Deck 8: Accounting for Intangibles
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Accounting for Intangibles
1
Compared to the requirement in the US,the treatment of research and development costs in Australia is less conservative (that is,likely to result in higher profits).
True
2
Continuously Contemporary Accounting (CoCoA)emphasises an entity's ability to adapt.Therefore goodwill is considered an important asset in this model.
False
3
AASB 138 requires that all intangibles,whether purchased or internally generated,be capitalised.
False
4
If the fair value of a revalued intangible asset can no longer be determined by reference to an active market,AASB 136 requires the use of the cost model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Research of market potential prior to the launch of a product is permissible to be capitalised as an intangible asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Expenditure on an intangible asset that was initially expensed may be recognised as part of an intangible asset at a later date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Internally generated brands,mastheads,publishing titles and customer lists are permitted to be recognised as intangible assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Goodwill is a term used for the composite asset of identifiable intangibles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
There are only rare occasions when an identifiable intangible asset should be amortised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
International convergence has meant that there is no longer one specific standard related to intangibles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The cost of a separately acquired intangible asset includes its purchase price and directly attributable cost for preparing the asset for its intended use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Development costs are less likely to meet the test for deferral than research costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Intangible assets that are amortised are no longer subjected to impairment testing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The revaluation model requires all intangible assets in the same class to have a fair value determined by reference to an active market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
AASB 138 prohibits the recognition of intangible assets using the revaluation model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to AASB 138 on intangible assets,if an entity buys another entity separate values can be assigned to purchased goodwill and to a brand name.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Intangible assets without a limited useful life cannot be recorded under AASB 138 as they cannot be amortised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
AASB 138 permits the use of revaluation model for intangible assets if there is an active market to determine fair value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Internally generated identifiable intangible assets may be recognised for financial accounting purposes in Australia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Where a revaluation occurs,it is to be to the fair value of the asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
AASB 138 defines development as:
A) the activities undertaken with specific commercial objectives, including original research, to develop plans or designs for new products or significant improvements to existing products.
B) the application of research findings or other knowledge to a plan or design for the production of new or substantially improved material, devices, processes, systems or services prior to the commencement of commercial production or use.
C) the activities undertaken to translate research findings into feasible projects for subsequent development for commercial objectives such that the recoverable amount is expected to be greater than the cost.
D) the activities undertaken with the expectation by management that future economic benefits in the form of new products or improvements to existing products are likely to result, based on research completed to date.
A) the activities undertaken with specific commercial objectives, including original research, to develop plans or designs for new products or significant improvements to existing products.
B) the application of research findings or other knowledge to a plan or design for the production of new or substantially improved material, devices, processes, systems or services prior to the commencement of commercial production or use.
C) the activities undertaken to translate research findings into feasible projects for subsequent development for commercial objectives such that the recoverable amount is expected to be greater than the cost.
D) the activities undertaken with the expectation by management that future economic benefits in the form of new products or improvements to existing products are likely to result, based on research completed to date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Identifiable intangible assets are those intangible assets that:
A) have been purchased by the entity from external parties.
B) have an unlimited life.
C) can have a value placed on them separately from other assets of the entity.
D) cannot be separately sold.
A) have been purchased by the entity from external parties.
B) have an unlimited life.
C) can have a value placed on them separately from other assets of the entity.
D) cannot be separately sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
There is a concern that research and development may be reduced as a result of the new requirements in AASB 138 because:
A) Companies will not have the cash available to pay for the research expenses up-front.
B) Recognising expenses early will allow for larger profits later, which will help smaller firms.
C) The 'horizon problem' suggests managers will not invest in long-term projects that do not immediately increase profits.
D) Shareholders are only interested in short-term profits and will not be impressed by strategies that attempt to increase the long-term value of their shares.
A) Companies will not have the cash available to pay for the research expenses up-front.
B) Recognising expenses early will allow for larger profits later, which will help smaller firms.
C) The 'horizon problem' suggests managers will not invest in long-term projects that do not immediately increase profits.
D) Shareholders are only interested in short-term profits and will not be impressed by strategies that attempt to increase the long-term value of their shares.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
AASB 138 states that intangible assets:
A) may not be revalued and must be amortised over their useful lives.
B) are only able to be revalued if they have been internally generated and there is an active market for them.
C) may only be revalued to their fair value as assessed by a licensed valuer.
D) may be measured by using either the cost model or the revaluation model.
A) may not be revalued and must be amortised over their useful lives.
B) are only able to be revalued if they have been internally generated and there is an active market for them.
C) may only be revalued to their fair value as assessed by a licensed valuer.
D) may be measured by using either the cost model or the revaluation model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the test for deferral of research costs as required by AASB 138?
A) Research costs can be deferred (recorded as an asset) when it is probable that the project they are applied to will bring future economic benefits.
B) Research costs may not be deferred unless it is almost certain that the project they are applied to will bring future economic benefits.
C) Research costs may not be recorded as an intangible asset.
D) Research costs may be deferred if the entity can demonstrate that an intangible asset exists and that it will generate future economic benefits.
A) Research costs can be deferred (recorded as an asset) when it is probable that the project they are applied to will bring future economic benefits.
B) Research costs may not be deferred unless it is almost certain that the project they are applied to will bring future economic benefits.
C) Research costs may not be recorded as an intangible asset.
D) Research costs may be deferred if the entity can demonstrate that an intangible asset exists and that it will generate future economic benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Glass 4 Windows is involved in a research and development project to create a filtering window that removes the need for curtains.For the current year ended 30 June 2011 expenditure on the project is as follows: The window is expected to earn revenues of $70 000 per year for the 10 years commencing 1 July 2011.Assuming straight-line amortisation,how much of the research and development cost should be expensed this period and what amount should be amortised in the year ended 30 June 2014?
A) Expensed in 2011: $58 500; amortisation in 2014: $58 500
B) Expensed in 2011: $235 000; amortisation in 2014: $35 000
C) Expensed in 2011: $235 000; amortisation in 2014: $28 000
D) Expensed in 2011: $350 000; amortisation in 2014: $23 500
A) Expensed in 2011: $58 500; amortisation in 2014: $58 500
B) Expensed in 2011: $235 000; amortisation in 2014: $35 000
C) Expensed in 2011: $235 000; amortisation in 2014: $28 000
D) Expensed in 2011: $350 000; amortisation in 2014: $23 500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
AASB 138 describes the distinction between the treatment of internally generated goodwill and purchased goodwill (as well as other intangibles)as arising because:
A) The two different sources of goodwill result in two different types of asset.
B) Internally generated goodwill is developed in order to be sold, so its value will be recognised at that time.
C) Internally generated goodwill cannot be reliably measured.
D) Recording purchased goodwill could lead to the manipulation of profit and asset amounts.
A) The two different sources of goodwill result in two different types of asset.
B) Internally generated goodwill is developed in order to be sold, so its value will be recognised at that time.
C) Internally generated goodwill cannot be reliably measured.
D) Recording purchased goodwill could lead to the manipulation of profit and asset amounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Walking on Air is developing a new form of individual transport that will act like a personal hovercraft.Costs for the year ended 30 June 2012 are: Due to the high individual cost of items,sales of this 'prototype' model will be small and generate $100 000 per year over the next 4 years.Following that time,a new and cheaper consumer model will be under production based on the research developed for the prototype; however,it will require additional development expenditure.How much of the research and development cost should be expensed in the period ended 30 June 2012 and what amount should be amortised in the year ended 30 June 2006 (rounded to the nearest dollar)?
A) Expensed in 2012: $1 200 000; amortisation in 2014: $100 000
B) Expensed in 2012: $950 000; amortisation in 2014: $216 667
C) Expensed in 2012: $950 000; amortisation in 2014: $65 000
D) Expensed in 2012: $1 200 000, amortisation in 2014: $30 000
A) Expensed in 2012: $1 200 000; amortisation in 2014: $100 000
B) Expensed in 2012: $950 000; amortisation in 2014: $216 667
C) Expensed in 2012: $950 000; amortisation in 2014: $65 000
D) Expensed in 2012: $1 200 000, amortisation in 2014: $30 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In order to determine whether or not expenditure should be treated as an intangible asset,the relevant test to apply in Australia is:
A) It should be recognised when (a) it is definite that future economic benefits will eventuate or (b) the asset possesses a cost or other value that can be measured reliably.
B) It should be recognised if (a) the expenditure is with an external party in an arm's length transaction for a separately identifiable intangible asset or (b) the intangible asset arises as the difference between the net tangible assets of an entity and the price paid for that entity.
C) It should be recognised if (a) it is part of a specified plan by management to develop and maintain a separately identifiable asset or (b) the intangible asset was purchased in an arm's length transaction and is actively traded in a market.
D) It should be recognised when and only when (a) it is probable that future economic benefits will eventuate and (b) the asset possesses a cost or other value that can be measured reliably.
A) It should be recognised when (a) it is definite that future economic benefits will eventuate or (b) the asset possesses a cost or other value that can be measured reliably.
B) It should be recognised if (a) the expenditure is with an external party in an arm's length transaction for a separately identifiable intangible asset or (b) the intangible asset arises as the difference between the net tangible assets of an entity and the price paid for that entity.
C) It should be recognised if (a) it is part of a specified plan by management to develop and maintain a separately identifiable asset or (b) the intangible asset was purchased in an arm's length transaction and is actively traded in a market.
D) It should be recognised when and only when (a) it is probable that future economic benefits will eventuate and (b) the asset possesses a cost or other value that can be measured reliably.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Far-flung Co Ltd purchases Local Co Ltd for the purchase consideration of: 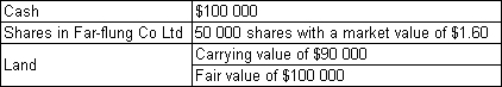 Far-flung incurred legal fees of $6000 to complete the acquisition.Local Co Ltd had the following assets and liabilities at the time of the purchase What is the value of goodwill,if any?
Far-flung incurred legal fees of $6000 to complete the acquisition.Local Co Ltd had the following assets and liabilities at the time of the purchase What is the value of goodwill,if any?
A) $0
B) $80 000
C) $141 000
D) $86 000
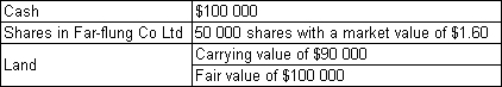 Far-flung incurred legal fees of $6000 to complete the acquisition.Local Co Ltd had the following assets and liabilities at the time of the purchase What is the value of goodwill,if any?
Far-flung incurred legal fees of $6000 to complete the acquisition.Local Co Ltd had the following assets and liabilities at the time of the purchase What is the value of goodwill,if any?A) $0
B) $80 000
C) $141 000
D) $86 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is correct with respect to research and development expenditures in accordance with AASB 138?
A) Activities aimed at obtaining knowledge that is likely to produce a viable commercial product can be capitalised.
B) Formulation, design, evaluation and final selection of alternative materials to be used in producing a viable commercial product can be capitalised.
C) Design, construction and operation of a pilot plant that is not of a scale economically feasible for commercial production can be capitalised.
D) Search for, evaluation and final selection of, applications of research findings and other knowledge can be capitalised.
A) Activities aimed at obtaining knowledge that is likely to produce a viable commercial product can be capitalised.
B) Formulation, design, evaluation and final selection of alternative materials to be used in producing a viable commercial product can be capitalised.
C) Design, construction and operation of a pilot plant that is not of a scale economically feasible for commercial production can be capitalised.
D) Search for, evaluation and final selection of, applications of research findings and other knowledge can be capitalised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Purchased goodwill is recognised as the amount of:
A) the excess of the cost of acquisition incurred by an acquirer over the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired.
B) the difference between the cost of acquisition of a subsidiary and the realisable value of net assets of the subsidiary.
C) the lower of the sum of related expenditures on advertising and promotion undertaken in the last 2 years by the subsidiary being purchased and the independent valuation of the market value of that subsidiary's goodwill.
D) the excess of the cost of acquisition incurred by an acquirer over the fair value of the identifiable net assets and contingent liabilities acquired.
A) the excess of the cost of acquisition incurred by an acquirer over the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired.
B) the difference between the cost of acquisition of a subsidiary and the realisable value of net assets of the subsidiary.
C) the lower of the sum of related expenditures on advertising and promotion undertaken in the last 2 years by the subsidiary being purchased and the independent valuation of the market value of that subsidiary's goodwill.
D) the excess of the cost of acquisition incurred by an acquirer over the fair value of the identifiable net assets and contingent liabilities acquired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Serendipity Ltd is working on two independent research and development projects.Project A has recently been fruitful and the resulting product has been marketed,unfortunately with limited success.Development of the product is continuing in an effort to improve its marketability.Project B is due for product release in one year's time.The initial marketing surveys and forward contracts suggest that the outcome for this product is very favourable.The following information relates to the expenditures for the current period and budgeted figures for the next 3 years.All research costs in prior periods were expensed.The budgeted figures are considered accurate beyond a reasonable doubt. 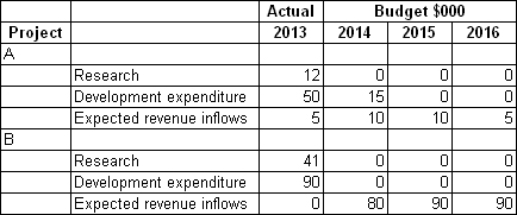 What is the research and development deferral for each project in 2013?
What is the research and development deferral for each project in 2013?
A) Project A $5000; Project B $0
B) Project A $47 000; Project B $131 000
C) Project A $30 000; Project B $90 000
D) Project A $62 000; Project B $131 000
 What is the research and development deferral for each project in 2013?
What is the research and development deferral for each project in 2013?A) Project A $5000; Project B $0
B) Project A $47 000; Project B $131 000
C) Project A $30 000; Project B $90 000
D) Project A $62 000; Project B $131 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Examples of intangible assets include:
A) loyal customers.
B) patents and trademarks.
C) provisions.
D) loyal customers, patents and trademarks.
A) loyal customers.
B) patents and trademarks.
C) provisions.
D) loyal customers, patents and trademarks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The treatment of internally generated goodwill varies from purchased goodwill under AASB 138 in that:
A) Purchased goodwill is not amortised whereas internally generated goodwill is assumed to be maintained indefinitely.
B) Purchased goodwill may be recorded as an asset, whereas internally generated goodwill may not.
C) Internally generated goodwill is to be amortised over a period of no greater than 20 years, whereas purchased goodwill may not be recorded.
D) Purchased goodwill is to be expensed in the period it is bought whereas internally generated goodwill is to be deferred and amortised over a period of no less than 20 years.
A) Purchased goodwill is not amortised whereas internally generated goodwill is assumed to be maintained indefinitely.
B) Purchased goodwill may be recorded as an asset, whereas internally generated goodwill may not.
C) Internally generated goodwill is to be amortised over a period of no greater than 20 years, whereas purchased goodwill may not be recorded.
D) Purchased goodwill is to be expensed in the period it is bought whereas internally generated goodwill is to be deferred and amortised over a period of no less than 20 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Because intangible assets have no physical form:
A) They are not subject to the recognition criteria of other assets and may be recorded if they satisfy the three elements of the definition.
B) They must be expensed immediately, as assets must be able to be measured.
C) They have no real value and should be excluded from accounting reports.
D) None of the given answers are correct.
A) They are not subject to the recognition criteria of other assets and may be recorded if they satisfy the three elements of the definition.
B) They must be expensed immediately, as assets must be able to be measured.
C) They have no real value and should be excluded from accounting reports.
D) None of the given answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An intangible asset may be recorded:
A) if acquired from an external party at a cost.
B) if it is internally generated and fits the definition of an asset and meets the associated recognition criteria.
C) at a value other than cost if that value more reliably records the worth of the intangible asset.
D) at the cost of the asset, which must exclude any additional expenditure required to prepare the asset for use.
A) if acquired from an external party at a cost.
B) if it is internally generated and fits the definition of an asset and meets the associated recognition criteria.
C) at a value other than cost if that value more reliably records the worth of the intangible asset.
D) at the cost of the asset, which must exclude any additional expenditure required to prepare the asset for use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Examples of elements of a business that commonly make up goodwill are:
A) patents and licences.
B) trademarks and brand names.
C) research and development.
D) established reputation and loyal customers.
A) patents and licences.
B) trademarks and brand names.
C) research and development.
D) established reputation and loyal customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The requirement of AASB 138 in relation to the amortisation of development cost is that:
A) It is to be amortised straight-line over a period not greater than 20 years.
B) It is to be amortised from the time of deferral so as to match the cost to the related benefits.
C) It is to be amortised using an accelerated depreciation rate over a period not exceeding 10 years.
D) It is to be amortised from the time the asset is available for use and shall reflect the consumption of the economic benefits by the entity.
A) It is to be amortised straight-line over a period not greater than 20 years.
B) It is to be amortised from the time of deferral so as to match the cost to the related benefits.
C) It is to be amortised using an accelerated depreciation rate over a period not exceeding 10 years.
D) It is to be amortised from the time the asset is available for use and shall reflect the consumption of the economic benefits by the entity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Castle Co Ltd is working on three research projects.Project Jonah is government-sponsored research on synthesising currently available research results on the possible triggers of asthma attacks.Project Beta involves researching the genetic tags associated with heart disease based on the genome project.A test to identify the predisposition to heart disease in children has been developed and will be on the market in 2013.Since 2011 research and development expenditures on this project are applied development costs only.Project Sigma is cutting edge research being conducted to try and discover a means of 'disassembling' molecules and then 'reassembling' them in their original form.The company hopes that this work will lay the basis for future dreams of teleportation as a method of transport.Details of expenditures and recoverable amounts expected beyond a reasonable doubt at this time are: 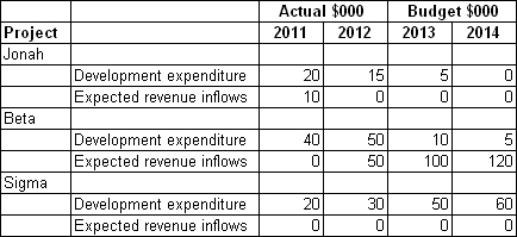 What is the total research and development deferral for each project as at the end of the year 2012?
What is the total research and development deferral for each project as at the end of the year 2012?
A) Jonah: $15 000; Beta $90 000; Sigma $0
B) Jonah: $20 000; Beta $50 000; Sigma $30 000
C) Jonah: $15 000; Beta $70 000; Sigma $50 000
D) Jonah: $0; Beta $90 000; Sigma $0
 What is the total research and development deferral for each project as at the end of the year 2012?
What is the total research and development deferral for each project as at the end of the year 2012?A) Jonah: $15 000; Beta $90 000; Sigma $0
B) Jonah: $20 000; Beta $50 000; Sigma $30 000
C) Jonah: $15 000; Beta $70 000; Sigma $50 000
D) Jonah: $0; Beta $90 000; Sigma $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
As part of adopting IFRS,goodwill acquired in a business combination is no longer amortised.Instead,the acquirer shall test goodwill for impairment (AASB 3 Business Combinations).When is goodwill considered to be impaired?
A) If the recoverable amount of the cash generating unit is greater than the unit's carrying amount.
B) If the recoverable amount of the cash generating unit is less than the unit's carrying amount.
C) If the value in use of the cash generating unit is greater than the unit's carrying amount.
D) If the fair value less costs to sell is greater than the unit's carrying amount.
A) If the recoverable amount of the cash generating unit is greater than the unit's carrying amount.
B) If the recoverable amount of the cash generating unit is less than the unit's carrying amount.
C) If the value in use of the cash generating unit is greater than the unit's carrying amount.
D) If the fair value less costs to sell is greater than the unit's carrying amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Buster Ltd had purchased goodwill to the value of $100 000 recorded in its consolidated financial statements.The goodwill has been determined to have an indefinite useful life.However,one year later Buster Ltd's cash generating units has been determined to have incurred an impairment loss of $13 000.What is the appropriate action for Buster limited to comply with AASB 138 Intangible Assets and AASB 136 Impairment of Assets?
A) Write-off goodwill in its entirety as goodwill no longer exists.
B) Recognise impairment loss of $13 000 and credit goodwill.
C) Amortise goodwill for 20 years using straight-line method.
D) Recognise impairment loss of $13 000 and credit equity.
A) Write-off goodwill in its entirety as goodwill no longer exists.
B) Recognise impairment loss of $13 000 and credit goodwill.
C) Amortise goodwill for 20 years using straight-line method.
D) Recognise impairment loss of $13 000 and credit equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Earth Ltd acquired Moon Ltd on 1 July 2009 for the sum of $100 000.On the same date Moon Ltd has the following assets and liabilities: What is the value of goodwill,if any?
A) They are not required to recognise goodwill.
B) $35 000
C) $75 000
D) surplus of $5000
A) They are not required to recognise goodwill.
B) $35 000
C) $75 000
D) surplus of $5000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
During 2001 the Financial Accounting Standards Board in the United States indicated they would look to change a requirement for the treatment of goodwill.That change is:
A) to remove the requirement to amortise goodwill and replace it with a requirement to write down goodwill to reflect any impairment in value.
B) to allow the recognition of internally generated goodwill.
C) to extend the period over which goodwill may be amortised.
D) to allow the inverted sum-of-digits method of amortisation.
A) to remove the requirement to amortise goodwill and replace it with a requirement to write down goodwill to reflect any impairment in value.
B) to allow the recognition of internally generated goodwill.
C) to extend the period over which goodwill may be amortised.
D) to allow the inverted sum-of-digits method of amortisation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Broadbeach Ltd is a manufacturing company with three subsidiaries.The following information relates to the goodwill account of Broadbeach Ltd for the year ended 30 June 2009: What is the carrying amount of goodwill as at 30 June 2009 consistent with AASB 136 Impairment of Assets?
A) Zero
B) $100 000
C) S140 000
D) $150 000
A) Zero
B) $100 000
C) S140 000
D) $150 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following statement(s)in regard to goodwill is/are correct in accordance with AASB 136 Impairment of Assets?
A) An impairment loss must be recognised when the carrying amount of a cash-generating unit exceeds its recoverable amount.
B) An impairment loss recognised for goodwill shall not be reversed in a subsequent period.
C) Value in use is the present value of future cash flows expected to be derived from a cash-generating unit.
D) All of the given statements are correct.
A) An impairment loss must be recognised when the carrying amount of a cash-generating unit exceeds its recoverable amount.
B) An impairment loss recognised for goodwill shall not be reversed in a subsequent period.
C) Value in use is the present value of future cash flows expected to be derived from a cash-generating unit.
D) All of the given statements are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements in regard to goodwill is/are correct in accordance with AASB 136 Impairment of Assets?
A) Goodwill may be amortised when it has a finite life.
B) Goodwill is subjected to impairment testing every three years.
C) Upward revaluation of goodwill is permitted as long as it is a reversal of prior years' impairment losses.
D) None of the given statements are correct.
A) Goodwill may be amortised when it has a finite life.
B) Goodwill is subjected to impairment testing every three years.
C) Upward revaluation of goodwill is permitted as long as it is a reversal of prior years' impairment losses.
D) None of the given statements are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Prior to the introduction of AASB 138 companies had found ways to circumvent the requirements of the revised (1996)version of AASB 1013.These methods included:
A) using the inverted sum-of-digits amortisation technique.
B) calculating goodwill as the difference between the carrying value of the net assets of the acquired company and the consideration paid.
C) requiring the purchased company to make excessive provisions for restructuring costs to be undertaken after the company is purchased.
D) attributing the excess of the cost of acquisition over the fair value of the net identifiable assets of the company acquired to brands, licences and other identifiable intangible assets.
A) using the inverted sum-of-digits amortisation technique.
B) calculating goodwill as the difference between the carrying value of the net assets of the acquired company and the consideration paid.
C) requiring the purchased company to make excessive provisions for restructuring costs to be undertaken after the company is purchased.
D) attributing the excess of the cost of acquisition over the fair value of the net identifiable assets of the company acquired to brands, licences and other identifiable intangible assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The argument by Pacific Dunlop (1994)is that the accounting treatment of goodwill,particularly the requirement to amortise it over 20 years,places Australian companies at a competitive disadvantage internationally.Miller (1995)analyses this view and argues that:
A) The research that has shown accounting figures to be used in a mechanistic way suggests that Australian firms will be disadvantaged relative to international competitors in the takeovers market.
B) Sophisticated users will be aware that there are no direct cash-flow effects of the different amortisation treatments for goodwill. The effect of differential taxation treatments (since the ATO does not permit a deduction for the amortisation of goodwill) will, however, have a negative impact on Australian companies.
C) The efficient market hypothesis maintains that the capital market will impound accounting information efficiently into the price of shares. Therefore if Australian companies are required to report lower earnings through goodwill amortisation they will be valued at a lower amount than they would otherwise be by investors in the capital market. This would reduce their ability to bid for other companies in a takeover situation.
D) The amortisation of goodwill can be a very significant cost for companies that have purchased a reasonable number of subsidiaries. Companies that are active in the takeover market in this way will be negatively impacted by the reporting of lower profits as a result of Australia's requirement that they amortise goodwill over a maximum of 20 years, whereas other countries permit a 40 year or unlimited life for goodwill.
A) The research that has shown accounting figures to be used in a mechanistic way suggests that Australian firms will be disadvantaged relative to international competitors in the takeovers market.
B) Sophisticated users will be aware that there are no direct cash-flow effects of the different amortisation treatments for goodwill. The effect of differential taxation treatments (since the ATO does not permit a deduction for the amortisation of goodwill) will, however, have a negative impact on Australian companies.
C) The efficient market hypothesis maintains that the capital market will impound accounting information efficiently into the price of shares. Therefore if Australian companies are required to report lower earnings through goodwill amortisation they will be valued at a lower amount than they would otherwise be by investors in the capital market. This would reduce their ability to bid for other companies in a takeover situation.
D) The amortisation of goodwill can be a very significant cost for companies that have purchased a reasonable number of subsidiaries. Companies that are active in the takeover market in this way will be negatively impacted by the reporting of lower profits as a result of Australia's requirement that they amortise goodwill over a maximum of 20 years, whereas other countries permit a 40 year or unlimited life for goodwill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following intangible assets should be recognised in the statement of financial position?
A) internally generated goodwill in excess of recoverable amount
B) licences with active market
C) purchased trademark
D) licences with active market and purchased trademark
A) internally generated goodwill in excess of recoverable amount
B) licences with active market
C) purchased trademark
D) licences with active market and purchased trademark

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The approach to accounting for intangibles raises some issues because:
A) Assets are now subject to impairment testing, which will remove the professional judgment required for amortisation.
B) Consistency has now been achieved regarding research and development meaning entities cannot claim to have expended resources on potential benefits while other entities could not.
C) Many intangible assets will not be recognised under this approach, particularly in regard to internally generated assets.
D) Intangible assets are more likely to be recorded at fair values because of the active market criteria, which may overstate asset values.
A) Assets are now subject to impairment testing, which will remove the professional judgment required for amortisation.
B) Consistency has now been achieved regarding research and development meaning entities cannot claim to have expended resources on potential benefits while other entities could not.
C) Many intangible assets will not be recognised under this approach, particularly in regard to internally generated assets.
D) Intangible assets are more likely to be recorded at fair values because of the active market criteria, which may overstate asset values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Broadbeach Ltd is a manufacturing company with three subsidiaries.The following information relates to the goodwill account of Broadbeach Ltd for the year ended 30 June 2009. In accordance with AASB 136,what is the net effect of above goodwill accounts on the statement of comprehensive income and statement of financial position of Broadbeach Ltd?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
AASB 138 contains some elements that seem to be reactions to opportunistic behaviour by preparers of accounts and to the degree of uncertainty surrounding goodwill as an unidentifiable intangible asset.These elements include:
A) the prohibition on recording internally generated goodwill.
B) the requirement to use a specific rate of amortisation.
C) the specification of impairment testing.
D) the prohibition on recording internally generated goodwill and the specification of impairment testing.
A) the prohibition on recording internally generated goodwill.
B) the requirement to use a specific rate of amortisation.
C) the specification of impairment testing.
D) the prohibition on recording internally generated goodwill and the specification of impairment testing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Prior to the introduction of impairment testing companies had attempted to manipulate their accounts through amortisation:
A) because where managers were rewarded based on profits attained it was in their best interests to reduce expenses while they held that position.
B) because contractual arrangements such as debt covenants often required asset values to be maximised.
C) because recording higher amortisation expenses allowed profits to be reduced, thus allowing tax payments to be minimised without any cash outflows.
D) because where managers were rewarded based on profits attained it was in their best interests to reduce expenses while they held that position and because contractual arrangements such as debt covenants often required asset values to be maximised.
A) because where managers were rewarded based on profits attained it was in their best interests to reduce expenses while they held that position.
B) because contractual arrangements such as debt covenants often required asset values to be maximised.
C) because recording higher amortisation expenses allowed profits to be reduced, thus allowing tax payments to be minimised without any cash outflows.
D) because where managers were rewarded based on profits attained it was in their best interests to reduce expenses while they held that position and because contractual arrangements such as debt covenants often required asset values to be maximised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following combination best demonstrates the value of goodwill?
I)purchase consideration of subsidiary
II)book value of net assets held by subsidiary
III)fair value of net identifiable assets
IV)contingent liabilities
A) I less II
B) I less III
C) I less (II-IV)
D) I less (III-IV)
I)purchase consideration of subsidiary
II)book value of net assets held by subsidiary
III)fair value of net identifiable assets
IV)contingent liabilities
A) I less II
B) I less III
C) I less (II-IV)
D) I less (III-IV)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The release of AASB 138 has had what impact on the methods of amortising goodwill?
A) The choice to use the inverted sum-of-digits method was phased out over a period of 15 years, to be replaced by straight-line depreciation.
B) The option to amortise goodwill was removed and replaced with annual impairment testing.
C) Entities were given the option of continuing to amortise goodwill or to subject it to impairment testing each year.
D) All entities were required to amortise goodwill over 20 years using the straight-line method to allow comparisons.
A) The choice to use the inverted sum-of-digits method was phased out over a period of 15 years, to be replaced by straight-line depreciation.
B) The option to amortise goodwill was removed and replaced with annual impairment testing.
C) Entities were given the option of continuing to amortise goodwill or to subject it to impairment testing each year.
D) All entities were required to amortise goodwill over 20 years using the straight-line method to allow comparisons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
After initial recognition,the acquirer shall recognise goodwill at:
A) historical cost.
B) fair value.
C) cost less accumulated amortisation.
D) cost less accumulated impairment losses.
A) historical cost.
B) fair value.
C) cost less accumulated amortisation.
D) cost less accumulated impairment losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following expenses are likely to satisfy the definition of an asset,and hence may be capitalised as an intangible asset?
A) expenses incurred to develop a brand name
B) advertising expenses
C) research expenses
D) none of the given answers
A) expenses incurred to develop a brand name
B) advertising expenses
C) research expenses
D) none of the given answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following statements is correct with respect to intangible assets?
A) Internally generated publishing titles may be revalued if fair value is determined by reference to an active market.
B) Purchased goodwill should be amortised over a period of 20 years.
C) Internally generated brands are not recognised as intangible assets because expenditures in these assets are not distinguishable from the cost of developing the business as a whole.
D) Internally generated brands are recognised as intangible assets because expenditures in these assets are not distinguishable from the cost of developing the business as a whole.
A) Internally generated publishing titles may be revalued if fair value is determined by reference to an active market.
B) Purchased goodwill should be amortised over a period of 20 years.
C) Internally generated brands are not recognised as intangible assets because expenditures in these assets are not distinguishable from the cost of developing the business as a whole.
D) Internally generated brands are recognised as intangible assets because expenditures in these assets are not distinguishable from the cost of developing the business as a whole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Big Ltd has purchased 100% of Little Ltd for a cash payment of $800 000.The additional costs to Big Ltd to complete the purchase were $3000.An extract from the statement of financial position for Little Ltd at the date of acquisition shows: Additional information:
The assets and liabilities of Little Ltd are stated at fair value except that:
Land and buildings have a fair value of $300 000
Accounts receivable have a fair value of $20 000.
Little owns a licence that has not been recorded in the accounts.Its fair value is $150 000.
What is the amount of purchased goodwill that has been acquired by Big Ltd?
A) $242 000
B) $344 000
C) $252 000
D) $102 000
The assets and liabilities of Little Ltd are stated at fair value except that:
Land and buildings have a fair value of $300 000
Accounts receivable have a fair value of $20 000.
Little owns a licence that has not been recorded in the accounts.Its fair value is $150 000.
What is the amount of purchased goodwill that has been acquired by Big Ltd?
A) $242 000
B) $344 000
C) $252 000
D) $102 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The gain or loss on the disposal of an intangible asset is determined as the difference between:
A) net proceeds from the disposal and the amortised amount.
B) net proceeds from the disposal and the recoverable amount.
C) net proceeds from the disposal and the carrying amount.
D) net proceeds from the disposal and the initial cost.
A) net proceeds from the disposal and the amortised amount.
B) net proceeds from the disposal and the recoverable amount.
C) net proceeds from the disposal and the carrying amount.
D) net proceeds from the disposal and the initial cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Palm Beach Ltd has a cash generating unit (CGU)and has been assessed for impairment and it has determined an impairment loss of $100 000. The following information relates to the assets as at 30 June 2012. In accordance with AASB 136 Impairment of Assets what should be the carrying amount of equipment as at 30 June 2012?
A) $0
B) $100 000
C) $150 000
D) $190 000
A) $0
B) $100 000
C) $150 000
D) $190 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Discuss the considerations outlined in AASB 138 on revaluation of intangible assets.What are the implications of this standard on the relevance of financial information?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Explain why research expenditures and expenditures on internally generated such as,brands,mastheads and publishing titles are not capitalised regardless of whether they are likely to generate future economic benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Outline the requirements of AASB 138 on recognition and measurement of research and development activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Explain why intangible assets are required to be reported as a separate class of asset in the statement of financial position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Shelley Beach Ltd has one cash generating unit (CGU)and it has been determined that the CGU has incurred an impairment loss of $80 000 for the year ended 30 June 2012. The carrying amounts of the assets as at 30 June 2012 are as follows:
In accordance with AASB 136 Impairment of Assets,what should be the carrying amounts for buildings,equipment and goodwill as at 30 June 2012,respectively?
A) $240 000; $300 000; $0
B) $260 000; $260 000; $20 000
C) $270 000; $270 000; $0
D) $300 000; $300 000; $20 000
In accordance with AASB 136 Impairment of Assets,what should be the carrying amounts for buildings,equipment and goodwill as at 30 June 2012,respectively?
A) $240 000; $300 000; $0
B) $260 000; $260 000; $20 000
C) $270 000; $270 000; $0
D) $300 000; $300 000; $20 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Discuss the benefits of subjecting goodwill to impairment testing as opposed to amortisation.In your answer,consider the relevance and faithfully represented qualitative characteristics of financial information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
An active market is defined in the standards as a market that has:
A) willing buyers and sellers.
B) prices are publicly available.
C) items traded are homogeneous.
D) All of the given answers are necessary.
A) willing buyers and sellers.
B) prices are publicly available.
C) items traded are homogeneous.
D) All of the given answers are necessary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Shelley Beach Ltd has one cash generating unit (CGU)and it has been determined that the CGU has incurred an impairment loss of $80 000 for the year ended 30 June 2012. The carrying amounts of the assets as at 30 June 2012 are as follows In accordance with AASB 136 Impairment of Assets,what is the appropriate journal entry to recognise the impairment loss for Shelley Beach Ltd?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An intangible asset with a finite useful life can be amortised when:
A) the asset has been purchased.
B) the asset is available for use.
C) the asset is derecognised.
D) None of the given answers are correct.
A) the asset has been purchased.
B) the asset is available for use.
C) the asset is derecognised.
D) None of the given answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Discuss the concerns held by Australia corporate executives on the amortisation of intangibles prior to Australia's 2005 adoption of IFRS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Palm Beach Ltd has a cash generating unit (CGU)and has been assessed for impairment and it has determined an impairment loss of $100 000. The following information relates to the assets as at 30 June 2012. In accordance with AASB 136 Impairment of Assets what should be the carrying amount of buildings as at 30 June 2012?
A) $720 000
B) $760 000
C) $800 000
D) $900 000
A) $720 000
B) $760 000
C) $800 000
D) $900 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Explain the difference between an 'infinite life' and an 'indefinite life'.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Explain how AASB 138 Intangible Assets may advantage Australian companies with heavy research and development activities.Contrast this with US companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is not a directly attributable cost of research and development?
A) costs of employee benefits arising from the generation of the intangible asset
B) fees to register a legal right
C) costs of materials consumed in generating the intangible asset
D) All of the given answers are correct.
A) costs of employee benefits arising from the generation of the intangible asset
B) fees to register a legal right
C) costs of materials consumed in generating the intangible asset
D) All of the given answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Discuss the factors considered to determine amortisation of deferred development costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



