Deck 2: Product Costing: Manufacturing Processes, cost Terminology and Cost Flows
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Product Costing: Manufacturing Processes, cost Terminology and Cost Flows
1
Which of the following statements is true about manufacturing companies over the past 20 years?
A) The grouping of machines into 'manufacturing cells' has increased.
B) Carrying large amounts of inventory is often less costly than carrying small amounts of inventory.
C) They have moved from a 'pull' approach to more of a 'push' approach.
D) The basic production process has changed very little over the past 20 years.
A) The grouping of machines into 'manufacturing cells' has increased.
B) Carrying large amounts of inventory is often less costly than carrying small amounts of inventory.
C) They have moved from a 'pull' approach to more of a 'push' approach.
D) The basic production process has changed very little over the past 20 years.
A
2
Under ideal conditions,companies operating in a _________ environment would reduce inventories of raw materials,work-in-process and finished goods to very low levels or even zero.
A) volatile
B) just-in-time
C) traditional manufacturing
D) favourable
A) volatile
B) just-in-time
C) traditional manufacturing
D) favourable
B
3
Which of the following types of organisations is most likely to have a raw materials inventory account?
A) A retailer
B) A manufacturer
C) A service provider
D) A government unit
A) A retailer
B) A manufacturer
C) A service provider
D) A government unit
B
4
Which of the following is an advantage of lean production and just-in-time (JIT)manufacturing systems?
A) Deliver the product to the customer on time,even if the workers go on a strike.
B) Improved product quality and reduced processing time.
C) Reduced reliance on highly skilled employees
D) Increased reliance on few suppliers.
A) Deliver the product to the customer on time,even if the workers go on a strike.
B) Improved product quality and reduced processing time.
C) Reduced reliance on highly skilled employees
D) Increased reliance on few suppliers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A 'manufacturing cell' is defined as:
A) grouping of all the machinery and equipment that are needed to make a product being available in one area of the factory.
B) restructuring of the factory so that the companies are able to manufacture products quickly.
C) an area in the warehouse where similar raw materials are grouped together.
D) grouping of all the factories that are engaged in manufacturing similar products.
A) grouping of all the machinery and equipment that are needed to make a product being available in one area of the factory.
B) restructuring of the factory so that the companies are able to manufacture products quickly.
C) an area in the warehouse where similar raw materials are grouped together.
D) grouping of all the factories that are engaged in manufacturing similar products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Materials that can be directly traced to a particular product and become an integral part of the finished product are called:
A) indirect materials.
B) direct materials.
C) supplies.
D) product materials.
A) indirect materials.
B) direct materials.
C) supplies.
D) product materials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is a risk that would more likely be seen in a lean production and just-in-time manufacturing environment than in a traditional production environment?
A) Reduced customer satisfaction due to higher product defects
B) Reduced raw material supply bringing the production process to a halt
C) Increased inventory storage costs
D) Increased production time resulting in lost sales
A) Reduced customer satisfaction due to higher product defects
B) Reduced raw material supply bringing the production process to a halt
C) Increased inventory storage costs
D) Increased production time resulting in lost sales

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A traditional manufacturing environment does not have which of the following?
A) An automated production process
B) Trained employees
C) Extremely low levels of work-in-process inventory
D) Product cost information available
A) An automated production process
B) Trained employees
C) Extremely low levels of work-in-process inventory
D) Product cost information available

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Manufacturing costs typically consist of:
A) direct materials,direct labour,and administrative costs.
B) production and shipping costs.
C) direct materials,direct labour,and manufacturing overhead.
D) manufacturing overhead and selling costs.
A) direct materials,direct labour,and administrative costs.
B) production and shipping costs.
C) direct materials,direct labour,and manufacturing overhead.
D) manufacturing overhead and selling costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In a just-in-time environment,the production process often begins when:
A) products are moved from raw materials to work-in-process.
B) a customer places an order.
C) the product is delivered to a customer.
D) products are moved from work-in-process to finished goods.
A) products are moved from raw materials to work-in-process.
B) a customer places an order.
C) the product is delivered to a customer.
D) products are moved from work-in-process to finished goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Companies that operate in a lean production and just-in-time manufacturing environment are more likely to experience which of the following?
A) Reduced manufacturing flexibility
B) Increased levels of raw materials inventory
C) Increased production time
D) Increased product quality
A) Reduced manufacturing flexibility
B) Increased levels of raw materials inventory
C) Increased production time
D) Increased product quality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In general,costs incurred in the factory that do not qualify as either direct material or direct labour are called:
A) manufacturing costs.
B) manufacturing overhead.
C) non-manufacturing costs.
D) selling and administrative costs.
A) manufacturing costs.
B) manufacturing overhead.
C) non-manufacturing costs.
D) selling and administrative costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements about manufacturing in a traditional environment is true?
A) Factories are organised so that machines that are dissimilar are grouped together.
B) It is not desirable to accumulate raw materials inventory to serve as buffers in case of unexpected demand for products.
C) The process begins with a customer order and products are 'pulled' through the manufacturing process.
D) Partially completed inventory is accumulated in a work-in-process inventory account.
A) Factories are organised so that machines that are dissimilar are grouped together.
B) It is not desirable to accumulate raw materials inventory to serve as buffers in case of unexpected demand for products.
C) The process begins with a customer order and products are 'pulled' through the manufacturing process.
D) Partially completed inventory is accumulated in a work-in-process inventory account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is a disadvantage of lean production and just-in-time (JIT)manufacturing systems?
A) Increased customer delivery time
B) Increased product defects
C) Decreased flexibility of manufacturing facilities
D) Increased reliance on fewer suppliers
A) Increased customer delivery time
B) Increased product defects
C) Decreased flexibility of manufacturing facilities
D) Increased reliance on fewer suppliers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Lean production is focused on eliminating waste associated with all of the following except:
A) moving products farther than required.
B) down time caused by people waiting for work to do.
C) providing excessive customer service.
D) over-processing a product.
A) moving products farther than required.
B) down time caused by people waiting for work to do.
C) providing excessive customer service.
D) over-processing a product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements is true regarding the lean production and just-in-time (JIT)manufacturing systems?
A) Customers are often less satisfied with the purchased product.
B) The number of product defects often increases.
C) The number of suppliers the company can purchase raw materials from often increases.
D) The factory is often restructured where dissimilar machines are grouped together.
A) Customers are often less satisfied with the purchased product.
B) The number of product defects often increases.
C) The number of suppliers the company can purchase raw materials from often increases.
D) The factory is often restructured where dissimilar machines are grouped together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a characteristic of a lean production and just-in-time (JIT)manufacturing environment but not of a traditional manufacturing environment?
A) Increased inventory levels
B) Increased product defects
C) Increased reliance on a select number of suppliers
D) Increased production time
A) Increased inventory levels
B) Increased product defects
C) Increased reliance on a select number of suppliers
D) Increased production time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements regarding the traditional manufacturing environment is not true?
A) Machines are often put into 'manufacturing cells' whereby dissimilar machines are grouped together.
B) Raw material is 'pushed' to the next production area in anticipation of customer demand.
C) Manufacturers often have raw material,work-in-process,and finished goods inventory on hand.
D) Buffers of inventory may result in workers being less efficient.
A) Machines are often put into 'manufacturing cells' whereby dissimilar machines are grouped together.
B) Raw material is 'pushed' to the next production area in anticipation of customer demand.
C) Manufacturers often have raw material,work-in-process,and finished goods inventory on hand.
D) Buffers of inventory may result in workers being less efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is not a type of manufacturing cost?
A) Direct material costs
B) Administrative costs
C) Factory overhead costs
D) Direct labour costs
A) Direct material costs
B) Administrative costs
C) Factory overhead costs
D) Direct labour costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a characteristic of a traditional production environment but not of a lean production and just-in-time (JIT)manufacturing environment?
A) Increase in the need for highly skilled labour
B) Increase in the need for highly reliable suppliers
C) Reduction in the motivation of the work force
D) Reduction in the processing time
A) Increase in the need for highly skilled labour
B) Increase in the need for highly reliable suppliers
C) Reduction in the motivation of the work force
D) Reduction in the processing time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following types of employees would most likely have their wage be classified as direct labour?
A) Factory maintenance worker
B) Factory supervisor
C) Managerial accountant
D) Assembly-line factory worker
A) Factory maintenance worker
B) Factory supervisor
C) Managerial accountant
D) Assembly-line factory worker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Manufacturing overhead includes:
A) advertising costs.
B) indirect materials.
C) sales commissions.
D) shipping charges for finished goods.
A) advertising costs.
B) indirect materials.
C) sales commissions.
D) shipping charges for finished goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following increases the work-in-process account?
A) Cost of goods sold
B) Raw material purchased
C) Administrative costs
D) Raw material used
A) Cost of goods sold
B) Raw material purchased
C) Administrative costs
D) Raw material used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is an example of a manufacturing overhead cost?
A) Supplies used by administrative staff
B) Supplies used by a salesperson
C) Materials easily traced to a specific product
D) Lubricants used by factory maintenance workers
A) Supplies used by administrative staff
B) Supplies used by a salesperson
C) Materials easily traced to a specific product
D) Lubricants used by factory maintenance workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is not an example of manufacturing overhead costs?
A) Fringe benefits paid to assembly-line workers
B) Depreciation of factory machinery
C) Overtime pay to factory supervisors
D) Insurance on factory machinery
A) Fringe benefits paid to assembly-line workers
B) Depreciation of factory machinery
C) Overtime pay to factory supervisors
D) Insurance on factory machinery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements is false regarding non-manufacturing costs?
A) They are incurred outside the factory.
B) They include selling and administrative costs.
C) They are not directly incurred to make a product.
D) They include indirect materials and indirect labour costs.
A) They are incurred outside the factory.
B) They include selling and administrative costs.
C) They are not directly incurred to make a product.
D) They include indirect materials and indirect labour costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Product costs that transfer out of finished goods are called:
A) work-in-process.
B) cost of goods manufactured.
C) cost of goods sold.
D) period costs.
A) work-in-process.
B) cost of goods manufactured.
C) cost of goods sold.
D) period costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following types of employees would most likely have their wage be classified as indirect labour?
A) Factory supervisor
B) Managerial accountant
C) Salesperson
D) Machine operator
A) Factory supervisor
B) Managerial accountant
C) Salesperson
D) Machine operator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following types of companies would be the least likely to have the following cost pattern?
Raw materials Work-in-Process Finished Goods Cost of goods sold
A) Tyre manufacturer
B) Computer software manufacturer
C) Retailer/merchandiser
D) Construction company
Raw materials Work-in-Process Finished Goods Cost of goods sold
A) Tyre manufacturer
B) Computer software manufacturer
C) Retailer/merchandiser
D) Construction company

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Product costs that transfer into finished goods inventory are called:
A) cost of goods manufactured.
B) cost of goods sold.
C) period costs.
D) raw materials used.
A) cost of goods manufactured.
B) cost of goods sold.
C) period costs.
D) raw materials used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Jasper Corporation incurred the following costs in April:
-Total period costs are:
A) $86 000
B) $38 000
C) $40 000
D) $80 000
-Total period costs are:
A) $86 000
B) $38 000
C) $40 000
D) $80 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is a product cost?
A) Insurance on factory machinery
B) Insurance on delivery trucks
C) Lease expense on office computer
D) Advertising costs
A) Insurance on factory machinery
B) Insurance on delivery trucks
C) Lease expense on office computer
D) Advertising costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Jasper Corporation incurred the following costs in April:
-Total product costs are:
A) $130 000
B) $155 000
C) $115 000
D) $117 000
-Total product costs are:
A) $130 000
B) $155 000
C) $115 000
D) $117 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following decreases the work-in-process account?
A) Raw materials used
B) Cost of goods manufactured
C) Direct labour
D) Manufacturing overhead
A) Raw materials used
B) Cost of goods manufactured
C) Direct labour
D) Manufacturing overhead

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Clyde Retailer's is a local merchandiser which buys vintage clothing and sells it to local college students.Clyde began the year with inventory costing $60 000.During the year inventory costing $300 000 was purchased.At the end of the year,inventory costing $45 000 still remained.What was Clyde's cost of goods sold for the year?
A) $255 000
B) $285 000
C) $300 000
D) $315 000
A) $255 000
B) $285 000
C) $300 000
D) $315 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is not an example of a manufacturing overhead cost?
A) Shipping charges on finished products
B) Indirect materials
C) Indirect labour
D) Depreciation on factory equipment
A) Shipping charges on finished products
B) Indirect materials
C) Indirect labour
D) Depreciation on factory equipment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Products and their costs flow through a production facility in the following order:
A) Work-in-process,finished goods,cost of goods sold
B) Raw materials,work-in-process,finished goods,cost of goods sold
C) Work-in-process,raw materials,cost of goods sold,finished goods
D) Work-in-process,cost of goods manufactured,cost of goods sold
A) Work-in-process,finished goods,cost of goods sold
B) Raw materials,work-in-process,finished goods,cost of goods sold
C) Work-in-process,raw materials,cost of goods sold,finished goods
D) Work-in-process,cost of goods manufactured,cost of goods sold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The journal entry to record raw materials used would include a:
A) debit to finished goods.
B) debit to raw materials.
C) debit to work-in-process.
D) debit to cost of goods sold.
A) debit to finished goods.
B) debit to raw materials.
C) debit to work-in-process.
D) debit to cost of goods sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements accurately describes manufacturing cost flows in a just-in-time (JIT)environment?
A) Direct labour and overhead are maintained in a work-in-process account for long periods of time.
B) There is little need to maintain a cost of goods sold account.
C) There is little need to maintain raw materials,work-in-process,or finished goods accounts.
D) Manufacturing costs are maintained in the finished goods account for long periods of time.
A) Direct labour and overhead are maintained in a work-in-process account for long periods of time.
B) There is little need to maintain a cost of goods sold account.
C) There is little need to maintain raw materials,work-in-process,or finished goods accounts.
D) Manufacturing costs are maintained in the finished goods account for long periods of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements is true regarding manufacturing costs?
A) They will be appear on the income statement as the product is made.
B) They will not appear on the income statement or the balance sheet until the product is completed.
C) They will appear on the balance sheet as an inventory cost until the product is sold.
D) They will appear on the balance sheet as an inventory cost after the product is sold.
A) They will be appear on the income statement as the product is made.
B) They will not appear on the income statement or the balance sheet until the product is completed.
C) They will appear on the balance sheet as an inventory cost until the product is sold.
D) They will appear on the balance sheet as an inventory cost after the product is sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Hillsborough Street Manufacturing Inc. incurred the following costs in 2009:
50 000 units were produced during the year out of which 40 000 units were sold for $10 each. There was no beginning or ending raw materials or work-in-process inventory.
-What is cost of goods sold for the year?
A) $ 88 000
B) $ 97 600
C) $122 000
D) $110 000
50 000 units were produced during the year out of which 40 000 units were sold for $10 each. There was no beginning or ending raw materials or work-in-process inventory.
-What is cost of goods sold for the year?
A) $ 88 000
B) $ 97 600
C) $122 000
D) $110 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When the cost of a product is matched with its sales price,the result (difference)is called:
A) net income.
B) gross margin.
C) cost of goods sold.
D) cost of goods manufactured.
A) net income.
B) gross margin.
C) cost of goods sold.
D) cost of goods manufactured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Michael’s Manufacturing, Inc. has the following information available for the month of July:
-Cost of goods sold for July is:
A) $227 000
B) $202 000
C) $249 000
D) $239 000
-Cost of goods sold for July is:
A) $227 000
B) $202 000
C) $249 000
D) $239 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Hillsborough Street Manufacturing Inc. incurred the following costs in 2009:
50 000 units were produced during the year out of which 40 000 units were sold for $10 each. There was no beginning or ending raw materials or work-in-process inventory.
-What is net income for the year?
A) $278 000
B) $312 000
C) $378 000
D) $300 000
50 000 units were produced during the year out of which 40 000 units were sold for $10 each. There was no beginning or ending raw materials or work-in-process inventory.
-What is net income for the year?
A) $278 000
B) $312 000
C) $378 000
D) $300 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Scott Products manufactures high-quality running shoes. The following information is available for 2009:
In addition, 42 400 pairs were produced in 2009 out of which 40 900 pairs were sold for $70 each.
-What is net income for 2009? (ignore taxes)
A) $1 920 000
B) $2 025 000
C) $1 890 000
D) $2 045 000
In addition, 42 400 pairs were produced in 2009 out of which 40 900 pairs were sold for $70 each.
-What is net income for 2009? (ignore taxes)
A) $1 920 000
B) $2 025 000
C) $1 890 000
D) $2 045 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When non-manufacturing costs are subtracted from gross margin,the result is called:
A) cost of goods sold.
B) net income.
C) sales.
D) non-manufacturing income.
A) cost of goods sold.
B) net income.
C) sales.
D) non-manufacturing income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Thompson Inc.has the following selected information available for 2009:
Manufacturing overhead costs in 2009 amounted to:
A) $39 000
B) $55 000
C) $49 000
D) $31 000
Manufacturing overhead costs in 2009 amounted to:
A) $39 000
B) $55 000
C) $49 000
D) $31 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Hudson Inc. has the following information available for September:
-Sales revenue for September totalled $400 000.Net income for September is:
A) $257 000
B) $260 000
C) $264 000
D) $278 000
-Sales revenue for September totalled $400 000.Net income for September is:
A) $257 000
B) $260 000
C) $264 000
D) $278 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Nate’s Novelties, Inc. has the following information available for July:
-Cost of goods manufactured for July is:
A) $153 000
B) $103 000
C) $130 000
D) $133 000
-Cost of goods manufactured for July is:
A) $153 000
B) $103 000
C) $130 000
D) $133 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Michael’s Manufacturing, Inc. has the following information available for the month of July:
-Raw materials used for July is:
A) $112 000
B) $108 000
C) $120 000
D) $132 000
-Raw materials used for July is:
A) $112 000
B) $108 000
C) $120 000
D) $132 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Nate’s Novelties, Inc. has the following information available for July:
-Cost of goods sold for July is:
A) $106 000
B) $157 000
C) $129 000
D) $109 000
-Cost of goods sold for July is:
A) $106 000
B) $157 000
C) $129 000
D) $109 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The journal entry to record cost of goods manufactured would include a:
A) credit to work-in-process.
B) credit to finished goods.
C) debit to work-in-process.
D) debit to cost of goods sold.
A) credit to work-in-process.
B) credit to finished goods.
C) debit to work-in-process.
D) debit to cost of goods sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Scott Products manufactures high-quality running shoes. The following information is available for 2009:
In addition, 42 400 pairs were produced in 2009 out of which 40 900 pairs were sold for $70 each.
-Cost of goods manufactured for 2009 is:
A) $990 000
B) $973 000
C) $848 000
D) $865 000
In addition, 42 400 pairs were produced in 2009 out of which 40 900 pairs were sold for $70 each.
-Cost of goods manufactured for 2009 is:
A) $990 000
B) $973 000
C) $848 000
D) $865 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Hudson Inc. has the following information available for September:
-Cost of goods sold for September is:
A) $119 000
B) $143 000
C) $140 000
D) $122 000
-Cost of goods sold for September is:
A) $119 000
B) $143 000
C) $140 000
D) $122 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In 2009 Bradshaw Inc.incurred $40 000 of manufacturing overhead costs which will be paid for in 2010.Which of the following would be the correct journal entry to record this transaction?
a.
b.
c.
d.
a.
b.
c.
d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Hudson Inc. has the following information available for September:
-Cost of goods manufactured for September is:
A) $118 000
B) $136 000
C) $115 000
D) $133 000
-Cost of goods manufactured for September is:
A) $118 000
B) $136 000
C) $115 000
D) $133 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Hillsborough Street Manufacturing Inc. incurred the following costs in 2009:
50 000 units were produced during the year out of which 40 000 units were sold for $10 each. There was no beginning or ending raw materials or work-in-process inventory.
-What is the product cost per unit?
A) $3.05
B) $2.75
C) $2.44
D) $2.20
50 000 units were produced during the year out of which 40 000 units were sold for $10 each. There was no beginning or ending raw materials or work-in-process inventory.
-What is the product cost per unit?
A) $3.05
B) $2.75
C) $2.44
D) $2.20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Michael’s Manufacturing, Inc. has the following information available for the month of July:
-Cost of goods manufactured for July is:
A) $188 000
B) $250 000
C) $238 000
D) $213 000
-Cost of goods manufactured for July is:
A) $188 000
B) $250 000
C) $238 000
D) $213 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Hudson Inc. has the following information available for September:
-Total non-manufacturing costs for September are:
A) $113 000
B) $161 000
C) $ 18 000
D) $ 43 000
-Total non-manufacturing costs for September are:
A) $113 000
B) $161 000
C) $ 18 000
D) $ 43 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Nate’s Novelties, Inc. has the following information available for July:
-Raw materials used for July is:
A) $21 000
B) $22 000
C) $25 000
D) $28 000
-Raw materials used for July is:
A) $21 000
B) $22 000
C) $25 000
D) $28 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Identify some of the benefits and risks of a lean production and just-in-time (JIT)environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Chancellor Industries,a manufacturing company,prepays its insurance coverage for a two-year period.The premium for two-year's worth of coverage is $14 400 and is paid at the beginning of the first year.Two-thirds of the premium relates to factory operations and one-third relates to selling and administrative activities.
The amount of premium that should be recorded as a product cost for the first year is:
A) $ 4800
B) $ 2400
C) $ 9600
D) $14 400
The amount of premium that should be recorded as a product cost for the first year is:
A) $ 4800
B) $ 2400
C) $ 9600
D) $14 400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Describe the cost accumulation process in a traditional manufacturing environment versus a just-in-time (JIT)environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Capital Manufacturing produces a unique souvenir product for various museums around the country.During the year,the company incurred the following costs:
During the year,25 000 units were produced out of which 20 000 units were sold for $15 each.
Required:
A. Calculate the total product costs incurred for the year.
B. What is the product cost per unit?
C. What is cost of goods sold for the year?
D. What is net income for the year?
During the year,25 000 units were produced out of which 20 000 units were sold for $15 each.
Required:
A. Calculate the total product costs incurred for the year.
B. What is the product cost per unit?
C. What is cost of goods sold for the year?
D. What is net income for the year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Jones Manufacturing Inc. incurred the following costs in November:
In addition, the following information is also available:
-Net income for November is: (ignore taxes)
A) $371 950
B) $411 950
C) $369 150
D) $382 000
In addition, the following information is also available:
-Net income for November is: (ignore taxes)
A) $371 950
B) $411 950
C) $369 150
D) $382 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Clapton Inc.would like to prepare an income statement for March.Their production department records show that total product costs in March were $225 000 when 50 000 units were produced.Their sales department records show that 46 000 units were sold for $16 each.Monthly administrative and marketing expenses totalled $60 000.What should be net income for March?
A) $529 000
B) $473 800
C) $451 000
D) $469 000
A) $529 000
B) $473 800
C) $451 000
D) $469 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
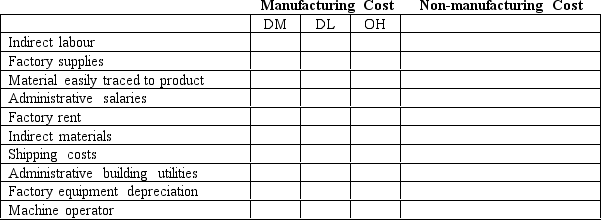
Identify with an 'X' the following costs as either a manufacturing (product)or non-manufacturing (period)cost.If it is a manufacturing cost,further identify it as either direct material (DM),direct labour (DL),or overhead (OH).


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Provide specific examples of why accurate product or service costing information is important for internal purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Johnson Manufacturing has the following selected information available for the year:
In addition,the cost of the finished goods inventory increased by $10 000 from the beginning to the end of the year.Cost of goods sold for the year is:
A) $ 80 000
B) $170 000
C) $ 90 000
D) $110 000
In addition,the cost of the finished goods inventory increased by $10 000 from the beginning to the end of the year.Cost of goods sold for the year is:
A) $ 80 000
B) $170 000
C) $ 90 000
D) $110 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Briefly describe the difference between a manufacturing and a non-manufacturing cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Jones Manufacturing Inc. incurred the following costs in November:
In addition, the following information is also available:
-Cost of goods manufactured in November is:
A) $ 91 000
B) $115 000
C) $155 000
D) $143 000
In addition, the following information is also available:
-Cost of goods manufactured in November is:
A) $ 91 000
B) $115 000
C) $155 000
D) $143 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Identify at least two characteristics of a lean production and just-in-time (JIT)manufacturing environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Franklin Street Manufacturing has the following cost information available for 2009:
20 000 units were produced during the year out of which 19 000 units were sold for $10 each.
-What is cost of goods sold for 2009?
A) $55 000
B) $52 250
C) $61 750
D) $65 000
20 000 units were produced during the year out of which 19 000 units were sold for $10 each.
-What is cost of goods sold for 2009?
A) $55 000
B) $52 250
C) $61 750
D) $65 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Brenda's Bakery has the following information available for October:
How much raw material was purchased in October?
A) $23 000
B) $25 000
C) $26 000
D) $28 000
How much raw material was purchased in October?
A) $23 000
B) $25 000
C) $26 000
D) $28 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Classify each of the following as either a direct material (DM),indirect material (IM),or period cost (P).
a.
Wood used to build custom bookshelves
b.
Sandpaper,glue,and nails used to build customer bookshelves
c.
Paper supplies used in the administrative offices
d.
Computer chips used in computer
e.
Cleaning supplies used in the factory
a.
Wood used to build custom bookshelves
b.
Sandpaper,glue,and nails used to build customer bookshelves
c.
Paper supplies used in the administrative offices
d.
Computer chips used in computer
e.
Cleaning supplies used in the factory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Briefly compare a traditional manufacturing environment with a lean production and just-in-time (JIT)manufacturing environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following statements is true regarding period costs?
A) They 'attach' themselves to the product.
B) They will appear on the balance sheet until the product is sold.
C) They will appear on the income statement in the year they are incurred.
D) They will not impact gross margin or net income.
A) They 'attach' themselves to the product.
B) They will appear on the balance sheet until the product is sold.
C) They will appear on the income statement in the year they are incurred.
D) They will not impact gross margin or net income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Jones Manufacturing Inc. incurred the following costs in November:
In addition, the following information is also available:
-The product cost per unit in November is:
A) $4.55
B) $7.75
C) $5.75
D) $5.37
In addition, the following information is also available:
-The product cost per unit in November is:
A) $4.55
B) $7.75
C) $5.75
D) $5.37

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Franklin Street Manufacturing has the following cost information available for 2009:
20 000 units were produced during the year out of which 19 000 units were sold for $10 each.
-What is net income for 2009?
A) $127 750
B) $137 750
C) $125 000
D) $128 250
20 000 units were produced during the year out of which 19 000 units were sold for $10 each.
-What is net income for 2009?
A) $127 750
B) $137 750
C) $125 000
D) $128 250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Hudson Inc. has the following information available for September:
-In a traditional manufacturing environment,as the cost of goods sold account increases,which account is most likely decreasing?
A) Work-in-process inventory
B) Finished goods inventory
C) Raw materials inventory
D) Cash
-In a traditional manufacturing environment,as the cost of goods sold account increases,which account is most likely decreasing?
A) Work-in-process inventory
B) Finished goods inventory
C) Raw materials inventory
D) Cash

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



