Deck 13: International Trade and Exchange Rates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/137
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: International Trade and Exchange Rates
1
If there is no comparative advantage between two countries:
A) one country must be more productive in producing all goods than the other.
B) the benefits resulting from trade are increased.
C) there are no gains from specialization and trade.
D) each country should specialize in the production of a particular commodity.
A) one country must be more productive in producing all goods than the other.
B) the benefits resulting from trade are increased.
C) there are no gains from specialization and trade.
D) each country should specialize in the production of a particular commodity.
C
2
The best example of a land-intensive commodity is:
A) tractors.
B) DVD players.
C) wheat.
D) chemicals.
A) tractors.
B) DVD players.
C) wheat.
D) chemicals.
C
3
The principle of comparative advantage indicates that mutually beneficial international trade can take place only when:
A) tariffs are eliminated.
B) transportation costs are almost zero.
C) relative costs of production differ between nations.
D) a country can produce more of some product than other nations can.
A) tariffs are eliminated.
B) transportation costs are almost zero.
C) relative costs of production differ between nations.
D) a country can produce more of some product than other nations can.
C
4
The domestic opportunity cost of producing a television in the United States is 20 bushels of wheat.In Korea,the domestic opportunity cost of producing a television is 10 bushels of wheat.In this case:
A) Korea has a comparative advantage in the production of wheat.
B) the United States has a comparative advantage in the production of televisions.
C) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports televisions from Korea and Korea imports wheat from the United States.
D) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports wheat from Korea and Korea imports televisions from the United States.
The United States has a comparative advantage in producing wheat because of its lower opportunity cost (1/20 vs.Korea's opportunity cost of 1/10),so Korea should import wheat from the United States.
A) Korea has a comparative advantage in the production of wheat.
B) the United States has a comparative advantage in the production of televisions.
C) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports televisions from Korea and Korea imports wheat from the United States.
D) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports wheat from Korea and Korea imports televisions from the United States.
The United States has a comparative advantage in producing wheat because of its lower opportunity cost (1/20 vs.Korea's opportunity cost of 1/10),so Korea should import wheat from the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which nation led the world in the volume of exports in 2009?
A) Britain
B) Japan
C) China
D) United States
A) Britain
B) Japan
C) China
D) United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Nation X has a comparative advantage in the production of a product compared to nation Y when:
A) it imposes a tariff on the import of the product.
B) the trading possibilities line shifts outward.
C) it is achieving full employment of resources.
D) it has the lower domestic opportunity cost of the two countries.
A) it imposes a tariff on the import of the product.
B) the trading possibilities line shifts outward.
C) it is achieving full employment of resources.
D) it has the lower domestic opportunity cost of the two countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The principal concept behind comparative advantage is that a nation should:
A) compare its volume of trade with other nations.
B) use tariffs and quotas to protect the production of vital products for the nation.
C) concentrate production on those products for which it has the lowest domestic opportunity cost.
D) make the nation self-sufficient in the production of essential goods and services.
A) compare its volume of trade with other nations.
B) use tariffs and quotas to protect the production of vital products for the nation.
C) concentrate production on those products for which it has the lowest domestic opportunity cost.
D) make the nation self-sufficient in the production of essential goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A trade surplus implies that:
A) exports of goods exceed imports of goods.
B) imports of goods exceed exports of goods.
C) exports of services exceed imports of services.
D) imports of services exceed exports of services.
A) exports of goods exceed imports of goods.
B) imports of goods exceed exports of goods.
C) exports of services exceed imports of services.
D) imports of services exceed exports of services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A trade deficit refers to an excess of:
A) imports of goods over exports of goods.
B) Exports of services over imports of services.
C) total debits over total credits in the capital account.
D) total payments over total revenues in the current account.
A) imports of goods over exports of goods.
B) Exports of services over imports of services.
C) total debits over total credits in the capital account.
D) total payments over total revenues in the current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which nation has greatly increased its role in international trade in recent years?
A) Zaire
B) Iran
C) Peru
D) China
A) Zaire
B) Iran
C) Peru
D) China

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When a nation has a comparative advantage in producing a product,then in comparison with any other nation it can produce that product:
A) at a lower average total cost.
B) at a lower domestic opportunity cost.
C) with less capital.
D) with less labor.
A) at a lower average total cost.
B) at a lower domestic opportunity cost.
C) with less capital.
D) with less labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which product is a leading export of the United States?
A) Steel
B) Clothes
C) Chemicals
D) Petroleum
A) Steel
B) Clothes
C) Chemicals
D) Petroleum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which nation has significantly increased its international trade in recent years to become an important trading nation?
A) Algeria
B) Argentina
C) China
D) Colombia
A) Algeria
B) Argentina
C) China
D) Colombia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a two-nation world,comparative advantage means that one nation can produce:
A) a product with fewer inputs than the other nation.
B) a product at lower average cost than the other nation.
C) a product at a lower domestic opportunity cost than the other nation.
D) more of a product than the other nation.
A) a product with fewer inputs than the other nation.
B) a product at lower average cost than the other nation.
C) a product at a lower domestic opportunity cost than the other nation.
D) more of a product than the other nation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Trade between individuals and between nations leads to:
A) greater self-sufficiency.
B) higher product prices.
C) lower living standards.
D) increased specialization.
A) greater self-sufficiency.
B) higher product prices.
C) lower living standards.
D) increased specialization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In 2010,the trade deficit in goods for the United States was about:
A) $55 billion.
B) $107 billion.
C) $455 billion.
D) $646 billion.
A) $55 billion.
B) $107 billion.
C) $455 billion.
D) $646 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Consider two countries that trade with each other.The degree of specialization according to their respective comparative advantages will be greater if the countries face:
A) constant costs.
B) high tariffs.
C) low unemployment rates.
D) increasing costs.
A) constant costs.
B) high tariffs.
C) low unemployment rates.
D) increasing costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In 2010,U.S.exports of services ______ U.S.imports of services by about ____.
A) exceeded;$146B
B) fell short of;$146B
C) exceeded;$257B
D) fell short of;$257B
A) exceeded;$146B
B) fell short of;$146B
C) exceeded;$257B
D) fell short of;$257B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which country is the United States' most important trading partner?
A) Germany
B) Japan
C) China
D) Canada
A) Germany
B) Japan
C) China
D) Canada

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
According to the principle of comparative advantage,worldwide output and consumption levels will be highest when goods are produced in nations where:
A) domestic opportunity costs are lowest.
B) inflation rates are low.
C) the balance of trade is in a surplus position.
D) the exchange rate is falling.
A) domestic opportunity costs are lowest.
B) inflation rates are low.
C) the balance of trade is in a surplus position.
D) the exchange rate is falling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Given the following production possibilities schedules,it can be seen that: 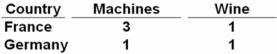
A) France has a comparative advantage in producing wine.
B) Germany can produce more machines than France.
C) France has a comparative advantage in producing machines.
D) Germany can produce more of both goods than France.
The opportunity cost of producing machines is lower in France (1/3)than in Germany (1).

A) France has a comparative advantage in producing wine.
B) Germany can produce more machines than France.
C) France has a comparative advantage in producing machines.
D) Germany can produce more of both goods than France.
The opportunity cost of producing machines is lower in France (1/3)than in Germany (1).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The production possibilities for country X are either 6000 bushels of soybeans or 10,000 bushels of wheat.The production possibilities for country Y are 2000 bushels of soybeans and 4000 bushels of wheat.Which of the following is true?
A) Country Y should specialize in the growing of soybeans according to the principle of comparative advantage.
B) Country X is the least-cost producer of wheat.
C) The domestic opportunity cost of wheat production is lower in country Y.
D) The high cost producer of soybeans is country X.
The opportunity cost of producing wheat is 3/5 in country X and ½ in country Y.
A) Country Y should specialize in the growing of soybeans according to the principle of comparative advantage.
B) Country X is the least-cost producer of wheat.
C) The domestic opportunity cost of wheat production is lower in country Y.
D) The high cost producer of soybeans is country X.
The opportunity cost of producing wheat is 3/5 in country X and ½ in country Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose the world economy is composed of just two countries: A and B.Each can produce steel or chemicals but at different levels of economic efficiency.The domestic production possibilities curves are shown in the graphs below 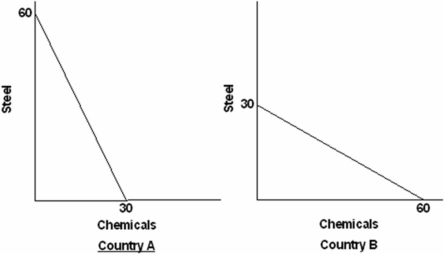 Refer to the above graphs and information.The opportunity costs of producing steel and chemicals in the two countries are:
Refer to the above graphs and information.The opportunity costs of producing steel and chemicals in the two countries are:
A) increasing in each nation.
B) decreasing in each nation.
C) the same in each nation.
D) different across nations.
 Refer to the above graphs and information.The opportunity costs of producing steel and chemicals in the two countries are:
Refer to the above graphs and information.The opportunity costs of producing steel and chemicals in the two countries are:A) increasing in each nation.
B) decreasing in each nation.
C) the same in each nation.
D) different across nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Autos and chemicals are in units of one million 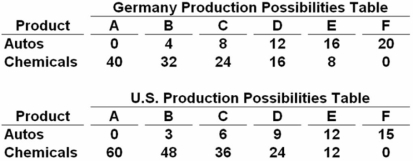 Refer to the above tables.If Germany and the United States engage in trade,the terms of trade will be between:
Refer to the above tables.If Germany and the United States engage in trade,the terms of trade will be between:
A) 3 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.
B) 2 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.
C) 2 and 4 units of chemicals for 1 unit of autos.
D) .33 and .5 unit of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.
In Germany,1 auto = 2 chemicals and in the United States,1 auto = 4 chemicals.Therefore,the terms of trade will be 1 auto = (between)2 to 4 chemicals.
 Refer to the above tables.If Germany and the United States engage in trade,the terms of trade will be between:
Refer to the above tables.If Germany and the United States engage in trade,the terms of trade will be between:A) 3 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.
B) 2 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.
C) 2 and 4 units of chemicals for 1 unit of autos.
D) .33 and .5 unit of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.
In Germany,1 auto = 2 chemicals and in the United States,1 auto = 4 chemicals.Therefore,the terms of trade will be 1 auto = (between)2 to 4 chemicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
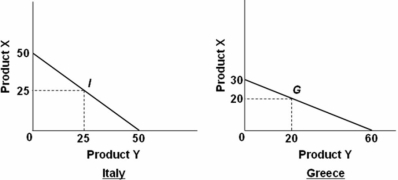 Refer to the above diagrams.Which of the following is a feasible rate at which X and Y might be exchanged?
Refer to the above diagrams.Which of the following is a feasible rate at which X and Y might be exchanged?A) 1X for 3Y
B) 1X for 1.5Y
C) 1X for 2.5Y
D) 1X for .5Y
Italy can specialize by making 50 units of product X and Greece can specialize by making 60 units of product Y.This is a ratio of 1X to 1.2Y.Therefore,a feasible rate to exchange X and Y is 1X for 1.5Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
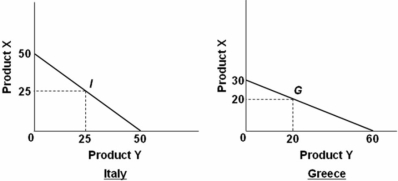 The data embodied in the above diagrams suggest that:
The data embodied in the above diagrams suggest that:A) Italy should export X and Greece should export Y.
B) Greece should export X and Italy should export Y.
C) Production in both countries is subject to increasing costs.
D) Italy should import both X and Y from Greece.
Italy has a comparative advantage in the production of product X because of its lower opportunity cost (1 vs.2),while Greece has a comparative advantage in the production of product Y because of its lower opportunity cost (½ vs.2).Therefore,Italy should export product X and Greece should export product Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The production possibilities table given below shows how many bushels of either wheat or rice can be produced in India and Canada with 1 unit of input.To achieve gains from specialization: 
A) India should export rice to Canada and import Canadian wheat.
B) India should export wheat to Canada and import Canadian rice.
C) Canada should produce both wheat and rice and not trade with India.
D) India should produce both wheat and rice and not trade with Canada.
India has a comparative advantage in producing rice (an opportunity cost of 1 vs.2)while Canada has a comparative advantage in producing wheat (an opportunity cost of ½ vs.1).Therefore,India should export rice and Canada should export wheat.

A) India should export rice to Canada and import Canadian wheat.
B) India should export wheat to Canada and import Canadian rice.
C) Canada should produce both wheat and rice and not trade with India.
D) India should produce both wheat and rice and not trade with Canada.
India has a comparative advantage in producing rice (an opportunity cost of 1 vs.2)while Canada has a comparative advantage in producing wheat (an opportunity cost of ½ vs.1).Therefore,India should export rice and Canada should export wheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
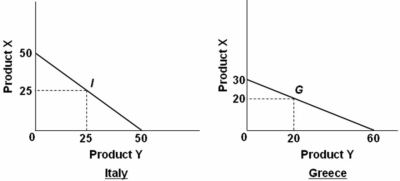 Refer to the above diagrams.Assume that prior to specialization and trade Italy and Greece preferred points I and G on their production possibilities curves.As a result of complete specialization according to comparative advantage,the resulting gains in output will be:
Refer to the above diagrams.Assume that prior to specialization and trade Italy and Greece preferred points I and G on their production possibilities curves.As a result of complete specialization according to comparative advantage,the resulting gains in output will be:A) 5X and 15Y.
B) 10Y.
C) 15X and 5Y.
D) 25X.
Italy should solely make product X (50 units)and Greece should solely make product Y (60 units).Initially,Italy made 25 units of both product X and product Y and Greece made 20 units of both product X and product Y,giving a combined output of 45 units of product X and 45 units of product Y.After specialization,there will be 50 units total of product X and 60 units total of product Y.This is a gain of 5 units of product X and 15 units of product Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The domestic opportunity cost of producing 100 barrels of chemicals in Germany is one ton of steel.In France,the domestic opportunity cost of producing 100 barrels of chemicals is two tons of steel.In this case:
A) France has a comparative advantage in the production of chemicals.
B) Germany has a comparative advantage in the production of chemicals.
C) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if Germany imports chemicals from France and France imports steel from Germany.
D) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if Germany exports steel to France and France exports chemicals to Germany.
The opportunity cost of producing chemicals is 1/100 in Germany and 1/50 in France.The country with the comparative advantage,or lowest opportunity cost,is Germany.
A) France has a comparative advantage in the production of chemicals.
B) Germany has a comparative advantage in the production of chemicals.
C) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if Germany imports chemicals from France and France imports steel from Germany.
D) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if Germany exports steel to France and France exports chemicals to Germany.
The opportunity cost of producing chemicals is 1/100 in Germany and 1/50 in France.The country with the comparative advantage,or lowest opportunity cost,is Germany.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Autos and chemicals are in units of one million 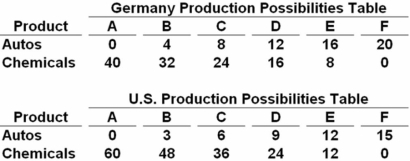 The data in the above tables show that production in:
The data in the above tables show that production in:
A) Germany is subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs and the United States to constant domestic opportunity costs.
B) the United States is subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs and Germany to constant domestic opportunity costs.
C) both Germany and the United States are subject to constant domestic opportunity costs.
D) both Germany and the United States are subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs.
Since both autos and chemicals change by equal amounts in both countries (as you move from one point to another),they are subject to constant opportunity costs.
 The data in the above tables show that production in:
The data in the above tables show that production in:A) Germany is subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs and the United States to constant domestic opportunity costs.
B) the United States is subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs and Germany to constant domestic opportunity costs.
C) both Germany and the United States are subject to constant domestic opportunity costs.
D) both Germany and the United States are subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs.
Since both autos and chemicals change by equal amounts in both countries (as you move from one point to another),they are subject to constant opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Given the following production possibilities schedules,it can be seen that: 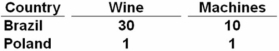
A) Brazil has a comparative advantage in producing wine.
B) Poland can produce more machines than Brazil.
C) Brazil has a comparative advantage in producing machines.
D) Poland can produce more of both goods than Brazil.
Brazil has a lower opportunity cost of producing wine,1/3 vs.1,so therefore it has the comparative advantage.

A) Brazil has a comparative advantage in producing wine.
B) Poland can produce more machines than Brazil.
C) Brazil has a comparative advantage in producing machines.
D) Poland can produce more of both goods than Brazil.
Brazil has a lower opportunity cost of producing wine,1/3 vs.1,so therefore it has the comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Autos and chemicals are in units of one million 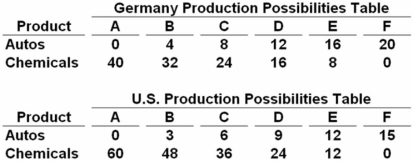 Refer to the above tables.Assume that prior to specialization and trade Germany and the C.Now if each specializes according to its comparative advantage,the resulting total gains from specialization and trade will be: United States both choose production possibility
Refer to the above tables.Assume that prior to specialization and trade Germany and the C.Now if each specializes according to its comparative advantage,the resulting total gains from specialization and trade will be: United States both choose production possibility
A) 8 units of autos.
B) 6 units of autos.
C) 6 units of autos and 8 units of chemicals.
D) 8 units of autos and 6 units of chemicals.
Germany has the comparative advantage in autos because of the lower opportunity cost (3 vs.6),while the United States has the comparative advantage in chemicals because of the lower opportunity cost (1/6 vs.1/3).So,Germany should produce autos and the United States should produce chemicals.Initially,combined output is 14 autos and 60 chemicals.After specialization,output will be 20 autos (from Germany)and 60 chemicals (from the United States).This is a net gain of 6 autos with no increase in chemicals.
 Refer to the above tables.Assume that prior to specialization and trade Germany and the C.Now if each specializes according to its comparative advantage,the resulting total gains from specialization and trade will be: United States both choose production possibility
Refer to the above tables.Assume that prior to specialization and trade Germany and the C.Now if each specializes according to its comparative advantage,the resulting total gains from specialization and trade will be: United States both choose production possibilityA) 8 units of autos.
B) 6 units of autos.
C) 6 units of autos and 8 units of chemicals.
D) 8 units of autos and 6 units of chemicals.
Germany has the comparative advantage in autos because of the lower opportunity cost (3 vs.6),while the United States has the comparative advantage in chemicals because of the lower opportunity cost (1/6 vs.1/3).So,Germany should produce autos and the United States should produce chemicals.Initially,combined output is 14 autos and 60 chemicals.After specialization,output will be 20 autos (from Germany)and 60 chemicals (from the United States).This is a net gain of 6 autos with no increase in chemicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Nation Statum can produce either 800 units of chemicals or 1600 units of clothing.Nation Timin can produce either 200 units of chemicals or 800 units of clothing.
A) Nation Statum has a comparative advantage in producing clothing.
B) Nation Timin has a comparative advantage in producing chemicals.
C) Nation Statum has a comparative advantage in producing chemicals.
D) Nation Timin is the high-cost producer of clothing.
Statum has the comparative advantage in producing chemicals because its opportunity cost is 2,while the opportunity cost in Timin is 4.The country with the lower opportunity cost has the comparative advantage.
A) Nation Statum has a comparative advantage in producing clothing.
B) Nation Timin has a comparative advantage in producing chemicals.
C) Nation Statum has a comparative advantage in producing chemicals.
D) Nation Timin is the high-cost producer of clothing.
Statum has the comparative advantage in producing chemicals because its opportunity cost is 2,while the opportunity cost in Timin is 4.The country with the lower opportunity cost has the comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Countries A and B produce only rubber bands and paper clips under the production possibilities schedules shown below:  In country A the opportunity cost of 1 paper clip is:
In country A the opportunity cost of 1 paper clip is:
A) 2 rubber bands
B) 1 rubber band
C) ½ rubber band
D) ¼ rubber band
The opportunity cost of 1 paper clip = 40/80 = ½ rubber band.
 In country A the opportunity cost of 1 paper clip is:
In country A the opportunity cost of 1 paper clip is:A) 2 rubber bands
B) 1 rubber band
C) ½ rubber band
D) ¼ rubber band
The opportunity cost of 1 paper clip = 40/80 = ½ rubber band.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In Germany,one worker can produce one cuckoo clock or one beer mug.In Taiwan,one worker can produce two cuckoo clocks or three beer mugs.Who has the comparative advantage in each good?
A) Taiwan in both goods
B) Taiwan in clocks and Germany in mugs
C) Germany in clocks and Taiwan in mugs
D) Germany in both goods
The country with the comparative advantage is the one with the lowest opportunity cost.Germany has a comparative advantage in producing clocks (1 vs.1½),while Taiwan has the comparative advantage in producing beer mugs (2/3 vs.1).
A) Taiwan in both goods
B) Taiwan in clocks and Germany in mugs
C) Germany in clocks and Taiwan in mugs
D) Germany in both goods
The country with the comparative advantage is the one with the lowest opportunity cost.Germany has a comparative advantage in producing clocks (1 vs.1½),while Taiwan has the comparative advantage in producing beer mugs (2/3 vs.1).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Answer the next question on the basis of the following production possibilities data for two countries,Alpha and Beta,which have populations of equal size. 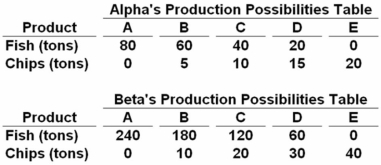 The domestic opportunity cost of:
The domestic opportunity cost of:
A) producing a ton of chips in Alpha is 1/5 of a ton of fish.
B) producing a ton of chips in Beta is 6 tons of fish.
C) catching a ton of fish in Alpha is 5 tons of chips.
D) catching a ton of fish in Beta is 6 tons of chips.
In Beta,the ratio is 60 fish = 10 chips,or 6 fish = 1 chip.
 The domestic opportunity cost of:
The domestic opportunity cost of:A) producing a ton of chips in Alpha is 1/5 of a ton of fish.
B) producing a ton of chips in Beta is 6 tons of fish.
C) catching a ton of fish in Alpha is 5 tons of chips.
D) catching a ton of fish in Beta is 6 tons of chips.
In Beta,the ratio is 60 fish = 10 chips,or 6 fish = 1 chip.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Answer the next question on the basis of the following production possibilities data for two countries,Alpha and Beta,which have populations of equal size. 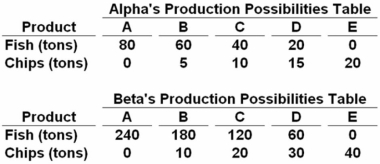 Beta:
Beta:
A) should specialize in catching fish and trade with Alpha for chips.
B) should specialize in producing chips and trade with Alpha for fish.
C) will not realize gains from specialization and trade.
D) will export both fish and chips to Alpha.
Beta has a lower opportunity cost of fish (1/6 vs.¼),so it should specialize in catching fish.
 Beta:
Beta:A) should specialize in catching fish and trade with Alpha for chips.
B) should specialize in producing chips and trade with Alpha for fish.
C) will not realize gains from specialization and trade.
D) will export both fish and chips to Alpha.
Beta has a lower opportunity cost of fish (1/6 vs.¼),so it should specialize in catching fish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If country A has a higher opportunity cost of producing good X than country B,then country:
A) B should impose a tariff on the exports of product X.
B) B has a comparative advantage in the production of product X.
C) A should impose a tariff on the imports of product X.
D) A has a comparative advantage in the production of product X.
A) B should impose a tariff on the exports of product X.
B) B has a comparative advantage in the production of product X.
C) A should impose a tariff on the imports of product X.
D) A has a comparative advantage in the production of product X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose the world economy is composed of just two countries: A and B.Each can produce steel or chemicals but at different levels of economic efficiency.The domestic production possibilities curves are shown in the graphs below. 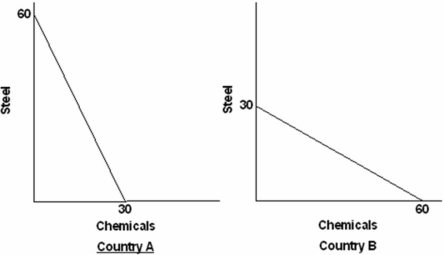 Refer to the above graphs and information.The assumption made about the domestic opportunity costs in countries A and B is that they are:
Refer to the above graphs and information.The assumption made about the domestic opportunity costs in countries A and B is that they are:
A) constant.
B) variable.
C) increasing.
D) decreasing.
 Refer to the above graphs and information.The assumption made about the domestic opportunity costs in countries A and B is that they are:
Refer to the above graphs and information.The assumption made about the domestic opportunity costs in countries A and B is that they are:A) constant.
B) variable.
C) increasing.
D) decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Nation Alpha has a comparative advantage in product X and nation Beta has a comparative advantage in product Y.Trade in the two products will only benefit the two nations if:
A) the exchange ratio of X for Y is fixed.
B) the terms of trade increase in both nations.
C) there is excess capacity in both economies.
D) the prices charged for X and Y reflect their domestic opportunity costs.
A) the exchange ratio of X for Y is fixed.
B) the terms of trade increase in both nations.
C) there is excess capacity in both economies.
D) the prices charged for X and Y reflect their domestic opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the equilibrium exchange rate changes so that fewer dollars are needed to buy a South Korean won,then:
A) Americans will buy fewer Korean goods and services.
B) the won has appreciated in value.
C) fewer U.S.goods and services will be demanded by the South Koreans.
D) the dollar has depreciated in value.
A) Americans will buy fewer Korean goods and services.
B) the won has appreciated in value.
C) fewer U.S.goods and services will be demanded by the South Koreans.
D) the dollar has depreciated in value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If an American can purchase 40,000 British pounds for $90,000,the dollar rate of exchange for the pound is:
A) $1.40.
B) $2.00.
C) $2.25.
D) $6.00.
The dollar rate of exchange is the value of a pound in terms of dollars.Since 40,000 pounds = $90,000,1 pound = $90,000/40,000 = $2.25.
A) $1.40.
B) $2.00.
C) $2.25.
D) $6.00.
The dollar rate of exchange is the value of a pound in terms of dollars.Since 40,000 pounds = $90,000,1 pound = $90,000/40,000 = $2.25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Answer the next question on the basis of the following table,which indicates the dollar price of libras,the currency used in the hypothetical nation of Libra.Assume that a system of freely floating exchange rates is in place. 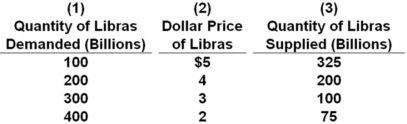 The equilibrium dollar price of libras is:
The equilibrium dollar price of libras is:
A) $5.
B) $4.
C) $3.
D) $2.
Equilibrium occurs where quantity demanded = quantity supplied.
 The equilibrium dollar price of libras is:
The equilibrium dollar price of libras is:A) $5.
B) $4.
C) $3.
D) $2.
Equilibrium occurs where quantity demanded = quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If a Japanese importer could buy $1000 U.S.for 122,000 yen,the rate of exchange for one dollar would be:
A) 112 yen.
B) 122 yen.
C) 1220 yen.
D) 12,200 yen.
Since $1000 = 122,000 yen,$1 = 122,000/1000 = 122 yen.
A) 112 yen.
B) 122 yen.
C) 1220 yen.
D) 12,200 yen.
Since $1000 = 122,000 yen,$1 = 122,000/1000 = 122 yen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
There is a fall in the relative prices of Japanese goods to American goods when the:
A) yen appreciates.
B) dollar appreciates.
C) inflation rate in the United States is higher than the inflation rate in Japan,and there are flexible exchange rates.
D) inflation rate in Japan is higher than the inflation rate in the United States and there are fixed exchange rates.
A) yen appreciates.
B) dollar appreciates.
C) inflation rate in the United States is higher than the inflation rate in Japan,and there are flexible exchange rates.
D) inflation rate in Japan is higher than the inflation rate in the United States and there are fixed exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In one year the dollar would buy 262 Japanese yen,but 10 years later,it would buy only 123 yen.Relative to the yen,the value of the dollar:
A) increased by about 25 percent.
B) decreased by about 53 percent.
C) decreased by about 75 percent.
D) decreased by about 79 percent.
Percentage change = (123 - 262)/262 = -0.53 * 100 = -53 percent.
A) increased by about 25 percent.
B) decreased by about 53 percent.
C) decreased by about 75 percent.
D) decreased by about 79 percent.
Percentage change = (123 - 262)/262 = -0.53 * 100 = -53 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Answer the next question on the basis of the following table,which indicates the dollar price of libras,the currency used in the hypothetical nation of Libra.Assume that a system of freely floating exchange rates is in place. 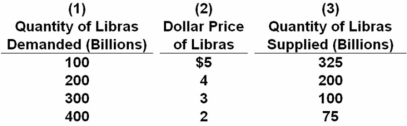 The exchange rate is:
The exchange rate is:
A) 4 libras for one dollar.
B) .25 libra for one dollar.
C) .40 libra for one dollar.
D) 3 libras for one dollar.
At equilibrium,1 libra = $4,so .25 libra = $1.
 The exchange rate is:
The exchange rate is:A) 4 libras for one dollar.
B) .25 libra for one dollar.
C) .40 libra for one dollar.
D) 3 libras for one dollar.
At equilibrium,1 libra = $4,so .25 libra = $1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the rate of exchange for a pound is $4,the rate of exchange for the dollar is:
A) ¼ pound.
B) 4 pounds.
C) $.25.
D) $1.00.
If 1 pound = $4,$1 = 1/4 pound.
A) ¼ pound.
B) 4 pounds.
C) $.25.
D) $1.00.
If 1 pound = $4,$1 = 1/4 pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A market in which the money of one nation is exchanged for the money of another nation is a:
A) resource market.
B) bond market.
C) stock market.
D) foreign exchange market.
A) resource market.
B) bond market.
C) stock market.
D) foreign exchange market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Answer the next question on the basis of the following table,which indicates the dollar price of libras,the currency used in the hypothetical nation of Libra.Assume that a system of freely floating exchange rates is in place. 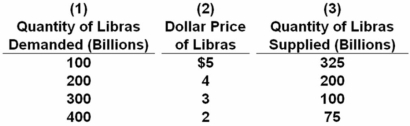 Suppose that Libra decided to import more U.S.products.We would expect the quantity of libras:
Suppose that Libra decided to import more U.S.products.We would expect the quantity of libras:
A) demanded at each dollar price to rise and the dollar to depreciate relative to the libra.
B) demanded at each dollar price to fall and the dollar to appreciate relative to the libra.
C) supplied at each dollar price to rise and the dollar to appreciate relative to the libra.
D) supplied at each dollar price to fall and the dollar to depreciate relative to the libra.
 Suppose that Libra decided to import more U.S.products.We would expect the quantity of libras:
Suppose that Libra decided to import more U.S.products.We would expect the quantity of libras:A) demanded at each dollar price to rise and the dollar to depreciate relative to the libra.
B) demanded at each dollar price to fall and the dollar to appreciate relative to the libra.
C) supplied at each dollar price to rise and the dollar to appreciate relative to the libra.
D) supplied at each dollar price to fall and the dollar to depreciate relative to the libra.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Answer the next question on the basis of the following production possibilities data for two countries,Alpha and Beta,which have populations of equal size. 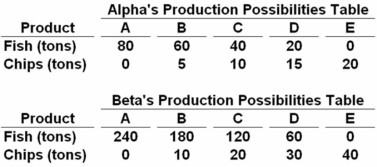 Assume the production possibilities in Beta double at alternatives A through E while remaining as shown in the table for Alpha.As a result Beta should:
Assume the production possibilities in Beta double at alternatives A through E while remaining as shown in the table for Alpha.As a result Beta should:
A) continue to specialize in producing chips.
B) continue to specialize in fishing.
C) no longer specialize and trade.
D) specialize both in fishing and in producing chips and sell the surplus to Alpha.
Doubling all the production possibilities of one country will give the same ratios when calculating opportunity costs.This won't change the results,so Beta should still specialize in fishing.
 Assume the production possibilities in Beta double at alternatives A through E while remaining as shown in the table for Alpha.As a result Beta should:
Assume the production possibilities in Beta double at alternatives A through E while remaining as shown in the table for Alpha.As a result Beta should:A) continue to specialize in producing chips.
B) continue to specialize in fishing.
C) no longer specialize and trade.
D) specialize both in fishing and in producing chips and sell the surplus to Alpha.
Doubling all the production possibilities of one country will give the same ratios when calculating opportunity costs.This won't change the results,so Beta should still specialize in fishing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In considering yen and dollars,when the dollar rate of exchange for the yen rises:
A) the yen rate of exchange for the dollar will fall.
B) the yen rate of exchange for the dollar will also rise.
C) the yen rate of exchange for the dollar may either fall or rise.
D) U.S.net exports to Japan will fall.
A) the yen rate of exchange for the dollar will fall.
B) the yen rate of exchange for the dollar will also rise.
C) the yen rate of exchange for the dollar may either fall or rise.
D) U.S.net exports to Japan will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Answer the next question on the basis of the following production possibilities data for two countries,Alpha and Beta,which have populations of equal size. 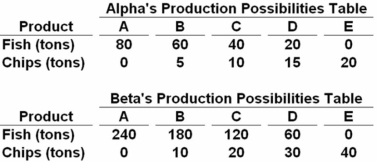 Suppose that before specialization and trade Alpha chose production alternative C and Beta chose production alternative B.After specialization and trade the gains will be:
Suppose that before specialization and trade Alpha chose production alternative C and Beta chose production alternative B.After specialization and trade the gains will be:
A) 20 tons of fish.
B) 20 tons of chips.
C) 20 tons of fish and 20 tons of chips.
D) 240 tons of fish and 20 tons of chips.
Before specialization,total output of fish was 220 (40 + 180)and total output of chips was 20 (10 + 10).After specialization,Beta will produce only fish (240 tons)and Alpha will produce only chips (20 tons).This is a net gain of 20 tons of fish and no change in the amount of chips.
 Suppose that before specialization and trade Alpha chose production alternative C and Beta chose production alternative B.After specialization and trade the gains will be:
Suppose that before specialization and trade Alpha chose production alternative C and Beta chose production alternative B.After specialization and trade the gains will be:A) 20 tons of fish.
B) 20 tons of chips.
C) 20 tons of fish and 20 tons of chips.
D) 240 tons of fish and 20 tons of chips.
Before specialization,total output of fish was 220 (40 + 180)and total output of chips was 20 (10 + 10).After specialization,Beta will produce only fish (240 tons)and Alpha will produce only chips (20 tons).This is a net gain of 20 tons of fish and no change in the amount of chips.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the dollar price of the yen rises,then:
A) the yen price of dollars also rises.
B) the dollar depreciates relative to the yen.
C) the yen depreciates relative to the dollar.
D) the dollar will buy fewer U.S.goods.
A) the yen price of dollars also rises.
B) the dollar depreciates relative to the yen.
C) the yen depreciates relative to the dollar.
D) the dollar will buy fewer U.S.goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In considering euros and dollars,the rates of exchange for the euro and the dollar:
A) are directly related.
B) are inversely related.
C) are unrelated.
D) move in the same direction.
A) are directly related.
B) are inversely related.
C) are unrelated.
D) move in the same direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The following are hypothetical exchange rates: 2 euros = 1 pound;$1 = 2 pounds.We can conclude that:
A) $1 = 4 euros.
B) $1 = .5 euro.
C) 1 euro = $.50.
D) 1 euro = $2.
Since $1 = 2 pounds,1 pound = $1/2 = $.50.Substituting into the first equation: 2 euros = $.50,so 4 euros = $1 (2 * 2 = $.50 * 2).
A) $1 = 4 euros.
B) $1 = .5 euro.
C) 1 euro = $.50.
D) 1 euro = $2.
Since $1 = 2 pounds,1 pound = $1/2 = $.50.Substituting into the first equation: 2 euros = $.50,so 4 euros = $1 (2 * 2 = $.50 * 2).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If the exchange rate between the U.S.dollar and the Japanese yen is $1 = 200 yen,then the dollar price of the yen is:
A) $.005.
B) $.05.
C) $.50.
D) $5.
Since $1 = 200 yen,1 yen = $1/200 = $.005.
A) $.005.
B) $.05.
C) $.50.
D) $5.
Since $1 = 200 yen,1 yen = $1/200 = $.005.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The following are hypothetical exchange rates: $1 = 140 yen;1 Swiss franc = $.10.We can conclude that:
A) 1 yen = 280 Swiss francs.
B) 1 yen = 14 Swiss francs.
C) 1 Swiss franc = 28 yen.
D) 1 Swiss franc = 14 yen.
If $1 = 140 yen,then $.10 = 14 yen.Since 1 Swiss franc = $.10,1 Swiss franc also = 14 yen.
A) 1 yen = 280 Swiss francs.
B) 1 yen = 14 Swiss francs.
C) 1 Swiss franc = 28 yen.
D) 1 Swiss franc = 14 yen.
If $1 = 140 yen,then $.10 = 14 yen.Since 1 Swiss franc = $.10,1 Swiss franc also = 14 yen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If the U.S.dollar appreciates relative to the British pound,then:
A) the pound will appreciate relative to the U.S.dollar.
B) the pound will depreciate relative to the U.S.dollar.
C) British goods will be more expensive for Americans.
D) American goods will be less expensive for the British.
A) the pound will appreciate relative to the U.S.dollar.
B) the pound will depreciate relative to the U.S.dollar.
C) British goods will be more expensive for Americans.
D) American goods will be less expensive for the British.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Foreign exchange rates refer to the:
A) price at which purchases and sales of foreign goods take place.
B) movement of goods and services from one nation to another.
C) price of one nation's currency in terms of a second nation's currency.
D) difference between exports and imports in a particular nation.
A) price at which purchases and sales of foreign goods take place.
B) movement of goods and services from one nation to another.
C) price of one nation's currency in terms of a second nation's currency.
D) difference between exports and imports in a particular nation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The following diagram is a flexible exchange market for foreign currency: 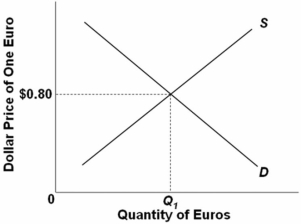 Other things equal,a rightward shift of the supply curve would:
Other things equal,a rightward shift of the supply curve would:
A) appreciate the euro.
B) cause a surplus of euros.
C) decrease the equilibrium quantity of euros.
D) appreciate the dollar.
 Other things equal,a rightward shift of the supply curve would:
Other things equal,a rightward shift of the supply curve would:A) appreciate the euro.
B) cause a surplus of euros.
C) decrease the equilibrium quantity of euros.
D) appreciate the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In comparing a tariff and an import quota,we find that:
A) the tariff and quota both generate the same amount of revenue for the U.S.Treasury.
B) the tariff generates revenue for the U.S.Treasury,but the quota does not.
C) the quota generates revenue for the U.S.Treasury,but the tariff does not.
D) neither the tariff nor the quota generates revenue for the U.S.Treasury.
A) the tariff and quota both generate the same amount of revenue for the U.S.Treasury.
B) the tariff generates revenue for the U.S.Treasury,but the quota does not.
C) the quota generates revenue for the U.S.Treasury,but the tariff does not.
D) neither the tariff nor the quota generates revenue for the U.S.Treasury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Depreciation of the dollar will:
A) decrease the prices of both U.S.imports and exports.
B) increase the prices of both U.S.imports and exports.
C) decrease the prices of U.S.imports but increase the prices to foreigners of U.S.exports.
D) increase the prices of U.S.imports but decrease the prices to foreigners of U.S.exports.
A) decrease the prices of both U.S.imports and exports.
B) increase the prices of both U.S.imports and exports.
C) decrease the prices of U.S.imports but increase the prices to foreigners of U.S.exports.
D) increase the prices of U.S.imports but decrease the prices to foreigners of U.S.exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Other things equal,economists would prefer:
A) free trade to tariffs and tariffs to import quotas.
B) free trade to import quotas and import quotas to tariffs.
C) import quotas to tariffs and tariffs to voluntary export restrictions.
D) import quotas to free trade and free trade to tariffs.
A) free trade to tariffs and tariffs to import quotas.
B) free trade to import quotas and import quotas to tariffs.
C) import quotas to tariffs and tariffs to voluntary export restrictions.
D) import quotas to free trade and free trade to tariffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The U.S.demand for British pounds is:
A) downsloping because a higher dollar price of pounds means British goods are cheaper to Americans.
B) downsloping because a lower dollar price of pounds means British goods are more expensive to Americans.
C) upsloping because a lower dollar price of pounds means British goods are cheaper to Americans.
D) downsloping because a lower dollar price of pounds means British goods are cheaper to Americans.
A) downsloping because a higher dollar price of pounds means British goods are cheaper to Americans.
B) downsloping because a lower dollar price of pounds means British goods are more expensive to Americans.
C) upsloping because a lower dollar price of pounds means British goods are cheaper to Americans.
D) downsloping because a lower dollar price of pounds means British goods are cheaper to Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A protective tariff will:
A) increase the sales of foreign exporters.
B) increase the price and sales of domestic producers.
C) increase the welfare of domestic consumers.
D) create an efficiency gain in the domestic economy.
A) increase the sales of foreign exporters.
B) increase the price and sales of domestic producers.
C) increase the welfare of domestic consumers.
D) create an efficiency gain in the domestic economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The increased-domestic-employment argument for tariff protection holds that:
A) domestic inflation is a desirable policy goal because it stimulates exports.
B) domestic deflation is a desirable policy goal because it stimulates imports.
C) an increase in tariffs will reduce net exports and stimulate domestic employment.
D) an increase in tariffs will increase net exports and stimulate domestic employment.
A) domestic inflation is a desirable policy goal because it stimulates exports.
B) domestic deflation is a desirable policy goal because it stimulates imports.
C) an increase in tariffs will reduce net exports and stimulate domestic employment.
D) an increase in tariffs will increase net exports and stimulate domestic employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If the exchange rate changes so that more Mexican pesos are required to buy a dollar,then:
A) the peso has appreciated in value.
B) Americans will buy more Mexican goods and services.
C) more U.S.goods and services will be demanded by the Mexicans.
D) the dollar has depreciated in value.
A) the peso has appreciated in value.
B) Americans will buy more Mexican goods and services.
C) more U.S.goods and services will be demanded by the Mexicans.
D) the dollar has depreciated in value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The U.S.supply of Japanese yen is:
A) downsloping because a lower dollar price of yen means U.S.goods are cheaper to the Japanese.
B) upsloping because a higher dollar price of yen means U.S.goods are cheaper to the Japanese.
C) upsloping because a lower dollar price of yen means U.S.goods are cheaper to the Japanese.
D) downsloping because a higher dollar price of yen means U.S.goods are cheaper to the Japanese.
A) downsloping because a lower dollar price of yen means U.S.goods are cheaper to the Japanese.
B) upsloping because a higher dollar price of yen means U.S.goods are cheaper to the Japanese.
C) upsloping because a lower dollar price of yen means U.S.goods are cheaper to the Japanese.
D) downsloping because a higher dollar price of yen means U.S.goods are cheaper to the Japanese.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following arguments comes closest to constituting a legitimate economic exception to the case for free trade?
A) The increase-domestic-employment argument
B) The cheap-foreign-labor argument
C) The diversification-for-stability argument
D) The infant-industry argument
A) The increase-domestic-employment argument
B) The cheap-foreign-labor argument
C) The diversification-for-stability argument
D) The infant-industry argument

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If the dollar depreciates relative to the Russian ruble,the ruble:
A) will be less expensive to Americans.
B) may either appreciate or depreciate relative to the dollar.
C) will appreciate relative to the dollar.
D) will depreciate relative to the dollar.
A) will be less expensive to Americans.
B) may either appreciate or depreciate relative to the dollar.
C) will appreciate relative to the dollar.
D) will depreciate relative to the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Appreciation of the Canadian dollar will:
A) intensify an existing disequilibrium in Canada' balance of payments.
B) make Canada's exports less expensive and its imports more expensive.
C) make Canada's exports more expensive and its imports less expensive.
D) make Canada's exports and imports both more expensive.
A) intensify an existing disequilibrium in Canada' balance of payments.
B) make Canada's exports less expensive and its imports more expensive.
C) make Canada's exports more expensive and its imports less expensive.
D) make Canada's exports and imports both more expensive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In effect tariffs on imports are:
A) special taxes on domestic producers.
B) subsidies to domestic consumers.
C) subsidies to foreign producers.
D) subsidies for domestic producers.
A) special taxes on domestic producers.
B) subsidies to domestic consumers.
C) subsidies to foreign producers.
D) subsidies for domestic producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The following diagram is a flexible exchange market for foreign currency: 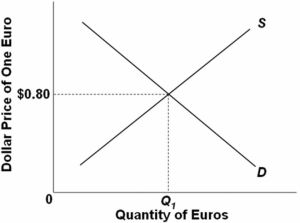 Other things equal,a leftward shift of the supply curve would:
Other things equal,a leftward shift of the supply curve would:
A) appreciate the euro.
B) cause a shortage of euros.
C) increase the equilibrium quantity of euros.
D) appreciate the dollar.
 Other things equal,a leftward shift of the supply curve would:
Other things equal,a leftward shift of the supply curve would:A) appreciate the euro.
B) cause a shortage of euros.
C) increase the equilibrium quantity of euros.
D) appreciate the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following will generate a demand for country X's currency in the foreign exchange market?
A) Travel by citizens of country X in other countries
B) The desire of foreigners to buy stocks and bonds of firms in country X
C) The imports of country X
D) Charitable contributions by country X's citizens to citizens of developing nations
A) Travel by citizens of country X in other countries
B) The desire of foreigners to buy stocks and bonds of firms in country X
C) The imports of country X
D) Charitable contributions by country X's citizens to citizens of developing nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The following diagram is a flexible exchange market for foreign currency: 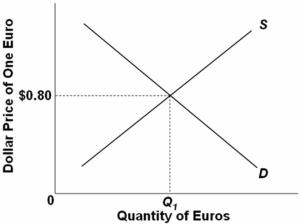 Other things equal,a rightward shift of the demand curve would:
Other things equal,a rightward shift of the demand curve would:
A) depreciate the dollar.
B) appreciate the dollar.
C) reduce the equilibrium quantity of euros.
D) depreciate the euro.
 Other things equal,a rightward shift of the demand curve would:
Other things equal,a rightward shift of the demand curve would:A) depreciate the dollar.
B) appreciate the dollar.
C) reduce the equilibrium quantity of euros.
D) depreciate the euro.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The following diagram is a flexible exchange market for foreign currency: 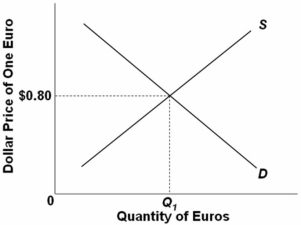 At the price $.80 for one euro:
At the price $.80 for one euro:
A) the quantity of euros demanded equals the quantity supplied.
B) the dollar-euro exchange rate is unstable.
C) the dollar price of one euro equals the euro price of one dollar.
D) there will be a surplus of euros in the foreign exchange market.
 At the price $.80 for one euro:
At the price $.80 for one euro:A) the quantity of euros demanded equals the quantity supplied.
B) the dollar-euro exchange rate is unstable.
C) the dollar price of one euro equals the euro price of one dollar.
D) there will be a surplus of euros in the foreign exchange market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The following diagram is a flexible exchange market for foreign currency: 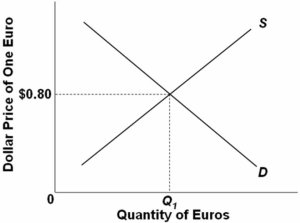 Other things equal,a leftward shift of the demand curve would:
Other things equal,a leftward shift of the demand curve would:
A) depreciate the dollar.
B) appreciate the euro.
C) reduce the equilibrium quantity of euros.
D) cause a shortage of euros.
 Other things equal,a leftward shift of the demand curve would:
Other things equal,a leftward shift of the demand curve would:A) depreciate the dollar.
B) appreciate the euro.
C) reduce the equilibrium quantity of euros.
D) cause a shortage of euros.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The U.S.demand for euros is:
A) downsloping because,at lower dollar prices for euros,Americans will want to buy more European goods and services.
B) downsloping because,at higher dollar prices for euros,Americans will want to buy more European goods and services.
C) downsloping because the dollar price of euros and the euro price of dollars are directly related.
D) upsloping because a higher dollar price of euros makes European goods and services more attractive to Americans.
A) downsloping because,at lower dollar prices for euros,Americans will want to buy more European goods and services.
B) downsloping because,at higher dollar prices for euros,Americans will want to buy more European goods and services.
C) downsloping because the dollar price of euros and the euro price of dollars are directly related.
D) upsloping because a higher dollar price of euros makes European goods and services more attractive to Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Other things equal,a tariff is:
A) superior to an import quota for Americans because a tariff increases the profits of foreign producers.
B) inferior to an import quota for Americans because a tariff increases the profits of domestic producers.
C) superior to an import quota for Americans because a tariff generates revenue for the U.S.Treasury.
D) inferior to an import quota for Americans because a tariff generates revenue for the U.S.Treasury.
A) superior to an import quota for Americans because a tariff increases the profits of foreign producers.
B) inferior to an import quota for Americans because a tariff increases the profits of domestic producers.
C) superior to an import quota for Americans because a tariff generates revenue for the U.S.Treasury.
D) inferior to an import quota for Americans because a tariff generates revenue for the U.S.Treasury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



