Deck 18: Accounting for Income Taxes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Accounting for Income Taxes
1
According to AASB 112,with one exception,the tax base of a liability is to be determined in the following manner:
Carrying amount - Future deductible amount + Future assessable amount.
Carrying amount - Future deductible amount + Future assessable amount.
True
2
The balance sheet approach to accounting for taxation relies on comparing the historical cost of an item with its appropriate tax base.
False
3
AASB 112 defines the tax base as the amount that is attributed to an asset or liability for tax purposes.
True
4
There are two types of temporary differences between the carrying value of assets and liabilities and the tax base-assessable temporary differences and neutral temporary differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
It is possible for a firm to legally make a large accounting profit but pay little or no tax based on its taxable income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Under AASB 112,where the carrying amount of an asset is less than the amount that is economically recoverable,the deferred tax asset should be adjusted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Profit for taxation purposes is determined in accordance with AASB 112.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When a non-current asset is revalued,the recognition of future tax associated with an asset that has a fair value in excess of cost,acts to reduce the amount of the revaluation reserve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The tax base of revenue received in advance is equal to zero where the revenue received is taxed in the reporting period that the revenue is received.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When a non-current asset is revalued the tax base is not affected as depreciation for tax purposes will continue to be based on original cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Non-deductible expenses in the current or subsequent periods results in a deferred tax asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its tax base,the amount that will be allowed as a deduction for tax purposes will exceed the amount of assessable economic benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Deferred tax assets arise as a result of tax losses.In Australia losses incurred in previous years can always be carried forward to offset taxable income derived in future years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The balance sheet approach compares the carrying value with the tax base of the assets and liabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The tax-effect of the temporary difference that arises from revaluation of non-current assets is recognised in profit and loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The tax figure calculated and recorded on the statement of comprehensive income is an accurate reflection of the entity's tax liability for the stated period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
AASB 112 required an entity to offset current tax assets and current tax liabilities if the entity intends to realise the asset and settle the liability simultaneously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Deferred tax assets may arise from amounts of income taxes recoverable in future periods that arise from carry forward of unused tax losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The difference between the carrying amount of an asset or liability in the balance sheet and its tax base is a temporary difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Deferred tax assets are the amounts of income taxes recoverable in future periods that arise from assessable temporary differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The generally accepted (a)accounting rule and (b)tax rule for development expenditure are:
A) (a) capitalise and amortise; (b) a tax deduction when paid for.
B) (b) expense when paid for; (b) a tax deduction when paid for.
C) (c) capitalise and amortise; (b) a tax deduction when amortised.
D) (d) expense when paid for; (b) a tax deduction when amortised.
A) (a) capitalise and amortise; (b) a tax deduction when paid for.
B) (b) expense when paid for; (b) a tax deduction when paid for.
C) (c) capitalise and amortise; (b) a tax deduction when amortised.
D) (d) expense when paid for; (b) a tax deduction when amortised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Tissues Ltd has a depreciable asset that is estimated for accounting purposes to have a useful life of 8 years.For taxation purposes the useful life is 5 years.The asset was purchased at the beginning of year 1,there is no residual value,and the straight-line method of depreciation is used for both tax and accounting purposes.The tax rate is 30% and the cost of the asset is $100 000.What is the amount of the deferred tax liability account generated by this asset at the end of years 1,2 and 3?
A) End of year 1 $0; year 2 $2250; year 3: $4500
B) End of year 1 $7500; year 2 $15,000; year 3: $22 500
C) End of year 1 $6750; year 2 $4500; year 3: $2250
D) End of year 1 $2250; year 2 $4500; year 3: $6750
A) End of year 1 $0; year 2 $2250; year 3: $4500
B) End of year 1 $7500; year 2 $15,000; year 3: $22 500
C) End of year 1 $6750; year 2 $4500; year 3: $2250
D) End of year 1 $2250; year 2 $4500; year 3: $6750

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A company has a loan with a carrying value of $60 000.The payment of the loan is not deductible for tax purposes.The tax rate is 30%.What is the tax base for this item?
A) $0
B) $60 000
C) $18 000
D) $78 000
A) $0
B) $60 000
C) $18 000
D) $78 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A deductible temporary difference is one that will result in:
A) a decrease in income tax recoverable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
B) an increase in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
C) a decrease in income tax recoverable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled, and an increase in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
D) a decrease in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
A) a decrease in income tax recoverable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
B) an increase in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
C) a decrease in income tax recoverable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled, and an increase in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
D) a decrease in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A company has received $40 000 for subscription revenue in advance and recorded a liability account 'revenue received in advance'.Revenue is taxed when it is received.The tax rate is 30%.What is the tax base for this item?
A) $0
B) $40 000
C) $12 000
D) $36 000
A) $0
B) $40 000
C) $12 000
D) $36 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Bulldog Supplies Ltd has an item of equipment that has a carrying value of $80 000.For taxation purposes the asset's net value is $60 000 and deferred tax liabilities of $3000 had previously been recorded.Bulldog also has accrued interest revenue of $5000 that will not be taxed until it is received in cash.The tax rate is 30%.What is the journal entry to record the tax effect?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A deferred tax asset arises if:
A) the carrying amount of an asset is greater than its tax base
B) the carrying amount of a liability is greater than its tax base
C) the carrying amount of a liability is less than its tax base
D) the carrying amount of an asset is greater than its tax base and the carrying amount of a liability is less than its tax base
A) the carrying amount of an asset is greater than its tax base
B) the carrying amount of a liability is greater than its tax base
C) the carrying amount of a liability is less than its tax base
D) the carrying amount of an asset is greater than its tax base and the carrying amount of a liability is less than its tax base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Snifful Industries has a depreciable asset that is estimated for accounting purposes to have a useful life of 7 years.For taxation purposes the useful life is 3 years.The asset was purchased at the beginning of year 1,there is no residual value,and the straight-line method of depreciation is used for both tax and accounting purposes.The tax rate is 30% and the cost of the asset is $210 000.What is the amount of the deferred tax liability account generated by this asset at the end of years 2,3 and 4?
A) End of year 2: $24 000; year 3: $36 000; year 4: $27 000
B) End of year 2: $80 000; year 3: $120 000; year 4: $90 000
C) End of year 2: $12 000; year 3: $24 000; year 4: $36 000
D) End of year 2: $12 000; year 3: $12 000; year 4: $(9000)
A) End of year 2: $24 000; year 3: $36 000; year 4: $27 000
B) End of year 2: $80 000; year 3: $120 000; year 4: $90 000
C) End of year 2: $12 000; year 3: $24 000; year 4: $36 000
D) End of year 2: $12 000; year 3: $12 000; year 4: $(9000)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
AASB 112 uses what term to describe the method for accounting for taxes that it mandates?
A) net balances method
B) financial position method
C) asset and liability method
D) balance sheet method
A) net balances method
B) financial position method
C) asset and liability method
D) balance sheet method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A taxable temporary difference is one that will result in:
A) an increase in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
B) a decrease in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
C) an increase in income tax recoverable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
D) a decrease in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled and an increase in income tax recoverable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
A) an increase in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
B) a decrease in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
C) an increase in income tax recoverable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
D) a decrease in income tax payable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled and an increase in income tax recoverable in future reporting periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The tax base is defined in AASB 112 as:
A) the amount of assessable income for the period.
B) the tax rate applicable to income levels under $60 000.
C) the amount that is attributed to an asset or liability for tax purposes.
D) the head office of the Australian Taxation Office in Canberra.
A) the amount of assessable income for the period.
B) the tax rate applicable to income levels under $60 000.
C) the amount that is attributed to an asset or liability for tax purposes.
D) the head office of the Australian Taxation Office in Canberra.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The correct method for calculating the amount of a deferred tax liability or asset may be expressed as a formula as follows:
A) (Carrying amount of assets or liabilities - tax bases of assets or liabilities) × tax rate
B) Carrying amount of assets or liabilities - (tax bases of assets or liabilities × tax rate)
C) Carrying amount of assets or liabilities - tax bases of assets or liabilities × tax rate
D) Carrying amount of assets or liabilities - tax bases of assets or liabilities
A) (Carrying amount of assets or liabilities - tax bases of assets or liabilities) × tax rate
B) Carrying amount of assets or liabilities - (tax bases of assets or liabilities × tax rate)
C) Carrying amount of assets or liabilities - tax bases of assets or liabilities × tax rate
D) Carrying amount of assets or liabilities - tax bases of assets or liabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Sinfonia Ltd made credit sales for this period of $100 000.The allowance for doubtful debts for these sales is $3000.For taxation purposes the amount provided for doubtful debts is not tax-deductible and the taxation office has included the $100 000 in taxable income.The tax rate is 30%.What is the deferral arising from this situation?
A) none
B) deferred tax liability of $900
C) deferred tax asset of $900
D) deferred tax liability of $3000
A) none
B) deferred tax liability of $900
C) deferred tax asset of $900
D) deferred tax liability of $3000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Some items are treated as a deduction for tax purposes when they are paid but are recognised as expenses when they are accrued for accounting purposes.Which of the following items are of that type?
A) long-service leave
B) goodwill amortisation
C) depreciation
D) entertainment
A) long-service leave
B) goodwill amortisation
C) depreciation
D) entertainment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Under the approach of AASB 112 to accounting for income taxes,a deductible temporary difference creates which account?
A) deferred tax revenue
B) deferred tax liability
C) deferred tax asset
D) provision for tax payable
A) deferred tax revenue
B) deferred tax liability
C) deferred tax asset
D) provision for tax payable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The AASB 112 approach has been adopted because:
A) it matches the revenues earned with tax payable on those revenues.
B) it is conservative.
C) it is considered consistent with the AASB Conceptual Framework.
D) it is considered acceptable by the ATO.
A) it matches the revenues earned with tax payable on those revenues.
B) it is conservative.
C) it is considered consistent with the AASB Conceptual Framework.
D) it is considered acceptable by the ATO.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A change in tax rates does not require any change in the carrying amount of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Under the approach of AASB 112 to accounting for income taxes,a taxable temporary difference creates which account?
A) provision for tax payable
B) deferred tax asset
C) general reserve
D) deferred tax liability
A) provision for tax payable
B) deferred tax asset
C) general reserve
D) deferred tax liability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Some items are typically not allowable tax deductions but are recognised as an expense for accounting purposes.Which of the following items are of that type?
A) research and development costs
B) warranty costs
C) sick leave payments
D) goodwill amortisation
A) research and development costs
B) warranty costs
C) sick leave payments
D) goodwill amortisation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The amount of tax assessed by the ATO based on the entity's operations for the period will be reflected in which account?
A) income tax expense
B) deferred income tax
C) deferred tax liability
D) income tax payable
A) income tax expense
B) deferred income tax
C) deferred tax liability
D) income tax payable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Casper Ltd incurred a loss of $500 000 for tax purposes in 2014.This was due to one-off circumstances and it is expected that Casper will make profits again in 2015 and subsequent years.There are no temporary differences in either year.In 2015 Casper makes a profit of $700 000.The tax rate is 30%.What are the journal entries for 2014 and 2015?
A)
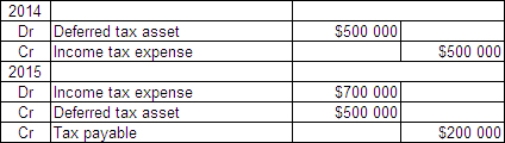
B)
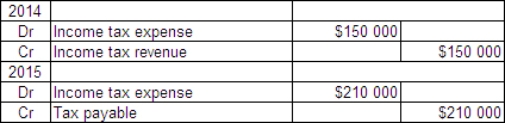
C)

D)
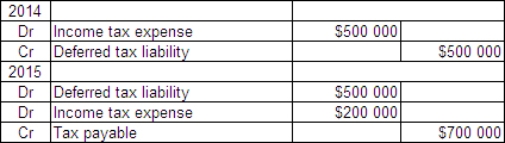
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Some items are typically not allowable tax deductions but are recognised as an expense for accounting purposes.Which of the following items are of that type?
A) research and development costs
B) warranty costs
C) sick leave payments
D) entertainment
A) research and development costs
B) warranty costs
C) sick leave payments
D) entertainment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The carrying amount of a deferred tax asset is reviewed:
A) annually
B) at each reporting date
C) when assets are revalued
D) None of the given answers are correct.
A) annually
B) at each reporting date
C) when assets are revalued
D) None of the given answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Digitor Industries Ltd accrues long-service leave as employees work towards their entitlement.For tax purposes,long-service leave is not deductible until it is paid.During the current period Digitor has accrued $50 000 in long-service leave expense and paid none.The tax rate is 30%.What is the journal entry to record the deferral?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Mighty Motors Ltd offers a warranty on all the spare parts it sells.This period the accrued warranty is $5000.For tax purposes there is no deduction for the warranty until payments are made.Mighty Motors also has equipment that has a useful life for accounting purposes of 4 years and for tax purposes 3 years.The equipment was purchased at the beginning of the current period,cost $9000 and has no residual value.The straight-line method of depreciation is used for both accounting and tax purposes.The accounting profit before tax this period is $80 000.The tax rate is 30%.What are the journal entries to record the tax expense and tax payable?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The carrying amount of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities can change:
A) with a change in the amount of the related temporary differences.
B) even if there is no change in the amount of the related temporary differences.
C) with a re-assessment of the recoverability of deferred tax liabilities.
D) with a change in the amount of the related temporary differences and even if there is no change in the amount of the related temporary differences.
A) with a change in the amount of the related temporary differences.
B) even if there is no change in the amount of the related temporary differences.
C) with a re-assessment of the recoverability of deferred tax liabilities.
D) with a change in the amount of the related temporary differences and even if there is no change in the amount of the related temporary differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The criterion for recognising a deferred tax asset is that:
A) it should be fully recognised if it is probable that future taxable amounts within the entity will be available against which the deductible temporary differences can be utilised.
B) it should be recognised if it is possible that future taxable amounts within the entity will be available against which the deductible temporary differences can be utilised.
C) it should be recognised to the extent, and only to the extent, that it is possible that future taxable amounts within the entity will be available against which the deductible temporary differences can be utilised.
D) it should be recognised to the extent, and only to the extent, that it is probable that future taxable amounts within the entity will be available against which the deductible temporary differences can be utilised.
A) it should be fully recognised if it is probable that future taxable amounts within the entity will be available against which the deductible temporary differences can be utilised.
B) it should be recognised if it is possible that future taxable amounts within the entity will be available against which the deductible temporary differences can be utilised.
C) it should be recognised to the extent, and only to the extent, that it is possible that future taxable amounts within the entity will be available against which the deductible temporary differences can be utilised.
D) it should be recognised to the extent, and only to the extent, that it is probable that future taxable amounts within the entity will be available against which the deductible temporary differences can be utilised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The amount of tax calculated based on the entity's operations for the period will be reflected in which account?
A) income tax expense
B) deferred income tax
C) deferred tax liability
D) income tax payable
A) income tax expense
B) deferred income tax
C) deferred tax liability
D) income tax payable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The balance sheet approach adopted in AASB 112:
A) will continue to be used as the alternatives are too simplistic.
B) will only be understood by the very sophisticated financial readers.
C) uses existing statement of financial position data thus reducing record keeping costs.
D) will only be understood by the very sophisticated financial readers and uses existing statement of financial position data thus reducing record keeping costs.
A) will continue to be used as the alternatives are too simplistic.
B) will only be understood by the very sophisticated financial readers.
C) uses existing statement of financial position data thus reducing record keeping costs.
D) will only be understood by the very sophisticated financial readers and uses existing statement of financial position data thus reducing record keeping costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Temporary differences:
A) arise due to differences between income tax legislation and accounting rules, in a particular period, and are reversed in subsequent periods.
B) can be both deductible temporary differences or taxable temporary differences.
C) must be considered, and accounted for, by the creation of deferred tax asset and liabilities for all statement of financial position items (e.g. including asset revaluations), rather than just statement of comprehensive income items, which is a major change created by the new standard.
D) arise due to changes in the income tax rate.
A) arise due to differences between income tax legislation and accounting rules, in a particular period, and are reversed in subsequent periods.
B) can be both deductible temporary differences or taxable temporary differences.
C) must be considered, and accounted for, by the creation of deferred tax asset and liabilities for all statement of financial position items (e.g. including asset revaluations), rather than just statement of comprehensive income items, which is a major change created by the new standard.
D) arise due to changes in the income tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Criteria used by an entity to assess the probability that taxable profit will be available against which unused tax losses can be utilised include:
A) whether the unused tax losses result from identifiable causes that are unlikely to recur.
B) whether it is probable that the entity will have taxable profits before the unused tax losses expire.
C) whether permission has been received from the Australian Taxation Office to carry forward tax losses.
D) whether the entity has unused tax losses relating to the same taxation authority and the same taxable entity, which will result in taxable amounts against which the unused tax losses can be utilised before they expire.
A) whether the unused tax losses result from identifiable causes that are unlikely to recur.
B) whether it is probable that the entity will have taxable profits before the unused tax losses expire.
C) whether permission has been received from the Australian Taxation Office to carry forward tax losses.
D) whether the entity has unused tax losses relating to the same taxation authority and the same taxable entity, which will result in taxable amounts against which the unused tax losses can be utilised before they expire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
As at 30 June 2012,net accounts receivables was $57 000,and the allowance for doubtful debts was $3000.On 30 June 2013,the respective balances were $64 000 and $4000.Assuming there were no other temporary differences,what is the journal entry to adjust for the changes in these balances as at 30 June 2013? The corporate tax rate is 30%.
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The tax base of a liability must be calculated as the liability's carrying amount as at the reporting date,less any future deductible amounts and plus any future assessable amounts that are expected to arise from settling the liability's carrying amount as at the reporting date.The exception to this rule is that:
A) In the case of revenue received in advance, the tax base must be calculated as the liability's carrying amount less any amount of the revenue received in advance that has been included in taxable amounts in the current or a previous reporting period.
B) In the case of carry forward tax losses, the tax base must be adjusted for any consideration paid by a company within the group that is receiving the transferred tax loss.
C) In the case of a downward revaluation of a non-current asset, the tax base must be calculated as the decrease in the asset plus any amount expected to be received in the future inflated by the index for capital gains tax.
D) In the case of a warranty liability, the tax base must be calculated as the liability's carrying amount less any amounts paid out this period that have not been included in taxable amounts in the current period.
A) In the case of revenue received in advance, the tax base must be calculated as the liability's carrying amount less any amount of the revenue received in advance that has been included in taxable amounts in the current or a previous reporting period.
B) In the case of carry forward tax losses, the tax base must be adjusted for any consideration paid by a company within the group that is receiving the transferred tax loss.
C) In the case of a downward revaluation of a non-current asset, the tax base must be calculated as the decrease in the asset plus any amount expected to be received in the future inflated by the index for capital gains tax.
D) In the case of a warranty liability, the tax base must be calculated as the liability's carrying amount less any amounts paid out this period that have not been included in taxable amounts in the current period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Spring Day Ltd has a piece of equipment that it has revalued to its fair value of $90 000 this period.It originally cost $80 000 and the accumulated depreciation for both accounting and tax purposes is $20 000.There is no intention to sell the equipment in the near future.The tax rate is 30%.What is the journal entry to reflect the revaluation's tax implications?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When the carrying amount of an asset exceeds the tax base,there will be a deferred tax ,because the taxation payments have effectively been .
A) asset; made in advance of recognising the expense
B) asset; deferred to future periods
C) liability; made in advance of recognising the expense
D) liability; deferred to future periods
A) asset; made in advance of recognising the expense
B) asset; deferred to future periods
C) liability; made in advance of recognising the expense
D) liability; deferred to future periods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Raging Dragons Ltd has a depreciable asset that is estimated for accounting purposes to have a useful life of 15 years.For taxation purposes the useful life is 10 years.The asset was purchased at the beginning of year 1,there is no residual value,and the straight-line method of depreciation is used for both tax and accounting purposes.The tax rate is 30% and the cost of the asset is $150 000.What adjustment will be required to the deferred tax liability account in years 10 and 11?
A) End of year 10 $1500; year 11 $1500
B) End of year 10 $5000; year 11 $(10 000)
C) End of year 10 $1500; year 11 $(3000)
D) End of year 10 $15 000; year 11 $(3000)
A) End of year 10 $1500; year 11 $1500
B) End of year 10 $5000; year 11 $(10 000)
C) End of year 10 $1500; year 11 $(3000)
D) End of year 10 $15 000; year 11 $(3000)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
As at 30 June 2012,the Provision for Long-service leave balance was $125 000.During 2011/12 $54 000 was charged to the provision account,and leave to the value of $34 000 was taken by staff.The balance on 30 June 2013 was $135 000,following the charging of long-service leave expense of the same amount as in 2011/12 ,i.e.$54 000.Assuming there were no other temporary differences,what is the journal entry to adjust for the changes in these balances as at 30 June 2013? The corporate tax rate is 30%.
A)
B)
C)
.
D)
A)
B)
C)
.
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Recognising deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities as per AASB 112 creates some conflict with the definition of assets and liabilities in the AASB Conceptual Framework.Key issues in this regard are:
A) It is questionable whether or not the company controls the benefits from the deferred tax asset, and there is not a present obligation to transfer the funds represented in the deferred tax liability to the government.
B) The company really has no claim against the government for the amount of the deferred tax asset and it is not probable that the company will have to pay the deferred tax liability.
C) Setting off the deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability does not meet the requirements of the AASB Conceptual Framework and there is a contingent element involved in the recognition of the deferred tax asset.
D) The AASB Conceptual Framework does not permit the recognition of the rights to future revenues implicit in assets to trigger obligations to future expenses implicit in liabilities and the extent to which a deferred tax liability is recognised should not depend on management's intention to sell a revalued asset.
A) It is questionable whether or not the company controls the benefits from the deferred tax asset, and there is not a present obligation to transfer the funds represented in the deferred tax liability to the government.
B) The company really has no claim against the government for the amount of the deferred tax asset and it is not probable that the company will have to pay the deferred tax liability.
C) Setting off the deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability does not meet the requirements of the AASB Conceptual Framework and there is a contingent element involved in the recognition of the deferred tax asset.
D) The AASB Conceptual Framework does not permit the recognition of the rights to future revenues implicit in assets to trigger obligations to future expenses implicit in liabilities and the extent to which a deferred tax liability is recognised should not depend on management's intention to sell a revalued asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following statements is not correct in relation to tax rate changes?
A) An increase in tax rates will create an expense where an entity has deferred tax liabilities.
B) Across time it is likely that governments will change tax rates.
C) A decrease in tax rates will create an income where an entity has deferred tax assets.
D) Changes in tax rates will have implications for the value attributed to pre-existing deferred tax assets.
A) An increase in tax rates will create an expense where an entity has deferred tax liabilities.
B) Across time it is likely that governments will change tax rates.
C) A decrease in tax rates will create an income where an entity has deferred tax assets.
D) Changes in tax rates will have implications for the value attributed to pre-existing deferred tax assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Shopping Malls Ltd has some land it purchased several years ago for $300 000.It has revalued the land this period to $480 000 and management intends to sell it in the near future.When the land was acquired the index for capital gains tax was 110 and at reporting date it is 132.The tax rate is 30%.What is the entry to record the tax implications of the revaluation?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements is correct with respect to AASB 112 Income Taxes when the government increase tax rates?
A) The entity applies a prospective application to deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities initially recognised subsequent to the announcement of the tax change.
B) Expense is recognised if the entity has deferred tax liabilities only.
C) Income is recognised if the entity has deferred tax liabilities only.
D) Expense is recognised if the entity has deferred tax assets only.
A) The entity applies a prospective application to deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities initially recognised subsequent to the announcement of the tax change.
B) Expense is recognised if the entity has deferred tax liabilities only.
C) Income is recognised if the entity has deferred tax liabilities only.
D) Expense is recognised if the entity has deferred tax assets only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Discuss how the carrying amounts of deferred tax assets and liabilities may change even though there are no changes in the amount of the underlying temporary differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The reversal of deductible temporary differences results in deductions in determining the:
A) income tax expense
B) future taxable profits
C) carrying amounts
D) income tax payable
A) income tax expense
B) future taxable profits
C) carrying amounts
D) income tax payable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Discuss the criteria for recognising deferred tax assets when there are unused tax losses?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the accounting treatment for goodwill that is consistent with AASB 112 Income Taxes?
A) treated as a deductible expense in the year of recognition
B) treated as a non-deductible expense in the year of recognition and subsequent periods
C) the difference between the carrying amount and the tax base results to a taxable temporary difference
D) the difference between the carrying amount and the tax base results to a deductible temporary difference
A) treated as a deductible expense in the year of recognition
B) treated as a non-deductible expense in the year of recognition and subsequent periods
C) the difference between the carrying amount and the tax base results to a taxable temporary difference
D) the difference between the carrying amount and the tax base results to a deductible temporary difference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Explain how a deferred tax liability arises from depreciation of machinery and equipment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Discuss the accounting treatment for the temporary difference that arises from revaluation of non-current assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How do deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities arise?
How do you calculate their balances at a point in time?
How do you calculate their balances at a point in time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Bogart Ltd has the following tax balances as at 30 June 2012: The balances were calculated when the tax rate was 30%.On 30 September 2012,the government announced a change to the company tax rate to 40%,effective immediately.What is the journal entry to adjust the carry-forward balances of the deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
On 1 January 2012,William Bay Ltd purchased a machine for $100 000.The entity adopts a straight-line depreciation method and uses 10% and 15% as depreciation rate and tax rate respectively.The salvage value is zero and the tax rate is 30%. At 31 December 2012,which of the journal entries is correct with respect to the transaction that is in accordance with AASB 112 Income Taxes only?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
On 1 January 2012,William Bay Ltd purchased a machine for $100 000.The entity adopts a straight-line depreciation method and uses 10% and 15% as depreciation rate and tax rate respectively.The salvage value is zero and the tax rate is 30%. At 31 December 2012,which of the following statements is correct with respect to the transaction that is in accordance with AASB 112 Income Taxes only?
A) There is a deductible temporary difference of $5000.
B) There is a deductible temporary difference of $1500.
C) There is a taxable temporary difference of $5000.
D) There is a taxable temporary difference of $1500.
A) There is a deductible temporary difference of $5000.
B) There is a deductible temporary difference of $1500.
C) There is a taxable temporary difference of $5000.
D) There is a taxable temporary difference of $1500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Some items are treated as a deduction for tax purposes when they are paid but are recognised as expenses when they are accrued for accounting purposes.Which of the following items are of that type?
A) warranty costs
B) goodwill amortisation
C) depreciation
D) entertainment
A) warranty costs
B) goodwill amortisation
C) depreciation
D) entertainment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Discuss the conditions that must be met to allow the set-off of current assets and current tax liabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Discuss the assumptions made when recognising a deferred tax asset or a deferred tax liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements is correct with respect to AASB 112 Income Taxes when a non-current asset is revalued?
A) On revaluation date, the revaluation reserve is increased by the product of the temporary difference and the tax rate.
B) On revaluation date, the revaluation reserve is decreased by the product of the temporary difference and the tax rate.
C) On revaluation date, a deferred tax liability is created equal to the amount of the temporary difference.
D) On revaluation date, a deferred tax asset is created equal to the amount of the temporary difference.
A) On revaluation date, the revaluation reserve is increased by the product of the temporary difference and the tax rate.
B) On revaluation date, the revaluation reserve is decreased by the product of the temporary difference and the tax rate.
C) On revaluation date, a deferred tax liability is created equal to the amount of the temporary difference.
D) On revaluation date, a deferred tax asset is created equal to the amount of the temporary difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The accounting profit multiplied by the tax rate is known as:
A) income tax payable
B) income tax expense
C) taxable amount
D) assessable amount
A) income tax payable
B) income tax expense
C) taxable amount
D) assessable amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When considering the recognition of assets and liabilities for tax purposes,reference is made to the:
A) depreciation rate
B) carrying amount
C) tax base
D) historical cost
A) depreciation rate
B) carrying amount
C) tax base
D) historical cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Evaluate deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities in terms of the AASB Conceptual Framework and the notion that they fail to meet the criteria outlined in the Framework.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If a tax rate change from 30% to 25% results in an adjustment to the deferred tax liability account of $50 000,what is (a)the amount of the temporary differences and (b)the type of temporary differences?
A) (a) $ 1 000 000; (b) taxable temporary differences
B) (a) $ 1 000 000; (b) deductible temporary differences
C) (a) $ 50 000; (b) taxable temporary differences
D) (a) $ 50 000; (b) deductible temporary differences
A) (a) $ 1 000 000; (b) taxable temporary differences
B) (a) $ 1 000 000; (b) deductible temporary differences
C) (a) $ 50 000; (b) taxable temporary differences
D) (a) $ 50 000; (b) deductible temporary differences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Explain,with examples,how changes in tax rates affect pre-existing deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



