N2(g)+ 6 H2(g)⇌ 4 NH3(g)?
A)4)4 × 10-7
B)3)3 × 10-4
C)6)7 × 10-4
D)2)3 × 106
2 N2(g)+ 6 H2(g)⇌ 4 NH3(g)?
A)4)4 × 10-7
B)3)3 × 10-4
C)6)7 × 10-4
D)2)3 × 106

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
As a rule,which of the following phases are not included in the equilibrium constant expression?
I.pure liquids
II.pure solids
III.aqueous solutions
IV.gases
A)I,II
B)I,IV
C)III,IV
D)II,III
I.pure liquids
II.pure solids
III.aqueous solutions
IV.gases
A)I,II
B)I,IV
C)III,IV
D)II,III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which equilibrium below is homogeneous?
A)BaSO4(s)⇌ Ba2+(aq)+ SO42-(aq)
B)2 H2O2(l)⇌ 2 H2O(l)+ O2(g)
C)NH4NO3(s)⇌ N2O(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
D)2 CO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 CO2(g)
A)BaSO4(s)⇌ Ba2+(aq)+ SO42-(aq)
B)2 H2O2(l)⇌ 2 H2O(l)+ O2(g)
C)NH4NO3(s)⇌ N2O(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
D)2 CO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 CO2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A 1.50 L vessel contains an equilibrium mixture of 0.100 mol of NO,0.150 mol of Br2,and
0)250 mol of NOBr at 25°C.What is the value of Kp for the reaction below?
2 NO(g)+ Br2(g)⇌ 2 NOBr(g)
A)2)56
B)62.5
C)1)28 × 102
D)1)53 × 103
0)250 mol of NOBr at 25°C.What is the value of Kp for the reaction below?
2 NO(g)+ Br2(g)⇌ 2 NOBr(g)
A)2)56
B)62.5
C)1)28 × 102
D)1)53 × 103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The esterification of acetic acid and ethanol is given by the reaction below:
C2H5OH(aq)+ CH3COOH(aq)⇌ CH3COOC2H5(aq)+ H2O(l)
When 1.00 mol of ethanol was mixed with 2.00 mol of acid in a 1.00 L flask,0.86 mol of ester was formed at room temperature.What is the value of the equilibrium constant,Kc?
A)0)43
B)2)3
C)4)6
D)5)4
C2H5OH(aq)+ CH3COOH(aq)⇌ CH3COOC2H5(aq)+ H2O(l)
When 1.00 mol of ethanol was mixed with 2.00 mol of acid in a 1.00 L flask,0.86 mol of ester was formed at room temperature.What is the value of the equilibrium constant,Kc?
A)0)43
B)2)3
C)4)6
D)5)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
At a certain temperature,bromine and nitric oxide react to form nitrosyl bromide:
Br2(g)+ 2 NO(g)⇌ 2 NOBr(g).
When initial amounts of Br2,NO,and NOBr are mixed,the concentration of NOBr increases.Which statement below is true?
A)Kc < Q
B)Kc > Q
C)Kc = Q
D)More information is needed to make a statement about Kc.
Br2(g)+ 2 NO(g)⇌ 2 NOBr(g).
When initial amounts of Br2,NO,and NOBr are mixed,the concentration of NOBr increases.Which statement below is true?
A)Kc < Q
B)Kc > Q
C)Kc = Q
D)More information is needed to make a statement about Kc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For the isomerization reaction:
Butane ⇌ isobutane
Kp equals 25 at 500°C.If the initial pressures of butane and isobutane are 10.atm and 0.0 atm,respectively,what are the pressures of the two gases at equilibrium?
A)P(butane)= 0.38 atm and P(isobutane)= 9.6 atm
B)P(butane)= 0.40 atm and P(isobutane)= 10.atm
C)P(butane)= 9.6 atm and P(isobutane)= 0.38 atm
D)P(butane)= 10 atm and P(isobutane)= 0.40 atm
Butane ⇌ isobutane
Kp equals 25 at 500°C.If the initial pressures of butane and isobutane are 10.atm and 0.0 atm,respectively,what are the pressures of the two gases at equilibrium?
A)P(butane)= 0.38 atm and P(isobutane)= 9.6 atm
B)P(butane)= 0.40 atm and P(isobutane)= 10.atm
C)P(butane)= 9.6 atm and P(isobutane)= 0.38 atm
D)P(butane)= 10 atm and P(isobutane)= 0.40 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An equilibrium mixture of CO,O2 and CO2 at a certain temperature contains 0.0010 M CO2 and 0.0015 M O2.At this temperature,Kc,equals 1.4 × 102 for the reaction:
2 CO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 CO2(g).
What is the equilibrium concentration of CO?
A)4)8 × 10-6 M
B)2)2 × 10-3 M
C)9)3 × 10-2 M
D)3)1 × 10-1 M
2 CO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 CO2(g).
What is the equilibrium concentration of CO?
A)4)8 × 10-6 M
B)2)2 × 10-3 M
C)9)3 × 10-2 M
D)3)1 × 10-1 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The equilibrium constant,Kp,equals 3.40 for the isomerization reaction:
Cis-2-butene ⇌ trans-2-butene.
If a flask initially contains 0.250 atm of cis-2-butene and 0.125 atm of trans-2-butene,what is the equilibrium pressure of each gas?
A)P(cis-2-butene)= 0.037 atm,P(trans-2-butene)= 0.125 atm
B)P(cis-2-butene)= 0.048 atm,P(trans-2-butene)= 0.165 atm
C)P(cis-2-butene)= 0.074 atm,P(trans-2-butene)= 0.250 atm
D)P(cis-2-butene)= 0.085 atm,P(trans-2-butene)= 0.290 atm
Cis-2-butene ⇌ trans-2-butene.
If a flask initially contains 0.250 atm of cis-2-butene and 0.125 atm of trans-2-butene,what is the equilibrium pressure of each gas?
A)P(cis-2-butene)= 0.037 atm,P(trans-2-butene)= 0.125 atm
B)P(cis-2-butene)= 0.048 atm,P(trans-2-butene)= 0.165 atm
C)P(cis-2-butene)= 0.074 atm,P(trans-2-butene)= 0.250 atm
D)P(cis-2-butene)= 0.085 atm,P(trans-2-butene)= 0.290 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
For the reaction: 4 HCl(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 Cl2(g)+ 2 H2O(l),the equilibrium constant is 0.063 at 400 K.If the reaction quotient is 0.100,which of the following statements is not correct?
A)[HCl] will increase.
B)[O2] will increase.
C)[Cl2] will decrease.
D)[H2O] will increase.
A)[HCl] will increase.
B)[O2] will increase.
C)[Cl2] will decrease.
D)[H2O] will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When baking soda is heated it decomposes according to the following reaction:
2 NaHCO3(s)⇌ Na2CO3(s)+ H2O(g)+ CO2(g)
If sufficient baking soda is placed in a container and heated to 90°C,the total pressure of the gases is 0.5451 atm.What is the value of Kp at that temperature?
A)0)07428
B)0)2973
C)0)4228
D)1)091
2 NaHCO3(s)⇌ Na2CO3(s)+ H2O(g)+ CO2(g)
If sufficient baking soda is placed in a container and heated to 90°C,the total pressure of the gases is 0.5451 atm.What is the value of Kp at that temperature?
A)0)07428
B)0)2973
C)0)4228
D)1)091

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The equilibrium constant is equal to 5.00 at 1300 K for the reaction:
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g).
If initial concentrations are [SO2] = 1.20 M,[O2] = 0.45 M,and [SO3] = 1.80 M,the system is
A)at equilibrium.
B)not at equilibrium and will remain in an unequilibrated state.
C)not at equilibrium and will shift to the left to achieve an equilibrium state.
D)not at equilibrium and will shift to the right to achieve an equilibrium state.
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g).
If initial concentrations are [SO2] = 1.20 M,[O2] = 0.45 M,and [SO3] = 1.80 M,the system is
A)at equilibrium.
B)not at equilibrium and will remain in an unequilibrated state.
C)not at equilibrium and will shift to the left to achieve an equilibrium state.
D)not at equilibrium and will shift to the right to achieve an equilibrium state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
At a certain temperature the equilibrium constant,Kc,equals 0.11 for the reaction:
2 ICl(g)⇌ I2(g)+ Cl2(g).
What is the equilibrium concentration of ICl if 0.75 mol of I2 and 0.75 mol of Cl2 are initially mixed in a 2.0-L flask?
A)0)23 M
B)0)28 M
C)0)45 M
D)0)56
2 ICl(g)⇌ I2(g)+ Cl2(g).
What is the equilibrium concentration of ICl if 0.75 mol of I2 and 0.75 mol of Cl2 are initially mixed in a 2.0-L flask?
A)0)23 M
B)0)28 M
C)0)45 M
D)0)56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
At a certain temperature,Kc equals 1.4 × 102 for the reaction:
2 CO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 CO2(g).
If a 2.50-L flask contains 0.400 mol of CO2 and 0.100 mol of O2 at equilibrium,how many moles of CO are also present in the flask?
A)0)422 mol
B)0)169 mol
C)0)107 mol
D)0)0114 mol
2 CO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 CO2(g).
If a 2.50-L flask contains 0.400 mol of CO2 and 0.100 mol of O2 at equilibrium,how many moles of CO are also present in the flask?
A)0)422 mol
B)0)169 mol
C)0)107 mol
D)0)0114 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For the reaction,A(g)+ 2 B(g)⇌ 2 C(g),Kc = 1 × 10-10 at 25°C.Which of the following statements is true?
A)Δn = +1
B)The concentration of the products is greater than the concentration of the reactants.
C)The reaction is favored in the reverse direction.
D)The value of Kp will be larger than the value for Kc.
A)Δn = +1
B)The concentration of the products is greater than the concentration of the reactants.
C)The reaction is favored in the reverse direction.
D)The value of Kp will be larger than the value for Kc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The following two isomers of C3H7NO exist in equilibrium with each other in solution: ![<strong>The following two isomers of C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>7</sub>NO exist in equilibrium with each other in solution: If K<sub>c</sub> = 0.57 at 25°C and the initial concentration of the reactant is 0.50 M and the product is 0.70 M,what are the concentrations at equilibrium?</strong> A)[reactant] = 0.43 M and [product] = 0.24 M B)[reactant] = 0.67 M and [product] = 0.38 M C)[reactant] = 0.76 M and [product] = 0.44 M D)[reactant] = 0.82 M and [product] = 0.47 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4939/11ea7a38_c958_ab56_aa4c_9d99f0ecc695_TB4939_00.jpg)
If Kc = 0.57 at 25°C and the initial concentration of the reactant is 0.50 M and the product is 0.70 M,what are the concentrations at equilibrium?
A)[reactant] = 0.43 M and [product] = 0.24 M
B)[reactant] = 0.67 M and [product] = 0.38 M
C)[reactant] = 0.76 M and [product] = 0.44 M
D)[reactant] = 0.82 M and [product] = 0.47 M
![<strong>The following two isomers of C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>7</sub>NO exist in equilibrium with each other in solution: If K<sub>c</sub> = 0.57 at 25°C and the initial concentration of the reactant is 0.50 M and the product is 0.70 M,what are the concentrations at equilibrium?</strong> A)[reactant] = 0.43 M and [product] = 0.24 M B)[reactant] = 0.67 M and [product] = 0.38 M C)[reactant] = 0.76 M and [product] = 0.44 M D)[reactant] = 0.82 M and [product] = 0.47 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4939/11ea7a38_c958_ab56_aa4c_9d99f0ecc695_TB4939_00.jpg)
If Kc = 0.57 at 25°C and the initial concentration of the reactant is 0.50 M and the product is 0.70 M,what are the concentrations at equilibrium?
A)[reactant] = 0.43 M and [product] = 0.24 M
B)[reactant] = 0.67 M and [product] = 0.38 M
C)[reactant] = 0.76 M and [product] = 0.44 M
D)[reactant] = 0.82 M and [product] = 0.47 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The equilibrium constant,Kp,equals 3.40 at 25°C for the isomerization reaction:
Cis-2-butene ⇌ trans-2-butene.
If a flask initially contains 1.00 atm of each gas,in what direction will the system shift to reach equilibrium?
A)It will shift left.
B)It will shift right.
C)The system is already at equilibrium.
D)The system is not at equilibrium and will remain in an unequilibrated state.
Cis-2-butene ⇌ trans-2-butene.
If a flask initially contains 1.00 atm of each gas,in what direction will the system shift to reach equilibrium?
A)It will shift left.
B)It will shift right.
C)The system is already at equilibrium.
D)The system is not at equilibrium and will remain in an unequilibrated state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Given the hypothetical reaction: 2 A(s)+ x B(g)⇌ 3 C(g),Kp = 0.0105 and Kc = 0.45 at 250°C.What is the value of the coefficient x?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Cyclohexane (C6H12)undergoes a molecular rearrangement in the presence of AlCl3 to form methylcyclopentane (MCP)according to the equation:
C6H12 ⇌ MCP
If Kc = 0.143 at 25°C for this reaction,predict the direction the reaction will shift if the initial concentrations of C6H12 and MCP are 0.200 M and 0.100 M,respectively.The system
A)will shift left.
B)will shift right.
C)is already at equilibrium.
D)is not at equilibrium and will remain in an unequilibrated state.
C6H12 ⇌ MCP
If Kc = 0.143 at 25°C for this reaction,predict the direction the reaction will shift if the initial concentrations of C6H12 and MCP are 0.200 M and 0.100 M,respectively.The system
A)will shift left.
B)will shift right.
C)is already at equilibrium.
D)is not at equilibrium and will remain in an unequilibrated state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Kp is equal to 48.70 at 731 K for the reaction: H2(g)+ I2(g)⇌ 2 HI(g).Initially the mixture contains 0.08592 atm each of H2 and I2 and 1.0000 atm of HI.What is the pressure of HI at equilibrium?
A)0)7955 atm
B)0)9108 atm
C)0)9140 atm
D)0)9498 atm
A)0)7955 atm
B)0)9108 atm
C)0)9140 atm
D)0)9498 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Phosphorus pentachloride decomposes to phosphorus trichloride at high temperatures according to the reaction:
PCl5(g)⇌ PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
At 250°C,0.250 M PCl5 is added to a flask.If Kc = 1.80,what are the equilibrium concentrations of each gas?
A)[PCl5] = 0.0280 M,[PCl3] = 0.222 M,[Cl2] = 0.222 M
B)[PCl5] = 1.25 M,[PCl3] = 0.474 M,[Cl2] = 0.474 M
C)[PCl5] = 1.80 M,[PCl3] = 1.80 M,[Cl2] = 1.80 M
D)[PCl5] = 2.27 M,[PCl3] = 2.02 M,[Cl2] = 2.02 M
PCl5(g)⇌ PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
At 250°C,0.250 M PCl5 is added to a flask.If Kc = 1.80,what are the equilibrium concentrations of each gas?
A)[PCl5] = 0.0280 M,[PCl3] = 0.222 M,[Cl2] = 0.222 M
B)[PCl5] = 1.25 M,[PCl3] = 0.474 M,[Cl2] = 0.474 M
C)[PCl5] = 1.80 M,[PCl3] = 1.80 M,[Cl2] = 1.80 M
D)[PCl5] = 2.27 M,[PCl3] = 2.02 M,[Cl2] = 2.02 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
At a certain temperature,bromine and nitric oxide react to form nitrosyl bromide:
Br2(g)+ 2 NO(g)⇌ 2 NOBr(g).
When 0.010 mol Br2 is mixed with 0.025 mol NO and 0.015 mol NOBr in a 2.50 L flask,the concentration of NOBr decreases.Which statement below is true?
A)Kc < 36
B)Kc > 36
C)Kc < 90
D)Kc > 90
Br2(g)+ 2 NO(g)⇌ 2 NOBr(g).
When 0.010 mol Br2 is mixed with 0.025 mol NO and 0.015 mol NOBr in a 2.50 L flask,the concentration of NOBr decreases.Which statement below is true?
A)Kc < 36
B)Kc > 36
C)Kc < 90
D)Kc > 90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which statement is true for a reaction with Kc equal to 2.43 × 10-12?
A)Increasing the temperature will not change the value of Kc.
B)There are appreciable concentrations of both reactants and products.
C)The reaction proceeds hardly at all towards completion.
D)The reaction proceeds nearly all the way to completion.
A)Increasing the temperature will not change the value of Kc.
B)There are appreciable concentrations of both reactants and products.
C)The reaction proceeds hardly at all towards completion.
D)The reaction proceeds nearly all the way to completion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Cyclohexane (C6H12)undergoes a molecular rearrangement in the presence of AlCl3 to form methylcyclopentane (CH3C5H9)according to the equation:
C6H12 ⇌ CH3C5H9
If Kc = 0.143 at 25°C for this reaction,find the equilibrium concentrations of C6H12 and CH3C5H9 if the initial concentrations are 0.200 M and 0.100 M,respectively.
A)[C6H12] = 0.0625 and [CH3C5H9] = 0.062 M
B)[C6H12] = 0.138 and [CH3C5H9] = 0.162 M
C)[C6H12] = 0.262 M and [CH3C5H9] = 0.038 M
D)[C6H12] = 0.282 and [CH3C5H9] = 0.018 M
C6H12 ⇌ CH3C5H9
If Kc = 0.143 at 25°C for this reaction,find the equilibrium concentrations of C6H12 and CH3C5H9 if the initial concentrations are 0.200 M and 0.100 M,respectively.
A)[C6H12] = 0.0625 and [CH3C5H9] = 0.062 M
B)[C6H12] = 0.138 and [CH3C5H9] = 0.162 M
C)[C6H12] = 0.262 M and [CH3C5H9] = 0.038 M
D)[C6H12] = 0.282 and [CH3C5H9] = 0.018 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Gaseous hydrogen bromide decomposes at elevated temperatures according to the following equation:
2 HBr(g)⇌ H2(g)+ Br2(g).
At a certain temperature a 2.00 L flask is initially filled only with 0.600 mol of HBr.What is the value of Kc at that temperature if the flask contains 0.104 mol of H2 at equilibrium?
A)7)04 × 10-2
B)4)40 × 10-2
C)3)00 × 10-2
D)2)10 × 10-1
2 HBr(g)⇌ H2(g)+ Br2(g).
At a certain temperature a 2.00 L flask is initially filled only with 0.600 mol of HBr.What is the value of Kc at that temperature if the flask contains 0.104 mol of H2 at equilibrium?
A)7)04 × 10-2
B)4)40 × 10-2
C)3)00 × 10-2
D)2)10 × 10-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The solubility of 1:1 salts is measured by the equilibrium constant for the general reaction: MX(s)= Mn+(aq)+ Xn-(aq).Given the following salts and their equilibrium constants for the reaction above at 25°C,which salt is the least soluble?
A)MgCO3,Kc = 6.8 × 10-6
B)CaCO3,Kc = 5.0 × 10-9
C)SrCO3,Kc = 5.6 × 10-10
D)BaCO3,Kc = 2.6 × 10-9
A)MgCO3,Kc = 6.8 × 10-6
B)CaCO3,Kc = 5.0 × 10-9
C)SrCO3,Kc = 5.6 × 10-10
D)BaCO3,Kc = 2.6 × 10-9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
For the reaction shown below,which change in conditions made to the system at equilibrium will result in a net reaction to the right to form more product?
C(s)+ 2 H2(g)⇌ CH4(g)ΔH° = -74.8 kJ
A)adding more C
B)decreasing the concentration of H2
C)increasing the concentration of H2
D)increasing the concentration of CH4
C(s)+ 2 H2(g)⇌ CH4(g)ΔH° = -74.8 kJ
A)adding more C
B)decreasing the concentration of H2
C)increasing the concentration of H2
D)increasing the concentration of CH4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The enthalpy for the following reaction is 136 kJ.If the reaction takes place in a closed container,which one of the following reaction conditions will not decrease the concentration of water vapor?
2 NaHCO3(s)⇌ Na2CO3(s)+ CO2(g)+ H2O(g)
A)add CO2
B)cool the container
C)decrease the volume of the container
D)remove some NaHCO3
2 NaHCO3(s)⇌ Na2CO3(s)+ CO2(g)+ H2O(g)
A)add CO2
B)cool the container
C)decrease the volume of the container
D)remove some NaHCO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A crude type of disappearing ink is based on the following endothermic equilibrium:
[Co(H2O)6]Cl2 (aq)⇌ [CoCl2(H2O)4] (aq)+ 2 H2O (l)
(colorless)(blue)
If the reactant solution is used to write on a piece of paper and the paper is allowed to partially dry,what can be done to bring out the colored handwriting?
A)add water
B)decrease the volume
C)put the paper in a freezer
D)put the paper in an oven
[Co(H2O)6]Cl2 (aq)⇌ [CoCl2(H2O)4] (aq)+ 2 H2O (l)
(colorless)(blue)
If the reactant solution is used to write on a piece of paper and the paper is allowed to partially dry,what can be done to bring out the colored handwriting?
A)add water
B)decrease the volume
C)put the paper in a freezer
D)put the paper in an oven

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
For acid solutions of the same molarity acid strength is proportional to the equilibrium concentration of H3O+.For equimolar solutions of acids,which equilibrium expression below corresponds to the strongest acid?
A)Kc =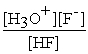 = 3.5 × 10-4
= 3.5 × 10-4
B)Kc =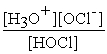 = 3.5 × 10-8
= 3.5 × 10-8
C)Kc =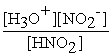 = 4.5 × 10-4
= 4.5 × 10-4
D)Kc =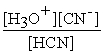 = 4.9 × 10-10
= 4.9 × 10-10
A)Kc =
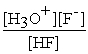 = 3.5 × 10-4
= 3.5 × 10-4B)Kc =
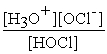 = 3.5 × 10-8
= 3.5 × 10-8C)Kc =
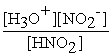 = 4.5 × 10-4
= 4.5 × 10-4D)Kc =
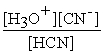 = 4.9 × 10-10
= 4.9 × 10-10
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Ammonium bromide is a crystalline solid that decomposes endothermically when heated:
NH4Br(s)⇌ NH3(g)+ HBr(g).When solid NH4Br is added to an evacuated flask at 300°C,which change in reaction conditions below will cause the equilibrium to shift to the right?
A)add more NH3
B)add more NH4Br
C)decrease the temperature
D)double the volume of the container
NH4Br(s)⇌ NH3(g)+ HBr(g).When solid NH4Br is added to an evacuated flask at 300°C,which change in reaction conditions below will cause the equilibrium to shift to the right?
A)add more NH3
B)add more NH4Br
C)decrease the temperature
D)double the volume of the container

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Ammonium carbamate can dissociate into gases at 25°C according to the reaction:
NH2COONH4(s)⇌ 2 NH3(g)+ CO2(g)
If sufficient ammonium carbamate is sealed in a flask,the total pressure will be 0.117 atm at equilibrium.What is the value of Kp at 25°C?
A)2)37 × 10-4
B)2)00 × 10-4
C)1)60 × 10-3
D)3)42 × 10-1
NH2COONH4(s)⇌ 2 NH3(g)+ CO2(g)
If sufficient ammonium carbamate is sealed in a flask,the total pressure will be 0.117 atm at equilibrium.What is the value of Kp at 25°C?
A)2)37 × 10-4
B)2)00 × 10-4
C)1)60 × 10-3
D)3)42 × 10-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
For a homogeneous equilibrium of gases,which of the following changes in reaction conditions will not alter the equilibrium concentrations?
A)addition of an inert gas to the reaction mixture
B)addition of reactants or products
C)decreasing the pressure or volume
D)increasing the temperature
A)addition of an inert gas to the reaction mixture
B)addition of reactants or products
C)decreasing the pressure or volume
D)increasing the temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Oxalic acid can donate two protons to water in successive reactions:
(1)H2C2O4(aq)+ H2O(l)⇌ H3O+(aq)+ HC2O4-(aq)
(2)HC2O4-(aq)+ H2O(l)⇌ H3O+(aq)+ C2O42-(aq)
If Kc1 = 5.9 × 10-2 and Kc2 = 6.4 × 10-5 at 25°C,what is the value of Kc for reaction (3)?
(3)H2C2O4(aq)+ 2 H2O(l)⇌ 2 H3O+(aq)+ C2O42-(aq)
A)3)8 × 10-6
B)1)1 × 10-3
C)5)9 × 10-2
D)9)2 × 102
(1)H2C2O4(aq)+ H2O(l)⇌ H3O+(aq)+ HC2O4-(aq)
(2)HC2O4-(aq)+ H2O(l)⇌ H3O+(aq)+ C2O42-(aq)
If Kc1 = 5.9 × 10-2 and Kc2 = 6.4 × 10-5 at 25°C,what is the value of Kc for reaction (3)?
(3)H2C2O4(aq)+ 2 H2O(l)⇌ 2 H3O+(aq)+ C2O42-(aq)
A)3)8 × 10-6
B)1)1 × 10-3
C)5)9 × 10-2
D)9)2 × 102

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The pink and blue species below form a violet colored mixture at equilibrium:
[Co(H2O)6]2+ (aq)+ 4 Cl- (aq)⇌ [CoCl4]2- (aq)+ 6 H2O (l)
(pink)(blue)
If the concentration of [Co(H2O)6]2+ is increased,what happens to the solution?
A)The concentration of [CoCl4]2- increases.
B)The concentration of [CoCl4]2- decreases.
C)The solution becomes colorless.
D)No color change is observed.
[Co(H2O)6]2+ (aq)+ 4 Cl- (aq)⇌ [CoCl4]2- (aq)+ 6 H2O (l)
(pink)(blue)
If the concentration of [Co(H2O)6]2+ is increased,what happens to the solution?
A)The concentration of [CoCl4]2- increases.
B)The concentration of [CoCl4]2- decreases.
C)The solution becomes colorless.
D)No color change is observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Iron oxide ores are reduced to iron metal by exothermic reaction with carbon monoxide:
FeO(s)+ CO(g)⇌ Fe(s)+ CO2(g)
Which of the following changes in condition will cause the equilibrium to shift to the right?
A)add FeO
B)add CO
C)add CO2
D)raise the temperature
FeO(s)+ CO(g)⇌ Fe(s)+ CO2(g)
Which of the following changes in condition will cause the equilibrium to shift to the right?
A)add FeO
B)add CO
C)add CO2
D)raise the temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For the reaction shown below,which change in conditions made to the system at equilibrium will result in a net reaction to the right to form more product?
C(s)+ 2 H2(g)⇌ CH4(g)ΔH° = - 74.8 kJ
A)adding He
B)adding more C
C)decreasing the volume
D)increasing the volume
C(s)+ 2 H2(g)⇌ CH4(g)ΔH° = - 74.8 kJ
A)adding He
B)adding more C
C)decreasing the volume
D)increasing the volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Salt solubilities can be compared by the concentration of cation formed when the salt dissolves in the general reaction: MaXb(s)⇌ a Mb+(aq)+ b Xa-(aq).Given the following salts and their equilibrium constants for the reaction above at 25°C,which salt is the least soluble?
A)AgCl,Kc = 1.8 × 10-10
B)Ag2SO4,Kc = 1.2 × 10-5
C)CaCO3,Kc = 2.6 × 10-9
D)CaF2,Kc = 1.5 × 10-10
A)AgCl,Kc = 1.8 × 10-10
B)Ag2SO4,Kc = 1.2 × 10-5
C)CaCO3,Kc = 2.6 × 10-9
D)CaF2,Kc = 1.5 × 10-10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
"If a stress is applied to a reaction mixture at equilibrium,the reaction occurs in the direction that will relieve the stress." This statement is called
A)the First Law of Thermodynamics.
B)the Law of Combining Volumes.
C)the Law of Mass Action.
D)Le Châtelier's principle.
A)the First Law of Thermodynamics.
B)the Law of Combining Volumes.
C)the Law of Mass Action.
D)Le Châtelier's principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Acids donate protons to water according to the general equation:
HA(aq)+ H2O(l)⇌ H3O+(aq)+ A-(aq)
Consider the following acids and their equilibrium constants for reaction with water at 25°C.If all the acids have the same initial concentration,which is the strongest acid (i.e.which donates the most protons to water)?
A)HBrO,Kc = 2.0 × 10-9
B)HNO2,Kc = 4.5 × 10-4
C)HF,Kc = 3.5 × 10-4
D)HIO3,Kc = 1.7 × 10-1
HA(aq)+ H2O(l)⇌ H3O+(aq)+ A-(aq)
Consider the following acids and their equilibrium constants for reaction with water at 25°C.If all the acids have the same initial concentration,which is the strongest acid (i.e.which donates the most protons to water)?
A)HBrO,Kc = 2.0 × 10-9
B)HNO2,Kc = 4.5 × 10-4
C)HF,Kc = 3.5 × 10-4
D)HIO3,Kc = 1.7 × 10-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction HF(aq)+ H2O(l)⇌ H3O+(aq)+F-(aq)is 3.5 × 10-4.What is the equilibrium concentration of H3O+ if the initial concentration of HF is 1.0 M?
A)1)0 M
B)3)5 × 10-2 M
C)1)9 × 10-2 M
D)1)9 × 10-4 M
A)1)0 M
B)3)5 × 10-2 M
C)1)9 × 10-2 M
D)1)9 × 10-4 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following changes in reaction conditions will alter the composition of an equilibrium mixture of gases for a reaction having unequal moles of gaseous products and gaseous reactants?
A)addition of reactants or products
B)decreasing the pressure or volume
C)increasing the temperature
D)All of these will alter the equilibrium concentrations.
A)addition of reactants or products
B)decreasing the pressure or volume
C)increasing the temperature
D)All of these will alter the equilibrium concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
For the reaction shown below,which change in conditions made to the system at equilibrium will result in a net reaction to the right to form more product?
C(s)+ 2 H2(g)⇌ CH4(g)ΔH° = -74.8 kJ
A)adding more C
B)increasing the volume
C)lowering the temperature
D)raising the temperature
C(s)+ 2 H2(g)⇌ CH4(g)ΔH° = -74.8 kJ
A)adding more C
B)increasing the volume
C)lowering the temperature
D)raising the temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which change in the system will drive equilibrium to the left in the reaction below?
N2O5(g)⇌ NO2(g)+ NO3(g)
A)decrease the amount of NO3
B)increase the amount of N2O5
C)increase the pressure
D)increase the volume
N2O5(g)⇌ NO2(g)+ NO3(g)
A)decrease the amount of NO3
B)increase the amount of N2O5
C)increase the pressure
D)increase the volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



