Deck 16: Acid-Base Equilibria
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/139
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Acid-Base Equilibria
1
According to the Arrhenius concept, an acid is a substance that ________.
A)is capable of donating one or more H+
B)causes an increase in the concentration of H+ in aqueous solutions
C)can accept a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond
D)reacts with the solvent to form the cation formed by autoionization of that solvent
E)tastes bitter
A)is capable of donating one or more H+
B)causes an increase in the concentration of H+ in aqueous solutions
C)can accept a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond
D)reacts with the solvent to form the cation formed by autoionization of that solvent
E)tastes bitter
causes an increase in the concentration of H+ in aqueous solutions
2
Which one of the following is a Br∅nsted-Lowry base?
A)(CH3)3N
B)CH3COOH
C)HF
D)HNO2
E)none of the above
A)(CH3)3N
B)CH3COOH
C)HF
D)HNO2
E)none of the above
(CH3)3N
3
The Ka of hypochlorous acid (HClO)is 3.0 × 10-8 at 25 °C. What is the percent ionization of hypochlorous acid in a 0.015 M aqueous solution of HClO at 25 °C?
A)4.5 × 10-8
B)14
C)2.1 × 10-5
D)0.14
E)1.4 × 10-3
A)4.5 × 10-8
B)14
C)2.1 × 10-5
D)0.14
E)1.4 × 10-3
0.14
4
Of the following, ________ is a weak acid.
A)HF
B)HCl
C)HBr
D)HNO3
E)HClO4
A)HF
B)HCl
C)HBr
D)HNO3
E)HClO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A substance that is capable of acting as both an acid and as a base is ________.
A)autosomal
B)conjugated
C)ambiprotic
D)saturated
E)miscible
A)autosomal
B)conjugated
C)ambiprotic
D)saturated
E)miscible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Of the following acids, ________ is a strong acid.
A)HNO2
B)H2CO3
C)HNO3
D)HClO
E)HF
A)HNO2
B)H2CO3
C)HNO3
D)HClO
E)HF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The molar concentration of hydroxide ion in pure water at 25 °C is ________.
A)1.00
B)0.00
C)1.0 × 10-14
D)1.0 × 10-7
E)7.00
A)1.00
B)0.00
C)1.0 × 10-14
D)1.0 × 10-7
E)7.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Classify the following compounds as weak acids (W)or strong acids (S): nitrous acid hydrochloric acid hydrofluoric acid
A)W W W
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W S S
E)W S W
A)W W W
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W S S
E)W S W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which one of the following is a Br∅nsted-Lowry acid?
A)(CH3)3NH+
B)CH3COOH
C)HF
D)HNO2
E)all of the above
A)(CH3)3NH+
B)CH3COOH
C)HF
D)HNO2
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A Br∅nsted-Lowry acid is defined as a substance that ________.
A)increases Ka when placed in H2O
B)decreases [H+] when placed in H2O
C)increases [OH-] when placed in H2O
D)acts as a proton acceptor
E)acts as a proton donor
A)increases Ka when placed in H2O
B)decreases [H+] when placed in H2O
C)increases [OH-] when placed in H2O
D)acts as a proton acceptor
E)acts as a proton donor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Classify the following compounds as weak acids (W)or strong acids (S): benzoic acid nitric acid acetic acid
A)W W W
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W S S
E)W S W
A)W W W
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W S S
E)W S W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which one of the following is the weakest acid?
A)HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10-4)
B)HClO (Ka = 3.0 × 10-8)
C)HNO2 (Ka = 4.5 × 10-4)
D)HCN (Ka = 4.9 × 10-10)
E)Acetic acid (Ka = 1.8 × 10-5)
A)HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10-4)
B)HClO (Ka = 3.0 × 10-8)
C)HNO2 (Ka = 4.5 × 10-4)
D)HCN (Ka = 4.9 × 10-10)
E)Acetic acid (Ka = 1.8 × 10-5)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The magnitude of Kw indicates that ________.
A)water autoionizes very slowly
B)water autoionizes very quickly
C)water autoionizes only to a very small extent
D)the autoionization of water is exothermic
A)water autoionizes very slowly
B)water autoionizes very quickly
C)water autoionizes only to a very small extent
D)the autoionization of water is exothermic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Classify the following compounds as weak acids (W)or strong acids (S): hydrocyanic acid hydrofluoric acid phenol
A)W W W
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W S S
E)W S W
A)W W W
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W S S
E)W S W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which one of the following statements regarding Kw is false?
A)pKw is 14.00 at 25 °C.
B)The value of Kw is always 1.0 × 10-14.
C)Kw changes with temperature.
D)The value of Kw shows that water is a weak acid.
E)Kw is known as the ion product of water.
A)pKw is 14.00 at 25 °C.
B)The value of Kw is always 1.0 × 10-14.
C)Kw changes with temperature.
D)The value of Kw shows that water is a weak acid.
E)Kw is known as the ion product of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The hydride ion, H-, is a stronger base than the hydroxide ion, OH-. The product(s)of the reaction of hydride ion with water is/are ________.
A)H3O+ (aq)
B)OH- (aq) + H2 (g)
C)OH- (aq) + 2H+ (aq)
D)no reaction occurs
E)H2O2 (aq)
A)H3O+ (aq)
B)OH- (aq) + H2 (g)
C)OH- (aq) + 2H+ (aq)
D)no reaction occurs
E)H2O2 (aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Of the acids in the table below, ________ is the strongest acid. 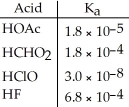
A)HOAc
B)HCHO2
C)HClO
D)HF
E)HOAc and HCHO2

A)HOAc
B)HCHO2
C)HClO
D)HF
E)HOAc and HCHO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Of the following acids, ________ is not a strong acid.
A)HNO2
B)H2SO4
C)HNO3
D)HClO4
E)HCl
A)HNO2
B)H2SO4
C)HNO3
D)HClO4
E)HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The molar concentration of hydronium ion in pure water at 25 °C is ________.
A)0.00
B)1.0 × 10-7
C)1.0 × 10-14
D)1.00
E)7.00
A)0.00
B)1.0 × 10-7
C)1.0 × 10-14
D)1.00
E)7.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A Br∅nsted-Lowry base is defined as a substance that ________.
A)increases [H+] when placed in H2O
B)decreases [H+] when placed in H2O
C)increases [OH-] when placed in H2O
D)acts as a proton acceptor
E)acts as a proton donor
A)increases [H+] when placed in H2O
B)decreases [H+] when placed in H2O
C)increases [OH-] when placed in H2O
D)acts as a proton acceptor
E)acts as a proton donor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate acids below is the weakest acid? 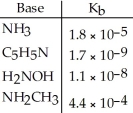
A)NH4+
B)C5H5NH+
C)H3NOH+
D)NH3CH3+
E)NH4+ and NH3CH3+

A)NH4+
B)C5H5NH+
C)H3NOH+
D)NH3CH3+
E)NH4+ and NH3CH3+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate acids below is the strongest acid? 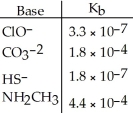
A)HClO
B)HCO3-
C)H2S
D)NH3CH3+
E)H2S and HClO

A)HClO
B)HCO3-
C)H2S
D)NH3CH3+
E)H2S and HClO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Ammonia is a ________.
A)weak acid
B)strong base
C)weak base
D)strong acid
E)salt
A)weak acid
B)strong base
C)weak base
D)strong acid
E)salt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following ions will act as a weak base in water?
A)OH-
B)Cl-
C)NO3-
D)ClO-
E)None of the above will act as a weak base in water.
A)OH-
B)Cl-
C)NO3-
D)ClO-
E)None of the above will act as a weak base in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following aqueous solutions has the lowest [OH-]?
A)a solution with a pH of 3.0
B)a 1 × 10-4 M solution of HNO3
C)a solution with a pOH of 12.0
D)pure water
E)a 1 × 10-3 M solution of NH4Cl
A)a solution with a pH of 3.0
B)a 1 × 10-4 M solution of HNO3
C)a solution with a pOH of 12.0
D)pure water
E)a 1 × 10-3 M solution of NH4Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A- is a weak base. Which equilibrium corresponds to the equilibrium constant Ka for HA?
A)HA (aq) + H2O (l) H2A+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
H2A+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
B)A- (aq) + H3O+ (aq) HA (aq) + H2O (l)
HA (aq) + H2O (l)
C)HA (aq) + H2O (l) H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
D)A- (aq) + H2O (l) HA (aq) + OH- (aq)
HA (aq) + OH- (aq)
E)A- (aq) + OH- (aq) HOA2- (aq)
HOA2- (aq)
A)HA (aq) + H2O (l)
 H2A+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
H2A+ (aq) + OH- (aq)B)A- (aq) + H3O+ (aq)
 HA (aq) + H2O (l)
HA (aq) + H2O (l)C)HA (aq) + H2O (l)
 H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)D)A- (aq) + H2O (l)
 HA (aq) + OH- (aq)
HA (aq) + OH- (aq)E)A- (aq) + OH- (aq)
 HOA2- (aq)
HOA2- (aq)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate acids below is the weakest acid? 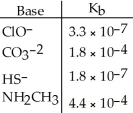
A)HClO
B)HCO3-
C)H2S
D)NH3CH3+
E)H2S and HClO

A)HClO
B)HCO3-
C)H2S
D)NH3CH3+
E)H2S and HClO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate bases below is the strongest base? 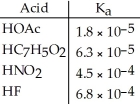
A)OAc-
B)C7H5O2-
C)NO2-
D)F-
E)OAc- and C7H5O2-

A)OAc-
B)C7H5O2-
C)NO2-
D)F-
E)OAc- and C7H5O2-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A 0.0035 M aqueous solution of a particular compound has pH = 2.46. The compound is ________.
A)a weak base
B)a weak acid
C)a strong acid
D)a strong base
E)a salt
A)a weak base
B)a weak acid
C)a strong acid
D)a strong base
E)a salt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Of the following substances, an aqueous solution of ________ will form basic solutions. NaHS Cu(NO3)2 KHCO3 NaF
A)NaHS, Cu(NO3)2
B)KHCO3, NaHS
C)NaF only
D)NaF, KHCO3
E)NaHS, KHCO3 and NaF
A)NaHS, Cu(NO3)2
B)KHCO3, NaHS
C)NaF only
D)NaF, KHCO3
E)NaHS, KHCO3 and NaF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Classify the following compounds as weak bases (W)or strong bases (S): methylamine carbonate ion potassium hydroxide
A)W W S
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W S S
E)W S W
A)W W S
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W S S
E)W S W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
HA is a weak acid. Which equilibrium corresponds to the equilibrium constant Kb for A-?
A)HA (aq) + H2O (l) H2A+ (aq) + OH-(aq)
H2A+ (aq) + OH-(aq)
B)A- (aq) + H3O+ (aq) HA (aq) + H2O (l)
HA (aq) + H2O (l)
C)HA (aq) + OH- (aq) H2O (l) + H+ (aq)
H2O (l) + H+ (aq)
D)A- (aq) + H2O (l) HA (aq) + OH- (aq)
HA (aq) + OH- (aq)
E)A- (aq) + OH- (aq) HOA2- (aq)
HOA2- (aq)
A)HA (aq) + H2O (l)
 H2A+ (aq) + OH-(aq)
H2A+ (aq) + OH-(aq)B)A- (aq) + H3O+ (aq)
 HA (aq) + H2O (l)
HA (aq) + H2O (l)C)HA (aq) + OH- (aq)
 H2O (l) + H+ (aq)
H2O (l) + H+ (aq)D)A- (aq) + H2O (l)
 HA (aq) + OH- (aq)
HA (aq) + OH- (aq)E)A- (aq) + OH- (aq)
 HOA2- (aq)
HOA2- (aq)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Classify the following compounds as weak bases (W)or strong bases (S): ammonia fluoride ion sodium hydroxide
A)W W S
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W S S
E)W S W
A)W W S
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W S S
E)W S W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate acids below is the strongest acid? 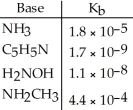
A)NH4+
B)C5H5NH+
C)H3NOH+
D)NH3CH3+
E)NH4+ and NH3CH3+

A)NH4+
B)C5H5NH+
C)H3NOH+
D)NH3CH3+
E)NH4+ and NH3CH3+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate bases below is the weakest base? 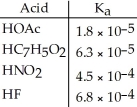
A)OAc-
B)C7H5O2-
C)NO2-
D)F-
E)OAc- and C7H5O2-

A)OAc-
B)C7H5O2-
C)NO2-
D)F-
E)OAc- and C7H5O2-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Classify the following compounds as weak acids (W)or strong acids (S): hypochlorous acid perchloric acid chloric acid
A)W S S
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W W W
E)W S W
A)W S S
B)S S S
C)S W W
D)W W W
E)W S W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following ions will act as a weak base in water?
A)HS-
B)F-
C)NO2-
D)ClO-
E)All of the above will act as a weak base in water.
A)HS-
B)F-
C)NO2-
D)ClO-
E)All of the above will act as a weak base in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate bases below is the weakest base? 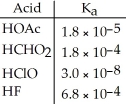
A)OAc-
B)CHO2-
C)ClO-
D)F-
E)OAc- and CHO2-

A)OAc-
B)CHO2-
C)ClO-
D)F-
E)OAc- and CHO2-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate bases below is the strongest base? 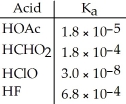
A)OAc-
B)CHO2-
C)ClO-
D)F-
E)OAc- and CHO2-

A)OAc-
B)CHO2-
C)ClO-
D)F-
E)OAc- and CHO2-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following aqueous solutions has the highest [OH-]?
A)a solution with a pH of 3.0
B)a 1 × 10-4 M solution of HNO3
C)a solution with a pOH of 12.0
D)pure water
E)a 1 × 10-3 M solution of NH4Cl
A)a solution with a pH of 3.0
B)a 1 × 10-4 M solution of HNO3
C)a solution with a pOH of 12.0
D)pure water
E)a 1 × 10-3 M solution of NH4Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The conjugate acid of CH3NH2 is ________.
A)CH3NH2
B)CH3NH3+
C)CH3NH2+
D)CH3NH+
E)none of the above
A)CH3NH2
B)CH3NH3+
C)CH3NH2+
D)CH3NH+
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Of the following, which is the strongest acid?
A)HClO
B)HClO3
C)HClO2
D)HClO4
E)HIO
A)HClO
B)HClO3
C)HClO2
D)HClO4
E)HIO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the pH of an aqueous solution at 25.0 °C that contains 3.98 × 10-9 M hydroxide ion?
A)8.40
B)5.60
C)9.00
D)3.98
E)7.00
A)8.40
B)5.60
C)9.00
D)3.98
E)7.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following acids will be the strongest?
A)H2SO4
B)HSO4-
C)H2SO3
D)H2SeO4
E)HSO3-
A)H2SO4
B)HSO4-
C)H2SO3
D)H2SeO4
E)HSO3-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Of the following substances, an aqueous solution of ________ will form basic solutions. NH4Cl Cu(NO3)2 K2CO3 NaF
A)NH4Cl, Cu(NO3)2
B)K2CO3, NH4Cl
C)NaF only
D)NaF, K2CO3
E)NH4Cl only
A)NH4Cl, Cu(NO3)2
B)K2CO3, NH4Cl
C)NaF only
D)NaF, K2CO3
E)NH4Cl only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The conjugate base of H2PO4- is ________.
A)PO43-
B)H2PO4
C)H3PO4
D)HPO42-
E)none of the above
A)PO43-
B)H2PO4
C)H3PO4
D)HPO42-
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The conjugate acid of HSO4- is ________.
A)SO42-
B)H2SO4
C)HSO4+
D)H+
E)HSO3+
A)SO42-
B)H2SO4
C)HSO4+
D)H+
E)HSO3+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the pOH of an aqueous solution at 25.0 °C that contains 3.98 × 10-9 M hydroxide ion?
A)8.40
B)5.60
C)9.00
D)3.98
E)7.00
A)8.40
B)5.60
C)9.00
D)3.98
E)7.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Calculate the pOH of a solution at 25.0 °C that contains 1.94 × 10-10 M hydronium ions.
A)1.94
B)4.29
C)7.00
D)14.0
E)9.71
A)1.94
B)4.29
C)7.00
D)14.0
E)9.71

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The conjugate base of HSO4- is ________.
A)OH-
B)H2SO4
C)SO42-
D)HSO4+
E)H3SO4+
A)OH-
B)H2SO4
C)SO42-
D)HSO4+
E)H3SO4+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the gas phase reaction below, NH3 is acting as a(n)________ base but not as a(n)________ base. 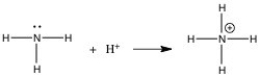
A)Arrhenius, Br∅nsted-Lowry
B)Br∅nsted-Lowry, Lewis
C)Lewis, Arrhenius
D)Lewis, Br∅nsted-Lowry
E)Arrhenius, Lewis

A)Arrhenius, Br∅nsted-Lowry
B)Br∅nsted-Lowry, Lewis
C)Lewis, Arrhenius
D)Lewis, Br∅nsted-Lowry
E)Arrhenius, Lewis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Of the compounds below, a 0.1 M aqueous solution of ________ will have the highest pH.
A)KCN, Ka of HCN = 4.0 × 10-10
B)NH4NO3, Kb of NH3 = 1.8 × 10-5
C)NaOAc, Ka of HOAc = 1.8 × 10-5
D)NaClO, Ka of HClO = 3.2 × 10-8
E)NaHS, Kb of HS- = 1.8 × 10-7
A)KCN, Ka of HCN = 4.0 × 10-10
B)NH4NO3, Kb of NH3 = 1.8 × 10-5
C)NaOAc, Ka of HOAc = 1.8 × 10-5
D)NaClO, Ka of HClO = 3.2 × 10-8
E)NaHS, Kb of HS- = 1.8 × 10-7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Calculate the concentration (in M)of hydronium ions in a solution at 25.0 °C with a pOH of 4.223.
A)5.98 × 10-5
B)1.67 × 10-10
C)1.67 × 104
D)5.99 × 10-19
E)1.00 × 10-7
A)5.98 × 10-5
B)1.67 × 10-10
C)1.67 × 104
D)5.99 × 10-19
E)1.00 × 10-7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the pH of an aqueous solution at 25.0 °C that contains 3.98 × 10-9 M hydronium ion?
A)8.400
B)5.600
C)9.000
D)3.980
E)7.000
A)8.400
B)5.600
C)9.000
D)3.980
E)7.000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the pOH of an aqueous solution at 25.0 °C that contains 3.98 × 10-9 M hydronium ion?
A)8.400
B)5.600
C)9.000
D)3.980
E)7.000
A)8.400
B)5.600
C)9.000
D)3.980
E)7.000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 0.1 M solution of ________ has a pH of 7.0.
A)Na2S
B)KF
C)NaNO3
D)NH4Cl
E)NaF
A)Na2S
B)KF
C)NaNO3
D)NH4Cl
E)NaF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the conjugate base of OH-?
A)O2
B)O-
C)H2O
D)O2-
E)H3O+
A)O2
B)O-
C)H2O
D)O2-
E)H3O+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is the conjugate acid of CO32- ?
A)CO22-
B)HCO22-
C)H2CO3
D)HCO3-
E)none of the above
A)CO22-
B)HCO22-
C)H2CO3
D)HCO3-
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Calculate the pH of a solution at 25.0 °C that contains 1.94 × 10-10 M hydronium ions.
A)1.94
B)4.29
C)7.00
D)14.0
E)9.71
A)1.94
B)4.29
C)7.00
D)14.0
E)9.71

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the conjugate acid of NH3?
A)NH3
B)NH2+
C)NH3+
D)NH4+
E)NH4OH
A)NH3
B)NH2+
C)NH3+
D)NH4+
E)NH4OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The Ka of acetic acid (HC2H3O2)is 1.8 × 10-5. What is the pH at 25.0 °C of an aqueous solution that is 0.100 M in acetic acid?
A)+2.87
B)-2.87
C)-11.13
D)+11.13
E)+6.61
A)+2.87
B)-2.87
C)-11.13
D)+11.13
E)+6.61

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The pH of a 0.10 M solution of a weak base is 9.82. What is the Kb for this base?
A)2.1 × 10-4
B)4.4 × 10-8
C)8.8 × 10-8
D)6.6 × 10-4
E)2.0 × 10-5
A)2.1 × 10-4
B)4.4 × 10-8
C)8.8 × 10-8
D)6.6 × 10-4
E)2.0 × 10-5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The pH of a 0.30 M solution of a weak acid is 2.67. What is the Ka for this acid?
A)2.1 × 10-4
B)4.4 × 10-4
C)1.5 × 10-4
D)6.6 × 10-4
E)none of the above
A)2.1 × 10-4
B)4.4 × 10-4
C)1.5 × 10-4
D)6.6 × 10-4
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An aqueous solution contains 0.050 M of methylamine. The concentration of H+ in this solution is ________ M. Kb for methylamine is 4.4 × 10-4.
A)0.050
B)2.2 × 10-13
C)2.9 × 10-13
D)4.5 × 10-13
E)2.2 × 10-12
A)0.050
B)2.2 × 10-13
C)2.9 × 10-13
D)4.5 × 10-13
E)2.2 × 10-12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Z- is a weak base. An aqueous solution of NaZ is prepared by dissolving 0.350 mol of NaZ in sufficient water to yield 1.0 L of solution. The pH of the solution was 8.93 at 25.0 °C. The Kb of Z- is ________.
A)1.2 × 10-5
B)6.9 × 10-9
C)2.1 × 10-10
D)9.9 × 10-2
E)2.8 × 10-12
A)1.2 × 10-5
B)6.9 × 10-9
C)2.1 × 10-10
D)9.9 × 10-2
E)2.8 × 10-12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A 0.15 M aqueous solution of the weak acid HA at 25.0 °C has a pH of 5.35. The value of Ka for HA is ________.
A)3.0 × 10-5
B)1.8 × 10-5
C)7.1 × 10-9
D)1.3 × 10-10
E)3.3 × 104
A)3.0 × 10-5
B)1.8 × 10-5
C)7.1 × 10-9
D)1.3 × 10-10
E)3.3 × 104

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
HZ is a weak acid. An aqueous solution of HZ is prepared by dissolving 0.020 mol of HZ in sufficient water to yield 1.0 L of solution. The pH of the solution was 4.93 at 25.0 °C. The Ka of HZ is ________.
A)1.2 × 10-5
B)6.9 × 10-9
C)1.4 × 10-10
D)9.9 × 10-2
E)2.8 × 10-12
A)1.2 × 10-5
B)6.9 × 10-9
C)1.4 × 10-10
D)9.9 × 10-2
E)2.8 × 10-12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The pH of a 0.55 M aqueous solution ammonia, NH3, at 25.0 °C is 11.50. What is the value of Kb for NH3?
A)2.0 × 10-9
B)1.1 × 10-9
C)6.0 × 10-5
D)1.8 × 10-5
E)none of the above
A)2.0 × 10-9
B)1.1 × 10-9
C)6.0 × 10-5
D)1.8 × 10-5
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The pH of a 0.25 M aqueous solution of hydrofluoric acid, HF, at 25.0 °C is 2.03. What is the value of Ka for HF?
A)2.0 × 10-9
B)1.1 × 10-9
C)6.0 × 10-5
D)3.5 × 10-4
E)none of the above
A)2.0 × 10-9
B)1.1 × 10-9
C)6.0 × 10-5
D)3.5 × 10-4
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Determine the pH of a 0.35 M aqueous solution of CH3NH2 (methylamine). The Kb of methylamine is 4.4 × 10-4.
A)10.00
B)3.86
C)12.09
D)1.96
E)13.24
A)10.00
B)3.86
C)12.09
D)1.96
E)13.24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An aqueous solution contains 0.100 M NaOH at 25.0 °C. The pH of the solution is ________.
A)0.100
B)1.00
C)13.00
D)7.00
E)-1.00
A)0.100
B)1.00
C)13.00
D)7.00
E)-1.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The acid-dissociation constants of phosphoric acid (H3PO4)are Ka1 = 7.5 × 10-3, Ka2 = 6.2 × 10-8, and Ka3 = 4.2 × 10-13 at 25.0 °C. What is the pH of a 2.5 M aqueous solution of phosphoric acid?
A)1.82
B)0.40
C)2.51
D)0.86
E)0.13
A)1.82
B)0.40
C)2.51
D)0.86
E)0.13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The acid-dissociation constants of sulfurous acid (H2SO3)are Ka1 = 1.7 × 10-2 and Ka2 = 6.4 × 10-8 at 25.0 °C. Calculate the pH of a 0.163 M aqueous solution of sulfurous acid.
A)4.53
B)1.28
C)1.86
D)6.21
E)1.93
A)4.53
B)1.28
C)1.86
D)6.21
E)1.93

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Calculate the concentration (in M)of hydroxide ions in a solution at 25.0 °C with a pOH of 4.223.
A)5.98 × 10-5
B)1.67 × 10-10
C)1.67 × 104
D)5.99 × 10-19
E)1.00 × 10-7
A)5.98 × 10-5
B)1.67 × 10-10
C)1.67 × 104
D)5.99 × 10-19
E)1.00 × 10-7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A 0.15 M aqueous solution of the weak base B at 25.0 °C has a pH of 8.88. The value of Kb for B is ________.
A)3.0 × 10-5
B)1.8 × 10-5
C)3.9 × 10-10
D)1.3 × 10-10
E)none of the above
A)3.0 × 10-5
B)1.8 × 10-5
C)3.9 × 10-10
D)1.3 × 10-10
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An aqueous solution contains 0.050 M of methylamine. The concentration of hydroxide ion in this solution is ________ M. Kb for methylamine is 4.4 × 10-4.
A)0.050
B)2.2 × 10-5
C)2.9 × 10-3
D)4.5 × 10-3
E)4.7 × 10-3
A)0.050
B)2.2 × 10-5
C)2.9 × 10-3
D)4.5 × 10-3
E)4.7 × 10-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The pH of a 0.60 M aqueous solution of formic acid, HCHO2, at 25.0 °C is 1.98. What is the value of Ka for formic acid?
A)2.0 × 10-5
B)1.8 × 10-4
C)6.0 × 10-5
D)3.5 × 10-4
E)none of the above
A)2.0 × 10-5
B)1.8 × 10-4
C)6.0 × 10-5
D)3.5 × 10-4
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
An aqueous solution contains 0.150 M HCl at 25.0 °C. The pH of the solution is ________.
A)0.150
B)1.00
C)13.00
D)7.00
E)0.82
A)0.150
B)1.00
C)13.00
D)7.00
E)0.82

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The pH of a 0.55 M aqueous solution of hypobromous acid, HBrO, at 25.0 °C is 4.48. What is the value of Ka for HBrO?
A)2.0 × 10-9
B)1.1 × 10-9
C)6.0 × 10-5
D)3.3 × 10-5
E)3.0 × 104
A)2.0 × 10-9
B)1.1 × 10-9
C)6.0 × 10-5
D)3.3 × 10-5
E)3.0 × 104

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The Ka of hypochlorous acid (HClO)is 3.00 × 10-8. What is the pH at 25.0 °C of an aqueous solution that is 0.0200 M in HClO?
A)+2.45
B)-2.45
C)-9.22
D)+9.22
E)+4.61
A)+2.45
B)-2.45
C)-9.22
D)+9.22
E)+4.61

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



