Deck 7: Chemical Reactions: Energy, rates, and Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Chemical Reactions: Energy, rates, and Equilibrium
1
Consider the reaction shown:
P4 (s)+ 10 Cl2 (g)→ 4 PCl5 (s)+ 452 kcal
When 50.00 g of P4 react,________ kcal will be ________.
A)182.4; consumed
B)452; produced
C)729.7; produced
D)182.4; produced
E)452; consumed
P4 (s)+ 10 Cl2 (g)→ 4 PCl5 (s)+ 452 kcal
When 50.00 g of P4 react,________ kcal will be ________.
A)182.4; consumed
B)452; produced
C)729.7; produced
D)182.4; produced
E)452; consumed
182.4; produced
2
If heat is consumed during a reaction,the reaction is said to be ________.
A)endothermic
B)exothermic
C)endergonic
D)exothermic.
E)can't tell.
A)endothermic
B)exothermic
C)endergonic
D)exothermic.
E)can't tell.
endothermic
3
The scientific principle which explains the observation that the amount of heat transfer accompanying a change in one direction is numerically equal but opposite in sign to the amount of heat transfer in the opposite direction is
A)the Law of Conservation of Energy.
B)the Law of Conservation of Mass.
C)the Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy.
D)the Law of Definite Proportions.
E)Avogadro's Law.
A)the Law of Conservation of Energy.
B)the Law of Conservation of Mass.
C)the Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy.
D)the Law of Definite Proportions.
E)Avogadro's Law.
the Law of Conservation of Energy.
4
P4 (s)+ 10 Cl2 (g)→ 4 PCl5 (s) ΔH = -435.2 kcal
Based on the reaction shown,which statement is true?
A)When 1 mol P4 (s)reacts,435.2 kcal are released.
B)When 1 mol PCl5 (s)is produced,435.2 kcal are released.
C)When 30.97 g P4 (s)react,435.2 kcal are released.
D)When 123.88 g P4 (s)react,435.2 kcal are consumed.
E)When 208.22 g PCl5 (s)are produced,435.2 kcal are consumed.
Based on the reaction shown,which statement is true?
A)When 1 mol P4 (s)reacts,435.2 kcal are released.
B)When 1 mol PCl5 (s)is produced,435.2 kcal are released.
C)When 30.97 g P4 (s)react,435.2 kcal are released.
D)When 123.88 g P4 (s)react,435.2 kcal are consumed.
E)When 208.22 g PCl5 (s)are produced,435.2 kcal are consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
N2 + O2 → 2 NO ΔH = 43.2 kcal
Based on the reaction shown,which statement is true?
A)43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 g of N2 reacts.
B)43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 g of O2 reacts.
C)43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 mole of O2 reacts.
D)43.2 kcal are produced when 1.00 mole of NO is produced.
E)43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 g of NO is produced.
Based on the reaction shown,which statement is true?
A)43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 g of N2 reacts.
B)43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 g of O2 reacts.
C)43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 mole of O2 reacts.
D)43.2 kcal are produced when 1.00 mole of NO is produced.
E)43.2 kcal are consumed when 1.00 g of NO is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Consider the reaction shown:
304.0 kcal + 4 PCl3 (l)→ P4 (s)+ 6 Cl2 (g)
When 50.00 g of PCl3 react,________ kcal will be ________.
A)304.0; produced
B)27.67; produced
C)304.0; consumed
D)110.7; consumed
E)27.67; consumed
304.0 kcal + 4 PCl3 (l)→ P4 (s)+ 6 Cl2 (g)
When 50.00 g of PCl3 react,________ kcal will be ________.
A)304.0; produced
B)27.67; produced
C)304.0; consumed
D)110.7; consumed
E)27.67; consumed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A process or reaction which releases heat to the surroundings is said to be
A)conservative.
B)endothermic.
C)exothermic.
D)isothermal.
E)exergonic.
A)conservative.
B)endothermic.
C)exothermic.
D)isothermal.
E)exergonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A process or reaction which takes in heat from the surroundings is said to be
A)conservative.
B)endothermic.
C)exothermic.
D)isothermal.
E)endergonic.
A)conservative.
B)endothermic.
C)exothermic.
D)isothermal.
E)endergonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
All of the statements regarding the symbol "ΔH" are correct except
A)it represents the difference between the energy used in breaking bonds and the energy released in forming bonds in a chemical reaction.
B)it can be called heat of reaction.
C)it can be called enthalpy change.
D)it can be called entropy change.
E)it has a negative value for an exothermic reaction.
A)it represents the difference between the energy used in breaking bonds and the energy released in forming bonds in a chemical reaction.
B)it can be called heat of reaction.
C)it can be called enthalpy change.
D)it can be called entropy change.
E)it has a negative value for an exothermic reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A reaction is said to be ________ if the bonds formed during the reaction are stronger than the bonds broken.
A)exothermic
B)endothermic
C)exergonic
D)endergonic
E)spontaneous
A)exothermic
B)endothermic
C)exergonic
D)endergonic
E)spontaneous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
S + O2 → SO2 + 70.8 kcal
Based on the reaction shown,which statement is true?
A)70.8 kcal are produced when 1 g of sulfur reacts.
B)70.8 kcal are consumed when 1 g of sulfur reacts.
C)70.8 kcal are produced when 32.1 g of sulfur reacts.
D)70.8 kcal are consumed when 32.1 g of sulfur reacts.
E)70.8 kcal are produced when 1 g of sulfur dioxide is produced.
Based on the reaction shown,which statement is true?
A)70.8 kcal are produced when 1 g of sulfur reacts.
B)70.8 kcal are consumed when 1 g of sulfur reacts.
C)70.8 kcal are produced when 32.1 g of sulfur reacts.
D)70.8 kcal are consumed when 32.1 g of sulfur reacts.
E)70.8 kcal are produced when 1 g of sulfur dioxide is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Calculate the enthalpy for the following reaction: N2 + O2 → 2 NO
Given the following bond dissociation energies: N2 = 226 kcal/mol,O2 = 199 kcal/mol and NO = 145 kcal/mol.
A)135 kcal/mol
B)-135 kcal/mol
C)280 kcal/mol
D)-280 kcal/mol
Given the following bond dissociation energies: N2 = 226 kcal/mol,O2 = 199 kcal/mol and NO = 145 kcal/mol.
A)135 kcal/mol
B)-135 kcal/mol
C)280 kcal/mol
D)-280 kcal/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the reaction shown:
C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + 488 kcal
We can say that this reaction is ________ and that the sign of ΔH is ________.
A)endothermic; positive
B)exothermic; positive
C)endothermic; negative
D)exothermic; negative
E)exothermic; neither positive nor negative
C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + 488 kcal
We can say that this reaction is ________ and that the sign of ΔH is ________.
A)endothermic; positive
B)exothermic; positive
C)endothermic; negative
D)exothermic; negative
E)exothermic; neither positive nor negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
To simplify comparisons,the energy value of fuels is expressed in units of
A)kcal.
B)kcal/mol.
C)kcal/g.
D)kcal/L.
E)some other unit
A)kcal.
B)kcal/mol.
C)kcal/g.
D)kcal/L.
E)some other unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
S + O2 → SO2 ΔH = -70.8 kcal
Based on the reaction shown,which statement is true?
A)70.8 kcal are produced when 1 g of sulfur reacts.
B)70.8 kcal are consumed when 1 g of sulfur reacts.
C)70.8 kcal are produced when 32.1 g of sulfur reacts.
D)70.8 kcal are consumed when 32.1 g of sulfur reacts.
E)70.8 kcal are produced when 1 g of sulfur dioxide is produced.
Based on the reaction shown,which statement is true?
A)70.8 kcal are produced when 1 g of sulfur reacts.
B)70.8 kcal are consumed when 1 g of sulfur reacts.
C)70.8 kcal are produced when 32.1 g of sulfur reacts.
D)70.8 kcal are consumed when 32.1 g of sulfur reacts.
E)70.8 kcal are produced when 1 g of sulfur dioxide is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
4 PCl3 (l)→ P4 (s)+ 6 Cl2 (g) ΔH = 304.0 kcal
Based on the reaction shown,which statement is true?
A)When 1 mol PCl3 (l)reacts,304.0 kcal are released.
B)When 1 mol P4 (s)is produced,304.0 kcal are consumed.
C)When 548.56 g PCl3 (l)react,304.0 kcal are released.
D)When 137.14 g PCl3 (l)react,304.0 kcal are consumed.
E)When 123.88 g P4 (s)are produced,304.0 kcal are released.
Based on the reaction shown,which statement is true?
A)When 1 mol PCl3 (l)reacts,304.0 kcal are released.
B)When 1 mol P4 (s)is produced,304.0 kcal are consumed.
C)When 548.56 g PCl3 (l)react,304.0 kcal are released.
D)When 137.14 g PCl3 (l)react,304.0 kcal are consumed.
E)When 123.88 g P4 (s)are produced,304.0 kcal are released.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Consider the reaction shown:
N2 + O2 → 2 NO ΔH = 43.2 kcal
When 50.0 g of N2 react,________ kcal will be ________.
A)43.2; produced
B)77.1; consumed
C)77.1; produced
D)2160; consumed
E)2160; produced
N2 + O2 → 2 NO ΔH = 43.2 kcal
When 50.0 g of N2 react,________ kcal will be ________.
A)43.2; produced
B)77.1; consumed
C)77.1; produced
D)2160; consumed
E)2160; produced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The label on a package of cookies states that there are 100 calories per serving.Explain the different meanings of this statement to a chemist and to a nutritionist.Be sure your answer explains the difference between kilocalories and Calorie.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Consider the reaction shown:
2 CO (g)+ O2 (g)→ CO2 (g)+ 135.2 kcal
This reaction is ________ because the sign of ΔH is ________.
A)endothermic; positive
B)exothermic; positive
C)endothermic; negative
D)exothermic; negative
E)exothermic; neither positive nor negative
2 CO (g)+ O2 (g)→ CO2 (g)+ 135.2 kcal
This reaction is ________ because the sign of ΔH is ________.
A)endothermic; positive
B)exothermic; positive
C)endothermic; negative
D)exothermic; negative
E)exothermic; neither positive nor negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consider the reaction shown:
452 kcal + 4 PCl5 (s)→ P4 (s)+ 10 Cl2 (g)
This reaction is ________ because the sign of ΔH is ________.
A)endothermic; positive
B)exothermic; positive
C)endothermic; negative
D)exothermic; negative
E)exothermic; neither positive nor negative
452 kcal + 4 PCl5 (s)→ P4 (s)+ 10 Cl2 (g)
This reaction is ________ because the sign of ΔH is ________.
A)endothermic; positive
B)exothermic; positive
C)endothermic; negative
D)exothermic; negative
E)exothermic; neither positive nor negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Activation energy can best be described as
A)the energy level of the products.
B)the maximum energy level of the reaction.
C)the energy level of the reactants.
D)the difference in energy between reactants and products.
E)the difference in energy between reactants and the maximum energy.
A)the energy level of the products.
B)the maximum energy level of the reaction.
C)the energy level of the reactants.
D)the difference in energy between reactants and products.
E)the difference in energy between reactants and the maximum energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
2 Al2O3 (s)→ 4 Al (s)+ 3 O2 (g) ΔG = +138 kcal
Consider the contribution of entropy to the spontaneity of this reaction.As written,the reaction is ________,and the entropy of the system ________.
A)spontaneous; increases
B)spontaneous; decreases
C)non-spontaneous; increases
D)non-spontaneous; decreases
E)non-spontaneous; does not change
Consider the contribution of entropy to the spontaneity of this reaction.As written,the reaction is ________,and the entropy of the system ________.
A)spontaneous; increases
B)spontaneous; decreases
C)non-spontaneous; increases
D)non-spontaneous; decreases
E)non-spontaneous; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
All of the statements regarding the symbol ΔG are true except
A)it refers to the free energy of the reaction.
B)it allows us to predict the spontaneity of a reaction.
C)it allows us to identify an exothermic reaction.
D)it allows us to identify an endergonic reaction.
E)it describes the effect of both enthalpy and entropy on a reaction.
A)it refers to the free energy of the reaction.
B)it allows us to predict the spontaneity of a reaction.
C)it allows us to identify an exothermic reaction.
D)it allows us to identify an endergonic reaction.
E)it describes the effect of both enthalpy and entropy on a reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The concept of free energy allows prediction of spontaneity of a process by considering the changes in ________ and ________ during the process.
A)enthalpy; entropy
B)enthalpy; mass
C)entropy; mass
D)enthalpy; temperature
E)entropy; temperature
A)enthalpy; entropy
B)enthalpy; mass
C)entropy; mass
D)enthalpy; temperature
E)entropy; temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A reaction that is spontaneous can be described as
A)proceeding in both the forward and reverse directions.
B)having the same rate in both the forward and reverse directions.
C)releasing heat to the surroundings.
D)proceeding without external influence once it has begun.
E)increasing in disorder.
A)proceeding in both the forward and reverse directions.
B)having the same rate in both the forward and reverse directions.
C)releasing heat to the surroundings.
D)proceeding without external influence once it has begun.
E)increasing in disorder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Entropy can be defined as
A)the amount of energy required to rearrange chemical bonds.
B)the amount of energy required to initiate a reaction.
C)the number of chemical bonds which are changed during a reaction.
D)the state of equilibrium in a system.
E)the amount of disorder in a system.
A)the amount of energy required to rearrange chemical bonds.
B)the amount of energy required to initiate a reaction.
C)the number of chemical bonds which are changed during a reaction.
D)the state of equilibrium in a system.
E)the amount of disorder in a system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the statements are true for spontaneous reactions except
A)the value of ΔG is less than zero.
B)the value of ΔG is unaffected by a catalyst.
C)they are said to be exergonic.
D)if the enthalpy change is unfavorable,they occur at a high temperature.
E)the reaction rate is determined by the value of ΔG.
A)the value of ΔG is less than zero.
B)the value of ΔG is unaffected by a catalyst.
C)they are said to be exergonic.
D)if the enthalpy change is unfavorable,they occur at a high temperature.
E)the reaction rate is determined by the value of ΔG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A reaction which is unfavorable with respect to entropy,but favorable with respect to enthalpy
A)could occur at any temperature.
B)could not occur regardless of temperature.
C)could occur at low temperatures but not at higher temperatures.
D)could occur at high temperatures but not at lower temperatures.
E)none of the above
A)could occur at any temperature.
B)could not occur regardless of temperature.
C)could occur at low temperatures but not at higher temperatures.
D)could occur at high temperatures but not at lower temperatures.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A rapid reaction is distinguished by
A)being unaffected by catalysts.
B)having a large heat of reaction.
C)having a small heat of reaction.
D)having a large value of activation energy.
E)having a small value of activation energy.
A)being unaffected by catalysts.
B)having a large heat of reaction.
C)having a small heat of reaction.
D)having a large value of activation energy.
E)having a small value of activation energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A process which is unfavorable with respect to enthalpy,but favorable with respect to entropy
A)could occur at low temperatures,but not at higher temperatures.
B)could occur at high temperatures,but not at lower temperatures.
C)could not occur regardless of temperature.
D)could occur at any temperature.
E)none of the above
A)could occur at low temperatures,but not at higher temperatures.
B)could occur at high temperatures,but not at lower temperatures.
C)could not occur regardless of temperature.
D)could occur at any temperature.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
For the reaction given below,what quantity of heat will be produced if 90.0 g of C3H8 are consumed in the reaction?
C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + 488 kcal
A)996 kcal
B)488 kcal
C)332 kcal
D)239 kcal
E)976 kcal
C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + 488 kcal
A)996 kcal
B)488 kcal
C)332 kcal
D)239 kcal
E)976 kcal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following processes involve an increase in entropy of the system?
I.Mothballs vaporize in a closet.
II.Blocks are assembled into a house.
III.Crystals grow from a sugar solution.
IV.Recyclable plastics are sorted.
V.Cake mix is manufactured from five basic ingredients.
A)II,IV
B)I,II,III
C)II,III,IV
D)I,V
E)I,III,V
I.Mothballs vaporize in a closet.
II.Blocks are assembled into a house.
III.Crystals grow from a sugar solution.
IV.Recyclable plastics are sorted.
V.Cake mix is manufactured from five basic ingredients.
A)II,IV
B)I,II,III
C)II,III,IV
D)I,V
E)I,III,V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements can be assumed to be true about how reactions occur?
A)Catalysts must be present in the reaction.
B)Energy must be absorbed as the reaction proceeds.
C)Reactant particles must collide with each other.
D)More than one statement can be true.
A)Catalysts must be present in the reaction.
B)Energy must be absorbed as the reaction proceeds.
C)Reactant particles must collide with each other.
D)More than one statement can be true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider the endothermic reaction:
N2 (g)+ 2 H2 (g)→ N2H4 (l)
The entropy change of this reaction is ________ and the enthalpy change is ________,so at a very high temperature,this reaction is probably ________.
A)favorable; unfavorable; nonspontaneous
B)favorable; unfavorable; spontaneous
C)unfavorable; unfavorable; spontaneous
D)unfavorable; unfavorable; nonspontaneous
E)unfavorable; favorable; spontaneous
N2 (g)+ 2 H2 (g)→ N2H4 (l)
The entropy change of this reaction is ________ and the enthalpy change is ________,so at a very high temperature,this reaction is probably ________.
A)favorable; unfavorable; nonspontaneous
B)favorable; unfavorable; spontaneous
C)unfavorable; unfavorable; spontaneous
D)unfavorable; unfavorable; nonspontaneous
E)unfavorable; favorable; spontaneous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
All of the statements concerning free energy and spontaneity are true except
A)if the value of ΔG for a reaction is 55.2 kcal,the value of ΔG for the reverse reaction will be -55.2 kcal.
B)if the value of ΔG for a reaction is negative,the reaction is said to be spontaneous.
C)a reaction which is nonspontaneous at low temperature cannot be spontaneous at higher temperatures.
D)enthalpy and entropy are of equal importance in determining the spontaneity of a reaction.
E)the speed of a reaction is not influenced by its spontaneity.
A)if the value of ΔG for a reaction is 55.2 kcal,the value of ΔG for the reverse reaction will be -55.2 kcal.
B)if the value of ΔG for a reaction is negative,the reaction is said to be spontaneous.
C)a reaction which is nonspontaneous at low temperature cannot be spontaneous at higher temperatures.
D)enthalpy and entropy are of equal importance in determining the spontaneity of a reaction.
E)the speed of a reaction is not influenced by its spontaneity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A solid sample at room temperature spontaneously sublimes forming a gas.This change in state is accompanied by which of the changes in the sample?
A)Entropy and energy decrease.
B)Entropy and energy increase.
C)Entropy decreases and energy increases.
D)Entropy increases and energy decreases.
A)Entropy and energy decrease.
B)Entropy and energy increase.
C)Entropy decreases and energy increases.
D)Entropy increases and energy decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following states of matter should have the lowest entropy value?
A)a crystalline solid
B)a liquid
C)a gas
D)Two of these have virtually the same entropy.
E)all of the above
A)a crystalline solid
B)a liquid
C)a gas
D)Two of these have virtually the same entropy.
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Entropy is used to
A)explain how energy is stored.
B)explain how an exothermic reaction can become endothermic.
C)indicate the disorder of a system.
D)explain why most chemical reactions are exothermic.
E)none of the above
A)explain how energy is stored.
B)explain how an exothermic reaction can become endothermic.
C)indicate the disorder of a system.
D)explain why most chemical reactions are exothermic.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the process of dissolving sugar in water,the entropy increases.This means that the sign of ΔS is ________,and that the randomness of the system ________.
A)undetermined; increases
B)positive; decreases
C)positive; increases
D)negative; decreases
E)negative; increases
A)undetermined; increases
B)positive; decreases
C)positive; increases
D)negative; decreases
E)negative; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Reaction rates are determined by all of the following factors except
A)the number of collisions between molecules.
B)the force of collisions between molecules.
C)the orientation of collisions between molecules.
D)the spontaneity of the reaction.
E)the activation energy of the reaction.
A)the number of collisions between molecules.
B)the force of collisions between molecules.
C)the orientation of collisions between molecules.
D)the spontaneity of the reaction.
E)the activation energy of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
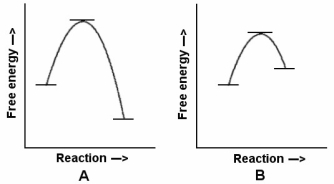
In the reaction energy diagrams shown,reaction A is ________,and it occurs ________ reaction B.
A)endergonic; faster than
B)exergonic; faster than
C)endergonic; slower than
D)exergonic; slower than
E)exergonic; at the same rate as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Sketch a diagram to illustrate the role of orientation in determining whether a collision between molecules of two different diatomic elements will lead to formation of a compound.How could you illustrate the influence of energy considerations on this reaction?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the reaction A + B → AB,which of the following will not increase the rate?
A)adding A
B)adding B
C)increasing the temperature
D)decreasing the temperature
E)adding a catalyst
A)adding A
B)adding B
C)increasing the temperature
D)decreasing the temperature
E)adding a catalyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The function of a catalyst in a reaction system is to
A)increase the yield of product.
B)decrease the amount of heat produced.
C)decrease the amount of energy consumed in the reaction.
D)increase the rate of the reaction.
E)decrease the amount of reactants consumed.
A)increase the yield of product.
B)decrease the amount of heat produced.
C)decrease the amount of energy consumed in the reaction.
D)increase the rate of the reaction.
E)decrease the amount of reactants consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Select the correct figure to match the description.
A slow reaction with a large positive free energy change
A)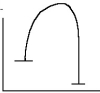
B)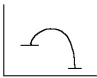
C)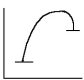
D)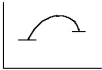
E)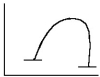
A slow reaction with a large positive free energy change
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which process is not likely to be considered reversible?
A)a round trip to Las Vegas
B)melting wax to make candles
C)a reaction using the symbol "↔"
D)cutting down a tree
E)dissolving salt in water
A)a round trip to Las Vegas
B)melting wax to make candles
C)a reaction using the symbol "↔"
D)cutting down a tree
E)dissolving salt in water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which factors would decrease the rate of a reaction?
I.Lowering the temperature
II.Increasing the concentration of reactants
III.Adding a catalyst
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)II and III
E)I and III
I.Lowering the temperature
II.Increasing the concentration of reactants
III.Adding a catalyst
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)II and III
E)I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Consider the reaction:
A + 2 B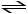
2 C + D
The equilibrium expression for this reaction is:
A)
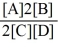
B)

C)
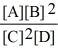
D)
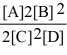
E)
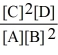
A + 2 B
2 C + D
The equilibrium expression for this reaction is:
A)
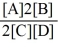
B)

C)
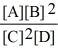
D)
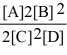
E)
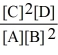

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

In the reaction energy diagrams shown,reaction B is ________,and it occurs ________ reaction B.
A)endergonic; faster than
B)exergonic; faster than
C)endergonic; slower than
D)exergonic; slower than
E)exergonic; at the same rate as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Select the correct figure to match the description.
A fast reaction with a small positive free energy change
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A fast reaction with a small positive free energy change
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which statement best describes the way a catalyst works?
A)It decreases the value of ΔH.
B)It increases the value of ΔH.
C)It decreases the value of Eact.
D)It increases the value of Eact.
E)It increases the value of ΔG.
A)It decreases the value of ΔH.
B)It increases the value of ΔH.
C)It decreases the value of Eact.
D)It increases the value of Eact.
E)It increases the value of ΔG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Select the correct figure to match the description.
A slow reaction with a large negative free energy change
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A slow reaction with a large negative free energy change
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consider the reaction:
2 CO (g)+ O2 (g)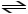
2 CO2 (g)
The equilibrium expression for this reaction is:
A)
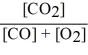
B)
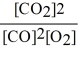
C)
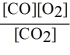
D)
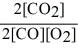
E)
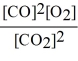
2 CO (g)+ O2 (g)
2 CO2 (g)
The equilibrium expression for this reaction is:
A)
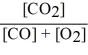
B)
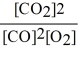
C)
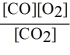
D)
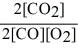
E)
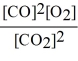

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Select the correct figure to match the description.
A slow reaction with a negative free energy change
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A slow reaction with a negative free energy change
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Select the correct figure to match the description.
A fast reaction with a large negative free energy change
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A fast reaction with a large negative free energy change
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following will affect all reaction rates?
A)the temperature of the reactants
B)the concentrations of the reactants
C)the presence of a catalyst
D)All are correct.
A)the temperature of the reactants
B)the concentrations of the reactants
C)the presence of a catalyst
D)All are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57

For a chemical reaction to occur,all of the following must happen except
A)chemical bonds in the reactants must break.
B)reactant particles must collide with enough energy for change to occur.
C)reactant particles must collide with the correct orientation.
D)a large enough number of collisions must occur.
E)chemical bonds in the products must form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which factors would increase the rate of a chemical reaction?
I.Increasing the temperature
II.Removing products as they are formed
III.Adding a catalyst
A)I and II
B)II and III
C)I,II,and III
D)I only
E)II only
I.Increasing the temperature
II.Removing products as they are formed
III.Adding a catalyst
A)I and II
B)II and III
C)I,II,and III
D)I only
E)II only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When a reaction system is at equilibrium
A)there is no more chemistry happening.
B)the amounts of reactants and products are exactly equal.
C)the reaction rate in the forward direction is at a maximum.
D)the reaction rate in the reverse direction is at a minimum.
E)the rates of the reaction in the forward and reverse directions are exactly equal.
A)there is no more chemistry happening.
B)the amounts of reactants and products are exactly equal.
C)the reaction rate in the forward direction is at a maximum.
D)the reaction rate in the reverse direction is at a minimum.
E)the rates of the reaction in the forward and reverse directions are exactly equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following conditions characterizes a system in a state of chemical equilibrium?
A)Concentrations of reactants and products are equal.
B)Rate of forward reaction has dropped to zero.
C)Reactants are being consumed at the same rate they are being produced.
D)Reactant molecules no longer react with each other.
E)Product concentrations are greater than reactant concentrations.
A)Concentrations of reactants and products are equal.
B)Rate of forward reaction has dropped to zero.
C)Reactants are being consumed at the same rate they are being produced.
D)Reactant molecules no longer react with each other.
E)Product concentrations are greater than reactant concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match the following.
A process or reaction that has a positive value of ΔG
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium
A process or reaction that has a positive value of ΔG
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
For the following reaction,increasing the pressure will cause the equilibrium to ________.
2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)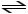
2 SO3 (g)+ heat
A)shift to the right,towards products
B)shift to the left,towards reactants
C)remain unchanged,but the reaction mixture will get warmer
D)remain unchanged,but the reaction mixture will get cooler
E)Pressure has no effect on equilibrium.
2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)
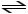
2 SO3 (g)+ heat
A)shift to the right,towards products
B)shift to the left,towards reactants
C)remain unchanged,but the reaction mixture will get warmer
D)remain unchanged,but the reaction mixture will get cooler
E)Pressure has no effect on equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match the following.
A process or reaction that has a negative value of ΔG
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium
A process or reaction that has a negative value of ΔG
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If we add a catalyst to the following equation,CO + H2O + heat 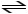
CO2 + H2,which way will the equilibrium shift?
A)to the left
B)no effect
C)to the right
D)not enough information
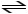
CO2 + H2,which way will the equilibrium shift?
A)to the left
B)no effect
C)to the right
D)not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Diatomic nitrogen is added to the equilibrium system:
N2 (g)+ H2 (g)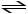
2 NH3(g)+ heat
When a new equilibrium is established the concentration of H2 will be ________ the amount at the original equilibrium,and the amount of NH3 will be ________ the amount at the original equilibrium.
A)greater than; greater than
B)greater than; less than
C)less than; greater than
D)less than; less than
E)Both changes will be impossible to determine.
N2 (g)+ H2 (g)
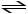
2 NH3(g)+ heat
When a new equilibrium is established the concentration of H2 will be ________ the amount at the original equilibrium,and the amount of NH3 will be ________ the amount at the original equilibrium.
A)greater than; greater than
B)greater than; less than
C)less than; greater than
D)less than; less than
E)Both changes will be impossible to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Match the following.
The amount of energy which must be invested in a reaction to get it started
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium
The amount of energy which must be invested in a reaction to get it started
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The position of the equilibrium for a system where K = 4.6 × 10-15 can be described as being favored to ________; the concentration of products is relatively ________.
A)the right; large
B)the right; small
C)the left; large
D)the left; small
E)neither direction; large
A)the right; large
B)the right; small
C)the left; large
D)the left; small
E)neither direction; large

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Match the following.
A process or reaction which releases heat
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium
A process or reaction which releases heat
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Match the following.
A process or reaction which consumes heat
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium
A process or reaction which consumes heat
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which change to this reaction system would cause the equilibrium to shift to the right?
N2 (g)+ 3 H2 (g)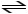
2 NH3 (g)+ heat
A)addition of a catalyst
B)addition of NH3 (g)
C)removal of H2 (g)
D)heating the system
E)lowering the temperature
N2 (g)+ 3 H2 (g)
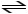
2 NH3 (g)+ heat
A)addition of a catalyst
B)addition of NH3 (g)
C)removal of H2 (g)
D)heating the system
E)lowering the temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction below if a tank was found to contain 0.106 M O2,0.00652 M SO3 and 0.00129 M SO2.
2 SO3 (g)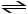
2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)
A)6.78 × 10-2
B)1.34 × 10-2
C)4.15 × 10-3
D)4.35 × 10-2
2 SO3 (g)
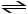
2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)
A)6.78 × 10-2
B)1.34 × 10-2
C)4.15 × 10-3
D)4.35 × 10-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Match the following.
A state in which the rate of the forward reaction is exactly equal to the rate of the reverse reaction
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium
A state in which the rate of the forward reaction is exactly equal to the rate of the reverse reaction
A)exergonic
B)endergonic
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)activation energy
F)chemical equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g) 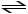
2 SO3 (g)+ heat K = 4.8 × 1027
Which statement about this system is not true?
A)At equilibrium SO3 is the predominant substance.
B)Heating the system will cause breakdown of SO3.
C)Adding SO2 will cause an increase in the amount of SO3.
D)Removing O2 will cause an increase in the amount of SO3.
E)The large value of K means that the reaction essentially goes to completion.
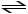
2 SO3 (g)+ heat K = 4.8 × 1027
Which statement about this system is not true?
A)At equilibrium SO3 is the predominant substance.
B)Heating the system will cause breakdown of SO3.
C)Adding SO2 will cause an increase in the amount of SO3.
D)Removing O2 will cause an increase in the amount of SO3.
E)The large value of K means that the reaction essentially goes to completion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



