Deck 19: Enzymes and Vitamins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Enzymes and Vitamins
1
Each of the following phrases correctly describes enzymes except
A)dissolve in water.
B)have a globular shape.
C)behave as substrates.
D)contain an active site.
E)act as catalysts.
A)dissolve in water.
B)have a globular shape.
C)behave as substrates.
D)contain an active site.
E)act as catalysts.
behave as substrates.
2
Which aspect of enzyme structure is related to our dietary need for trace minerals?
A)cofactor
B)active site
C)turnover number
D)chirality
E)none of these
A)cofactor
B)active site
C)turnover number
D)chirality
E)none of these
cofactor
3
Explain the term specificity as it applies to enzyme activity.
Specificity describes the degree of restriction of the activity of an enzyme.Most enzymes only catalyze a specific type of reaction,as evidenced by the broad terms transferase,oxidoreductase,etc.However,some enzymes may act on only one specific substrate molecule.For example,one hydrolase may act on any amide linkage in a peptide,while another hydrolase will only act on the linkage between a specific pair of amino acids.The precise shape of the active site is often the determining factor in specificity.One analogy for describing this is using the specific key for your office versus using a master key that opens your office and many others.
4
The tertiary structure of most enzymes is
A)an α-helix.
B)a β-pleated sheet.
C)fibrous.
D)globular.
E)none of these.
A)an α-helix.
B)a β-pleated sheet.
C)fibrous.
D)globular.
E)none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Transaminase can be classified as a(an)________ because its function is moving an amine group from one molecule to another.
A)ligase
B)isomerase
C)oxidoreductase
D)transferase
E)hydrolase
A)ligase
B)isomerase
C)oxidoreductase
D)transferase
E)hydrolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An enzyme that is classified as a hydrolase is involved in ________ reactions.
A)oxidation
B)reduction
C)isomerization
D)polymerization
E)hydrolysis
A)oxidation
B)reduction
C)isomerization
D)polymerization
E)hydrolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Enzymes function as catalysts by
A)changing the value of the free energy change to a more favorable value.
B)changing the value of the equilibrium constant to a more favorable value.
C)lowering the value of the activation energy.
D)increasing the amount of time needed to reach equilibrium.
E)becoming one of the reactants.
A)changing the value of the free energy change to a more favorable value.
B)changing the value of the equilibrium constant to a more favorable value.
C)lowering the value of the activation energy.
D)increasing the amount of time needed to reach equilibrium.
E)becoming one of the reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following combinations is required to create a holoenzyme?
A)effector + coenzyme
B)apoenzyme + activator
C)apoenzyme + coenzyme
D)None of the above are correct combinations.
A)effector + coenzyme
B)apoenzyme + activator
C)apoenzyme + coenzyme
D)None of the above are correct combinations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is called the
A)hormone.
B)substrate.
C)cofactor.
D)inhibitor.
E)vitamin.
A)hormone.
B)substrate.
C)cofactor.
D)inhibitor.
E)vitamin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Enzymes are members of which class of biomolecules?
A)carbohydrates
B)lipids
C)nucleic acids
D)proteins
E)steroids
A)carbohydrates
B)lipids
C)nucleic acids
D)proteins
E)steroids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The nonprotein portion required by some enzymes for proper functioning is called a(an)
A)zymogen.
B)substrate.
C)inhibitor.
D)cofactor.
E)activator.
A)zymogen.
B)substrate.
C)inhibitor.
D)cofactor.
E)activator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A synthetase can be classified as a(an)________ because its function is joining two molecules together.
A)ligase
B)isomerase
C)oxidoreductase
D)transferase
E)hydrolase
A)ligase
B)isomerase
C)oxidoreductase
D)transferase
E)hydrolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Enzymes increase the rates of only certain reactions involving certain substances.This general characteristic is called
A)selectivity.
B)specificity.
C)enzyme regulation.
D)catalytic efficiency.
E)enzyme inhibition.
A)selectivity.
B)specificity.
C)enzyme regulation.
D)catalytic efficiency.
E)enzyme inhibition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An enzyme that catalyzes addition or removal of hydrogen or oxygen on substrate molecules is a(an)________.
A)ligase
B)isomerase
C)oxidoreductase
D)transferase
E)hydrolase
A)ligase
B)isomerase
C)oxidoreductase
D)transferase
E)hydrolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the function of enzymes?
A)structure and support
B)energy reserves
C)biochemical catalysts
D)communication between cells
E)physical protection
A)structure and support
B)energy reserves
C)biochemical catalysts
D)communication between cells
E)physical protection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which term identifies the relatively small portion of the enzyme that is directly involved in the biochemical reaction being catalyzed?
A)substrate
B)active site
C)N-terminal
D)C-terminal
E)precursor
A)substrate
B)active site
C)N-terminal
D)C-terminal
E)precursor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The following reaction would most likely be catalyzed by an enzyme of which class?
Sucrose + H2O → glucose + fructose
A)synthetase or ligase
B)oxidoreductase
C)hydrolase
D)transferase
E)isomerase
Sucrose + H2O → glucose + fructose
A)synthetase or ligase
B)oxidoreductase
C)hydrolase
D)transferase
E)isomerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of a cis double bond to a trans double bond is classified as a(an)
A)ligase.
B)isomerase.
C)oxidoreductase.
D)transferase.
E)hydrolase.
A)ligase.
B)isomerase.
C)oxidoreductase.
D)transferase.
E)hydrolase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The maximum number of substrate molecules that one enzyme molecule can act on in a given unit of time is the
A)turnover number.
B)equilibrium constant.
C)rate constant.
D)reduction factor.
E)catalytic multiplier.
A)turnover number.
B)equilibrium constant.
C)rate constant.
D)reduction factor.
E)catalytic multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The name of an enzyme can often be recognized by the ending
A)-ase.
B)-ate.
C)-ic acid.
D)-ene.
E)-ose.
A)-ase.
B)-ate.
C)-ic acid.
D)-ene.
E)-ose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Substances the bind to an enzyme and increase its activity are called
A)negative regulators.
B)positive regulators.
C)allosteric regulators.
D)neutral regulators.
A)negative regulators.
B)positive regulators.
C)allosteric regulators.
D)neutral regulators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The mechanism of enzyme control that is similar to noncompetitive inhibition because both involve interactions with the enzyme at locations other than the active site is
A)feedback inhibition.
B)zymogen production.
C)zymogen activation.
D)allosteric interaction.
E)genetic control.
A)feedback inhibition.
B)zymogen production.
C)zymogen activation.
D)allosteric interaction.
E)genetic control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Explain how an allosteric enzyme is regulated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The theory of enzyme mechanism that suggests a flexible molecule whose shape is altered by the reaction conditions is the ________ model.
A)coenzyme
B)induced-fit
C)lock-and-key
D)substrate specific
E)active site
A)coenzyme
B)induced-fit
C)lock-and-key
D)substrate specific
E)active site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Enzymes that are affected by the binding of an inhibitor are called
A)induced enzymes.
B)allosteric enzymes.
C)proenzymes.
D)zymogens.
E)controlled enzymes.
A)induced enzymes.
B)allosteric enzymes.
C)proenzymes.
D)zymogens.
E)controlled enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A multi-step biochemical process in which the rate of an early step is affected by the concentration of products of a later step is said to be subject to
A)decomposition.
B)feedback control.
C)hydrolysis.
D)pH control.
E)all of the above
A)decomposition.
B)feedback control.
C)hydrolysis.
D)pH control.
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a normal biochemical system,the rate of a specific reaction is determined by
A)pH and temperature.
B)pH and enzyme efficiency.
C)temperature and enzyme efficiency.
D)temperature and substrate concentration.
E)enzyme efficiency and substrate concentration.
A)pH and temperature.
B)pH and enzyme efficiency.
C)temperature and enzyme efficiency.
D)temperature and substrate concentration.
E)enzyme efficiency and substrate concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How is the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction affected by increasing enzyme concentration?
A)The rate increases as the concentration of enzyme increases with excess substrate.
B)The rate decreases as the concentration of enzyme increases.
C)The rate initially increases as the concentration of enzyme increases,but then remains constant in spite of increasing amount of enzyme.
D)The rate initially increases as the concentration of enzyme increases,but then decreases once the concentration of enzyme passes an optimum level.
E)none of the above
A)The rate increases as the concentration of enzyme increases with excess substrate.
B)The rate decreases as the concentration of enzyme increases.
C)The rate initially increases as the concentration of enzyme increases,but then remains constant in spite of increasing amount of enzyme.
D)The rate initially increases as the concentration of enzyme increases,but then decreases once the concentration of enzyme passes an optimum level.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When there is an increase in temperature it can affect an enzyme-catalyzed reaction by
A)increasing the reaction rate
B)decreasing the reaction rate
C)both increasing and decreasing the reaction rate
D)causing a different substrate to be used
A)increasing the reaction rate
B)decreasing the reaction rate
C)both increasing and decreasing the reaction rate
D)causing a different substrate to be used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is the typical shape of a plot showing the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of the pH?
A)
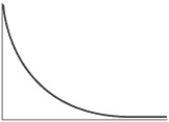
B)
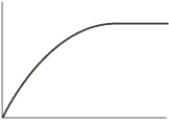
C)
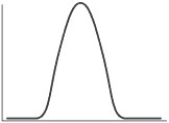
D)
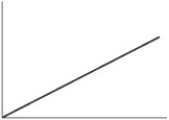
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which factor is not important in explaining how enzymes work?
A)Two different substrate molecules are brought into close contact.
B)Substrates are brought into solution more easily.
C)The bonds in substrates are subjected to strains which weaken them.
D)Substrates are forced into the correct orientation for interaction.
E)Substrates are placed near acidic or basic sites.
A)Two different substrate molecules are brought into close contact.
B)Substrates are brought into solution more easily.
C)The bonds in substrates are subjected to strains which weaken them.
D)Substrates are forced into the correct orientation for interaction.
E)Substrates are placed near acidic or basic sites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When an enzyme is saturated it
A)has been completely consumed,and that reaction cannot occur again until new enzymes are produced.
B)is in high concentration relative to the substrate,and the reaction rate is directly proportional to substrate concentration.
C)is in low concentration relative to the substrate,and the reaction rate is directly proportional to enzyme concentration.
D)is in low concentration relative to the substrate,and the reaction rate approaches its maximum.
E)none of the above
A)has been completely consumed,and that reaction cannot occur again until new enzymes are produced.
B)is in high concentration relative to the substrate,and the reaction rate is directly proportional to substrate concentration.
C)is in low concentration relative to the substrate,and the reaction rate is directly proportional to enzyme concentration.
D)is in low concentration relative to the substrate,and the reaction rate approaches its maximum.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The theory of enzyme mechanism that suggests a rigid,inflexible molecule is the ________ model.
A)coenzyme
B)induced-fit
C)lock-and-key
D)substrate specific
E)active site
A)coenzyme
B)induced-fit
C)lock-and-key
D)substrate specific
E)active site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When substrate molecules occupy all of the active sites in the enzyme available for a particular reaction,the enzyme is said to be
A)denatured.
B)hydrolyzed.
C)activated.
D)inhibited.
E)saturated.
A)denatured.
B)hydrolyzed.
C)activated.
D)inhibited.
E)saturated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Enzymes that are affected by the binding of an activator are called
A)zymogens.
B)proenzymes.
C)allosteric enzymes.
D)induced enzymes.
A)zymogens.
B)proenzymes.
C)allosteric enzymes.
D)induced enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Enzymes have an optimum temperature for their catalytic activity.This is best explained by the balance between the ________ number of collisions and the ________ rate of denaturation of the enzyme as temperatures increase.
A)increased; increased
B)decreased; increased
C)increased; decreased
D)decreased; decreased
E)none of the above
A)increased; increased
B)decreased; increased
C)increased; decreased
D)decreased; decreased
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
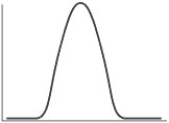
Which of the following is the typical shape of a plot showing the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of the enzyme concentration with excess substrate?
A)
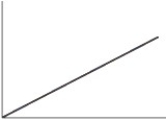
B)
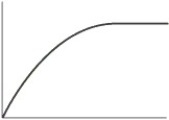
C)
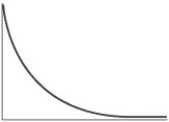
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following does not generally increase the rate of a reaction?
A)increasing the reactants
B)increasing the products
C)increasing the temperature
D)adding the catalyst
A)increasing the reactants
B)increasing the products
C)increasing the temperature
D)adding the catalyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When a molecule similar to the correct substrate interacts with the active site of an enzyme,the process is called
A)competitive inhibition.
B)noncompetitive inhibition.
C)irreversible inhibition.
D)activation.
E)covalent modification.
A)competitive inhibition.
B)noncompetitive inhibition.
C)irreversible inhibition.
D)activation.
E)covalent modification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Explain the term feedback as a mechanism for control of biochemical reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
All of the following statements concerning vitamins are true except
A)fat-soluble vitamins have a high proportion of polar carbonyl and hydroxyl groups.
B)it is possible to overdose on fat-soluble vitamins because they accumulate in fatty tissues.
C)it is difficult to overdose on water-soluble vitamins because excess amounts can be excreted in the urine.
D)vitamins A,D,E,and K are fat-soluble.
E)vitamin C and the B vitamins are water-soluble.
A)fat-soluble vitamins have a high proportion of polar carbonyl and hydroxyl groups.
B)it is possible to overdose on fat-soluble vitamins because they accumulate in fatty tissues.
C)it is difficult to overdose on water-soluble vitamins because excess amounts can be excreted in the urine.
D)vitamins A,D,E,and K are fat-soluble.
E)vitamin C and the B vitamins are water-soluble.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The genetic control strategy of enzyme control is most useful for production of enzymes that
A)act as hydrolases.
B)function for only one specific reaction.
C)are produced as zymogens.
D)require vitamins as cofactors.
E)are needed only at certain stages of development.
A)act as hydrolases.
B)function for only one specific reaction.
C)are produced as zymogens.
D)require vitamins as cofactors.
E)are needed only at certain stages of development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Activation of zymogens involves the chemical process of
A)hydrogen bonding.
B)covalent modification.
C)complete hydrolysis.
D)denaturation.
E)oxidation-reduction.
A)hydrogen bonding.
B)covalent modification.
C)complete hydrolysis.
D)denaturation.
E)oxidation-reduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Another term for substances that bind irreversibly with the active site of an enzyme is
A)activators.
B)poisons.
C)coenzymes.
D)hormones.
E)zymogens.
A)activators.
B)poisons.
C)coenzymes.
D)hormones.
E)zymogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When a metal ion such as Pb(II)interferes with the functioning of an enzyme,the most probable mechanism is
A)feedback control.
B)reversible noncompetitive inhibition.
C)genetic control.
D)reversible competitive inhibition.
E)irreversible inhibition.
A)feedback control.
B)reversible noncompetitive inhibition.
C)genetic control.
D)reversible competitive inhibition.
E)irreversible inhibition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following fat-soluble vitamins is associated with good night vision?
A)Vitamin A
B)Vitamin D
C)Vitamin E
D)Vitamin K
E)More than one answer is possible.
A)Vitamin A
B)Vitamin D
C)Vitamin E
D)Vitamin K
E)More than one answer is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
All of the following vitamins are fat soluble except
A)Vitamin A.
B)Vitamin K.
C)Vitamin C.
D)Vitamin D.
E)Vitamin E.
A)Vitamin A.
B)Vitamin K.
C)Vitamin C.
D)Vitamin D.
E)Vitamin E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If a covalent bond forms between an enzyme and an inhibitor the reaction catalyzed by this enzyme will have undergone ________.
A)irreversible inhibition
B)competitive inhibition
C)noncompetitive inhibition
D)feedback control
E)genetic control
A)irreversible inhibition
B)competitive inhibition
C)noncompetitive inhibition
D)feedback control
E)genetic control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A compound that is necessary for the synthesis of another compound is called a(an)
A)allosteric inhibitor.
B)cofactor.
C)precursor.
D)proenzyme.
E)zymogen.
A)allosteric inhibitor.
B)cofactor.
C)precursor.
D)proenzyme.
E)zymogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Antioxidants contribute to good health by reacting with
A)coenzymes.
B)vitamins.
C)hormones.
D)free radicals.
E)hydrogen ions.
A)coenzymes.
B)vitamins.
C)hormones.
D)free radicals.
E)hydrogen ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Poisons such as heavy metal ions or insecticides can disrupt enzyme function by
A)competitive inhibition.
B)irreversible inhibition.
C)disruption of tertiary structure.
D)covalent modification.
E)all of the above
A)competitive inhibition.
B)irreversible inhibition.
C)disruption of tertiary structure.
D)covalent modification.
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
All of the following are mechanisms for control of enzyme activity except
A)inhibition.
B)feedback.
C)allosteric interactions.
D)genetic regulation.
E)hydrolysis.
A)inhibition.
B)feedback.
C)allosteric interactions.
D)genetic regulation.
E)hydrolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which mechanism of enzyme control determines the amount of enzyme available?
A)allosteric control
B)competitive inhibition
C)zymogen production
D)covalent modification
E)genetic control
A)allosteric control
B)competitive inhibition
C)zymogen production
D)covalent modification
E)genetic control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When a molecule other than the correct substrate interacts with some part of an enzyme to alter the shape of the active site,the process is called
A)competitive inhibition.
B)noncompetitive inhibition.
C)irreversible inhibition.
D)activation.
E)covalent modification.
A)competitive inhibition.
B)noncompetitive inhibition.
C)irreversible inhibition.
D)activation.
E)covalent modification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which is the correct term for the inactive form of an enzyme,often used for transport or storage?
A)coenzyme
B)apoenzyme
C)zymogen
D)inhibitor
E)activator
A)coenzyme
B)apoenzyme
C)zymogen
D)inhibitor
E)activator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Some enzymes are produced as zymogens because
A)the reactions they catalyze are undesirable at the site of production.
B)they must have both an active site and an allosteric site,and these can't be produced simultaneously.
C)the actual enzyme molecules are so large that they must be produced in pieces and assembled as needed.
D)the pH at the site of production is very different from the pH at the site where they are used.
E)none of these
A)the reactions they catalyze are undesirable at the site of production.
B)they must have both an active site and an allosteric site,and these can't be produced simultaneously.
C)the actual enzyme molecules are so large that they must be produced in pieces and assembled as needed.
D)the pH at the site of production is very different from the pH at the site where they are used.
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
All of the following are B vitamins except
A)ascorbic acid.
B)cobalamin.
C)niacin.
D)pantothenic acid.
E)thiamine.
A)ascorbic acid.
B)cobalamin.
C)niacin.
D)pantothenic acid.
E)thiamine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A vitamin is
A)a nutrient involving trace metals that is necessary for good health.
B)a polypeptide used to manufacture enzymes.
C)a lipid complex which is an important part of all cells.
D)a small organic molecule obtained from the diet and necessary for good health.
E)a complex molecule of four interlocking hydrocarbon rings.
A)a nutrient involving trace metals that is necessary for good health.
B)a polypeptide used to manufacture enzymes.
C)a lipid complex which is an important part of all cells.
D)a small organic molecule obtained from the diet and necessary for good health.
E)a complex molecule of four interlocking hydrocarbon rings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following fat-soluble vitamins is associated with blood clotting factors?
A)Vitamin A
B)Vitamin D
C)Vitamin E
D)Vitamin K
E)More than one answer is possible.
A)Vitamin A
B)Vitamin D
C)Vitamin E
D)Vitamin K
E)More than one answer is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Noncompetitive inhibition can be overcome by
A)increasing the concentration of substrate.
B)increasing the concentration of enzyme.
C)decreasing the concentration of inhibitor.
D)decreasing the concentration of products.
E)decreasing the concentration of substrate.
A)increasing the concentration of substrate.
B)increasing the concentration of enzyme.
C)decreasing the concentration of inhibitor.
D)decreasing the concentration of products.
E)decreasing the concentration of substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match the following.
lyase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
lyase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match the following.
antioxidant
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
antioxidant
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match the following.
ligase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
ligase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Match the following.
inhibition
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
inhibition
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match the following.
transferase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
transferase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Overdosing on vitamins A and D is more likely than overdosing on vitamin C because
A)vitamins A and D are fat soluble and thus can accumulate in body fat,where vitamin C is water soluble and the excess will be excreted in urine.
B)vitamin C is fat soluble and thus can accumulate in body fat,where vitamins A and D are water soluble and the excess will be excreted in urine.
C)vitamin C is biologically active as consumed in foods,but vitamins A and D must be converted into biologically active forms before utilization.
D)vitamins A and D are biologically active as consumed in foods,but vitamin C must be converted into biologically active forms before utilization.
E)vitamins A and D are needed in much larger doses than vitamin C.
A)vitamins A and D are fat soluble and thus can accumulate in body fat,where vitamin C is water soluble and the excess will be excreted in urine.
B)vitamin C is fat soluble and thus can accumulate in body fat,where vitamins A and D are water soluble and the excess will be excreted in urine.
C)vitamin C is biologically active as consumed in foods,but vitamins A and D must be converted into biologically active forms before utilization.
D)vitamins A and D are biologically active as consumed in foods,but vitamin C must be converted into biologically active forms before utilization.
E)vitamins A and D are needed in much larger doses than vitamin C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Match the following.
induced-fit model
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
induced-fit model
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Match the following.
oxidoreductase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
oxidoreductase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Match the following.
vitamin
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
vitamin
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Match the following.
lock-and-key model
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
lock-and-key model
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Match the following.
hydrolase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
hydrolase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Match the following.
turnover number
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
turnover number
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Match the following.
isomerase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
isomerase
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match the following.
zymogen
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
zymogen
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match the following.
activation
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
activation
A)a description of the catalytic activity of an enzyme,where a small value means that very few molecules are acted on in a unit of time
B)a substance that prevents harmful reactions of free radicals
C)any process that increases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
D)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a small molecule from a larger one
E)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the internal rearrangement of molecules
F)an inactive form of an enzyme; also called a proenzyme
G)a description of enzyme activity based on an exact match between the shapes of the active site and the substrate molecule
H)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules together
I)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
J)a type of enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of large molecules by reaction with water
K)a description of enzyme activity based on the ability of the enzyme to change shape in order to accommodate substrate molecules
L)a type of enzyme that catalyzes oxidation or reduction reactions
M)a small organic molecule necessary for good health that must be obtained in the diet
N)any process which decreases the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



