Deck 19: Chemical Thermodynamics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Chemical Thermodynamics
1
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Processes that are spontaneous in one direction are spontaneous in the opposite direction.
B)Processes are spontaneous because they occur at an observable rate.
C)Spontaneity can depend on the temperature.
D)All of the statements are true.
A)Processes that are spontaneous in one direction are spontaneous in the opposite direction.
B)Processes are spontaneous because they occur at an observable rate.
C)Spontaneity can depend on the temperature.
D)All of the statements are true.
Spontaneity can depend on the temperature.
2
Which one of the following correctly indicates the relationship between the entropy of a system and the number of different arrangements, W, in the system?
A)S = kW
B)S =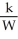
C)S =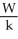
D)S = k lnW
E)S = Wk
A)S = kW
B)S =
C)S =
D)S = k lnW
E)S = Wk
S = k lnW
3
ΔS is positive for the reaction ________.
A)2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) → 2 CaO (s)
B)2 KClO3 (s) → 2KCl (s) + 3 O2 (g)
C)HCl (g) + NH3 (g) → NH4Cl (s)
D)Pb2+ (aq) + 2Cl- (aq) → PbCl2 (s)
E)CO2 (g) → CO2 (s)
A)2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) → 2 CaO (s)
B)2 KClO3 (s) → 2KCl (s) + 3 O2 (g)
C)HCl (g) + NH3 (g) → NH4Cl (s)
D)Pb2+ (aq) + 2Cl- (aq) → PbCl2 (s)
E)CO2 (g) → CO2 (s)
2 KClO3 (s) → 2KCl (s) + 3 O2 (g)
4
A reversible process is one that ________.
A)can be reversed with no net change in either system or surroundings
B)happens spontaneously
C)is spontaneous in both directions
D)must be carried out at low temperature
E)must be carried out at high temperature
A)can be reversed with no net change in either system or surroundings
B)happens spontaneously
C)is spontaneous in both directions
D)must be carried out at low temperature
E)must be carried out at high temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
ΔS is positive for the reaction ________.
A)2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (g)
B)2NO2 (g) → N2O4 (g)
C)CO2 (g) → CO2 (s)
D)BaF2 (s) → Ba2+ (aq) + 2F- (aq)
E)2Hg (l) + O2 (g) → 2HgO (s)
A)2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (g)
B)2NO2 (g) → N2O4 (g)
C)CO2 (g) → CO2 (s)
D)BaF2 (s) → Ba2+ (aq) + 2F- (aq)
E)2Hg (l) + O2 (g) → 2HgO (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
For an isothermal process, ΔS = ________.
A)q
B)qrev/T
C)qrev
D)Tqrev
E)q + w
A)q
B)qrev/T
C)qrev
D)Tqrev
E)q + w

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The thermodynamic quantity that expresses the extent of randomness in a system is ________.
A)enthalpy
B)internal energy
C)bond energy
D)entropy
E)heat flow
A)enthalpy
B)internal energy
C)bond energy
D)entropy
E)heat flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Of the following, only ________ is not a state function.
A)S
B)H
C)q
D)E
E)T
A)S
B)H
C)q
D)E
E)T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A reaction that is spontaneous as written ________.
A)is very rapid
B)will proceed without outside intervention
C)is also spontaneous in the reverse direction
D)has an equilibrium position that lies far to the left
E)is very slow
A)is very rapid
B)will proceed without outside intervention
C)is also spontaneous in the reverse direction
D)has an equilibrium position that lies far to the left
E)is very slow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which one of the following processes produces a decrease of the entropy of the system?
A)dissolving sodium chloride in water
B)sublimation of naphthalene
C)dissolving oxygen in water
D)boiling of alcohol
E)explosion of nitroglycerine
A)dissolving sodium chloride in water
B)sublimation of naphthalene
C)dissolving oxygen in water
D)boiling of alcohol
E)explosion of nitroglycerine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The first law of thermodynamics can be given as ________.
A)ΔE = q + w
B)Δ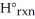 =
= 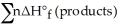 -
- 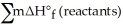
C)for any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases
D)the entropy of a pure crystalline substance at absolute zero is zero
E)ΔS = qrev/T at constant temperature
A)ΔE = q + w
B)Δ
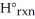 =
= 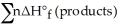 -
- 
C)for any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases
D)the entropy of a pure crystalline substance at absolute zero is zero
E)ΔS = qrev/T at constant temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The entropy of the universe is ________.
A)constant
B)continually decreasing
C)continually increasing
D)zero
E)the same as the energy, E
A)constant
B)continually decreasing
C)continually increasing
D)zero
E)the same as the energy, E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
ΔS is positive for the reaction ________.
A)2NO (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g)
B)2N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g)
C)C3H8 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 3CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (g)
D)Mg (s) + Cl2 (g) → MgCl2 (s)
E)C2H4 (g) + H2 (g) → C2H6 (g)
A)2NO (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g)
B)2N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g)
C)C3H8 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 3CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (g)
D)Mg (s) + Cl2 (g) → MgCl2 (s)
E)C2H4 (g) + H2 (g) → C2H6 (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Consider a pure crystalline solid that is heated from absolute zero to a temperature above the boiling point of the liquid. Which of the following processes produces the greatest increase in the entropy of the substance?
A)melting the solid
B)heating the liquid
C)heating the gas
D)heating the solid
E)vaporizing the liquid
A)melting the solid
B)heating the liquid
C)heating the gas
D)heating the solid
E)vaporizing the liquid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The entropy change accompanying any process is given by the equation:
A)ΔS = k lnWfinal
B)ΔS = k Wfinal - k Winitial
C)ΔS = k ln(Wfinal / Winitial)
D)ΔS = k final - k initial
E)ΔS = Wfinal - Winitial
A)ΔS = k lnWfinal
B)ΔS = k Wfinal - k Winitial
C)ΔS = k ln(Wfinal / Winitial)
D)ΔS = k final - k initial
E)ΔS = Wfinal - Winitial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
ΔS is positive for the reaction ________.
A)CaO (s) + CO2 (g) → CaCO3 (s)
B)N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g)
C)2SO3 (g) → 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
D)Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) → AgCl (s)
E)H2O (l) → H2O (s)
A)CaO (s) + CO2 (g) → CaCO3 (s)
B)N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g)
C)2SO3 (g) → 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
D)Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) → AgCl (s)
E)H2O (l) → H2O (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which one of the following is always positive when a spontaneous process occurs?
A)ΔSsystem
B)ΔSsurroundings
C)ΔSuniverse
D)ΔHuniverse
E)ΔHsurroundings
A)ΔSsystem
B)ΔSsurroundings
C)ΔSuniverse
D)ΔHuniverse
E)ΔHsurroundings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When a system is at equilibrium, ________.
A)the reverse process is spontaneous but the forward process is not
B)the forward and the reverse processes are both spontaneous
C)the forward process is spontaneous but the reverse process is not
D)the process is not spontaneous in either direction
E)both forward and reverse processes have stopped
A)the reverse process is spontaneous but the forward process is not
B)the forward and the reverse processes are both spontaneous
C)the forward process is spontaneous but the reverse process is not
D)the process is not spontaneous in either direction
E)both forward and reverse processes have stopped

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements is false?
A)The change in entropy in a system depends on the initial and final states of the system and the path taken from one state to the other.
B)Any irreversible process results in an overall increase in entropy.
C)The total entropy of the universe increases in any spontaneous process.
D)Entropy increases with the number of microstates of the system.
A)The change in entropy in a system depends on the initial and final states of the system and the path taken from one state to the other.
B)Any irreversible process results in an overall increase in entropy.
C)The total entropy of the universe increases in any spontaneous process.
D)Entropy increases with the number of microstates of the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The second law of thermodynamics states that ________.
A)ΔE = q + w
B)ΔH°rxn = Σ nΔH°f (products)- Σ mΔH°f (reactants)
C)for any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases
D)the entropy of a pure crystalline substance is zero at absolute zero
E)ΔS = qrev/T at constant temperature
A)ΔE = q + w
B)ΔH°rxn = Σ nΔH°f (products)- Σ mΔH°f (reactants)
C)for any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases
D)the entropy of a pure crystalline substance is zero at absolute zero
E)ΔS = qrev/T at constant temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which reaction produces a decrease in the entropy of the system?
A)CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
B)2C (s) + O2 (g) → 2CO (g)
C)CO2 (s) → CO2 (g)
D)2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
E)H2O (l) → H2O (g)
A)CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
B)2C (s) + O2 (g) → 2CO (g)
C)CO2 (s) → CO2 (g)
D)2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
E)H2O (l) → H2O (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
ΔS is positive for the reaction ________.
A)Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI(aq) → PbI2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
B)2H2O (g) → 2H2 (g) + O2 (g)
C)H2O (g) → H2O (s)
D)NO (g) + O2 (g) → NO2 (g)
E)Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) → AgCl (s)
A)Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI(aq) → PbI2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
B)2H2O (g) → 2H2 (g) + O2 (g)
C)H2O (g) → H2O (s)
D)NO (g) + O2 (g) → NO2 (g)
E)Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) → AgCl (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Consider the reaction: NH3 (g) + HCl (g) → NH4Cl (s)
Given the following table of thermodynamic data,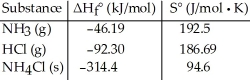 determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous.
determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous.
A)This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B)618.1
C)432.8
D)345.0
E)1235
Given the following table of thermodynamic data,
 determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous.
determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous.A)This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B)618.1
C)432.8
D)345.0
E)1235

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consider the reaction: Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) → AgCl (s)
Given the following table of thermodynamic data,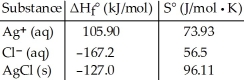 determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous under standard conditions.
determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous under standard conditions.
A)1230
B)150
C)432
D)133
E)1640
Given the following table of thermodynamic data,
 determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous under standard conditions.
determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous under standard conditions.A)1230
B)150
C)432
D)133
E)1640

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The combustion of acetylene in the presence of excess oxygen yields carbon dioxide and water: 2C2H2 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 4CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
The value of ΔS° for this reaction is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+689.3
B)+122.3
C)+432.4
D)-122.3
E)-432.4
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The combustion of acetylene in the presence of excess oxygen yields carbon dioxide and water: 2C2H2 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 4CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
The value of ΔS° for this reaction is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+689.3
B)+122.3
C)+432.4
D)-122.3
E)-432.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the catalytic hydrogenation of acetylene to ethene, C2H2 (g) + H2 (g) → C2H4 (g)
Is ________ J/K∙ mol.
A)+18.6
B)+550.8
C)+112.0
D)-112.0
E)-18.6
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the catalytic hydrogenation of acetylene to ethene, C2H2 (g) + H2 (g) → C2H4 (g)
Is ________ J/K∙ mol.
A)+18.6
B)+550.8
C)+112.0
D)-112.0
E)-18.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which reaction produces an increase in the entropy of the system?
A)Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) → AgCl (s)
B)CO2 (s) → CO2 (g)
C)H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2 HCl (g)
D)N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g)
E)H2O (l) → H2O (s)
A)Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) → AgCl (s)
B)CO2 (s) → CO2 (g)
C)H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2 HCl (g)
D)N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g)
E)H2O (l) → H2O (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A reaction that is not spontaneous at low temperature can become spontaneous at high temperature if ΔH is ________ and ΔS is ________.
A)+, +
B)-, -
C)+, -
D)-, +
E)+, 0
A)+, +
B)-, -
C)+, -
D)-, +
E)+, 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
For the reaction C2H6 (g) → C2H4 (g) + H2 (g)
ΔH° is +137 kJ/mol and ΔS° is +120 J/K ∙ mol. This reaction is ________.
A)spontaneous at all temperatures
B)spontaneous only at high temperature
C)spontaneous only at low temperature
D)nonspontaneous at all temperatures
ΔH° is +137 kJ/mol and ΔS° is +120 J/K ∙ mol. This reaction is ________.
A)spontaneous at all temperatures
B)spontaneous only at high temperature
C)spontaneous only at low temperature
D)nonspontaneous at all temperatures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which reaction produces a decrease in the entropy of the system?
A)4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 NO (g) + 6 H2O (g)
B)Na (s) + 1/2 Cl2 (g) → NaCl (s)
C)2 HgO (s) → 2 Hg (l) + O2 (g)
D)UF6 (s)→ U (s) + 3F2 (g)
E)H2O (s) → H2O (g)
A)4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 NO (g) + 6 H2O (g)
B)Na (s) + 1/2 Cl2 (g) → NaCl (s)
C)2 HgO (s) → 2 Hg (l) + O2 (g)
D)UF6 (s)→ U (s) + 3F2 (g)
E)H2O (s) → H2O (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
For the reaction 2 C4H10 (g) + 13 O2 (g)→ 8 CO2 (g) + 10 H2O (g)
ΔH° is -125 kJ/mol and ΔS° is +253 J/K ∙ mol. This reaction is ________.
A)spontaneous at all temperatures
B)spontaneous only at high temperature
C)spontaneous only at low temperature
D)nonspontaneous at all temperatures
E)unable to determine without more information
ΔH° is -125 kJ/mol and ΔS° is +253 J/K ∙ mol. This reaction is ________.
A)spontaneous at all temperatures
B)spontaneous only at high temperature
C)spontaneous only at low temperature
D)nonspontaneous at all temperatures
E)unable to determine without more information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which one of the following statements is true about the equilibrium constant for a reaction if ΔG° for the reaction is negative?
A)K = 0
B)K = 1
C)K > 1
D)K < 1
E)More information is needed.
A)K = 0
B)K = 1
C)K > 1
D)K < 1
E)More information is needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the catalytic hydrogenation of ethene to ethane, C2H4 (g) + H2(g) → C2H6 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-101.9
B)-120.5
C)-232.5
D)+112.0
E)+101.9
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the catalytic hydrogenation of ethene to ethane, C2H4 (g) + H2(g) → C2H6 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-101.9
B)-120.5
C)-232.5
D)+112.0
E)+101.9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
ΔS is negative for the reaction ________.
A)2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2SO3 (g)
B)NH4Cl (s) → NH3 (g) + HCl (g)
C)PbCl2 (s) → Pb2+ (aq) + 2Cl- (aq)
D)2C (s) + O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g)
E)H2O (l) → H2O (g)
A)2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2SO3 (g)
B)NH4Cl (s) → NH3 (g) + HCl (g)
C)PbCl2 (s) → Pb2+ (aq) + 2Cl- (aq)
D)2C (s) + O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g)
E)H2O (l) → H2O (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Given the following table of thermodynamic data,  complete the following sentence. The vaporization of TiCl4 is ________.
complete the following sentence. The vaporization of TiCl4 is ________.
A)spontaneous at all temperatures
B)spontaneous at low temperature and nonspontaneous at high temperature
C)nonspontaneous at low temperature and spontaneous at high temperature
D)nonspontaneous at all temperatures
E)not enough information given to draw a conclusion
 complete the following sentence. The vaporization of TiCl4 is ________.
complete the following sentence. The vaporization of TiCl4 is ________.A)spontaneous at all temperatures
B)spontaneous at low temperature and nonspontaneous at high temperature
C)nonspontaneous at low temperature and spontaneous at high temperature
D)nonspontaneous at all temperatures
E)not enough information given to draw a conclusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For an isothermal process, the entropy change of the surroundings is given by the equation:
A)ΔS = qsys T
B)ΔS = -qsys T
C)ΔS = q lnT
D)ΔS = -q lnT
E)ΔS = -qsys / T
A)ΔS = qsys T
B)ΔS = -qsys T
C)ΔS = q lnT
D)ΔS = -q lnT
E)ΔS = -qsys / T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The equilibrium position corresponds to which letter on the graph of G vs. f (course of reaction)below? 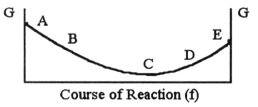
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the reaction 2C (s, diamond) + O2 (g) → 2CO (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-185.9
B)+185.9
C)-9.5
D)+9.5
E)-195.7
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the reaction 2C (s, diamond) + O2 (g) → 2CO (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-185.9
B)+185.9
C)-9.5
D)+9.5
E)-195.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider the reaction: FeO (s) + Fe (s) + O2 (g) → Fe2O3 (s)
Given the following table of thermodynamic data,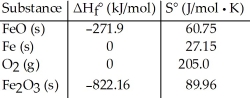 determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous.
determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous.
A)This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B)618.1
C)756.3
D)2438
E)1235
Given the following table of thermodynamic data,
 determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous.
determine the temperature (in °C)above which the reaction is nonspontaneous.A)This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B)618.1
C)756.3
D)2438
E)1235

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
With thermodynamics, one cannot determine ________.
A)the speed of a reaction
B)the direction of a spontaneous reaction
C)the extent of a reaction
D)the value of the equilibrium constant
E)the temperature at which a reaction will be spontaneous
A)the speed of a reaction
B)the direction of a spontaneous reaction
C)the extent of a reaction
D)the value of the equilibrium constant
E)the temperature at which a reaction will be spontaneous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide, C (s, graphite) + O2 (g) → CO2(g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol. The combustion of carbon, as in charcoal briquettes, in the presence of abundant oxygen produces carbon dioxide.
A)+424.3
B)+205.0
C)-205.0
D)-2.9
E)+2.9
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide, C (s, graphite) + O2 (g) → CO2(g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol. The combustion of carbon, as in charcoal briquettes, in the presence of abundant oxygen produces carbon dioxide.
A)+424.3
B)+205.0
C)-205.0
D)-2.9
E)+2.9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The value of ΔH° for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur dioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, SO2 (g) → S (s,rhombic) + O2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)0.0
B)+135.0
C)-135.90
D)-269.9
E)+269.9
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)0.0
B)+135.0
C)-135.90
D)-269.9
E)+269.9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The value of ΔS° for the formation of calcium chloride from its constituent elements, Ca (s) + Cl2 (g) → CaCl2 (s)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-104.6
B)+104.6
C)+369.0
D)-159.8
E)+159.8
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-104.6
B)+104.6
C)+369.0
D)-159.8
E)+159.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The combustion of ethene in the presence of excess oxygen yields carbon dioxide and water: C2H4 (g) + 3O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
The value of ΔS° for this reaction is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-267.4
B)-140.9
C)-347.6
D)+347.6
E)+140.9
The value of ΔS° for this reaction is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-267.4
B)-140.9
C)-347.6
D)+347.6
E)+140.9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The value of ΔH° for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur trioxide to its component elements, 2SO3 (g) → 2S (s, rhombic) + 3O2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+790.4
B)-790.4
C)+395.2
D)-395.2
E)+105.1
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+790.4
B)-790.4
C)+395.2
D)-395.2
E)+105.1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The value of ΔS° for the oxidation of solid elemental sulfur to gaseous sulfur dioxide, S (s, rhombic)+ O2(g) → SO2(g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+485.4
B)+248.5
C)-11.6
D)-248.5
E)+11.6
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+485.4
B)+248.5
C)-11.6
D)-248.5
E)+11.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The value of ΔS° for the formation of POCl3 from its constituent elements, P2 (g) + O2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g) → 2POCl3 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-442.0
B)+771.0
C)-321.0
D)-771.0
E)+321.0
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-442.0
B)+771.0
C)-321.0
D)-771.0
E)+321.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The value of ΔH° for the oxidation of solid elemental sulfur to gaseous sulfur dioxide, S (s, rhombic) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+269.9
B)-269.9
C)+0.00
D)-11.6
E)+11.6
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+269.9
B)-269.9
C)+0.00
D)-11.6
E)+11.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The value of ΔS° for the formation of phosphorous trichloride from its constituent elements, P2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g) → 2PCl3 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-311.7
B)+311.7
C)-263.6
D)+129.4
E)-129.4
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-311.7
B)+311.7
C)-263.6
D)+129.4
E)-129.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The value of ΔS° for the decomposition of phosphorous trichloride into its constituent elements, 2PCl3 (g) → P2 (g) + 3Cl2( g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-311.7
B)+311.7
C)+263.6
D)+129.4
E)-129.4
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-311.7
B)+311.7
C)+263.6
D)+129.4
E)-129.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Calcium
Ca (s)0 0 41.4
CaCl2 (s)-795.8 -748.1 104.6
Ca2+ (aq)226.7 209.2 200.8
Chlorine
Cl2 (g) 0 0 222.96
Cl- (aq)-167.2 -131.2 56.5
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
Phosphorus
P2 (g)144.3 103.7 218.1
PCl3 (g)-288.1 -269.6 311.7
POCl3 (g)-542.2 -502.5 325
Sulfur
S (s, rhombic)0 0 31.88
SO2(g)-269.9 -300.4 248.5
SO3(g)-395.2 -370.4 256.2
The value of ΔS° for the oxidation of solid elemental sulfur to gaseous sulfur trioxide, 2S (s, rhombic) + 3O2(g) → 2SO3 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+19.3
B)-19.3
C)+493.1
D)-166.4
E)-493.1
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Calcium
Ca (s)0 0 41.4
CaCl2 (s)-795.8 -748.1 104.6
Ca2+ (aq)226.7 209.2 200.8
Chlorine
Cl2 (g) 0 0 222.96
Cl- (aq)-167.2 -131.2 56.5
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
Phosphorus
P2 (g)144.3 103.7 218.1
PCl3 (g)-288.1 -269.6 311.7
POCl3 (g)-542.2 -502.5 325
Sulfur
S (s, rhombic)0 0 31.88
SO2(g)-269.9 -300.4 248.5
SO3(g)-395.2 -370.4 256.2
The value of ΔS° for the oxidation of solid elemental sulfur to gaseous sulfur trioxide, 2S (s, rhombic) + 3O2(g) → 2SO3 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+19.3
B)-19.3
C)+493.1
D)-166.4
E)-493.1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The value of ΔS° for the decomposition of calcium chloride into its constituent elements, CaCl2 (s) → Ca (s) + Cl2 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-104.6
B)+104.6
C)+369.0
D)-159.8
E)+159.8
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-104.6
B)+104.6
C)+369.0
D)-159.8
E)+159.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The value of ΔH° for the oxidation of solid elemental sulfur to gaseous sulfur trioxide, 2S (s, rhombic) + 3O2( g) → 2SO3 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+790.4
B)-790.4
C)+395.2
D)-395.2
E)+105.1
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+790.4
B)-790.4
C)+395.2
D)-395.2
E)+105.1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The value of ΔS° for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur dioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, SO2 (g) → S (s, rhombic) + O2 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+485.4
B)+248.5
C)-11.6
D)-248.5
E)+11.6
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+485.4
B)+248.5
C)-11.6
D)-248.5
E)+11.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The value of ΔS° for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur trioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, 2SO3 (g) → 2S (s, rhombic) + 3O2 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+19.3
B)-19.3
C)+493.1
D)+166.4
E)-493.1
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+19.3
B)-19.3
C)+493.1
D)+166.4
E)-493.1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The combustion of hydrogen in the presence of excess oxygen yields water: 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O (l)
The value of ΔS° for this reaction is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+405.5
B)-405.5
C)-326.3
D)-265.7
E)+265.7
The value of ΔS° for this reaction is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+405.5
B)-405.5
C)-326.3
D)-265.7
E)+265.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The value of ΔS° for the decomposition of POCl3 into its constituent elements, 2POCl3 (g) → P2 (g) + O2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+771.0
B)+442.0
C)-321.0
D)-771.0
E)+321.0
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+771.0
B)+442.0
C)-321.0
D)-771.0
E)+321.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the oxidation of carbon to carbon monoxide, 2C (s, graphite) + O2 (g) → 2CO (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol. Carbon monoxide is produced in the combustion of carbon with limited oxygen.
A)-12.8
B)+408.6
C)-408.6
D)+179.4
E)+395.8
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the oxidation of carbon to carbon monoxide, 2C (s, graphite) + O2 (g) → 2CO (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol. Carbon monoxide is produced in the combustion of carbon with limited oxygen.
A)-12.8
B)+408.6
C)-408.6
D)+179.4
E)+395.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the catalytic hydrogenation of acetylene to ethane, C2H2 (g) + 2H2 (g) → C2H6 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-76.0
B)+440.9
C)-232.5
D)+232.5
E)+28.7
Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25 °C)
Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol)ΔG°f (kJ/mol)S (J/K-mol)
Carbon
C (s, diamond)1.88 2.84 2.43
C (s, graphite)0 0 5.69
C2H2 (g)226.7 209.2 200.8
C2H4 (g)52.30 68.11 219.4
C2H6 (g)-84.68 -32.89 229.5
CO (g)-110.5 -137.2 197.9
CO2 (g)-393.5 -394.4 213.6
Hydrogen
H2( g)0 0 130.58
Oxygen
O2 (g)0 0 205.0
H2O (l)-285.83 -237.13 69.91
The value of ΔS° for the catalytic hydrogenation of acetylene to ethane, C2H2 (g) + 2H2 (g) → C2H6 (g)
Is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)-76.0
B)+440.9
C)-232.5
D)+232.5
E)+28.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The combustion of ethane in the presence of excess oxygen yields carbon dioxide and water: 2C2H6 (g) + 7O2 (g) → 4CO2 (g) + 6H2O (l)
The value of ΔS° for this reaction is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+718.0
B)-620.1
C)-718.0
D)-151.0
E)+151.0
The value of ΔS° for this reaction is ________ J/K ∙ mol.
A)+718.0
B)-620.1
C)-718.0
D)-151.0
E)+151.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The value of ΔH° for the formation of POCl3 from its constituent elements, P2 (g) + O2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g) → 2POCl3 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-1228.7
B)-397.7
C)-686.5
D)+1228.7
E)+686.5
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-1228.7
B)-397.7
C)-686.5
D)+1228.7
E)+686.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The value of ΔG° at 25 °C for the decomposition of phosphorous trichloride into its constituent elements, 2PCl3 (g) → P2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-539.2
B)+539.2
C)-642.9
D)+642.9
E)-373.3
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-539.2
B)+539.2
C)-642.9
D)+642.9
E)-373.3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The value of ΔG° at 25 °C for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur trioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, 2SO3 (g) → 2S (s, rhombic) + 3O2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+740.8
B)-370.4
C)+370.4
D)-740.8
E)+185.2
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+740.8
B)-370.4
C)+370.4
D)-740.8
E)+185.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The value of ΔH° for the decomposition of POCl3 into its constituent elements, 2POCl3 (g) → P2 (g) + O2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-1228.7
B)+1228.7
C)-940.1
D)+940.1
E)0.00
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-1228.7
B)+1228.7
C)-940.1
D)+940.1
E)0.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The value of ΔH° for the decomposition of calcium chloride into its constituent elements, CaCl2 (s) → Ca (s) + Cl2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)0.00
B)-397.9
C)+397.9
D)-795.8
E)+795.8
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)0.00
B)-397.9
C)+397.9
D)-795.8
E)+795.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The value of ΔG° for a reaction conducted at 25 °C is 3.05 kJ/mol. The equilibrium constant for a reaction is ________ at this temperature.
A)0.292
B)-4.20
C)0.320
D)-1.13
E)More information is needed.
A)0.292
B)-4.20
C)0.320
D)-1.13
E)More information is needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The value of ΔH° for the formation of calcium chloride from its constituent elements, Ca (s) + Cl2 (g) → CaCl2 (s)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)0.00
B)-397.9
C)+397.9
D)-795.8
E)+795.8
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)0.00
B)-397.9
C)+397.9
D)-795.8
E)+795.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The value of ΔG° at 25 °C for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur dioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, SO2 (g) → S (s, rhombic) + O2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+395.2
B)+269.9
C)-269.9
D)+300.4
E)-300.4
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+395.2
B)+269.9
C)-269.9
D)+300.4
E)-300.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The value of ΔG° at 25 °C for the decomposition of calcium chloride into its constituent elements, CaCl2 (s) → Ca (s) + Cl2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-795.8
B)+795.8
C)+763.7
D)+748.1
E)-748.1
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-795.8
B)+795.8
C)+763.7
D)+748.1
E)-748.1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The value of ΔG° at 25 °C for the oxidation of solid elemental sulfur to gaseous sulfur trioxide, 2S (s, rhombic) + 3O2 (g) → 2SO3 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+740.8
B)-370.4
C)+370.4
D)-740.8
E)+185.2
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+740.8
B)-370.4
C)+370.4
D)-740.8
E)+185.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The value of ΔG° at 25 °C for the decomposition of POCl3 into its constituent elements, 2POCl3 (g) → P2 (g) + O2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-1108.7
B)+1108.7
C)-606.2
D)+606.2
E)-1,005
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-1108.7
B)+1108.7
C)-606.2
D)+606.2
E)-1,005

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The value of ΔG° at 25 °C for the following reaction: C2H4 (g) + H2 (g) → C2H6 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol. At 298 K, ΔH° for this reaction is -137.5 kJ/mol, and ΔS° is +120.5 J/K.
A)-35800
B)-173.4
C)35800
D)-101.7
E)-274.2
Is ________ kJ/mol. At 298 K, ΔH° for this reaction is -137.5 kJ/mol, and ΔS° is +120.5 J/K.
A)-35800
B)-173.4
C)35800
D)-101.7
E)-274.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The value of ΔG° at 25 °C for the formation of calcium chloride from its constituent elements, Ca (s) + Cl2 (g) → CaCl2 (s)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-795.8
B)+795.8
C)+763.7
D)+748.1
E)-748.1
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-795.8
B)+795.8
C)+763.7
D)+748.1
E)-748.1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The value of ΔG° at 25 °C for the formation of POCl3 from its constituent elements, P2 (g) + O2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g) → 2POCl3 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-1108.7
B)+1108.7
C)-606.2
D)+606.2
E)-1,005
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-1108.7
B)+1108.7
C)-606.2
D)+606.2
E)-1,005

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Given the thermodynamic data in the table below, calculate the equilibrium constant (at 298 K)for the reaction: 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)  2 SO3 (g)
2 SO3 (g) 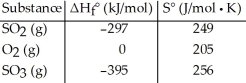
A)2.40 × 1024
B)1.06
C)1.95
D)3.82 × 1023
E)More data are needed.
 2 SO3 (g)
2 SO3 (g) 
A)2.40 × 1024
B)1.06
C)1.95
D)3.82 × 1023
E)More data are needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The value of ΔG° at 25 °C for the oxidation of solid elemental sulfur to gaseous sulfur dioxide, S (s, rhombic) + O2(g) → SO2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+395.2
B)+269.9
C)-269.9
D)+300.4
E)-300.4
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+395.2
B)+269.9
C)-269.9
D)+300.4
E)-300.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The value of ΔG° at 25 °C for the formation of phosphorous trichloride from its constituent elements, P2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g) → 2PCl3 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-539.2
B)+539.2
C)-642.9
D)+642.9
E)-373.3
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)-539.2
B)+539.2
C)-642.9
D)+642.9
E)-373.3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The value of ΔH° for the formation of phosphorous trichloride from its constituent elements, P2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g) → 2PCl3 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol
A)-288.1
B)+432.4
C)-720.5
D)+720.5
E)-432.4
Is ________ kJ/mol
A)-288.1
B)+432.4
C)-720.5
D)+720.5
E)-432.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The value of ΔH° for the decomposition of phosphorous trichloride into its constituent elements, 2PCl3 (g) → P2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+576.2
B)-288.1
C)+720.5
D)+288.1
E) -720.5
Is ________ kJ/mol.
A)+576.2
B)-288.1
C)+720.5
D)+288.1
E) -720.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The value of ΔG° at 373 K for the oxidation of solid elemental sulfur to gaseous sulfur dioxide, S (s, rhombic) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
Is ________ kJ/mol. At 298 K, ΔH° for this reaction is -269.9 kJ/mol, and ΔS° is +11.6 J/K.
A)-300.4
B)+300.4
C)-4,597
D)+4,597
E)-274.2
Is ________ kJ/mol. At 298 K, ΔH° for this reaction is -269.9 kJ/mol, and ΔS° is +11.6 J/K.
A)-300.4
B)+300.4
C)-4,597
D)+4,597
E)-274.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



