Deck 19: Introduction to Decision Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Introduction to Decision Analysis
1
For each decision alternative there is only one payoff possible.
False
2
Payoff refers to the net profit or loss resulting from a combination of alternative and state of nature.
True
3
Probabilistic decision criteria are used when the probabilities associated with the possible payoffs are unknown.
False
4
The complexity of a decision is affected by the number of alternatives,the number of possible outcomes,and the general level of uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Decision analysis is essential for all business decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Under certainty the outcome of each alternative is known before the decision made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Payoff and state of nature are two different terms for the same thing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The two primary decision environments are certainty and uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Good decisions always result in good outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The more complex the decision the less useful decision analysis is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The goal of decision analysis is to focus on obtaining good outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
There are two main categories of decision criteria; nonprobabilistic and probabilistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The maximax criterion is a nonprobabilistic decision criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Uncertainty in the decision environment is defined to mean the decision maker is uncertain which alternative to choose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When the outcome of a decision is bad this does not necessarily mean that the decision was bad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Most business decisions are made in an environment of certainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A payoff table shows the payoff for each combination of alternative and state of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The possible outcomes of a decision,over which the decision maker has no control,are referred to as states of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In order to choose among two or more alternatives it is important to establish the decision criteria that will be used to evaluate each alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Decision analysis refers to a set of tools that can be helpful in analyzing business decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 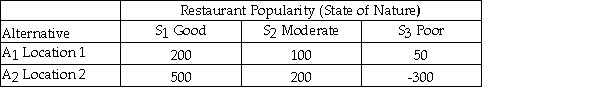 Using the maximax criterion she should choose location 2.
Using the maximax criterion she should choose location 2.
 Using the maximax criterion she should choose location 2.
Using the maximax criterion she should choose location 2.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The minimax regret criterion can be thought of as; the decision maker is trying to minimize how much he/she might regret the decision that was made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When using the minimax regret criterion,after finding the opportunity loss table,the next step is to choose the minimum regret for each alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 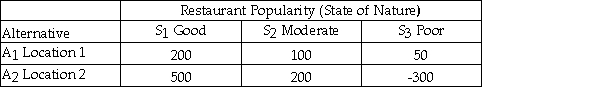 Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity.
Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity. 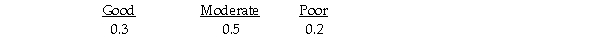 The expected value of Location 1 is 120.
The expected value of Location 1 is 120.
 Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity.
Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity. 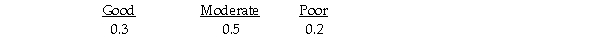 The expected value of Location 1 is 120.
The expected value of Location 1 is 120.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Expected value refers to the average outcome (payoff)that the decision maker would expect to receive over the long run if the decision is repeated many times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 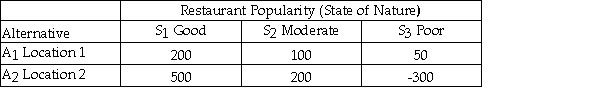 The opportunity loss for Location 1 and Good restaurant popularity is 150.
The opportunity loss for Location 1 and Good restaurant popularity is 150.
 The opportunity loss for Location 1 and Good restaurant popularity is 150.
The opportunity loss for Location 1 and Good restaurant popularity is 150.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 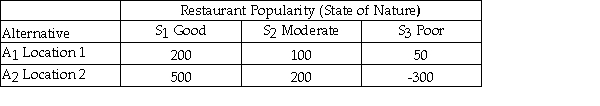 Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity.
Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity. 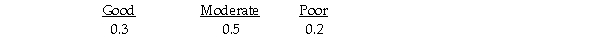 The expected value of Location 2 is 310.
The expected value of Location 2 is 310.
 Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity.
Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity. 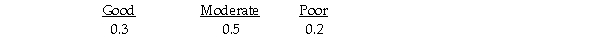 The expected value of Location 2 is 310.
The expected value of Location 2 is 310.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Opportunity loss values are used by the maximax criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The maximax criterion,maximin criterion,minimax regret criterion,and expected value criterion are all nonprobabilistic decision criteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Opportunity loss is the difference between the actual payoff that occurs for a decision and the optimal payoff for a given state of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The maximin criterion is an optimistic decision criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the decision to be made is a one-time decision,the expected value method can be misleading because it represents the average outcome from repeating the decision many times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The expected value criterion is a probabilistic decision criterion because it involves probability values for each possible outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 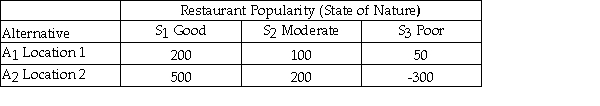 The opportunity loss for Location 2 and Poor restaurant popularity is 350.
The opportunity loss for Location 2 and Poor restaurant popularity is 350.
 The opportunity loss for Location 2 and Poor restaurant popularity is 350.
The opportunity loss for Location 2 and Poor restaurant popularity is 350.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The first step in the minimax regret criterion is to construct the opportunity loss table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The term expected value refers to the exact value that the decision maker can expect to receive when a given alternative is chosen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Regret is another term for opportunity loss because it refers to how much a decision maker would regret having made a particular decision after the state of nature is known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Making decisions under certainty means that the state of nature is known prior to choosing an alternative so the optimal decision can be chosen which will produce the best outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 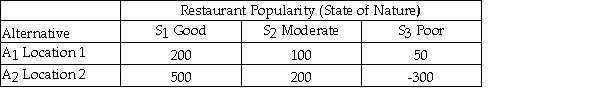 Using the maximin criterion she should choose location 2.
Using the maximin criterion she should choose location 2.
 Using the maximin criterion she should choose location 2.
Using the maximin criterion she should choose location 2.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 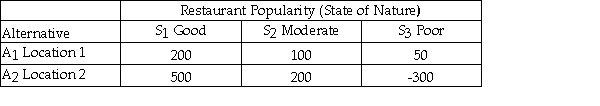 Using the minimax regret criterion,she should choose location 1.
Using the minimax regret criterion,she should choose location 1.
 Using the minimax regret criterion,she should choose location 1.
Using the minimax regret criterion,she should choose location 1.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A bakery makes fresh donuts every morning.If any are left at the end of the day they are donated to a homeless shelter.The number of donuts that can be sold each day is uncertain and the bakery must decide early each morning,how many donuts to make that day.The bakery has created the following payoff table to summarize the situation. 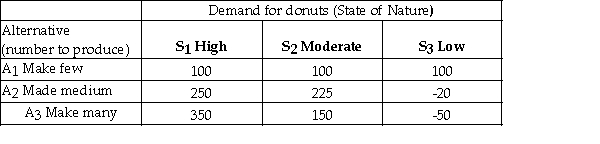 The opportunity loss for making a medium number of donuts (A2)and demand being high (S1)is 100.
The opportunity loss for making a medium number of donuts (A2)and demand being high (S1)is 100.
 The opportunity loss for making a medium number of donuts (A2)and demand being high (S1)is 100.
The opportunity loss for making a medium number of donuts (A2)and demand being high (S1)is 100.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A bakery makes fresh donuts every morning.If any are left at the end of the day they are donated to a homeless shelter.The number of donuts that can be sold each day is uncertain and the bakery must decide early each morning,how many donuts to make that day.The bakery has created the following payoff table to summarize the situation. 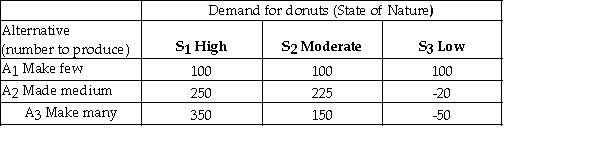 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 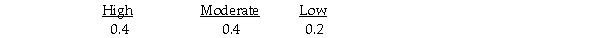 If the bakery had perfect information about that day's demand,the expected value of perfect information is 60.
If the bakery had perfect information about that day's demand,the expected value of perfect information is 60.
 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 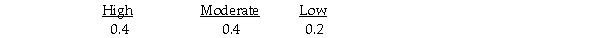 If the bakery had perfect information about that day's demand,the expected value of perfect information is 60.
If the bakery had perfect information about that day's demand,the expected value of perfect information is 60.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A bakery makes fresh donuts every morning.If any are left at the end of the day they are donated to a homeless shelter.The number of donuts that can be sold each day is uncertain and the bakery must decide early each morning,how many donuts to make that day.The bakery has created the following payoff table to summarize the situation. 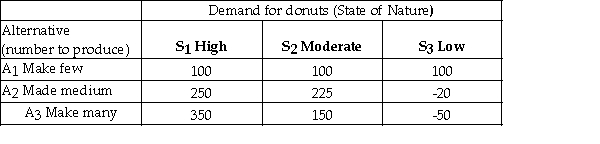 The opportunity loss for making a medium number of donuts (A2)and demand being low (S3)is 120.
The opportunity loss for making a medium number of donuts (A2)and demand being low (S3)is 120.
 The opportunity loss for making a medium number of donuts (A2)and demand being low (S3)is 120.
The opportunity loss for making a medium number of donuts (A2)and demand being low (S3)is 120.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A payoff table and a decision tree both show the alternatives,states of nature,and payoffs,but the decision tree also shows the order of events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 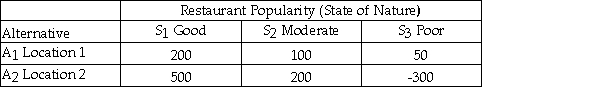 The opportunity loss for Location 2 and Poor restaurant popularity is 800.
The opportunity loss for Location 2 and Poor restaurant popularity is 800.
 The opportunity loss for Location 2 and Poor restaurant popularity is 800.
The opportunity loss for Location 2 and Poor restaurant popularity is 800.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The "expected cost of uncertainty" and the "expected value of perfect information" are the same thing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 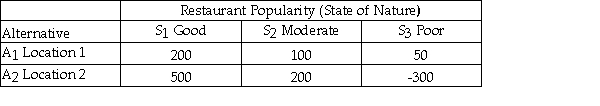 Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity.
Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity. 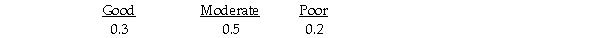 The expected payoff or value under uncertainty is 190.
The expected payoff or value under uncertainty is 190.
 Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity.
Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity. 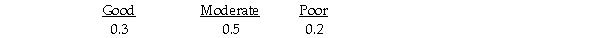 The expected payoff or value under uncertainty is 190.
The expected payoff or value under uncertainty is 190.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A bakery makes fresh donuts every morning.If any are left at the end of the day they are donated to a homeless shelter.The number of donuts that can be sold each day is uncertain and the bakery must decide early each morning,how many donuts to make that day.The bakery has created the following payoff table to summarize the situation. 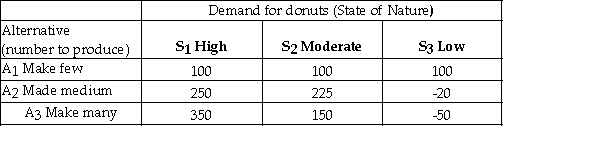 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 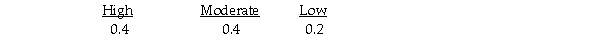 If on a given day the bakery knew in advance that demand was going to be high,then the payoff that day would be 350.
If on a given day the bakery knew in advance that demand was going to be high,then the payoff that day would be 350.
 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 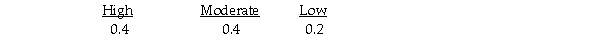 If on a given day the bakery knew in advance that demand was going to be high,then the payoff that day would be 350.
If on a given day the bakery knew in advance that demand was going to be high,then the payoff that day would be 350.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 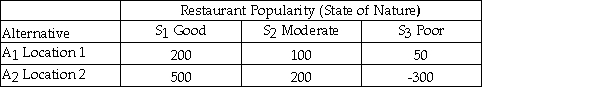 The opportunity loss for Location 1 and Poor restaurant popularity is 150.
The opportunity loss for Location 1 and Poor restaurant popularity is 150.
 The opportunity loss for Location 1 and Poor restaurant popularity is 150.
The opportunity loss for Location 1 and Poor restaurant popularity is 150.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A bakery makes fresh donuts every morning.If any are left at the end of the day they are donated to a homeless shelter.The number of donuts that can be sold each day is uncertain and the bakery must decide early each morning,how many donuts to make that day.The bakery has created the following payoff table to summarize the situation. 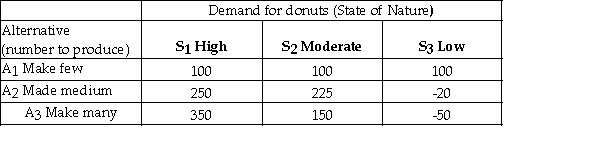 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 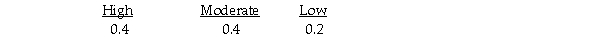 The expected value of A3 (making many donuts)is 210.
The expected value of A3 (making many donuts)is 210.
 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 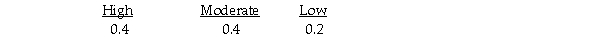 The expected value of A3 (making many donuts)is 210.
The expected value of A3 (making many donuts)is 210.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A bakery makes fresh donuts every morning.If any are left at the end of the day they are donated to a homeless shelter.The number of donuts that can be sold each day is uncertain and the bakery must decide early each morning,how many donuts to make that day.The bakery has created the following payoff table to summarize the situation. 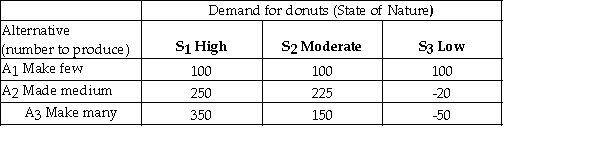 The opportunity loss for making many donuts (A3)and demand being Moderate (S2)is 200.
The opportunity loss for making many donuts (A3)and demand being Moderate (S2)is 200.
 The opportunity loss for making many donuts (A3)and demand being Moderate (S2)is 200.
The opportunity loss for making many donuts (A3)and demand being Moderate (S2)is 200.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 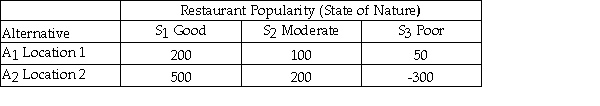 Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity.
Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity. 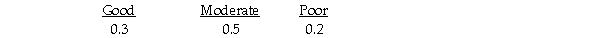 If Julie had perfect information,the expected payoff under certainty is 310.
If Julie had perfect information,the expected payoff under certainty is 310.
 Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity.
Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity. 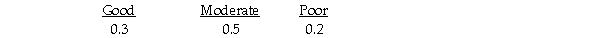 If Julie had perfect information,the expected payoff under certainty is 310.
If Julie had perfect information,the expected payoff under certainty is 310.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Assume that a decision maker is facing a decision under uncertainty and has calculated the expected value of perfect information is 75.If the decision maker could obtain perfect information at a cost of 85,then he/she should purchase the perfect information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A bakery makes fresh donuts every morning.If any are left at the end of the day they are donated to a homeless shelter.The number of donuts that can be sold each day is uncertain and the bakery must decide early each morning,how many donuts to make that day.The bakery has created the following payoff table to summarize the situation. 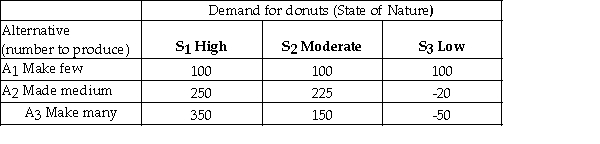 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 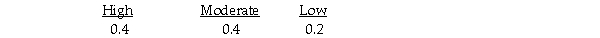 The expected value of A2 (making a medium number of donuts)is 186.
The expected value of A2 (making a medium number of donuts)is 186.
 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 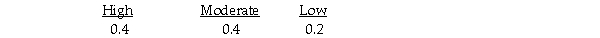 The expected value of A2 (making a medium number of donuts)is 186.
The expected value of A2 (making a medium number of donuts)is 186.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The expected value or payoff is lower in an uncertain environment than in a certain environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The expected value of perfect information (EVPI)is the minimum amount a manager would expect to pay to obtain perfect information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A bakery makes fresh donuts every morning.If any are left at the end of the day they are donated to a homeless shelter.The number of donuts that can be sold each day is uncertain and the bakery must decide early each morning,how many donuts to make that day.The bakery has created the following payoff table to summarize the situation. 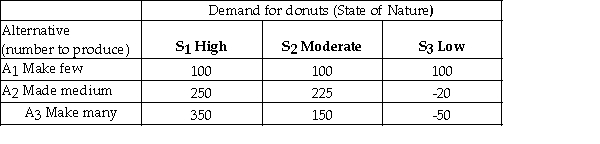 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 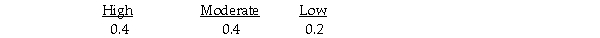 If the bakery had perfect information about that day's demand,the expected value under certainty is 275.
If the bakery had perfect information about that day's demand,the expected value under certainty is 275.
 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 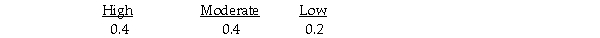 If the bakery had perfect information about that day's demand,the expected value under certainty is 275.
If the bakery had perfect information about that day's demand,the expected value under certainty is 275.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The expected value under certainty is equal to the difference between the expected value under uncertainty and the expected cost of uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A bakery makes fresh donuts every morning.If any are left at the end of the day they are donated to a homeless shelter.The number of donuts that can be sold each day is uncertain and the bakery must decide early each morning,how many donuts to make that day.The bakery has created the following payoff table to summarize the situation. 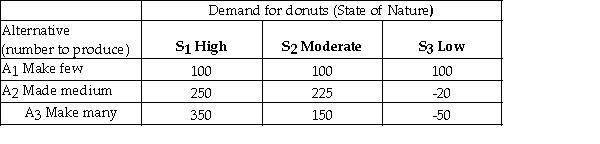 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 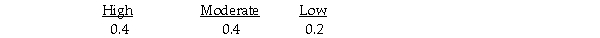 The overall expected value or payoff of making this decision under uncertainty is 190.
The overall expected value or payoff of making this decision under uncertainty is 190.
 It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand.
It estimates the following probabilities for the respective levels of demand. 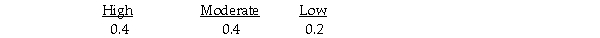 The overall expected value or payoff of making this decision under uncertainty is 190.
The overall expected value or payoff of making this decision under uncertainty is 190.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Julie is planning to open a restaurant and is considering two possible locations.She has estimated the payoff for each location for each of three different possible levels of restaurant popularity (state of nature)as shown below. 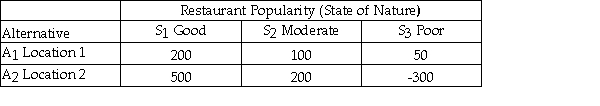 Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity.
Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity. 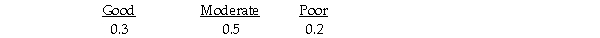 The expected value of perfect information is 70.
The expected value of perfect information is 70.
 Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity.
Suppose that Julie estimates the following probabilities for each level of restaurant popularity. 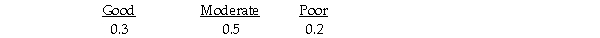 The expected value of perfect information is 70.
The expected value of perfect information is 70.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In folding back a decision tree,one works from left to right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When is decision analysis most useful?
A)For decisions that are not complex
B)For decisions that are complex
C)For decision that affect only one functional area of an organization
D)For decisions that are made in an environment of certainty
A)For decisions that are not complex
B)For decisions that are complex
C)For decision that affect only one functional area of an organization
D)For decisions that are made in an environment of certainty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In conducting sensitivity analysis in a decision tree,the probability that is solved for is the value that would make one alternative much more preferable than the other alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Decision trees are helpful in visually structuring the problem and seeing all the possible sequences of events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A decision tree is shown below where the expected value of alternative 1 is known to be 400. 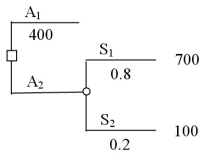 After folding back the decision tree,you conclude that you should choose alternative 1 over alternative 2.
After folding back the decision tree,you conclude that you should choose alternative 1 over alternative 2.
 After folding back the decision tree,you conclude that you should choose alternative 1 over alternative 2.
After folding back the decision tree,you conclude that you should choose alternative 1 over alternative 2.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In conducting sensitivity analysis for a probability in a decision tree,where there are only two alternatives,you solve to find the probability where the expected values of the two alternatives are equal to one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Assume that you need to choose between two alternatives and know that the expected value for A1 is 400,as shown in the decision tree below. 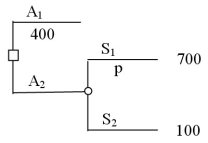 You want to determine how sensitive the choice between the two alternatives is to the probability of S1 occurring.In conducting sensitivity analysis on the probability of S1,the probability value that you would find is p = 0.5.
You want to determine how sensitive the choice between the two alternatives is to the probability of S1 occurring.In conducting sensitivity analysis on the probability of S1,the probability value that you would find is p = 0.5.
 You want to determine how sensitive the choice between the two alternatives is to the probability of S1 occurring.In conducting sensitivity analysis on the probability of S1,the probability value that you would find is p = 0.5.
You want to determine how sensitive the choice between the two alternatives is to the probability of S1 occurring.In conducting sensitivity analysis on the probability of S1,the probability value that you would find is p = 0.5.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Assume that you have a riding lawn mower that is in need of repairs.You can choose to repair or replace it.You are interested in your net cost over the next two years.If you choose to repair,it will cost $300 and there is a 50/50 chance of whether or not it will need additional repairs within the next two years.If it does need additional repairs,there is a 40 percent chance of needing another $400 of repairs,and a 60 percent chance of needing another $200 of repairs.At the end of the two years you estimate that the repaired mower would be worthless.
If you choose to replace the mower by trading in the old mower,the cost after deducting the trade in value is $1500.At the end of the two years you estimate there is a 75 percent chance you could resell it for $1000,and a 25 percent chance that you can resell it for $1300.
After constructing the decision tree and folding it back you should choose to repair the mower because the expected value is a cost of $140.
If you choose to replace the mower by trading in the old mower,the cost after deducting the trade in value is $1500.At the end of the two years you estimate there is a 75 percent chance you could resell it for $1000,and a 25 percent chance that you can resell it for $1300.
After constructing the decision tree and folding it back you should choose to repair the mower because the expected value is a cost of $140.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Assume that you have a riding lawn mower that is in need of repairs.You can choose to repair or replace it.You are interested in your net cost over the next two years.If you choose to repair,it will cost $300 and there is a 50/50 chance of whether or not it will need additional repairs within the next two years.If it does need additional repairs,there is a 40 percent chance of needing another $400 of repairs,and a 60 percent chance of needing another $200 of repairs.At the end of the two years you estimate that the repaired mower would be worthless.
If you choose to replace the mower by trading in the old mower,the cost after deducting the trade in value is $1500.At the end of the two years you estimate there is a 75 percent chance you could resell it for $1000,and a 25 percent chance that you can resell it for $1300.
After drawing the tree and folding back,the expected value of replacing the mower (by trading in)is a cost of $425.
If you choose to replace the mower by trading in the old mower,the cost after deducting the trade in value is $1500.At the end of the two years you estimate there is a 75 percent chance you could resell it for $1000,and a 25 percent chance that you can resell it for $1300.
After drawing the tree and folding back,the expected value of replacing the mower (by trading in)is a cost of $425.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In using a decision tree,future decisions have no influence on the current decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A decision tree can show only one decision and outcome combination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is true regarding decision making environments?
A)Most business decisions are made in an environment of uncertainty.
B)Most business decisions are made in an environment of certainty.
C)Certainty means that probabilities of each possible outcome are known.
D)Uncertainty means that probabilities of each possible outcome are known.
A)Most business decisions are made in an environment of uncertainty.
B)Most business decisions are made in an environment of certainty.
C)Certainty means that probabilities of each possible outcome are known.
D)Uncertainty means that probabilities of each possible outcome are known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The goal of decision analysis is to:
A)always get the best possible outcome.
B)make good decisions that guarantee the best outcome.
C)use probabilistic criteria.
D)make good decisions that in the long run increase the number of good outcomes.
A)always get the best possible outcome.
B)make good decisions that guarantee the best outcome.
C)use probabilistic criteria.
D)make good decisions that in the long run increase the number of good outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is not a factor affecting the complexity of a decision?
A)The number of alternatives
B)The number of possible outcomes
C)The values of the various payoffs
D)The general level of uncertainty
A)The number of alternatives
B)The number of possible outcomes
C)The values of the various payoffs
D)The general level of uncertainty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
To "fold back" the decision tree means to show the events and outcomes in the reverse order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In a decision tree,the decision maker can choose the desired branch at all branch points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In a decision tree the sum of all probabilities in the tree must be equal to 1.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Sensitivity analysis for a decision tree involves analyzing how sensitive decisions are to the probability values used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
At each branch point in a decision tree,where the decision maker does not have control,the probabilities must sum to 1.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Assume that you have a riding lawn mower that is in need of repairs.You can choose to repair or replace it.You are interested in your net cost over the next two years.If you choose to repair,it will cost $300 and there is a 50/50 chance of whether or not it will need additional repairs within the next two years.If it does need additional repairs,there is a 40 percent chance of needing another $400 of repairs,and a 60 percent chance of needing another $200 of repairs.At the end of the two years you estimate that the repaired mower would be worthless.
If you choose to replace the mower by trading in the old mower,the cost after deducting the trade in value is $1500.At the end of the two years you estimate there is a 75 percent chance you could resell it for $1000,and a 25 percent chance that you can resell it for $1300.
After drawing out the decision tree from situation above,there will be a total of three branching points including the initial decision.
If you choose to replace the mower by trading in the old mower,the cost after deducting the trade in value is $1500.At the end of the two years you estimate there is a 75 percent chance you could resell it for $1000,and a 25 percent chance that you can resell it for $1300.
After drawing out the decision tree from situation above,there will be a total of three branching points including the initial decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



