Deck 4: Marine Sediments
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
tektites
tektites
tektites
tektites
halite
halite
halite
halite
coccolithophores
coccolithophores
coccolithophores
coccolithophores
abyssal clay
abyssal clay
abyssal clay
abyssal clay
Responses:
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Marine Sediments
1
Texture refers to the size and shape of sediment particles.
True
2
A well-sorted sand deposit with rounded particles might be called immature.
False
3
Which of the following contains calcium carbonate (CaCO3)?
A)diatoms
B)foraminiferans
C)glauconite
D)phosphorites
E)radiolarians
A)diatoms
B)foraminiferans
C)glauconite
D)phosphorites
E)radiolarians
B
4
Organisms that live on the ocean floor may be responsible for keeping manganese nodules from being buried in the sediment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Sediments derived from weathered rock and volcanic activity are called biogenous sediments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Sediments which are poorly sorted and made of a variety of minerals could have been deposited by:
A)a glacier.
B)a river delta.
C)turbidity currents.
D)a volcanic eruption.
E)the wind.
A)a glacier.
B)a river delta.
C)turbidity currents.
D)a volcanic eruption.
E)the wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A glacial deposit is well-sorted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following contains silica (SiO2)?
A)coccolithophores
B)corals
C)foraminiferans
D)phosphorites
E)radiolarians
A)coccolithophores
B)corals
C)foraminiferans
D)phosphorites
E)radiolarians

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The deposition of radiolarian oozes is affected by the carbonate compensation depth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The Wentworth scale is used to arrange the amount of sorting in a sediment deposit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
High energy environments are most likely to contain which one of the following?
A)clay-sized particles
B)cosmogenous sediments
C)large particles such as gravel
D)manganese nodules
E)silt-sized particles
A)clay-sized particles
B)cosmogenous sediments
C)large particles such as gravel
D)manganese nodules
E)silt-sized particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not an important control on oceanic sediment accumulation?
A)degree of preservation
B)dilution
C)input from other sediment types
D)rate of deposition
E)All of the above factors are important.
A)degree of preservation
B)dilution
C)input from other sediment types
D)rate of deposition
E)All of the above factors are important.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The major force bringing continental sediments to the open ocean is (are):
A)glaciers.
B)neritic currents.
C)rivers.
D)turbidity currents.
E)wind.
A)glaciers.
B)neritic currents.
C)rivers.
D)turbidity currents.
E)wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Calcareous shells will not accumulate on the ocean floor when the water depth exceeds about 4500 meters (around 15,000 feet).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Beach sand is usually well-sorted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The organisms in this photograph would most likely produce oceanic sediments that are:

A)calcareous.
B)cosmogenous.
C)lithogenous.
D)neritic.
E)siliceous.

A)calcareous.
B)cosmogenous.
C)lithogenous.
D)neritic.
E)siliceous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Radiolarian oozes form near the equator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Phosphate nodules are found on the continental shelf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Refer to the figure below illustrating the world-wide distribution of marine sediments.Different areas of ocean sediments are indicated by different numbers.Use these numbers to answer the questions below.
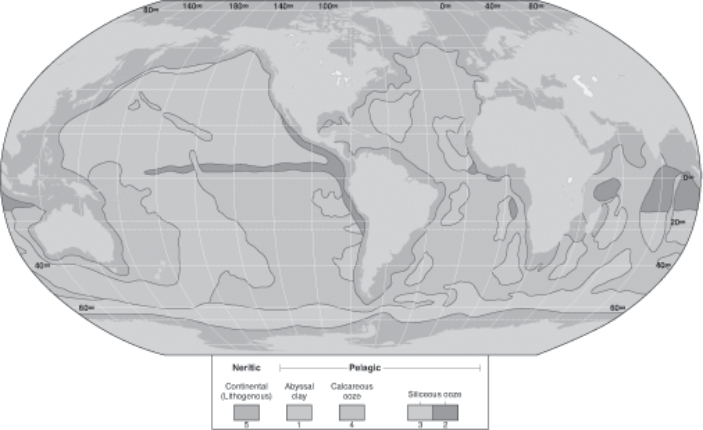
The sediments that are produced in areas of high primary productivity are indicated by the number(s):
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)2 & 3.
E)3 & 4.

The sediments that are produced in areas of high primary productivity are indicated by the number(s):
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)2 & 3.
E)3 & 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Sediments produced as a result of chemical reactions in seawater are called:
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcagenic.
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcagenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Sediments found on continental margins are called:
A)continental.
B)estuarine.
C)neritic.
D)oceanic.
E)pelagic.
A)continental.
B)estuarine.
C)neritic.
D)oceanic.
E)pelagic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In general,polar neritic sediment has more:
A)clay than in temperate waters.
B)coral debris than in tropical waters.
C)rock and gravel than in tropical waters.
D)shell fragments than in temperate waters.
E)silt and sand than in tropical waters.
A)clay than in temperate waters.
B)coral debris than in tropical waters.
C)rock and gravel than in tropical waters.
D)shell fragments than in temperate waters.
E)silt and sand than in tropical waters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In contrast to manganese nodules which form on the abyssal plain,phosphate-rich nodules form in:
A)continental shelf waters..
B)estuaries.
C)hydrothermal vent areas.
D)intermediate to shallow depth water.
E)mid-ocean ridges.
A)continental shelf waters..
B)estuaries.
C)hydrothermal vent areas.
D)intermediate to shallow depth water.
E)mid-ocean ridges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The most likely place to find abundant manganese nodules is on the:
A)abyssal plain far from a continent.
B)continental rise.
C)continental shelf.
D)crest of a mid-ocean ridge.
E)All of the above locations are contain manganese nodules.
A)abyssal plain far from a continent.
B)continental rise.
C)continental shelf.
D)crest of a mid-ocean ridge.
E)All of the above locations are contain manganese nodules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Sediments derived form preexisting rocks are called:
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcagenic.
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcagenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Calcium carbonate is most likely to dissolve in water with which characteristics?
A)low carbon dioxide and warm temperatures
B)lots of carbon dioxide and cold temperatures
C)lots of carbon dioxide and warm temperatures
D)low pressure and warm temperatures
E)low pressure and cold temperatures
A)low carbon dioxide and warm temperatures
B)lots of carbon dioxide and cold temperatures
C)lots of carbon dioxide and warm temperatures
D)low pressure and warm temperatures
E)low pressure and cold temperatures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Sediments produced by plants and animals in the sea called:
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)terriginous.
E)volcagenic.
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)terriginous.
E)volcagenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the figure below illustrating the world-wide distribution of marine sediments.Different areas of ocean sediments are indicated by different numbers.Use these numbers to answer the questions below.

Biogenous sediments are indicated by the number(s):
A)1.
B)2 & 3.
C)2 & 4.
D)2,3,& 4.
E)2,3,4,& 5.

Biogenous sediments are indicated by the number(s):
A)1.
B)2 & 3.
C)2 & 4.
D)2,3,& 4.
E)2,3,4,& 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A pelagic clay contains lots of material that settle to the seafloor through the water column and are:
A)less than 30% biogenous material.
B)more than 30% biogenous material.
C)more than 30% hydrogenous material.
D)less than 30% neritic material.
E)more than 30% neritic material.
A)less than 30% biogenous material.
B)more than 30% biogenous material.
C)more than 30% hydrogenous material.
D)less than 30% neritic material.
E)more than 30% neritic material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The element found in some sediments which suggest that a meteorite or asteroid impact occurred nearby is:
A)iridium.
B)manganese.
C)strontium.
D)uranium.
E)yttrium.
A)iridium.
B)manganese.
C)strontium.
D)uranium.
E)yttrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
All of the following are hydrogenous sediments except:
A)evaporites.
B)halites.
C)manganese nodule.
D)phosphates.
E)stromatolites.
A)evaporites.
B)halites.
C)manganese nodule.
D)phosphates.
E)stromatolites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
All of the following are lithogenous sediments except:
A)beach sand.
B)diatom ooze.
C)glacial deposits.
D)illite clays.
E)volcanogenic particles.
A)beach sand.
B)diatom ooze.
C)glacial deposits.
D)illite clays.
E)volcanogenic particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Manganese nodules are an example of a:
A)biogenous sediments.
B)cosmogenous sediments.
C)hydrogenous sediments.
D)terrigenous sediments.
E)volcagenic sediments.
A)biogenous sediments.
B)cosmogenous sediments.
C)hydrogenous sediments.
D)terrigenous sediments.
E)volcagenic sediments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Sediments with an extraterrestrial origin are called:
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcagenic.
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcagenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the figure below illustrating the world-wide distribution of marine sediments.Different areas of ocean sediments are indicated by different numbers.Use these numbers to answer the questions below.

Sediments that are derived primarily from the weathering on continental material are indicated by the number(s):
A)1.
B)2.
C)2 & 3.
D)3 &4.
E)1 & 5.

Sediments that are derived primarily from the weathering on continental material are indicated by the number(s):
A)1.
B)2.
C)2 & 3.
D)3 &4.
E)1 & 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the figure below illustrating the world-wide distribution of marine sediments.Different areas of ocean sediments are indicated by different numbers.Use these numbers to answer the questions below.

Calcareous oozes are represented by the number(s);
A)1.
B)2 .
C)4.
D)2 & 3.
E)3 & 4.

Calcareous oozes are represented by the number(s);
A)1.
B)2 .
C)4.
D)2 & 3.
E)3 & 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A very important way to increase the settling rate of fine particles in the open ocean is via:
A)carbonate dissolution.
B)deposit feeders.
C)fecal pellets.
D)precipitation.
E)wind.
A)carbonate dissolution.
B)deposit feeders.
C)fecal pellets.
D)precipitation.
E)wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Match between columns
Premises:
tektites
tektites
tektites
tektites
halite
halite
halite
halite
coccolithophores
coccolithophores
coccolithophores
coccolithophores
abyssal clay
abyssal clay
abyssal clay
abyssal clay
Responses:
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment
terrigenous sediment
biogenous sediment
hydrogenous sediment
cosmogenous sediment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



