Deck 4: The Market Forces of Supply and Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: The Market Forces of Supply and Demand
1
The quantity demanded of a good is the amount that buyers are
A)willing to purchase.
B)willing and able to purchase.
C)willing,able,and need to purchase.
D)able to purchase.
A)willing to purchase.
B)willing and able to purchase.
C)willing,able,and need to purchase.
D)able to purchase.
B
2
Figure 4-1 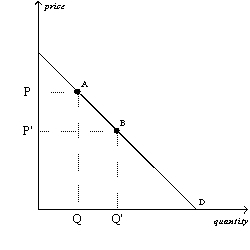
Refer to Figure 4-1.The movement from point A to point B on the graph shows
A)a decrease in demand.
B)an increase in demand.
C)a decrease in quantity demanded.
D)an increase in quantity demanded.

Refer to Figure 4-1.The movement from point A to point B on the graph shows
A)a decrease in demand.
B)an increase in demand.
C)a decrease in quantity demanded.
D)an increase in quantity demanded.
B
3
The demand for a good or service is determined by
A)those who buy the good or service.
B)the government.
C)those who sell the good or service.
D)both those who buy and those who sell the good or service.
A)those who buy the good or service.
B)the government.
C)those who sell the good or service.
D)both those who buy and those who sell the good or service.
A
4
Which of the following would shift the demand curve for gasoline to the right?
A)a decrease in the price of gasoline
B)an increase in consumer income,assuming gasoline is a normal good
C)an increase in the price of cars,a complement for gasoline
D)a decrease in the expected future price of gasoline
A)a decrease in the price of gasoline
B)an increase in consumer income,assuming gasoline is a normal good
C)an increase in the price of cars,a complement for gasoline
D)a decrease in the expected future price of gasoline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The forces that make market economies work are
A)work and leisure.
B)politics and religion.
C)supply and demand.
D)taxes and government spending.
A)work and leisure.
B)politics and religion.
C)supply and demand.
D)taxes and government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a market economy,supply and demand are important because they
A)are direct policy tools used by government agencies to regulate the economy.
B)illustrate when an market is in equilibrium,but they are not helpful when a market is out of equilibrium.
C)can be used to predict the impact on the economy of various events and policies.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)are direct policy tools used by government agencies to regulate the economy.
B)illustrate when an market is in equilibrium,but they are not helpful when a market is out of equilibrium.
C)can be used to predict the impact on the economy of various events and policies.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Table 4-1
-Refer to Table 4-1.If the market consists of Laura and Hillary only and the price falls by $1,the quantity demanded in the market increases by
A)2 units.
B)3 units.
C)4 units.
D)5 units.
-Refer to Table 4-1.If the market consists of Laura and Hillary only and the price falls by $1,the quantity demanded in the market increases by
A)2 units.
B)3 units.
C)4 units.
D)5 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Most markets in the economy are
A)markets in which sellers,rather than buyers,control the price of the product.
B)markets in which buyers,rather than sellers,control the price of the product.
C)perfectly competitive.
D)highly competitive.
A)markets in which sellers,rather than buyers,control the price of the product.
B)markets in which buyers,rather than sellers,control the price of the product.
C)perfectly competitive.
D)highly competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When all market participants are price takers who have no influence over prices,the markets have
A)only a few buyers and sellers.
B)numerous sellers but only a few buyers.
C)numerous buyers but only a few sellers.
D)numerous buyers and sellers.
A)only a few buyers and sellers.
B)numerous sellers but only a few buyers.
C)numerous buyers but only a few sellers.
D)numerous buyers and sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An increase in quantity demanded
A)results in a movement downward and to the right along a demand curve.
B)results in a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve.
C)shifts the demand curve to the left.
D)shifts the demand curve to the right.
A)results in a movement downward and to the right along a demand curve.
B)results in a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve.
C)shifts the demand curve to the left.
D)shifts the demand curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A decrease in the price of a good will
A)increase demand.
B)decrease demand.
C)increase quantity demanded.
D)decrease quantity demanded.
A)increase demand.
B)decrease demand.
C)increase quantity demanded.
D)decrease quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Table 4-1
-Refer to Table 4-1.Which of the following illustrates the market demand curve?
A)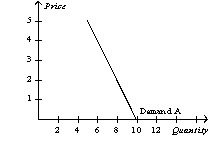
B)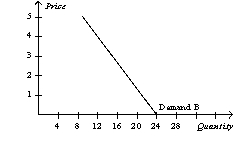
C)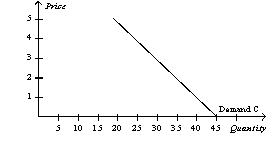
D)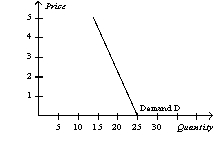
-Refer to Table 4-1.Which of the following illustrates the market demand curve?
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The supply of a good or service is determined by
A)those who buy the good or service.
B)the government.
C)those who sell the good or service.
D)both those who buy and those who sell the good or service.
A)those who buy the good or service.
B)the government.
C)those who sell the good or service.
D)both those who buy and those who sell the good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a perfectly competitive market,at the market price,buyers
A)cannot buy all they want,and sellers cannot sell all they want.
B)cannot buy all they want,but sellers can sell all they want.
C)can buy all they want,but sellers cannot sell all they want.
D)can buy all they want,and sellers can sell all they want.
A)cannot buy all they want,and sellers cannot sell all they want.
B)cannot buy all they want,but sellers can sell all they want.
C)can buy all they want,but sellers cannot sell all they want.
D)can buy all they want,and sellers can sell all they want.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following would most likely serve as an example of a monopoly?
A)a bakery in a large city
B)a bank in a large city
C)a local cable television company
D)a small group of corn farmers
A)a bakery in a large city
B)a bank in a large city
C)a local cable television company
D)a small group of corn farmers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In a competitive market,the quantity of a product produced and the price of the product are determined by
A)buyers.
B)sellers.
C)both buyers and sellers.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)buyers.
B)sellers.
C)both buyers and sellers.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A monopoly is a market with one
A)seller,and that seller is a price taker.
B)seller,and that seller sets the price.
C)buyer,and that buyer is a price taker.
D)buyer,and that buyer sets the price.
A)seller,and that seller is a price taker.
B)seller,and that seller sets the price.
C)buyer,and that buyer is a price taker.
D)buyer,and that buyer sets the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is an example of a market?
A)a gas station
B)a garage sale
C)a barber shop
D)All of the above are examples of markets.
A)a gas station
B)a garage sale
C)a barber shop
D)All of the above are examples of markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a seller in a competitive market chooses to charge more than the going price,then
A)the sellers' profits must increase.
B)the owners of the raw materials used in production would raise the prices for the raw materials.
C)other sellers would also raise their prices.
D)buyers will make purchases from other sellers.
A)the sellers' profits must increase.
B)the owners of the raw materials used in production would raise the prices for the raw materials.
C)other sellers would also raise their prices.
D)buyers will make purchases from other sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Soup is an inferior good if the demand
A)for soup falls when the price of a substitute for soup rises.
B)for soup rises when the price of soup falls.
C)curve for soup slopes upward.
D)for soup falls when income rises.
A)for soup falls when the price of a substitute for soup rises.
B)for soup rises when the price of soup falls.
C)curve for soup slopes upward.
D)for soup falls when income rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the price of a good is low,
A)firms would increase profit by increasing output.
B)the quantity supplied of the good could be zero.
C)the supply curve for the good will shift to the left.
D)firms can and should raise the price of the product.
A)firms would increase profit by increasing output.
B)the quantity supplied of the good could be zero.
C)the supply curve for the good will shift to the left.
D)firms can and should raise the price of the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 4-2
The graph below pertains to the supply of paper to colleges and universities.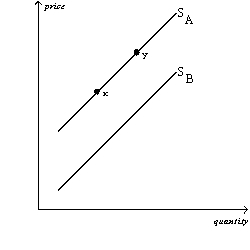
Refer to Figure 4-2.All else equal,buyers expecting paper to be more expensive in the future would cause a current move from
A)x to y.
B)y to x.
C)SA to SB.
D)SB to SA.
The graph below pertains to the supply of paper to colleges and universities.

Refer to Figure 4-2.All else equal,buyers expecting paper to be more expensive in the future would cause a current move from
A)x to y.
B)y to x.
C)SA to SB.
D)SB to SA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following would cause price to decrease?
A)a decrease in supply
B)an increase in demand
C)a surplus of the good
D)a shortage of the good
A)a decrease in supply
B)an increase in demand
C)a surplus of the good
D)a shortage of the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In markets,prices move toward equilibrium because of
A)the actions of buyers and sellers.
B)government regulations placed on market participants.
C)increased competition among sellers.
D)buyers' ability to affect market outcomes.
A)the actions of buyers and sellers.
B)government regulations placed on market participants.
C)increased competition among sellers.
D)buyers' ability to affect market outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What will happen in the artichoke market now if buyers expect higher artichoke prices in the near future?
A)The demand for artichokes will increase.
B)The demand for artichokes will decrease.
C)The demand for artichokes will be unaffected.
D)The supply of artichokes will increase.
A)The demand for artichokes will increase.
B)The demand for artichokes will decrease.
C)The demand for artichokes will be unaffected.
D)The supply of artichokes will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The sum of all the individual supply curves for a product is called
A)total supply.
B)market supply.
C)aggregate supply.
D)total output.
A)total supply.
B)market supply.
C)aggregate supply.
D)total output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An increase in the price of a good will
A)increase supply.
B)decrease supply.
C)increase quantity supplied.
D)decrease quantity supplied.
A)increase supply.
B)decrease supply.
C)increase quantity supplied.
D)decrease quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The unique point at which the supply and demand curves intersect is called
A)market harmony.
B)coincidence.
C)equivalence.
D)equilibrium.
A)market harmony.
B)coincidence.
C)equivalence.
D)equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
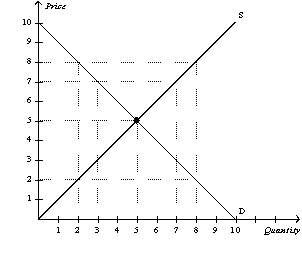
From the above figure,at a price of
A)$2,there is a surplus of 6 units.
B)$5,there is a surplus of 25 units.
C)$5,there is a shortage of $25.
D)$7,there is a surplus of 4 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Table 4-2
-Refer to Table 4-2.Which supply schedules obey the law of supply?
A)Firm A's only
B)Firm B's,Firm C's,and Firm D's only
C)Firm A's and Firm C's only
D)Firm B's and Firm D's only
-Refer to Table 4-2.Which supply schedules obey the law of supply?
A)Firm A's only
B)Firm B's,Firm C's,and Firm D's only
C)Firm A's and Firm C's only
D)Firm B's and Firm D's only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When the price of a good is lower than the equilibrium price,
A)a surplus will exist.
B)buyers desire to purchase more than is produced.
C)sellers desire to produce and sell more than buyers wish to purchase.
D)quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded.
A)a surplus will exist.
B)buyers desire to purchase more than is produced.
C)sellers desire to produce and sell more than buyers wish to purchase.
D)quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The difference between a supply schedule and a supply curve is that a supply schedule
A)incorporates demand and a supply curve does not.
B)incorporates profit and a supply curve does not.
C)can shift,but a supply curve cannot shift.
D)is a table,and a supply curve is drawn on a graph.
A)incorporates demand and a supply curve does not.
B)incorporates profit and a supply curve does not.
C)can shift,but a supply curve cannot shift.
D)is a table,and a supply curve is drawn on a graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Table 4-2
-Refer to Table 4-4.If these are the only four sellers in the market,then when the price increases from $6 to $8,the market quantity supplied
A)increases by 0.5 units.
B)increases by 2 units.
C)decreases by 4 units.
D)increases by 42 units.
-Refer to Table 4-4.If these are the only four sellers in the market,then when the price increases from $6 to $8,the market quantity supplied
A)increases by 0.5 units.
B)increases by 2 units.
C)decreases by 4 units.
D)increases by 42 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
At the equilibrium price,the quantity of the good that buyers are willing and able to buy
A)is greater than the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
B)exactly equals the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
C)is less than the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
D)Either a)or c)could be correct.
A)is greater than the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
B)exactly equals the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
C)is less than the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
D)Either a)or c)could be correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
"Other things equal,when the price of a good rises,the quantity supplied of the good also rises,and when the price falls,the quantity supplied falls as well." This relationship between price and quantity supplied
A)is referred to as the law of supply.
B)applies only to a few goods in the economy.
C)is represented by a downward-sloping supply curve.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)is referred to as the law of supply.
B)applies only to a few goods in the economy.
C)is represented by a downward-sloping supply curve.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When quantity supplied increases at every possible price,we know that the supply curve has
A)shifted to the left.
B)shifted to the right.
C)not shifted; rather,we have moved along the supply curve to a new point on the same curve.
D)not shifted; rather,the supply curve has become flatter.
A)shifted to the left.
B)shifted to the right.
C)not shifted; rather,we have moved along the supply curve to a new point on the same curve.
D)not shifted; rather,the supply curve has become flatter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The quantity supplied of a good is the amount that
A)buyers are willing and able to purchase.
B)sellers are able to produce.
C)buyers and sellers agree will be brought to market.
D)sellers are willing and able to sell.
A)buyers are willing and able to purchase.
B)sellers are able to produce.
C)buyers and sellers agree will be brought to market.
D)sellers are willing and able to sell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Figure 4-2
The graph below pertains to the supply of paper to colleges and universities.
Refer to Figure 4-2.All else equal,an increase in the price of the pulp used in the paper production process would cause a move from
A)x to y.
B)y to x.
C)SA to SB.
D)SB to SA.
The graph below pertains to the supply of paper to colleges and universities.

Refer to Figure 4-2.All else equal,an increase in the price of the pulp used in the paper production process would cause a move from
A)x to y.
B)y to x.
C)SA to SB.
D)SB to SA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An increase in quantity supplied
A)results in a movement downward and to the left along a fixed supply curve.
B)results in a movement upward and to the right along a fixed supply curve.
C)shifts the supply curve to the left.
D)shifts the supply curve to the right.
A)results in a movement downward and to the left along a fixed supply curve.
B)results in a movement upward and to the right along a fixed supply curve.
C)shifts the supply curve to the left.
D)shifts the supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Equilibrium price must increase when demand
A)increases and supply does not change,when demand does not change and supply decreases,and when demand decreases and supply increases simultaneously.
B)increases and supply does not change,when demand does not change and supply decreases,and when demand increases and supply decreases simultaneously.
C)decreases and supply does not change,when demand does not change and supply increases,and when demand decreases and supply increases simultaneously.
D)decreases and supply does not change,when demand does not change and supply increases,and when demand increases and supply decreases simultaneously.
A)increases and supply does not change,when demand does not change and supply decreases,and when demand decreases and supply increases simultaneously.
B)increases and supply does not change,when demand does not change and supply decreases,and when demand increases and supply decreases simultaneously.
C)decreases and supply does not change,when demand does not change and supply increases,and when demand decreases and supply increases simultaneously.
D)decreases and supply does not change,when demand does not change and supply increases,and when demand increases and supply decreases simultaneously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A market is a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A shortage will occur at any price below equilibrium price and a surplus will occur at any price above equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In a market economy,supply and demand determine both the quantity of each good produced and the price at which it is sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When a supply curve or a demand curve shifts,the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a market economy,prices are the signals that guide the allocation of scarce resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The quantity supplied of a good or service is the amount that sellers are willing and able to sell at a particular price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Fill in the table below,showing whether equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity go up,go down,stay the same,or change ambiguously. 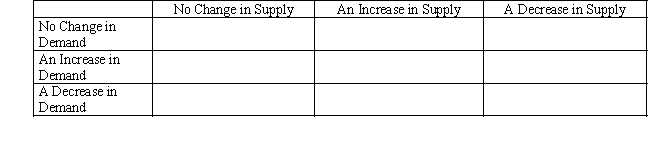


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An increase in the price of a product and an increase in the number of sellers in the market affect the supply curve in the same general way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A decrease in income will shift the demand curve for an inferior good to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An increase in the price of ink will shift the supply curve for pens to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The signals that guide the allocation of resources in a market economy are
A)surpluses and shortages.
B)quantities.
C)government policies.
D)prices.
A)surpluses and shortages.
B)quantities.
C)government policies.
D)prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a determinant of demand other than price changes,the demand curve shifts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 4-2
The graph below pertains to the supply of paper to colleges and universities.
Refer to Figure 4-2.All else equal,the return of college students to campus in the fall would cause a move from
A)x to y.
B)y to x.
C)SA to SB.
D)SB to SA.
The graph below pertains to the supply of paper to colleges and universities.

Refer to Figure 4-2.All else equal,the return of college students to campus in the fall would cause a move from
A)x to y.
B)y to x.
C)SA to SB.
D)SB to SA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If a good or service has only one seller,then the seller is called a monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Prices allocate a market economy's scarce resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The law of demand states that,other things equal,when the price of a good rises,the quantity demanded of the good falls,and when the price falls,the quantity demanded rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In a perfectly competitive market,buyers and sellers are price setters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Who gets scarce resources in a market economy?
A)the government
B)whoever the government decides gets them
C)whoever wants them
D)whoever is willing and able to pay the price
A)the government
B)whoever the government decides gets them
C)whoever wants them
D)whoever is willing and able to pay the price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In a competitive market,the quantity of each good produced and the price at which it is sold are not determined by any single buyer or seller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



