Deck 15: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/97
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Chemical Equilibrium
1
In what year was Fritz Haber awarded the Nobel Prize in chemistry for his development of a process for synthesizing ammonia directly from nitrogen and hydrogen?
A)1954
B)1933
C)1918
D)1900
E)1912
A)1954
B)1933
C)1918
D)1900
E)1912
1918
2
The equilibrium expression for Kp for the reaction below is ________. N2 (g) + O2 (g)  2NO (g)
2NO (g)
A)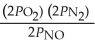
B)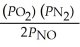
C)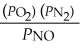
D)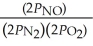
E)none of the above
 2NO (g)
2NO (g)A)
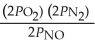
B)
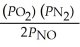
C)
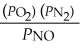
D)
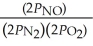
E)none of the above
none of the above
3
Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? CO2 (s) + H2O (l) ![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? CO<sub>2</sub> (s) + H<sub>2</sub>O (l) H<sup>+</sup> (aq) + HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq)</strong> A)[H<sup>+</sup>][HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>] / [CO<sub>2</sub>] B)[CO<sub>2</sub>] / [H<sup>+</sup>][HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>] C)[H<sup>+</sup>][HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>] / [CO<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>O] D)[CO<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>O] / [H<sup>+</sup>][HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>] E)[H<sup>+</sup>][HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f67_9328_a2ab_b5a0ac5a2b57_TB2701_11.jpg) H+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq)
H+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq)
A)[H+][HCO3-] / [CO2]
B)[CO2] / [H+][HCO3-]
C)[H+][HCO3-] / [CO2][H2O]
D)[CO2][H2O] / [H+][HCO3-]
E)[H+][HCO3-]
![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? CO<sub>2</sub> (s) + H<sub>2</sub>O (l) H<sup>+</sup> (aq) + HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq)</strong> A)[H<sup>+</sup>][HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>] / [CO<sub>2</sub>] B)[CO<sub>2</sub>] / [H<sup>+</sup>][HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>] C)[H<sup>+</sup>][HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>] / [CO<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>O] D)[CO<sub>2</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>O] / [H<sup>+</sup>][HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>] E)[H<sup>+</sup>][HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f67_9328_a2ab_b5a0ac5a2b57_TB2701_11.jpg) H+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq)
H+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq)A)[H+][HCO3-] / [CO2]
B)[CO2] / [H+][HCO3-]
C)[H+][HCO3-] / [CO2][H2O]
D)[CO2][H2O] / [H+][HCO3-]
E)[H+][HCO3-]
[H+][HCO3-]
4
Which one of the following is true concerning the Haber process?
A)It is a process used for shifting equilibrium positions to the right for more economical chemical synthesis of a variety of substances.
B)It is a process used for the synthesis of ammonia.
C)It is another way of stating Le Châtelier's principle.
D)It is an industrial synthesis of sodium chloride that was discovered by Karl Haber.
E)It is a process for the synthesis of elemental chlorine.
A)It is a process used for shifting equilibrium positions to the right for more economical chemical synthesis of a variety of substances.
B)It is a process used for the synthesis of ammonia.
C)It is another way of stating Le Châtelier's principle.
D)It is an industrial synthesis of sodium chloride that was discovered by Karl Haber.
E)It is a process for the synthesis of elemental chlorine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What role did Karl Bosch play in development of the Haber-Bosch process?
A)He discovered the reaction conditions necessary for formation of ammonia.
B)He originally isolated ammonia from camel dung and found a method for purifying it.
C)Haber was working in his lab with his instructor at the time he worked out the process.
D)He developed the equipment necessary for industrial production of ammonia.
E)He was the German industrialist who financed the research done by Haber.
A)He discovered the reaction conditions necessary for formation of ammonia.
B)He originally isolated ammonia from camel dung and found a method for purifying it.
C)Haber was working in his lab with his instructor at the time he worked out the process.
D)He developed the equipment necessary for industrial production of ammonia.
E)He was the German industrialist who financed the research done by Haber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which one of the following will change the value of an equilibrium constant?
A)changing temperature
B)adding other substances that do not react with any of the species involved in the equilibrium
C)varying the initial concentrations of reactants
D)varying the initial concentrations of products
E)changing the volume of the reaction vessel
A)changing temperature
B)adding other substances that do not react with any of the species involved in the equilibrium
C)varying the initial concentrations of reactants
D)varying the initial concentrations of products
E)changing the volume of the reaction vessel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The Keq for the equilibrium below is 7.52 × 10-2 at 480.0 °C. 2Cl2 (g) + 2H2O (g)  4HCl (g) + O2 (g)
4HCl (g) + O2 (g)
What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
2HCl (g) + O2 (g)
O2 (g)  Cl2 (g) + H2O (g)
Cl2 (g) + H2O (g)
A)13.3
B)3.65
C)-0.0376
D)5.66 × 10-3
E)0.274
 4HCl (g) + O2 (g)
4HCl (g) + O2 (g)What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
2HCl (g) +
 O2 (g)
O2 (g)  Cl2 (g) + H2O (g)
Cl2 (g) + H2O (g)A)13.3
B)3.65
C)-0.0376
D)5.66 × 10-3
E)0.274

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Keq for the equilibrium below is 0.112 at 700.0 °C. SO2 (g) +  O2 (g)
O2 (g)  SO3 (g)
SO3 (g)
What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
2SO3 (g) 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
A)79.7
B)2.99
C)17.86
D)4.46
E)8.93
 O2 (g)
O2 (g)  SO3 (g)
SO3 (g)What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
2SO3 (g)
 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)A)79.7
B)2.99
C)17.86
D)4.46
E)8.93

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? HF (aq)+ H2O (l) ![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? HF (aq)+ H<sub>2</sub>O (l) H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ F<sup>-</sup> (aq)</strong> A)[HF][H<sub>2</sub>O] / [H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] B)1 / [HF] C)[H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] / [HF][H<sub>2</sub>O] D)[H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] / [HF] E)[F<sup>-</sup>] / [HF]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f67_ba39_a2ab_bb03ce7ec614_TB2701_11.jpg) H3O+ (aq)+ F- (aq)
H3O+ (aq)+ F- (aq)
A)[HF][H2O] / [H3O+][F-]
B)1 / [HF]
C)[H3O+][F-] / [HF][H2O]
D)[H3O+][F-] / [HF]
E)[F-] / [HF]
![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? HF (aq)+ H<sub>2</sub>O (l) H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ F<sup>-</sup> (aq)</strong> A)[HF][H<sub>2</sub>O] / [H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] B)1 / [HF] C)[H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] / [HF][H<sub>2</sub>O] D)[H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] / [HF] E)[F<sup>-</sup>] / [HF]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f67_ba39_a2ab_bb03ce7ec614_TB2701_11.jpg) H3O+ (aq)+ F- (aq)
H3O+ (aq)+ F- (aq)A)[HF][H2O] / [H3O+][F-]
B)1 / [HF]
C)[H3O+][F-] / [HF][H2O]
D)[H3O+][F-] / [HF]
E)[F-] / [HF]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The equilibrium expression for Kp for the reaction below is ________. 2O3 (g)  3O2 (g)
3O2 (g)
A)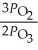
B)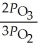
C)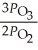
D)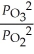
E)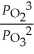
 3O2 (g)
3O2 (g)A)
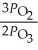
B)
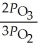
C)
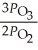
D)
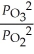
E)
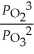

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The equilibrium constant for reaction 1 is K. The equilibrium constant for reaction 2 is ________. (1) SO2 (g) + (1/2)O2 (g)  SO3 (g)
SO3 (g)
(2) 2SO3 (g) 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
A)K2
B)2K
C)1/2K
D)1/K2
E)-K2
 SO3 (g)
SO3 (g)(2) 2SO3 (g)
 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)A)K2
B)2K
C)1/2K
D)1/K2
E)-K2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the following reaction? CO2 (g)+ 2H2 (g)  CH3OH (g)
CH3OH (g)
A)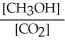
B)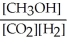
C)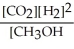
D)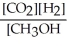
E)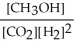
 CH3OH (g)
CH3OH (g)A)
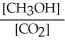
B)
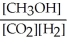
C)
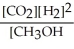
D)
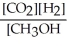
E)
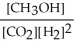

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Keq for the equilibrium below is 5.4 × 1013 at 480.0 °C. 2NO (g) + O2 (g)  2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)
What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
NO2 (g) NO (g) +
NO (g) + 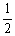 O2 (g)
O2 (g)
A)5.4 × 10-13
B)5.4 × 1013
C)1.4 × 10-7
D)5.66 × 10-3
E)none of the above
 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
NO2 (g)
 NO (g) +
NO (g) + 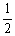 O2 (g)
O2 (g)A)5.4 × 10-13
B)5.4 × 1013
C)1.4 × 10-7
D)5.66 × 10-3
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The Keq for the equilibrium below is 0.112 at 700.0 °C. SO2 (g) +  O2 (g)
O2 (g)  SO3 (g)
SO3 (g)
What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
SO3 (g) SO2 (g) +
SO2 (g) +  O2 (g)
O2 (g)
A)0.224
B)0.0125
C)0.112
D)8.93
E)-0.112
 O2 (g)
O2 (g)  SO3 (g)
SO3 (g)What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
SO3 (g)
 SO2 (g) +
SO2 (g) +  O2 (g)
O2 (g)A)0.224
B)0.0125
C)0.112
D)8.93
E)-0.112

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The equilibrium-constant expression depends on the ________ of the reaction.
A)stoichiometry
B)mechanism
C)stoichiometry and mechanism
D)the quantities of reactants and products initially present
E)temperature
A)stoichiometry
B)mechanism
C)stoichiometry and mechanism
D)the quantities of reactants and products initially present
E)temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? 2SO2 (g)+ O2 (g) ![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? 2SO<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g) 2SO<sub>3</sub> (g)</strong> A)[SO<sub>3</sub>] / [SO<sub>2</sub>][O<sub>2</sub>] B)[SO<sub>2</sub>] / [SO<sub>3</sub>] C)[SO<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup> / [SO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>] D)[SO<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup> / [SO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E)[SO<sub>3</sub>] / [SO<sub>2</sub>][O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f67_6c16_a2ab_87d83d8869b7_TB2701_11.jpg) 2SO3 (g)
2SO3 (g)
A)[SO3] / [SO2][O2]
B)[SO2] / [SO3]
C)[SO3]2 / [SO2]2[O2]
D)[SO3]2 / [SO2]2[O2]2
E)[SO3] / [SO2][O2]2
![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? 2SO<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g) 2SO<sub>3</sub> (g)</strong> A)[SO<sub>3</sub>] / [SO<sub>2</sub>][O<sub>2</sub>] B)[SO<sub>2</sub>] / [SO<sub>3</sub>] C)[SO<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup> / [SO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>] D)[SO<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup> / [SO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E)[SO<sub>3</sub>] / [SO<sub>2</sub>][O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f67_6c16_a2ab_87d83d8869b7_TB2701_11.jpg) 2SO3 (g)
2SO3 (g)A)[SO3] / [SO2][O2]
B)[SO2] / [SO3]
C)[SO3]2 / [SO2]2[O2]
D)[SO3]2 / [SO2]2[O2]2
E)[SO3] / [SO2][O2]2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? N2O4 (g) ![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> (g) 2NO<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D)[NO<sub>2</sub>][N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>] E)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f65_e551_a2ab_7f73b986081e_TB2701_11.jpg) 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)
A)![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> (g) 2NO<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D)[NO<sub>2</sub>][N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>] E)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f65_e552_a2ab_97762c5622e0_TB2701_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> (g) 2NO<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D)[NO<sub>2</sub>][N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>] E)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f65_e553_a2ab_a99792004356_TB2701_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> (g) 2NO<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D)[NO<sub>2</sub>][N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>] E)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f65_e554_a2ab_c336a2cd0791_TB2701_11.jpg)
D)[NO2][N2O4]
E)[NO2]2[N2O4]
![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> (g) 2NO<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D)[NO<sub>2</sub>][N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>] E)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f65_e551_a2ab_7f73b986081e_TB2701_11.jpg) 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)A)
![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> (g) 2NO<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D)[NO<sub>2</sub>][N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>] E)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f65_e552_a2ab_97762c5622e0_TB2701_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> (g) 2NO<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D)[NO<sub>2</sub>][N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>] E)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f65_e553_a2ab_a99792004356_TB2701_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> (g) 2NO<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D)[NO<sub>2</sub>][N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>] E)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f65_e554_a2ab_c336a2cd0791_TB2701_11.jpg)
D)[NO2][N2O4]
E)[NO2]2[N2O4]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? (NH4)2Se (s) ![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? (NH<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Se (s) 2NH<sub>3</sub> (g) + H<sub>2</sub>Se (g)</strong> A)[NH<sub>3</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>Se] / [(NH<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Se] B)[(NH<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Se] / [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>Se] C)1 / [(NH<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Se] D)[NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>Se] E)[NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>Se] / [(NH<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Se]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f67_6c17_a2ab_ed8418460b40_TB2701_11.jpg) 2NH3 (g) + H2Se (g)
2NH3 (g) + H2Se (g)
A)[NH3][H2Se] / [(NH4)2Se]
B)[(NH4)2Se] / [NH3]2[H2Se]
C)1 / [(NH4)2Se]
D)[NH3]2[H2Se]
E)[NH3]2[H2Se] / [(NH4)2Se]
![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? (NH<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Se (s) 2NH<sub>3</sub> (g) + H<sub>2</sub>Se (g)</strong> A)[NH<sub>3</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>Se] / [(NH<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Se] B)[(NH<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Se] / [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>Se] C)1 / [(NH<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Se] D)[NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>Se] E)[NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>Se] / [(NH<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Se]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f67_6c17_a2ab_ed8418460b40_TB2701_11.jpg) 2NH3 (g) + H2Se (g)
2NH3 (g) + H2Se (g)A)[NH3][H2Se] / [(NH4)2Se]
B)[(NH4)2Se] / [NH3]2[H2Se]
C)1 / [(NH4)2Se]
D)[NH3]2[H2Se]
E)[NH3]2[H2Se] / [(NH4)2Se]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Given the following reaction at equilibrium, if Kc = 1.90 × 1019 at 25.0 °C, Kp = ________. H2 (g) + Br2 (g)  2 HBr (g)
2 HBr (g)
A)5.26 × 10-20
B)1.56 × 104
C)6.44 × 105
D)1.90 × 1019
E)none of the above
 2 HBr (g)
2 HBr (g)A)5.26 × 10-20
B)1.56 × 104
C)6.44 × 105
D)1.90 × 1019
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
At equilibrium, ________.
A)all chemical reactions have ceased
B)the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal
C)the rate constants of the forward and reverse reactions are equal
D)the value of the equilibrium constant is 1
E)the limiting reagent has been consumed
A)all chemical reactions have ceased
B)the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal
C)the rate constants of the forward and reverse reactions are equal
D)the value of the equilibrium constant is 1
E)the limiting reagent has been consumed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In which of the following reactions would increasing pressure at constant temperature not change the concentrations of reactants and products, based on Le Châtelier's principle?
A)N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g)
B)N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)
C)N2 (g) + 2O2 (g) 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)
D)2N2 (g) + O2 (g) 2N2O (g)
2N2O (g)
E)N2 (g) + O2 (g) 2NO (g)
2NO (g)
A)N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
 2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g)B)N2O4 (g)
 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)C)N2 (g) + 2O2 (g)
 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)D)2N2 (g) + O2 (g)
 2N2O (g)
2N2O (g)E)N2 (g) + O2 (g)
 2NO (g)
2NO (g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How is the reaction quotient used to determine whether a system is at equilibrium?
A)The reaction quotient must be satisfied for equilibrium to be achieved.
B)At equilibrium, the reaction quotient is undefined.
C)The reaction is at equilibrium when Q < Keq.
D)The reaction is at equilibrium when Q > Keq.
E)The reaction is at equilibrium when Q = Keq.
A)The reaction quotient must be satisfied for equilibrium to be achieved.
B)At equilibrium, the reaction quotient is undefined.
C)The reaction is at equilibrium when Q < Keq.
D)The reaction is at equilibrium when Q > Keq.
E)The reaction is at equilibrium when Q = Keq.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The equilibrium constant for the gas phase reaction N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)  2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g)
Is Keq = 4.34 × 10-3 at 300 °C. At equilibrium, ________.
A)products predominate
B)reactants predominate
C)roughly equal amounts of products and reactants are present
D)only products are present
E)only reactants are present
 2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g)Is Keq = 4.34 × 10-3 at 300 °C. At equilibrium, ________.
A)products predominate
B)reactants predominate
C)roughly equal amounts of products and reactants are present
D)only products are present
E)only reactants are present

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Of the following equilibria, only ________ will shift to the left in response to a decrease in volume.
A)H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) 2 HCl (g)
2 HCl (g)
B)2 SO3 (g) 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
C)N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g)
2 NH3 (g)
D)4 Fe (s) + 3 O2 (g) 2 Fe2O3 (s)
2 Fe2O3 (s)
E)2HI (g) H2 (g) + I2 (g)
H2 (g) + I2 (g)
A)H2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
 2 HCl (g)
2 HCl (g)B)2 SO3 (g)
 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)C)N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
 2 NH3 (g)
2 NH3 (g)D)4 Fe (s) + 3 O2 (g)
 2 Fe2O3 (s)
2 Fe2O3 (s)E)2HI (g)
 H2 (g) + I2 (g)
H2 (g) + I2 (g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2NH3 (g)  N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that the moles of H2 in the reaction container will increase with ________.
A)some removal of NH3 from the reaction vessel (V and T constant)
B)a decrease in the total pressure (T constant)
C)addition of some N2 to the reaction vessel (V and T constant)
D)a decrease in the total volume of the reaction vessel (T constant)
E)an increase in total pressure by the addition of helium gas (V and T constant)
 N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)Le Châtelier's principle predicts that the moles of H2 in the reaction container will increase with ________.
A)some removal of NH3 from the reaction vessel (V and T constant)
B)a decrease in the total pressure (T constant)
C)addition of some N2 to the reaction vessel (V and T constant)
D)a decrease in the total volume of the reaction vessel (T constant)
E)an increase in total pressure by the addition of helium gas (V and T constant)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The equilibrium constant for the gas phase reaction N2 (g) + O2 (g)  2NO (g)
2NO (g)
Is Keq = 4.20 × 10-31 at 30 °C. At equilibrium, ________.
A)products predominate
B)reactants predominate
C)roughly equal amounts of products and reactants are present
D)only products are present
E)only reactants are present
 2NO (g)
2NO (g)Is Keq = 4.20 × 10-31 at 30 °C. At equilibrium, ________.
A)products predominate
B)reactants predominate
C)roughly equal amounts of products and reactants are present
D)only products are present
E)only reactants are present

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The value of Keq for the equilibrium H2 (g) + I2 (g)  2HI (g)
2HI (g)
Is 794 at 25 °C. What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?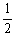 H2 (g) +
H2 (g) + 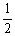 I2 (g)
I2 (g)  HI (g)
HI (g)
A)397
B)0.035
C)28
D)1588
E)0.0013
 2HI (g)
2HI (g)Is 794 at 25 °C. What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
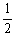 H2 (g) +
H2 (g) + 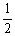 I2 (g)
I2 (g)  HI (g)
HI (g)A)397
B)0.035
C)28
D)1588
E)0.0013

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Of the following equilibria, only ________ will shift to the right in response to a decrease in volume.
A)H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) 2 HCl (g)
2 HCl (g)
B)2 SO3 (g) 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
C)N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g)
D)2 Fe2O3 (s) 4 Fe (s) + 3O2 (g)
4 Fe (s) + 3O2 (g)
E)2HI (g) H2 (g) + I2 (g)
H2 (g) + I2 (g)
A)H2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
 2 HCl (g)
2 HCl (g)B)2 SO3 (g)
 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)C)N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
 2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g)D)2 Fe2O3 (s)
 4 Fe (s) + 3O2 (g)
4 Fe (s) + 3O2 (g)E)2HI (g)
 H2 (g) + I2 (g)
H2 (g) + I2 (g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The expression for Kp for the reaction below is ________. 4CuO (s) + CH4 (g)  CO2 (g) + 4Cu (s) + 2H2O (g)
CO2 (g) + 4Cu (s) + 2H2O (g)
A)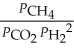
B)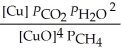
C)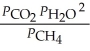
D)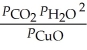
E)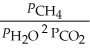
 CO2 (g) + 4Cu (s) + 2H2O (g)
CO2 (g) + 4Cu (s) + 2H2O (g)A)
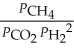
B)
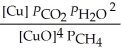
C)
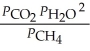
D)
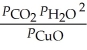
E)
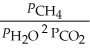

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2CO2 (g)  2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJ
2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJ
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that an increase in temperature will ________.
A)increase the partial pressure of O2 (g)
B)decrease the partial pressure of CO2 (g)
C)decrease the value of the equilibrium constant
D)increase the value of the equilibrium constant
E)increase the partial pressure of CO
 2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJ
2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJLe Châtelier's principle predicts that an increase in temperature will ________.
A)increase the partial pressure of O2 (g)
B)decrease the partial pressure of CO2 (g)
C)decrease the value of the equilibrium constant
D)increase the value of the equilibrium constant
E)increase the partial pressure of CO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Q does not change with temperature.
B)Keq does not change with temperature, whereas Q is temperature dependent.
C)K does not depend on the concentrations or partial pressures of reaction components.
D)Q does not depend on the concentrations or partial pressures of reaction components.
E)Q is the same as Keq when a reaction is at equilibrium.
A)Q does not change with temperature.
B)Keq does not change with temperature, whereas Q is temperature dependent.
C)K does not depend on the concentrations or partial pressures of reaction components.
D)Q does not depend on the concentrations or partial pressures of reaction components.
E)Q is the same as Keq when a reaction is at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The effect of a catalyst on an equilibrium is to ________.
A)increase the rate of the forward reaction only
B)increase the equilibrium constant so that products are favored
C)slow the reverse reaction only
D)increase the rate at which equilibrium is achieved without changing the composition of the equilibrium mixture
E)shift the equilibrium to the right
A)increase the rate of the forward reaction only
B)increase the equilibrium constant so that products are favored
C)slow the reverse reaction only
D)increase the rate at which equilibrium is achieved without changing the composition of the equilibrium mixture
E)shift the equilibrium to the right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium. 2CO2 (g)  2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJ
2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJ
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that the equilibrium partial pressure of CO (g)can be maximized by carrying out the reaction ________.
A)at high temperature and high pressure
B)at high temperature and low pressure
C)at low temperature and low pressure
D)at low temperature and high pressure
E)in the presence of solid carbon
 2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJ
2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJLe Châtelier's principle predicts that the equilibrium partial pressure of CO (g)can be maximized by carrying out the reaction ________.
A)at high temperature and high pressure
B)at high temperature and low pressure
C)at low temperature and low pressure
D)at low temperature and high pressure
E)in the presence of solid carbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
At 400 K, the equilibrium constant for the reaction Br2 (g) + Cl2 (g)  2BrCl (g)
2BrCl (g)
Is Kp = 7.0. A closed vessel at 400 K is charged with 1.00 atm of Br2 (g), 1.00 atm of Cl2 (g), and 2.00 atm of BrCl (g). Use Q to determine which of the statements below is true.
A)The equilibrium partial pressures of Br2, Cl2, and BrCl will be the same as the initial values.
B)The equilibrium partial pressure of Br2 will be greater than 1.00 atm.
C)At equilibrium, the total pressure in the vessel will be less than the initial total pressure.
D)The equilibrium partial pressure of BrCl (g)will be greater than 2.00 atm.
E)The reaction will go to completion since there are equal amounts of Br2 and Cl2.
 2BrCl (g)
2BrCl (g)Is Kp = 7.0. A closed vessel at 400 K is charged with 1.00 atm of Br2 (g), 1.00 atm of Cl2 (g), and 2.00 atm of BrCl (g). Use Q to determine which of the statements below is true.
A)The equilibrium partial pressures of Br2, Cl2, and BrCl will be the same as the initial values.
B)The equilibrium partial pressure of Br2 will be greater than 1.00 atm.
C)At equilibrium, the total pressure in the vessel will be less than the initial total pressure.
D)The equilibrium partial pressure of BrCl (g)will be greater than 2.00 atm.
E)The reaction will go to completion since there are equal amounts of Br2 and Cl2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The value of Keq for the equilibrium H2 (g) + I2 (g)  2HI (g)
2HI (g)
Is 794 at 25 °C. At this temperature, what is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
HI (g)
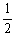 H2 (g) +
H2 (g) + 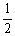 I2 (g)
I2 (g)
A)1588
B)28
C)397
D)0.035
E)0.0013
 2HI (g)
2HI (g)Is 794 at 25 °C. At this temperature, what is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
HI (g)

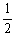 H2 (g) +
H2 (g) + 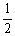 I2 (g)
I2 (g)A)1588
B)28
C)397
D)0.035
E)0.0013

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In which of the following reactions would increasing pressure at constant temperature change the concentrations of reactants and products, based on Le Châteliers principle?
A)N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g)
B)N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)
C)N2 (g) + 2O2 (g) 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)
D)2N2 (g) + O2 (g) 2N2O (g)
2N2O (g)
E)all of the above
A)N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
 2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g)B)N2O4 (g)
 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)C)N2 (g) + 2O2 (g)
 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)D)2N2 (g) + O2 (g)
 2N2O (g)
2N2O (g)E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The equilibrium constant for the gas phase reaction 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)  2SO3 (g)
2SO3 (g)
Is Keq = 2.80 × 102 at 999 K. At equilibrium, ________.
A)products predominate
B)reactants predominate
C)roughly equal amounts of products and reactants are present
D)only products are present
E)only reactants are present
 2SO3 (g)
2SO3 (g)Is Keq = 2.80 × 102 at 999 K. At equilibrium, ________.
A)products predominate
B)reactants predominate
C)roughly equal amounts of products and reactants are present
D)only products are present
E)only reactants are present

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction Ti (s) + 2Cl2 (g) ![<strong>The equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction Ti (s) + 2Cl<sub>2 </sub>(g) TiCl<sub>4 </sub>(l) Is given by</strong> A) B) C) D)[Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)]<sup>-2</sup><sup> </sup> E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f67_e150_a2ab_31c7e9f0d2a0_TB2701_11.jpg) TiCl4 (l)
TiCl4 (l)
Is given by
A)![<strong>The equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction Ti (s) + 2Cl<sub>2 </sub>(g) TiCl<sub>4 </sub>(l) Is given by</strong> A) B) C) D)[Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)]<sup>-2</sup><sup> </sup> E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f68_0861_a2ab_dd9a619d9f06_TB2701_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>The equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction Ti (s) + 2Cl<sub>2 </sub>(g) TiCl<sub>4 </sub>(l) Is given by</strong> A) B) C) D)[Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)]<sup>-2</sup><sup> </sup> E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f68_0862_a2ab_f157163dc03f_TB2701_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>The equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction Ti (s) + 2Cl<sub>2 </sub>(g) TiCl<sub>4 </sub>(l) Is given by</strong> A) B) C) D)[Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)]<sup>-2</sup><sup> </sup> E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f68_0863_a2ab_2589dcc1f8c5_TB2701_11.jpg)
D)[Cl2 (g)]-2
E)![<strong>The equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction Ti (s) + 2Cl<sub>2 </sub>(g) TiCl<sub>4 </sub>(l) Is given by</strong> A) B) C) D)[Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)]<sup>-2</sup><sup> </sup> E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f68_0864_a2ab_f55358549867_TB2701_11.jpg)
![<strong>The equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction Ti (s) + 2Cl<sub>2 </sub>(g) TiCl<sub>4 </sub>(l) Is given by</strong> A) B) C) D)[Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)]<sup>-2</sup><sup> </sup> E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f67_e150_a2ab_31c7e9f0d2a0_TB2701_11.jpg) TiCl4 (l)
TiCl4 (l)Is given by
A)
![<strong>The equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction Ti (s) + 2Cl<sub>2 </sub>(g) TiCl<sub>4 </sub>(l) Is given by</strong> A) B) C) D)[Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)]<sup>-2</sup><sup> </sup> E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f68_0861_a2ab_dd9a619d9f06_TB2701_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>The equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction Ti (s) + 2Cl<sub>2 </sub>(g) TiCl<sub>4 </sub>(l) Is given by</strong> A) B) C) D)[Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)]<sup>-2</sup><sup> </sup> E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f68_0862_a2ab_f157163dc03f_TB2701_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>The equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction Ti (s) + 2Cl<sub>2 </sub>(g) TiCl<sub>4 </sub>(l) Is given by</strong> A) B) C) D)[Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)]<sup>-2</sup><sup> </sup> E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f68_0863_a2ab_2589dcc1f8c5_TB2701_11.jpg)
D)[Cl2 (g)]-2
E)
![<strong>The equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction Ti (s) + 2Cl<sub>2 </sub>(g) TiCl<sub>4 </sub>(l) Is given by</strong> A) B) C) D)[Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)]<sup>-2</sup><sup> </sup> E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f68_0864_a2ab_f55358549867_TB2701_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The equilibrium constant for the gas phase reaction 2NH3 (g)  N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
Is Keq = 230 at 300 °C. At equilibrium, ________.
A)products predominate
B)reactants predominate
C)roughly equal amounts of products and reactants are present
D)only products are present
E)only reactants are present
 N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)Is Keq = 230 at 300 °C. At equilibrium, ________.
A)products predominate
B)reactants predominate
C)roughly equal amounts of products and reactants are present
D)only products are present
E)only reactants are present

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the following equilibrium. 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)  2 SO3 (g)
2 SO3 (g)
The equilibrium cannot be established when ________ is/are placed in a 1.0-L container.
A)0.25 mol SO2 (g)and 0.25 mol O2 (g)
B)0.75 mol SO2 (g)
C)0.25 mol of SO2 (g)and 0.25 mol of SO3 (g)
D)0.50 mol O2 (g)and 0.50 mol SO3 (g)
E)1.0 mol SO3 (g)
 2 SO3 (g)
2 SO3 (g)The equilibrium cannot be established when ________ is/are placed in a 1.0-L container.
A)0.25 mol SO2 (g)and 0.25 mol O2 (g)
B)0.75 mol SO2 (g)
C)0.25 mol of SO2 (g)and 0.25 mol of SO3 (g)
D)0.50 mol O2 (g)and 0.50 mol SO3 (g)
E)1.0 mol SO3 (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Dinitrogentetraoxide partially decomposes according to the following equilibrium: N2O4 (g)  2 NO2 (g)
2 NO2 (g)
A 1.00-L flask is charged with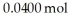 ofN2O4. At equilibrium at 373 K, 0.0055 mol of N2O4 remains. Keq for this reaction is ________.
ofN2O4. At equilibrium at 373 K, 0.0055 mol of N2O4 remains. Keq for this reaction is ________.
A)2.2 × 10-4
B)13
C)0.22
D)0.022
E)0.87
 2 NO2 (g)
2 NO2 (g)A 1.00-L flask is charged with
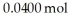 ofN2O4. At equilibrium at 373 K, 0.0055 mol of N2O4 remains. Keq for this reaction is ________.
ofN2O4. At equilibrium at 373 K, 0.0055 mol of N2O4 remains. Keq for this reaction is ________.A)2.2 × 10-4
B)13
C)0.22
D)0.022
E)0.87

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? 5N2O4(g) ![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? 5N<sub>2</sub>O4(g) 10NO<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>10</sup>/[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>5</sup> B)[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>10</sup>/[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> C)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup>/[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>10</sup> D)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup>/[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E)[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>5</sup>/[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f6b_14dc_a2ab_f36dc15fb491_TB2701_11.jpg) 10NO2 (g)
10NO2 (g)
A)[NO2]10/[N2O4]5
B)[N2O4]10/[NO2]5
C)[NO2]5/[N2O4]10
D)[NO2]5/[N2O4]5
E)[N2O4]5/[NO2]5
![<strong>Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? 5N<sub>2</sub>O4(g) 10NO<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>10</sup>/[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>5</sup> B)[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>10</sup>/[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> C)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup>/[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>10</sup> D)[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup>/[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E)[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>5</sup>/[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f6b_14dc_a2ab_f36dc15fb491_TB2701_11.jpg) 10NO2 (g)
10NO2 (g)A)[NO2]10/[N2O4]5
B)[N2O4]10/[NO2]5
C)[NO2]5/[N2O4]10
D)[NO2]5/[N2O4]5
E)[N2O4]5/[NO2]5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The equilibrium constant (Kp)for the interconversion of PCl5 and PCl3 is 0.0121: PCl5 (g)  PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
A vessel is charged with PCl5 giving an initial pressure of 0.123 atm. At equilibrium, the partial pressure of PCl3 is ________ atm.
A)0.0782
B)0.0455
C)0.0908
D)0.0330
E)0.123
 PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)A vessel is charged with PCl5 giving an initial pressure of 0.123 atm. At equilibrium, the partial pressure of PCl3 is ________ atm.
A)0.0782
B)0.0455
C)0.0908
D)0.0330
E)0.123

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Given the following reaction: CO (g) + 2 H2(g)  CH3OH (g)
CH3OH (g)
In an experiment, 0.42 mol of CO and 0.42 mol of H2 were placed in a 1.00-L reaction vessel. At equilibrium, there were 0.29 mol of CO remaining. Keq at the temperature of the experiment is ________.
A)2.80
B)0.357
C)14.5
D)17.5
E)none of the above
 CH3OH (g)
CH3OH (g)In an experiment, 0.42 mol of CO and 0.42 mol of H2 were placed in a 1.00-L reaction vessel. At equilibrium, there were 0.29 mol of CO remaining. Keq at the temperature of the experiment is ________.
A)2.80
B)0.357
C)14.5
D)17.5
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A sealed 1.0 L flask is charged with 0.500 mol of I2 and 0.500 mol of Br2. An equilibrium reaction ensues: I2 (g) + Br2 (g)  2IBr (g)
2IBr (g)
When the container contents achieve equilibrium, the flask contains 0.84 mol of IBr. The value of Keq is ________.
A)11
B)4.0
C)110
D)6.1
E)2.8
 2IBr (g)
2IBr (g)When the container contents achieve equilibrium, the flask contains 0.84 mol of IBr. The value of Keq is ________.
A)11
B)4.0
C)110
D)6.1
E)2.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The Keq for the equilibrium below is 0.112 at 700.0 °C. SO2 (g) +  O2 (g)
O2 (g)  SO3 (g)
SO3 (g)
What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2SO3 (g)
2SO3 (g)
A)1.25 × 10-2
B)2.24 × 10-1
C)7.97 × 101
D)4.46
E)0.112
 O2 (g)
O2 (g)  SO3 (g)
SO3 (g)What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
 2SO3 (g)
2SO3 (g)A)1.25 × 10-2
B)2.24 × 10-1
C)7.97 × 101
D)4.46
E)0.112

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Given the following reaction at equilibrium at 300.0 K: NH4HS (s)  NH3 (g) + H2S (g)
NH3 (g) + H2S (g)
If pNH3 = pH2S = 0.105 atm, Kp = ________.
A).0110
B)4.99 × 10-4
C).105
D).0821
E)5.66 × 10-3
 NH3 (g) + H2S (g)
NH3 (g) + H2S (g)If pNH3 = pH2S = 0.105 atm, Kp = ________.
A).0110
B)4.99 × 10-4
C).105
D).0821
E)5.66 × 10-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
At 200 °C, the equilibrium constant (Kp)for the reaction below is 2.40 × 103. 2NO (g)  N2 (g) + O2 (g)
N2 (g) + O2 (g)
A closed vessel is charged with 36.1 atm of NO. At equilibrium, the partial pressure of O2 is ________ atm.
A)294
B)35.7
C)17.9
D)6.00
E)1.50 × 10-2
 N2 (g) + O2 (g)
N2 (g) + O2 (g)A closed vessel is charged with 36.1 atm of NO. At equilibrium, the partial pressure of O2 is ________ atm.
A)294
B)35.7
C)17.9
D)6.00
E)1.50 × 10-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The value of Keq for the equilibrium CO2 (g) + 2H2 (g)  CH3OH (g)
CH3OH (g)
Is 14.5 at 483 °C. What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?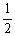 CO2 + H2 (g)
CO2 + H2 (g) 
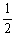 CH3OH (g)
CH3OH (g)
A)7.30
B)7.35
C)0.136
D)3.81
E)6.90 × 10-2
 CH3OH (g)
CH3OH (g)Is 14.5 at 483 °C. What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
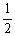 CO2 + H2 (g)
CO2 + H2 (g) 
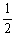 CH3OH (g)
CH3OH (g)A)7.30
B)7.35
C)0.136
D)3.81
E)6.90 × 10-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Keq for the equilibrium below is 7.52 × 10-2 at 480.0 °C. 2Cl2 (g) + 2H2O (g)  4HCl (g) + O2 (g)
4HCl (g) + O2 (g)
What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
8HCl (g) + 2O2 (g) 4Cl2 (g) + 4H2O (g)
4Cl2 (g) + 4H2O (g)
A)1.77 × 102
B)5.66 × 10-3
C)1.50 × 10-1
D)-7.52 × 10-2
E)7.52 × 10-2
 4HCl (g) + O2 (g)
4HCl (g) + O2 (g)What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
8HCl (g) + 2O2 (g)
 4Cl2 (g) + 4H2O (g)
4Cl2 (g) + 4H2O (g)A)1.77 × 102
B)5.66 × 10-3
C)1.50 × 10-1
D)-7.52 × 10-2
E)7.52 × 10-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A reaction vessel is charged with hydrogen iodide, which partially decomposes to molecular hydrogen and iodine: 2HI (g)  H2(g) + I2(g)
H2(g) + I2(g)
When the system comes to equilibrium at 425 °C, PHI = 0.708 atm, and PH2 = PI2 = 0.0960 atm. The value of Kp at this temperature is ________.
A)6.80 × 10-2
B)1.30 × 10-2
C)54.3
D)1.84 × 10-2
E)Kp cannot be calculated for this gas reaction when the volume of the reaction vessel is not given.
 H2(g) + I2(g)
H2(g) + I2(g)When the system comes to equilibrium at 425 °C, PHI = 0.708 atm, and PH2 = PI2 = 0.0960 atm. The value of Kp at this temperature is ________.
A)6.80 × 10-2
B)1.30 × 10-2
C)54.3
D)1.84 × 10-2
E)Kp cannot be calculated for this gas reaction when the volume of the reaction vessel is not given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The value of Keq for the following reaction is 0.25: SO2 (g) + NO2 (g)  SO3 (g) + NO (g)
SO3 (g) + NO (g)
The value of Keq at the same temperature for the reaction below is ________.
3SO2 (g) + 3NO2 (g) 3SO3 (g) + 3NO (g)
3SO3 (g) + 3NO (g)
A)1.6 × 10-2
B)7.5 × 10-1
C)8.3 × 10-2
D)6.4 × 101
E)0.25
 SO3 (g) + NO (g)
SO3 (g) + NO (g)The value of Keq at the same temperature for the reaction below is ________.
3SO2 (g) + 3NO2 (g)
 3SO3 (g) + 3NO (g)
3SO3 (g) + 3NO (g)A)1.6 × 10-2
B)7.5 × 10-1
C)8.3 × 10-2
D)6.4 × 101
E)0.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Acetic acid is a weak acid that dissociates into the acetate ion and a proton in aqueous solution: HC2H3O2 (aq) ![<strong>Acetic acid is a weak acid that dissociates into the acetate ion and a proton in aqueous solution: HC<sub>2</sub>H<sub>3</sub>O<sub>2</sub> (aq) C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>3</sub>O<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq) + H<sup>+</sup> (aq) At equilibrium at 25 °C a 0.100 M solution of acetic acid has the following concentrations: [HC<sub>2</sub>H<sub>3</sub>O<sub>2</sub>] = 0.0990 M, [C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>3</sub>O<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] = 1.33 × 10<sup>-3</sup><sup> </sup>M and [H+] = 1.33 × 10<sup>-3</sup><sup> </sup>M. The equilibrium constant, K<sub>eq</sub>, for the ionization of acetic acid at 25 °C is ________.</strong> A)5.71 × 10<sup>4</sup> B)0.100 C)1.75 × 10<sup>-7</sup> D)1.79 × 10<sup>-5</sup> E)5.71 × 10<sup>6</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f6a_9fa5_a2ab_afb72bbd682d_TB2701_11.jpg) C2H3O2- (aq) + H+ (aq)
C2H3O2- (aq) + H+ (aq)
At equilibrium at 25 °C a 0.100 M solution of acetic acid has the following concentrations:
[HC2H3O2] = 0.0990 M, [C2H3O2-] = 1.33 × 10-3 M and [H+] = 1.33 × 10-3 M. The equilibrium constant, Keq, for the ionization of acetic acid at 25 °C is ________.
A)5.71 × 104
B)0.100
C)1.75 × 10-7
D)1.79 × 10-5
E)5.71 × 106
![<strong>Acetic acid is a weak acid that dissociates into the acetate ion and a proton in aqueous solution: HC<sub>2</sub>H<sub>3</sub>O<sub>2</sub> (aq) C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>3</sub>O<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq) + H<sup>+</sup> (aq) At equilibrium at 25 °C a 0.100 M solution of acetic acid has the following concentrations: [HC<sub>2</sub>H<sub>3</sub>O<sub>2</sub>] = 0.0990 M, [C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>3</sub>O<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] = 1.33 × 10<sup>-3</sup><sup> </sup>M and [H+] = 1.33 × 10<sup>-3</sup><sup> </sup>M. The equilibrium constant, K<sub>eq</sub>, for the ionization of acetic acid at 25 °C is ________.</strong> A)5.71 × 10<sup>4</sup> B)0.100 C)1.75 × 10<sup>-7</sup> D)1.79 × 10<sup>-5</sup> E)5.71 × 10<sup>6</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f6a_9fa5_a2ab_afb72bbd682d_TB2701_11.jpg) C2H3O2- (aq) + H+ (aq)
C2H3O2- (aq) + H+ (aq)At equilibrium at 25 °C a 0.100 M solution of acetic acid has the following concentrations:
[HC2H3O2] = 0.0990 M, [C2H3O2-] = 1.33 × 10-3 M and [H+] = 1.33 × 10-3 M. The equilibrium constant, Keq, for the ionization of acetic acid at 25 °C is ________.
A)5.71 × 104
B)0.100
C)1.75 × 10-7
D)1.79 × 10-5
E)5.71 × 106

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Given the following reaction at equilibrium, if Kc = 5.84 x 105 at 230.0 °C, Kp = ________. 2NO (g) + O2 (g)  2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)
A)3.67 × 10-2
B)1.41 × 104
C)6.44 × 105
D)2.40 × 106
E)2.41 × 107
 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)A)3.67 × 10-2
B)1.41 × 104
C)6.44 × 105
D)2.40 × 106
E)2.41 × 107

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The value of Keq for the equilibrium H2 (g) + I2 (g)  2HI (g)
2HI (g)
Is 54.0 at 427 °C. What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
HI (g)
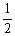 H2 (g) +
H2 (g) + 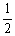 I2(g)
I2(g)
A)27
B)7.35
C)0.136
D)2.92 × 103
E)3.43 × 10-4
 2HI (g)
2HI (g)Is 54.0 at 427 °C. What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
HI (g)

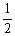 H2 (g) +
H2 (g) + 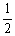 I2(g)
I2(g)A)27
B)7.35
C)0.136
D)2.92 × 103
E)3.43 × 10-4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Given the following reaction at equilibrium at 450.0 °C: CaCO3 (s)  CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
If pCO2 = 0.0155 atm, Kc = ________.
A)155
B)0.0821
C)0.920
D)2.61 × 10-4
E)9.20
 CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
CaO (s) + CO2 (g)If pCO2 = 0.0155 atm, Kc = ________.
A)155
B)0.0821
C)0.920
D)2.61 × 10-4
E)9.20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Given the following reaction at equilibrium, if Kp = 1.10 at 250.0 °C, Kc = ________. PCl5 (g)  PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
A)3.90 × 10-6
B)2.56 × 10-2
C)1.10
D)42.9
E)47.2
 PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)A)3.90 × 10-6
B)2.56 × 10-2
C)1.10
D)42.9
E)47.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider the following chemical reaction: CO (g) + 2H2(g)  CH3OH(g)
CH3OH(g)
At equilibrium in a particular experiment, the concentrations of CO and H2 were 0.15 M and 0.36, M respectively. What is the equilibrium concentration of CH3OH? The value of Keq for this reaction is 14.5 at the temperature of the experiment.
A)14.5
B)7.61 × 10-3
C)2.82 × 10-1
D)3.72 × 10-3
E)1.34 × 10-3
 CH3OH(g)
CH3OH(g)At equilibrium in a particular experiment, the concentrations of CO and H2 were 0.15 M and 0.36, M respectively. What is the equilibrium concentration of CH3OH? The value of Keq for this reaction is 14.5 at the temperature of the experiment.
A)14.5
B)7.61 × 10-3
C)2.82 × 10-1
D)3.72 × 10-3
E)1.34 × 10-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The Keq for the equilibrium below is 5.4 × 1013 at 480.0 °C. 2NO (g) + O2 (g)  2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)
What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
4NO (g) + 2O2 (g) 4NO2 (g)
4NO2 (g)
A)2.9 × 1027
B)8.5 × 1054
C)3.4 × 10-28
D)-1.1 × 1014
E)5.4 × 1013
 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
4NO (g) + 2O2 (g)
 4NO2 (g)
4NO2 (g)A)2.9 × 1027
B)8.5 × 1054
C)3.4 × 10-28
D)-1.1 × 1014
E)5.4 × 1013

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The value of Keq for the equilibrium N2 (g) + O2 (g)  2 NO (g)
2 NO (g)
Is 4.2 × 10-31 at 27 °C. What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
4 NO (g) 2 N2 (g) + 2 O2 (g)
2 N2 (g) + 2 O2 (g)
A)5.7 × 1060
B)8.4 × 10-31
C)4.2 × 1031
D)8.4 × 1031
E)none of the above
 2 NO (g)
2 NO (g)Is 4.2 × 10-31 at 27 °C. What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
4 NO (g)
 2 N2 (g) + 2 O2 (g)
2 N2 (g) + 2 O2 (g)A)5.7 × 1060
B)8.4 × 10-31
C)4.2 × 1031
D)8.4 × 1031
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
At 24° C, Kp = 0.080 for the equilibrium: NH4HS (s)  NH3 (g) + H2S (g)
NH3 (g) + H2S (g)
A sample of solid NH4HS is placed in a closed vessel and allowed to equilibrate. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure (atm)of ammonia, assuming that some solid NH4HS remains.
A)0.28
B)0.080
C)0.052
D)0.0049
E)3.8
 NH3 (g) + H2S (g)
NH3 (g) + H2S (g)A sample of solid NH4HS is placed in a closed vessel and allowed to equilibrate. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure (atm)of ammonia, assuming that some solid NH4HS remains.
A)0.28
B)0.080
C)0.052
D)0.0049
E)3.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The Kp for the reaction below is 1.49 × 108 at 100.0 °C: CO (g)+ Cl2 (g) → COCl2 (g)
In an equilibrium mixture of the three gases, PCO = PCl2 = 1.00 × 10-4 atm. The partial pressure of the product, phosgene (COCl2), is ________ atm.
A)1.49
B)1.49 × 1016
C)6.71 × 10-17
D)1.49 × 104
E)1.49 × 1012
In an equilibrium mixture of the three gases, PCO = PCl2 = 1.00 × 10-4 atm. The partial pressure of the product, phosgene (COCl2), is ________ atm.
A)1.49
B)1.49 × 1016
C)6.71 × 10-17
D)1.49 × 104
E)1.49 × 1012

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Kp = 0.0198 at 721 K for the reaction 2HI (g)  H2 (g) + I2 (g)
H2 (g) + I2 (g)
In a particular experiment, the partial pressures of H2 and I2 at equilibrium are 0.678 and 0.788 atm, respectively. The partial pressure of HI is ________ atm.
A)7.87
B)27.0
C)5.19
D)0.103
E)0.0106
 H2 (g) + I2 (g)
H2 (g) + I2 (g)In a particular experiment, the partial pressures of H2 and I2 at equilibrium are 0.678 and 0.788 atm, respectively. The partial pressure of HI is ________ atm.
A)7.87
B)27.0
C)5.19
D)0.103
E)0.0106

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2NH3 (g)  N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)ΔH° = +92.4 kJ
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)ΔH° = +92.4 kJ
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that removing N2 (g)to the system at equilibrium will result in ________.
A)an increase in the concentration of H2
B)a decrease in the concentration of H2
C)removal of all of the H2
D)a lower partial pressure of H2
E)an increase in the value of the equilibrium constant
 N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)ΔH° = +92.4 kJ
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)ΔH° = +92.4 kJLe Châtelier's principle predicts that removing N2 (g)to the system at equilibrium will result in ________.
A)an increase in the concentration of H2
B)a decrease in the concentration of H2
C)removal of all of the H2
D)a lower partial pressure of H2
E)an increase in the value of the equilibrium constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2CO2 (g)  2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJ
2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJ
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that removing O2 (g)to the reaction container will ________.
A)increase the partial pressure of CO
B)decrease the partial pressure of CO
C)increase the partial pressure of CO2
D)increase the value of the equilibrium constant
E)decrease the value of the equilibrium constant
 2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJ
2CO (g) + O2 (g)ΔH° = -514 kJLe Châtelier's principle predicts that removing O2 (g)to the reaction container will ________.
A)increase the partial pressure of CO
B)decrease the partial pressure of CO
C)increase the partial pressure of CO2
D)increase the value of the equilibrium constant
E)decrease the value of the equilibrium constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Dinitrogen tetroxide partially decomposes according to the following equilibrium: N2O4 (g) → 2NO2 (g)
A 1.000-L flask is charged with 9.20 × 10-3 mol of N2O4. At equilibrium, 5.98 × 10-3 mol of N2O4 remains. Keq for this reaction is ________.
A)0.183
B)0.197
C)0.212
D)6.94 × 10-3
E)2.96 × 10-5
A 1.000-L flask is charged with 9.20 × 10-3 mol of N2O4. At equilibrium, 5.98 × 10-3 mol of N2O4 remains. Keq for this reaction is ________.
A)0.183
B)0.197
C)0.212
D)6.94 × 10-3
E)2.96 × 10-5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
At 1000.0 K, the equilibrium constant for the reaction 2NO (g) + Br2 (g)  2NOBr (g)
2NOBr (g)
Is Kp = 0.016. Calculate Kp for the reverse reaction,
2NOBr (g) 2NO (g) + Br2 (g).
2NO (g) + Br2 (g).
A)0.016
B)1.6 × 10-4
C)63
D)0.99
E)1.1
 2NOBr (g)
2NOBr (g)Is Kp = 0.016. Calculate Kp for the reverse reaction,
2NOBr (g)
 2NO (g) + Br2 (g).
2NO (g) + Br2 (g).A)0.016
B)1.6 × 10-4
C)63
D)0.99
E)1.1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The value of Keq for the following reaction is 0.26: A (g) + B (g)  C (g) + D (g)
C (g) + D (g)
The value of Keq at the same temperature for the reaction below is ________.
2A (g) + 2B (g) 2C (g) + 2D (g)
2C (g) + 2D (g)
A)0.068
B)0.52
C)1.2
D)0.065
E)0.26
 C (g) + D (g)
C (g) + D (g)The value of Keq at the same temperature for the reaction below is ________.
2A (g) + 2B (g)
 2C (g) + 2D (g)
2C (g) + 2D (g)A)0.068
B)0.52
C)1.2
D)0.065
E)0.26

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
At elevated temperatures, molecular hydrogen and molecular bromine react to partially form hydrogen bromide: H2 (g) + Br2 (g)  2HBr (g)
2HBr (g)
A mixture of 0.682 mol of H2 and 0.440 mol of Br2 is combined in a reaction vessel with a volume of
2.00 L. At equilibrium at 700 K, there are 0.546 mol of H2 present. At equilibrium, there are ________ mol of Br2 present in the reaction vessel.
A)0.000
B)0.440
C)0.546
D)0.136
E)0.304
 2HBr (g)
2HBr (g)A mixture of 0.682 mol of H2 and 0.440 mol of Br2 is combined in a reaction vessel with a volume of
2.00 L. At equilibrium at 700 K, there are 0.546 mol of H2 present. At equilibrium, there are ________ mol of Br2 present in the reaction vessel.
A)0.000
B)0.440
C)0.546
D)0.136
E)0.304

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The Keq for the equilibrium below is 7.16 × 10-2 at 440.0 °C. 2Cl2 (g) + 2H2O (g)  4HCl (g) + O2 (g)
4HCl (g) + O2 (g)
What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
Cl2 (g) + H2O (g) 2HCl (g) +
2HCl (g) +  O2 (g)
O2 (g)
A)0.0716
B)5.13 × 10-3
C)0.268
D)0.0376
E)0.150
 4HCl (g) + O2 (g)
4HCl (g) + O2 (g)What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
Cl2 (g) + H2O (g)
 2HCl (g) +
2HCl (g) +  O2 (g)
O2 (g)A)0.0716
B)5.13 × 10-3
C)0.268
D)0.0376
E)0.150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The expression of Keq for the following reaction will not include ________. A(g) + B (g) ![<strong>The expression of K<sub>eq</sub> for the following reaction will not include ________. A(g) + B (g) C (l) + D (g)</strong> A)[C] B)[A] C)[B] D)[D] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f6c_c2a7_a2ab_b147cb5956d6_TB2701_11.jpg) C (l) + D (g)
C (l) + D (g)
A)[C]
B)[A]
C)[B]
D)[D]
E)none of the above
![<strong>The expression of K<sub>eq</sub> for the following reaction will not include ________. A(g) + B (g) C (l) + D (g)</strong> A)[C] B)[A] C)[B] D)[D] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f6c_c2a7_a2ab_b147cb5956d6_TB2701_11.jpg) C (l) + D (g)
C (l) + D (g)A)[C]
B)[A]
C)[B]
D)[D]
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The value of Keq for the following reaction is 0.50: A (g) + 2B (g)  C (g) + 4D (g)
C (g) + 4D (g)
The value of Keq at the same temperature for the reaction below is ________.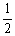 A (g) + B (g)
A (g) + B (g) 
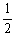 C (g) + 2D (g)
C (g) + 2D (g)
A)7.1 × 10-1
B)2.5 × 10-1
C)0.25
D)1.0
E)0.50
 C (g) + 4D (g)
C (g) + 4D (g)The value of Keq at the same temperature for the reaction below is ________.
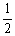 A (g) + B (g)
A (g) + B (g) 
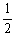 C (g) + 2D (g)
C (g) + 2D (g)A)7.1 × 10-1
B)2.5 × 10-1
C)0.25
D)1.0
E)0.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For the endothermic reaction CaCO3 (s)  CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that ________ will result in an increase in the number of moles of CO2.
A)increasing the temperature
B)decreasing the temperature
C)increasing the pressure
D)removing some of the CaCO3(s)
E)none of the above
 CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
CaO (s) + CO2 (g)Le Châtelier's principle predicts that ________ will result in an increase in the number of moles of CO2.
A)increasing the temperature
B)decreasing the temperature
C)increasing the pressure
D)removing some of the CaCO3(s)
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The reaction below is exothermic: 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)  2SO3 (g)
2SO3 (g)
Le Châtelier's Principle predicts that ________ will result in an increase in the number of moles of SO3 (g)in the reaction container.
A)increasing the amount of SO2
B)decreasing the pressure
C)increasing the temperature
D)removing some oxygen
E)increasing the volume of the container
 2SO3 (g)
2SO3 (g)Le Châtelier's Principle predicts that ________ will result in an increase in the number of moles of SO3 (g)in the reaction container.
A)increasing the amount of SO2
B)decreasing the pressure
C)increasing the temperature
D)removing some oxygen
E)increasing the volume of the container

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Phosphorous trichloride and phosphorous pentachloride equilibrate in the presence of molecular chlorine according to the reaction: PCl3 (g)+ Cl2 (g) → PCl5 (g)
An equilibrium mixture at 450 K contains
PPCl3 = 0.224 atm,
PCl2 = 0.284 atm, and
PPCl5 = 4.24 atm. What is the value of Kp at this temperature?
A)66.7
B)1.50 × 10-2
C)2.70 × 10-1
D)3.74
E)8.36
An equilibrium mixture at 450 K contains
PPCl3 = 0.224 atm,
PCl2 = 0.284 atm, and
PPCl5 = 4.24 atm. What is the value of Kp at this temperature?
A)66.7
B)1.50 × 10-2
C)2.70 × 10-1
D)3.74
E)8.36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The value of Keq for the following reaction is 0.16: A (g) + B (g)  C (g) + D (g)
C (g) + D (g)
The value of Keq at the same temperature for the reaction below is ________.
3C (g) + 3D (g) 3A (g) + 3B (g)
3A (g) + 3B (g)
A)2.4 × 102
B)2.1
C)4.1 × 10-3
D)5.3 × 10-2
E)6.3
 C (g) + D (g)
C (g) + D (g)The value of Keq at the same temperature for the reaction below is ________.
3C (g) + 3D (g)
 3A (g) + 3B (g)
3A (g) + 3B (g)A)2.4 × 102
B)2.1
C)4.1 × 10-3
D)5.3 × 10-2
E)6.3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
At 900.0 K, the equilibrium constant (Kp)for the following reaction is 0.345. 2SO2 + O2 (g) → 2SO3 (g)
At equilibrium, the partial pressure of SO2 is 36.9 atm and that of O2 is 16.8 atm. The partial pressure of SO3 is ________ atm.
A)88.8
B)3.89 × 10-3
C)214
D)5.57 × 10-4
E)42.4
At equilibrium, the partial pressure of SO2 is 36.9 atm and that of O2 is 16.8 atm. The partial pressure of SO3 is ________ atm.
A)88.8
B)3.89 × 10-3
C)214
D)5.57 × 10-4
E)42.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the coal-gasification process, carbon monoxide is converted to carbon dioxide via the following reaction: CO (g) + H2O (g)  CO2 (g) + H2 (g)
CO2 (g) + H2 (g)
In an experiment, 0.35 mol of CO and 0.40 mol of H2O were placed in a 1.00-L reaction vessel. At equilibrium, there were 0.22 mol of CO remaining. Keq at the temperature of the experiment is ________.
A)5.5
B)0.75
C)3.5
D)0.28
E)1.0
 CO2 (g) + H2 (g)
CO2 (g) + H2 (g)In an experiment, 0.35 mol of CO and 0.40 mol of H2O were placed in a 1.00-L reaction vessel. At equilibrium, there were 0.22 mol of CO remaining. Keq at the temperature of the experiment is ________.
A)5.5
B)0.75
C)3.5
D)0.28
E)1.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the following chemical reaction: H2 (g) + I2 (g)  2HI (g)
2HI (g)
At equilibrium in a particular experiment, the concentrations of H2, I2, and HI were 0.20 M, 0.034 M, and 0.55 M, respectively. The value of Keq for this reaction is ________.
A)23
B)81
C)0.0090
D)5.1
E)44
 2HI (g)
2HI (g)At equilibrium in a particular experiment, the concentrations of H2, I2, and HI were 0.20 M, 0.034 M, and 0.55 M, respectively. The value of Keq for this reaction is ________.
A)23
B)81
C)0.0090
D)5.1
E)44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Nitrosyl bromide decomposes according to the following equation. 2NOBr (g)  2NO (g) + Br2 (g)
2NO (g) + Br2 (g)
A sample of NOBr (0.64 mol)was placed in a 1.00-L flask containing no NO or Br2. At equilibrium the flask contained 0.16 mol of NOBr. How many moles of NO and Br2, respectively, are in the flask at equilibrium?
A)0.48, 0.24
B)0.48, 0.48
C)0.16, 0.08
D)0.16, 0.16
E)0.24, 0.42
 2NO (g) + Br2 (g)
2NO (g) + Br2 (g)A sample of NOBr (0.64 mol)was placed in a 1.00-L flask containing no NO or Br2. At equilibrium the flask contained 0.16 mol of NOBr. How many moles of NO and Br2, respectively, are in the flask at equilibrium?
A)0.48, 0.24
B)0.48, 0.48
C)0.16, 0.08
D)0.16, 0.16
E)0.24, 0.42

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



