Deck 4: The Energy of Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/78
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: The Energy of Life
1
Coupled reactions are reactions in which a
A) exergonic reaction drives an endergonic reaction.
B) exergonic reaction drives a spontaneous reaction.
C) endergonic reaction drives an exergonic reaction.
D) endergonic reaction drives a spontaneous reaction.
A) exergonic reaction drives an endergonic reaction.
B) exergonic reaction drives a spontaneous reaction.
C) endergonic reaction drives an exergonic reaction.
D) endergonic reaction drives a spontaneous reaction.
A
2
Entropy is a measure of
A) complexity.
B) disorder.
C) order.
D) kinetic energy.
E) potential energy.
A) complexity.
B) disorder.
C) order.
D) kinetic energy.
E) potential energy.
B
3
An enzyme is
A) always a protein.
B) an organic molecule that catalyzes a cellular reaction.
C) not necessary to sustain life in a cell.
D) used up in a reaction.
E) All of the answer choices are correct.
A) always a protein.
B) an organic molecule that catalyzes a cellular reaction.
C) not necessary to sustain life in a cell.
D) used up in a reaction.
E) All of the answer choices are correct.
B
4
An endergonic reaction is a reaction that is characterized by
A) yielding larger product molecules than the original reactants.
B) yielding smaller product molecules than the original reactants.
C) having products with lower energy than the reactants.
D) having products with higher energy than the reactants.
E) often having higher energy in product molecules than the reactants, and yielding larger product molecules.
A) yielding larger product molecules than the original reactants.
B) yielding smaller product molecules than the original reactants.
C) having products with lower energy than the reactants.
D) having products with higher energy than the reactants.
E) often having higher energy in product molecules than the reactants, and yielding larger product molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Oxidation means
A) the loss of electrons from a molecule.
B) the loss of oxygen by a cell.
C) the gain of electrons by a molecule.
D) the gain of oxygen by a cell.
A) the loss of electrons from a molecule.
B) the loss of oxygen by a cell.
C) the gain of electrons by a molecule.
D) the gain of oxygen by a cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
At chemical equilibrium
A) there are no more products being formed.
B) the amount of reactants is equal to the amount of products.
C) reaction rates are in balance.
D) there are no more reactants for the cell to utilize.
E) no reactions are occurring in either direction.
A) there are no more products being formed.
B) the amount of reactants is equal to the amount of products.
C) reaction rates are in balance.
D) there are no more reactants for the cell to utilize.
E) no reactions are occurring in either direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of water by 1° Celsius is a
A) joule.
B) kilocalorie.
C) calorie.
D) measure of density.
E) None of the answer choices are correct.
A) joule.
B) kilocalorie.
C) calorie.
D) measure of density.
E) None of the answer choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Reduction means
A) the loss of electrons by a molecule.
B) the gain of electrons by a molecule.
C) the loss of oxygen from a cell.
D) the gain of oxygen by a cell.
A) the loss of electrons by a molecule.
B) the gain of electrons by a molecule.
C) the loss of oxygen from a cell.
D) the gain of oxygen by a cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Each protein in an electron transport chain is sequentially oxidized,then reduced,allowing the work of actively transporting oxygen molecules by active membrane transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An example (or examples)of potential energy is (are)
A) light and chemical bonds.
B) concentration gradients.
C) chemical bonds and concentration gradients.
D) chemical bonds.
E) light.
A) light and chemical bonds.
B) concentration gradients.
C) chemical bonds and concentration gradients.
D) chemical bonds.
E) light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The metabolic rate of individuals is influenced by
A) the amount of body fat.
B) the amount of thyroxin produced by the thyroid.
C) age.
D) All of the answer choices are correct.
E) weight.
A) the amount of body fat.
B) the amount of thyroxin produced by the thyroid.
C) age.
D) All of the answer choices are correct.
E) weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
You are cold.Your body begins a shivering response.You quickly rub your hands together,and the friction produces a small amount of heat.The heat is evidence of increasing entropy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Oxidation-reduction reactions
A) transfer electrons from one molecule to another.
B) increase the amount of oxygen in the cell.
C) transfer protons from one molecule to another.
D) are not used by living cells.
E) reduce the amount of oxygen in the cell.
A) transfer electrons from one molecule to another.
B) increase the amount of oxygen in the cell.
C) transfer protons from one molecule to another.
D) are not used by living cells.
E) reduce the amount of oxygen in the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water is an
A) exergonic reaction in photosynthesis.
B) exergonic reaction in cellular respiration.
C) endergonic reaction in photosynthesis.
D) endergonic reaction in cellular respiration.
A) exergonic reaction in photosynthesis.
B) exergonic reaction in cellular respiration.
C) endergonic reaction in photosynthesis.
D) endergonic reaction in cellular respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The process of phosphorylation
A) adds a phosphate group to a molecule.
B) removes a phosphate group from a molecule.
C) may change the shape of the target molecule.
D) All of the answer choices are correct.
E) may energize the target molecule.
A) adds a phosphate group to a molecule.
B) removes a phosphate group from a molecule.
C) may change the shape of the target molecule.
D) All of the answer choices are correct.
E) may energize the target molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is not an example of kinetic energy?
A) sound
B) light
C) heat
D) the energy in chemical bonds
E) random molecular movement
A) sound
B) light
C) heat
D) the energy in chemical bonds
E) random molecular movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A serving of 30 grams of almonds may have 190 Calories listed on a nutrition label.This represents
A) enough energy to raise the temperature of 190 grams of water 1 °C.
B) enough energy to raise the temperature of 30 grams of water 190 °C.
C) enough energy to raise the temperature of 30 kilograms of water 190 °C.
D) enough energy to raise the temperature of 190 kilograms of water 1 °C.
A) enough energy to raise the temperature of 190 grams of water 1 °C.
B) enough energy to raise the temperature of 30 grams of water 190 °C.
C) enough energy to raise the temperature of 30 kilograms of water 190 °C.
D) enough energy to raise the temperature of 190 kilograms of water 1 °C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which statement is not part of the first law of thermodynamics?
A) The amount of energy in the universe is constant.
B) None of the answer choices are correct.
C) Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
D) Energy can be converted to other forms of energy.
E) Any energy transformation loses some energy to its surroundings as heat.
A) The amount of energy in the universe is constant.
B) None of the answer choices are correct.
C) Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
D) Energy can be converted to other forms of energy.
E) Any energy transformation loses some energy to its surroundings as heat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A raw peanut having almost 2 Calories of energy has 2,000 times the energy to raise the temperature of 1 gram water by 1 °C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Oxidation-reduction reactions
A) remove protons from one molecule and join them to another molecule.
B) remove electrons from both molecules involved.
C) remove oxygen from the cell.
D) never occur at the same time.
E) occur simultaneously.
A) remove protons from one molecule and join them to another molecule.
B) remove electrons from both molecules involved.
C) remove oxygen from the cell.
D) never occur at the same time.
E) occur simultaneously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Simple diffusion
A) does not require energy.
B) utilizes proteins to move molecules across a membrane.
C) requires energy.
D) cannot occur without a membrane present.
E) moves molecules against a concentration gradient.
A) does not require energy.
B) utilizes proteins to move molecules across a membrane.
C) requires energy.
D) cannot occur without a membrane present.
E) moves molecules against a concentration gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the environment surrounding a cell has a lower concentration of solute than the cell,the
A) environment is hypotonic to the cell.
B) environment is isotonic to the cell.
C) cell will not experience a net gain or loss of water.
D) environment is hypertonic to the cell.
E) cell will die.
A) environment is hypotonic to the cell.
B) environment is isotonic to the cell.
C) cell will not experience a net gain or loss of water.
D) environment is hypertonic to the cell.
E) cell will die.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Noncompetitive inhibition of enzymes occurs
A) when a cofactor, instead of a reactant, binds to the enzyme active site.
B) when a substance binds to an enzyme at a site away from the active site.
C) by blocking the production of an enzyme.
D) when a substance other than the substrate binds at the active site of an enzyme.
A) when a cofactor, instead of a reactant, binds to the enzyme active site.
B) when a substance binds to an enzyme at a site away from the active site.
C) by blocking the production of an enzyme.
D) when a substance other than the substrate binds at the active site of an enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Much medical advice towards heart health indicates that you should eat less sodium (table salt).Notable higher risks of high sodium may include high blood pressure and damage to arteries or organs in your body.If you eat a single meal with large amounts of salt to suit your taste,which of these may result within minutes,as the sodium enters your bloodstream?
A) Simple diffusion of water and sodium will both balance in an isotonic condition between arteries and body tissues.
B) You should expect no change in the concentration gradient because of a single meal, rather than lifestyle and diet.
C) Your blood will become hypotonic, and water in your body tissues will flow into your arteries, inflating them.
D) Your blood will become hypertonic, and water in your body tissues will flow into your arteries, inflating them.
A) Simple diffusion of water and sodium will both balance in an isotonic condition between arteries and body tissues.
B) You should expect no change in the concentration gradient because of a single meal, rather than lifestyle and diet.
C) Your blood will become hypotonic, and water in your body tissues will flow into your arteries, inflating them.
D) Your blood will become hypertonic, and water in your body tissues will flow into your arteries, inflating them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Enzymes speed chemical reactions by
A) supplying energy to the reaction process.
B) raising the temperature of the surroundings.
C) lowering the amount of reactants that are needed.
D) lowering the energy required to start a chemical reaction.
E) maintaining chemical equilibrium.
A) supplying energy to the reaction process.
B) raising the temperature of the surroundings.
C) lowering the amount of reactants that are needed.
D) lowering the energy required to start a chemical reaction.
E) maintaining chemical equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Determine which of these statements best summarizes the cellular regulation of concentration gradients.
A) Enzymes are used in the cell to build molecules on one side of membranes to establish concentration gradients.
B) Passive and active transport both function when vesicles transport materials across the cell membranes.
C) Membrane phospholipids and proteins regulate transport functions to establish concentration gradients or equilibria.
D) Selective permeability of the cell membranes results in equal amounts of substances inside and outside the cell.
A) Enzymes are used in the cell to build molecules on one side of membranes to establish concentration gradients.
B) Passive and active transport both function when vesicles transport materials across the cell membranes.
C) Membrane phospholipids and proteins regulate transport functions to establish concentration gradients or equilibria.
D) Selective permeability of the cell membranes results in equal amounts of substances inside and outside the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figuer:
This diagram shows the basic structure and function of an enzyme, acting to catalyze a cell's chemical reaction.
The region of an enzyme that catalyzes reactions is called a(n)
A) active site.
B) binding pocket.
C) catalyst site.
D) reaction site.
E) cofactor site.
This diagram shows the basic structure and function of an enzyme, acting to catalyze a cell's chemical reaction.

The region of an enzyme that catalyzes reactions is called a(n)
A) active site.
B) binding pocket.
C) catalyst site.
D) reaction site.
E) cofactor site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A cell produces proteins when ribosomes (a form of RNA and protein)and transfer RNA (tRNA)work together.Specific amino acids are brought by tRNA into the ribosome,where they are rapidly connected by covalent bonds.This indicates that ribosomes are acting as
A) active sites.
B) substrates.
C) reactants.
D) enzymes.
A) active sites.
B) substrates.
C) reactants.
D) enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Competitive inhibition of enzymes occurs
A) when a substance binds to an enzyme at a site away from the active site.
B) when the product, instead of the reactant of a reaction binds to the active site.
C) when a substance other than the substrate binds at the active site of an enzyme.
D) when the product, or other substances, instead of the reactant, bind to the active site of the enzyme.
E) by blocking the production of an enzyme.
A) when a substance binds to an enzyme at a site away from the active site.
B) when the product, instead of the reactant of a reaction binds to the active site.
C) when a substance other than the substrate binds at the active site of an enzyme.
D) when the product, or other substances, instead of the reactant, bind to the active site of the enzyme.
E) by blocking the production of an enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Active transport is different from simple diffusion in that active transport
A) moves molecules against a concentration gradient.
B) All of the answer choices are correct.
C) requires proteins embedded within the cell membrane.
D) requires energy.
E) moves molecules from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration.
A) moves molecules against a concentration gradient.
B) All of the answer choices are correct.
C) requires proteins embedded within the cell membrane.
D) requires energy.
E) moves molecules from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Cofactors,required for correct action of enzymes,are often in our diets as vitamins,minerals,and coenzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Phagocytosis of an infective bacterium by a white blood cell is a subset type of
A) exocytosis.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) simple diffusion.
D) endocytosis.
A) exocytosis.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) simple diffusion.
D) endocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Turgor pressure in plant cells is
A) a result of the walled cell being in a hypotonic environment.
B) due in part to osmosis.
C) necessary to keep plants from wilting.
D) the force of water against the inside of the cell wall.
E) All of the answer choices are correct.
A) a result of the walled cell being in a hypotonic environment.
B) due in part to osmosis.
C) necessary to keep plants from wilting.
D) the force of water against the inside of the cell wall.
E) All of the answer choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a cell has a 95% concentration of water in its cytoplasm and the environment surrounding the cell has a 90% concentration of water,water will flow
A) into the cell by osmosis.
B) out of the cell by active transport.
C) out of the cell by osmosis.
D) into the cell by active transport.
E) into the cell by facilitated diffusion.
A) into the cell by osmosis.
B) out of the cell by active transport.
C) out of the cell by osmosis.
D) into the cell by active transport.
E) into the cell by facilitated diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following are examples of kinetic energy?
A) electrons in chemical bonds of the food molecules, proton gradients established, ATP molecules
B) protons moving through ATPase by facilitated diffusion, ATP molecules
C) electrons from food molecules moving through electron transport chain, proton gradients established
D) electrons from food molecules moving through the electron transport chain, and protons moving through ATPase
A) electrons in chemical bonds of the food molecules, proton gradients established, ATP molecules
B) protons moving through ATPase by facilitated diffusion, ATP molecules
C) electrons from food molecules moving through electron transport chain, proton gradients established
D) electrons from food molecules moving through the electron transport chain, and protons moving through ATPase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If a cell has a greater concentration of solute than its environment,the cell
A) will not experience a net gain or loss of water.
B) is hypertonic to the environment.
C) will die.
D) is isotonic to the environment.
E) is hypotonic to the environment.
A) will not experience a net gain or loss of water.
B) is hypertonic to the environment.
C) will die.
D) is isotonic to the environment.
E) is hypotonic to the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable (biological)membrane is
A) osmosis.
B) active transport.
C) always beneficial to a cell.
D) a rare occurrence.
E) a process that always requires proteins.
A) osmosis.
B) active transport.
C) always beneficial to a cell.
D) a rare occurrence.
E) a process that always requires proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Figuer:
This diagram shows the basic structure and function of an enzyme, acting to catalyze a cell's chemical reaction.
The molecule that fits into the active site of an enzyme and reacts with the enzyme is
A) an analog.
B) a substrate.
C) always a carbohydrate.
D) always broken down by the enzyme.
E) always a protein.
This diagram shows the basic structure and function of an enzyme, acting to catalyze a cell's chemical reaction.

The molecule that fits into the active site of an enzyme and reacts with the enzyme is
A) an analog.
B) a substrate.
C) always a carbohydrate.
D) always broken down by the enzyme.
E) always a protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following are examples of potential energy associated with our food consumption and metabolism?
A) electrons in chemical bonds of food molecules, proton gradients, and ATP molecules
B) electrons moving through the electron transport chain, and protons moving through ATPase
C) protons moving through ATPase by facilitated diffusion, ATP molecules
D) All of the answer choices are correct.
E) electrons from food molecules moving through the electron transport chain, and a proton gradient
A) electrons in chemical bonds of food molecules, proton gradients, and ATP molecules
B) electrons moving through the electron transport chain, and protons moving through ATPase
C) protons moving through ATPase by facilitated diffusion, ATP molecules
D) All of the answer choices are correct.
E) electrons from food molecules moving through the electron transport chain, and a proton gradient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When electrons are removed from a food molecule it is
A) an exergonic reaction.
B) an endergonic reaction.
C) in equilibrium.
D) being reduced.
E) being oxidized.
A) an exergonic reaction.
B) an endergonic reaction.
C) in equilibrium.
D) being reduced.
E) being oxidized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
CFTR moves chloride ions out of cells by active transport.What can be inferred from this statement?
A) Normal initial chloride concentrations are lower on the inside of the cell.
B) Normal resulting chloride concentrations are higher on the outside of the cell.
C) CFTR functions as the cystic fibers attach to and pull chlorides through holes in the membrane.
D) Water will also cross the membrane, with the chlorides, through the CFTR proteins.
A) Normal initial chloride concentrations are lower on the inside of the cell.
B) Normal resulting chloride concentrations are higher on the outside of the cell.
C) CFTR functions as the cystic fibers attach to and pull chlorides through holes in the membrane.
D) Water will also cross the membrane, with the chlorides, through the CFTR proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
After the active transport of chloride ions out of the cell by CFTR,why does water follow by osmosis?
A) The cell is now in a hypotonic solution.
B) The cell must pump out water to avoid bursting.
C) The cell is now in a hypertonic solution.
D) The cell needs to regenerate the ATP used in active transport.
E) The cell is now in an isotonic solution.
A) The cell is now in a hypotonic solution.
B) The cell must pump out water to avoid bursting.
C) The cell is now in a hypertonic solution.
D) The cell needs to regenerate the ATP used in active transport.
E) The cell is now in an isotonic solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For animals and other organisms consuming food,the molecular reactants to cellular respiration are
A) carbon dioxide and water.
B) entropy.
C) digestive enzymes.
D) glucose and oxygen.
A) carbon dioxide and water.
B) entropy.
C) digestive enzymes.
D) glucose and oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
During low tide a plant cell will have an advantage over an animal cell because of its
A) chloroplasts.
B) nucleus.
C) cell wall.
D) plasma membrane.
E) mitochondria.
A) chloroplasts.
B) nucleus.
C) cell wall.
D) plasma membrane.
E) mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The CFTR is a normal membrane protein used to move chloride ions out of a cell by active transport.This is an example of
A) a reaction coupled with the production of ATP.
B) equilibrium.
C) a reaction coupled with the hydrolysis of ATP.
D) a reduction reaction.
E) an oxidation reaction.
A) a reaction coupled with the production of ATP.
B) equilibrium.
C) a reaction coupled with the hydrolysis of ATP.
D) a reduction reaction.
E) an oxidation reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If a person is poisoned with cyanide,they cannot generate ATP,and die within a few minutes.In relation to the sodium-potassium pump,what specific impact would cyanide have on concentrations across the cell membrane?
A) Sodium and potassium concentrations would both be higher inside the cell.
B) Both sodium and potassium concentrations would become isotonic outside the cell.
C) Sodium concentration would be higher outside the cell, while potassium concentration would be higher inside the cell.
D) Sodium and potassium concentrations would both be higher outside the cell.
E) Both sodium and potassium concentrations would reach equilibrium conditions across the cell membrane.
A) Sodium and potassium concentrations would both be higher inside the cell.
B) Both sodium and potassium concentrations would become isotonic outside the cell.
C) Sodium concentration would be higher outside the cell, while potassium concentration would be higher inside the cell.
D) Sodium and potassium concentrations would both be higher outside the cell.
E) Both sodium and potassium concentrations would reach equilibrium conditions across the cell membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Simple diffusion occurs naturally as it ___ of a system.
A) decreases the kinetic energy
B) increases the potential energy
C) decreases the equilibrium
D) increases the entropy
E) All of the answer choices are correct.
A) decreases the kinetic energy
B) increases the potential energy
C) decreases the equilibrium
D) increases the entropy
E) All of the answer choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
At high tide a coastal plant or animal cell will be in
A) equilibrium.
B) osmosis.
C) a hypertonic solution.
D) a hypotonic solution.
E) an isotonic solution.
A) equilibrium.
B) osmosis.
C) a hypertonic solution.
D) a hypotonic solution.
E) an isotonic solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Once ATP donates its phosphate to a coupled reaction it becomes ADP.The ADP
A) can be recharged in an exergonic reaction to form ATP.
B) is a waste product that must be broken down.
C) can be recharged in an endergonic reaction to form ATP.
D) becomes the needed potential energy source for another coupled reaction.
E) can be recharged in an oxidation reaction to form ATP.
A) can be recharged in an exergonic reaction to form ATP.
B) is a waste product that must be broken down.
C) can be recharged in an endergonic reaction to form ATP.
D) becomes the needed potential energy source for another coupled reaction.
E) can be recharged in an oxidation reaction to form ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The molecular reactants for photosynthesis are
A) glucose and carbon dioxide.
B) glucose and sunlight.
C) organic compounds.
D) glucose and water.
E) water and carbon dioxide.
A) glucose and carbon dioxide.
B) glucose and sunlight.
C) organic compounds.
D) glucose and water.
E) water and carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Firewood is made up of cellulose,which is a polymer of glucose molecules.When burning,heat and light are given off,indicating that a(n)________ reaction is occurring.
A) endergonic
B) equilibrium
C) exergonic
D) potential energy
E) kinetic energy
A) endergonic
B) equilibrium
C) exergonic
D) potential energy
E) kinetic energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A bowl of sugar water is very stable.In a cell,however,it is rapidly broken down into carbon dioxide and water,releasing stored energy.What is the best explanation for this observation?
A) Glucose becomes more chemically reactive inside of a cell.
B) Cells use energy to break down the glucose.
C) Glucose is only broken down while dissolving into a watery solution, such as inside the cell.
D) Glucose cannot be broken down outside of a cell.
E) Enzymes in the cell catalyze the breakdown of the glucose.
A) Glucose becomes more chemically reactive inside of a cell.
B) Cells use energy to break down the glucose.
C) Glucose is only broken down while dissolving into a watery solution, such as inside the cell.
D) Glucose cannot be broken down outside of a cell.
E) Enzymes in the cell catalyze the breakdown of the glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
One way to produce a vaccine is to heat a virus or bacteria and then inject the inactive pathogen as a vaccination.How would the heat inactivate a virus?
A) by denaturing proteins
B) All of the answer choices are correct.
C) by inhibiting its metabolism
D) by blocking facilitated diffusion
E) by destroying the membrane
A) by denaturing proteins
B) All of the answer choices are correct.
C) by inhibiting its metabolism
D) by blocking facilitated diffusion
E) by destroying the membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If you drop a rubber ball it doesn't bounce back to the height you dropped it from.This is consistent with
A) conversion of kinetic energy into entropy.
B) conversion of entropy into potential energy.
C) the first law of thermodynamics.
D) the second law of thermodynamics.
E) conversion of kinetic energy into potential energy.
A) conversion of kinetic energy into entropy.
B) conversion of entropy into potential energy.
C) the first law of thermodynamics.
D) the second law of thermodynamics.
E) conversion of kinetic energy into potential energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The sodium-potassium pump catalyzes
A) equilibrium.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) osmosis.
D) active transport.
E) diffusion.
A) equilibrium.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) osmosis.
D) active transport.
E) diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Figuer:
This diagram summarizes energy transfers and molecule exchanges among plants and animals, as you will learn later we call producers and consumers.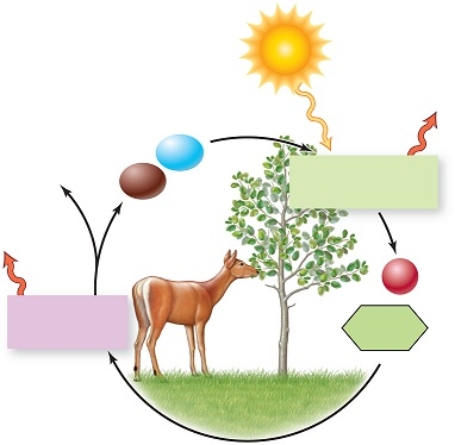
Plants require energy to perform photosynthesis,in which glucose is formed from carbon dioxide and water,and stores energy.This is a(n)_____ reaction.
A) kinetic energy
B) exergonic
C) endergonic
D) potential energy
E) equilibrium
This diagram summarizes energy transfers and molecule exchanges among plants and animals, as you will learn later we call producers and consumers.

Plants require energy to perform photosynthesis,in which glucose is formed from carbon dioxide and water,and stores energy.This is a(n)_____ reaction.
A) kinetic energy
B) exergonic
C) endergonic
D) potential energy
E) equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Your liver produces 90% of the cholesterol found in your body.When cholesterol levels get too high,the first enzyme in the pathway of cholesterol synthesis is inhibited.This is an example of
A) positive feedback.
B) denaturation.
C) negative feedback.
D) equilibrium.
E) a coenzyme.
A) positive feedback.
B) denaturation.
C) negative feedback.
D) equilibrium.
E) a coenzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The energy source that powers the process of photosynthesis is
A) oxygen.
B) glucose.
C) carbon dioxide.
D) water.
E) sunlight.
A) oxygen.
B) glucose.
C) carbon dioxide.
D) water.
E) sunlight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why does phenylalanine accumulate in patients with phenylketonuria?
A) They lack an enzyme to break down phenylalanine.
B) They produce too much phenylalanine.
C) They lack an enzyme to produce phenylalanine.
D) They lack an inhibitor of an enzyme to break down phenylalanine.
A) They lack an enzyme to break down phenylalanine.
B) They produce too much phenylalanine.
C) They lack an enzyme to produce phenylalanine.
D) They lack an inhibitor of an enzyme to break down phenylalanine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
During high tide a plant or animal would be at risk of
A) dehydration by facilitated diffusion of salts.
B) cells bursting due to active transport of salts.
C) dehydration by osmosis of water.
D) cells bursting by osmosis of water.
E) dehydration due to active transport of salts.
A) dehydration by facilitated diffusion of salts.
B) cells bursting due to active transport of salts.
C) dehydration by osmosis of water.
D) cells bursting by osmosis of water.
E) dehydration due to active transport of salts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Figuer: 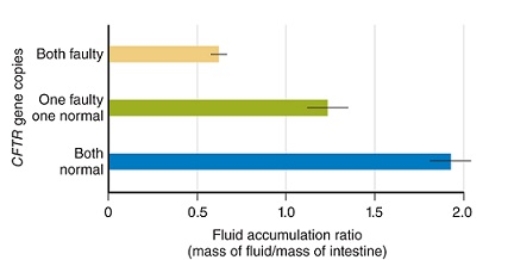
What did the researchers conclude from the data shown in this figure?
A) The more cholera toxin an organism was exposed to, fewer copies of its CFTR gene that became defective.
B) The number of defective CFTR genes did not correlate with resistance to cholera toxin.
C) The fewer copies of a defective CFTR gene an organism has, the more resistant it is to cholera toxin.
D) The more copies of a defective CFTR gene an organism has, the more resistant it is to cholera toxin.
E) The more cholera toxin an organism was exposed to, the more copies of its CFTR gene that became defective.

What did the researchers conclude from the data shown in this figure?
A) The more cholera toxin an organism was exposed to, fewer copies of its CFTR gene that became defective.
B) The number of defective CFTR genes did not correlate with resistance to cholera toxin.
C) The fewer copies of a defective CFTR gene an organism has, the more resistant it is to cholera toxin.
D) The more copies of a defective CFTR gene an organism has, the more resistant it is to cholera toxin.
E) The more cholera toxin an organism was exposed to, the more copies of its CFTR gene that became defective.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What hypothesis was tested by researcher Sherif Gabriel and his colleagues?
A) Does defective CFTR make people more sensitive to cholera?
B) Does cholera causes cystic fibrosis?
C) Does cholera increase the risk of transmission of cystic fibrosis?
D) Does defective CFTR give people natural resistance to cholera?
A) Does defective CFTR make people more sensitive to cholera?
B) Does cholera causes cystic fibrosis?
C) Does cholera increase the risk of transmission of cystic fibrosis?
D) Does defective CFTR give people natural resistance to cholera?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An enzyme is a lipid that catalyzes chemical reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The first and second laws of thermodynamics apply to nonliving systems like gasoline engines but do not apply to reactions in living cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Of these membrane transport processes,which do (does)not make use of a vesicle?
A) phagocytosis
B) facilitated diffusion
C) neither osmosis nor facilitated diffusion
D) pinocytosis
E) osmosis
A) phagocytosis
B) facilitated diffusion
C) neither osmosis nor facilitated diffusion
D) pinocytosis
E) osmosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A reason that some antibiotics harm bacteria but not humans is because humans have many more cells than bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
One in 25 Caucasians is a carrier for the defective CFTR gene,making it the most common genetic disease in this population.Why would the frequency of defects in CFTR be so common in this population,given the relationship between cholera and CFTR is similar in humans?
A) Carriers with one copy of the defective CFTR gene have decreased resistance to cholera compared to those with no defective copies.
B) Carriers with one copy of the defective CFTR gene have increased resistance to cholera compared to those with no defective copies.
C) Only carriers would be able to survive exposure to cholera.
D) These individuals were exposed to cholera, causing mutations in their CFTR gene that can then be passed on to their children.
E) Carriers will be more likely to have children who develop cystic fibrosis.
A) Carriers with one copy of the defective CFTR gene have decreased resistance to cholera compared to those with no defective copies.
B) Carriers with one copy of the defective CFTR gene have increased resistance to cholera compared to those with no defective copies.
C) Only carriers would be able to survive exposure to cholera.
D) These individuals were exposed to cholera, causing mutations in their CFTR gene that can then be passed on to their children.
E) Carriers will be more likely to have children who develop cystic fibrosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Movement of molecules down a concentration gradient is an example of
A) reduction.
B) kinetic energy.
C) active transport.
D) oxidation.
E) potential energy.
A) reduction.
B) kinetic energy.
C) active transport.
D) oxidation.
E) potential energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Exergonic reactions do not require activation energy to get started.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Figuer: 
What is the dependent variable in the figure shown?
A) the number of defective copies of the CFTR gene in humans
B) the amount of fluid in the intestines after exposure to cholera toxin
C) whether or not the subjects were exposed to Vibrio cholera bacteria
D) whether or not the subjects were exposed to cholera toxin
E) the number of defective copies of the CFTR gene in mice

What is the dependent variable in the figure shown?
A) the number of defective copies of the CFTR gene in humans
B) the amount of fluid in the intestines after exposure to cholera toxin
C) whether or not the subjects were exposed to Vibrio cholera bacteria
D) whether or not the subjects were exposed to cholera toxin
E) the number of defective copies of the CFTR gene in mice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Receptor-mediated endocytosis is a specialized,more selective method of cell membrane transport than pinocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When an end product of a reaction pathway is in excess and inhibits the first enzyme of the pathway,this is an example of positive feedback.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Whenever ATP is produced by a chemical reaction some energy is lost into the surroundings as heat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
How does the bacteria that causes cholera,Vibrio cholera,trigger potentially life-threatening diarrhea?
A) Cholera toxin inhibits CFTR leading to decreased transport of water into the intestines.
B) Cholera toxin inhibits CFTR leading to increased transport of water into the intestines.
C) Cholera toxin stimulates CFTR leading to decreased transport of water into the intestines.
D) Cholera toxin stimulates CFTR leading to increased transport of water into the intestines.
E) Cholera toxin causes a DNA genetic mutation that modifies the function of CFTR proteins.
A) Cholera toxin inhibits CFTR leading to decreased transport of water into the intestines.
B) Cholera toxin inhibits CFTR leading to increased transport of water into the intestines.
C) Cholera toxin stimulates CFTR leading to decreased transport of water into the intestines.
D) Cholera toxin stimulates CFTR leading to increased transport of water into the intestines.
E) Cholera toxin causes a DNA genetic mutation that modifies the function of CFTR proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of these membrane transport processes does not require membrane proteins?
A) active transport pumps
B) facilitated diffusion
C) endocytosis
D) osmosis
A) active transport pumps
B) facilitated diffusion
C) endocytosis
D) osmosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Figuer: 
What is the independent variable in the figure shown?
A) whether or not the subjects were exposed to cholera toxin
B) the amount of fluid in the intestines
C) whether or not the subjects were exposed to Vibrio cholera bacteria
D) the number of defective copies of the CFTR gene in humans
E) the number of defective copies of the CFTR gene in mice

What is the independent variable in the figure shown?
A) whether or not the subjects were exposed to cholera toxin
B) the amount of fluid in the intestines
C) whether or not the subjects were exposed to Vibrio cholera bacteria
D) the number of defective copies of the CFTR gene in humans
E) the number of defective copies of the CFTR gene in mice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Phagocytosis is a process that cells use to move materials in through the cell membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Reduction is the gain of electrons by an atom or molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



