Deck 18: Electrochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/212
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Electrochemistry
1
What is the reduction half reaction for the following chemical reaction in a basic solution? ClO-(aq)+ Cr(OH)4-(aq)→ CrO42-(aq)+ Cl-(aq)
A)ClO-(aq)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2e- → Cl-(aq)+ H2O(l)
B)ClO-(aq)+ H2O(l)+ 2e- → Cl-(aq)+ 2 OH-(aq)
C)Cr(OH)4-(aq)+ 4 OH-(aq)→ CrO42-(aq)+ 4 H2O(l)+ 3e-
D)Cr(OH)4-(aq)→ CrO42-(aq)+ 4 H+(aq)+ 3e-
A)ClO-(aq)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2e- → Cl-(aq)+ H2O(l)
B)ClO-(aq)+ H2O(l)+ 2e- → Cl-(aq)+ 2 OH-(aq)
C)Cr(OH)4-(aq)+ 4 OH-(aq)→ CrO42-(aq)+ 4 H2O(l)+ 3e-
D)Cr(OH)4-(aq)→ CrO42-(aq)+ 4 H+(aq)+ 3e-
ClO-(aq)+ H2O(l)+ 2e- → Cl-(aq)+ 2 OH-(aq)
2
Determine the number of water molecules necessary to balance the reduction half reaction of 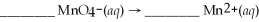 that occurs in an acidic solution.
that occurs in an acidic solution.
A)2
B)4
C)5
D)7
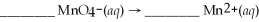 that occurs in an acidic solution.
that occurs in an acidic solution.A)2
B)4
C)5
D)7
4
3
What species is oxidized in the reaction: CuSO4(aq)+ Mg(s)→ MgSO4(aq)+ Cu(s)?
A)CuSO4 (aq)
B)Mg (s)
C)MgSO4 (aq)
D)Cu (s)
A)CuSO4 (aq)
B)Mg (s)
C)MgSO4 (aq)
D)Cu (s)
Mg (s)
4
For a galvanic cell,the cathode has a ________ sign and is the site of ________.
A)negative,oxidation
B)negative,reduction
C)positive,oxidation
D)positive,reduction
A)negative,oxidation
B)negative,reduction
C)positive,oxidation
D)positive,reduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Determine the number of water molecules necessary to balance the following chemical equation. Cr2O72-(aq)+ Cl-(aq)+ H+(aq)→ Cr3+(aq)+ Cl2(g)+ ________ H2O(l)
A)3
B)5
C)7
D)14
A)3
B)5
C)7
D)14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the molarity of a potassium triiodide solution,KI3(aq),if 30.00 mL of the solution is required to completely react with 25.00 mL of a 0.200 M thiosulfate solution,Na2S2O3(aq)? The chemical equation for the reaction is: 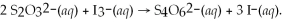
A)0.0833 M
B)0.120 M
C)0.167 M
D)0.333 M
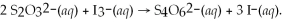
A)0.0833 M
B)0.120 M
C)0.167 M
D)0.333 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What are the coefficients in front of NO3-(aq)and Cu(s)when the following redox equation is balanced in an acidic solution: ________ NO3-(aq)+ ________ Cu(s)→ ________ NO(g)+ ________ Cu2+(aq)?
A)2,3
B)2,6
C)3,4
D)3,6
A)2,3
B)2,6
C)3,4
D)3,6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Based on the balanced chemical equation shown below,determine the mass percent of Fe3+ in a 0.6450 gram sample of iron ore,if 22.40 mL of a 0.1000 M stannous chloride,SnCl2(aq),solution is required to completely react with the Fe3+ present in the ore sample.The chemical equation for the reaction is: 2 Fe3+(aq)+ Sn2+(aq)→ 2 Fe2+(aq)+ Sn4+(aq).
A)6.196%
B)9.697%
C)19.40%
D)38.79%
A)6.196%
B)9.697%
C)19.40%
D)38.79%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Based on the balanced chemical equation shown below,determine the molarity of a solution containing Fe2+(aq),if 40.00 mL of the Fe2+(aq)solution is required to completely react with 30.00 mL of a 0.125 M potassium bromate,KBrO3(aq),solution.The chemical equation for the reaction is: 6 Fe2+(aq)+ BrO3-(aq)+ 6 H+(aq)→ 6 Fe3+(aq)+ Br-(aq)+ 3 H2O(l).
A)0.0156 M
B)0.0938 M
C)0.562 M
D)1.00 M
A)0.0156 M
B)0.0938 M
C)0.562 M
D)1.00 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In a galvanic cell,the half-reaction H2(g)+ 2 OH-(aq)→ 2 H2O(l)+ 2 e- is
A)an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the anode.
B)an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the cathode.
C)a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the anode.
D)a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the cathode.
A)an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the anode.
B)an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the cathode.
C)a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the anode.
D)a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
According to the balanced equation shown below,1.00 mole of oxalic acid,H2C2O4,reacts with ________ moles of permanganate ion,MnO4-. 5 H2C2O4(aq)+ 2 MnO4-(aq)+ 6 H+(aq)→ 10 CO2(g)+ 2 Mn2+(aq)+ 8 H2O(l)
A)0.400
B)1.00
C)2.00
D)2.25
A)0.400
B)1.00
C)2.00
D)2.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
During an electrochemical reaction,electrons move through the external circuit toward the ________ and positive ions in the cell move toward the ________.
A)anode,anode
B)anode,cathode
C)cathode,anode
D)cathode,cathode
A)anode,anode
B)anode,cathode
C)cathode,anode
D)cathode,cathode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following terms can be used to describe an electrochemical cell in which a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current? I.an electrolytic cell
II.a galvanic cell
III.a voltaic cell
A)only I
B)only II
C)only III
D)II and III
II.a galvanic cell
III.a voltaic cell
A)only I
B)only II
C)only III
D)II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the oxidation half reaction in the following chemical reaction? Cr2O72-(aq)+ 6 Cl-(aq)+ 14 H+(aq)→ 2 Cr3+(aq)+ 3 Cl2(aq)+ 7 H2O(l)
A)Cr2O72-(aq)+ 14 H+(aq)+ 6e- → 2 Cr3+(aq)+ 7 H2O(l)
B)Cr2O72-(aq)+ 14 H+(aq)→ 2 Cr3+(aq)+ 7 H2O(l)+ 6e-
C)2 Cl-(aq)→ Cl2(aq)+ 2e-
D)Cl2(aq)+ 2e- → 2 Cl-(aq)
A)Cr2O72-(aq)+ 14 H+(aq)+ 6e- → 2 Cr3+(aq)+ 7 H2O(l)
B)Cr2O72-(aq)+ 14 H+(aq)→ 2 Cr3+(aq)+ 7 H2O(l)+ 6e-
C)2 Cl-(aq)→ Cl2(aq)+ 2e-
D)Cl2(aq)+ 2e- → 2 Cl-(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is true when the following equation is balanced in basic solution? P(s)+ PO43-(aq)→ HPO32-(aq)
A)H+ appears on the left side of the equation.
B)H+ appears on the right side of the equation.
C)OH- appears on the left side of the equation.
D)OH- appears on the right side of the equation.
A)H+ appears on the left side of the equation.
B)H+ appears on the right side of the equation.
C)OH- appears on the left side of the equation.
D)OH- appears on the right side of the equation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In a galvanic cell,the half-reaction MnO4-(aq)+ 8 H+(aq)+ 5 e- → Mn2+(aq)+ 4 H2O(l)is
A)an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the anode.
B)an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the cathode.
C)a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the anode.
D)a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the cathode.
A)an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the anode.
B)an oxidation half-reaction and occurs at the cathode.
C)a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the anode.
D)a reduction half-reaction and occurs at the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Based on the balanced chemical equation shown below,what volume of 0.250 M K2S2O3(aq) is needed to completely react with 12.44 mL of 0.125 M KI3(aq)? 2 S2O32-(aq)+ I3-(aq)→ S4O62-(aq)+ 3 I-(aq)
A)3.11 mL
B)6.22 mL
C)12.4 mL
D)49.8 mL
A)3.11 mL
B)6.22 mL
C)12.4 mL
D)49.8 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Determine the number of water molecules necessary to balance the reduction half reaction of 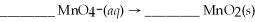 that occurs in a basic solution.
that occurs in a basic solution.
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)5
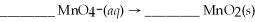 that occurs in a basic solution.
that occurs in a basic solution.A)2
B)3
C)4
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to the balanced chemical equation 5 H2C2O4(aq)+ 2 MnO4-(aq)+ 6 H+(aq)→ 10 CO2(g)+ 2 Mn2+(aq)+ 8 H2O(l)
0.3500 grams of oxalic acid,H2C2O4 will react with ________ mL of 0.100 M potassium permanganate,KMnO4 solution.
A)15.5 mL
B)38.9 mL
C)77.7 mL
D)97.2 mL
0.3500 grams of oxalic acid,H2C2O4 will react with ________ mL of 0.100 M potassium permanganate,KMnO4 solution.
A)15.5 mL
B)38.9 mL
C)77.7 mL
D)97.2 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which cell involves a nonspontaneous redox reaction?
A)concentration cell
B)electrolytic cell
C)fuel cell
D)galvanic cell
A)concentration cell
B)electrolytic cell
C)fuel cell
D)galvanic cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the balanced chemical equation for the galvanic cell reaction expressed using shorthand notation below? Al(s)∣ Al3+(aq)∣∣ Ni2+(aq)∣ Ni(s)
A)2 Al(s)+ 3 Ni2+(aq)→ 2 Al3+(aq)+ 3 Ni(s)
B)3 Al(s)+ 2 Ni2+(aq)→ 3 Al3+(aq)+ 2 Ni(s)
C)2 Ni(s)+ 3 Al3+(aq)→ 2 Ni2+(aq)+ 3 Al(s)
D)3 Ni(s)+ 2 Al3+(aq)→ 3 Ni2+(aq)+ 2 Al(s)
A)2 Al(s)+ 3 Ni2+(aq)→ 2 Al3+(aq)+ 3 Ni(s)
B)3 Al(s)+ 2 Ni2+(aq)→ 3 Al3+(aq)+ 2 Ni(s)
C)2 Ni(s)+ 3 Al3+(aq)→ 2 Ni2+(aq)+ 3 Al(s)
D)3 Ni(s)+ 2 Al3+(aq)→ 3 Ni2+(aq)+ 2 Al(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The nickel-cadmium battery cell has a standard potential of +1.20 V.The cell reaction is 2 NiO(OH)(s)+ Cd(s)+ 2 H2O(l)→ 2 Ni(OH)2(s)+ Cd(OH)2(s).
What is the standard free energy change for this reaction?
A)-38.7 kJ
B)-116 kJ
C)-232 kJ
D)-463 kJ
What is the standard free energy change for this reaction?
A)-38.7 kJ
B)-116 kJ
C)-232 kJ
D)-463 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
For the hypothetical reaction A + Bx → Ax + B,E° = 1.19 V = and ΔG° = -115 kJ.For this reaction the value of x = .
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which is not true for standard electrode potentials?
A)Cell constituents are in their standard states.
B)E° for oxidation is the negative of E° for reduction.
C)The half-reactions are written as reductions.
D)The potential for the standard hydrogen electrode is chosen to be +1.00 V.
A)Cell constituents are in their standard states.
B)E° for oxidation is the negative of E° for reduction.
C)The half-reactions are written as reductions.
D)The potential for the standard hydrogen electrode is chosen to be +1.00 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the shorthand notation that represents the following galvanic cell reaction? 2 Fe2+(aq)+ Cl2(g)→ 2 Fe3+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq)
A)Fe2+(aq)∣ Fe3+(aq)∣∣ Cl2(g)∣ Cl-(aq)
B)Fe(s)∣ Fe2+(aq)∣∣ Fe3+(aq)Cl2(g)∣ Cl-(aq)∣ C(s)
C)Pt(s)∣ Fe3+(aq),Fe2+(aq),Cl2(g)∣∣ Cl-(aq)∣ C(s)
D)Pt(s)∣ Fe2+(aq),Fe3+(aq)∣∣ Cl2(g)∣ Cl-(aq)∣ C(s)
A)Fe2+(aq)∣ Fe3+(aq)∣∣ Cl2(g)∣ Cl-(aq)
B)Fe(s)∣ Fe2+(aq)∣∣ Fe3+(aq)Cl2(g)∣ Cl-(aq)∣ C(s)
C)Pt(s)∣ Fe3+(aq),Fe2+(aq),Cl2(g)∣∣ Cl-(aq)∣ C(s)
D)Pt(s)∣ Fe2+(aq),Fe3+(aq)∣∣ Cl2(g)∣ Cl-(aq)∣ C(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the shorthand notation that represents the following galvanic cell reaction? Fe(s)+ Cu(NO3)2(aq)→ Fe(NO3)2(aq)+ Cu(s)
A)Fe(s)∣ Fe2+(aq)∣∣ Cu2+(aq)∣ Cu(s)
B)Cu(s)∣ Cu2+(aq)∣∣ Fe2+(aq)∣ Fe(s)
C)Fe(s)∣ NO3-(aq)∣∣ NO3-(aq)∣ Cu(s)
D)Cu(s)∣ Cu(NO3)2(aq)∣∣ Fe(NO3)2(aq)∣ Fe(s)
A)Fe(s)∣ Fe2+(aq)∣∣ Cu2+(aq)∣ Cu(s)
B)Cu(s)∣ Cu2+(aq)∣∣ Fe2+(aq)∣ Fe(s)
C)Fe(s)∣ NO3-(aq)∣∣ NO3-(aq)∣ Cu(s)
D)Cu(s)∣ Cu(NO3)2(aq)∣∣ Fe(NO3)2(aq)∣ Fe(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The cell reaction for a dry cell battery is Zn(s)+ 2 MnO2(s)+ 2 NH4+(aq)→ 2 NH3(aq)+ Mn2O3(s)+ Zn2+(aq)+ H2O(l).
The standard cell potential for this cell is 1.56 V.What is the standard free energy change for this cell?
A)+151 kJ
B)-151 kJ
C)-301 kJ
D)-602 kJ
The standard cell potential for this cell is 1.56 V.What is the standard free energy change for this cell?
A)+151 kJ
B)-151 kJ
C)-301 kJ
D)-602 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The shorthand notation for the galvanic cell reaction Fe3+(aq)+ 2 I-(aq)→ Fe2+(aq)+ I2(s)requires an inert electrode on
A)both sides of the salt bridge.
B)neither side of the salt bridge.
C)only on the left side of the salt bridge.
D)only on the right side of the salt bridge.
A)both sides of the salt bridge.
B)neither side of the salt bridge.
C)only on the left side of the salt bridge.
D)only on the right side of the salt bridge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Write the overall cell reaction for the galvanic cell given below. Pt(s)∣ H2(g)∣ H+(aq)∣∣ Cl2(g)∣ Cl-(aq)∣ Pt(s)
A)Pt(s)+ H2(g)+ Cl-(aq)→ Pt(s)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 Cl2(g)
B)2 H+(aq)+ 2 Cl2(g)→ 2 HCl(aq)
C)H2(g)+ Cl2(g)→ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq)
D)No reaction would occur because there is no salt bridge.
A)Pt(s)+ H2(g)+ Cl-(aq)→ Pt(s)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 Cl2(g)
B)2 H+(aq)+ 2 Cl2(g)→ 2 HCl(aq)
C)H2(g)+ Cl2(g)→ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq)
D)No reaction would occur because there is no salt bridge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the reduction half-reaction for the following overall cell reaction? Ni2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)→ Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)
A)Ag(s)+ e- → Ag+(aq)
B)Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)
C)Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Ni(s)
D)Ni2+(aq)+ e- → Ni(s)
A)Ag(s)+ e- → Ag+(aq)
B)Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)
C)Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Ni(s)
D)Ni2+(aq)+ e- → Ni(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the balanced equation for the galvanic cell reaction expressed using shorthand notation below? Mg(s)∣ Mg2+(aq)∣∣ Cl2(g)∣ Cl-(aq)∣ C(s)
A)Mg(s)+ 2 Cl-(aq)→ Mg2+(aq)+ Cl2(g)
B)Mg(s)+ Cl2(g)→ Mg2+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq)
C)Mg2+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq)→ Mg(s)+ Cl2(g)
D)Mg2+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq)→ MgCl2(s)
A)Mg(s)+ 2 Cl-(aq)→ Mg2+(aq)+ Cl2(g)
B)Mg(s)+ Cl2(g)→ Mg2+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq)
C)Mg2+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq)→ Mg(s)+ Cl2(g)
D)Mg2+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq)→ MgCl2(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
For the reaction 2 Al(s)+ 3 Co2+(aq)→ 2 Al3+(aq)+ 3 Co(s),ΔG° is -799 kJ.What is E° for a standard cell based on this reaction?
A)+1.38 V
B)+2.76 V
C)+4.14 V
D)+8.28 V
A)+1.38 V
B)+2.76 V
C)+4.14 V
D)+8.28 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the shorthand notation for a galvanic cell that represents the following galvanic cell reaction? Br2(l)+ 2 I-(aq)→ 2 Br-(aq)+ I2(s)
A)I-(aq)|I2(s)∣∣Br2(l)|Br-(aq)
B)I-(aq)|I2(s)∣∣Br2(l)|Br-(aq)|Pt(s)
C)Pt(s)|I-(aq)|I2(s)∣∣Br2(l)|Br-(aq)
D)Pt(s)|I-(aq)|I2(s)∣∣Br2(l)|Br-(aq)}Pt(s)
A)I-(aq)|I2(s)∣∣Br2(l)|Br-(aq)
B)I-(aq)|I2(s)∣∣Br2(l)|Br-(aq)|Pt(s)
C)Pt(s)|I-(aq)|I2(s)∣∣Br2(l)|Br-(aq)
D)Pt(s)|I-(aq)|I2(s)∣∣Br2(l)|Br-(aq)}Pt(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
For the galvanic cell reaction,expressed below using shorthand notation,what half-reaction occurs at the cathode? Zn(s)∣ Zn2+(aq)∣∣ Ni2+(aq)∣ Ni(s)
A)Zn(s)→ Zn2+(aq)+ 2 e-
B)Zn2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Zn(s)
C)Ni(s)→ Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e-
D)Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Ni(s)
A)Zn(s)→ Zn2+(aq)+ 2 e-
B)Zn2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Zn(s)
C)Ni(s)→ Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e-
D)Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Ni(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The iron content of foods can be determined by dissolving them in acid (forming Fe3+),reducing the iron(III)to iron(II),and titrating with cerium(IV): Fe2+(aq)+ Ce4+(aq)→ Fe3+(aq)+ Ce3+(aq).
Identify the two half-reactions in the above reaction.
A)oxidation half-reaction reduction half-reaction
Fe2+(aq)+ e-→ Fe3+(aq)Ce4+(aq)→ Ce3+(aq)+ e-
B)oxidation half-reaction reduction half-reaction
Fe2+(aq)→ Fe3+(aq)+ e- Ce4+(aq)+ e- → Ce3+(aq)
C)oxidation half-reaction reduction half-reaction
Ce4+(aq)+ e- → Ce3+(aq)Fe2+(aq)→ Fe3+(aq)+ e-
D)oxidation half-reaction reduction half-reaction
Ce4+(aq)→ Ce3+(aq)+ e- Fe2+(aq)+ e- → Fe3+(aq)
Identify the two half-reactions in the above reaction.
A)oxidation half-reaction reduction half-reaction
Fe2+(aq)+ e-→ Fe3+(aq)Ce4+(aq)→ Ce3+(aq)+ e-
B)oxidation half-reaction reduction half-reaction
Fe2+(aq)→ Fe3+(aq)+ e- Ce4+(aq)+ e- → Ce3+(aq)
C)oxidation half-reaction reduction half-reaction
Ce4+(aq)+ e- → Ce3+(aq)Fe2+(aq)→ Fe3+(aq)+ e-
D)oxidation half-reaction reduction half-reaction
Ce4+(aq)→ Ce3+(aq)+ e- Fe2+(aq)+ e- → Fe3+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Doubling all the coefficients in the equation for the cell reaction
A)doubles both E° and ΔG°.
B)doubles E°,but does not change ΔG°.
C)doubles ΔG°,but does not change E°.
D)does not change E° or ΔG°.
A)doubles both E° and ΔG°.
B)doubles E°,but does not change ΔG°.
C)doubles ΔG°,but does not change E°.
D)does not change E° or ΔG°.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For a galvanic cell that uses the following two half-reactions, Cr2O72-(aq)+ 14 H+(aq)+ 6 e- → 2 Cr3+(aq)+ 7 H2O(l)
Pb(s)→ Pb2+(aq)+ 2 e-
How many moles of Pb(s)are oxidized by one mole of Cr2O72-?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)6
Pb(s)→ Pb2+(aq)+ 2 e-
How many moles of Pb(s)are oxidized by one mole of Cr2O72-?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In a galvanic cell constructed from Pb(s)| Pb+2(aq)|| Hg+1 | Hg(s),which of the electrodes will gain mass?
A)the anode,Pb (s)
B)the cathode,Pb (s)
C)the anode,Hg (s)
D)the cathode,Hg (s)
A)the anode,Pb (s)
B)the cathode,Pb (s)
C)the anode,Hg (s)
D)the cathode,Hg (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the relation between joules (J),volts (V),and coulombs (C)?
A)1 J = 1 V × 1 C
B)1 J = 1 V ÷ 1 C
C)1 J = 1 C ÷ 1 V
D)1 J = 1 V × 1 C2
A)1 J = 1 V × 1 C
B)1 J = 1 V ÷ 1 C
C)1 J = 1 C ÷ 1 V
D)1 J = 1 V × 1 C2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
For the hypothetical reaction A + 2 Bx → Ay + 2 B,E° = 1.50 V = and ΔG° = -305 kJ.For this reaction,if the value of x is 4,then the value of y = .
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider the galvanic cell,Pt(s)∣ H2(1 atm)|H+(1 M)∣∣ Cl-(1 M)∣ Hg2Cl2(s)|Hg(l).Which one of the following changes to the cell would cause the cell potential to increase (i.e. ,become more positive)?
A)decrease the mass of Pt
B)increase the mass of Pt
C)decrease the pH
D)increase the pH
A)decrease the mass of Pt
B)increase the mass of Pt
C)decrease the pH
D)increase the pH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
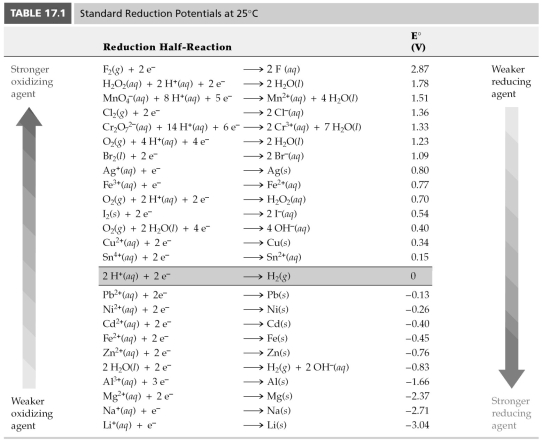
Using Table 17.1,find E° for 2 H2O(l)→ 2 H2(g)+ O2(g).
A)-2.06 V
B)-1.23 V
C)-0.80 V
D)-0.40 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Calculate the cell potential E at 25°C for the reaction 2 Al(s)+ 3 Fe2+(aq)→ 2 Al3+(aq)+ 3 Fe(s)
Given that [Fe2+] = 0.020 M,[Al3+] = 0.10 M,and the standard reduction potential is -1.66 V for Al3+/Al and -0.45 V for Fe2+/Fe.
A)+1.03 V
B)+1.17 V
C)+1.18 V
D)+1.20 V
Given that [Fe2+] = 0.020 M,[Al3+] = 0.10 M,and the standard reduction potential is -1.66 V for Al3+/Al and -0.45 V for Fe2+/Fe.
A)+1.03 V
B)+1.17 V
C)+1.18 V
D)+1.20 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the Al3+:Ag+concentration ratio in the cell Al(s)|Al3+(aq)∣∣ Ag+(aq)|Ag(s)if the measured cell potential is 2.34 V?
A)0.0094:1
B)0.21:1
C)4.7:1
D)110:1
A)0.0094:1
B)0.21:1
C)4.7:1
D)110:1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Given: Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)E° = +0.799 V AgI(s)+ e- → Ag(s)+ I-(aq)E° = -0.152 V
Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Ni(s)E° = -0.267 V
Which of the following reactions should be spontaneous under standard conditions?
I.2 AgI(s)+ Ni(s)→ 2 Ag(s)+ 2 I-(aq)+ Ni2+(aq)
II.Ag+(aq)+ I-(aq)→ AgI(s)
A)I and II are both nonspontaneous.
B)I is nonspontaneous and II is spontaneous.
C)I is spontaneous and II is nonspontaneous.
D)I and II are both spontaneous.
Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Ni(s)E° = -0.267 V
Which of the following reactions should be spontaneous under standard conditions?
I.2 AgI(s)+ Ni(s)→ 2 Ag(s)+ 2 I-(aq)+ Ni2+(aq)
II.Ag+(aq)+ I-(aq)→ AgI(s)
A)I and II are both nonspontaneous.
B)I is nonspontaneous and II is spontaneous.
C)I is spontaneous and II is nonspontaneous.
D)I and II are both spontaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Based on the half-reactions and their respective standard reduction potentials below,which addition to an aqueous solution containing Fe(NO3)2 will result in a reaction under standard-state conditions? O2(g)+ 4 H+ +4 e- → 2 H2O(l)1.23 V
Fe3+(aq)+ e- → Fe2+(aq)0.77 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Cu(s)0.34 V
2 H+(aq)+ 2 e- → H2(g)0.00 V
Ni2+(aq)+ + 2 e- → Ni(s)-0.26 V
Fe2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Fe(s)-0.45 V
A)aqueous copper(II)acetate
B)nickel wire
C)hydrogen gas
D)oxygen gas
Fe3+(aq)+ e- → Fe2+(aq)0.77 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Cu(s)0.34 V
2 H+(aq)+ 2 e- → H2(g)0.00 V
Ni2+(aq)+ + 2 e- → Ni(s)-0.26 V
Fe2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Fe(s)-0.45 V
A)aqueous copper(II)acetate
B)nickel wire
C)hydrogen gas
D)oxygen gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Based on the half-reactions and their respective standard reduction potentials below,what is the standard cell potential for the reaction that is expected to occur? Fe3+(aq)+ e- → Fe2+(aq)0.77 V
Sn4+(aq)+ 2 e- → Sn2+(aq)0.15 V
Pb2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Pb(s)-0.13 V
A)0.28 V
B)0.64 V
C)0.90 V
D)1.03 V
Sn4+(aq)+ 2 e- → Sn2+(aq)0.15 V
Pb2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Pb(s)-0.13 V
A)0.28 V
B)0.64 V
C)0.90 V
D)1.03 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When suspected drunk drivers are tested with a Breathalyzer,the alcohol (ethanol)in the exhaled breath is oxidized to acetic acid with an acidic solution of potassium dichromate: 3CH3CH2OH(aq)+ 2Cr2O7-2 (aq)+ 16H+(aq)3CH3CO2H(aq)+ 4Cr+3(aq)+ 11H2O (l)
If Eº for this cell is 1.30V and the standard half-cell potential of Cr2O7-2(aq)to Cr+3 is 1.358 V,what is the standard half-cell reduction potential for the conversion of acetic acid to ethanol?
A)2.658 V
B)-2.658 V
C)+ 0.058 V
D)-0.058 V
If Eº for this cell is 1.30V and the standard half-cell potential of Cr2O7-2(aq)to Cr+3 is 1.358 V,what is the standard half-cell reduction potential for the conversion of acetic acid to ethanol?
A)2.658 V
B)-2.658 V
C)+ 0.058 V
D)-0.058 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A galvanic cell consists of a La3+/La half-cell and a standard hydrogen electrode.If the La3+/La half-cell standard cell functions as the anode,and the standard cell potential is 2.52 V,what is the standard reduction potential for the La3+/La half-cell?
A)-2.52 V
B)-0.84 V
C)+0.84 V
D)+2.52 V
A)-2.52 V
B)-0.84 V
C)+0.84 V
D)+2.52 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Given that E° = +0.897 V,calculate E at 25°C for Pb(s)∣ Pb2+(0.0400 M)∣∣ Fe3+(0.200 M),Fe2+(0.0100 M)∣ Pt(s)
A)+0.779 V
B)+0.935 V
C)+1.015 V
D)+1.134 V
A)+0.779 V
B)+0.935 V
C)+1.015 V
D)+1.134 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The standard potential for the following galvanic cell is +0.90 V: 3 Cu2+(aq)+ 2 Ga(s)⇌ 3 Cu(s)+ 2 Ga3+(aq)
Given that the standard reduction potential for the Cu2+/Cu half-cell is +0.34 V,what is the standard reduction potential for the Ga3+/Ga half-cell?
A)-1.34 V
B)-0.56 V
C)+0.56 V
D)+1.36 V
Given that the standard reduction potential for the Cu2+/Cu half-cell is +0.34 V,what is the standard reduction potential for the Ga3+/Ga half-cell?
A)-1.34 V
B)-0.56 V
C)+0.56 V
D)+1.36 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
At 25°C,E° = +1.88 V for a cell based on the reaction 3 AgCl(s)+ Al(s)→ 3 Ag(s)+ Al3+(aq)+ 3 Cl-(aq).
Find the cell potential E if [Al3+] = 0.20 M and [Cl-] = 0.010 M.
A)+2.01 V
B)+2.04 V
C)+2.28 V
D)cannot be calculated without the amounts of AgCl,Al,and Ag
Find the cell potential E if [Al3+] = 0.20 M and [Cl-] = 0.010 M.
A)+2.01 V
B)+2.04 V
C)+2.28 V
D)cannot be calculated without the amounts of AgCl,Al,and Ag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Using the following standard reduction potentials Fe3+(aq)+ e- → Fe2+(aq)E° = +0.77 V
Pb2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Pb(s)E° = -0.13 V
Calculate the standard cell potential for the galvanic cell reaction given below,and determine whether or not this reaction is spontaneous under standard conditions.
Pb2+(aq)+ 2 Fe2+(aq)→ 2 Fe3+(aq)+ Pb(s)
A)E° = -0.90 V,nonspontaneous
B)E° = -0.90 V,spontaneous
C)E° = +0.90 V,nonspontaneous
D)E° = +0.90 V,spontaneous
Pb2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Pb(s)E° = -0.13 V
Calculate the standard cell potential for the galvanic cell reaction given below,and determine whether or not this reaction is spontaneous under standard conditions.
Pb2+(aq)+ 2 Fe2+(aq)→ 2 Fe3+(aq)+ Pb(s)
A)E° = -0.90 V,nonspontaneous
B)E° = -0.90 V,spontaneous
C)E° = +0.90 V,nonspontaneous
D)E° = +0.90 V,spontaneous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Consider the galvanic cell,Pb(s)∣ Pb2+(aq)∣∣ Cu2+(aq)∣ Cu(s).Which one of the following changes to the cell would cause the cell potential to increase (i.e. ,become more positive)?
A)increase the [Pb2+] concentration
B)increase the [Cu2+] concentration
C)increase the mass of Pb(s)
D)decrease the mass of Pb(s)
A)increase the [Pb2+] concentration
B)increase the [Cu2+] concentration
C)increase the mass of Pb(s)
D)decrease the mass of Pb(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55

According to Table 17.1,which will reduce water but not Mg2+?
A)Al3+(aq)
B)Al(s)
C)Na+(aq)
D)Na(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Consider the following standard reduction potentials, Al3+(aq)+ 3 e- → Al(s)E° = -1.66 V
I2(s)+ 2 e- → 2 I-(aq)E° = +0.54 V
Under standard conditions,
A)Al3+(aq)is a stronger oxidizing agent than I2(s),and I-(aq)is a stronger reducing agent than Al(s).
B)I2(s)is a stronger oxidizing agent than Al3+(aq),and Al(s)is a stronger reducing agent than I-(aq).
C)Al(s)is a stronger oxidizing agent than I-(aq),and Al3+(aq)is a stronger reducing agent than I2(s).
D)I-(aq)is a stronger oxidizing agent than Al(s),and I2(s)is a stronger reducing agent than Al3+(aq).
I2(s)+ 2 e- → 2 I-(aq)E° = +0.54 V
Under standard conditions,
A)Al3+(aq)is a stronger oxidizing agent than I2(s),and I-(aq)is a stronger reducing agent than Al(s).
B)I2(s)is a stronger oxidizing agent than Al3+(aq),and Al(s)is a stronger reducing agent than I-(aq).
C)Al(s)is a stronger oxidizing agent than I-(aq),and Al3+(aq)is a stronger reducing agent than I2(s).
D)I-(aq)is a stronger oxidizing agent than Al(s),and I2(s)is a stronger reducing agent than Al3+(aq).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Calculate the cell potential at 25°C for the cell Fe(s)∣ (Fe2+(0.100 M)∣∣ Pd2+(1.0 × 10-5 M)∣ Pd(s)
Given that the standard reduction potential for Fe2+/Fe is -0.45 V and for Pd2+/Pd is +0.95 V.
A)+1.16 V
B)+1.28 V
C)+1.52 V
D)+1.68 V
Given that the standard reduction potential for Fe2+/Fe is -0.45 V and for Pd2+/Pd is +0.95 V.
A)+1.16 V
B)+1.28 V
C)+1.52 V
D)+1.68 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider the following table of standard reduction potentials: 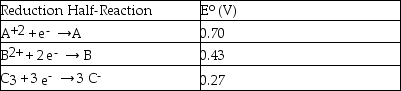 Which substance is the strongest reducing agent?
Which substance is the strongest reducing agent?
A)A
B)B
C)C3
D)C-
 Which substance is the strongest reducing agent?
Which substance is the strongest reducing agent?A)A
B)B
C)C3
D)C-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A galvanic cell consists of one half-cell that contains Ag(s)and Ag+(aq),and one half-cell that contains Cu(s)and Cu2+(aq).What species are produced at the electrodes under standard conditions? Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)E° = +0.80 V
Cu2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Cu(s)E° = +0.34 V
A)Ag(s)is formed at the cathode,and Cu(s)is formed at the anode.
B)Ag(s)is formed at the cathode,and Cu2+ (aq)is formed at the anode.
C)Cu(s)is formed at the cathode,and Ag+(aq)is formed at the anode.
D)Cu2+(aq)is formed at the cathode,and Cu(s)is formed at the anode.
Cu2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Cu(s)E° = +0.34 V
A)Ag(s)is formed at the cathode,and Cu(s)is formed at the anode.
B)Ag(s)is formed at the cathode,and Cu2+ (aq)is formed at the anode.
C)Cu(s)is formed at the cathode,and Ag+(aq)is formed at the anode.
D)Cu2+(aq)is formed at the cathode,and Cu(s)is formed at the anode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60

According to Table 17.1,which aqueous metal ion will reduce Ag+,but not Cu2+?
A)Fe2+
B)Fe3+
C)Mn2+
D)Sn2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which statement below is not true?
A)The cell reactants in a fuel cell are continuously supplied from an external source.
B)A fuel cell is a galvanic cell.
C)Modern fuel cells can be easily regenerated using household current.
D)One of the reactants in a fuel cell is a traditional fuel.
A)The cell reactants in a fuel cell are continuously supplied from an external source.
B)A fuel cell is a galvanic cell.
C)Modern fuel cells can be easily regenerated using household current.
D)One of the reactants in a fuel cell is a traditional fuel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A cell based on the reaction below has a standard potential of +0.42 V at 25°C.If all of the species are at standard conditions except [H+],at what pH will the cell have a potential of zero? H2O2(aq)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 Cl-(aq)→ Cl2(aq)+ 2 H2O(l)
A)3.55
B)7.09
C)10.6
D)14.2
A)3.55
B)7.09
C)10.6
D)14.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The cell reaction for a lead storage battery is: Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 HSO4-(aq)→ 2 PbSO4(s)+ 2 H2O(l)
E° = +1.92 V
To provide a potential of about 12 V,one could
A)adjust the pH to 12.
B)adjust the pH to 1.
C)connect six cells in series.
D)greatly increase the surface area of the Pb(s)and PbO2(s).
E° = +1.92 V
To provide a potential of about 12 V,one could
A)adjust the pH to 12.
B)adjust the pH to 1.
C)connect six cells in series.
D)greatly increase the surface area of the Pb(s)and PbO2(s).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following reactions is most suitable for a fuel cell?
A)MnO2(s)+ Li(s)→ LiMnO2(s)
B)Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 2 H+(aq)+ HSO4-(aq)→ PbSO4(s)+ 2 H2O(l)
C)HgO(l)+ Zn(s)→ ZnO(s)+ Hg(l)
D)2 CO(g)+ O2(g)→ 2 CO2(g)
A)MnO2(s)+ Li(s)→ LiMnO2(s)
B)Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 2 H+(aq)+ HSO4-(aq)→ PbSO4(s)+ 2 H2O(l)
C)HgO(l)+ Zn(s)→ ZnO(s)+ Hg(l)
D)2 CO(g)+ O2(g)→ 2 CO2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)E° = +0.800 V AgBr(s)+ e- → Ag(s)+ Br-(aq)E° = +0.071 V
Br2(l)+ 2 e- → 2 Br-(aq)E° = +1.066 V
Use some of the data above to calculate Ksp at 25°C for AgBr.
A)6.3 × 10-2
B)4.9 × 10-13
C)1.9 × 10-15
D)12.4× 10-34
Br2(l)+ 2 e- → 2 Br-(aq)E° = +1.066 V
Use some of the data above to calculate Ksp at 25°C for AgBr.
A)6.3 × 10-2
B)4.9 × 10-13
C)1.9 × 10-15
D)12.4× 10-34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which is most often used in the laboratory to measure pH?
A)a standard hydrogen electrode
B)a glass electrode
C)a Daniell cell
D)a conductivity cell
A)a standard hydrogen electrode
B)a glass electrode
C)a Daniell cell
D)a conductivity cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following statements concerning a lithium battery is false?
A)A lithium battery is rechargeable.
B)A lithium battery has a relatively high voltage,due in part to the high oxidation potential of lithium.
C)It takes a small mass of lithium to provide one mole of electrons in the cell reaction.
D)The cell reaction produces toxic mercury,so the batteries should be recycled.
A)A lithium battery is rechargeable.
B)A lithium battery has a relatively high voltage,due in part to the high oxidation potential of lithium.
C)It takes a small mass of lithium to provide one mole of electrons in the cell reaction.
D)The cell reaction produces toxic mercury,so the batteries should be recycled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How many moles of electrons,n,are transferred in the following reduction-oxidation reaction? 2 MnO4-(aq)+ 16 H+(aq)+ 10 Cl-(aq)→ 2 Mn2+(aq)+ 5 Cl2(g)+ 8 H2O(l)
A)2
B)4
C)5
D)10
A)2
B)4
C)5
D)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The equilibrium constant,K,can be calculated from
A)E°.
B)E.
C)either E° or E.
D)neither E° nor E.
A)E°.
B)E.
C)either E° or E.
D)neither E° nor E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Consider the following cell: Pt(s)∣ H2(g,p1)∣ H+(aq,pHA)∣∣ H+(aq,pHC)∣ H2(g,p2)∣ Pt(s)
Where pHA is the pH of the aqueous solution in the anode half-cell and pHC is the pH of the aqueous solution in the cathode half-cell.If the partial pressure of H2(g)is the same for both half-cells, (p1 = p2),then E for the cell at 25°C is
A)0.0296 V log (pHA/pHC).
B)0.0296 V log (pHC/pHA).
C)0.0592 V (pHA - pHC).
D)0.0592 V (pHC - pHA).
Where pHA is the pH of the aqueous solution in the anode half-cell and pHC is the pH of the aqueous solution in the cathode half-cell.If the partial pressure of H2(g)is the same for both half-cells, (p1 = p2),then E for the cell at 25°C is
A)0.0296 V log (pHA/pHC).
B)0.0296 V log (pHC/pHA).
C)0.0592 V (pHA - pHC).
D)0.0592 V (pHC - pHA).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Given that E°red = -0.26 V for Ni2+/Ni at 25°C,find E° and E for the concentration cell expressed using shorthand notation below. Ni(s)∣ Ni2+(aq,1.0 × 10-5 M)∣∣ Ni2+(aq,0.100 M)∣ Ni(s)
A)E° = 0.00 V and E = +0.24 V
B)E° = 0.00 V and E = +0.12 V
C)E° = -0.26 V and E = -0.02 V
D)E° = -0.26 V and E = -0.14 V
A)E° = 0.00 V and E = +0.24 V
B)E° = 0.00 V and E = +0.12 V
C)E° = -0.26 V and E = -0.02 V
D)E° = -0.26 V and E = -0.14 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If the cell reaction involves ions in solution,as the cell reaction in a galvanic cell continues,
A)E for the cell increases.
B)E for the cell decreases.
C)E° for the cell increases.
D)E° for the cell decreases.
A)E for the cell increases.
B)E for the cell decreases.
C)E° for the cell increases.
D)E° for the cell decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Consider the half-reaction: MnO4-(aq)+ 8 H+(aq)+ 5 e- → Mn2+(aq)+ 4 H2O(l).The formation of MnO4- from Mn2+ occurs most readily when the solution is
A)acidic.
B)neutral.
C)basic.
D)The reaction is not dependent upon pH.
A)acidic.
B)neutral.
C)basic.
D)The reaction is not dependent upon pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
For a particular battery based on one of the following reactions,E is expected to remain constant with time until the cell reactants are almost completely consumed.Which is the appropriate reaction?
A)Zn(s)+ 2 MnO2(s)+ 2 NH4+(aq)→ 2 NH3(aq)+ Mn2O3(s)+ Zn2+(aq)+ H2O(l)
B)2 NiO(OH)(s)+ Cd(s)+ 2 H2O(l)→ 2 Ni(OH)2(s)+ Cd(OH)2(s)
C)Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 HSO4-(aq)→ 2 PbSO4(s)+ 2 H2O(l)
D)Zn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Zn2+(aq)+ Cu(s)
A)Zn(s)+ 2 MnO2(s)+ 2 NH4+(aq)→ 2 NH3(aq)+ Mn2O3(s)+ Zn2+(aq)+ H2O(l)
B)2 NiO(OH)(s)+ Cd(s)+ 2 H2O(l)→ 2 Ni(OH)2(s)+ Cd(OH)2(s)
C)Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 HSO4-(aq)→ 2 PbSO4(s)+ 2 H2O(l)
D)Zn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Zn2+(aq)+ Cu(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When a cell reaction reaches equilibrium,
A)E° = 0.
B)E = 0.
C)both E° and E = 0.
D)neither E° nor E = 0.
A)E° = 0.
B)E = 0.
C)both E° and E = 0.
D)neither E° nor E = 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
For a particular cell based on the reaction: 3 AgCl(s)+ Al(s)→ 3 Ag(s)+ Al3+(aq)+ 3 Cl-(aq)
E = +1.750 V and E° = +1.884 V at 25°C.
What is the value of the equilibrium constant,K,at 25°C for the reaction?
A)3.6 × 1029
B)6.7 × 1031
C)4.8 × 1088
D)3.0 × 1095
E = +1.750 V and E° = +1.884 V at 25°C.
What is the value of the equilibrium constant,K,at 25°C for the reaction?
A)3.6 × 1029
B)6.7 × 1031
C)4.8 × 1088
D)3.0 × 1095

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The following cell has a potential of 0.45 V at 25°C. Pt(s)∣ H2(1 atm)|H+(? M)∣∣ Cl-(1 M)∣ Hg2Cl2(s)|Hg(l)
The standard half-cell potential for the half-reaction Hg2Cl2(s)+ 2 e- → 2 Hg(l)+ 2 Cl-(aq)is 0.28 V.What is the pH in the anode compartment?
A)2.9
B)4.7
C)7.6
D)12.3
The standard half-cell potential for the half-reaction Hg2Cl2(s)+ 2 e- → 2 Hg(l)+ 2 Cl-(aq)is 0.28 V.What is the pH in the anode compartment?
A)2.9
B)4.7
C)7.6
D)12.3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Shown below are the reactions occurring in the direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC). I.2 CH3OH(aq)+ 2 H2O(l)→ 2 CO2(g)+12 H+(aq)+12 e-
II.3 O2(g)+ 12 H+(aq)+ 12 e- → 6 H2O(l)
Overall 2 CH3OH(aq)+ 3 O2(g)→ 2 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)
Which is the anode reaction,and what is being oxidized in the overall reaction?
A)I,CH3OH
B)I,H2O
C)II,O2
D)II,H+
II.3 O2(g)+ 12 H+(aq)+ 12 e- → 6 H2O(l)
Overall 2 CH3OH(aq)+ 3 O2(g)→ 2 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)
Which is the anode reaction,and what is being oxidized in the overall reaction?
A)I,CH3OH
B)I,H2O
C)II,O2
D)II,H+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Given 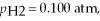
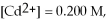 and
and 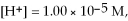 calculate E at 25°C for a cell based on the reaction:
calculate E at 25°C for a cell based on the reaction: 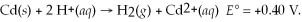
A)-0.09 V
B)+0.12 V
C)+0.15 V
D)+0.30 V
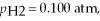
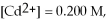 and
and 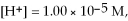 calculate E at 25°C for a cell based on the reaction:
calculate E at 25°C for a cell based on the reaction: 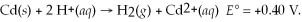
A)-0.09 V
B)+0.12 V
C)+0.15 V
D)+0.30 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When suspected drunk drivers are tested with a Breathalyzer,the alcohol (ethanol)in the exhaled breath is oxidized to acetic acid with an acidic solution of potassium dichromate: 3 CH3CH2OH(aq)+ 2 Cr2O7-2 (aq)+ 16 H+(aq)3CH3CO2H(aq)+ 4Cr+3(aq)+ 11H2O (l)
What is the value of E for the reaction when the concentrations of ethanol,acetic acid,Cr2O7-2,and Cr+3,are 1.0M and the pH is 4.00? (Eº for this cell is 1.30V and the temperature is 298K).
Equations to solve this problem are below.
Ε = ε° -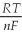 lnQ
lnQ
Ε = 1.30 -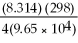 ln
ln 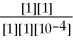
A)1.62 V
B)1.30 V
C)0.98 V
D)1.24 V
What is the value of E for the reaction when the concentrations of ethanol,acetic acid,Cr2O7-2,and Cr+3,are 1.0M and the pH is 4.00? (Eº for this cell is 1.30V and the temperature is 298K).
Equations to solve this problem are below.
Ε = ε° -
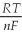 lnQ
lnQΕ = 1.30 -
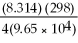 ln
ln 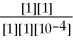
A)1.62 V
B)1.30 V
C)0.98 V
D)1.24 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



