Deck 32: Ionizing Radiation, Nuclear Energy, and Elementary Particles
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 32: Ionizing Radiation, Nuclear Energy, and Elementary Particles
1
A 75-kg worker is accidentally exposed to a 44-rad dose of gamma radiation. How much energy does the worker absorb?
A)25 J
B)17 J
C)74 J
D)59 J
E)33 J
A)25 J
B)17 J
C)74 J
D)59 J
E)33 J
33 J
2
A biological tissue is irradiated with neutrons. The biologically equivalent dose of the neutrons is 2.6 × 102 rem. Determine the RBE of the neutrons if the absorbed dose is 130 rd.
A)0.5
B)2.0
C)4.0
D)5.0
E)25
A)0.5
B)2.0
C)4.0
D)5.0
E)25
2.0
3
A particular nuclear fission reaction produces 1.50 × 102 MeV per fission. How many fissions per second are required to generate 3.00 × 108 W of power?
A)2.00 × 1016
B)5.25 × 1017
C)3.20 × 1018
D)1.25 × 1019
E)6.02 × 1023
A)2.00 × 1016
B)5.25 × 1017
C)3.20 × 1018
D)1.25 × 1019
E)6.02 × 1023
1.25 × 1019
4
Which source of radiation contributes most to the average biological equivalent dose received by a United States resident?
A)radon gas
B)cosmic rays
C)consumer products
D)medical diagnostics
E)internal radioactive nuclei
A)radon gas
B)cosmic rays
C)consumer products
D)medical diagnostics
E)internal radioactive nuclei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Complete the following statement: The average biologically equivalent dose of radiation from consumer products received by a resident of the United States is about
A)10 mrem/yr.
B)15 mrem/yr.
C)20 mrem/yr.
D)50 mrem/yr.
E)200 mrem/yr.
A)10 mrem/yr.
B)15 mrem/yr.
C)20 mrem/yr.
D)50 mrem/yr.
E)200 mrem/yr.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What radiation absorbed dose of slow neutrons (RBE = 2.5) is equivalent to a dose of 35.0 rad of fast neutrons (RBE = 9.0)?
A)9.7 rad
B)130 rad
C)160 rad
D)260 rad
E)320 rad
A)9.7 rad
B)130 rad
C)160 rad
D)260 rad
E)320 rad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which one of the following quantities is not necessarily conserved in nuclear reactions?
A)electric charge
B)number of protons
C)linear momentum
D)angular momentum
E)number of protons and neutrons
A)electric charge
B)number of protons
C)linear momentum
D)angular momentum
E)number of protons and neutrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Determine the atomic number Z and the nucleon number A in the following reaction: 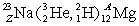 .
. 
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
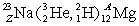 .
. 
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the importance of thermal neutrons in nuclear processes?
A)Thermal neutron capture results in uranium fission.
B)Thermal neutrons are released in radioactive decay.
C)Thermal neutrons are necessary in the fusion of deuterium.
D)Thermal neutrons are commonly released in fusion reactions.
E)Thermal neutrons are sources of gamma rays.
A)Thermal neutron capture results in uranium fission.
B)Thermal neutrons are released in radioactive decay.
C)Thermal neutrons are necessary in the fusion of deuterium.
D)Thermal neutrons are commonly released in fusion reactions.
E)Thermal neutrons are sources of gamma rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A radiologist absorbs 4.0 × 10-5 J of radiation. Determine the absorbed dose if his mass is 74.0 kg.
A)3.8 × 10-7 Gy
B)6.3 × 10-7 Gy
C)5.4 × 10-7 Gy
D)4.6 × 10-7 Gy
E)5.1 × 10-7 Gy
A)3.8 × 10-7 Gy
B)6.3 × 10-7 Gy
C)5.4 × 10-7 Gy
D)4.6 × 10-7 Gy
E)5.1 × 10-7 Gy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The first induced nuclear reaction, 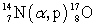 , in a laboratory was studied by Rutherford in 1919. How much energy is absorbed in this reaction if the atomic masses are:
, in a laboratory was studied by Rutherford in 1919. How much energy is absorbed in this reaction if the atomic masses are: 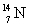 = 14.003 074 u,
= 14.003 074 u, 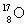 = 16.999 133 u, = 4.002 603 u, and p = 1.007 825 u? Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV.
= 16.999 133 u, = 4.002 603 u, and p = 1.007 825 u? Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV.
A)1.193 MeV
B)3.338 MeV
C)6.603 MeV
D)15.08 MeV
E)27.91 MeV
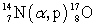 , in a laboratory was studied by Rutherford in 1919. How much energy is absorbed in this reaction if the atomic masses are:
, in a laboratory was studied by Rutherford in 1919. How much energy is absorbed in this reaction if the atomic masses are: 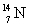 = 14.003 074 u,
= 14.003 074 u, 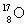 = 16.999 133 u, = 4.002 603 u, and p = 1.007 825 u? Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV.
= 16.999 133 u, = 4.002 603 u, and p = 1.007 825 u? Note: 1 u = 931.5 MeV.A)1.193 MeV
B)3.338 MeV
C)6.603 MeV
D)15.08 MeV
E)27.91 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Complete the following statement: The term ionizing radiation does not apply to
A)alpha particles.
B)electrons.
C)X-ray photons.
D)positrons.
E)radio photons.
A)alpha particles.
B)electrons.
C)X-ray photons.
D)positrons.
E)radio photons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What absorbed dose of protons with an RBE of 17 will cause the same damage to biological tissue as a 200 rd dose of neutrons that have an RBE of 2.6?
A)3.8 rd
B)12 rd
C)26 rd
D)52 rd
E)520 rd
A)3.8 rd
B)12 rd
C)26 rd
D)52 rd
E)520 rd

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A beam of 4.5-MeV neutrons is directed at a 0.030-kg tissue sample. Each second, 1.5 × 106 neutrons strike the sample. If the relative biological effectiveness of these neutrons is 7.0, what biologically equivalent dose (in rem) is received by the sample in 65 seconds?
A)0.23 rem
B)0.55 rem
C)1.6 rem
D)19 rem
E)33 rem
A)0.23 rem
B)0.55 rem
C)1.6 rem
D)19 rem
E)33 rem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A physicist wishes to measure the exposure of a beam of gamma rays. The beam is passed through 2.00 × 10-2 kg of dry air at STP. The beam produces positive ions in the air which have a total charge of 3.87 × 10-6 C. What is the exposure (in roentgens) of the beam?
A)7.74 × 10-8 R
B)1.94 × 10-4 R
C)3.25 × 10-2 R
D)0.750 R
E)1.25 R
A)7.74 × 10-8 R
B)1.94 × 10-4 R
C)3.25 × 10-2 R
D)0.750 R
E)1.25 R

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A medical researcher wishes to compare the tissue damage produced by slow neutrons, which have a relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of 2.2, to that produced by fast neutrons with an RBE of 8.8. For the slow neutrons, the absorbed dose is 560 rd. What absorbed dose (in rd) of fast neutrons will produce the same biologically equivalent dose (in rem) as that for the slow neutrons?
A)140 rd
B)29 rd
C)560 rd
D)310 rd
E)2240 rd
A)140 rd
B)29 rd
C)560 rd
D)310 rd
E)2240 rd

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the induced nuclear reaction, 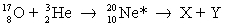 , the reaction produces neon in an excited state, which subsequently decays into a nucleus X and a particle Y. Which one of the following X and Y pairs is not possible?
, the reaction produces neon in an excited state, which subsequently decays into a nucleus X and a particle Y. Which one of the following X and Y pairs is not possible?

A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
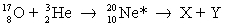 , the reaction produces neon in an excited state, which subsequently decays into a nucleus X and a particle Y. Which one of the following X and Y pairs is not possible?
, the reaction produces neon in an excited state, which subsequently decays into a nucleus X and a particle Y. Which one of the following X and Y pairs is not possible? 
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which one of the following processes causes the explosion of a nuclear bomb?
A)beta decay
B)alpha decay
C)moderation
D)photon absorption
E)chain reaction
A)beta decay
B)alpha decay
C)moderation
D)photon absorption
E)chain reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which one of the following energy values would be characteristic of a thermal neutron?
A)0.03 eV
B)0.4 eV
C)3 eV
D)100 eV
E)0.04 MeV
A)0.03 eV
B)0.4 eV
C)3 eV
D)100 eV
E)0.04 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A single, whole-body dose of 450 rem is considered a lethal dose for approximately fifty percent of all individuals receiving such a dose. If a 62-kg person were exposed to such a dose of radiation that has an RBE of 0.845, how much energy has the person absorbed?
A)480 J
B)5.3 J
C)75 J
D)120 J
E)330 J
A)480 J
B)5.3 J
C)75 J
D)120 J
E)330 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Determine the amount of energy released in the following reaction: 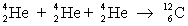 where
where 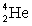 = 4.002 603 u and
= 4.002 603 u and 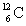 = 12.000 000 u.
= 12.000 000 u.
A)2.27 MeV
B)3.01 MeV
C)3.73 MeV
D)4.37 MeV
E)7.27 MeV
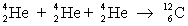 where
where 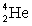 = 4.002 603 u and
= 4.002 603 u and 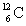 = 12.000 000 u.
= 12.000 000 u.A)2.27 MeV
B)3.01 MeV
C)3.73 MeV
D)4.37 MeV
E)7.27 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Note the forces:
(1) weak nuclear force
(2) strong nuclear force
(3) gravitational force
(4) electromagnetic force
Through which force(s) can leptons interact?
A)only 1
B)only 2
C)only 1 and 2
D)only 2, 3 and 4
E)only 1, 3, and 4
(1) weak nuclear force
(2) strong nuclear force
(3) gravitational force
(4) electromagnetic force
Through which force(s) can leptons interact?
A)only 1
B)only 2
C)only 1 and 2
D)only 2, 3 and 4
E)only 1, 3, and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How many members are in the photon family?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which one of the following particles is not a baryon?
A)proton
B)neutron
C)pion
D)sigma particle
E)lambda particle
A)proton
B)neutron
C)pion
D)sigma particle
E)lambda particle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which one of the following statements is true concerning the proton?
A)The proton cannot be further subdivided.
B)The proton is composed of two up quarks and a down quark.
C)The proton is composed of two down quarks and an up quark.
D)The proton is composed of a down quark and an up antiquark.
E)The proton is composed of an up quark and a down antiquark.
A)The proton cannot be further subdivided.
B)The proton is composed of two up quarks and a down quark.
C)The proton is composed of two down quarks and an up quark.
D)The proton is composed of a down quark and an up antiquark.
E)The proton is composed of an up quark and a down antiquark.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which one of the following particles is not composed of quarks?
A)neutron
B)muon
C)pion
D)kaon
E)proton
A)neutron
B)muon
C)pion
D)kaon
E)proton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which one of the following statements concerning pions is true?
A)They are stable particles.
B)They belong to the lepton family.
C)They are composed of three quarks.
D)They only exist in two charge states.
E)They interact with protons via the strong interaction.
A)They are stable particles.
B)They belong to the lepton family.
C)They are composed of three quarks.
D)They only exist in two charge states.
E)They interact with protons via the strong interaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which one of the following names is not one that is used to name quarks?
A)charm
B)top
C)strange
D)exotic
E)down
A)charm
B)top
C)strange
D)exotic
E)down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the function of the moderator in a fission reactor?
A)The moderator absorbs gamma rays.
B)The moderator absorbs slow neutrons.
C)The moderator decreases the speeds of fast neutrons.
D)The moderator prevents heat loss from the reactor core.
E)The moderator prevents the reactor from reaching a critical state.
A)The moderator absorbs gamma rays.
B)The moderator absorbs slow neutrons.
C)The moderator decreases the speeds of fast neutrons.
D)The moderator prevents heat loss from the reactor core.
E)The moderator prevents the reactor from reaching a critical state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the antiparticle of an electron?
A) +
B)v+
C)electron (self)
D)photon
E) +
A) +
B)v+
C)electron (self)
D)photon
E) +

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which one of the following statements is true concerning the reaction 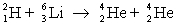 where
where 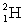 has a mass of 2.014 u;
has a mass of 2.014 u; 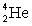 has a mass of 4.003 u;
has a mass of 4.003 u; 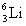 has a mass of 6.015 u; and 1 u = 931.5 MeV?
has a mass of 6.015 u; and 1 u = 931.5 MeV?
A)The reaction releases 14 MeV.
B)The reaction releases 21 MeV.
C)The reaction releases 36 MeV.
D)The reaction requires 14 MeV to occur.
E)The reaction requires 21 MeV to occur.
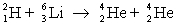 where
where 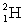 has a mass of 2.014 u;
has a mass of 2.014 u; 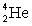 has a mass of 4.003 u;
has a mass of 4.003 u; 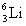 has a mass of 6.015 u; and 1 u = 931.5 MeV?
has a mass of 6.015 u; and 1 u = 931.5 MeV?A)The reaction releases 14 MeV.
B)The reaction releases 21 MeV.
C)The reaction releases 36 MeV.
D)The reaction requires 14 MeV to occur.
E)The reaction requires 21 MeV to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
One of the nuclear fusion reactions that occurs in stars is: 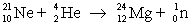 where the masses are
where the masses are 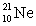 = 20.993 849 u;
= 20.993 849 u; 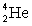 = 4.002 603 u;
= 4.002 603 u; 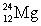 = 23.985 042 u; and
= 23.985 042 u; and 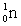 = 1.008 665 u. How much energy is released in this reaction?
= 1.008 665 u. How much energy is released in this reaction?
A)2.557 MeV
B)4.572 MeV
C)6.452 MeV
D)8.493 MeV
E)9.370 MeV
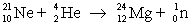 where the masses are
where the masses are 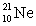 = 20.993 849 u;
= 20.993 849 u; 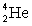 = 4.002 603 u;
= 4.002 603 u; 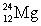 = 23.985 042 u; and
= 23.985 042 u; and 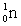 = 1.008 665 u. How much energy is released in this reaction?
= 1.008 665 u. How much energy is released in this reaction?A)2.557 MeV
B)4.572 MeV
C)6.452 MeV
D)8.493 MeV
E)9.370 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A nuclear reactor continuously generates 150 MW of power through the fissioning of uranium. Suppose that each fission releases 190 MeV. If one mole of uranium (6.023 × 1023 nuclei) has a mass of 0.235 kg, what mass of uranium has undergone fission in a 4.0 day period?
A)0.33 kg
B)0.67 kg
C)1.3 kg
D)2.6 kg
E)5.2 kg
A)0.33 kg
B)0.67 kg
C)1.3 kg
D)2.6 kg
E)5.2 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Determine the amount of energy released in the following reaction: 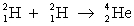 . Use the following information for your calculation:
. Use the following information for your calculation: 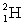 has a mass of 2.014 102 u,
has a mass of 2.014 102 u, 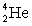 has a mass of 4.002 603 u, and 1 u = 931.5 MeV.
has a mass of 4.002 603 u, and 1 u = 931.5 MeV.
A)0.20 MeV
B)11.9 MeV
C)23.8 MeV
D)257 MeV
E)7480 MeV
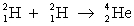 . Use the following information for your calculation:
. Use the following information for your calculation: 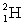 has a mass of 2.014 102 u,
has a mass of 2.014 102 u, 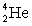 has a mass of 4.002 603 u, and 1 u = 931.5 MeV.
has a mass of 4.002 603 u, and 1 u = 931.5 MeV.A)0.20 MeV
B)11.9 MeV
C)23.8 MeV
D)257 MeV
E)7480 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How many neutrons are produced in the following reaction: 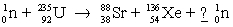
A)11
B)12
C)22
D)24
E)48
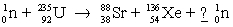
A)11
B)12
C)22
D)24
E)48

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which one of the following statements is the best explanation as to why nuclear fusion is not at present used to generate electric power?
A)Fusion produces too much radiation.
B)Fusion requires isotopes that are scarce.
C)Fusion processes can result in nuclear explosions.
D)Fusion results in large amounts of radioactive waste.
E)Fusion requires very high temperatures that are difficult to contain.
A)Fusion produces too much radiation.
B)Fusion requires isotopes that are scarce.
C)Fusion processes can result in nuclear explosions.
D)Fusion results in large amounts of radioactive waste.
E)Fusion requires very high temperatures that are difficult to contain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the medical diagnostic technique known as positron emission tomography (PET), a positron and an electron annihilate each other and two -ray photons are emitted. What is the angle between the momentum vectors of the two photons?
A)zero degrees
B)45°
C)90°
D)180°
E)Any angle is possible.
A)zero degrees
B)45°
C)90°
D)180°
E)Any angle is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Determine the amount of energy released in the following reaction: 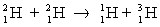 where the masses are
where the masses are 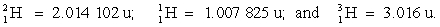
A)2.02 eV
B)4.03 eV
C)2.02 MeV
D)4.03 MeV
E)8.00 MeV
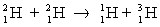 where the masses are
where the masses are 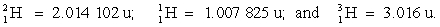
A)2.02 eV
B)4.03 eV
C)2.02 MeV
D)4.03 MeV
E)8.00 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How many kilowatt . hours of energy are released from 25 g of deuterium 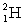 fuel in the fusion reaction:
fuel in the fusion reaction: 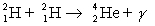 where the masses are
where the masses are 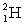 = 2.014 102 u and
= 2.014 102 u and 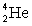 = 4.002 603 u. Notes: Ignore the energy carried off by the gamma ray.
= 4.002 603 u. Notes: Ignore the energy carried off by the gamma ray.
Conversion factors: 1 kWh = 3.600 × 106 J; 1 eV = 1.602 × 10-19 J.
A)1 × 106 kWh
B)2 × 106 kWh
C)3 × 106 kWh
D)4 × 106 kWh
E)5 × 106 kWh
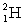 fuel in the fusion reaction:
fuel in the fusion reaction: 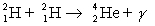 where the masses are
where the masses are 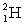 = 2.014 102 u and
= 2.014 102 u and 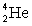 = 4.002 603 u. Notes: Ignore the energy carried off by the gamma ray.
= 4.002 603 u. Notes: Ignore the energy carried off by the gamma ray.Conversion factors: 1 kWh = 3.600 × 106 J; 1 eV = 1.602 × 10-19 J.
A)1 × 106 kWh
B)2 × 106 kWh
C)3 × 106 kWh
D)4 × 106 kWh
E)5 × 106 kWh

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which one of the following particles is not a member of the hadron family?
A)pion
B)neutron
C)muon
D)kaon
E)proton
A)pion
B)neutron
C)muon
D)kaon
E)proton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider the nuclear reaction 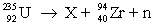 and the masses:
and the masses: 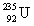 = 235.0439 u;
= 235.0439 u; 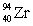 = 93.9063 u; n = 1.008 67 u. If 208.66 MeV of energy is released in this reaction, determine the mass of X.
= 93.9063 u; n = 1.008 67 u. If 208.66 MeV of energy is released in this reaction, determine the mass of X.
A)38.970 u
B)39.962 u
C)40.962 u
D)84.589 u
E)139.905 u
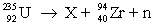 and the masses:
and the masses: 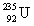 = 235.0439 u;
= 235.0439 u; 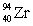 = 93.9063 u; n = 1.008 67 u. If 208.66 MeV of energy is released in this reaction, determine the mass of X.
= 93.9063 u; n = 1.008 67 u. If 208.66 MeV of energy is released in this reaction, determine the mass of X.A)38.970 u
B)39.962 u
C)40.962 u
D)84.589 u
E)139.905 u

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which one of the following statements about the standard model is false?
A)The weak nuclear force and the electromagnetic force are manifestations of a more fundamental interaction called the electroweak interaction.
B)The strong nuclear force between quarks is described in terms of the concept of color.
C)The standard model provides an explanation for the strong nuclear and weak nuclear forces.
D)The gravitational force and the strong nuclear force are manifestations of a more fundamental interaction called the quark interaction.
E)Nucleons are composed of quarks.
A)The weak nuclear force and the electromagnetic force are manifestations of a more fundamental interaction called the electroweak interaction.
B)The strong nuclear force between quarks is described in terms of the concept of color.
C)The standard model provides an explanation for the strong nuclear and weak nuclear forces.
D)The gravitational force and the strong nuclear force are manifestations of a more fundamental interaction called the quark interaction.
E)Nucleons are composed of quarks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Astronomers studying the light from calcium atoms located in a galaxy in the constellation Boötes find that the spectral lines are shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. The redshift indicates that the galaxy is moving away at a speed of 3.9 × 106 m/s. What is the distance (in light . years) to the galaxy?
A)4.7 × 109 light . years
B)2.3 × 108 light .years
C)1.1 × 107 light . years
D)8.4 × 106 light . years
E)6.6 × 104 light . years
A)4.7 × 109 light . years
B)2.3 × 108 light .years
C)1.1 × 107 light . years
D)8.4 × 106 light . years
E)6.6 × 104 light . years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which one of the following statements concerning the standard cosmological model is false?
A)Shortly after the Big Bang, all of the fundamental forces behaved as a single force.
B)About 0.5 million years after the Big Bang, hydrogen and helium atoms began to form.
C)The first distinguishable particles in existence after the Big Bang were quarks and leptons.
D)The Grand Unified Theory describes the universe immediately before and shortly after the Big Bang.
E)At 10-43 s after the Big Bang, the gravitational force was distinguishable from the other fundamental forces.
A)Shortly after the Big Bang, all of the fundamental forces behaved as a single force.
B)About 0.5 million years after the Big Bang, hydrogen and helium atoms began to form.
C)The first distinguishable particles in existence after the Big Bang were quarks and leptons.
D)The Grand Unified Theory describes the universe immediately before and shortly after the Big Bang.
E)At 10-43 s after the Big Bang, the gravitational force was distinguishable from the other fundamental forces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Nucleus A has Z protons and N neutrons. Nucleus B has 2Z protons and 2N neutrons. Nucleus A has a smaller binding energy per nucleon than B. Which entry in the table below is correct? 
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



