Deck 16: Acid-Base Equilibria and Solubility Equilibria
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/131
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Acid-Base Equilibria and Solubility Equilibria
1
Calculate the pH of a buffer solution prepared by dissolving 0.2 mole of sodium cyanate (NaCNO)and 1.0 mole of cyanic acid (HCNO)in enough water to make 1.0 liter of solution.[Ka(HCNO)= 2.0 × 10-4]
A)0
B)3.0
C)3.7
D)4.4
E)5.0
A)0
B)3.0
C)3.7
D)4.4
E)5.0
3.0
2
In which one of the following solutions will acetic acid have the greatest percent ionization?
A)0.1 M CH3COOH
B)0.1 M CH3COOH dissolved in 1.0 M HCl
C)0.1 M CH3COOH plus 0.1 M CH3COONa
D)0.1 M CH3COOH plus 0.2 M CH3COONa
A)0.1 M CH3COOH
B)0.1 M CH3COOH dissolved in 1.0 M HCl
C)0.1 M CH3COOH plus 0.1 M CH3COONa
D)0.1 M CH3COOH plus 0.2 M CH3COONa
0.1 M CH3COOH
3
What is the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when small amounts of hydrochloric acid are added to a HOCl/NaOCl buffer solution?
A)H+ + H2O H3O+
B)H+ + OCl- HOCl
C)HOCl H+ + OCl-
D)H+ + HOCl H2OCl+
E)HCl + HOCl H2O + Cl2
A)H+ + H2O H3O+
B)H+ + OCl- HOCl
C)HOCl H+ + OCl-
D)H+ + HOCl H2OCl+
E)HCl + HOCl H2O + Cl2
H+ + OCl- HOCl
4
A solution is prepared by mixing 500.mL of 0.10 M NaOCl and 500.mL of 0.20 M HOCl.What is the pH of this solution? [Ka(HOCl)= 3.2 × 10-8]
A)4.10
B)7.00
C)7.19
D)7.49
E)7.80
A)4.10
B)7.00
C)7.19
D)7.49
E)7.80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
You have 500.0 mL of a buffer solution containing 0.20 M acetic acid (CH3COOH)and 0.30 M sodium acetate (CH3COONa).What will the pH of this solution be after the addition of 20.0 mL of 1.00 M NaOH solution? [Ka = 1.8 × 10-5]
A)4.41
B)4.74
C)4.56
D)4.92
E)5.07
A)4.41
B)4.74
C)4.56
D)4.92
E)5.07

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Assuming equal concentrations of conjugate base and acid, which one of the following mixtures is suitable for making a buffer solution with an optimum pH of 4.6-4.8?
A)CH3COO2Na / CH3COOH (Ka = 1.8 × 10-5)
B)NH3 / NH4Cl (Ka = 5.6 × 10-10)
C)NaOCl / HOCl (Ka = 3.2 × 10-8)
D)NaNO2 / HNO2 (Ka = 4.5 × 10-4)
E)NaCl / HCl
A)CH3COO2Na / CH3COOH (Ka = 1.8 × 10-5)
B)NH3 / NH4Cl (Ka = 5.6 × 10-10)
C)NaOCl / HOCl (Ka = 3.2 × 10-8)
D)NaNO2 / HNO2 (Ka = 4.5 × 10-4)
E)NaCl / HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.410 M in HOCl and 0.050 M in NaOCl.[Ka(HOCl)= 3.2 × 10-8]
A)0.39
B)3.94
C)6.58
D)7.49
E)8.40
A)0.39
B)3.94
C)6.58
D)7.49
E)8.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which one of the following combinations cannot function as a buffer solution?
A)HCN and KCN
B)NH3 and (NH4)2SO4
C)HNO3 and NaNO3
D)HF and NaF
E)HNO2 and NaNO2
A)HCN and KCN
B)NH3 and (NH4)2SO4
C)HNO3 and NaNO3
D)HF and NaF
E)HNO2 and NaNO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following yields a buffer solution when equal volumes of the two solutions are mixed?
A)0.10M HCl and 0.10 M NaCl
B)0.15 M HNO3 and 0.15 M NaNO3
C)0.10M HF and 0.10M NaF
D)0.10M HClO4 and 0.10 NaClO4
E)0.15M HBr and 0.15M NaBr
A)0.10M HCl and 0.10 M NaCl
B)0.15 M HNO3 and 0.15 M NaNO3
C)0.10M HF and 0.10M NaF
D)0.10M HClO4 and 0.10 NaClO4
E)0.15M HBr and 0.15M NaBr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Calculate the pH of a buffer solution prepared by dissolving 0.20 mole of cyanic acid (HCNO)and 0.80 mole of sodium cyanate (NaCNO)in enough water to make 1.0 liter of solution. [Ka(HCNO)= 2.0 × 10-4]
A)0.97
B)3.10
C)4.40
D)3.70
E)4.30
A)0.97
B)3.10
C)4.40
D)3.70
E)4.30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following yields a buffer solution when equal volumes of the two solutions are mixed?
A)0.10 M NH3 and 0.10 M HCl
B)0.10 M NH4+ and 0.10 M KOH
C)0.20 M NH3 0.10 M KOH
D)0.20 M NH3 and 0.10 M HCl
E)0.20 M NH4+ and 0.10M HCl
A)0.10 M NH3 and 0.10 M HCl
B)0.10 M NH4+ and 0.10 M KOH
C)0.20 M NH3 0.10 M KOH
D)0.20 M NH3 and 0.10 M HCl
E)0.20 M NH4+ and 0.10M HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What pH range is a HOCl - NaOCl buffer effective?
A)pH 2.0 - pH 4.0
B)pH 7.5 - pH 9.5
C)pH 6.5 - pH 8.5
D)pH 6.5 - pH 9.5
E)pH 1.0 - pH 14.0
A)pH 2.0 - pH 4.0
B)pH 7.5 - pH 9.5
C)pH 6.5 - pH 8.5
D)pH 6.5 - pH 9.5
E)pH 1.0 - pH 14.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
You are asked to go into the lab and prepare an acetic acid - sodium acetate buffer solution with a pH of 4.00 ± 0.02.What molar ratio of CH3COOH to CH3COONa should be used?
A)0.18
B)0.84
C)1.19
D)5.50
E)0.10
A)0.18
B)0.84
C)1.19
D)5.50
E)0.10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Assuming equal concentrations of conjugate base and acid, which one of the following mixtures is suitable for making a buffer solution with an optimum pH of 9.2-9.3?
A)CH3COONa / CH3COOH (Ka = 1.8 × 10-5)
B)NH3 / NH4Cl (Ka = 5.6 × 10-10)
C)NaOCl / HOCl (Ka = 3.2 × 10-8)
D)NaNO2 / HNO2 (Ka = 4.5 × 10-4)
E)NaCl / HCl
A)CH3COONa / CH3COOH (Ka = 1.8 × 10-5)
B)NH3 / NH4Cl (Ka = 5.6 × 10-10)
C)NaOCl / HOCl (Ka = 3.2 × 10-8)
D)NaNO2 / HNO2 (Ka = 4.5 × 10-4)
E)NaCl / HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which one of the following is a buffer solution?
A)0.40 M HCN and 0.10 KCN
B)0.20 M CH3COOH
C)1.0 M HNO3 and 1.0 M NaNO3
D)0.10 M KCN
E)0.50 M HCl and 0.10 NaCl
A)0.40 M HCN and 0.10 KCN
B)0.20 M CH3COOH
C)1.0 M HNO3 and 1.0 M NaNO3
D)0.10 M KCN
E)0.50 M HCl and 0.10 NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider a buffer solution prepared from HOCl and NaOCl.Which is the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when NaOH is added to this buffer?
A)OH- + HOCl H2O + OCl-
B)OH- + OCl- HOCl + O2-
C)Na+ + HOCl NaCl + OH-
D)H+ + HOCl H2 + OCl-
E)NaOH + HOCl H2O + NaCl
A)OH- + HOCl H2O + OCl-
B)OH- + OCl- HOCl + O2-
C)Na+ + HOCl NaCl + OH-
D)H+ + HOCl H2 + OCl-
E)NaOH + HOCl H2O + NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Calculate the pH of a buffer solution that contains 0.25 M benzoic acid (C6H5CO2H)and 0.15M sodium benzoate (C6H5COONa).[Ka = 6.5 × 10-5 for benzoic acid]
A)3.97
B)4.83
C)4.19
D)3.40
E)4.41
A)3.97
B)4.83
C)4.19
D)3.40
E)4.41

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is the most acidic solution?
A)0.10 M CH3COOH and 0.10 M CH3COONa
B)0.10 M CH3COOH
C)0.10 M HNO2
D)0.10 M HNO2 and 0.10 M NaNO2
E)0.10 M CH3COONa
A)0.10 M CH3COOH and 0.10 M CH3COONa
B)0.10 M CH3COOH
C)0.10 M HNO2
D)0.10 M HNO2 and 0.10 M NaNO2
E)0.10 M CH3COONa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following yields a buffer solution when equal volumes of the two solutions are mixed?
A)0.10M H2CO3 and 0.050M HCl
B)0.10M H2CO3 and 0.10M KOH
C)0.10M H2CO3 and 0.10M HCl
D)0.10M H2CO3 and 0.050M KOH
E)0.10M K2CO3 and 0.050M KOH
A)0.10M H2CO3 and 0.050M HCl
B)0.10M H2CO3 and 0.10M KOH
C)0.10M H2CO3 and 0.10M HCl
D)0.10M H2CO3 and 0.050M KOH
E)0.10M K2CO3 and 0.050M KOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following yields a buffer solution when equal volumes of the two solutions are mixed?
A)0.050 M H3PO4 and 0.050M HCl
B)0.050M H3PO4 and 0.025 M HCl
C)0.050M NaH2PO4 and 0.025M NaOH
D)0.050M Na3PO4 and 0.050M M NaOH
E)0.050M Na3PO4 and 0.025M NaOH
A)0.050 M H3PO4 and 0.050M HCl
B)0.050M H3PO4 and 0.025 M HCl
C)0.050M NaH2PO4 and 0.025M NaOH
D)0.050M Na3PO4 and 0.050M M NaOH
E)0.050M Na3PO4 and 0.025M NaOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Acid dissociation constants for phosphoric acid are given below. 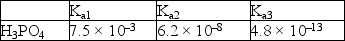 A buffer with a pH = 7.4 can best be made by using
A buffer with a pH = 7.4 can best be made by using
A)H3PO4 and NaH2PO4.
B)NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4.
C)Na2HPO4 and Na3PO4.
D)only NaH2PO4.
E)only Na2HPO4.
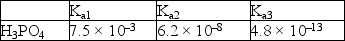 A buffer with a pH = 7.4 can best be made by using
A buffer with a pH = 7.4 can best be made by usingA)H3PO4 and NaH2PO4.
B)NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4.
C)Na2HPO4 and Na3PO4.
D)only NaH2PO4.
E)only Na2HPO4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What mass of sodium fluoride must be added to 250.mL of a 0.100 M HF solution to give a buffer solution having a pH of 3.50? [Ka(HF)= 7.1 × 10-4]
A)0.49 g
B)1.5 g
C)3.4 g
D)2.3 g
E)0.75 g
A)0.49 g
B)1.5 g
C)3.4 g
D)2.3 g
E)0.75 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Calculate the pH of the solution resulting from the addition of 25.0 mL of 0.20 M HCl to 50.0 mL of 0.10 M aniline (C6H5NH2).Kb (C6H5NH2)= 3.8 x 10-10
A)9.42
B)9.12
C)7.00
D)2.30
E)2.88
A)9.42
B)9.12
C)7.00
D)2.30
E)2.88

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Calculate the pH at the equivalence point for the titration of 0.20 M HCl with 0.20 M NH3 (Kb = 1.8 × 10-5).
A)2.87
B)4.98
C)5.12
D)7.00
E)11.12
A)2.87
B)4.98
C)5.12
D)7.00
E)11.12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In which one of the following solutions will acetic acid have the greatest percent ionization?
A)0.1 M CH3COOH
B)0.1 M CH3COOH dissolved in 0.1 M HCl
C)0.1 M CH3COOH dissolved in 0.2 M HCl
D)0.1 M CH3COOH plus 0.1 M CH3COONa
E)0.1 M CH3COOH plus 0.2 M CH3COONa
A)0.1 M CH3COOH
B)0.1 M CH3COOH dissolved in 0.1 M HCl
C)0.1 M CH3COOH dissolved in 0.2 M HCl
D)0.1 M CH3COOH plus 0.1 M CH3COONa
E)0.1 M CH3COOH plus 0.2 M CH3COONa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What mass of ammonium nitrate must be added to 350.mL of a 0.150 M solution of ammonia to give a buffer having a pH of 9.00? (Kb(NH3)= 1.8 × 10-5)
A)7.6 g
B)2.4 g
C)5.4 g
D)11 g
E)3.3 g
A)7.6 g
B)2.4 g
C)5.4 g
D)11 g
E)3.3 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
You have 500.0 mL of a buffer solution containing 0.30 M acetic acid (CH3COOH)and 0.20 M sodium acetate (CH3COONa).What will the pH of this solution be after the addition of 20.0 mL of 1.00 M NaOH solution? [Ka = 1.8 × 10-5]
A)4.65
B)4.71
C)4.56
D)4.84
E)5.07
A)4.65
B)4.71
C)4.56
D)4.84
E)5.07

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The pH at the equivalence point of a titration may differ from 7.0 due to
A)the initial concentration of the standard solution.
B)the indicator used.
C)the self-ionization of H2O.
D)the initial pH of the unknown.
E)hydrolysis of the salt formed.
A)the initial concentration of the standard solution.
B)the indicator used.
C)the self-ionization of H2O.
D)the initial pH of the unknown.
E)hydrolysis of the salt formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Calculate the pH of the solution resulting from the addition of 10.0 mL of 0.10 M NaOH to 50.0 mL of 0.10 M HCN (Ka = 4.9 × 10-10)solution.
A)5.15
B)8.71
C)5.85
D)9.91
E)13.0
A)5.15
B)8.71
C)5.85
D)9.91
E)13.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
For which type of titration will the pH be neutral at the equivalence point?
A)Strong acid vs.strong base.
B)Strong acid vs.weak base.
C)Weak acid vs.strong base.
D)All of the above.
E)None of the above.
A)Strong acid vs.strong base.
B)Strong acid vs.weak base.
C)Weak acid vs.strong base.
D)All of the above.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Calculate the pH of the solution resulting from the addition of 75.0 mL of 0.15 M KOH to 35.0 mL of 0.20 M HCN (Ka (HCN)= 4.9 × 10-10).
A)9.31
B)9.18
C)9.52
D)11.63
E)12.59
A)9.31
B)9.18
C)9.52
D)11.63
E)12.59

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
For which type of titration will the pH be basic at the equivalence point?
A)Strong acid vs.strong base.
B)Strong acid vs.weak base.
C)Weak acid vs.strong base.
D)All of the above.
E)None of the above.
A)Strong acid vs.strong base.
B)Strong acid vs.weak base.
C)Weak acid vs.strong base.
D)All of the above.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Methyl red is a common acid-base indicator.It has a Ka equal to 6.3 × 10-6.Its un-ionized form is red and its anionic form is yellow.What color would a methyl red solution have at pH = 7.8?
A)green
B)red
C)blue
D)yellow
E)violet
A)green
B)red
C)blue
D)yellow
E)violet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Starting with 0.750L of a buffer solution containing 0.30 M benzoic acid (C6H5COOH)and 0.35 M sodium benzoate (C6H5COONa), what will the pH of the solution be after the addition of 340.0 mL of 0.350M HCl? (Ka (C6H5COOH)= 6.5 x 10-5)
A)4.19
B)4.25
C)3.81
D)0.45
E)6.54
A)4.19
B)4.25
C)3.81
D)0.45
E)6.54

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A titration of an acid and base to the equivalence point results in a noticeably acidic solution.It is likely this titration involves
A)a strong acid and a weak base.
B)a weak acid and a strong base.
C)a weak acid and a weak base (where Ka equals Kb).
D)a strong acid and a strong base.
A)a strong acid and a weak base.
B)a weak acid and a strong base.
C)a weak acid and a weak base (where Ka equals Kb).
D)a strong acid and a strong base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the pH at the equivalence point in the titration of 100 mL of 0.10 M HCN (Ka = 4.9 × 10-10)with 0.10 M NaOH?
A)3.0
B)6.0
C)7.0
D)11.0
E)12.0
A)3.0
B)6.0
C)7.0
D)11.0
E)12.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the pH at the equivalence point in the titration of 100 mL of 0.10 M HCl with 0.10 M NaOH?
A)1.0
B)6.0
C)7.0
D)8.0
E)13.0
A)1.0
B)6.0
C)7.0
D)8.0
E)13.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Starting with 0.250L of a buffer solution containing 0.250 M benzoic acid (C6H5COOH)and 0.20 M sodium benzoate (C6H5COONa), what will the pH of the solution be after the addition of 25.0 mL of 0.100M HCl? (Ka (C6H5COOH)= 6.5 x 10-5)
A)4.19
B)4.10
C)4.28
D)4.05
E)3.78
A)4.19
B)4.10
C)4.28
D)4.05
E)3.78

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Calculate the percent ionization of cyanic acid, Ka = 2.0 × 10-4, in a buffer solution that is 0.50 M HCNO and 0.10 M NaCNO.
A)0.02%
B)0.10%
C)0.20%
D)2.0%
E)20%
A)0.02%
B)0.10%
C)0.20%
D)2.0%
E)20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Calculate the pH of the solution resulting from the addition of 85.0 mL of 0.35 M HCl to 30.0 mL of 0.40 M aniline (C6H5NH2).Kb (C6H5NH2)= 3.8 x 10-10
A)1.75
B)0.81
C)4.64
D)4.19
E)9.09
A)1.75
B)0.81
C)4.64
D)4.19
E)9.09

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The Ksp value for lead(II)chloride is 2.4 × 10-4.What is the molar solubility of lead(II)chloride?
A)2.4 × 10-4 mol/L
B)6.2 × 10-2 mol/L
C)7.7 × 10-3 mol/L
D)3.9 × 10-2 mol/L
E)6.0 × 10-5 mol/L
A)2.4 × 10-4 mol/L
B)6.2 × 10-2 mol/L
C)7.7 × 10-3 mol/L
D)3.9 × 10-2 mol/L
E)6.0 × 10-5 mol/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The solubility of strontium carbonate is 0.0011 g/100 mL at 20ºC.Calculate the Ksp value for this compound.
A)7.5 × 10-5
B)1.5 × 10-4
C)5.6 × 10-9
D)7.5 × 10-6
E)1.5 × 10-3
A)7.5 × 10-5
B)1.5 × 10-4
C)5.6 × 10-9
D)7.5 × 10-6
E)1.5 × 10-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The molar solubility of manganese(II)carbonate is 4.2 × 10-6 M.What is Ksp for this compound?
A)4.2 × 10-6
B)8.4 × 10-6
C)3.0 × 10-16
D)1.8 × 10-11
E)2.0 × 10-3
A)4.2 × 10-6
B)8.4 × 10-6
C)3.0 × 10-16
D)1.8 × 10-11
E)2.0 × 10-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The solubility product for barium sulfate is 1.1 × 10-10.Calculate the molar solubility of barium sulfate.
A)5.5 × 10-11 mol/L
B)1.1 × 10-5 mol/L
C)2.1 × 10-5 mol/L
D)1.1 × 10-10 mol/L
E)2.2 × 10-10 mol/L
A)5.5 × 10-11 mol/L
B)1.1 × 10-5 mol/L
C)2.1 × 10-5 mol/L
D)1.1 × 10-10 mol/L
E)2.2 × 10-10 mol/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The solubility product for calcium phosphate is Ksp = 1.3 × 10-26.What is the molar solubility of calcium phosphate?
A)1.3 × 10-26 M
B)1.5 × 10-7 M
C)2.6 × 10-6 M
D)4.6 × 10-6 M
E)6.6 × 10-6 M
A)1.3 × 10-26 M
B)1.5 × 10-7 M
C)2.6 × 10-6 M
D)4.6 × 10-6 M
E)6.6 × 10-6 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The Ksp for silver(I)phosphate is 1.8 × 10-18.Calculate the molar solubility of silver(I)phosphate.
A)1.6 × 10-5 M
B)2.1 × 10-5 M
C)3.7 × 10-5 M
D)7.2 × 10-1 M
E)1.8 × 10-1 M
A)1.6 × 10-5 M
B)2.1 × 10-5 M
C)3.7 × 10-5 M
D)7.2 × 10-1 M
E)1.8 × 10-1 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Calculate the silver ion concentration in a saturated solution of silver(I)sulfate (Ksp = 1.4 × 10-5).
A)1.5 × 10-2 M
B)2.4 × 10-2 M
C)3.0 × 10-2 M
D)1.4 × 10-5 M
E)None of the above.
A)1.5 × 10-2 M
B)2.4 × 10-2 M
C)3.0 × 10-2 M
D)1.4 × 10-5 M
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The Ksp for silver(I)phosphate is 1.8 × 10-18.Determine the silver ion concentration in a saturated solution of silver(I)phosphate.
A)1.6 × 10-5 M
B)2.1 × 10-5 M
C)3.7 × 10-5 M
D)1.1 × 10-13 M
E)4.8 × 10-5 M
A)1.6 × 10-5 M
B)2.1 × 10-5 M
C)3.7 × 10-5 M
D)1.1 × 10-13 M
E)4.8 × 10-5 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Calculate the concentration of chloride ions in a saturated lead(II)chloride (Ksp = 2.4 × 10-4)solution.
A)2.4 × 10-4 M
B)4.8 × 10-4 M
C)3.9 × 10-2 M
D)1.2 × 10-1 M
E)7.8 × 10-2 M
A)2.4 × 10-4 M
B)4.8 × 10-4 M
C)3.9 × 10-2 M
D)1.2 × 10-1 M
E)7.8 × 10-2 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following would decrease the Ksp for PbI2?
A)Lowering the pH of the solution
B)Adding a solution of Pb(NO3)2
C)Adding a solution of KI
D)None of the above-the Ksp of a compound is constant at constant temperature.
A)Lowering the pH of the solution
B)Adding a solution of Pb(NO3)2
C)Adding a solution of KI
D)None of the above-the Ksp of a compound is constant at constant temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For PbCl2 (Ksp = 2.4 × 10-4), will a precipitate of PbCl2 form when 0.10 L of 3.0 × 10-2 M Pb(NO3)2 is added to 400 mL of 9.0 × 10-2 M NaCl?
A)Yes, because Q > Ksp..
B)No, because Q < Ksp.
C)No, because Q = Ksp
D)Yes, because Q < Ksp.
A)Yes, because Q > Ksp..
B)No, because Q < Ksp.
C)No, because Q = Ksp
D)Yes, because Q < Ksp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Calculate the silver ion concentration in a saturated solution of silver(I)carbonate (Ksp = 8.1 × 10-12).
A)5.0 × 10-5 M
B)2.5 × 10-4 M
C)1.3 × 10-4 M
D)2.0 × 10-4 M
E)8.1 × 10-4 M
A)5.0 × 10-5 M
B)2.5 × 10-4 M
C)1.3 × 10-4 M
D)2.0 × 10-4 M
E)8.1 × 10-4 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The molar solubility of magnesium carbonate is 1.8 × 10-4 mol/L.What is Ksp for this compound?
A)1.8 × 10-4
B)3.6 × 10-4
C)1.3 × 10-7
D)3.2 × 10-8
E)2.8 × 10-14
A)1.8 × 10-4
B)3.6 × 10-4
C)1.3 × 10-7
D)3.2 × 10-8
E)2.8 × 10-14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The solubility product for chromium(III)fluoride is Ksp = 6.6 × 10-11.What is the molar solubility of chromium(III)fluoride?
A)1.6 × 10-3 M
B)1.2 × 10-3 M
C)6.6 × 10-11 M
D)2.2 × 10-3 M
E)1.6 × 10-6 M
A)1.6 × 10-3 M
B)1.2 × 10-3 M
C)6.6 × 10-11 M
D)2.2 × 10-3 M
E)1.6 × 10-6 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Calculate the minimum concentration of Mg2+ that must be added to 0.10 M NaF in order to initiate a precipitate of magnesium fluoride.(For MgF2 , Ksp = 6.9 × 10-9.)
A)1.4 × 107 M
B)6.9 × 10-9 M
C)6.9 × 10-8 M
D)1.7 × 10-7 M
E)6.9 × 10-7 M
A)1.4 × 107 M
B)6.9 × 10-9 M
C)6.9 × 10-8 M
D)1.7 × 10-7 M
E)6.9 × 10-7 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Calculate the minimum concentration of Cr3+ that must be added to 0.095 M NaF in order to initiate a precipitate of chromium(III)fluoride.(For CrF3 , Ksp = 6.6 × 10-11.)
A)0.023 M
B)0.032 M
C)7.7 × 10-8 M
D)2.9 × 10-9 M
E)6.9 × 10-10 M
A)0.023 M
B)0.032 M
C)7.7 × 10-8 M
D)2.9 × 10-9 M
E)6.9 × 10-10 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The solubility of lead(II)iodide is 0.064 g/100 mL at 20ºC.What is the solubility product for lead(II)iodide?
A)1.1 × 10-8
B)3.9 × 10-6
C)1.1 × 10-11
D)2.7 × 10-12
E)1.4 × 10-3
A)1.1 × 10-8
B)3.9 × 10-6
C)1.1 × 10-11
D)2.7 × 10-12
E)1.4 × 10-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The molar solubility of tin(II)iodide is 1.28 × 10-2 mol/L.What is Ksp for this compound?
A)8.4 × 10-6
B)1.28 × 10-2
C)4.2 × 10-6
D)1.6 × 10-4
E)2.1 × 10-6
A)8.4 × 10-6
B)1.28 × 10-2
C)4.2 × 10-6
D)1.6 × 10-4
E)2.1 × 10-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Calculate the concentration of fluoride ions in a saturated barium fluoride (Ksp = 1.7 × 10-6)solution.
A)7.6 × 10-3 M
B)1.5 × 10-2 M
C)3.4 × 10-5 M
D)1.7 × 10-6 M
E)3.4 × 10-6 M
A)7.6 × 10-3 M
B)1.5 × 10-2 M
C)3.4 × 10-5 M
D)1.7 × 10-6 M
E)3.4 × 10-6 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The molar solubility of lead(II)iodate in water is 4.0 × 10-5 mol/L.Calculate Ksp for lead(II)iodate.
A)1.6 × 10-9
B)6.4 × 10-14
C)2.6 × 10-13
D)4.0 × 10-5
E)4.0 × 10-15
A)1.6 × 10-9
B)6.4 × 10-14
C)2.6 × 10-13
D)4.0 × 10-5
E)4.0 × 10-15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following compounds is more soluble in acidic solution than in pure neutral water?
A)PbI2
B)CuBr
C)KClO4
D)FeS
E)NaNO3
A)PbI2
B)CuBr
C)KClO4
D)FeS
E)NaNO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
To 1.00 L of a 0.100 M aqueous solution of benzoic acid (C6H5COOH)is added 1.00 mL of 12.0 M HCl.What is the percentage ionization of the benzoic acid in the resulting solution? [Ka(C6H5COOH)= 6.5 × 10-5]
A)3.3%
B)12%
C)1.3%
D)0.52%
E)0.065%
A)3.3%
B)12%
C)1.3%
D)0.52%
E)0.065%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which response has both answers correct? Will a precipitate form when 250 mL of 0.33 M Na2CrO4 are added to 250 mL of 0.12 M AgNO3? [Ksp(Ag2CrO4)= 1.1 × 10-12] What is the concentration of the silver ion remaining in solution?
A)Yes, [Ag+] = 2.9 × 10-6 M.
B)Yes, [Ag+] = 0.060 M.
C)Yes, [Ag+] = 1.3 × 10-4 M.
D)No, [Ag+] = 0.060 M.
E)No, [Ag+] = 0.105 M.
A)Yes, [Ag+] = 2.9 × 10-6 M.
B)Yes, [Ag+] = 0.060 M.
C)Yes, [Ag+] = 1.3 × 10-4 M.
D)No, [Ag+] = 0.060 M.
E)No, [Ag+] = 0.105 M.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following compounds is more soluble in acidic solution than in pure neutral water?
A)BaCO3
B)CuI
C)PbCl2
D)AgBr
E)NH4NO3
A)BaCO3
B)CuI
C)PbCl2
D)AgBr
E)NH4NO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A saturated sodium carbonate solution at 100°C contains 45.5 g of dissolved sodium carbonate per 100.mL of solution.The solubility product constant for sodium carbonate at this temperature is
A)79.0
B)0.316
C)0.0790
D)36.8
E)316
A)79.0
B)0.316
C)0.0790
D)36.8
E)316

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Find the concentration of Pb2+ ions in a solution made by adding 5.00 g of lead(II)iodide to 500.mL of 0.150 M KI.[For PbI2, Ksp = 1.39 × 10-8.]
A)3.04 × 10-4 M
B)1.54 × 10-7 M
C)6.18 × 10-7 M
D)1.52 × 10-4 M
E)9.27 × 10-8 M
A)3.04 × 10-4 M
B)1.54 × 10-7 M
C)6.18 × 10-7 M
D)1.52 × 10-4 M
E)9.27 × 10-8 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Calculate the molar solubility of AgCl in a 0.15 M solution of NH3(aq). (Ksp (AgCl)= 1.6 x 10-10; Kf (Ag(NH3)2+)= 1.5 x 107)
A)6.7 x 10-3 M
B)1.3 x 10-5 M
C)3.9 x 103 M
D)7.5 x 10-2 M
E)3.3 x 10-5 M
A)6.7 x 10-3 M
B)1.3 x 10-5 M
C)3.9 x 103 M
D)7.5 x 10-2 M
E)3.3 x 10-5 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Calculate the molar solubility of AgBr in a 0.25M solution of NH3(aq)(Ksp (AgBr)= 7.7 x 10-13 ; Kf (Ag(NH3)2+)= 1.5 x 107.
A)8.8 x 10-7 M
B)3.4 x 10-3 M
C)8.4 x 10-4 M
D)2.5 x 10-1 M
E)9.7 x 102 M
A)8.8 x 10-7 M
B)3.4 x 10-3 M
C)8.4 x 10-4 M
D)2.5 x 10-1 M
E)9.7 x 102 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A saturated sodium carbonate solution at 0°C contains 7.1 g of dissolved sodium carbonate per 100.mL of solution.The solubility product constant for sodium carbonate at this temperature is
A)1.2
B)0.30
C)3.0 × 10-4
D)0.90
E)1.2 × 10-3
A)1.2
B)0.30
C)3.0 × 10-4
D)0.90
E)1.2 × 10-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Calculate the molar solubility of BaCO3 in a 0.10 M solution of Na2CO3(aq).(Ksp (BaCO3)= 8.1 x 10-9)
A)8.1 x 10-9 M
B)9.0 x 10-5 M
C)8.1 x 10-8 M
D)2.8 x 10-4 M
E)0.10 M
A)8.1 x 10-9 M
B)9.0 x 10-5 M
C)8.1 x 10-8 M
D)2.8 x 10-4 M
E)0.10 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Will a precipitate of magnesium fluoride form when 300.mL of 1.1 × 10-3 M MgCl2 are added to 500.mL of 1.2 × 10-3 M NaF? [Ksp (MgF2)= 6.9 × 10-9]
A)Yes, Q > Ksp
B)No, Q < Ksp
C)No, Q = Ksp
D)Yes, Q < Ksp
E)Yes, Q = Ksp
A)Yes, Q > Ksp
B)No, Q < Ksp
C)No, Q = Ksp
D)Yes, Q < Ksp
E)Yes, Q = Ksp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Calculate the molar solubility of CaF2 in a 0.25 M solution of NaF(aq).(Ksp (CaF2)= 4.0 x 10-11)
A)4.0 x 10-11 M
B)6.4 x 10-10 M
C)1.6 x 10-10 M
D)1.3 x 10-5 M
E)2.2 x 10-4 M
A)4.0 x 10-11 M
B)6.4 x 10-10 M
C)1.6 x 10-10 M
D)1.3 x 10-5 M
E)2.2 x 10-4 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Find the concentration of calcium ions in a solution made by adding 3.50 g of calcium fluoride to 750.mL of 0.125 M NaF.[For CaF2, Ksp = 3.95 × 10-11.]
A)3.16 × 10-10 M
B)2.53 × 10-9 M
C)4.29 × 10-4 M
D)6.32 × 10-10 M
E)2.15 × 10-4 M
A)3.16 × 10-10 M
B)2.53 × 10-9 M
C)4.29 × 10-4 M
D)6.32 × 10-10 M
E)2.15 × 10-4 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Calculate the molar solubility of Fe(OH)2 in a solution with pH = 13.15. (Ksp Fe(OH)2 = 1.6 x 10-14)
A)1.6 x 10-14 M
B)1.1 x 10-13 M
C)1.6 x 10-5 M
D)8.0 x 10-13 M
E)3.4 x 10-7 M
A)1.6 x 10-14 M
B)1.1 x 10-13 M
C)1.6 x 10-5 M
D)8.0 x 10-13 M
E)3.4 x 10-7 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Calculate the molar solubility of Mg(OH)2 in a solution with pH = 12.20. (Ksp (Mg(OH)2 = 1.2 x 10-11)
A)4.8 x 10-8 M
B)7.6 x 10-10 M
C)3.5 x 10-6 M
D)1.4 x 10-4 M
E)2.4 x 10-6 M
A)4.8 x 10-8 M
B)7.6 x 10-10 M
C)3.5 x 10-6 M
D)1.4 x 10-4 M
E)2.4 x 10-6 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Will a precipitate (ppt)form when 20.0 mL of 1.1 × 10-3 M Ba(NO3)2 are added to 80.0 mL of 8.4 × 10-4 M Na2CO3?
A)Yes, the ppt is Ba(NO3 )2.
B)Yes, the ppt is NaNO3.
C)Yes, the ppt is BaCO3.
D)Yes, the ppt is Na2CO3.
E)No, a precipitate will not form.
A)Yes, the ppt is Ba(NO3 )2.
B)Yes, the ppt is NaNO3.
C)Yes, the ppt is BaCO3.
D)Yes, the ppt is Na2CO3.
E)No, a precipitate will not form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Will a precipitate (ppt)form when 300.mL of 5.0 × 10-5 M AgNO3 are added to 200.mL of 2.5 × 10-7 M NaBr? Answer yes or no, and identify the precipitate if there is one.
A)Yes, the ppt is AgNO3(s).
B)Yes, the ppt is AgBr(s).
C)Yes, the ppt is NaBr(s).
D)Yes, the ppt is NaNO3(s).
E)No, a precipitate will not form.
A)Yes, the ppt is AgNO3(s).
B)Yes, the ppt is AgBr(s).
C)Yes, the ppt is NaBr(s).
D)Yes, the ppt is NaNO3(s).
E)No, a precipitate will not form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Will a precipitate form (yes or no)when 50.0 mL of 1.2 × 10-3 M Pb(NO3)2 are added to 50.0 mL of 2.0 × 10-4 M Na2S? If so, identify the precipitate.
A)Yes, the precipitate is PbS.
B)Yes, the precipitate is NaNO3.
C)Yes, the precipitate is Na2S.
D)Yes, the precipitate is Pb(NO3)2.
E)No, a precipitate will not form.
A)Yes, the precipitate is PbS.
B)Yes, the precipitate is NaNO3.
C)Yes, the precipitate is Na2S.
D)Yes, the precipitate is Pb(NO3)2.
E)No, a precipitate will not form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Will a precipitate (ppt)form when 300.mL of 2.0 × 10-5 M AgNO3 are added to 200.mL of 2.5 × 10-9 M NaI? Answer yes or no, and identify the precipitate if there is one.
A)Yes, the ppt is AgNO3(s).
B)Yes, the ppt is NaNO3(s).
C)Yes, the ppt is NaI(s).
D)Yes, the ppt is AgI(s).
E)No, a precipitate will not form.
A)Yes, the ppt is AgNO3(s).
B)Yes, the ppt is NaNO3(s).
C)Yes, the ppt is NaI(s).
D)Yes, the ppt is AgI(s).
E)No, a precipitate will not form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Will a precipitate of magnesium fluoride form when 200.mL of 1.9 × 10-3 M MgCl2 are added to 300.mL of 1.4 × 10-2 M NaF? [Ksp (MgF2)= 6.9 × 10-9]
A)Yes, Q > Ksp
B)No, Q < Ksp
C)No, Q = Ksp
D)Yes, Q < Ksp
E)Yes, Q = Ksp
A)Yes, Q > Ksp
B)No, Q < Ksp
C)No, Q = Ksp
D)Yes, Q < Ksp
E)Yes, Q = Ksp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



