Deck 16: The Valuation of Fixed-Income Securities
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: The Valuation of Fixed-Income Securities
1
If a bond sells for a premium,the current yield exceeds the yield to maturity.
True
2
The prices of low coupon bonds tend to fluctuate more than the prices of high coupon bonds.
True
3
If interest rates increase,a bond may be called.
False
4
If bond prices were to decline,the current yield would increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a $1,000 bond with a 7 percent coupon were to sell for $978,interest rates exceed 7 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A call feature will have no impact on the value of a bond if interest rates rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A bond is more likely to be called after interest rates have fallen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If bond prices rise,the yield to maturity declines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An investor may expect a bond to be called if its current yield exceeds the yield to maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Bonds that are callable often have a call penalty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
As interest rates increase,the prices of existing bonds increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A call penalty is a payment made to the firm to encourage early retirement of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The value of a bond depends on the amount of principal,when it matures,and the interest it pays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A few bonds called "perpetuals" never mature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The current yield exceeds the yield to maturity if interest rates fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If interest rates have fallen,a firm may prefer to repurchase the bonds on the market instead of calling and redeeming them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If investors expect interest rates to decline,they should buy bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Most bonds pay interest semi-annually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a $1,000 bond has a coupon of 8 percent and matures after eight years,the price of the bond will exceed $1,000 if interest rates are 9 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a bond sells for a discount,the yield to maturity exceeds the current yield.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Preferred stock pays a fixed amount of interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The term and duration of a bond are equal for zero coupon bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The spread between the yields on AAA-rated bonds and B-rated bonds tends to rise when yields increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Fluctuations in yields is one means by which the economy allocates scarce credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If interest rates decline after a bond is issued and the investor reinvests the interest payment,the realized yield exceeds the yield to maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Preferred stock is legally equity and represents ownership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The possibility of default is higher when interest rates are higher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The prices of twenty-year bonds tend to fluctuate less than bonds with five years to maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The smaller the duration,the more volatile the bond's price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The prices of zero coupon bonds fluctuate less than bonds with large coupons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Matching a bond's duration with the time the funds are needed reduces reinvestment risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Since preferred stock represents equity,it generally has the right to vote.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a cumulative preferred stock pays a dividend,it is said to be in arrears.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The concept of duration stresses when a bond will make its payments to bondholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Preferred stock dividends are usually cumulative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A conservative investor will prefer a bond with a smaller duration even though it may have a longer term to maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Since preferred stock is equity,it cannot have a sinking fund.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The smaller a bond's coupon implies a longer duration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
From the viewpoint of the firm,preferred stock is both cheaper and less risky than bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Since preferred stock pays a fixed dividend,it is often analyzed as if it were debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A bond's call feature may be exercised if
1)the yield to maturity exceeds the current yield
2)the yield to maturity is less than the current yield
3)interest rates have risen
4)interest rates have fallen
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
1)the yield to maturity exceeds the current yield
2)the yield to maturity is less than the current yield
3)interest rates have risen
4)interest rates have fallen
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The concept of duration considers the
A) timing of interest payments
B) timing of principal repayment
C) current rate of interest
D) timing of both interest and principal repayment
A) timing of interest payments
B) timing of principal repayment
C) current rate of interest
D) timing of both interest and principal repayment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
While bond prices fluctuate,
A) yields are constant
B) coupons are constant
C) the spread between yields is constant
D) short-term bond prices fluctuate more
A) yields are constant
B) coupons are constant
C) the spread between yields is constant
D) short-term bond prices fluctuate more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The current yield on a long-term bond is the
A) coupon interest divided by the price of the bond
B) coupon
C) interest paid, adjusted for price changes
D) going rate of interest
A) coupon interest divided by the price of the bond
B) coupon
C) interest paid, adjusted for price changes
D) going rate of interest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Preferred stock dividend payments are exempt from federal income taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If investors expect interest rates to rise,they should sell preferred stock and buy bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If preferred stock is subject to mandatory retirement,its price is more volatile than preferred stock without the retirement feature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The yield to call
A) is important if interest rates have fallen
B) is important if interest rates have risen
C) equals the yield to maturity
D) equals the current yield
A) is important if interest rates have fallen
B) is important if interest rates have risen
C) equals the yield to maturity
D) equals the current yield

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The market price of preferred stock moves directly with changes in interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The analysis of the coverage of preferred stock dividends uses earnings before interest and taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If an investor were to anticipate that interest rates were going to fall,that individual should
A) take no action
B) buy bonds
C) sell bonds
D) acquire money market securities
A) take no action
B) buy bonds
C) sell bonds
D) acquire money market securities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a bond pays $90 interest annually,matures after ten years,and costs $1,100,the current yield is
4)If a $1,000 bond costs $1,000 and pays $90 interest,
1)the current yield is 9 percent
2)the yield to maturity is 9 percent
3)the bond is selling for par
A) 8.2 percent
B) 10.1 percent
C) 9.0 percent
D) 9.6 percent
4)If a $1,000 bond costs $1,000 and pays $90 interest,
1)the current yield is 9 percent
2)the yield to maturity is 9 percent
3)the bond is selling for par
A) 8.2 percent
B) 10.1 percent
C) 9.0 percent
D) 9.6 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If interest rates in general were to fall,
1)the prices of existing bonds would rise
2)the prices of existing bonds would fall
3)yields to maturity would rise
4)yields to maturity would fall
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
1)the prices of existing bonds would rise
2)the prices of existing bonds would fall
3)yields to maturity would rise
4)yields to maturity would fall
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The value of a bond depends on the
1)coupon rate
2)terms of the indenture
3)maturity date
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of these choices
1)coupon rate
2)terms of the indenture
3)maturity date
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a $1,000 bond costs $1,000 and pays $90 interest,
1)the current yield is 9 percent
2)the yield to maturity is 9 percent
3)the bond is selling for par
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of these choices
1)the current yield is 9 percent
2)the yield to maturity is 9 percent
3)the bond is selling for par
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If a 7 percent,$1,000 bond matures after ten years and current interest rates are 9 percent,the current price of the bond should not be
1)$1,000
2)$872
3)$1,140
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) only 2
1)$1,000
2)$872
3)$1,140
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) only 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a bond is selling for a premium,
A) the yield to maturity exceeds the current yield
B) the current yield exceeds the yield to maturity
C) the current yield has risen
D) the bond cannot be called
A) the yield to maturity exceeds the current yield
B) the current yield exceeds the yield to maturity
C) the current yield has risen
D) the bond cannot be called

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
From the viewpoint of the investor,preferred stock is riskier than bonds issued by the same firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If a firm's earnings grow,the dividends paid by preferred stock also are increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Buying a bond with a duration equal to when the funds are needed
A) reduces reinvestment rate risk
B) increases impact of higher interest rates
C) reduces the impact of default
D) increases the bond's yield
A) reduces reinvestment rate risk
B) increases impact of higher interest rates
C) reduces the impact of default
D) increases the bond's yield

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If a preferred stock pays an annual $4.50 dividend,what should be the price of the stock if comparable yields are 10 percent? What would be the loss if yields rose to 12 percent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In general firms prefer to issue bonds instead of preferred stock because
1)debt is less risky to the firm
2)dividends are not tax deductible
3)effective cost of debt is cheaper
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of these choices
1)debt is less risky to the firm
2)dividends are not tax deductible
3)effective cost of debt is cheaper
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Junk Corp.'s high-yield bond has the following features:
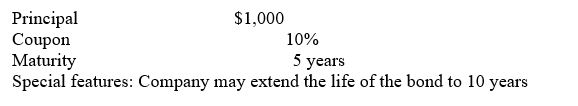 a.If interest rates are currently 12 percent on comparable high-yield securities and are not expected to change,what is the price of this bond?
a.If interest rates are currently 12 percent on comparable high-yield securities and are not expected to change,what is the price of this bond?
b.If interest rates are currently 9 percent on comparable high-yield securities and are not expected to change,what is the price of this bond?
c.If interest rates are currently 9 percent on comparable high-yield securities but the investor has no forecast as to future rates,what is the possible range of prices for this bond?
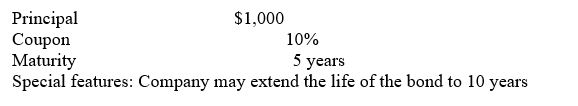 a.If interest rates are currently 12 percent on comparable high-yield securities and are not expected to change,what is the price of this bond?
a.If interest rates are currently 12 percent on comparable high-yield securities and are not expected to change,what is the price of this bond?b.If interest rates are currently 9 percent on comparable high-yield securities and are not expected to change,what is the price of this bond?
c.If interest rates are currently 9 percent on comparable high-yield securities but the investor has no forecast as to future rates,what is the possible range of prices for this bond?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If interest rates rise,the price of preferred stock
A) rises
B) falls
C) is not affected
D) rises or falls
A) rises
B) falls
C) is not affected
D) rises or falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A bond with a 5 percent coupon ($50 a year)that matures after eight years is selling for $779.What is the yield to maturity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Preferred stock and long-term bonds are similar because
A) they both have voting power
B) interest and dividend payments are fixed
C) interest and dividend payments are legal obligations
D) interest and dividend payments are tax-deductible expenses
A) they both have voting power
B) interest and dividend payments are fixed
C) interest and dividend payments are legal obligations
D) interest and dividend payments are tax-deductible expenses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Analysis of preferred stock uses
A) operating income (EBIT)
B) earnings after dividends to common stock
C) earnings after taxes
D) earnings after interest but before taxes
A) operating income (EBIT)
B) earnings after dividends to common stock
C) earnings after taxes
D) earnings after interest but before taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Compute the durations of the following bonds and rank them on the basis of their price volatility.Assume that the current rate of interest is 8 percent.
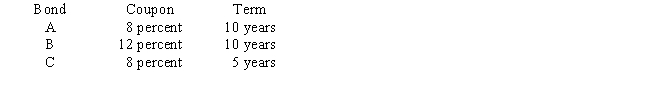 Confirm your ranking by calculating the percentage change in the price of each bond when interest rates rise from 8 to 12 percent.
Confirm your ranking by calculating the percentage change in the price of each bond when interest rates rise from 8 to 12 percent.
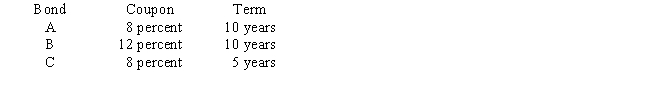 Confirm your ranking by calculating the percentage change in the price of each bond when interest rates rise from 8 to 12 percent.
Confirm your ranking by calculating the percentage change in the price of each bond when interest rates rise from 8 to 12 percent.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Preferred stock dividends are
1)a legal obligation
2)not a legal obligation
3)exempt from federal income taxation
4)not exempt from federal income taxation
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
1)a legal obligation
2)not a legal obligation
3)exempt from federal income taxation
4)not exempt from federal income taxation
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Earnings per preferred share are
A) earnings before interest and taxes
B) the ratio of earnings to number of preferred shares
C) the ratio of EBIT to number of preferred shares
D) the ratio of preferred shares to common shares
A) earnings before interest and taxes
B) the ratio of earnings to number of preferred shares
C) the ratio of EBIT to number of preferred shares
D) the ratio of preferred shares to common shares

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A bond has the following terms:
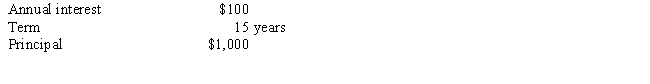 a.What is the current price of the bond if comparable yields are 7 percent?
a.What is the current price of the bond if comparable yields are 7 percent?
b.What are the current yield and yield to maturity given the price of the bond in the previous question?
c.If you expect the bond to be called at the end of the year,what would be the maximum price you should pay for the bond?
d.Is there a reason to expect that the bond will be called?
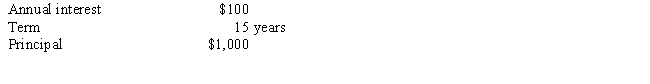 a.What is the current price of the bond if comparable yields are 7 percent?
a.What is the current price of the bond if comparable yields are 7 percent?b.What are the current yield and yield to maturity given the price of the bond in the previous question?
c.If you expect the bond to be called at the end of the year,what would be the maximum price you should pay for the bond?
d.Is there a reason to expect that the bond will be called?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If you purchase a $5 preferred stock for $40 a share,what is the current yield? If you anticipate that yields will decline to 10 percent,what will be the anticipated capital gain on this investment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An individual may purchase preferred stock
1)in anticipation of lower interest rates
2)in anticipation of higher interest rates
3)to receive a flow of tax-free income
4)to receive a flow of income
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
1)in anticipation of lower interest rates
2)in anticipation of higher interest rates
3)to receive a flow of tax-free income
4)to receive a flow of income
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Preferred stock generally pays
A) a variable dividend
B) a fixed dividend
C) a stock dividend
D) no dividend
A) a variable dividend
B) a fixed dividend
C) a stock dividend
D) no dividend

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a $100 par value preferred stock pays an annual dividend of $5 and comparable yields are 10 percent,the price of this preferred stock will be
A) $100
B) $75
C) $50
D) $25
A) $100
B) $75
C) $50
D) $25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Features of preferred stock may include
1)cumulative dividends
2)a call feature
3)mandatory retirement
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of these choices
1)cumulative dividends
2)a call feature
3)mandatory retirement
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



