Deck 16: Eye and Ear
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Eye and Ear
1
________ External acoustic meatus
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme
D
The external acoustic meatus is the adult derivative of the dorsal part of the first pharyngeal groove.It grows inward as a funnel-shaped tube until it reaches the endodermal tubotympanic recess,primordium of the tympanic cavity,tympanic antrum,pharyngotympanic (auditory)tube,and mastoid cells.
The external acoustic meatus is the adult derivative of the dorsal part of the first pharyngeal groove.It grows inward as a funnel-shaped tube until it reaches the endodermal tubotympanic recess,primordium of the tympanic cavity,tympanic antrum,pharyngotympanic (auditory)tube,and mastoid cells.
2
________ Congenital glaucoma
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane
A
Absence or incomplete development of the scleral venous sinus results in congenital glaucoma or buphthalmos.This abnormality usually is caused by recessive mutant genes,but sometimes it results from a maternal rubella infection during early pregnancy.The embryological basis of blockage or incomplete development of the scleral venous sinus is abnormal persistence of mesenchymal tissue in the angle of the anterior chamber.As a result of inadequate drainage of the aqueous humor through the canal,intraocular tension rises,the eye gradually enlarges,and the cornea becomes hazy.Retinal damage causes visual impairment.
Absence or incomplete development of the scleral venous sinus results in congenital glaucoma or buphthalmos.This abnormality usually is caused by recessive mutant genes,but sometimes it results from a maternal rubella infection during early pregnancy.The embryological basis of blockage or incomplete development of the scleral venous sinus is abnormal persistence of mesenchymal tissue in the angle of the anterior chamber.As a result of inadequate drainage of the aqueous humor through the canal,intraocular tension rises,the eye gradually enlarges,and the cornea becomes hazy.Retinal damage causes visual impairment.
3
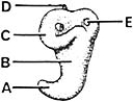 ________ Gives rise to the spiral organ
________ Gives rise to the spiral organA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
A
The spiral organ (of Corti)differentiates from cells in the wall of the cochlear duct.Ganglion cells of the eighth cranial nerve migrate along the coils of the cochlea and form the cochlear ganglion.Nerve processes grow from this ganglion to the spiral organ.
The spiral organ (of Corti)differentiates from cells in the wall of the cochlear duct.Ganglion cells of the eighth cranial nerve migrate along the coils of the cochlea and form the cochlear ganglion.Nerve processes grow from this ganglion to the spiral organ.
4
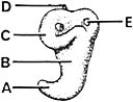 ________ Primordium of the cochlea
________ Primordium of the cochleaA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
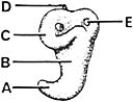 ________ Saccular part of the otic vesicle
________ Saccular part of the otic vesicleA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
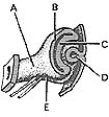 ________ Becomes specialized for sensitivity to light
________ Becomes specialized for sensitivity to lightA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
________ Neuroectoderm
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
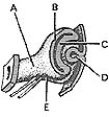 ________ Future optic nerve
________ Future optic nerveA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
________ Sclera and choroid
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
________ Ganglion cells of retina
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
________ Hyaloid artery
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
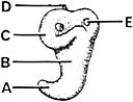 ________ Absorption focus
________ Absorption focusA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
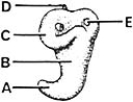 ________ Endolymphatic duct
________ Endolymphatic ductA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
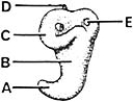 ________ Gives rise to a semicircular duct
________ Gives rise to a semicircular ductA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
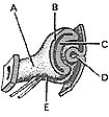 ________ Differentiates into the nonpigmented portion of the ciliary epithelium
________ Differentiates into the nonpigmented portion of the ciliary epitheliumA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
________ Tunica vasculosa lentis
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
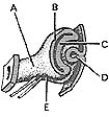 ________ Retinal fissure
________ Retinal fissureA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
________ Surface ectoderm
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane
A)Scleral venous sinus
B)Optic nerve
C)Corneal epithelium
D)Central artery of retina
E)Pupillary membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
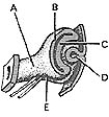 ________ Gives rise to the lens
________ Gives rise to the lensA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
 ________ Becomes the pigmented layer of the retina
________ Becomes the pigmented layer of the retinaA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
________ Tympanic cavity
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
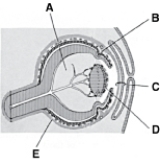 ________ Ciliary body
________ Ciliary bodyA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
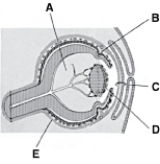 ________ Develops from mesenchyme
________ Develops from mesenchymeA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
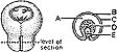 ________ Hyaloid vessels
________ Hyaloid vesselsA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
________ Mastoid cells
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
________ Bipolar cells of the retina
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
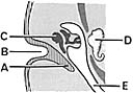 ________ Derived from the first pharyngeal arch cartilage
________ Derived from the first pharyngeal arch cartilageA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
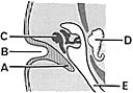 ________ External acoustic meatus
________ External acoustic meatusA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
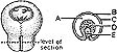 ________ Contains axons of ganglion cells
________ Contains axons of ganglion cellsA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
 ________ Gives rise to the utricle
________ Gives rise to the utricleA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
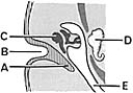 ________ Derived from the tubotympanic recess
________ Derived from the tubotympanic recessA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
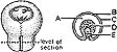 ________ Continuous with the pigmented epithelium of the retina
________ Continuous with the pigmented epithelium of the retinaA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
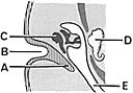 ________ Membranous labyrinth
________ Membranous labyrinthA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
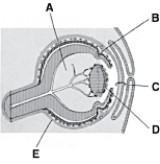 ________ Only derived from surface ectoderm
________ Only derived from surface ectodermA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
________ Has same origin as the cornea
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme
A)Conjunctival epithelium
B)Neuroectoderm
C)First pharyngeal pouch
D)First pharyngeal groove
E)Mesenchyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
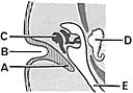 ________ Meatal plug
________ Meatal plugA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
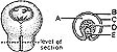 ________ Continuous with the cranial meninges
________ Continuous with the cranial meningesA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
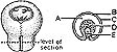 ________ Gradually obliterates
________ Gradually obliteratesA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
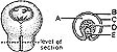 ________ Continuous with the neural layer of the retina
________ Continuous with the neural layer of the retinaA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
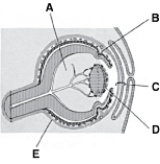 ________ Composed of vitreous humor
________ Composed of vitreous humorA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
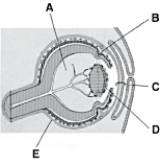 ________ Cornea
________ CorneaA)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



