Deck 19: Electrochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/122
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Electrochemistry
1
Which of the following cell reactions would require the use of an inert electrode?
A)Cu(s)+ 2Ag+(aq)→ 2Ag(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
B)3Fe(s)+ 2Au3+(aq)→ 3Fe2+ + 2Au(s)
C)Zn(s)+ 2Ag+(aq)→ Zn2+(aq)+ 2Ag(s)
D)Ni(s)+ 2MnO2(s)+ 2NH4+(aq)→ Ni2+(aq)+ Mn2O3(s)+ 2NH3(aq)+ H2O(l)
E)3Zn2+(aq)+ 2Al(s)→ 3Zn(s)+ 2Al3+(aq)
A)Cu(s)+ 2Ag+(aq)→ 2Ag(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
B)3Fe(s)+ 2Au3+(aq)→ 3Fe2+ + 2Au(s)
C)Zn(s)+ 2Ag+(aq)→ Zn2+(aq)+ 2Ag(s)
D)Ni(s)+ 2MnO2(s)+ 2NH4+(aq)→ Ni2+(aq)+ Mn2O3(s)+ 2NH3(aq)+ H2O(l)
E)3Zn2+(aq)+ 2Al(s)→ 3Zn(s)+ 2Al3+(aq)
Ni(s)+ 2MnO2(s)+ 2NH4+(aq)→ Ni2+(aq)+ Mn2O3(s)+ 2NH3(aq)+ H2O(l)
2
When the following oxidation-reduction reaction in basic solution is balanced,what is the lowest whole-number coefficient for OH-,and on which side of the balanced equation should it appear?
Cr2O3(s)→ Cr(OH)2(aq)+ CrO42-(aq)
A)2,reactant side
B)10,product side
C)4,product side
D)4,reactant side
E)2,product side
Cr2O3(s)→ Cr(OH)2(aq)+ CrO42-(aq)
A)2,reactant side
B)10,product side
C)4,product side
D)4,reactant side
E)2,product side
2,reactant side
3
Which statement concerning the anode in an electrochemical cell is correct?
A)Metal ions may be deposited as metal atoms on the anode during cell discharge.
B)When connected to an external circuit,the anode develops a positive charge.
C)Reduction occurs at the anode during cell discharge.
D)Positive ions flow towards the anode during cell discharge.
E)None of the above.
A)Metal ions may be deposited as metal atoms on the anode during cell discharge.
B)When connected to an external circuit,the anode develops a positive charge.
C)Reduction occurs at the anode during cell discharge.
D)Positive ions flow towards the anode during cell discharge.
E)None of the above.
None of the above.
4
When the following oxidation-reduction reaction in acidic solution is balanced,what is the lowest whole-number coefficient for Rb+(aq)?
Rb(s)+ Sr2+(aq)→ Rb+(aq)+ Sr(s)
A)5
B)4
C)1
D)3
E)2
Rb(s)+ Sr2+(aq)→ Rb+(aq)+ Sr(s)
A)5
B)4
C)1
D)3
E)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A strip of iron is placed in a 1 M solution of iron(II)sulfate,and a strip of copper is placed in a 1 M solution of copper(II)chloride.The two solutions are connected with a salt bridge,and the two metals are connected by a wire.
Reduction Half-Reaction
E° (V)
Fe2+(aq)+ 2e- Fe(s)
Fe(s)
-0)41Cu2+(aq)+ 2e- Cu(s)
Cu(s)
0)34
Which of the following takes place?
A)Sulfur deposits at the iron electrode.
B)The Fe(II)concentration of the iron half-cell decreases.
C)Copper atoms deposit at the cathode.
D)Chlorine is produced at the copper electrode.
E)Chlorine is produced at the iron electrode.
Reduction Half-Reaction
E° (V)
Fe2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Fe(s)
Fe(s)-0)41Cu2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Cu(s)
Cu(s)0)34
Which of the following takes place?
A)Sulfur deposits at the iron electrode.
B)The Fe(II)concentration of the iron half-cell decreases.
C)Copper atoms deposit at the cathode.
D)Chlorine is produced at the copper electrode.
E)Chlorine is produced at the iron electrode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which reaction would be most likely to occur at the anode of a voltaic cell?
A)PbSO4(s)+ 2e- → Pb(s)+ SO42-(aq)
B)2H2O(l)+ 2e- → H2(g)+ 2OH-(aq)
C)2H2O(l)→ O2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e-
D)PbSO4(s)→ Pb2+(aq)+ SO42-(aq)
E)2H2O(l)→ 2H2(g)+ O2(g)
A)PbSO4(s)+ 2e- → Pb(s)+ SO42-(aq)
B)2H2O(l)+ 2e- → H2(g)+ 2OH-(aq)
C)2H2O(l)→ O2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e-
D)PbSO4(s)→ Pb2+(aq)+ SO42-(aq)
E)2H2O(l)→ 2H2(g)+ O2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Balance the following oxidation-reduction occurring in acidic solution.
MnO4-(aq)+ Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ Co3+(aq)
A)MnO4-(aq)+ 8H+(aq)+ 5Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 4H2O(aq)+ 5Co3+(aq)
B)MnO4-(aq)+ 8H+(aq)+ Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 4H2O(aq)+ Co3+(aq)
C)MnO4-(aq)+ 4H2(g)+ 5Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 4H2O(aq)+ 5Co3+(aq)
D)MnO4-(aq)+ 8H+(aq)+ 2Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 4H2O(aq)+ 2Co3+(aq)
E)MnO4-(aq)+ Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 2O2(g)+ Co3+(aq)
MnO4-(aq)+ Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ Co3+(aq)
A)MnO4-(aq)+ 8H+(aq)+ 5Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 4H2O(aq)+ 5Co3+(aq)
B)MnO4-(aq)+ 8H+(aq)+ Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 4H2O(aq)+ Co3+(aq)
C)MnO4-(aq)+ 4H2(g)+ 5Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 4H2O(aq)+ 5Co3+(aq)
D)MnO4-(aq)+ 8H+(aq)+ 2Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 4H2O(aq)+ 2Co3+(aq)
E)MnO4-(aq)+ Co2+(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 2O2(g)+ Co3+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Balance the following half-reaction occurring in basic solution.
MnO2(s)→ Mn(OH)2(s)
A)MnO2(s)+ 2H2O(l)+ 2e−→ Mn(OH)2(s)+ 2OH−(aq)
B)MnO2(s)+ 2H2O(l)+ 4e−→ Mn(OH)2(s)+ (OH)2−(aq)
C)MnO2(s)+ H22+(aq)+ 2e−→ Mn(OH)2(s)
D)MnO2(s)+ H2(g)→ Mn(OH)2(s)+ 2e−
E)MnO2(s)+ 2H2O(l)→ Mn(OH)2(s)+ 2OH−(aq)
MnO2(s)→ Mn(OH)2(s)
A)MnO2(s)+ 2H2O(l)+ 2e−→ Mn(OH)2(s)+ 2OH−(aq)
B)MnO2(s)+ 2H2O(l)+ 4e−→ Mn(OH)2(s)+ (OH)2−(aq)
C)MnO2(s)+ H22+(aq)+ 2e−→ Mn(OH)2(s)
D)MnO2(s)+ H2(g)→ Mn(OH)2(s)+ 2e−
E)MnO2(s)+ 2H2O(l)→ Mn(OH)2(s)+ 2OH−(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following reactions take place in a lead storage battery.
Discharging: Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)→ 2PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
Charging: 2PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)→ Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)
Which of the following statements is true?
A)The concentration of H2SO4 increases as the battery discharges.
B)Pb is formed at the anode during discharge.
C)Pb is formed at the cathode during charging.
D)The mass of Pb decreases during charging.
E)The mass of PbSO4 remains constant during charging and discharging.
Discharging: Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)→ 2PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
Charging: 2PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)→ Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)
Which of the following statements is true?
A)The concentration of H2SO4 increases as the battery discharges.
B)Pb is formed at the anode during discharge.
C)Pb is formed at the cathode during charging.
D)The mass of Pb decreases during charging.
E)The mass of PbSO4 remains constant during charging and discharging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements is true concerning half-cell I as the voltaic cell shown below discharges? ![<strong>Which of the following statements is true concerning half-cell I as the voltaic cell shown below discharges? </strong> A)[Zn<sup>2+</sup>] increases with time,and [Cl-] increases with time. B)[Zn<sup>2+</sup>] decreases with time,and [Cl-] increases with time. C)[Zn<sup>2+</sup>] decreases with time,and [Cl-] decreases with time. D)[Zn<sup>2+</sup>] decreases with time,and [NO<sub>3</sub>-] increases with time. E)[Zn<sup>2+</sup>] increases with time,and [NO<sub>3</sub>-] increases with time.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f3a_6f52_a82d_f3caed6e7299_TB2288_00.jpg)
A)[Zn2+] increases with time,and [Cl-] increases with time.
B)[Zn2+] decreases with time,and [Cl-] increases with time.
C)[Zn2+] decreases with time,and [Cl-] decreases with time.
D)[Zn2+] decreases with time,and [NO3-] increases with time.
E)[Zn2+] increases with time,and [NO3-] increases with time.
![<strong>Which of the following statements is true concerning half-cell I as the voltaic cell shown below discharges? </strong> A)[Zn<sup>2+</sup>] increases with time,and [Cl-] increases with time. B)[Zn<sup>2+</sup>] decreases with time,and [Cl-] increases with time. C)[Zn<sup>2+</sup>] decreases with time,and [Cl-] decreases with time. D)[Zn<sup>2+</sup>] decreases with time,and [NO<sub>3</sub>-] increases with time. E)[Zn<sup>2+</sup>] increases with time,and [NO<sub>3</sub>-] increases with time.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f3a_6f52_a82d_f3caed6e7299_TB2288_00.jpg)
A)[Zn2+] increases with time,and [Cl-] increases with time.
B)[Zn2+] decreases with time,and [Cl-] increases with time.
C)[Zn2+] decreases with time,and [Cl-] decreases with time.
D)[Zn2+] decreases with time,and [NO3-] increases with time.
E)[Zn2+] increases with time,and [NO3-] increases with time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When balancing oxidation-reduction reactions in acidic solution by the half-reaction method,the addition of the reactant H+ is required to balance the product
A)O2.
B)OH-.
C)O.
D)H2O.
E)none of these
A)O2.
B)OH-.
C)O.
D)H2O.
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When the following oxidation-reduction reaction in acidic solution is balanced,what is the lowest whole-number coefficient for H+,and on which side of the balanced equation should it appear?
S2O82-(aq)+ NO(g)→ SO42-(aq)+ NO3-(aq)
A)4,product side
B)8,reactant side
C)12,reactant side
D)8,product side
E)4,reactant side
S2O82-(aq)+ NO(g)→ SO42-(aq)+ NO3-(aq)
A)4,product side
B)8,reactant side
C)12,reactant side
D)8,product side
E)4,reactant side

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The anode in a voltaic cell and in an electrolytic cell is
A)the site of oxidation and of reduction,respectively.
B)the site of reduction and of oxidation,respectively.
C)positive in both cells.
D)the site of reduction in both cells.
E)the site of oxidation in both cells.
A)the site of oxidation and of reduction,respectively.
B)the site of reduction and of oxidation,respectively.
C)positive in both cells.
D)the site of reduction in both cells.
E)the site of oxidation in both cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements is true concerning the voltaic cell shown below? 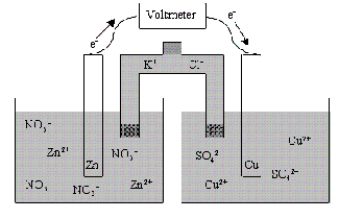
A)The Zn anode mass decreases as the cell discharges.
B)The Zn cathode mass increases as the cell discharges.
C)The Zn cathode mass decreases as the cell discharges.
D)The Zn anode mass increases as the cell discharges.
E)The mass of the Zn electrode neither increases nor decreases as the cell discharges.

A)The Zn anode mass decreases as the cell discharges.
B)The Zn cathode mass increases as the cell discharges.
C)The Zn cathode mass decreases as the cell discharges.
D)The Zn anode mass increases as the cell discharges.
E)The mass of the Zn electrode neither increases nor decreases as the cell discharges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The electrochemical reaction which powers a lead-acid storage battery is as follows:
Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)→ 2PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
A single cell of this battery consists of a Pb electrode and a PbO2 electrode,each submerged in sulfuric acid.What reaction occurs at the cathode during discharge?
A)Pb(s)is reduced to PbSO4(s).
B)PbO2(s)is reduced to PbSO4(s).
C)PbO2(s)is oxidized to PbSO4(s).
D)Pb(s)is oxidized to PbSO4(s).
E)H+ is oxidized to H2O(l).
Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)→ 2PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
A single cell of this battery consists of a Pb electrode and a PbO2 electrode,each submerged in sulfuric acid.What reaction occurs at the cathode during discharge?
A)Pb(s)is reduced to PbSO4(s).
B)PbO2(s)is reduced to PbSO4(s).
C)PbO2(s)is oxidized to PbSO4(s).
D)Pb(s)is oxidized to PbSO4(s).
E)H+ is oxidized to H2O(l).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to the following cell notation,which species is undergoing oxidation?
Zn | Zn2+(aq)|| Mn2+(aq)| MnO2(s)| Pt(s)
A)Mn2+(aq)
B)Zn2+(aq)
C)MnO2(s)
D)Zn(s)
E)Pt(s)
Zn | Zn2+(aq)|| Mn2+(aq)| MnO2(s)| Pt(s)
A)Mn2+(aq)
B)Zn2+(aq)
C)MnO2(s)
D)Zn(s)
E)Pt(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Balance the following half-reaction occurring in acidic solution.
NO3-(aq)→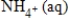
A)NO3-(aq)+ 10H+(aq)+ 8e− →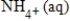 + 3H2O(l)
+ 3H2O(l)
B)NO3-(aq)+ 3H2O(l)+ 10e− →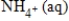 + 10H+(aq)
+ 10H+(aq)
C)NO3-(aq)+ 10H+(aq)→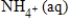 + 3H2O(l)+ 10e−
+ 3H2O(l)+ 10e−
D)NO3-(aq)+ 8e− →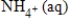 + 8H+(aq)+ 3H2O(l)
+ 8H+(aq)+ 3H2O(l)
E)NO3-(aq)+ 10H+(aq)→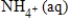 + 3H2O(l)
+ 3H2O(l)
NO3-(aq)→
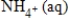
A)NO3-(aq)+ 10H+(aq)+ 8e− →
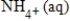 + 3H2O(l)
+ 3H2O(l)B)NO3-(aq)+ 3H2O(l)+ 10e− →
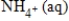 + 10H+(aq)
+ 10H+(aq)C)NO3-(aq)+ 10H+(aq)→
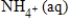 + 3H2O(l)+ 10e−
+ 3H2O(l)+ 10e−D)NO3-(aq)+ 8e− →
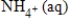 + 8H+(aq)+ 3H2O(l)
+ 8H+(aq)+ 3H2O(l)E)NO3-(aq)+ 10H+(aq)→
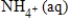 + 3H2O(l)
+ 3H2O(l)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A lead storage battery involves the following two half-reactions:
PbSO4(s)+ 2e- → Pb(s)+ SO42-(aq); E° = -0.36 V
PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ SO42-(aq)+ 2e- → PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 1.69 V
During the discharge reaction of the lead storage battery at 1.0 M concentrations,the cell potential and the reducing agent are,respectively,
A)2.05 V and PbO2.
B)-2.05 V and PbO2.
C)1.33 V and Pb.
D)-2.05 V and Pb.
E)2.05 V and Pb.
PbSO4(s)+ 2e- → Pb(s)+ SO42-(aq); E° = -0.36 V
PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ SO42-(aq)+ 2e- → PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 1.69 V
During the discharge reaction of the lead storage battery at 1.0 M concentrations,the cell potential and the reducing agent are,respectively,
A)2.05 V and PbO2.
B)-2.05 V and PbO2.
C)1.33 V and Pb.
D)-2.05 V and Pb.
E)2.05 V and Pb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements is true for a voltaic (galvanic)cell?
A)The electron flow is from the anode to the cathode.
B)The electron flow is from the positive electrode to the negative electrode.
C)The electron flow is from the negative cathode to the positive anode.
D)The electron flow is through the salt bridge.
E)The electron flow is from the oxidizing agent to the reducing agent through an external circuit.
A)The electron flow is from the anode to the cathode.
B)The electron flow is from the positive electrode to the negative electrode.
C)The electron flow is from the negative cathode to the positive anode.
D)The electron flow is through the salt bridge.
E)The electron flow is from the oxidizing agent to the reducing agent through an external circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When the following oxidation-reduction reaction in acidic solution is balanced,what is the lowest whole-number coefficient for H+,and on which side of the balanced equation should it appear?
MnO4-(aq)+ I-(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ I2(s)
A)1,reactant side
B)2,product side
C)8,reactant side
D)16,reactant side
E)4,product side
MnO4-(aq)+ I-(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ I2(s)
A)1,reactant side
B)2,product side
C)8,reactant side
D)16,reactant side
E)4,product side

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the cell reaction for the following electrochemical cell?
Cu | Cu2+(aq)|| Mn2+(aq)| Mn
A)2Cu(s)+ Mn2+(aq)→ Mn(s)+ 2Cu2+(aq)
B)Cu(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Mn(s)+ Mn2+(aq)
C)Cu(s)+ Mn2+(aq)→ Mn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
D)2Mn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ 2Mn2+(aq)
E)Mn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ Mn2+(aq)
Cu | Cu2+(aq)|| Mn2+(aq)| Mn
A)2Cu(s)+ Mn2+(aq)→ Mn(s)+ 2Cu2+(aq)
B)Cu(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Mn(s)+ Mn2+(aq)
C)Cu(s)+ Mn2+(aq)→ Mn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
D)2Mn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ 2Mn2+(aq)
E)Mn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ Mn2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
For a galvanic cell using Fe | Fe2+(1.0 M)and Pb | Pb2+(1.0 M)half-cells,which of the following statements is correct?
Fe2+(aq)+ 2e- → Fe(s); E° = -0.41 V
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e- → Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
A)The iron electrode is the cathode.
B)When the cell has completely discharged,the concentration of Pb2+ is zero.
C)The mass of the iron electrode increases during discharge.
D)The concentration of Pb2+ decreases during discharge.
E)Electrons leave the lead electrode to pass through the external circuit during discharge.
Fe2+(aq)+ 2e- → Fe(s); E° = -0.41 V
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e- → Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
A)The iron electrode is the cathode.
B)When the cell has completely discharged,the concentration of Pb2+ is zero.
C)The mass of the iron electrode increases during discharge.
D)The concentration of Pb2+ decreases during discharge.
E)Electrons leave the lead electrode to pass through the external circuit during discharge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the following electrochemical cell,what is the role of the platinum?
Cu(s)| Cu2+(aq)|| Fe3+(aq),Fe2+(aq)| Pt(s)
A)The platinum serves as the anode.
B)The oxidation of Fe2+ takes place at the surface of the platinum as the cell discharges.
C)The reduction of Fe3+ takes place at the surface of the platinum as the cell discharges.
D)A and C.
E)A and B.
Cu(s)| Cu2+(aq)|| Fe3+(aq),Fe2+(aq)| Pt(s)
A)The platinum serves as the anode.
B)The oxidation of Fe2+ takes place at the surface of the platinum as the cell discharges.
C)The reduction of Fe3+ takes place at the surface of the platinum as the cell discharges.
D)A and C.
E)A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the correct cell notation for a cell in which the hydrogen electrode is the anode and the cathode half-reaction is Ce4+(aq)+ e− → Ce3+(aq).
A)Pt(s)| H2(g)| H+(aq)|| Ce4+(aq),Ce3+(aq)| Pt(s)
B)Pt(s)| H2(g)| H+(aq)|| Ce4+(aq),Ce3+(aq)
C)Ce3+(aq),Ce4+(aq)|| H+(aq)| H2(g)| Pt(s)
D)Pt(s)| Ce3+(aq),Ce4+(aq)|| H+(aq)| H2(g)| Pt(s)
E)H2(g)| H+(aq)|| Ce3+(aq),Ce4+(aq)
A)Pt(s)| H2(g)| H+(aq)|| Ce4+(aq),Ce3+(aq)| Pt(s)
B)Pt(s)| H2(g)| H+(aq)|| Ce4+(aq),Ce3+(aq)
C)Ce3+(aq),Ce4+(aq)|| H+(aq)| H2(g)| Pt(s)
D)Pt(s)| Ce3+(aq),Ce4+(aq)|| H+(aq)| H2(g)| Pt(s)
E)H2(g)| H+(aq)|| Ce3+(aq),Ce4+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the SI unit of potential difference?
A)coulomb
B)farad
C)volt
D)joule
E)ampere
A)coulomb
B)farad
C)volt
D)joule
E)ampere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Given:
Mn2+(aq)+ 2e-
Mn(s); E° = -1.18 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2e-
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cr2O72-(aq)+ 14H+(aq)+ 6e-
2Cr3+(aq)+ 7H2O(l); E° = 1.33 V
Which of the following species is the strongest reducing agent?
A)Mn
B)Cu
C)Cr3+
D)Mn2+
E)Cr2O72-
Mn2+(aq)+ 2e-

Mn(s); E° = -1.18 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2e-

Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cr2O72-(aq)+ 14H+(aq)+ 6e-

2Cr3+(aq)+ 7H2O(l); E° = 1.33 V
Which of the following species is the strongest reducing agent?
A)Mn
B)Cu
C)Cr3+
D)Mn2+
E)Cr2O72-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The cell potential of an electrochemical cell with the cell reaction
Al(s)+ Cr3+(aq)→ Cr(s)+ Al3+(aq)
Is 1.63 V.What is the maximum electrical work obtainable from this cell when 0.50 g of Al is consumed?
A)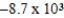 J
J
B)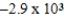 J
J
C)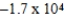 J
J
D)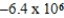 J
J
E)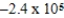 J
J
Al(s)+ Cr3+(aq)→ Cr(s)+ Al3+(aq)
Is 1.63 V.What is the maximum electrical work obtainable from this cell when 0.50 g of Al is consumed?
A)
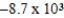 J
JB)
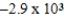 J
JC)
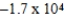 J
JD)
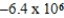 J
JE)
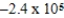 J
J
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the following electrochemical cell,what is the reduction half reaction?
Mn(s)| Mn2+(aq)|| Fe3+(aq),Fe2+(aq)| Pt(s)
A)Fe3+(aq)+ e− → Fe2+(aq)
B)Fe2+(aq)+ e− → Fe3+(aq)
C)Fe2+(aq)+ Pt(s)→ Fe3+(aq)+ e−
D)Mn2+(aq)→ Mn(s)+ 2e−
E)Mn(s)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 2e−
Mn(s)| Mn2+(aq)|| Fe3+(aq),Fe2+(aq)| Pt(s)
A)Fe3+(aq)+ e− → Fe2+(aq)
B)Fe2+(aq)+ e− → Fe3+(aq)
C)Fe2+(aq)+ Pt(s)→ Fe3+(aq)+ e−
D)Mn2+(aq)→ Mn(s)+ 2e−
E)Mn(s)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 2e−

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A fuel cell designed to react grain alcohol with oxygen has the following net reaction:
C2H5OH(l)+ 3O2(g)→ 2CO2(g)+ 3H2O(l)
The maximum work that 1 mol of alcohol can yield by this process is 1320 kJ.What is the theoretical maximum voltage that this cell can achieve?
A)1.14 V
B)2.28 V
C)2.01 V
D)0.760 V
E)13.7 V
C2H5OH(l)+ 3O2(g)→ 2CO2(g)+ 3H2O(l)
The maximum work that 1 mol of alcohol can yield by this process is 1320 kJ.What is the theoretical maximum voltage that this cell can achieve?
A)1.14 V
B)2.28 V
C)2.01 V
D)0.760 V
E)13.7 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the cell reaction for the following electrochemical cell?
Zn | Zn2+(aq)|| Sc3+(aq)| Sc
A)3Zn(s)+ 2Sc3+(aq)→ 2Sc(s)+ 3Zn2+(aq)
B)2Sc(s)+ 3Zn2+(aq)→ 3Zn(s)+ 2Sc3+(aq)
C)Zn(s)+ Zn2+(aq)→ Sc(s)+ Sc3+(aq)
D)Zn(s)+ Sc3+(aq)→ Sc(s)+ Zn2+(aq)
E)Sc(s)+ Zn2+(aq)→ Zn(s)+ Sc3+(aq)
Zn | Zn2+(aq)|| Sc3+(aq)| Sc
A)3Zn(s)+ 2Sc3+(aq)→ 2Sc(s)+ 3Zn2+(aq)
B)2Sc(s)+ 3Zn2+(aq)→ 3Zn(s)+ 2Sc3+(aq)
C)Zn(s)+ Zn2+(aq)→ Sc(s)+ Sc3+(aq)
D)Zn(s)+ Sc3+(aq)→ Sc(s)+ Zn2+(aq)
E)Sc(s)+ Zn2+(aq)→ Zn(s)+ Sc3+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The cell potential of an electrochemical cell with the cell reaction
2Al(s)+ 3Zn2+(aq)→ 3Zn(s)+ 2Al3+(aq)
Is 1.607 V.What is the maximum electrical work obtainable from this cell when 2.0 mol of Al is consumed?
A)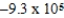 J
J
B)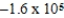 J
J
C)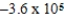 J
J
D)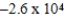 J
J
E)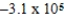 J
J
2Al(s)+ 3Zn2+(aq)→ 3Zn(s)+ 2Al3+(aq)
Is 1.607 V.What is the maximum electrical work obtainable from this cell when 2.0 mol of Al is consumed?
A)
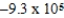 J
JB)
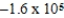 J
JC)
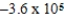 J
JD)
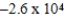 J
JE)
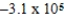 J
J
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the balanced spontaneous reaction and standard cell potential of an electrochemical cell constructed from half cells with the following half reactions?
Cu2+(aq)+ 2e¯ → Cu(s)E° = 0.337 V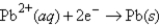
E° = -0.130 V
A)Cu2+(aq)+ Pb(s)→ Cu(s)+ Pb2+(aq); 0.467 V
B)Cu(s)+ Pb2+(aq)→ Cu2+(aq)+ Pb(s); −0.467 V
C)Cu2+(aq)+ Pb2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ Pb(s); 0.207 V
D)Cu2+(aq)+ Pb(s)→ Cu(s)+ Pb2+(aq); 0.234 V
E)Cu(s)+ Pb2+(aq)→ Cu2+(aq)+ Pb(s); −0.234 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2e¯ → Cu(s)E° = 0.337 V
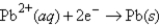
E° = -0.130 V
A)Cu2+(aq)+ Pb(s)→ Cu(s)+ Pb2+(aq); 0.467 V
B)Cu(s)+ Pb2+(aq)→ Cu2+(aq)+ Pb(s); −0.467 V
C)Cu2+(aq)+ Pb2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ Pb(s); 0.207 V
D)Cu2+(aq)+ Pb(s)→ Cu(s)+ Pb2+(aq); 0.234 V
E)Cu(s)+ Pb2+(aq)→ Cu2+(aq)+ Pb(s); −0.234 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Given:
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e- Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2e- Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cr2O72-(aq)+ 14H+(aq)+ 6e- 2Cr3+(aq)+ 7H2O(l); E° = 1.33 V
2Cr3+(aq)+ 7H2O(l); E° = 1.33 V
Which of the following species is the strongest oxidizing agent?
A)Zn
B)Cr3+
C)Cr2O72-
D)Zn2+
E)Cu
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 VCu2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 VCr2O72-(aq)+ 14H+(aq)+ 6e-
 2Cr3+(aq)+ 7H2O(l); E° = 1.33 V
2Cr3+(aq)+ 7H2O(l); E° = 1.33 VWhich of the following species is the strongest oxidizing agent?
A)Zn
B)Cr3+
C)Cr2O72-
D)Zn2+
E)Cu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the cell notation for the voltaic cell shown below? 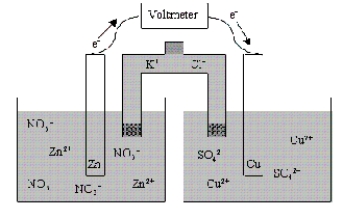
A)Zn2+(aq)| Zn(s)|| Cu2+(aq)| Cu(s)
B)Zn(s)| Zn2+(aq)|| Cu(s)| Cu2+(aq)
C)Zn(s)| Cu(s)|| Zn2+(aq)| Cu2+(aq)
D)Zn(s)| Zn2+(aq)|| Cu2+(aq)| Cu(s)
E)Zn2+(aq)| Zn(s)|| Cu(s)| Cu2+(aq)

A)Zn2+(aq)| Zn(s)|| Cu2+(aq)| Cu(s)
B)Zn(s)| Zn2+(aq)|| Cu(s)| Cu2+(aq)
C)Zn(s)| Cu(s)|| Zn2+(aq)| Cu2+(aq)
D)Zn(s)| Zn2+(aq)|| Cu2+(aq)| Cu(s)
E)Zn2+(aq)| Zn(s)|| Cu(s)| Cu2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the following standard electrode potentials:
Ag+(aq)+ e- Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Mn2+(aq)+ 2e- Mn(s); E° = -1.18 V
Mn(s); E° = -1.18 V
Which of the following statements is false concerning the electrochemical cell given below?
Mn(s)| Mn2+(aq)|| Ag+(aq)| Ag(s)
A)The anode half-cell reaction is Mn(s)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 2e-.
B)The reducing agent is Ag(s).
C)Under standard-state conditions,the cell potential is 1.98 V.
D)The cell potential decreases with time.
E)The oxidizing agent is Ag+(aq).
Ag+(aq)+ e-
 Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Ag(s); E° = 0.80 VMn2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Mn(s); E° = -1.18 V
Mn(s); E° = -1.18 VWhich of the following statements is false concerning the electrochemical cell given below?
Mn(s)| Mn2+(aq)|| Ag+(aq)| Ag(s)
A)The anode half-cell reaction is Mn(s)→ Mn2+(aq)+ 2e-.
B)The reducing agent is Ag(s).
C)Under standard-state conditions,the cell potential is 1.98 V.
D)The cell potential decreases with time.
E)The oxidizing agent is Ag+(aq).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the cell reaction for the following electrochemical cell?
Pt | Fe2+(aq),Fe3+(aq)|| Cr3+(aq)| Cr
A)3Fe2+(aq)+ Cr3+(s)→ Cr(s)+ 3Fe3+(aq)
B)3Fe2+(aq)+ 3Fe3+(aq)→ Cr(s)+ Cr3+(aq)
C)Cr(s)+ 3Fe3+(aq)→ Cr3+(aq)+ 3Fe2+(aq)
D)Pt(s)+ Fe2+(aq)+ Cr3+(aq)→ Cr(s)+ Pt2+(aq)+ Fe3+(aq)
E)Cr(s)+ Cr3+(aq)→ 3Fe2+(aq)+ 3Fe3+(aq)
Pt | Fe2+(aq),Fe3+(aq)|| Cr3+(aq)| Cr
A)3Fe2+(aq)+ Cr3+(s)→ Cr(s)+ 3Fe3+(aq)
B)3Fe2+(aq)+ 3Fe3+(aq)→ Cr(s)+ Cr3+(aq)
C)Cr(s)+ 3Fe3+(aq)→ Cr3+(aq)+ 3Fe2+(aq)
D)Pt(s)+ Fe2+(aq)+ Cr3+(aq)→ Cr(s)+ Pt2+(aq)+ Fe3+(aq)
E)Cr(s)+ Cr3+(aq)→ 3Fe2+(aq)+ 3Fe3+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the cell reaction for the following voltaic cell?
Cr(s)| Cr3+(aq)|| Br-(aq)| Br2(g)| Pt(s)
A)2Cr(s)+ 3Br2(g) 2Cr3+(aq)+ 6Br-(aq)
2Cr3+(aq)+ 6Br-(aq)
B)Cr(s)+ Cr3+(aq) Br-(aq)+ Br2(g)
Br-(aq)+ Br2(g)
C)2Cr3+(aq)+ 6Br-(aq) 2Cr(s)+ 3Br2(g)
2Cr(s)+ 3Br2(g)
D)Cr(s)+ 3Br2(g) Cr3+(s)+ 2Br-(aq)
Cr3+(s)+ 2Br-(aq)
E)Cr(s)+ 2Br-(aq) Br2(g)+ Cr3+(aq)
Br2(g)+ Cr3+(aq)
Cr(s)| Cr3+(aq)|| Br-(aq)| Br2(g)| Pt(s)
A)2Cr(s)+ 3Br2(g)
 2Cr3+(aq)+ 6Br-(aq)
2Cr3+(aq)+ 6Br-(aq)B)Cr(s)+ Cr3+(aq)
 Br-(aq)+ Br2(g)
Br-(aq)+ Br2(g)C)2Cr3+(aq)+ 6Br-(aq)
 2Cr(s)+ 3Br2(g)
2Cr(s)+ 3Br2(g)D)Cr(s)+ 3Br2(g)
 Cr3+(s)+ 2Br-(aq)
Cr3+(s)+ 2Br-(aq)E)Cr(s)+ 2Br-(aq)
 Br2(g)+ Cr3+(aq)
Br2(g)+ Cr3+(aq)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A zinc-copper voltaic cell is represented as follows:
Zn(s)| Zn2+(1.0 M)|| Cu2+(1.0 M)| Cu(s)
Which of the following statements is false?
A)The copper electrode is the anode.
B)Reduction occurs at the copper electrode during discharge.
C)The mass of the zinc electrode decreases during discharge.
D)Electrons flow through the external circuit from the zinc electrode to the copper electrode.
E)The concentration of Cu2+ decreases during discharge.
Zn(s)| Zn2+(1.0 M)|| Cu2+(1.0 M)| Cu(s)
Which of the following statements is false?
A)The copper electrode is the anode.
B)Reduction occurs at the copper electrode during discharge.
C)The mass of the zinc electrode decreases during discharge.
D)Electrons flow through the external circuit from the zinc electrode to the copper electrode.
E)The concentration of Cu2+ decreases during discharge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In a table of standard reduction potentials,the strongest reducing agents are the _______ species in the half-reactions with the _______ E° values.
A)reduced,most negative
B)oxidized,most positive
C)reduced,most positive
D)oxidized,most negative
E)none of these
A)reduced,most negative
B)oxidized,most positive
C)reduced,most positive
D)oxidized,most negative
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The Faraday constant is defined as
A)The charge per mole of electrons.
B)The charge on a single electron.
C)The maximum work obtainable from an electrochemical cell.
D)The electromotive force of the cell.
E)The amount of charge moved between electrodes.
A)The charge per mole of electrons.
B)The charge on a single electron.
C)The maximum work obtainable from an electrochemical cell.
D)The electromotive force of the cell.
E)The amount of charge moved between electrodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Given:
Ni2+(aq)+ 2e- Ni(s); E° = -0.23 V
Ni(s); E° = -0.23 V
2H+(aq)+ 2e- H2(g); E° = 0.00 VAg+(aq)+ e-
H2(g); E° = 0.00 VAg+(aq)+ e-  Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
NO3-(aq)+ 4H+(aq)+ 3e- NO(g)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 0.96 V
NO(g)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 0.96 V
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Ni2+ reacts spontaneously with 1 M H+(aq)to form H2.
B)Ni2+ reacts spontaneously with H2(g).
C)Ag(s)reacts spontaneously with Ni2+.
D)Ag(s)reacts spontaneously with 1 M NO3- in 1 M H+(aq).
E)Ag(s)reacts spontaneously with 1 M H+(aq).
Ni2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Ni(s); E° = -0.23 V
Ni(s); E° = -0.23 V2H+(aq)+ 2e-
 H2(g); E° = 0.00 VAg+(aq)+ e-
H2(g); E° = 0.00 VAg+(aq)+ e-  Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Ag(s); E° = 0.80 VNO3-(aq)+ 4H+(aq)+ 3e-
 NO(g)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 0.96 V
NO(g)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 0.96 VWhich of the following statements is true?
A)Ni2+ reacts spontaneously with 1 M H+(aq)to form H2.
B)Ni2+ reacts spontaneously with H2(g).
C)Ag(s)reacts spontaneously with Ni2+.
D)Ag(s)reacts spontaneously with 1 M NO3- in 1 M H+(aq).
E)Ag(s)reacts spontaneously with 1 M H+(aq).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider the following standard reduction potentials:
2H+(aq)+ 2e- H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
Sn2+(aq)+ 2e- Sn(s); E° = -0.15 V
Sn(s); E° = -0.15 V
Cd2+(aq)+ 2e- Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Which pair of substances will react spontaneously under standard-state conditions?
A)Cd with H+
B)Cd with Sn
C)Sn2+ with Cd2+
D)Sn with Cd2+
E)Sn2+ with H+
2H+(aq)+ 2e-
 H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
H2(g); E° = 0.00 VSn2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Sn(s); E° = -0.15 V
Sn(s); E° = -0.15 VCd2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Cd(s); E° = -0.40 VWhich pair of substances will react spontaneously under standard-state conditions?
A)Cd with H+
B)Cd with Sn
C)Sn2+ with Cd2+
D)Sn with Cd2+
E)Sn2+ with H+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For a certain oxidation-reduction reaction,E°cell is negative.This means that
A)ΔG° is positive and K is less than 1.
B)ΔG° is negative and K is greater than 1.
C)ΔG° is positive and K is greater than 1.
D)ΔG° is negative and K is less than 1.
E)ΔG° is zero and K is greater than 1.
A)ΔG° is positive and K is less than 1.
B)ΔG° is negative and K is greater than 1.
C)ΔG° is positive and K is greater than 1.
D)ΔG° is negative and K is less than 1.
E)ΔG° is zero and K is greater than 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Given:
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e- Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Mg2+(aq)+ 2e- Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
Ag+(aq)+ e- Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
2H+(aq)+ 2e- H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
Under standard-state conditions,which of the following species is the best reducing agent?
A)H2
B)Mg2+
C)Ag+
D)Pb
E)Ag
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 VMg2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
Mg(s); E° = -2.38 VAg+(aq)+ e-
 Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V2H+(aq)+ 2e-
 H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
H2(g); E° = 0.00 VUnder standard-state conditions,which of the following species is the best reducing agent?
A)H2
B)Mg2+
C)Ag+
D)Pb
E)Ag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Given:
Hg2+(aq)+ 2e- Hg(s); E° = 0.85 V
Hg(s); E° = 0.85 V
Li+(aq)+ e- Li(s); E° = -3.04 V
Li(s); E° = -3.04 V
Br2(l)+ 2e- 2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
Au+(aq)+ e- Au(s); E° = 1.69 V
Au(s); E° = 1.69 V
Cl2(g)+ 2e- 2Cl-(aq); E° = 1.36 V
2Cl-(aq); E° = 1.36 V
Which of the following species is the best reducing agent?
A)Hg
B)Li+
C)Au
D)Cl-
E)Br-
Hg2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Hg(s); E° = 0.85 V
Hg(s); E° = 0.85 VLi+(aq)+ e-
 Li(s); E° = -3.04 V
Li(s); E° = -3.04 VBr2(l)+ 2e-
 2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 VAu+(aq)+ e-
 Au(s); E° = 1.69 V
Au(s); E° = 1.69 VCl2(g)+ 2e-
 2Cl-(aq); E° = 1.36 V
2Cl-(aq); E° = 1.36 VWhich of the following species is the best reducing agent?
A)Hg
B)Li+
C)Au
D)Cl-
E)Br-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consider the following standard reduction potentials:
Mg2+(aq)+ 2e-
Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
V2+(aq)+ 2e-
V(s); E° = -1.18 V
Cu2+(aq)+ e-
Cu+(aq); E° = 0.15 V
Which of the following reactions will proceed spontaneously from left to right under standard-state conditions?
A)Mg(s)+ 2Cu2+(aq)→ Mg2+(aq)+ 2Cu+(aq)
B)V2+(aq)+ 2Cu+(aq)→ V(s)+ 2Cu2+(aq)
C)Mg2+(aq)+ 2Cu+(aq)→ 2Cu2+(aq)+ Mg(s)
D)Mg2+(aq)+ V(s)→ V2+(aq)+ Mg(s)
E)2Cu2+(aq)+ 2Cu+(aq)→ Mg2+(aq)+ Mg(s)
Mg2+(aq)+ 2e-

Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
V2+(aq)+ 2e-

V(s); E° = -1.18 V
Cu2+(aq)+ e-

Cu+(aq); E° = 0.15 V
Which of the following reactions will proceed spontaneously from left to right under standard-state conditions?
A)Mg(s)+ 2Cu2+(aq)→ Mg2+(aq)+ 2Cu+(aq)
B)V2+(aq)+ 2Cu+(aq)→ V(s)+ 2Cu2+(aq)
C)Mg2+(aq)+ 2Cu+(aq)→ 2Cu2+(aq)+ Mg(s)
D)Mg2+(aq)+ V(s)→ V2+(aq)+ Mg(s)
E)2Cu2+(aq)+ 2Cu+(aq)→ Mg2+(aq)+ Mg(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is E°cell for the cell reaction 2Cr(s)+ 3Sn4+ (aq)→ 3Sn2+(aq)+ 2Cr3+ (aq)?
Cr3+ (aq)+ 3e- Cr(s); E° = -0.74V
Cr(s); E° = -0.74V 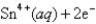

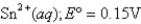
A)0.89V
B)-0.59V
C)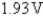
D)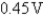
E)0.59V
Cr3+ (aq)+ 3e-
 Cr(s); E° = -0.74V
Cr(s); E° = -0.74V 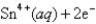

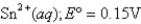
A)0.89V
B)-0.59V
C)
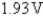
D)
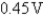
E)0.59V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Given:
W3+(aq)+ 3e- W(s); E° = 2.72 V
W(s); E° = 2.72 V
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e- Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Ni2+(aq)+ 2e- Ni(s); E° = -0.23 V
Ni(s); E° = -0.23 V
Cd2+(aq)+ 2e- Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e- Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Al3+(aq)+ 3e- Al(s); E° = -1.66 V
Al(s); E° = -1.66 V
Mg2+(aq)+ 2e- Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
Under standard-state conditions,which of the following metals will reduce W3+ to W but will not reduce Ni2+ to Ni?
A)Cd
B)Pb
C)Al
D)Zn
E)Mg
W3+(aq)+ 3e-
 W(s); E° = 2.72 V
W(s); E° = 2.72 VPb2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 VNi2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Ni(s); E° = -0.23 V
Ni(s); E° = -0.23 VCd2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Cd(s); E° = -0.40 VZn2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 VAl3+(aq)+ 3e-
 Al(s); E° = -1.66 V
Al(s); E° = -1.66 VMg2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
Mg(s); E° = -2.38 VUnder standard-state conditions,which of the following metals will reduce W3+ to W but will not reduce Ni2+ to Ni?
A)Cd
B)Pb
C)Al
D)Zn
E)Mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Given:
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e- Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e- Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Al3+(aq)+ 3e- Al(s); E° = -1.66 V
Al(s); E° = -1.66 V
Mg2+(aq)+ 2e- Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
V2+(aq)+ 2e- V(s); E° = -1.18 V
V(s); E° = -1.18 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2e- Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Which of the following cations is capable of oxidizing Pb to Pb2+ under standard-state conditions?
A)Al3+
B)V2+
C)Cu2+
D)Mg2+
E)Zn2+
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 VZn2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 VAl3+(aq)+ 3e-
 Al(s); E° = -1.66 V
Al(s); E° = -1.66 VMg2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
Mg(s); E° = -2.38 VV2+(aq)+ 2e-
 V(s); E° = -1.18 V
V(s); E° = -1.18 VCu2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 VWhich of the following cations is capable of oxidizing Pb to Pb2+ under standard-state conditions?
A)Al3+
B)V2+
C)Cu2+
D)Mg2+
E)Zn2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements is true about a voltaic cell for which E°cell = 1.00 V?
A)The cathode is at a higher energy than the anode.
B)It has ΔG° > 0.
C)The reaction is spontaneous.
D)The system is at equilibrium.
E)It has K = 1.
A)The cathode is at a higher energy than the anode.
B)It has ΔG° > 0.
C)The reaction is spontaneous.
D)The system is at equilibrium.
E)It has K = 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Given:
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e- Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
2H+(aq)+ 2e- H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
I2(s)+ 2e- 2I-(aq); E° = 0.54 V
2I-(aq); E° = 0.54 V
Br2(l)+ 2e- 2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
Ni2+(aq)+ 2e- Ni(s); E° = -0.23 V
Ni(s); E° = -0.23 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2e- Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Which of the following species will oxidize Ni but not Cu?
A)Zn2+
B)Br-
C)H+
D)I2
E)Zn
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V2H+(aq)+ 2e-
 H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
H2(g); E° = 0.00 VI2(s)+ 2e-
 2I-(aq); E° = 0.54 V
2I-(aq); E° = 0.54 VBr2(l)+ 2e-
 2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 VNi2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Ni(s); E° = -0.23 V
Ni(s); E° = -0.23 VCu2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 VWhich of the following species will oxidize Ni but not Cu?
A)Zn2+
B)Br-
C)H+
D)I2
E)Zn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Given:
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e- Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Co2+(aq)+ 2e- Co(s); E° = -0.28 V
Co(s); E° = -0.28 V
Sn2+(aq)+ 2e- Sn(s); E° = -0.15 V
Sn(s); E° = -0.15 V
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e- Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Fe3+(aq)+ e- Fe2+(aq); E° = 0.77 V
Fe2+(aq); E° = 0.77 V
Under standard-state conditions,which of the following pairs of elements or ions is capable of reducing Sn2+(aq)to Sn(s)?
A)Zn(s)or Co(s)
B)Pb(s)or Fe2+(aq)
C)Co(s)or Pb(s)
D)Fe2+(aq)or Zn(s)
E)Zn2+(aq)or Co2+(aq)
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 VCo2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Co(s); E° = -0.28 V
Co(s); E° = -0.28 VSn2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Sn(s); E° = -0.15 V
Sn(s); E° = -0.15 VPb2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 VFe3+(aq)+ e-
 Fe2+(aq); E° = 0.77 V
Fe2+(aq); E° = 0.77 VUnder standard-state conditions,which of the following pairs of elements or ions is capable of reducing Sn2+(aq)to Sn(s)?
A)Zn(s)or Co(s)
B)Pb(s)or Fe2+(aq)
C)Co(s)or Pb(s)
D)Fe2+(aq)or Zn(s)
E)Zn2+(aq)or Co2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consider the following cell reaction:
2Cr(s)+ 6H+(aq)→ 2Cr3+(aq)+ 3H2(g); E°cell = 0.74V
Under standard-state conditions,what is E° for the following half-reaction?
Cr3+(aq)+ 3e− → Cr(s)
A)-0.74 V
B)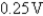
C)-0.37 V
D)0.37 V
E)0.74 V
2Cr(s)+ 6H+(aq)→ 2Cr3+(aq)+ 3H2(g); E°cell = 0.74V
Under standard-state conditions,what is E° for the following half-reaction?
Cr3+(aq)+ 3e− → Cr(s)
A)-0.74 V
B)
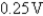
C)-0.37 V
D)0.37 V
E)0.74 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Given:
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e- Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
2H+(aq)+ 2e- H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
NO3-(aq)+4H+(aq)+ 3e- NO(g)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 0.96 V
NO(g)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 0.96 V
O2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e- 2H2O(l); E° = 1.23 V
2H2O(l); E° = 1.23 V
PbO2(s)+ SO42-(aq)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2e- PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 1.69 V
PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 1.69 V
Under standard-state conditions,which of the following is the best oxidizing agent?
A)H+
B)Pb2+
C)PbO2
D)O2
E)NO3-
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V2H+(aq)+ 2e-
 H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
H2(g); E° = 0.00 VNO3-(aq)+4H+(aq)+ 3e-
 NO(g)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 0.96 V
NO(g)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 0.96 VO2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e-
 2H2O(l); E° = 1.23 V
2H2O(l); E° = 1.23 VPbO2(s)+ SO42-(aq)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2e-
 PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 1.69 V
PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l); E° = 1.69 VUnder standard-state conditions,which of the following is the best oxidizing agent?
A)H+
B)Pb2+
C)PbO2
D)O2
E)NO3-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Consider the following cell reaction:
2Hg2+(aq)+ H2(g)→ 2H+(aq)+ Hg22+(aq); E°cell = 0.92 V
Under standard-state conditions,what is E° for the following half-reaction?
Hg2+(aq)+ 2e- → Hg22+(aq)
A)0.92 V
B)-0.46 V
C)0.46 V
D)-0.92 V
E)1.10 V
2Hg2+(aq)+ H2(g)→ 2H+(aq)+ Hg22+(aq); E°cell = 0.92 V
Under standard-state conditions,what is E° for the following half-reaction?
Hg2+(aq)+ 2e- → Hg22+(aq)
A)0.92 V
B)-0.46 V
C)0.46 V
D)-0.92 V
E)1.10 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Consider the following reduction potentials:
Cd2+(aq)+ 2e- Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e- Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2e- Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Br2(l)+ 2e- 2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
Under standard-state conditions,which of the following reactions is spontaneous?
A)Cd2+(aq)+ Pb(s)→ Cd(s)+ Pb2+(aq)
B)Pb2+(aq)+ Cu(s)→ Pb(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
C)2Br-(aq)+ Pb2+(aq)→ Br2(l)+ Pb(s)
D)2Br-(aq)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Br2(l)+ Cu(s)
E)Cu2+(aq)+ Cd(s)→ Cu(s)+ Cd2+(aq)
Cd2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Cd(s); E° = -0.40 VPb2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 VCu2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 VBr2(l)+ 2e-
 2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 VUnder standard-state conditions,which of the following reactions is spontaneous?
A)Cd2+(aq)+ Pb(s)→ Cd(s)+ Pb2+(aq)
B)Pb2+(aq)+ Cu(s)→ Pb(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
C)2Br-(aq)+ Pb2+(aq)→ Br2(l)+ Pb(s)
D)2Br-(aq)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Br2(l)+ Cu(s)
E)Cu2+(aq)+ Cd(s)→ Cu(s)+ Cd2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is true for a reaction that is nonspontaneous as written?
A)ΔG° > 0; E°cell < 0
B)ΔG° < 0; E°cell < 0
C)ΔG° < 0; E°cell < 0
D)ΔG° > 0; E°cell > 0
E)ΔG° > 0; E°cell = 0
A)ΔG° > 0; E°cell < 0
B)ΔG° < 0; E°cell < 0
C)ΔG° < 0; E°cell < 0
D)ΔG° > 0; E°cell > 0
E)ΔG° > 0; E°cell = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Given:
Li+(aq)+ e- Li(s); E° = -3.04 V
Li(s); E° = -3.04 V
Mg2+(aq)+ 2e- Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
Fe2+(aq)+ 2e- Fe(s); E° = -0.41 V
Fe(s); E° = -0.41 V
Ag+(aq)+ e- Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Br2(l)+ 2e- 2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
Which of the following species is the best oxidizing agent?
A)Mg2+
B)Br-
C)Fe2+
D)Li
E)Ag+
Li+(aq)+ e-
 Li(s); E° = -3.04 V
Li(s); E° = -3.04 VMg2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Mg(s); E° = -2.38 V
Mg(s); E° = -2.38 VFe2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Fe(s); E° = -0.41 V
Fe(s); E° = -0.41 VAg+(aq)+ e-
 Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Ag(s); E° = 0.80 VBr2(l)+ 2e-
 2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 V
2Br-(aq); E° = 1.07 VWhich of the following species is the best oxidizing agent?
A)Mg2+
B)Br-
C)Fe2+
D)Li
E)Ag+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Given:
2H+(aq)+ 2e- H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
K+(aq)+ e- K(s); E° = 2.7182818285 V
K(s); E° = 2.7182818285 V
F2(g)+ 2e- 2FS1U1
2FS1U1
1-(aq); E° = 2.87 V
Al3+(aq)+ 3e- Al(s); E° = -1.66 V
Al(s); E° = -1.66 V
Pb2+(aq)+ 2e- Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Under standard-state conditions,which is the strongest reducing agent?
A)Pb2+
B)Al3+
C)F-
D)K
E)H+
2H+(aq)+ 2e-
 H2(g); E° = 0.00 V
H2(g); E° = 0.00 VK+(aq)+ e-
 K(s); E° = 2.7182818285 V
K(s); E° = 2.7182818285 VF2(g)+ 2e-
 2FS1U1
2FS1U11-(aq); E° = 2.87 V
Al3+(aq)+ 3e-
 Al(s); E° = -1.66 V
Al(s); E° = -1.66 VPb2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Pb(s); E° = -0.13 V
Pb(s); E° = -0.13 VUnder standard-state conditions,which is the strongest reducing agent?
A)Pb2+
B)Al3+
C)F-
D)K
E)H+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Given:
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e- Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Cr3+(aq)+ 3e- Cr(s); E° = -0.74 V
Cr(s); E° = -0.74 V
Fe2+(aq)+ 2e- Fe(s); E° = -0.41 V
Fe(s); E° = -0.41 V
Cd2+(aq)+ 2e- Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Sn2+(aq)+ 2e- Sn(s); E° = -0.15 V
Sn(s); E° = -0.15 V
Hg2+(aq)+ 2e- Hg(s); E° = 0.85 V
Hg(s); E° = 0.85 V
Au+(aq)+ e- Au(s); E° = 1.69 V
Au(s); E° = 1.69 V
Under standard-state conditions,which of the following metals will reduce Hg2+ to Hg but will not reduce Cd2+ to Cd?
A)Cr
B)Zn
C)Fe
D)Sn
E)Au
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 VCr3+(aq)+ 3e-
 Cr(s); E° = -0.74 V
Cr(s); E° = -0.74 VFe2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Fe(s); E° = -0.41 V
Fe(s); E° = -0.41 VCd2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Cd(s); E° = -0.40 V
Cd(s); E° = -0.40 VSn2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Sn(s); E° = -0.15 V
Sn(s); E° = -0.15 VHg2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Hg(s); E° = 0.85 V
Hg(s); E° = 0.85 VAu+(aq)+ e-
 Au(s); E° = 1.69 V
Au(s); E° = 1.69 VUnder standard-state conditions,which of the following metals will reduce Hg2+ to Hg but will not reduce Cd2+ to Cd?
A)Cr
B)Zn
C)Fe
D)Sn
E)Au

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Given: 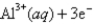

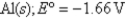
Cl2 (g)+ 2e¯ 2Cl¯ (aq); Eº = 1.36V
2Cl¯ (aq); Eº = 1.36V
What is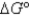
For the following cell reaction?
2AlCl3(aq) 2Al(s)+ 3Cl2(g)
2Al(s)+ 3Cl2(g)
A)-5.8 × 105 J
B)5.8 × 105 J
C)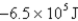
D)-1.7 × 106 J
E)1.7 × 106 J
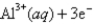

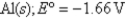
Cl2 (g)+ 2e¯
 2Cl¯ (aq); Eº = 1.36V
2Cl¯ (aq); Eº = 1.36VWhat is
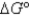
For the following cell reaction?
2AlCl3(aq)
 2Al(s)+ 3Cl2(g)
2Al(s)+ 3Cl2(g)A)-5.8 × 105 J
B)5.8 × 105 J
C)
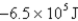
D)-1.7 × 106 J
E)1.7 × 106 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is [H+] given that the measured cell potential is -0.464 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C?
Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H+(aq,? M)| H2(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)
A)![<strong>The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is [H<sup>+</sup>] given that the measured cell potential is -0.464 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C? Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H<sup>+</sup>(aq,? M)| H<sub>2</sub>(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)</strong> A) M B) M C) M D) M E) M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f43_6f8e_a82d_49fc1b032c3c_TB2288_11.jpg) M
M
B)![<strong>The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is [H<sup>+</sup>] given that the measured cell potential is -0.464 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C? Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H<sup>+</sup>(aq,? M)| H<sub>2</sub>(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)</strong> A) M B) M C) M D) M E) M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f43_6f8f_a82d_2961b83b13e1_TB2288_11.jpg) M
M
C)![<strong>The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is [H<sup>+</sup>] given that the measured cell potential is -0.464 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C? Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H<sup>+</sup>(aq,? M)| H<sub>2</sub>(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)</strong> A) M B) M C) M D) M E) M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f43_96a0_a82d_4f0aa18fb8a5_TB2288_11.jpg) M
M
D)![<strong>The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is [H<sup>+</sup>] given that the measured cell potential is -0.464 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C? Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H<sup>+</sup>(aq,? M)| H<sub>2</sub>(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)</strong> A) M B) M C) M D) M E) M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f43_96a1_a82d_67c4968829e6_TB2288_11.jpg) M
M
E)![<strong>The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is [H<sup>+</sup>] given that the measured cell potential is -0.464 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C? Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H<sup>+</sup>(aq,? M)| H<sub>2</sub>(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)</strong> A) M B) M C) M D) M E) M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f43_96a2_a82d_6b70702b703a_TB2288_11.jpg) M
M
Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H+(aq,? M)| H2(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)
A)
![<strong>The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is [H<sup>+</sup>] given that the measured cell potential is -0.464 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C? Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H<sup>+</sup>(aq,? M)| H<sub>2</sub>(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)</strong> A) M B) M C) M D) M E) M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f43_6f8e_a82d_49fc1b032c3c_TB2288_11.jpg) M
MB)
![<strong>The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is [H<sup>+</sup>] given that the measured cell potential is -0.464 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C? Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H<sup>+</sup>(aq,? M)| H<sub>2</sub>(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)</strong> A) M B) M C) M D) M E) M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f43_6f8f_a82d_2961b83b13e1_TB2288_11.jpg) M
MC)
![<strong>The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is [H<sup>+</sup>] given that the measured cell potential is -0.464 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C? Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H<sup>+</sup>(aq,? M)| H<sub>2</sub>(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)</strong> A) M B) M C) M D) M E) M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f43_96a0_a82d_4f0aa18fb8a5_TB2288_11.jpg) M
MD)
![<strong>The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is [H<sup>+</sup>] given that the measured cell potential is -0.464 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C? Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H<sup>+</sup>(aq,? M)| H<sub>2</sub>(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)</strong> A) M B) M C) M D) M E) M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f43_96a1_a82d_67c4968829e6_TB2288_11.jpg) M
ME)
![<strong>The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is [H<sup>+</sup>] given that the measured cell potential is -0.464 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C? Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H<sup>+</sup>(aq,? M)| H<sub>2</sub>(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)</strong> A) M B) M C) M D) M E) M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2288/11ea7a3a_9f43_96a2_a82d_6b70702b703a_TB2288_11.jpg) M
M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the cell is initially at standard-state conditions,which of the following statements is true? 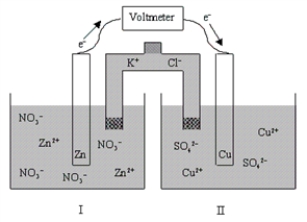 Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-  Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2e- Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
A)Initially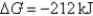 ,and it will become more positive with time.
,and it will become more positive with time.
B)Initially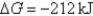 ,and it will not change with time.
,and it will not change with time.
C)Initially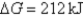 ,and it will become more negative with time.
,and it will become more negative with time.
D)Initially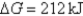 ,and it will become more positive with time.
,and it will become more positive with time.
E)Initially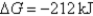 ,and it will become more negative with time.
,and it will become more negative with time.
 Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-  Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 VCu2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 VA)Initially
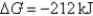 ,and it will become more positive with time.
,and it will become more positive with time.B)Initially
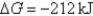 ,and it will not change with time.
,and it will not change with time.C)Initially
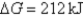 ,and it will become more negative with time.
,and it will become more negative with time.D)Initially
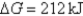 ,and it will become more positive with time.
,and it will become more positive with time.E)Initially
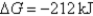 ,and it will become more negative with time.
,and it will become more negative with time.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the logarithm of the equilibrium constant,log K,at 25°C of the voltaic cell constructed from the following two half-reactions?
Fe2+ (aq)+ 2e¯ Fe(s); E° = - 0.41V
Fe(s); E° = - 0.41V
Ag+(aq)+ e-
 Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
A)6.7
B)40.9
C)20.3
D)13.2
E)67.6
Fe2+ (aq)+ 2e¯
 Fe(s); E° = - 0.41V
Fe(s); E° = - 0.41VAg+(aq)+ e-
 Ag(s); E° = 0.80 V
Ag(s); E° = 0.80 VA)6.7
B)40.9
C)20.3
D)13.2
E)67.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The cell potential of the following cell is determined using an unspecified concentration of acid.What is the pH of the acid solution given that the measured cell potential is -0.508 V and the anode reduction potential (E°)is 0.222 V at 25°C?
Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H+(aq,? M)| H2(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)
A)4.83
B)12.30
C)5.33
D)9.66
E)2.16
Ag(s)| AgCl(s)| Cl−(1.0 M)|| H+(aq,? M)| H2(g,1.0 atm)| Pt(s)
A)4.83
B)12.30
C)5.33
D)9.66
E)2.16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Calculate the maximum electrical work obtainable at 25oC from the following voltaic cell.
Cd(s)|Cd2+(0.840M)||Cl2(g,0.0354atm)|Cl-(0.0473M)|Pt;Eºcell = 1.76V
A)-3.39 × 105 J
B)-3.55 × 105 J
C)-3.32 × 105 J
D)-3.47 × 105 J
E)-3.40 × 105 J
Cd(s)|Cd2+(0.840M)||Cl2(g,0.0354atm)|Cl-(0.0473M)|Pt;Eºcell = 1.76V
A)-3.39 × 105 J
B)-3.55 × 105 J
C)-3.32 × 105 J
D)-3.47 × 105 J
E)-3.40 × 105 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Given: 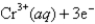

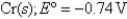
Pb2+ (aq)+ 2e-
 Pb(s); Eº = -0.13 V
Pb(s); Eº = -0.13 V
What is the standard cell potential for the following reaction?
2Cr(s)+ 3Pb2+ (aq)→ 3Pb(s)+ 2Cr3+ (aq)
A)-0.87V
B)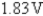
C)-0.61V
D)0.61V
E)0.87V
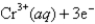

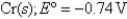
Pb2+ (aq)+ 2e-
 Pb(s); Eº = -0.13 V
Pb(s); Eº = -0.13 VWhat is the standard cell potential for the following reaction?
2Cr(s)+ 3Pb2+ (aq)→ 3Pb(s)+ 2Cr3+ (aq)
A)-0.87V
B)
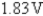
C)-0.61V
D)0.61V
E)0.87V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Calculate the solubility product of silver iodide at 25°C given the following data:
E°(V)
AgI(s)+ e- → Ag(s)+ I-
-0)15
I2(s)+ 2e- → 2I-
+0)54
Ag+ + e- → Ag(s)
+0)80
A)2 × 10-12
B)3 × 10-3
C)2 × 10-24
D)9 × 10-17
E)2 × 10-4
E°(V)
AgI(s)+ e- → Ag(s)+ I-
-0)15
I2(s)+ 2e- → 2I-
+0)54
Ag+ + e- → Ag(s)
+0)80
A)2 × 10-12
B)3 × 10-3
C)2 × 10-24
D)9 × 10-17
E)2 × 10-4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Given: 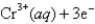

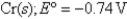
Pb2+ (aq)+ 2e¯ Pb(s); Eº = -0.13V
Pb(s); Eº = -0.13V
What is the standard Gibbs free-energy change for the following reaction?
2Cr(s)+ 3Pb2+ (aq)→ 3Pb(s)+ 2Cr3+ (aq)
A)353kJ
B)118kJ
C)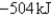
D)-353kJ
E)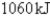
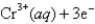

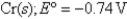
Pb2+ (aq)+ 2e¯
 Pb(s); Eº = -0.13V
Pb(s); Eº = -0.13VWhat is the standard Gibbs free-energy change for the following reaction?
2Cr(s)+ 3Pb2+ (aq)→ 3Pb(s)+ 2Cr3+ (aq)
A)353kJ
B)118kJ
C)
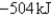
D)-353kJ
E)
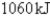

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements is true concerning the electrochemical cell depicted below?
Zn | Zn2+(aq)|| Cu2+(aq)| Cu
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e− Zn(s); E° = -2.87 V
Zn(s); E° = -2.87 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2e− Cu(s); E° = -2.38 V
Cu(s); E° = -2.38 V
A)The cell is at equilibrium.
B)The cell reaction is spontaneous with a standard cell potential of 0.49 V.
C)The cell reaction is spontaneous with a standard cell potential of 5.25 V.
D)The cell reaction is nonspontaneous with a standard cell potential of -5.25 V.
E)The cell reaction is nonspontaneous with a standard cell potential of -0.49 V.
Zn | Zn2+(aq)|| Cu2+(aq)| Cu
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e−
 Zn(s); E° = -2.87 V
Zn(s); E° = -2.87 VCu2+(aq)+ 2e−
 Cu(s); E° = -2.38 V
Cu(s); E° = -2.38 VA)The cell is at equilibrium.
B)The cell reaction is spontaneous with a standard cell potential of 0.49 V.
C)The cell reaction is spontaneous with a standard cell potential of 5.25 V.
D)The cell reaction is nonspontaneous with a standard cell potential of -5.25 V.
E)The cell reaction is nonspontaneous with a standard cell potential of -0.49 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is the equilibrium constant (K)at 25°C for the following cell reaction?
Sn(s)+ Pb2+ (aq)→ Sn2+ (aq)+ Pb(s); E°cell = 0.014 V
A)0.014
B)1.7
C)0.4
D)1.0
E)3
Sn(s)+ Pb2+ (aq)→ Sn2+ (aq)+ Pb(s); E°cell = 0.014 V
A)0.014
B)1.7
C)0.4
D)1.0
E)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
For a certain reaction,ΔHº = -75.4kJ and ΔSº = -225J/K.If n = 3,calculate E°cell for the reaction at 25°C.
A)0.0288 V
B)0.0961 V
C)0.241 V
D)0.492 V
E)0.0654 V
A)0.0288 V
B)0.0961 V
C)0.241 V
D)0.492 V
E)0.0654 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A voltaic cell is made by placing an iron electrode in a compartment in which the Fe2+ concentration is 2.0 × 10-5 M and by placing a Pt electrode in the other compartment,in which the H+ concentration is 3.4 M and 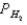 = 1.00 atm.The Fe2+/Fe half-cell reduction potential is -0.41 V,and the H+/H2 half-cell reduction potential is 0.00 V.What is the value of E° for this cell,and which electrode is the anode?
= 1.00 atm.The Fe2+/Fe half-cell reduction potential is -0.41 V,and the H+/H2 half-cell reduction potential is 0.00 V.What is the value of E° for this cell,and which electrode is the anode?
A)0.41 V,Fe
B)0.90 V,Pt
C)-0.41 V,Pt
D)-0.41 V,Fe
E)0.41 V,Pt
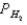 = 1.00 atm.The Fe2+/Fe half-cell reduction potential is -0.41 V,and the H+/H2 half-cell reduction potential is 0.00 V.What is the value of E° for this cell,and which electrode is the anode?
= 1.00 atm.The Fe2+/Fe half-cell reduction potential is -0.41 V,and the H+/H2 half-cell reduction potential is 0.00 V.What is the value of E° for this cell,and which electrode is the anode?A)0.41 V,Fe
B)0.90 V,Pt
C)-0.41 V,Pt
D)-0.41 V,Fe
E)0.41 V,Pt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A voltaic cell is made by placing a zinc electrode in a compartment in which the Zn2+ concentration is 2.0 × 10-5 M and by placing a Pt electrode in the other compartment,in which the H+ concentration is 3.4 M and PH2 = 1.00 atm.The Zn2+/Zn half-cell reduction potential is -0.76 V,and the H+/H2 half-cell reduction potential is 0.00 V.What is the equilibrium constant at 25°C for the spontaneous cell reaction?
A)4 × 104
B)5 × 1020
C)5 × 1022
D)7 × 10 12
E)5 × 10 25
A)4 × 104
B)5 × 1020
C)5 × 1022
D)7 × 10 12
E)5 × 10 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements is true concerning the hypthetical electrochemical cell depicted below? (M1 and M2 are differing metals)
M1 | M12+(aq)|| M2+(aq)| M2
M12+(aq)+ 2e− M1(s); E° = -2.91 V
M1(s); E° = -2.91 V
M22+(aq)+ e− M2(s); E° = -2.98 V
M2(s); E° = -2.98 V
A)The cell reaction is nonspontaneous with a standard cell potential of -0.07 V.
B)The cell reaction is spontaneous with a standard cell potential of 5.89 V.
C)The cell is at equilibrium.
D)The cell reaction is spontaneous with a standard cell potential of 0.07 V.
E)The cell reaction is nonspontaneous with a standard cell potential of -5.89 V.
M1 | M12+(aq)|| M2+(aq)| M2
M12+(aq)+ 2e−
 M1(s); E° = -2.91 V
M1(s); E° = -2.91 VM22+(aq)+ e−
 M2(s); E° = -2.98 V
M2(s); E° = -2.98 VA)The cell reaction is nonspontaneous with a standard cell potential of -0.07 V.
B)The cell reaction is spontaneous with a standard cell potential of 5.89 V.
C)The cell is at equilibrium.
D)The cell reaction is spontaneous with a standard cell potential of 0.07 V.
E)The cell reaction is nonspontaneous with a standard cell potential of -5.89 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
For a reaction in a voltaic cell,both ΔH° and ΔS° are positive.Which of the following statements is true?
A)E°cell will increase with an increase in temperature.
B)E°cell will not change when the temperature increases.
C)E°cell will decrease with an increase in temperature.
D)ΔG° > 0 for all temperatures.
E)None of the above statements is true.
A)E°cell will increase with an increase in temperature.
B)E°cell will not change when the temperature increases.
C)E°cell will decrease with an increase in temperature.
D)ΔG° > 0 for all temperatures.
E)None of the above statements is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If E°cell for a certain reaction is 1 V (n = 4),and ΔS° is 11.2 J/(K⋅mol),what is ΔH° in units of J/mol at 25°C?
A)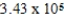 × 105 J/mol
× 105 J/mol
B)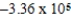 × 105 J/mol
× 105 J/mol
C)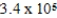 × 105 J/mol
× 105 J/mol
D)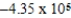 × 104 J/mol
× 104 J/mol
E)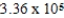 J/mol
J/mol
A)
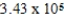 × 105 J/mol
× 105 J/molB)
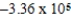 × 105 J/mol
× 105 J/molC)
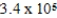 × 105 J/mol
× 105 J/molD)
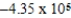 × 104 J/mol
× 104 J/molE)
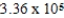 J/mol
J/mol
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If the value of E°cell is 2.10 V for the reaction
F2 (g)+ 2Fe2+ (aq)→ 2Fe3+ (aq)+ 2F- (aq),
What is the value of E°cell for
F- (aq)+ Fe3+ (aq)→ Fe2+ (aq)+ 1/2 F2(g)?
A)-4.20 V
B)-1.05 V
C)2.10V
D)1.05 V
E)-2.10V
F2 (g)+ 2Fe2+ (aq)→ 2Fe3+ (aq)+ 2F- (aq),
What is the value of E°cell for
F- (aq)+ Fe3+ (aq)→ Fe2+ (aq)+ 1/2 F2(g)?
A)-4.20 V
B)-1.05 V
C)2.10V
D)1.05 V
E)-2.10V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is E of the following cell reaction at 25°C? E°cell = 0.460 V.Cu(s)| Cu2+(0.020M)|| Ag+(0.16M)| Ag(s)
A)0.463 V
B)0.282 V
C)0.460 V
D)0.487 V
E)0.467 V
A)0.463 V
B)0.282 V
C)0.460 V
D)0.487 V
E)0.467 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If the cell is initially at standard-state conditions,which of the following statements is true? 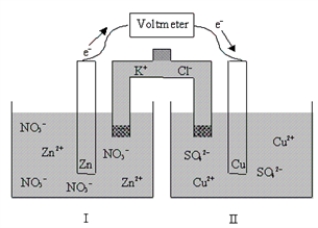 Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-  Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2e- Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
A)Initially Kc = 2 × 10-37,and it decreases with time.
B)Initially Kc = 2 × 1037,and it does not change with time.
C)Initially Kc = 2 × 1037,and it decreases with time.
D)Initially Kc = 2 × 1037,and it increases with time.
E)Initially Kc = 2 × 10-37,and it increases with time.
 Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e-  Zn(s); E° = -0.76 V
Zn(s); E° = -0.76 VCu2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Cu(s); E° = 0.34 V
Cu(s); E° = 0.34 VA)Initially Kc = 2 × 10-37,and it decreases with time.
B)Initially Kc = 2 × 1037,and it does not change with time.
C)Initially Kc = 2 × 1037,and it decreases with time.
D)Initially Kc = 2 × 1037,and it increases with time.
E)Initially Kc = 2 × 10-37,and it increases with time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



