Deck 8: Application: The Costs of Taxation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Application: The Costs of Taxation
1
Figure 8-3
The vertical distance between points A and C represents a tax in the market.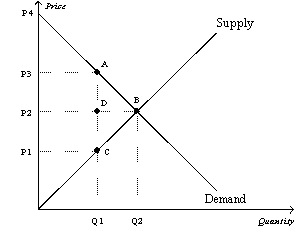
Refer to Figure 8-3.The price that buyers effectively pay after the tax is imposed is
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.
The vertical distance between points A and C represents a tax in the market.

Refer to Figure 8-3.The price that buyers effectively pay after the tax is imposed is
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.
C
2
Figure 8-3
The vertical distance between points A and C represents a tax in the market.
Refer to Figure 8-3.The price that sellers effectively receive after the tax is imposed is
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.
The vertical distance between points A and C represents a tax in the market.

Refer to Figure 8-3.The price that sellers effectively receive after the tax is imposed is
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.
A
3
Figure 8-1 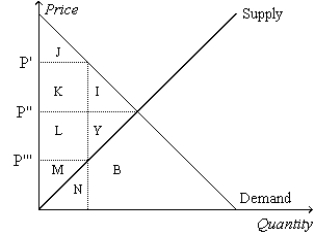
Refer to Figure 8-1.Suppose the government imposes a tax of P' - P'''.The producer surplus before the tax is measured by the area
A)I+J+K.
B)I+Y.
C)L+M+Y.
D)M.

Refer to Figure 8-1.Suppose the government imposes a tax of P' - P'''.The producer surplus before the tax is measured by the area
A)I+J+K.
B)I+Y.
C)L+M+Y.
D)M.
C
4
The benefit to buyers of participating in a market is measured by
A)the price elasticity of demand.
B)consumer surplus.
C)the maximum amount that buyers are willing to pay for the good.
D)the equilibrium price.
A)the price elasticity of demand.
B)consumer surplus.
C)the maximum amount that buyers are willing to pay for the good.
D)the equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When a tax is levied on a good,the buyers and sellers of the good share the burden,
A)provided the tax is levied on the sellers.
B)provided the tax is levied on the buyers.
C)provided a portion of the tax is levied on the buyers,with the remaining portion levied on the sellers.
D)regardless of how the tax is levied.
A)provided the tax is levied on the sellers.
B)provided the tax is levied on the buyers.
C)provided a portion of the tax is levied on the buyers,with the remaining portion levied on the sellers.
D)regardless of how the tax is levied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Figure 8-1 
Refer to Figure 8-1.Suppose the government imposes a tax of P' - P'''.Total surplus before the tax is measured by the area
A)I+Y.
B)J+K+L+M.
C)L+M+Y.
D)I+J+K+L+M+Y.

Refer to Figure 8-1.Suppose the government imposes a tax of P' - P'''.Total surplus before the tax is measured by the area
A)I+Y.
B)J+K+L+M.
C)L+M+Y.
D)I+J+K+L+M+Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If a tax shifts the demand curve downward (or to the left),we can infer that the tax was levied on
A)buyers of the good.
B)sellers of the good.
C)both buyers and sellers of the good.
D)We cannot infer anything because the shift described is not consistent with a tax.
A)buyers of the good.
B)sellers of the good.
C)both buyers and sellers of the good.
D)We cannot infer anything because the shift described is not consistent with a tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
For a good that is taxed,the area on the relevant supply-and-demand graph that represents government's tax revenue is
A)smaller than the area that represents the loss of consumer surplus and producer surplus caused by the tax.
B)bounded by the supply curve,the demand curve,the effective price paid by buyers,and the effective price received by sellers.
C)a right triangle.
D)a triangle,but not necessarily a right triangle.
A)smaller than the area that represents the loss of consumer surplus and producer surplus caused by the tax.
B)bounded by the supply curve,the demand curve,the effective price paid by buyers,and the effective price received by sellers.
C)a right triangle.
D)a triangle,but not necessarily a right triangle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The benefit to sellers of participating in a market is measured by the
A)amount of taxes collected on sales of the good.
B)producer surplus.
C)amount sellers receive for their product.
D)sellers' willingness to sell.
A)amount of taxes collected on sales of the good.
B)producer surplus.
C)amount sellers receive for their product.
D)sellers' willingness to sell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 8-3
The vertical distance between points A and C represents a tax in the market.
Refer to Figure 8-3.The per-unit burden of the tax on sellers is
A)P3 - P1.
B)P3 - P2.
C)P2 - P1.
D)P4 - P3.
The vertical distance between points A and C represents a tax in the market.

Refer to Figure 8-3.The per-unit burden of the tax on sellers is
A)P3 - P1.
B)P3 - P2.
C)P2 - P1.
D)P4 - P3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Figure 8-3
The vertical distance between points A and C represents a tax in the market.
Refer to Figure 8-3.The amount of tax revenue received by the government is equal to the area
A)P3ACP1.
B)ABC.
C)P2DAP3.
D)P1CDP2.
The vertical distance between points A and C represents a tax in the market.

Refer to Figure 8-3.The amount of tax revenue received by the government is equal to the area
A)P3ACP1.
B)ABC.
C)P2DAP3.
D)P1CDP2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following quantities decrease in response to a tax on a good?
A)the equilibrium quantity in the market for the good,the effective price of the good paid by buyers,and consumer surplus
B)the equilibrium quantity in the market for the good,producer surplus,and the well-being of buyers of the good
C)the effective price received by sellers of the good,the wedge between the effective price paid by buyers and the effective price received by sellers,and consumer surplus
D)None of the above is necessarily correct unless we know whether the tax is levied on buyers or on sellers.
A)the equilibrium quantity in the market for the good,the effective price of the good paid by buyers,and consumer surplus
B)the equilibrium quantity in the market for the good,producer surplus,and the well-being of buyers of the good
C)the effective price received by sellers of the good,the wedge between the effective price paid by buyers and the effective price received by sellers,and consumer surplus
D)None of the above is necessarily correct unless we know whether the tax is levied on buyers or on sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The decrease in total surplus that results from a market distortion,such as a tax,is called a
A)wedge loss.
B)revenue loss.
C)deadweight loss.
D)consumer surplus loss.
A)wedge loss.
B)revenue loss.
C)deadweight loss.
D)consumer surplus loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
It does not matter whether a tax is levied on the buyers or the sellers of a good because
A)sellers always bear the full burden of the tax.
B)buyers always bear the full burden of the tax.
C)buyers and sellers will share the burden of the tax.
D)None of the above is correct; the incidence of the tax does depend on whether the buyers or the sellers are required to pay the tax.
A)sellers always bear the full burden of the tax.
B)buyers always bear the full burden of the tax.
C)buyers and sellers will share the burden of the tax.
D)None of the above is correct; the incidence of the tax does depend on whether the buyers or the sellers are required to pay the tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What happens to the total surplus in a market when the government imposes a tax?
A)Total surplus increases by the amount of the tax.
B)Total surplus increases but by less than the amount of the tax.
C)Total surplus decreases.
D)Total surplus is unaffected by the tax.
A)Total surplus increases by the amount of the tax.
B)Total surplus increases but by less than the amount of the tax.
C)Total surplus decreases.
D)Total surplus is unaffected by the tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Figure 8-1 
Refer to Figure 8-1.Suppose the government imposes a tax of P' - P'''.The tax revenue is measured by the area
A)K+L.
B)I+Y.
C)J+K+L+M.
D)I+J+K+L+M+Y.

Refer to Figure 8-1.Suppose the government imposes a tax of P' - P'''.The tax revenue is measured by the area
A)K+L.
B)I+Y.
C)J+K+L+M.
D)I+J+K+L+M+Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Deadweight loss measures the loss
A)in a market to buyers and sellers that is not offset by an increase in government revenue.
B)in revenue to the government when buyers choose to buy less of the product because of the tax.
C)of equality in a market due to government intervention.
D)of total revenue to business firms due to the price wedge caused by the tax.
A)in a market to buyers and sellers that is not offset by an increase in government revenue.
B)in revenue to the government when buyers choose to buy less of the product because of the tax.
C)of equality in a market due to government intervention.
D)of total revenue to business firms due to the price wedge caused by the tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When a tax is placed on the buyers of a product,a result is that buyers effectively pay
A)less than before the tax,and sellers effectively receive less than before the tax.
B)less than before the tax,and sellers effectively receive more than before the tax.
C)more than before the tax,and sellers effectively receive less than before the tax.
D)more than before the tax,and sellers effectively receive more than before the tax.
A)less than before the tax,and sellers effectively receive less than before the tax.
B)less than before the tax,and sellers effectively receive more than before the tax.
C)more than before the tax,and sellers effectively receive less than before the tax.
D)more than before the tax,and sellers effectively receive more than before the tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The benefit that government receives from a tax is measured by
A)the change in the equilibrium quantity of the good.
B)the change in the equilibrium price of the good.
C)tax revenue.
D)total surplus.
A)the change in the equilibrium quantity of the good.
B)the change in the equilibrium price of the good.
C)tax revenue.
D)total surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
To fully understand how taxes affect economic well-being,we must
A)assume that economic well-being is not affected if all tax revenue is spent on goods and services for the people who are being taxed.
B)compare the taxes raised in the United States with those raised in other countries,especially France.
C)compare the reduced welfare of buyers and sellers to the amount of revenue the government raises.
D)take into account the fact that almost all taxes reduce the welfare of buyers,increase the welfare of sellers,and raise revenue for the government.
A)assume that economic well-being is not affected if all tax revenue is spent on goods and services for the people who are being taxed.
B)compare the taxes raised in the United States with those raised in other countries,especially France.
C)compare the reduced welfare of buyers and sellers to the amount of revenue the government raises.
D)take into account the fact that almost all taxes reduce the welfare of buyers,increase the welfare of sellers,and raise revenue for the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure 8-10 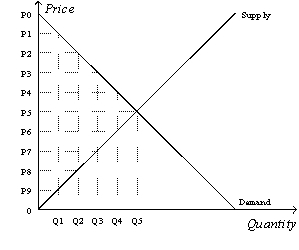
Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The size of the tax is
A)P0-P2.
B)P2-P8.
C)P2-P5.
D)P5-P8.

Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The size of the tax is
A)P0-P2.
B)P2-P8.
C)P2-P5.
D)P5-P8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The size of a tax and the deadweight loss that results from the tax are
A)positively related.
B)negatively related.
C)independent of each other.
D)equal to each other.
A)positively related.
B)negatively related.
C)independent of each other.
D)equal to each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 8-10 ![<strong>Figure 8-10 -Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.Without the tax,the total surplus is</strong> A)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ 1 / 2 x (P5-0)x Q5]. B)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ 1 / 2 x (P8-0)x Q2]. C)(P2-P8)x Q2. D) 1 / 2 x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4793/11ea7a3f_c077_178b_81a2_85956bef03a3_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00.jpg)
-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.Without the tax,the total surplus is
A)[ x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ x (P5-0)x Q5].
B)[ x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ x (P8-0)x Q2].
C)(P2-P8)x Q2.
D) x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).
![<strong>Figure 8-10 -Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.Without the tax,the total surplus is</strong> A)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ 1 / 2 x (P5-0)x Q5]. B)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ 1 / 2 x (P8-0)x Q2]. C)(P2-P8)x Q2. D) 1 / 2 x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4793/11ea7a3f_c077_178b_81a2_85956bef03a3_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00.jpg)
-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.Without the tax,the total surplus is
A)[ x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ x (P5-0)x Q5].
B)[ x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ x (P8-0)x Q2].
C)(P2-P8)x Q2.
D) x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose a tax of 5 dollars per unit is imposed on a good.The supply curve is a typical upward-sloping straight line,and the demand curve is a typical downward-sloping straight line.The tax decreases consumer surplus by 10,000 dollars and decreases producer surplus by 15,000 dollars.The deadweight loss of the tax is 2,500 pounds.The tax decreased the equilibrium quantity of the good from
A)6,500 to 5,500.
B)5,500 to 4,500.
C)5,000 to 3,000.
D)6,000 to 4,000.
A)6,500 to 5,500.
B)5,500 to 4,500.
C)5,000 to 3,000.
D)6,000 to 4,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 8-10 ![<strong>Figure 8-10 -Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The deadweight loss of the tax is</strong> A)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ 1 / 2 x (P5-0)x Q5]. B)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ 1 / 2 x (P8-0)x Q2]. C)(P2-P8)x Q2. D) 1 / 2 x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4793/11ea7a3f_c077_178b_81a2_85956bef03a3_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00.jpg)
-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The deadweight loss of the tax is
A)[ x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ x (P5-0)x Q5].
B)[ x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ x (P8-0)x Q2].
C)(P2-P8)x Q2.
D) x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).
![<strong>Figure 8-10 -Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The deadweight loss of the tax is</strong> A)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ 1 / 2 x (P5-0)x Q5]. B)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ 1 / 2 x (P8-0)x Q2]. C)(P2-P8)x Q2. D) 1 / 2 x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4793/11ea7a3f_c077_178b_81a2_85956bef03a3_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00.jpg)
-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The deadweight loss of the tax is
A)[ x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ x (P5-0)x Q5].
B)[ x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ x (P8-0)x Q2].
C)(P2-P8)x Q2.
D) x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The price elasticities of supply and demand affect
A)both the size of the deadweight loss from a tax and the tax incidence.
B)the size of the deadweight loss from a tax but not the tax incidence.
C)the tax incidence but not the size of the deadweight loss from a tax.
D)neither the size of the deadweight loss from a tax nor the tax incidence.
A)both the size of the deadweight loss from a tax and the tax incidence.
B)the size of the deadweight loss from a tax but not the tax incidence.
C)the tax incidence but not the size of the deadweight loss from a tax.
D)neither the size of the deadweight loss from a tax nor the tax incidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The deadweight loss from a 3 pound tax will be largest in a market with
A)inelastic supply and elastic demand.
B)inelastic supply and inelastic demand.
C)elastic supply and elastic demand.
D)elastic supply and inelastic demand.
A)inelastic supply and elastic demand.
B)inelastic supply and inelastic demand.
C)elastic supply and elastic demand.
D)elastic supply and inelastic demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When a tax is imposed on a good for which the supply is relatively elastic and the demand is relatively inelastic,
A)buyers of the good will bear most of the burden of the tax.
B)sellers of the good will bear most of the burden of the tax.
C)buyers and sellers will each bear 50 percent of the burden of the tax.
D)both equilibrium price and quantity will increase.
A)buyers of the good will bear most of the burden of the tax.
B)sellers of the good will bear most of the burden of the tax.
C)buyers and sellers will each bear 50 percent of the burden of the tax.
D)both equilibrium price and quantity will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 8-10 
-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.With the tax,the consumer surplus is
A)(P0-P2)x Q2.
B) x (P0-P2)x Q2.
C)(P0-P5)x Q5.
D) x (P0-P5)x Q5.

-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.With the tax,the consumer surplus is
A)(P0-P2)x Q2.
B) x (P0-P2)x Q2.
C)(P0-P5)x Q5.
D) x (P0-P5)x Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure 8-10 
Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The tax revenue is
A)(P0-P2)x Q2.
B)(P2-P8)x Q2.
C)(P2-P5)x Q5.
D)(P5-P8)x Q5.

Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The tax revenue is
A)(P0-P2)x Q2.
B)(P2-P8)x Q2.
C)(P2-P5)x Q5.
D)(P5-P8)x Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Figure 8-10 
Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The price that sellers receive is
A)P0.
B)P2.
C)P5.
D)P8.

Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The price that sellers receive is
A)P0.
B)P2.
C)P5.
D)P8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the imposition of a tax on gasoline?
A)The incidence of the tax depends upon whether the buyers or the sellers are required to remit tax payments to the government.
B)The incidence of the tax depends upon the price elasticities of demand and supply.
C)The amount of tax revenue raised by the tax depends upon whether the buyers or the sellers are required to remit tax payments to the government.
D)The amount of tax revenue raised by the tax does not depend upon the amount of the tax per unit.
A)The incidence of the tax depends upon whether the buyers or the sellers are required to remit tax payments to the government.
B)The incidence of the tax depends upon the price elasticities of demand and supply.
C)The amount of tax revenue raised by the tax depends upon whether the buyers or the sellers are required to remit tax payments to the government.
D)The amount of tax revenue raised by the tax does not depend upon the amount of the tax per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Labor taxes may distort labor markets greatly if
A)labor supply is highly inelastic.
B)many workers choose to work 40 hours per week regardless of their earnings.
C)the number of hours many part-time workers want to work is very sensitive to the wage rate.
D)"underground" workers do not respond to changes in the wages of legal jobs because they prefer not to pay taxes.
A)labor supply is highly inelastic.
B)many workers choose to work 40 hours per week regardless of their earnings.
C)the number of hours many part-time workers want to work is very sensitive to the wage rate.
D)"underground" workers do not respond to changes in the wages of legal jobs because they prefer not to pay taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Figure 8-10 
-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.With the tax,the producer surplus is
A)(P5-0)x Q5.
B) x (P5-0)x Q5.
C)(P8-0)x Q2.
D) x (P8-0)x Q2.

-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.With the tax,the producer surplus is
A)(P5-0)x Q5.
B) x (P5-0)x Q5.
C)(P8-0)x Q2.
D) x (P8-0)x Q2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Figure 8-10 
-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.Without the tax,the producer surplus is
A)(P5-0)x Q5.
B) x (P5-0)x Q5.
C)(P8-0)x Q2.
D) x (P8-0)x Q2.

-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.Without the tax,the producer surplus is
A)(P5-0)x Q5.
B) x (P5-0)x Q5.
C)(P8-0)x Q2.
D) x (P8-0)x Q2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The demand for potted plants is more elastic than the demand for wallpaper.Suppose the government levies an equivalent tax on potted plants and wallpaper.The deadweight loss would be larger in the market for
A)potted plants than in the market for wallpaper because the quantity of potted plants would fall by more than the quantity of wallpaper.
B)potted plants than in the market for wallpaper because the quantity of wallpaper would fall by more than the quantity of potted plants.
C)wallpaper than in the market for potted plants because the quantity of potted plants would fall by more than the quantity of wallpaper.
D)wallpaper than in the market for potted plants because the quantity of wallpaper would fall by more than the quantity of potted plants.
A)potted plants than in the market for wallpaper because the quantity of potted plants would fall by more than the quantity of wallpaper.
B)potted plants than in the market for wallpaper because the quantity of wallpaper would fall by more than the quantity of potted plants.
C)wallpaper than in the market for potted plants because the quantity of potted plants would fall by more than the quantity of wallpaper.
D)wallpaper than in the market for potted plants because the quantity of wallpaper would fall by more than the quantity of potted plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 8-10 ![<strong>Figure 8-10 -Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.With the tax,the total surplus is</strong> A)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ 1 / 2 x (P5-0)x Q5]. B)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ 1 / 2 x (P8-0)x Q2]. C)(P2-P8)x Q2. D) 1 / 2 x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4793/11ea7a3f_c077_178b_81a2_85956bef03a3_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00.jpg)
-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.With the tax,the total surplus is
A)[ x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ x (P5-0)x Q5].
B)[ x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ x (P8-0)x Q2].
C)(P2-P8)x Q2.
D) x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).
![<strong>Figure 8-10 -Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.With the tax,the total surplus is</strong> A)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ 1 / 2 x (P5-0)x Q5]. B)[ 1 / 2 x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ 1 / 2 x (P8-0)x Q2]. C)(P2-P8)x Q2. D) 1 / 2 x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4793/11ea7a3f_c077_178b_81a2_85956bef03a3_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00.jpg)
-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.With the tax,the total surplus is
A)[ x (P0-P5)x Q5] + [ x (P5-0)x Q5].
B)[ x (P0-P2)x Q2] +[(P2-P8)x Q2] + [ x (P8-0)x Q2].
C)(P2-P8)x Q2.
D) x (P2-P8)x (Q5-Q2).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Figure 8-3
The vertical distance between points A and C represents a tax in the market.
Refer to Figure 8-3.The amount of deadweight loss associated with the tax is equal to
A)P3ACP1.
B)ABC.
C)P2ADP3.
D)P1DCP2.
The vertical distance between points A and C represents a tax in the market.

Refer to Figure 8-3.The amount of deadweight loss associated with the tax is equal to
A)P3ACP1.
B)ABC.
C)P2ADP3.
D)P1DCP2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Figure 8-10 
-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.Without the tax,the consumer surplus is
A)(P0-P2)x Q2.
B) x (P0-P2)x Q2.
C)(P0-P5)x Q5.
D) x (P0-P5)x Q5.

-Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.Without the tax,the consumer surplus is
A)(P0-P2)x Q2.
B) x (P0-P2)x Q2.
C)(P0-P5)x Q5.
D) x (P0-P5)x Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Figure 8-10 
Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The price that buyers pay is
A)P0.
B)P2.
C)P5.
D)P8.

Refer to Figure 8-10.Suppose the government imposes a tax that reduces the quantity sold in the market after the tax to Q2.The price that buyers pay is
A)P0.
B)P2.
C)P5.
D)P8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Taxes on labor encourage which of the following?
A)labor demand to be more inelastic
B)mothers to stay at home rather than work in the labor force
C)workers to work overtime
D)fathers to take on second jobs
A)labor demand to be more inelastic
B)mothers to stay at home rather than work in the labor force
C)workers to work overtime
D)fathers to take on second jobs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Total surplus in a market does not change when the government imposes a tax on that market because the loss of consumer surplus and producer surplus is equal to the gain of government revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following ideas is the most plausible?
A)Tax revenue is more likely to increase when a low tax rate is increased than when a high tax rate is increased.
B)Tax revenue is less likely to increase when a low tax rate is increased than when a high tax rate is increased.
C)Tax revenue is likely to increase by the same amount when a low tax rate is increased and when a high tax rate is increased.
D)Decreasing a tax rate can never increase tax revenue.
A)Tax revenue is more likely to increase when a low tax rate is increased than when a high tax rate is increased.
B)Tax revenue is less likely to increase when a low tax rate is increased than when a high tax rate is increased.
C)Tax revenue is likely to increase by the same amount when a low tax rate is increased and when a high tax rate is increased.
D)Decreasing a tax rate can never increase tax revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)A decrease in the size of a tax always decreases the tax revenue raised by that tax.
B)A decrease in the size of a tax always decreases the deadweight loss of that tax.
C)Tax revenue decreases when there is a small decrease in the tax rate and the economy is on the downward-sloping part of the Laffer curve.
D)An increase in the size of a tax leads to an increase in the deadweight loss of the tax only if the economy is on the upward-sloping part of the Laffer curve.
A)A decrease in the size of a tax always decreases the tax revenue raised by that tax.
B)A decrease in the size of a tax always decreases the deadweight loss of that tax.
C)Tax revenue decreases when there is a small decrease in the tax rate and the economy is on the downward-sloping part of the Laffer curve.
D)An increase in the size of a tax leads to an increase in the deadweight loss of the tax only if the economy is on the upward-sloping part of the Laffer curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The Laffer curve illustrates that
A)deadweight loss rises by the square of the increase in a tax.
B)deadweight loss rises exponentially as a tax increases.
C)tax revenue first rises,then falls as a tax increases.
D)Both a)and b)are correct.
A)deadweight loss rises by the square of the increase in a tax.
B)deadweight loss rises exponentially as a tax increases.
C)tax revenue first rises,then falls as a tax increases.
D)Both a)and b)are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A tax raises the price received by sellers and lowers the price paid by buyers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
As the price elasticities of supply and demand increase,the deadweight loss from a tax increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The view held by Arthur Laffer and Ronald Reagan that cuts in tax rates would encourage people to increase the quantity of labor they supplied became known as
A)California economics.
B)welfare economics.
C)supply-side economics.
D)elasticity economics.
A)California economics.
B)welfare economics.
C)supply-side economics.
D)elasticity economics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Taxes cause deadweight losses because they prevent buyers and sellers from realizing some of the gains from trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the tax on a good is doubled,the deadweight loss of the tax
A)increases by 50 percent.
B)doubles.
C)triples.
D)quadruples.
A)increases by 50 percent.
B)doubles.
C)triples.
D)quadruples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A tax places a wedge between the price buyers pay and the price sellers receive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When a tax is imposed,the loss of consumer surplus and producer surplus as a result of the tax exceeds the tax revenue collected by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Total surplus is always equal to the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When a tax is imposed on sellers,consumer surplus and producer surplus both decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A decrease in the size of a tax is most likely to increase tax revenue in a market with
A)elastic demand and elastic supply.
B)elastic demand and inelastic supply.
C)inelastic demand and elastic supply.
D)inelastic demand and inelastic supply.
A)elastic demand and elastic supply.
B)elastic demand and inelastic supply.
C)inelastic demand and elastic supply.
D)inelastic demand and inelastic supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When a tax is imposed on a good,consumer surplus decreases and producer surplus remains unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Assume that for good X the supply curve for a good is a typical,upward-sloping straight line,and the demand curve is a typical downward-sloping straight line.If the good is taxed,and the tax is doubled,the
A)base of the triangle that represents the deadweight loss quadruples.
B)height of the triangle that represents the deadweight loss doubles.
C)deadweight loss of the tax doubles.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)base of the triangle that represents the deadweight loss quadruples.
B)height of the triangle that represents the deadweight loss doubles.
C)deadweight loss of the tax doubles.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Taxes are costly to market participants because they
A)transfer resources from market participants to the government.
B)alter incentives.
C)distort market outcomes.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)transfer resources from market participants to the government.
B)alter incentives.
C)distort market outcomes.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The higher a country's tax rates,the more likely that country will be
A)at the top of the Laffer curve.
B)on the positively sloped part of the Laffer curve.
C)on the negatively sloped part of the Laffer curve.
D)experiencing small deadweight losses.
A)at the top of the Laffer curve.
B)on the positively sloped part of the Laffer curve.
C)on the negatively sloped part of the Laffer curve.
D)experiencing small deadweight losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When a tax is imposed on buyers,consumer surplus and producer surplus both decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The more elastic the supply,the larger the deadweight loss from a tax,all else equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following graph shown to fill in the table that follows. 
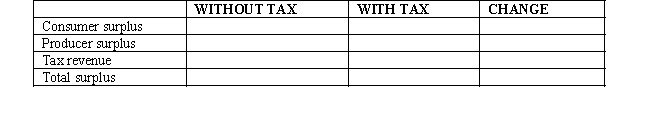



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Illustrate on three demand-and-supply graphs how the size of a tax (small,medium and large)can alter total revenue and deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If a tax did not induce buyers or sellers to change their behavior,it would not cause a deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Economists disagree on whether labor taxes have a small or large deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Using demand and supply diagrams,show the difference in deadweight loss between (a)a market with inelastic demand and supply and (b)a market with elastic demand and supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
John has been in the habit of mowing Carl's lawn each week for 20 dinar.John's opportunity cost is 15 dinar,and Carl would be willing to pay 25 dinar to have his lawn mowed.What is the maximum tax the government can impose on lawn mowing without discouraging John and Carl from continuing their mutually beneficial arrangement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Taxes on labor tend to increase the number of hours that people choose to work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The Laffer curve is the curve showing how tax revenue varies as the size of the tax varies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



