Deck 5: Classification and Balancing of Chemical Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/61
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Classification and Balancing of Chemical Reactions
1
In a balanced chemical equation
A)there are equal numbers of atoms on each side of the reaction arrow.
B)there are equal numbers of molecules on each side of the reaction arrow.
C)there are always the same number of products as there are reactants.
D)the number of atoms present in a reaction can vary when the conditions change during the reaction.
E)none of the above
A)there are equal numbers of atoms on each side of the reaction arrow.
B)there are equal numbers of molecules on each side of the reaction arrow.
C)there are always the same number of products as there are reactants.
D)the number of atoms present in a reaction can vary when the conditions change during the reaction.
E)none of the above
there are equal numbers of atoms on each side of the reaction arrow.
2
When the reaction shown is correctly balanced,the coefficients are:
________ KClO3 → ________ KCl + ________ O2
A)1;1;1
B)2;2;2
C)2;2;3
D)2;2;1
E)4;4;6
________ KClO3 → ________ KCl + ________ O2
A)1;1;1
B)2;2;2
C)2;2;3
D)2;2;1
E)4;4;6
2;2;3
3
Which statement regarding balanced chemical equations is not true?
A)The number of each kind of atom must be the same on each side.
B)Coefficients are used in front of formulas to balance the equation.
C)Subscripts may be changed to make an equation simpler to balance.
D)When no coefficient is written in front of a formula,the number "one" is assumed.
E)Reactants are written to the left of the arrow.
A)The number of each kind of atom must be the same on each side.
B)Coefficients are used in front of formulas to balance the equation.
C)Subscripts may be changed to make an equation simpler to balance.
D)When no coefficient is written in front of a formula,the number "one" is assumed.
E)Reactants are written to the left of the arrow.
Subscripts may be changed to make an equation simpler to balance.
4
Which is the correct equation for the reaction of magnesium with hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen and magnesium chloride?
A)Mg + 2 HCl → H2 + MgCl2
B)Mg + HCl → H + MgCl
C)2 Mg + 6 HCl → 3 H2 + 2 MgCl2
D)Mg + 2 HCl → 2 H + MgCl2
E)Mg + 3 HCl → 3 H + MgCl2
A)Mg + 2 HCl → H2 + MgCl2
B)Mg + HCl → H + MgCl
C)2 Mg + 6 HCl → 3 H2 + 2 MgCl2
D)Mg + 2 HCl → 2 H + MgCl2
E)Mg + 3 HCl → 3 H + MgCl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When the reaction shown is correctly balanced,the coefficients are:
________ Li + ________ Br2 → ________ LiBr
A)1;1;1
B)1;2;2
C)1;2;1
D)2;2;1
E)2;1;2
________ Li + ________ Br2 → ________ LiBr
A)1;1;1
B)1;2;2
C)1;2;1
D)2;2;1
E)2;1;2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following equations is not balanced?
A)C7H16 + O2 → 7 CO2 + 8 H2O
B)K2CrO4 + Pb(NO3)2 → 2 KNO3 + PbCrO4
C)4 Fe3O4 + O2 → 6 Fe2O3
D)3 AgNO3 + (NH4)3PO4 → Ag3PO4 + 3 NH4NO3
E)2 Al2O3 → 4 Al + 3 O2
A)C7H16 + O2 → 7 CO2 + 8 H2O
B)K2CrO4 + Pb(NO3)2 → 2 KNO3 + PbCrO4
C)4 Fe3O4 + O2 → 6 Fe2O3
D)3 AgNO3 + (NH4)3PO4 → Ag3PO4 + 3 NH4NO3
E)2 Al2O3 → 4 Al + 3 O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When the reaction shown is balanced,there are ________ atoms of oxygen and ________ atoms of hydrogen on each side.
_______ (NH4)2SO4(aq)+ _______ Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq)→ _______ BaSO4(s)+ _______ NH4C2H3O2(aq)
A)6;11
B)16;18
C)8;14
D)4;7
E)16;28
_______ (NH4)2SO4(aq)+ _______ Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq)→ _______ BaSO4(s)+ _______ NH4C2H3O2(aq)
A)6;11
B)16;18
C)8;14
D)4;7
E)16;28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Consider the balanced equation shown and identify the statement that is not true.
Na2SO4(aq)+ BaCl2(aq)→ 2 NaCl(aq)+ BaSO4(s)
A)The coefficient of sodium sulfate is one.
B)Barium sulfate is produced in solid form.
C)Barium chloride is dissolved in water.
D)The products are barium sulfate and sodium chloride.
E)2 NaCl (aq)could also be correctly written as Na2Cl2 (aq).
Na2SO4(aq)+ BaCl2(aq)→ 2 NaCl(aq)+ BaSO4(s)
A)The coefficient of sodium sulfate is one.
B)Barium sulfate is produced in solid form.
C)Barium chloride is dissolved in water.
D)The products are barium sulfate and sodium chloride.
E)2 NaCl (aq)could also be correctly written as Na2Cl2 (aq).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When the following reaction is balanced,the coefficient in front of carbon dioxide is:
________ C5H12 + ________ O2 → ________ CO2 + ________ H2O
A)5
B)6
C)12
D)10
E)11
________ C5H12 + ________ O2 → ________ CO2 + ________ H2O
A)5
B)6
C)12
D)10
E)11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The balanced equation for the reaction occurring when iron(III)oxide,a solid,is reduced with pure carbon to produce carbon dioxide and molten iron is
A)2 Fe3O(s)+ C(s)→ 6 Fe(l)+ CO2(g).
B)2 FeO3(s)+ 3 C(s)→ 2 Fe(l)+ 3 CO2(g).
C)4 Fe2O3(s) + 6 C s)→ 8 Fe l)+ 6 CO2(g).
D)2 FeO(s)+ C s)→ 2 Fe l)+ CO2(g).
E)2 Fe2O3(s) + 3 C(s)→ 4 Fe l)+ 3 CO2(g).
A)2 Fe3O(s)+ C(s)→ 6 Fe(l)+ CO2(g).
B)2 FeO3(s)+ 3 C(s)→ 2 Fe(l)+ 3 CO2(g).
C)4 Fe2O3(s) + 6 C s)→ 8 Fe l)+ 6 CO2(g).
D)2 FeO(s)+ C s)→ 2 Fe l)+ CO2(g).
E)2 Fe2O3(s) + 3 C(s)→ 4 Fe l)+ 3 CO2(g).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider the reaction shown and identify the statement that is not true.
CaCO3(s)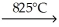 CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
A)This reaction is balanced as written.
B)The reactant must be heated for this reaction to occur.
C)The products are a solid and a gas.
D)Water must be present for this reaction to occur.
E)There are no solutions used in this reaction.
CaCO3(s)
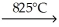 CaO(s)+ CO2(g)
CaO(s)+ CO2(g)A)This reaction is balanced as written.
B)The reactant must be heated for this reaction to occur.
C)The products are a solid and a gas.
D)Water must be present for this reaction to occur.
E)There are no solutions used in this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When the reaction shown is correctly balanced,the coefficients are:
________ C6H14(l)+ ________ O2(g)→ ________ CO2(g)+ ________ H2O(g)
A)1;6;6;7
B)2;19;12;14
C)1;3.5;6;7
D)1;9.5;6;7
E)2;16.5;12;7
________ C6H14(l)+ ________ O2(g)→ ________ CO2(g)+ ________ H2O(g)
A)1;6;6;7
B)2;19;12;14
C)1;3.5;6;7
D)1;9.5;6;7
E)2;16.5;12;7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the correctly balanced reaction,the coefficient for H2O is:
________ Al(OH)3 + ________ H2SO4 → ________ Al2(SO4)3 + ________ H2O
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)6
E)8
________ Al(OH)3 + ________ H2SO4 → ________ Al2(SO4)3 + ________ H2O
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)6
E)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When the reaction shown is correctly balanced,the coefficients are:
________ HNO3 + ________ KOH → ________ KNO3 + ________ H2O
A)0;0;0;0
B)1;1;1;1
C)2;2;2;2
D)3;1;1;3
E)2;1;2;1
________ HNO3 + ________ KOH → ________ KNO3 + ________ H2O
A)0;0;0;0
B)1;1;1;1
C)2;2;2;2
D)3;1;1;3
E)2;1;2;1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a precipitation reaction the insoluble product can be identified by the symbol
A)(aq).
B)(l).
C)(g).
D)(s).
E)none of the above
A)(aq).
B)(l).
C)(g).
D)(s).
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When the reaction shown is correctly balanced,the coefficients are:
________ HBr + ________ Ca(OH)2 → ________ CaBr2 + ________ H2O
A)2;1;1;1
B)1;1;1;2
C)2;1;1;2
D)2;2;1;1
E)2;1;2;2
________ HBr + ________ Ca(OH)2 → ________ CaBr2 + ________ H2O
A)2;1;1;1
B)1;1;1;2
C)2;1;1;2
D)2;2;1;1
E)2;1;2;2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The scientific principle which is the basis for balancing chemical equations is
A)the Law of Conservation of Energy.
B)the Law of Conservation of Mass.
C)the Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy.
D)the Law of Definite Proportions.
E)Avogadro's Law.
A)the Law of Conservation of Energy.
B)the Law of Conservation of Mass.
C)the Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy.
D)the Law of Definite Proportions.
E)Avogadro's Law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following equations is not balanced?
A)2 Na + 2 H2O → 2 NaOH + H2
B)C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3 CO2 + 4 H2O
C)2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
D)SO2 + O2 → SO3
E)2 Al + 6 HCl → 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2
A)2 Na + 2 H2O → 2 NaOH + H2
B)C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3 CO2 + 4 H2O
C)2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
D)SO2 + O2 → SO3
E)2 Al + 6 HCl → 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The balanced equation for the reaction occurring when calcium nitrate solution is mixed with sodium phosphate solution is
A)3 Ca(NO3)2(aq)+ 2 Na3PO4(aq)→ Ca3(PO4)2(aq)+ 6 NaNO3(aq).
B)2 Ca(NO3)2(aq)+ 3 Na3PO4(aq)→ 2 Ca3(PO4)2(s)+ 6 NaNO3(aq).
C)3 CaNO3(aq)+ Na3PO4(aq)→ Ca3PO4(aq)+ 3 NaNO3(s).
D)3 Ca(NO3)2(aq)+ 2 Na3PO4(aq)→ Ca3(PO4)2(s)+ 6 NaNO3(aq).
E)Ca(NO3)2(aq)+ 2 NaPO4(aq)→ Ca(PO4)2(s)+ 2 NaNO3(aq).
A)3 Ca(NO3)2(aq)+ 2 Na3PO4(aq)→ Ca3(PO4)2(aq)+ 6 NaNO3(aq).
B)2 Ca(NO3)2(aq)+ 3 Na3PO4(aq)→ 2 Ca3(PO4)2(s)+ 6 NaNO3(aq).
C)3 CaNO3(aq)+ Na3PO4(aq)→ Ca3PO4(aq)+ 3 NaNO3(s).
D)3 Ca(NO3)2(aq)+ 2 Na3PO4(aq)→ Ca3(PO4)2(s)+ 6 NaNO3(aq).
E)Ca(NO3)2(aq)+ 2 NaPO4(aq)→ Ca(PO4)2(s)+ 2 NaNO3(aq).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When the following reaction is balanced,the coefficient in front of oxygen is:
________ C8H18 + ________ O2 → ________ CO2 + ________ H2O
A)25
B)12
C)18
D)9
E)17
________ C8H18 + ________ O2 → ________ CO2 + ________ H2O
A)25
B)12
C)18
D)9
E)17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Write and balance the following acid-base neutralization reaction:
KOH(aq)+ H2SO4 aq)→
KOH(aq)+ H2SO4 aq)→

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which one of the following substances is produced during an acid/base (or neutralization)reaction?
A)H2
B)H2O
C)CO2
D)NaOH
E)NaCl
A)H2
B)H2O
C)CO2
D)NaOH
E)NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The balanced equation for the reaction between aqueous ammonium sulfate and aqueous barium acetate is
A)(NH4)2SO4(aq)+ Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq)→ BaSO4(s)+ NH4C2H3O2(aq).
B)(NH4)2SO4(aq)+ Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq)→ BaSO4(s)+ 2 NH4C2H3O2(aq).
C)NH4SO4(aq)+ BaC2H3O2(aq)→ BaSO4(s)+ NH4C2H3O2(aq).
D)(NH4)2SO4(aq)+ Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq)→ BaSO4(aq)+ 2 NH4C2H3O2(s).
E)(NH4)2SO3(aq)+ Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq)→ BaSO3(aq)+ NH4C2H3O2(aq).
A)(NH4)2SO4(aq)+ Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq)→ BaSO4(s)+ NH4C2H3O2(aq).
B)(NH4)2SO4(aq)+ Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq)→ BaSO4(s)+ 2 NH4C2H3O2(aq).
C)NH4SO4(aq)+ BaC2H3O2(aq)→ BaSO4(s)+ NH4C2H3O2(aq).
D)(NH4)2SO4(aq)+ Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq)→ BaSO4(aq)+ 2 NH4C2H3O2(s).
E)(NH4)2SO3(aq)+ Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq)→ BaSO3(aq)+ NH4C2H3O2(aq).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which reaction is not an example of a redox reaction?
A)2 Hg(l)+ O2(g)→ 2 HgO(s)
B)2 (NH4)3PO4(aq)+ 3 Ba(NO3)2(aq)→ Ba3(PO4)2(s)+ 6 NH4NO3(aq)
C)CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
D)6 HCl(aq)+ 2 Al(s)→ 2 AlCl3(aq)+ 3 H2(g)
E)2 Al2O3(s)→ 4 Al(s)+ 3 O(g)
A)2 Hg(l)+ O2(g)→ 2 HgO(s)
B)2 (NH4)3PO4(aq)+ 3 Ba(NO3)2(aq)→ Ba3(PO4)2(s)+ 6 NH4NO3(aq)
C)CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
D)6 HCl(aq)+ 2 Al(s)→ 2 AlCl3(aq)+ 3 H2(g)
E)2 Al2O3(s)→ 4 Al(s)+ 3 O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The formation of which one of the compounds below will act as the driving force for an acid-base reaction?
A)H2O
B)MgCl2
C)NaNO3
D)KOH
E)all of these
A)H2O
B)MgCl2
C)NaNO3
D)KOH
E)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Write and balance the following acid-base neutralization reaction:
HBr(aq)+ Li2CO3(aq)→
HBr(aq)+ Li2CO3(aq)→

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the statements regarding redox reactions are true except
A)a reducing agent causes another substance to be reduced.
B)halogens usually behave as oxidizing agents because they readily gain electrons.
C)metal ions are produced when pure metals are oxidized.
D)when a substance is oxidized its charge (or oxidation number)decreases.
E)alkali metals often behave as reducing agents because they readily lose electrons.
A)a reducing agent causes another substance to be reduced.
B)halogens usually behave as oxidizing agents because they readily gain electrons.
C)metal ions are produced when pure metals are oxidized.
D)when a substance is oxidized its charge (or oxidation number)decreases.
E)alkali metals often behave as reducing agents because they readily lose electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The reaction 2 AgNO3(aq)+ K2SO4(aq)→ 2 KNO3(aq)+ Ag2SO4(s)is an example of a(an)________ reaction.
A)acid-base
B)oxidation-reduction
C)precipitation
D)combustion
E)none of the above
A)acid-base
B)oxidation-reduction
C)precipitation
D)combustion
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In a typical oxidation-reduction reaction the electrons are transferred
A)from the oxidizing agent to the reducing agent.
B)from what is being oxidized to the substance being reduced.
C)from what is being reduced to the substance being oxidized.
D)from what is being oxidized to the reducing agent.
E)none of these.
A)from the oxidizing agent to the reducing agent.
B)from what is being oxidized to the substance being reduced.
C)from what is being reduced to the substance being oxidized.
D)from what is being oxidized to the reducing agent.
E)none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When potassium hydroxide and hydrobromic acid are combined the products are
A)potassium bromide and water.
B)potasium bromate and water.
C)potassium bromide and hydrogen gas.
D)potassium hypobromite and water.
E)potassium bromite and hydrogen gas.
A)potassium bromide and water.
B)potasium bromate and water.
C)potassium bromide and hydrogen gas.
D)potassium hypobromite and water.
E)potassium bromite and hydrogen gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
All of the reactions shown are oxidation-reduction reactions except
A)N2(g)+ O2(g)→ 2 NO(g).
B)2 Fe2O3(s)→ 4 Fe(s)+ 3 O2(g).
C)Zn(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)→ ZnCl2(aq)+ H2(g).
D)2 NaI(aq)+ Cl2(g)→ 2 NaCl(aq)+ I2.
E)K2SO4(aq)+ BaCl2(aq)→ BaSO4(s)+ 2 KCl(aq).
A)N2(g)+ O2(g)→ 2 NO(g).
B)2 Fe2O3(s)→ 4 Fe(s)+ 3 O2(g).
C)Zn(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)→ ZnCl2(aq)+ H2(g).
D)2 NaI(aq)+ Cl2(g)→ 2 NaCl(aq)+ I2.
E)K2SO4(aq)+ BaCl2(aq)→ BaSO4(s)+ 2 KCl(aq).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which reaction is an example of a precipitation reaction?
A)H2CO3(aq)→ H2O(l)+ CO2(g)
B)H2SO4(aq)+ Ca(OH)2(aq)→ CaSO4(aq)+ 2 H2O(l)
C)6 HCl(aq)+ 2 Al(s)→ 2 AlCl3(aq)+ 3 H2(g)
D)FeCl3(aq)+ 3 KOH(aq)→ Fe(OH)3(s)+ 3 KCl(aq)
E)2 Hg(l)+ O2(g)→ 2 HgO(s)
A)H2CO3(aq)→ H2O(l)+ CO2(g)
B)H2SO4(aq)+ Ca(OH)2(aq)→ CaSO4(aq)+ 2 H2O(l)
C)6 HCl(aq)+ 2 Al(s)→ 2 AlCl3(aq)+ 3 H2(g)
D)FeCl3(aq)+ 3 KOH(aq)→ Fe(OH)3(s)+ 3 KCl(aq)
E)2 Hg(l)+ O2(g)→ 2 HgO(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is not soluble in water?
A)potassium sulfide
B)iron(II)bromide
C)iron(III)hydroxide
D)iron(III)nitrate
E)ammonium sulfate
A)potassium sulfide
B)iron(II)bromide
C)iron(III)hydroxide
D)iron(III)nitrate
E)ammonium sulfate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which reaction is an example of an acid-base reaction?
A)H2CO3(aq)→ H2O(l)+ CO2(g)
B)H2SO4(aq)+ Ca(OH)2(aq)→ CaSO4(aq)+ 2 H2O(l)
C)6 HCl(aq)+ 2 Al(s)→ 2 AlCl3(aq)+ 3 H2(g)
D)FeCl3(aq)+ 3 KOH(aq)→ Fe(OH)3(s)+ 3 KCl(aq)
E)2 Hg(l)+ O2(g)→2 HgO(s)
A)H2CO3(aq)→ H2O(l)+ CO2(g)
B)H2SO4(aq)+ Ca(OH)2(aq)→ CaSO4(aq)+ 2 H2O(l)
C)6 HCl(aq)+ 2 Al(s)→ 2 AlCl3(aq)+ 3 H2(g)
D)FeCl3(aq)+ 3 KOH(aq)→ Fe(OH)3(s)+ 3 KCl(aq)
E)2 Hg(l)+ O2(g)→2 HgO(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The combination of ions least likely to produce a precipitate is
A)Ba2+ and SO42-.
B)Pb+ and Cl-.
C)Ca2+ and PO43-.
D)Fe3+ and OH-.
E)Mg2+ and C2H3O2-.
A)Ba2+ and SO42-.
B)Pb+ and Cl-.
C)Ca2+ and PO43-.
D)Fe3+ and OH-.
E)Mg2+ and C2H3O2-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When a solution of iron(III)nitrate is mixed with a solution of sodium hydroxide,a rust colored precipitate forms.This precipitate is probably
A)iron(III)nitrate.
B)sodium hydroxide.
C)sodium nitrate.
D)iron(III)hydroxide.
E)none of the above
A)iron(III)nitrate.
B)sodium hydroxide.
C)sodium nitrate.
D)iron(III)hydroxide.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In order to form the salt calcium sulfate,which acid and base combination should you choose?
A)H2SO3 and CaOH
B)H2SO4 and CaOH
C) H2SO3 and Ca(OH)2
D) H2SO4 and Ca(OH)2
E)none of the above
A)H2SO3 and CaOH
B)H2SO4 and CaOH
C) H2SO3 and Ca(OH)2
D) H2SO4 and Ca(OH)2
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The combination of ions most likely to produce a precipitate is
A)Li+ and PO43-.
B)Pb2+ and NO3-.
C)NH4+ and SO42-.
D)Fe3+ and OH-.
E)Mg2+ and C2H3O2-.
A)Li+ and PO43-.
B)Pb2+ and NO3-.
C)NH4+ and SO42-.
D)Fe3+ and OH-.
E)Mg2+ and C2H3O2-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which reaction is an example of both a precipitation and a neutralization?
A)H3PO4(aq)+ 3 KOH(aq)→ K3PO4(aq)+ 3 H2O(l)
B)FeCl3(aq)+ 3 KOH(aq)→ Fe(OH)3(s)+ 3 KCl(aq)
C)(NH4)2CO3(s)→ 2 NH3(g)+ CO2(g)+ H2O(l)
D) H2SO4(aq)+ Ba(OH)2(aq)→ BaSO4(s)+ 2 H2O(l)
E) 2 C(s)+ O2(g)→ 2 CO(g)
A)H3PO4(aq)+ 3 KOH(aq)→ K3PO4(aq)+ 3 H2O(l)
B)FeCl3(aq)+ 3 KOH(aq)→ Fe(OH)3(s)+ 3 KCl(aq)
C)(NH4)2CO3(s)→ 2 NH3(g)+ CO2(g)+ H2O(l)
D) H2SO4(aq)+ Ba(OH)2(aq)→ BaSO4(s)+ 2 H2O(l)
E) 2 C(s)+ O2(g)→ 2 CO(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The following reaction can be classified as what type(s)of reaction(s)?
2 Al(OH)3(aq)+ 3 H2SO4(aq)→ Al2(SO4)3(s)+ 6 H2O(l)
A)precipitation
B)acid-base neutralization
C)redox reaction
D)combustion
E)both A and B
2 Al(OH)3(aq)+ 3 H2SO4(aq)→ Al2(SO4)3(s)+ 6 H2O(l)
A)precipitation
B)acid-base neutralization
C)redox reaction
D)combustion
E)both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Match the following.
M(s)+ 2 LX(aq)→ 2 L(s)+ M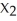 (aq)
(aq)
A)redox
B)acid-base
C)precipitation
M(s)+ 2 LX(aq)→ 2 L(s)+ M
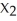 (aq)
(aq)A)redox
B)acid-base
C)precipitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the typical net ionic equation for an acid-base neutralization of KOH and HCl?
A)HCl(aq)+ KOH(aq)→ H2O(l)+ KCl(aq)
B)KOH(aq)→ K+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
C)H2O(l)→ H+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
D)K+(aq)+ OH-(aq)→ KOH(aq)
E)H+(aq)+ OH-(aq)→ H2O(l)
A)HCl(aq)+ KOH(aq)→ H2O(l)+ KCl(aq)
B)KOH(aq)→ K+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
C)H2O(l)→ H+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
D)K+(aq)+ OH-(aq)→ KOH(aq)
E)H+(aq)+ OH-(aq)→ H2O(l)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In which of the following is the oxidation number for oxygen equal to zero?
A)Ca(OH)2
B)HNO3
C)O2
D)H2O2
E)all of the above
A)Ca(OH)2
B)HNO3
C)O2
D)H2O2
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
2 AgNO3(aq)+ K2SO4(aq)→ 2 KNO3(aq)+ Ag2SO4(s)
The spectator ions in the reaction shown are
A)silver ion and nitrate ion.
B)potassium ion and sulfate ion.
C)potassium ion and nitrate ion.
D)silver ion and sulfate ion.
E)hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion.
The spectator ions in the reaction shown are
A)silver ion and nitrate ion.
B)potassium ion and sulfate ion.
C)potassium ion and nitrate ion.
D)silver ion and sulfate ion.
E)hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The net ionic equation for the reaction between zinc and hydrochloric acid solution is
A)Zn(s)+ 2 H+(aq)→ Zn2+(aq)+ H2(g).
B)Zn(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)→ ZnCl2(aq)+ H2(g).
C)Zn2+(aq)+ H2(g)→ ZnS(s)+ 2 H+(aq).
D)ZnCl2(aq)+ H2(g)→ ZnS(s)+ 2 HCl(aq).
E)none of these
A)Zn(s)+ 2 H+(aq)→ Zn2+(aq)+ H2(g).
B)Zn(s)+ 2 HCl(aq)→ ZnCl2(aq)+ H2(g).
C)Zn2+(aq)+ H2(g)→ ZnS(s)+ 2 H+(aq).
D)ZnCl2(aq)+ H2(g)→ ZnS(s)+ 2 HCl(aq).
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The element chlorine is very reactive as a(an)________ agent because it readily ________ electrons to form the chloride ion.
A)oxidizing;loses
B)oxidizing;gains
C)reducing;loses
D)reducing;gains
E)none of the above
A)oxidizing;loses
B)oxidizing;gains
C)reducing;loses
D)reducing;gains
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the following reaction which species is being oxidized and which is being reduced?
2 Cr(s)+ 3 Cl2(g)→ 2 CrCl3(s)
A)oxidized: Cr;reduced: CrCl3
B)oxidized:CrCl3;reduced: Cr
C)oxidized: Cr;reduced: Cl2
D)oxidized: Cl2;reduced: Cr
E)oxidized: Cl2;reduced: CrCl3
2 Cr(s)+ 3 Cl2(g)→ 2 CrCl3(s)
A)oxidized: Cr;reduced: CrCl3
B)oxidized:CrCl3;reduced: Cr
C)oxidized: Cr;reduced: Cl2
D)oxidized: Cl2;reduced: Cr
E)oxidized: Cl2;reduced: CrCl3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
2 AgNO3(aq) + K2SO4 (aq) → 2 KNO3 (aq) + Ag2SO4(s)
The net ionic reaction for the balanced equation shown above is
A) Ag+(aq)+ NO3-(aq)→ AgNO3(s)
B)2 K+(aq)+ SO42-(aq)→ K2SO4(aq)
C)K+(aq)+ NO3-(aq)→ KNO3(aq)
D)2 Ag+(aq)+ SO42-(aq)→ Ag2SO4(s)
E)H+(aq)+ OH-(aq)→ H2O(l)
The net ionic reaction for the balanced equation shown above is
A) Ag+(aq)+ NO3-(aq)→ AgNO3(s)
B)2 K+(aq)+ SO42-(aq)→ K2SO4(aq)
C)K+(aq)+ NO3-(aq)→ KNO3(aq)
D)2 Ag+(aq)+ SO42-(aq)→ Ag2SO4(s)
E)H+(aq)+ OH-(aq)→ H2O(l)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
As a pure element the oxidation number of zinc is ________,but in compounds such as ZnCO3 its oxidation number is ________.
A)0;0
B)0;+1
C)+1;0
D)0;+2
E)none of the above
A)0;0
B)0;+1
C)+1;0
D)0;+2
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is always a spectator ion in aqueous chemical reactions?
A)Na+
B)Cl-
C)S2-
D)Mg2+
E)all of these ions.
A)Na+
B)Cl-
C)S2-
D)Mg2+
E)all of these ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the reaction shown,________ is the oxidizing agent because it ________.
Ni(s)+ CuCl2(aq)→ Cu(s)+ NiCl2(aq)
A)Ni;causes reduction
B)Ni;gets reduced
C)CuCl2;causes reduction
D)CuCl2;gets reduced
E)NiCl2;gets reduced
Ni(s)+ CuCl2(aq)→ Cu(s)+ NiCl2(aq)
A)Ni;causes reduction
B)Ni;gets reduced
C)CuCl2;causes reduction
D)CuCl2;gets reduced
E)NiCl2;gets reduced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The oxidation number of chlorine in the compound FeCl3 is
A)-3.
B)-2.
C)-1.
D)+2.
E)+3.
A)-3.
B)-2.
C)-1.
D)+2.
E)+3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The oxidation number of iron in the compound FeBr3 is
A)-2.
B)-1.
C)+1.
D)+2.
E)+3.
A)-2.
B)-1.
C)+1.
D)+2.
E)+3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Match the following.
LX(aq)+ MY(aq)→ LY(s)+ MX(aq)
A)redox
B)acid-base
C)precipitation
LX(aq)+ MY(aq)→ LY(s)+ MX(aq)
A)redox
B)acid-base
C)precipitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the redox reaction shown,________ is oxidized and becomes ________.
Fe(s)+ CuCl2 aq)→ Cu(s)+ FeCl2(aq)
A)Fe;Fe+
B)Fe;Fe2+
C)Cu;Cu2+
D)Cu2+;Cu
E)none of the above
Fe(s)+ CuCl2 aq)→ Cu(s)+ FeCl2(aq)
A)Fe;Fe+
B)Fe;Fe2+
C)Cu;Cu2+
D)Cu2+;Cu
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Reduction is the process of
A)gaining hydrogen.
B)losing oxygen.
C)gaining electrons.
D)forming an anion from a neutral atom.
E)all of the above
A)gaining hydrogen.
B)losing oxygen.
C)gaining electrons.
D)forming an anion from a neutral atom.
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What are the spectator ions in the reaction between KOH and HNO3?
A)K+ and H+
B)H+ and OH-
C)K+ and NO3-
D) H+and NO3-
E)none of these
A)K+ and H+
B)H+ and OH-
C)K+ and NO3-
D) H+and NO3-
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The oxidation number of sulfur in calcium sulfate,CaSO4,is
A)+6.
B)+4.
C)+2.
D)0.
E)-2.
A)+6.
B)+4.
C)+2.
D)0.
E)-2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When a substance loses electrons it is ________;the substance itself is acting as a(an)________ agent.
A)oxidized;oxidizing
B)oxidized;reducing
C)reduced;oxidizing
D)reduced;reducing
E)dissolved;neutralizing
A)oxidized;oxidizing
B)oxidized;reducing
C)reduced;oxidizing
D)reduced;reducing
E)dissolved;neutralizing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the oxidation number of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide,H2O2?
A)0
B)-1
C)-2
D)+1
E)+2
A)0
B)-1
C)-2
D)+1
E)+2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match the following.
HR(aq)+ XOH(aq)→ XR(aq)+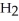 O(l)
O(l)
A)redox
B)acid-base
C)precipitation
HR(aq)+ XOH(aq)→ XR(aq)+
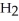 O(l)
O(l)A)redox
B)acid-base
C)precipitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



