Deck 16: Investment Decision Applications
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Investment Decision Applications
1
Sean and Jessica want to sell their interest in a small business. They have received two offers. If they accept Offer A they will receive $40 000 immediately and $30 000 in two years. If the accept Offer B they will receive $50000 now and $2000 at the end of every six months for 5 years. If interest is 8%, which offer is preferable?
p = 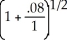 -1 = .0392305
-1 = .0392305
ALT. A = 40000.00 + 30000.00(1.08)-2
= 40000.00 + 30000.00(.857339) =40000.00 + 25720.16 = $65720.16=$65 720.
ALT. B = 50000.00 + 2000.00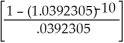 = 50000.00 + 2000.00(8.142056025) =50000.00 + 16284.11 = $66284.11=$66 284. BEST
= 50000.00 + 2000.00(8.142056025) =50000.00 + 16284.11 = $66284.11=$66 284. BEST
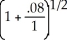 -1 = .0392305
-1 = .0392305ALT. A = 40000.00 + 30000.00(1.08)-2
= 40000.00 + 30000.00(.857339) =40000.00 + 25720.16 = $65720.16=$65 720.
ALT. B = 50000.00 + 2000.00
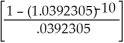 = 50000.00 + 2000.00(8.142056025) =50000.00 + 16284.11 = $66284.11=$66 284. BEST
= 50000.00 + 2000.00(8.142056025) =50000.00 + 16284.11 = $66284.11=$66 284. BEST 2
Donna and Keith want to sell their business. They have received two offers. If they accept Offer A they will receive $61 000 immediately and $20 000 in three years. If the accept Offer B they will receive $37000 now and $3000 at the end of every six months for 5 years. If interest is 6.67%, which offer is preferable?
p = 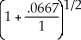 -1 = .0328117
-1 = .0328117
ALT. A = 61000.00 + 20000.00(1.0667)-3
= 61000.00 + 20000.00(.8238974) = 61000.00 + 16477.95 = $77477.95=$77 478. BEST
ALT. B = 37000.00 + 3000.00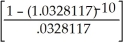 = 37000.00 + 3000.00(8.4090961) = 37000.00 + 25227.29 = $62227.29=$62 227.
= 37000.00 + 3000.00(8.4090961) = 37000.00 + 25227.29 = $62227.29=$62 227.
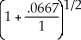 -1 = .0328117
-1 = .0328117ALT. A = 61000.00 + 20000.00(1.0667)-3
= 61000.00 + 20000.00(.8238974) = 61000.00 + 16477.95 = $77477.95=$77 478. BEST
ALT. B = 37000.00 + 3000.00
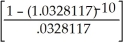 = 37000.00 + 3000.00(8.4090961) = 37000.00 + 25227.29 = $62227.29=$62 227.
= 37000.00 + 3000.00(8.4090961) = 37000.00 + 25227.29 = $62227.29=$62 227. 3
A company has two investment choices. Alternative A requires an immediate outlay of $4000.00 and offers a return of $14 000.00 after seven years. Alternative B requires an immediate outlay of $3600.00 in return for which $500.00 will be received at the end of every six months for the next seven years. If the rate of return is 6% compounded semi-annually, determine which alternative is preferable.
Alterative A:
PV of 14 000: n = 7(2) = 14; i =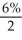 = 0.03; FV = 14 000; I/Y = 6; P/Y = C/Y = 2
= 0.03; FV = 14 000; I/Y = 6; P/Y = C/Y = 2
PV = 14000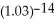 = $9 255.65
= $9 255.65
Programmed solution: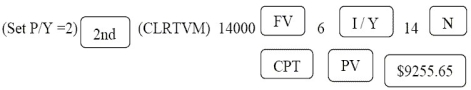 NPVA = 9255.65 - 4000.00 = $5255.65 =$5 256.
NPVA = 9255.65 - 4000.00 = $5255.65 =$5 256.
Alternative B:
PMT = 500; n = 7(2) = 14; i = 0.03; I/Y = 6; P/Y = C/Y = 2
PV = 500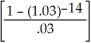 = $5648.04
= $5648.04
Programmed solution: NPVB= 5648.04 - 3600.00 = $2048.04 = $2 048.
NPVB= 5648.04 - 3600.00 = $2048.04 = $2 048.
Since NPVA > NPVB, alternative A is preferred.
PV of 14 000: n = 7(2) = 14; i =
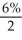 = 0.03; FV = 14 000; I/Y = 6; P/Y = C/Y = 2
= 0.03; FV = 14 000; I/Y = 6; P/Y = C/Y = 2PV = 14000
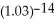 = $9 255.65
= $9 255.65Programmed solution:
 NPVA = 9255.65 - 4000.00 = $5255.65 =$5 256.
NPVA = 9255.65 - 4000.00 = $5255.65 =$5 256.Alternative B:
PMT = 500; n = 7(2) = 14; i = 0.03; I/Y = 6; P/Y = C/Y = 2
PV = 500
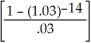 = $5648.04
= $5648.04Programmed solution:
 NPVB= 5648.04 - 3600.00 = $2048.04 = $2 048.
NPVB= 5648.04 - 3600.00 = $2048.04 = $2 048.Since NPVA > NPVB, alternative A is preferred.
4
A car costs $29 700. Alternatively, the car can be leased for three years by making payments of $540 at the beginning of each month and can be bought at the end of the lease for $14750. If interest is 9.2% compounded semi-annually, which alternative is preferable?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
You win a lottery and have a choice of taking $200 000.00 immediately or taking payments of $8000.00 at the end of every three months for ten years. Which offer is preferable if interest is 8% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An obligation can be settled by making a payment of $7500.00 now and a final payment of $10 000.00 in five years. Alternatively the obligation can be settled by payments of $750.00 at the end of every three months for five years. If interest rate is 10% compounded quarterly, determine the preferred alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Replacing old equipment at an immediate cost of $75 000 and an additional outlay of $10 000 six years from now will result in savings of $3120 per quarter for 11 years. The required rate of return is 8% compounded annually. Use the net present value method to determine whether the company should replace old equipment or not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A piece of property may be acquired by making an immediate payment of $125 000 and payments of $37 500 and $50 000 three and five years from now respectively. Alternatively, the property may be purchased by making quarterly payments of $11 150 in advance for five years. Which alternative is preferable if money is worth 12.2% compounded semi-annually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Tamia Industries plans to replace the outdated equipment that will cost the company $100 000.00 now and $60 000.00 six years from now. This replacement will result in revenues of $6000.00 at the end of each quarter for twelve years. At an interest rate of 9% compounded annually and using the Net Present Value criterion, should the company replace this equipment or not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An expenditure may be met by outlays of $1 700 now and $2210 at the end of every six months for 6 years or by making monthly payments of $500 in advance for seven years. Interest is 11% compounded annually.
Compute the present value of each alternative and determine the preferred alternative according to the discounted cash flow criterion.
Compute the present value of each alternative and determine the preferred alternative according to the discounted cash flow criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Replacing old equipment at an immediate cost of $75 000 and an additional outlay of $10 000 six years from now will result in savings of $3120 per quarter for 11 years. The required rate of return is 11.4% compounded annually. Use the net present value method to determine whether the company should replace old equipment or not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A telephone system with a disposable value of $4200 after five years can be purchased for $16 600. Alternatively, a leasing agreement is available that requires an immediate payment of $1900 plus payments of $150.00 at the beginning of each month for five years. If money is worth 9.6% compounded monthly, should the telephone system be leased or purchased?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A new car costs $21 000. Alternatively, the car can be leased for three years by making payments of $360 at the beginning of each month and can be bought at the end of the lease for $10 000. If interest is 8% compounded semi-annually, which alternative is preferable?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A selection has to be made between two investment alternatives. The first alternative offers a net return of $47 000.00 after three years, $30 000.00 after five years and $26 000.00 after seven years. The second alternative provides a net return of $13 000.00 per year for seven years. Determine the preferred alternative according to the discounted cash flow criterion if money is worth 11%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A contract is estimated to yield net returns of $7000.00 quarterly for seven years. To secure the contract, an immediate outlay of $80 000.00 and a further outlay of $60 000.00 three years from now are required. If interest is 6% compounded quarterly, determine if the investment should be accepted or rejected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An obligation can be settled by making a payment of $12 000 now and a final payment of $32 000 in 4 years. Alternatively, the obligation can be settled by payments of $2700 at the end of every three months for five years. Interest is 10% compounded quarterly.
Compute the present value of each alternative and determine the preferred alternative according to the discounted cash flow criterion.
Compute the present value of each alternative and determine the preferred alternative according to the discounted cash flow criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A wireless telephone system with a disposable value of $5 000 after five years can be purchased for $15 000. Alternatively, a leasing agreement is available that requires an immediate payment of $2000 plus payments of $100.00 at the beginning of each month for five years. If money is worth 6% compounded monthly, should the telephone system be leased or purchased?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An investment project requires an initial expenditure of $160 000.00 with a salvage value of $30 000.00 after ten years. It is estimated that it will have annual returns of $21 000.00 for ten years. Should the company undertake this project if it wants to achieve a 9% rate of return?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An obligation can be settled by making a payment of $16 000 now and a final payment of $30 000 in 3 years. Alternatively, the obligation can be settled by payments of $2500 at the end of every three months for four years. Interest is 12% compounded quarterly.
Compute the present value of each alternative and determine the preferred alternative according to the discounted cash flow criterion.
Compute the present value of each alternative and determine the preferred alternative according to the discounted cash flow criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An expenditure may be met by outlays of $3 000 now and $1000 at the end of every six months for 5 years or by making monthly payments of $250 in advance for three years. Interest is 12% compounded annually.
Compute the present value of each alternative and determine the preferred alternative according to the discounted cash flow criterion.
Compute the present value of each alternative and determine the preferred alternative according to the discounted cash flow criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A company is considering a project that will require a cost outlay of $17 200 per year for 3 years. At the end of the project the salvage value will be $15 000. The project will yield returns of $60 000 in Year 4 and $20 000 in Year 5. There are no returns after Year 5. Alternative investments are available that will yield a return of 14.2%. Should the company undertake the project?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The SHREK Company has to make a decision about expanding its production facilities. Research indicates that the desired expansion would require an immediate outlay of $160 000 and an outlay of a further $60 000 in five years. Net returns are estimated to be $25 000 per year for the first five years and $20 000 per year for the following 9 years. Find the net present value of the project. Should the expansion project be undertaken if the required rate of return is 10% compounded annually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Replacing old equipment at an immediate cost of $5 000 and $7 000 six years from now will result in a savings of $3000 semi-annually for ten years. At 11% compounded annually, should the old equipment be replaced?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Replacing old office equipment at an immediate cost of $3 000 and $4 000 four years from now will result in savings of $400 semi-annually for ten years. Should the old equipment be replaced
a) at 8% compounded annually?
b) at 12% compounded annually?
a) at 8% compounded annually?
b) at 12% compounded annually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A company is considering a project that will require a cost outlay of $25 000 per year for 3 years. At the end of the project the salvage value will be $15 000. The project will yield annual net returns of $17 500 for 5 years. Alternative investments are available that will yield a return of 15%. Should the company undertake the project?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The introduction of a new product requires an immediate outlay of $145 000 and has a residual value of $30 000 after 10 years. The anticipated net returns from the marketing of the product are expected to be $25 500 per year for ten years. What is the rate of return on the investment (correct to the nearest tenth of a percent)?
a) Use linear interpolation to find the approximate value of the rate of return.
b) Find the answer using Cash Flow and IRR.
a) Use linear interpolation to find the approximate value of the rate of return.
b) Find the answer using Cash Flow and IRR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A company is considering a project that will require a cost outlay of $30 000 per year for three years. At the end of the project, the company expects to salvage the physical assets for $50 000. The project is estimated to yield net returns of $60 000 in Year 4, $40 000 in Year 5, and $15 000 for each of the following five years. Alternative investments are available yielding a rate of return of 14.5%. Compute the net present value of the project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A once in a lifetime project requires an immediate outlay of $100 000 and $25 000 at the end of each year for 3 years. Net returns are nil for the first 3 years and $30 000 per year thereafter for fourteen years. What is the net present value of the project at 16%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Assume that the net present value of a project is $ 220 at 22%, and -$305 at 24%. Use linear
interpolation to compute the rate of return correct to the nearest tenth of a percent.
interpolation to compute the rate of return correct to the nearest tenth of a percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
LD Winery expects a demand of 10 000 bottles per year for a special purpose wine for six years. Net return per unit is $6.10. To produce the wine, LD must buy equipment costing $200 000 with a life of six years and a salvage value of $10 000 after six years. The company estimates that repair costs will be $8 000 per year during Years 2 to 6. Should LD invest in the equipment if it requires a return of 16% on its investment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A project requires an initial outlay of $350 000 and a further outlay of $100 000 after one year. Net returns are $105 000 per year for five years. What is the net present value of the project at 9.9%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Big Sky Company expects a demand of 30 000 units per year for a special purpose component for six years. Net return per unit is $4.10. To produce the component, the company must buy a machine costing $245 000 with a life of six years and a salvage value of $47 000 after six years. The company estimates that repair costs will be $18 000 per year during Years 2 to 6. If Big Sky company requires a return on investment of 15.5%, should it market the component?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Project A requires an immediate investment of $18 000 and another $16 000 in three years. Net returns are $4500 after two years, $13 000 after four years, and $8900 after six years. Project B requires an immediate investment of $4000, another $6000 after two years, and $4000 after four years. Net returns are $3375 per year for 8 years. Determine the net present value at 11%. Which project is preferable according to the net present value criterion?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A commitment on the project requires an initial outlay of $10 000.00 and a further outlay of $5 000.00 after one year. Net returns are $5 000.00 per year for five years. What is the net present value of the project at 16%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A special chemical development project requires an immediate outlay of $110 000 and $50 000 at the end of each year for 3 years. Net returns are nil for the first 3 years and $60 000 per year thereafter for fourteen years. What is the net present value of the project at 17%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A new venture that requires outlays of $127 000 for each of the first two years will yield net returns of $85 000 in each year for years 3 to 6 and $70 000 for each of the following four years. A residual value of $130 000 can be recovered at the end of the last income period. Should the venture be undertaken if a yield of 11.56% is required?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Assume that the net present value of a project is $ 3870 at 10%, and -$1853 at 12%. Use linear interpolation to compute the rate of return correct to the nearest tenth of a percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A restaurant may be purchased for $250 000. Annual net income from the operation of the restaurant is expected to be $61 000 for each of the first 4 years and $30 000 for each of the next three years. After 7 years, the restaurant can be sold for $315 000. Determine the rate of return on the investment correct to the nearest tenth of a percent.
a) Use linear interpolation to find the approximate value of the rate of return.
b) Find the answer using Cash Flow and IRR.
a) Use linear interpolation to find the approximate value of the rate of return.
b) Find the answer using Cash Flow and IRR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An investment of $180 000 yields annual net returns of $27 700 for seven years. What is the rate of return on the investment (correct to the nearest tenth of a percent) if part of the initial investment, in the amount of, $80 000 is recovered at the end of 7 years?
a) Use linear interpolation to find the approximate value of the rate of return.
b) Find the answer using Cash Flow and IRR.
a) Use linear interpolation to find the approximate value of the rate of return.
b) Find the answer using Cash Flow and IRR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose you are offered two investment alternatives. If you choose Alternative 1, you will have to make an immediate outlay of $26 000. In return, you will receive $1500 at the end of every three months for the next ten years. If you choose Alternative 2, you will have to make an outlay of $14 000 now and $8000 in two years. In return, you will receive $60 000 ten years from now. Interest is 8.22% compounded semi-annually. Compute the net present value for each alternative and determine which investment should be accepted or rejected according to the net present value criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A project requiring an immediate investment of $150 000 and a further outlay of $60 000 after four years has a residual value of $50 000 after nine years. The project yields a negative net return of $10 000 in Year 1, a zero net return in Year 2, $60 000 per year for the following four years, and $70 000 per year for the last three years. Find the rate of return (correct to the nearest tenth of a percent).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A project requires an initial outlay of $100 000 and promises net returns of $18500 per year over a twelve-year period. If the project has a residual value of $4000 after twelve years, what is the rate of return?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A company buys equipment for $15000 today and has annual net cash inflows of $6000 for 3 years. The discount rate is 12% compounded annually. What is the Net Present Value (NPV)?
A) -$525.90
B) $552.90
C) $992.50
D) $652.90
E) -$652.90
A) -$525.90
B) $552.90
C) $992.50
D) $652.90
E) -$652.90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A company is looking to invest in a very risky project. They have a required rate of return of 27% compounded annually. The project has the following cash inflows: Year 1 $17500, Year 2 $15000, Year 3 $27500. It also has the following cash outflows: Immediately -$10000, Year 1 -$15000, Year 3 -$9500. What is the NPV?
A) $9718.06
B) $7918.06
C) $7819.06
D) $9918.06
E) -$9718.06
A) $9718.06
B) $7918.06
C) $7819.06
D) $9918.06
E) -$9718.06

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A company is planning on investing the following monies. They spend Today -$26000, Year 1 -$7000, Year 4 -$11000, and Year 7 -$10100. Their cash inflows are Years 1-3 inclusive +$12000, Years 4-9 inclusive +$16000. What is their IRR?
A) 15.18%
B) 25.18%
C) 5.18%
D) 35.18%
E) 10.18%
A) 15.18%
B) 25.18%
C) 5.18%
D) 35.18%
E) 10.18%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The Radium Hot Springs plans to install a swimming pool. Construction of the lift is estimated to require an immediate outlay of $420 000. The life of the pool is estimated to be 20 years with a salvage value of $20 000. Cost of preparing the area is expected to be $30 000 for each of the first 2 years of operation. Net cash inflows from the pool are expected to be $49 000 for each of the first five years and $90 000 for each of the following 15 years. Find the rate of return (correct to the nearest tenth of a percent).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A company has an immediate cash outlay of -$325000 and additional subsequent cash outlays of -$6000 per year for the life of the project. They will receive cash inflows in year 3 for +$77000 and increasing by $3000 per year until the project ends 7 years later (total of 10 years). What is the IRR?
A) 9.79%
B) 0.79%
C) 7.79%
D) 10.91%
E) 3.79%
A) 9.79%
B) 0.79%
C) 7.79%
D) 10.91%
E) 3.79%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Billy Bob wants to convert his farm into a ski resort. He asked you to determine his rate of return based on the following estimates.
- Development cost for each of the first 2 years, $87 000.
- Construction of a chalet in Year 3, $1240 000.
- Upon his retirement in fifteen years, improvements in the property will yield him $270 000.
- Net returns from the operation of the golf course will be nil for the first three years and $200 000 per year afterwards until his retirement.
- Development cost for each of the first 2 years, $87 000.
- Construction of a chalet in Year 3, $1240 000.
- Upon his retirement in fifteen years, improvements in the property will yield him $270 000.
- Net returns from the operation of the golf course will be nil for the first three years and $200 000 per year afterwards until his retirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the IRR for the following net annual cash flows today -$45000, Year 1 +$12000, Year 2 +$37000, Year 3 +$12000, Year 4 +$17000?
A) 26.722%
B) 16.722%
C) 6.722%
D) 36.722%
E) 46.722%
A) 26.722%
B) 16.722%
C) 6.722%
D) 36.722%
E) 46.722%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The owner of a video store is considering remodeling the store in order to carry a larger inventory. The cost of remodeling and additional inventory is $43 200. The expected increase in net profit is $7000 per year for the next 3 years and $10 000 each year for the following 7 years. After ten years, the owner plans to retire and sell the business. She expects to recover the additional $40 000 invested in inventory but not the $43 200 invested in remodeling. Compute the rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A company spends $117 500 today and has positive cash inflows of $34 000 for each of the next 6 years. What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR)?
A) 14.87%
B) 18.47%
C) 17.48%
D) 16.84%
E) 15.87%
A) 14.87%
B) 18.47%
C) 17.48%
D) 16.84%
E) 15.87%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A company has the following pattern of cash flows. Today -$47000, Year 1 -$15500, Year 2 +$16000, Year 3 +$35000, Year 4 +$57000. What is the IRR?
A) 9.301%
B) 29.301%
C) 19.301%
D) 39.301%
E) 49.301%
A) 9.301%
B) 29.301%
C) 19.301%
D) 39.301%
E) 49.301%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A company needs to spend $15000 for each of the next three years. Net returns beginning in Year 4 are estimated at $2500 per year for ten years. The required rate of return is 9.75% compounded annually. The NPV is?
A) -$27521.41
B) -$27721.41
C) -$25721.41
D) $25217.41
E) $27521.41
A) -$27521.41
B) -$27721.41
C) -$25721.41
D) $25217.41
E) $27521.41

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A company has the following net cash inflows. Today -$7000, Year 1 -$15000, Year 2 -$9000, Year 3 +$12000, Year 4 -$3000, Year 5 +$19000. Compute the net present value if the required rate of return is 7.22% compounded annually.
A) -$4709.89
B) -$3000.00
C) -$7009.89
D) -$7409.89
E) $4709.89
A) -$4709.89
B) -$3000.00
C) -$7009.89
D) -$7409.89
E) $4709.89

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The introduction of a new product requires an initial outlay of $610 000. The anticipated net returns from the marketing of the product are expected to be $92 300 per year for 12 years. Find the rate of return (correct to the nearest tenth of a percent).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A company has cash outflows of $21 275 starting today for each of the next 5 years. After that they will have cash inflows of $16 000 for each of the following 7 years. The discount rate is 9% compounded annually. What is the NPV?
A) -$30415.15
B) -$34015.15
C) -$4015.15
D) -$341.51
E) -$41.51
A) -$30415.15
B) -$34015.15
C) -$4015.15
D) -$341.51
E) -$41.51

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



