Deck 18: Amino Acids and Proteins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/88
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Amino Acids and Proteins
1
All of the following are major functions of proteins except
A)transport of necessary chemicals.
B)protection against foreign substances.
C)support for organs or tissues.
D)control of biochemical reactions.
E)storage of energy.
A)transport of necessary chemicals.
B)protection against foreign substances.
C)support for organs or tissues.
D)control of biochemical reactions.
E)storage of energy.
storage of energy.
2
Which molecule is an alpha amino acid?
A)
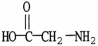
B)
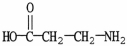
C)
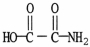
D)
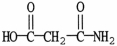
E)
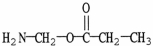
A)
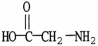
B)
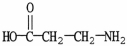
C)
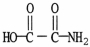
D)

E)

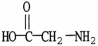
3
The side chains or R groups of amino acids can be classified into each of the following categories except
A)polar.
B)non-polar.
C)basic.
D)acidic.
E)isoelectric.
A)polar.
B)non-polar.
C)basic.
D)acidic.
E)isoelectric.
isoelectric.
4
Polar R groups,along with acidic and basic R groups,are said to be ________ because they are attracted to water molecules.
A)hydrophilic
B)hydrophobic
C)ionized
D)unreactive
E)none of these
A)hydrophilic
B)hydrophobic
C)ionized
D)unreactive
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An amino acid whose R group is predominantly hydrocarbon would be classified as
A)polar.
B)non-polar.
C)basic.
D)acidic.
E)isoelectric.
A)polar.
B)non-polar.
C)basic.
D)acidic.
E)isoelectric.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Insulin is an example of a(an)
A)enzyme.
B)structural protein.
C)storage protein.
D)transport protein.
E)hormone.
A)enzyme.
B)structural protein.
C)storage protein.
D)transport protein.
E)hormone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
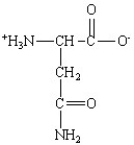
Which of the following is the structure for the amino acid with the abbreviation of Asn?
A)
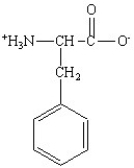
B)
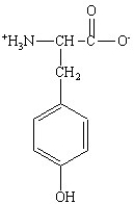
C)
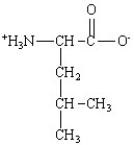
D)
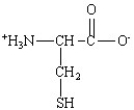
E)
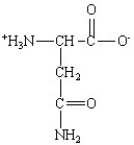
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Oxytocin is a small protein that induces smooth muscle causing contractions during labor.What class of proteins would this belong to?
A)storage protein
B)transport protein
C)hormone
D)structural protein
E)protective protein
A)storage protein
B)transport protein
C)hormone
D)structural protein
E)protective protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which functional group is least important in biochemistry?
A)amide
B)amine
C)aromatic
D)ester
E)hydroxyl
A)amide
B)amine
C)aromatic
D)ester
E)hydroxyl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Non-polar R groups on amino acids are said to be ________ because they are not attracted to water molecules.
A)hydrophilic
B)hydrophobic
C)ionized
D)unreactive
E)none of these
A)hydrophilic
B)hydrophobic
C)ionized
D)unreactive
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except
A)carbohydrates.
B)proteins.
C)lipids.
D)nucleic acids.
E)All of the above are biomolecules.
A)carbohydrates.
B)proteins.
C)lipids.
D)nucleic acids.
E)All of the above are biomolecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is the structure for the amino acid with the abbreviation of Phe?
A)
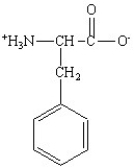
B)
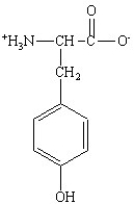
C)
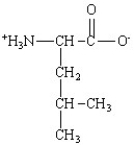
D)
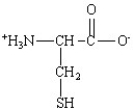
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which category of amino acid contains R groups that are hydrophobic?
A)polar
B)non-polar
C)basic
D)acidic
E)basic and acidic
A)polar
B)non-polar
C)basic
D)acidic
E)basic and acidic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Collagen is an example of a(an)
A)enzyme.
B)structural protein.
C)storage protein.
D)transport protein.
E)hormone.
A)enzyme.
B)structural protein.
C)storage protein.
D)transport protein.
E)hormone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Two functional groups that are present in all amino acids are the ________ group and the ________ group.
A)hydroxyl;amide
B)carboxyl;amine
C)carboxyl;phosphate ester
D)acetal;amine
E)carbonyl;amide
A)hydroxyl;amide
B)carboxyl;amine
C)carboxyl;phosphate ester
D)acetal;amine
E)carbonyl;amide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following amino acids contains an alcohol group?
A)Phe
B)Val
C)Asp
D)Thr
E)Cys
A)Phe
B)Val
C)Asp
D)Thr
E)Cys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Serum albumin is an example of a(an)
A)enzyme.
B)structural protein.
C)storage protein.
D)transport protein.
E)protective protein.
A)enzyme.
B)structural protein.
C)storage protein.
D)transport protein.
E)protective protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Myoglobin is a protein that contains oxygen in the muscle.What class of protein does it belong to?
A)storage protein
B)transport protein
C)structural protein
D)protective protein
E)enzyme
A)storage protein
B)transport protein
C)structural protein
D)protective protein
E)enzyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which amino acid is a secondary amine with its nitrogen and the alpha-carbon joined as part of a ring structure?
A)arginine
B)glycine
C)histidine
D)lysine
E)proline
A)arginine
B)glycine
C)histidine
D)lysine
E)proline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Members of which class of biomolecules are the building blocks of proteins?
A)glycerols
B)monosaccharides
C)fatty acids
D)amino acids
E)nucleic acids
A)glycerols
B)monosaccharides
C)fatty acids
D)amino acids
E)nucleic acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of these amino acids has a thiol group as part of its side chain?
A)cysteine
B)tyrosine
C)histidine
D)threonine
E)methionine
A)cysteine
B)tyrosine
C)histidine
D)threonine
E)methionine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Using three letter designation,write the six tripeptides that can be formed from the combination of serine,tyrosine and aspartate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which amino acid is classified as basic?
A)valine
B)threonine
C)phenylalanine
D)lysine
E)glutamic acid
A)valine
B)threonine
C)phenylalanine
D)lysine
E)glutamic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which amino acid is not chiral?
A)alanine
B)arginine
C)cysteine
D)glycine
E)phenylalanine
A)alanine
B)arginine
C)cysteine
D)glycine
E)phenylalanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An amino acid has the form shown at 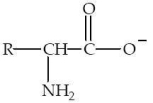
A)a pH of 7.0.
B)any pH other than 7.0.
C)a pH greater than its isoelectric point.
D)its isoelectric point.
E)a pH less than its isoelectric point.

A)a pH of 7.0.
B)any pH other than 7.0.
C)a pH greater than its isoelectric point.
D)its isoelectric point.
E)a pH less than its isoelectric point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How many different tripeptides can be formed from one molecule each of the amino acids tyrosine,valine,and alanine?
A)3
B)6
C)9
D)12
E)24
A)3
B)6
C)9
D)12
E)24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
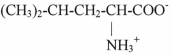
This question has four parts:
A) For the amino acid shown above in zwitterion form,circle the carboxyl group,underline the amine group,label the alpha carbon,and draw a box around the R group.
B) Write the name and abbreviation of your amino acid.
C) Classify the amino acid as polar,non-polar,acidic,or basic.Explain the basis for your classification.
D)Draw the structure of the amino acid at a pH well below its isoelectric point and well above its isoelectric point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The peptide bond joining amino acids into proteins is a specific example of the ________ bond.
A)amide
B)carbonyl
C)ester
D)glycosidic
E)hydrogen
A)amide
B)carbonyl
C)ester
D)glycosidic
E)hydrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Amino acids used in proteins generally are
A)α-amino acids.
B)l-amino acids.
C)d-amino acids.
D)All are correct.
E)None are correct.
A)α-amino acids.
B)l-amino acids.
C)d-amino acids.
D)All are correct.
E)None are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The pH at which the positive and negative charges of an amino acid balance each other is called the
A)isoelectric point.
B)isobaric point.
C)isobestic point.
D)isotonic point.
E)isomer point.
A)isoelectric point.
B)isobaric point.
C)isobestic point.
D)isotonic point.
E)isomer point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Amino acids are least soluble in water at
A)their isoelectric point.
B)low pH.
C)neutral pH.
D)high pH.
E)both high and low pH.
A)their isoelectric point.
B)low pH.
C)neutral pH.
D)high pH.
E)both high and low pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which structure represents a zwitterion?
A)
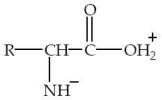
B)
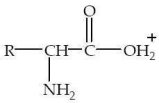
C)
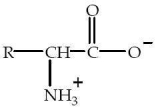
D)

E)
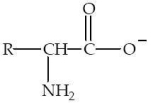
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which amino acid is classified as neutral and non-polar?
A)aspartic acid
B)histidine
C)phenylalanine
D)lysine
E)tyrosine
A)aspartic acid
B)histidine
C)phenylalanine
D)lysine
E)tyrosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Amino acids found in proteins all have which of the following features?
A)All are α-amino acids.
B)All are l-amino acids.
C)All are d-amino acids.
D)All are correct.
E)None are correct.
A)All are α-amino acids.
B)All are l-amino acids.
C)All are d-amino acids.
D)All are correct.
E)None are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An amino acid will have the form shown at 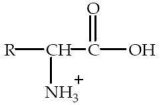
A)a pH of 7.0.
B)any pH other than 7.0.
C)a pH greater than its isoelectric point.
D)its isoelectric point.
E)a pH less than its isoelectric point.

A)a pH of 7.0.
B)any pH other than 7.0.
C)a pH greater than its isoelectric point.
D)its isoelectric point.
E)a pH less than its isoelectric point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The isoelectric point of an amino acid is the pH
A)at which it exists in the basic form.
B)at which it exists in the acid form.
C)at which it exists in the zwitterion form.
D)equal to its pKa.
E)equal to its pKb.
A)at which it exists in the basic form.
B)at which it exists in the acid form.
C)at which it exists in the zwitterion form.
D)equal to its pKa.
E)equal to its pKb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The reaction of amino acids to give peptides involves which pair of functional groups?
A)two amino groups
B)two carboxyl groups
C)an amino and a carboxyl group
D)a carboxyl and an alcohol group
A)two amino groups
B)two carboxyl groups
C)an amino and a carboxyl group
D)a carboxyl and an alcohol group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The tripeptide represented as ala-leu-gly is named
A)alanine-glycine-leucine.
B)alanylglycylleucine.
C)alanine-leucine-glycine.
D)alanylleucylglycine.
E)none of these
A)alanine-glycine-leucine.
B)alanylglycylleucine.
C)alanine-leucine-glycine.
D)alanylleucylglycine.
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following amino acids contains two chiral centers?
A)leucine
B)isoleucine
C)proline
D)valine
E)phenylalanine
A)leucine
B)isoleucine
C)proline
D)valine
E)phenylalanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Draw the tripeptide as it would be found at pH = 7: ala-gly-phe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
All of the following are globular proteins except
A)myosin.
B)ribonuclease.
C)hemoglobin.
D)albumin.
E)immunoglobulin.
A)myosin.
B)ribonuclease.
C)hemoglobin.
D)albumin.
E)immunoglobulin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Illustrate the backbone of a protein using a planar unit from one Ca carbon to the next Ca.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which type of forces form the primary structure of a protein?
A)peptide
B)hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl group and amino group
C)salt bridges
D)dipole-dipole interactions
E)disulfide bonds
A)peptide
B)hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl group and amino group
C)salt bridges
D)dipole-dipole interactions
E)disulfide bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which protein is considered to be a globular protein?
A)albumin
B)keratin
C)collagen
D)myosin
A)albumin
B)keratin
C)collagen
D)myosin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In the tetrapeptide Ala-Cys-Val-Leu,the N-terminal amino acid is
A)Ala.
B)Cys.
C)Val.
D)Leu.
E)none of the above
A)Ala.
B)Cys.
C)Val.
D)Leu.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The beta-pleated sheet is an example of
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)quaternary structure.
E)none of the above
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)quaternary structure.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
All of the following are examples of fibrous proteins except
A)wool.
B)fingernails.
C)skin.
D)insulin.
E)bones.
A)wool.
B)fingernails.
C)skin.
D)insulin.
E)bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The two protein chains in insulin are held together by
A)disulfide linkages.
B)hydrophobic interactions.
C)hydrogen bonds.
D)salt bridges.
E)all of the above
A)disulfide linkages.
B)hydrophobic interactions.
C)hydrogen bonds.
D)salt bridges.
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Where in a protein structure are basic groups located?
A)at the N-terminal end
B)at the C-terminal end
C)on the Lys,Arg,and His side chains
D)both A and C
E)none of the above
A)at the N-terminal end
B)at the C-terminal end
C)on the Lys,Arg,and His side chains
D)both A and C
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The difference between normal and sickle cell hemoglobin is in which structure?
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
All of the following are non-covalent interactions important in maintaining the secondary,tertiary,and quaternary aspects of amino acids except
A)sulfur-sulfur bonds.
B)hydrogen bonding along the backbone.
C)hydrogen bonding between R groups.
D)salt bridges between R groups.
E)hydrophobic interactions between R groups.
A)sulfur-sulfur bonds.
B)hydrogen bonding along the backbone.
C)hydrogen bonding between R groups.
D)salt bridges between R groups.
E)hydrophobic interactions between R groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The type of bond that is most important in maintaining secondary structure of a protein is
A)disulfide bridges.
B)hydrogen bonding within the backbone.
C)hydrogen bonding between R groups.
D)salt bridges.
E)hydrophobic interactions.
A)disulfide bridges.
B)hydrogen bonding within the backbone.
C)hydrogen bonding between R groups.
D)salt bridges.
E)hydrophobic interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the tetrapeptide Ala-Cys-Val-Leu,the C-terminal amino acid is
A)Ala.
B)Cys.
C)Val.
D)Leu.
E)none of the above
A)Ala.
B)Cys.
C)Val.
D)Leu.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The type of bonding that maintains the secondary structure in a protein is the
A)hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl and amino groups of the backbone.
B)covalent bond between the carbonyl and amino groups of the amino acids.
C)hydrogen bonds between two amino acids.
D)disulfide bonds that hold two polypeptide chains together.
E)hydrogen bonds between two amino groups.
A)hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl and amino groups of the backbone.
B)covalent bond between the carbonyl and amino groups of the amino acids.
C)hydrogen bonds between two amino acids.
D)disulfide bonds that hold two polypeptide chains together.
E)hydrogen bonds between two amino groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
By convention,the N-terminal end of a protein is usually placed on the ________ of a protein structure.
A)right side
B)left side
C)center
D)bottom
E)top
A)right side
B)left side
C)center
D)bottom
E)top

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The N-terminal amino acid in the peptide Ala-Leu-Gly-His-Pro is
A)alanine.
B)leucine.
C)glycine.
D)histidine.
E)proline.
A)alanine.
B)leucine.
C)glycine.
D)histidine.
E)proline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The amino acid sequence of a protein is known as its
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)quaternary structure.
E)none of the above
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)quaternary structure.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Keratin,the protein of hair and skin,has extensive sections with which secondary structure?
A)beta-pleated sheet
B)alpha-helix
C)random coil
D)alpha-beta
A)beta-pleated sheet
B)alpha-helix
C)random coil
D)alpha-beta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which structure among the following represents an amide (protein)bond?
A)
B)
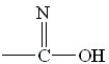
C)
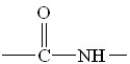
D)
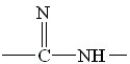
E)
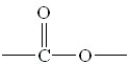
A)

B)
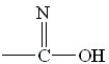
C)
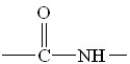
D)
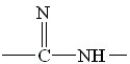
E)
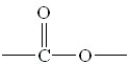

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The C-terminal amino acid in the peptide Ala-Leu-Gly-His-Pro is
A)alanine.
B)leucine.
C)glycine.
D)histidine.
E)proline.
A)alanine.
B)leucine.
C)glycine.
D)histidine.
E)proline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When a protein is ________,its primary structure is destroyed,thus destroying the other aspects of its structure.
A)denatured
B)hydrolyzed
C)ionized
D)polymerized
E)esterified
A)denatured
B)hydrolyzed
C)ionized
D)polymerized
E)esterified

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which type of interaction is not directly involved in maintaining tertiary structure?
A)disulfide bridges
B)hydrogen bonding
C)peptide bonds
D)salt bridges
E)hydrophobic interactions
A)disulfide bridges
B)hydrogen bonding
C)peptide bonds
D)salt bridges
E)hydrophobic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match the following.
hydrophobic
A)refers to R groups which form hydrogen bonds with water because of their polarity
B)refers to R groups that do not interact readily with water because they are non-polar
C)a protein that is usually insoluble in water,is very tough,and has a long shape
D)a carbon atom bonded to four different groups and therefore able to form enantiomers
E)a protein that produces amino acids and other biomolecules or inorganic substances
F)a protein with the tertiary structure in which it normally occurs in living systems
G)a protein that produces only amino acids upon hydrolysis
H)a protein that is usually water soluble,having a hydrophilic exterior and hydrophobic interior,and an overall rounded shape
I)the form of an amino acid in which both the carboxyl group and the amine group are charged,but the overall molecule remains neutral
hydrophobic
A)refers to R groups which form hydrogen bonds with water because of their polarity
B)refers to R groups that do not interact readily with water because they are non-polar
C)a protein that is usually insoluble in water,is very tough,and has a long shape
D)a carbon atom bonded to four different groups and therefore able to form enantiomers
E)a protein that produces amino acids and other biomolecules or inorganic substances
F)a protein with the tertiary structure in which it normally occurs in living systems
G)a protein that produces only amino acids upon hydrolysis
H)a protein that is usually water soluble,having a hydrophilic exterior and hydrophobic interior,and an overall rounded shape
I)the form of an amino acid in which both the carboxyl group and the amine group are charged,but the overall molecule remains neutral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
All of the following can denature proteins without hydrolysis except
A)heat.
B)mechanical stress.
C)enzyme treatment.
D)lowering of pH.
E)heavy metal ions.
A)heat.
B)mechanical stress.
C)enzyme treatment.
D)lowering of pH.
E)heavy metal ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
List three denaturing agents that can act on proteins and explain how each one disrupts the protein's structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which pair of amino acids can have ionic interactions?
A)arginine and glutamic acid
B)asparagine and lysine
C)leucine and alanine
D)glutamic acid and serine
E)glycine and asparagine
A)arginine and glutamic acid
B)asparagine and lysine
C)leucine and alanine
D)glutamic acid and serine
E)glycine and asparagine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which amino acid can form covalent sulfur-sulfur bonds?
A)cysteine
B)glycine
C)proline
D)methionine
E)phenylalanine
A)cysteine
B)glycine
C)proline
D)methionine
E)phenylalanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When a protein is ________,its primary structure is maintained,but other aspects of its structure are disrupted.
A)denatured
B)hydrolyzed
C)ionized
D)polymerized
E)esterified
A)denatured
B)hydrolyzed
C)ionized
D)polymerized
E)esterified

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
All of the following are conjugated proteins except
A)cytochrome oxidase.
B)low-density lipoproteins.
C)myoglobin.
D)collagen.
E)casein.
A)cytochrome oxidase.
B)low-density lipoproteins.
C)myoglobin.
D)collagen.
E)casein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What type of forces are responsible for maintaining the quaternary structure of a protein?
A)ionic bonds
B)hydrogen bonds
C)dipole-dipole
D)hydrophobic interactions
E)all of these
A)ionic bonds
B)hydrogen bonds
C)dipole-dipole
D)hydrophobic interactions
E)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
All of the following are examples of denaturing proteins except
A)souring of milk.
B)a mild sunburn.
C)using a curling iron on your hair.
D)pounding meat to tenderize it.
E)digestion of a meal.
A)souring of milk.
B)a mild sunburn.
C)using a curling iron on your hair.
D)pounding meat to tenderize it.
E)digestion of a meal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which pair of amino acids can form hydrogen bonds between their R groups?
A)arginine and glutamate
B)aspartate and lysine
C)leucine and alanine
D)glutamine and serine
E)glycine and asparagine
A)arginine and glutamate
B)aspartate and lysine
C)leucine and alanine
D)glutamine and serine
E)glycine and asparagine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Protein denaturation results in a disruption of the
A)primary structure.
B)secondary and tertiary structure.
C)primary and secondary structure.
D)quaternary structure.
A)primary structure.
B)secondary and tertiary structure.
C)primary and secondary structure.
D)quaternary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Detergents would most likely disrupt what type of stabilizing interaction?
A)salt bridges
B)hydrogen bonds
C)disulfide bonds
D)hydrophobic interactions
E)hydrophilic interactions
A)salt bridges
B)hydrogen bonds
C)disulfide bonds
D)hydrophobic interactions
E)hydrophilic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The quaternary structure of hemoglobin contains
A)two subunits.
B)four subunits.
C)six subunits.
D)eight subunits.
A)two subunits.
B)four subunits.
C)six subunits.
D)eight subunits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When a glycoprotein is hydrolyzed,the products would include
A)amino acids only.
B)amino acids plus metal ions.
C)amino acids plus carbohydrates.
D)amino acids plus lipids.
E)amino acids plus RNA.
A)amino acids only.
B)amino acids plus metal ions.
C)amino acids plus carbohydrates.
D)amino acids plus lipids.
E)amino acids plus RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which pair of amino acids can have hydrophobic interactions?
A)arginine and glutamic acid
B)aspartic acid and lysine
C)leucine and alanine
D)glutamic acid and serine
E)glycine and asparagine
A)arginine and glutamic acid
B)aspartic acid and lysine
C)leucine and alanine
D)glutamic acid and serine
E)glycine and asparagine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The protein configuration that is primarily determined from interactions between R groups is the
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)quaternary structure.
E)none of the above
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)quaternary structure.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Proteins that consist of two or more chains assembled into a large 3-dimensional structure are said to display
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)quaternary structure.
E)none of the above
A)primary structure.
B)secondary structure.
C)tertiary structure.
D)quaternary structure.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following processes involve protein denaturation?
A)permanent waving of hair
B)whipping cream
C)cooking egg whites
D)More than one response is correct.
A)permanent waving of hair
B)whipping cream
C)cooking egg whites
D)More than one response is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



