Deck 30: The Nature of the Atom
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/74
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: The Nature of the Atom
1
Complete the following statement: An individual copper atom emits electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths that are
A)evenly spaced across the spectrum.
B)unique to that particular copper atom.
C)the same as other elements in the same column of the periodic table.
D)unique to all copper atoms.
E)the same as those of all elements.
A)evenly spaced across the spectrum.
B)unique to that particular copper atom.
C)the same as other elements in the same column of the periodic table.
D)unique to all copper atoms.
E)the same as those of all elements.
unique to all copper atoms.
2
Electrons have been removed from a lithium atom (Z = 3) until only one remains. Determine the energy of the photon that can be emitted if the remaining electron is in the n = 2 level.
A)33.7 eV
B)54.4 eV
C)91.9 eV
D)163 eV
E)181 eV
A)33.7 eV
B)54.4 eV
C)91.9 eV
D)163 eV
E)181 eV
91.9 eV
3
Complete the following statement: For the ground state of the hydrogen atom, the Bohr model correctly predicts
A)only the energy.
B)only the angular momentum.
C)only the angular momentum and the spin.
D)the angular momentum and the energy.
E)the energy, the angular momentum, and the spin.
A)only the energy.
B)only the angular momentum.
C)only the angular momentum and the spin.
D)the angular momentum and the energy.
E)the energy, the angular momentum, and the spin.
only the energy.
4
Why was it necessary for Bohr to require that electrons remain in stationary orbits?
A)An electron must travel in a circular path.
B)It was required by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
C)No two electrons can be in the same region in the atom.
D)It was required by the Pauli exclusion principle.
E)Classical physics predicts that the electron should spiral into the nucleus.
A)An electron must travel in a circular path.
B)It was required by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
C)No two electrons can be in the same region in the atom.
D)It was required by the Pauli exclusion principle.
E)Classical physics predicts that the electron should spiral into the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Each atom in the periodic table has a unique set of spectral lines. The model of atomic structure that provides the best explanation for this observation was proposed by
A)Balmer.
B)Bohr.
C)Einstein.
D)Rutherford.
E)Thomson.
A)Balmer.
B)Bohr.
C)Einstein.
D)Rutherford.
E)Thomson.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the longest wavelength in the Paschen series of atomic spectra?
A)8.204 × 10-7 m
B)1.875 × 10-6 m
C)2.216 × 10-6 m
D)5.522 × 10-6 m
E)6.756 × 10-5 m
A)8.204 × 10-7 m
B)1.875 × 10-6 m
C)2.216 × 10-6 m
D)5.522 × 10-6 m
E)6.756 × 10-5 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An electron is in the ground state of a hydrogen atom. A photon is absorbed by the atom and the electron is excited to the n = 2 state. What is the energy in eV of the photon?
A)13.6 eV
B)10.2 eV
C)3.40 eV
D)1.51 eV
E)0.54 eV
A)13.6 eV
B)10.2 eV
C)3.40 eV
D)1.51 eV
E)0.54 eV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Determine the energy of the photon emitted when the electron in a hydrogen atom undergoes a transition from the n = 7 level to the n = 4 level.
A)0.17 eV
B)0.21 eV
C)0.36 eV
D)0.57 eV
E)1.3 eV
A)0.17 eV
B)0.21 eV
C)0.36 eV
D)0.57 eV
E)1.3 eV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which one of the following statements is the assumption that Niels Bohr made about the angular momentum of the electron in the hydrogen atom?
A)The angular momentum of the electron is zero.
B)The angular momentum can have only certain discrete values.
C)Angular momentum is not quantized.
D)The angular momentum can have any value greater than zero because it's proportional to the radius of the orbit.
E)The angular momentum is independent of the mass of the electron.
A)The angular momentum of the electron is zero.
B)The angular momentum can have only certain discrete values.
C)Angular momentum is not quantized.
D)The angular momentum can have any value greater than zero because it's proportional to the radius of the orbit.
E)The angular momentum is independent of the mass of the electron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Determine the maximum wavelength of incident radiation that can be used to remove the remaining electron from a singly ionized helium atom He+ (Z = 2). Assume the electron is in its ground state.
A)6.2 nm
B)12.4 nm
C)22.8 nm
D)45.6 nm
E)54.4 nm
A)6.2 nm
B)12.4 nm
C)22.8 nm
D)45.6 nm
E)54.4 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The nucleus of a certain atom has a radius of 4.0 × 10-15 m. An electron orbits the nucleus at a radius of 1.5 × 10-10 m. Imagine the electron orbit is on the surface of a sphere and that the shape of the nucleus is spherical. Approximately how many nuclei would fit into the sphere on which the electron orbits?
A)5.3 × 1013
B)4.9 × 1011
C)1.4 × 109
D)7.5 × 107
E)3.8 × 104
A)5.3 × 1013
B)4.9 × 1011
C)1.4 × 109
D)7.5 × 107
E)3.8 × 104

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The second ionization energy (the energy required to remove the second outermost electron) of calcium is 11.9 eV. Determine the maximum wavelength of incident radiation that can be used to remove the second electron from a calcium atom?
A)16.6 nm
B)52 nm
C)104 nm
D)208 nm
E)416 nm
A)16.6 nm
B)52 nm
C)104 nm
D)208 nm
E)416 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Determine the wavelength of incident electromagnetic radiation required to cause an electron transition from the n = 5 to the n = 7 level in a hydrogen atom.
A)1.1 × 103 nm
B)2.8 × 103 nm
C)3.5 × 103 nm
D)4.6 × 103 nm
E)5.2 × 103 nm
A)1.1 × 103 nm
B)2.8 × 103 nm
C)3.5 × 103 nm
D)4.6 × 103 nm
E)5.2 × 103 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which one of the following statements concerning the plum-pudding model of the atom is false?
A)There is no nucleus at the center of the plum-pudding model atom.
B)The plum-pudding model was proven correct in experiments by Ernest Rutherford.
C)The plum-pudding model was proposed by Joseph J. Thomson.
D)Positive charge is spread uniformly throughout the plum-pudding model atom.
E)Negative electrons are dispersed uniformly within the positively charged "pudding" within the plum-pudding model atom.
A)There is no nucleus at the center of the plum-pudding model atom.
B)The plum-pudding model was proven correct in experiments by Ernest Rutherford.
C)The plum-pudding model was proposed by Joseph J. Thomson.
D)Positive charge is spread uniformly throughout the plum-pudding model atom.
E)Negative electrons are dispersed uniformly within the positively charged "pudding" within the plum-pudding model atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which model of atomic structure was developed to explain the results of the experiment shown? 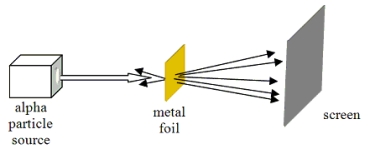
A)Bohr model
B)quantum mechanical atom
C)billiard ball atom
D)plum-pudding model
E)nuclear atom

A)Bohr model
B)quantum mechanical atom
C)billiard ball atom
D)plum-pudding model
E)nuclear atom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which one of the following pairs of characteristics of light is best explained by assuming that light can be described in terms of photons?
A)photoelectric effect and the effect observed in Young's experiment
B)diffraction and the formation of atomic spectra
C)polarization and the photoelectric effect
D)existence of line spectra and the photoelectric effect
E)polarization and the formation of line spectra
A)photoelectric effect and the effect observed in Young's experiment
B)diffraction and the formation of atomic spectra
C)polarization and the photoelectric effect
D)existence of line spectra and the photoelectric effect
E)polarization and the formation of line spectra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which one of the following will result in an electron transition from the n = 4 level to the n = 7 level in a hydrogen atom?
A)emission of a 0.28 eV photon
B)emission of a 0.57 eV photon
C)absorption of a 0.85 eV photon
D)absorption of a 0.28 eV photon
E)absorption of a 0.57 eV photon
A)emission of a 0.28 eV photon
B)emission of a 0.57 eV photon
C)absorption of a 0.85 eV photon
D)absorption of a 0.28 eV photon
E)absorption of a 0.57 eV photon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the planetary model of the atom where electrons orbit a centralized nucleus, what is the approximate ratio of the radius of the nucleus to that of the electron orbits, rn/re?
A)105
B)10-3
C)103
D)10-5
E)10-7
A)105
B)10-3
C)103
D)10-5
E)10-7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The kinetic energy of the ground state electron in hydrogen is +13.6 eV. What is its potential energy?
A)-13.6 eV
B)+27.2 eV
C)-27.2 eV
D)+56.2 eV
E)zero eV
A)-13.6 eV
B)+27.2 eV
C)-27.2 eV
D)+56.2 eV
E)zero eV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Each atom in the periodic table has a unique set of spectral lines. Which one of the following statements is the best explanation for this observation?
A)Each atom has a dense central nucleus.
B)Electrons in atoms orbit the nucleus.
C)Each atom has a unique set of energy levels that electrons can move between.
D)Electrons in atoms are in constant motion.
E)Each atom is composed of positive and negative charges.
A)Each atom has a dense central nucleus.
B)Electrons in atoms orbit the nucleus.
C)Each atom has a unique set of energy levels that electrons can move between.
D)Electrons in atoms are in constant motion.
E)Each atom is composed of positive and negative charges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the shortest possible wavelength in the Lyman series for atomic hydrogen?
A)91.3 nm
B)104 nm
C)122 nm
D)364 nm
E)820 nm
A)91.3 nm
B)104 nm
C)122 nm
D)364 nm
E)820 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How many electrons could be accommodated in an f subshell?
A)6
B)8
C)10
D)14
E)18
A)6
B)8
C)10
D)14
E)18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Complete the following statement: An h subshell refers to orbital quantum number
A)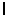 = 1.
= 1.
B)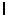 = 2.
= 2.
C)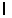 = 3.
= 3.
D)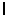 = 4.
= 4.
E)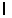 = 5.
= 5.
A)
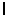 = 1.
= 1.B)
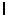 = 2.
= 2.C)
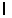 = 3.
= 3.D)
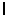 = 4.
= 4.E)
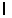 = 5.
= 5.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
According to the quantum mechanical picture of the atom, which one of the following statements is true concerning the magnitude of the angular momentum L of an electron in the n = 3 level of the hydrogen atom?
A)L is 0.318h.
B)L is 0.390h.
C)L could be 0.159h or 0.318h.
D)L could be 0.225h or 0.276h.
E)L could be 0.225h or 0.390h.
A)L is 0.318h.
B)L is 0.390h.
C)L could be 0.159h or 0.318h.
D)L could be 0.225h or 0.276h.
E)L could be 0.225h or 0.390h.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The principle quantum number for the electron in a hydrogen atom is n = 5. According to the quantum mechanical picture of the atom, what is the maximum possible value for the magnitude of the z-component of the angular momentum of the electron?
A)3.17 × 10-34 kg .m2/s
B)4.22 × 10-34 kg . m2/s
C)1.99 × 10-34 kg . m2/s
D)1.06 × 10-34 kg . m2/s
E)2.11 × 10-33 kg . m2/s
A)3.17 × 10-34 kg .m2/s
B)4.22 × 10-34 kg . m2/s
C)1.99 × 10-34 kg . m2/s
D)1.06 × 10-34 kg . m2/s
E)2.11 × 10-33 kg . m2/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which quantum number applies to most of the electrons in a collection of hydrogen atoms at room temperature?
A)n = 1
B)n = 2
C)n = 3
D)n = 4
E)n = 5
A)n = 1
B)n = 2
C)n = 3
D)n = 4
E)n = 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which one of the following electronic configurations corresponds to an atomic ground state?
A)1s2 2s1 2p6
B)1s1 2s1 2p1
C)1s1 2s2 3p1
D)1s2 2s2 2p1
E)1s1 2s2 2p1
A)1s2 2s1 2p6
B)1s1 2s1 2p1
C)1s1 2s2 3p1
D)1s2 2s2 2p1
E)1s1 2s2 2p1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Determine the kinetic energy of an electron that has a de Broglie wavelength equal to twice the diameter of the hydrogen atom. Assume that the hydrogen atom is a sphere of radius 5.3 × 10-11 m.
A)13.6 eV
B)27.2 eV
C)33.6 eV
D)48.9 eV
E)65.2 eV
A)13.6 eV
B)27.2 eV
C)33.6 eV
D)48.9 eV
E)65.2 eV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which one of the following sets of quantum numbers is not possible? 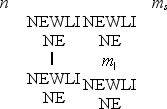
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
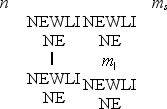
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
According to the Bohr model, what is the radius of a hydrogen atom when its electron is excited to the n = 9 state?
A)5.87 × 10-12 m
B)5.29 × 10-11 m
C)4.76 × 10-10 m
D)4.28 × 10-9 m
E)1.51 × 10-8 m
A)5.87 × 10-12 m
B)5.29 × 10-11 m
C)4.76 × 10-10 m
D)4.28 × 10-9 m
E)1.51 × 10-8 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which one of the following factors best explains why the six electrons of a carbon atom are not all in the 1s state?
A)electron spin
B)Coulomb's law
C)Pauli exclusion principle
D)Heisenberg uncertainty principle
E)Rutherford model of atomic structure
A)electron spin
B)Coulomb's law
C)Pauli exclusion principle
D)Heisenberg uncertainty principle
E)Rutherford model of atomic structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An electron in a hydrogen atom is described by the quantum numbers: n = 7 and ml = 4. What are the possible values for the orbital quantum number 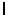 ?
?
A)only 0 or 4
B)only 4 or 7
C)only 5 or 6
D)only 4, 5, or 6
E)only 5, 6, or 7
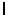 ?
?A)only 0 or 4
B)only 4 or 7
C)only 5 or 6
D)only 4, 5, or 6
E)only 5, 6, or 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What energy (in eV) is required to remove the remaining electron from a singly ionized helium atom, He+ (Z = 2)?
A)3.40 eV
B)13.6 eV
C)27.2 eV
D)54.4 eV
E)76.9 eV
A)3.40 eV
B)13.6 eV
C)27.2 eV
D)54.4 eV
E)76.9 eV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two possible states for the hydrogen atom are labeled A and B. The maximum magnetic quantum number for state A is +3. For state B, the maximum value is +1. What is the ratio of the magnitudes of the orbital angular momenta, LA/LB, of an electron in these two states?
A)1.22
B)1.73
C)2.00
D)2.45
E)3.46
A)1.22
B)1.73
C)2.00
D)2.45
E)3.46

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which one of the following subshells is not compatible with a principle quantum number of n = 4?
A)s
B)p
C)d
D)f
E)g
A)s
B)p
C)d
D)f
E)g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
To which model of atomic structure does the Pauli exclusion principle apply?
A)the nuclear atom
B)the quantum mechanical atom
C)the billiard ball atom
D)the plum-pudding model
E)the planetary model
A)the nuclear atom
B)the quantum mechanical atom
C)the billiard ball atom
D)the plum-pudding model
E)the planetary model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Determine the maximum number of electron states with principal quantum number n = 3?
A)2
B)3
C)6
D)9
E)18
A)2
B)3
C)6
D)9
E)18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How many electron states (including spin states) are possible in a hydrogen atom if its energy is -3.4 eV?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
E)10
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
According to the quantum mechanical picture of the atom, which one of the following is a true statement concerning the ground state electron in a hydrogen atom?
A)The ground state electron has zero kinetic energy.
B)The ground state electron has zero binding energy.
C)The ground state electron has zero ionization energy.
D)The ground state electron has zero spin angular momentum.
E)The ground state electron has zero orbital angular momentum.
A)The ground state electron has zero kinetic energy.
B)The ground state electron has zero binding energy.
C)The ground state electron has zero ionization energy.
D)The ground state electron has zero spin angular momentum.
E)The ground state electron has zero orbital angular momentum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The electron in a hydrogen atom is in the n = 3 state. What is(are) the possible value(s) for an emitted photon?
A)1.89 eV or 12.09 eV
B)1.89 eV or 13.6 eV
C)0.66 eV or 13.6 eV
D)0.66 eV or 12.09 eV
E)1.51 eV only
A)1.89 eV or 12.09 eV
B)1.89 eV or 13.6 eV
C)0.66 eV or 13.6 eV
D)0.66 eV or 12.09 eV
E)1.51 eV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Complete the following sentence: In the condition known as population inversion,
A)the amount of one type of gas atoms is larger than that of another in a mixture.
B)the number of energy levels that are populated is larger than that of unpopulated levels.
C)there are more electrons occupying lower energy levels than occupying higher energy levels.
D)there are more electrons occupying higher energy levels than occupying lower energy levels.
E)there are more photons than electrons in a given system.
A)the amount of one type of gas atoms is larger than that of another in a mixture.
B)the number of energy levels that are populated is larger than that of unpopulated levels.
C)there are more electrons occupying lower energy levels than occupying higher energy levels.
D)there are more electrons occupying higher energy levels than occupying lower energy levels.
E)there are more photons than electrons in a given system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the total number of subshells in the n = 3 level?
A)3
B)6
C)7
D)9
E)18
A)3
B)6
C)7
D)9
E)18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider the following list of electron configurations: 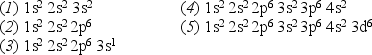
Which one of the above configurations represents an excited state of a neutral atom?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
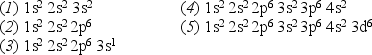
Which one of the above configurations represents an excited state of a neutral atom?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In an X-ray tube, electrons with energy 38 keV are incident on a cobalt (Z = 27) target. Determine the cutoff wavelength for X-ray production.
A)1.9 × 10-11 m
B)2.4 × 10-11 m
C)2.8 × 10-11 m
D)3.3 × 10-11 m
E)3.6 × 10-11 m
A)1.9 × 10-11 m
B)2.4 × 10-11 m
C)2.8 × 10-11 m
D)3.3 × 10-11 m
E)3.6 × 10-11 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Consider the following list of electron configurations: 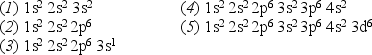
Which one of the above configurations represents a transition element?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
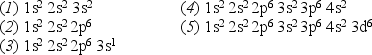
Which one of the above configurations represents a transition element?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A neutral atom has the following electronic configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
How many electrons are in the M shell?
A)2
B)5
C)6
D)7
E)8
How many electrons are in the M shell?
A)2
B)5
C)6
D)7
E)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A neutral atom has the following electronic configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
To which group of the periodic table does this element belong?
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)VI
E)VII
To which group of the periodic table does this element belong?
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)VI
E)VII

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Consider the following list of electron configurations: 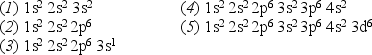
Which electronic configuration is characteristic of noble gases?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
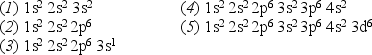
Which electronic configuration is characteristic of noble gases?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Electrons in an X-ray tube are accelerated through a potential difference of 40 kV. The electrons then strike a zirconium (Z = 40) target. Determine the cutoff frequency for X-ray production.
A)4.7 × 1019 Hz
B)9.7 × 1018 Hz
C)3.2 × 1018 Hz
D)6.7 × 1017 Hz
E)1.1 × 1016 Hz
A)4.7 × 1019 Hz
B)9.7 × 1018 Hz
C)3.2 × 1018 Hz
D)6.7 × 1017 Hz
E)1.1 × 1016 Hz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider the following list of electron configurations: 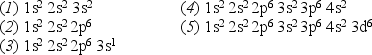
Which one of the above lists represents the electronic configuration for the ground state of the atom with Z = 11?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
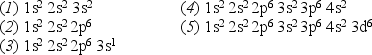
Which one of the above lists represents the electronic configuration for the ground state of the atom with Z = 11?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which one of the following statements concerning the cutoff wavelength typically exhibited in X-ray spectra is true?
A)The cutoff wavelength depends on the target material.
B)The cutoff wavelength depends on the potential difference across the X-ray tube.
C)The cutoff wavelength is independent of the energy of the incident electrons.
D)The cutoff wavelength occurs because of the mutual shielding effects of K-shell electrons.
E)The cutoff wavelength occurs because an incident electron cannot give up all of its energy.
A)The cutoff wavelength depends on the target material.
B)The cutoff wavelength depends on the potential difference across the X-ray tube.
C)The cutoff wavelength is independent of the energy of the incident electrons.
D)The cutoff wavelength occurs because of the mutual shielding effects of K-shell electrons.
E)The cutoff wavelength occurs because an incident electron cannot give up all of its energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is the operating voltage of a medical X-ray machine that has a cut-off wavelength of 2.20 × 10-11 m?
A)83 800 V
B)10 900 V
C)30 700 V
D)44 900 V
E)56 500 V
A)83 800 V
B)10 900 V
C)30 700 V
D)44 900 V
E)56 500 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A neutral atom has the following electronic configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
How many protons are in the atomic nucleus?
A)4
B)7
C)12
D)17
E)34
How many protons are in the atomic nucleus?
A)4
B)7
C)12
D)17
E)34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An electron in an atom has the following set of quantum numbers:
n = 2,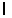 = 1,
= 1, 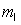 = -1, ms = +1/2.
= -1, ms = +1/2.
What shell is this electron occupying?
A)K shell
B)L shell
C)M shell
D)N shell
E)O shell
n = 2,
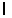 = 1,
= 1, 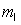 = -1, ms = +1/2.
= -1, ms = +1/2.What shell is this electron occupying?
A)K shell
B)L shell
C)M shell
D)N shell
E)O shell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An electron in an atom has the following set of quantum numbers:
n = 2,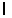 = 1,
= 1, 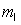 = -1, ms = +1/2.
= -1, ms = +1/2.
In which subshell can the electron be found?
A)s
B)p
C)d
D)f
E)g
n = 2,
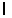 = 1,
= 1, 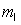 = -1, ms = +1/2.
= -1, ms = +1/2.In which subshell can the electron be found?
A)s
B)p
C)d
D)f
E)g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Consider the following list of electron configurations: 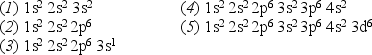
Which one of the above configurations represents a neutral atom that readily forms a singly charged positive ion?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
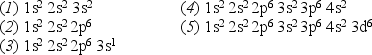
Which one of the above configurations represents a neutral atom that readily forms a singly charged positive ion?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which electron energy will produce the largest cutoff wavelength for X-ray production from a nickel (Z = 28) surface?
A)25 keV
B)30 keV
C)35 keV
D)40 keV
E)45 keV
A)25 keV
B)30 keV
C)35 keV
D)40 keV
E)45 keV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the Bohr model to estimate the K X-ray wavelength for a gold atom (Z = 79).
A)5.13 × 10-10 m
B)8.54 × 10-10 m
C)2.00 × 10-11 m
D)3.60 × 10-11 m
E)2.47 × 10-13 m
A)5.13 × 10-10 m
B)8.54 × 10-10 m
C)2.00 × 10-11 m
D)3.60 × 10-11 m
E)2.47 × 10-13 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The ground state electronic configuration of a neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6. How many of these electrons have magnetic quantum number ml = 0?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
E)10
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Name the physicist credited with the following statement: No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of values for the four quantum numbers.
A)Werner Heisenberg
B)Wolfgang Pauli
C)Arthur Compton
D)Niels Bohr
E)Erwin Schrödinger
A)Werner Heisenberg
B)Wolfgang Pauli
C)Arthur Compton
D)Niels Bohr
E)Erwin Schrödinger

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An argon-ion laser emits a blue-green beam of light with a wavelength of 514.5 nm in a vacuum. What is the difference in energy in joules between the two energy states for the atomic transition that produces this light?
A)6.08 × 10-19 J
B)1.05 × 10-20 J
C)5.18 × 10-19 J
D)3.86 × 10-19 J
E)4.10 × 10-20 J
A)6.08 × 10-19 J
B)1.05 × 10-20 J
C)5.18 × 10-19 J
D)3.86 × 10-19 J
E)4.10 × 10-20 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An atom will emit photons when one of its electrons goes from
A)the K shell to the L shell.
B)the M shell to the N shell.
C)the K shell to the M shell.
D)the N shell to the L shell.
E)the K shell to the N shell.
A)the K shell to the L shell.
B)the M shell to the N shell.
C)the K shell to the M shell.
D)the N shell to the L shell.
E)the K shell to the N shell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Complete the following statement: In the laser-based medical procedure known as photorefractive keratectomy (PRK), nearsightedness and farsightedness can be treated using the laser to
A)remove small amounts of tissue from the lens and change its curvature.
B)remove small amounts of tissue from the cornea and change its curvature.
C)change the index of refraction of the aqueous humor.
D)alter the fluid pressure within the eye.
E)stimulate unused rods and cones on the retina.
A)remove small amounts of tissue from the lens and change its curvature.
B)remove small amounts of tissue from the cornea and change its curvature.
C)change the index of refraction of the aqueous humor.
D)alter the fluid pressure within the eye.
E)stimulate unused rods and cones on the retina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The figure shows an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. Several transitions are shown and are labeled by letters. 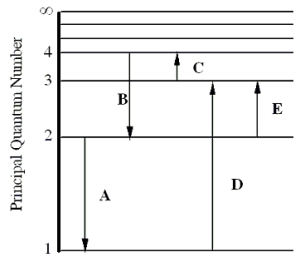 Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Which transition will occur when a hydrogen atom is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 103 nm?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
 Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.Which transition will occur when a hydrogen atom is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 103 nm?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The figure shows an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. Several transitions are shown and are labeled by letters.  Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Determine the wavelength of the radiation involved in transition B.
A)291 nm
B)364 nm
C)487 nm
D)652 nm
E)1910 nm
 Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.Determine the wavelength of the radiation involved in transition B.
A)291 nm
B)364 nm
C)487 nm
D)652 nm
E)1910 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The figure shows an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. Several transitions are shown and are labeled by letters.  Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
In which transition is a Balmer series photon absorbed?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
 Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.In which transition is a Balmer series photon absorbed?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A pulsed laser has an average output power of 4.0 W. Each pulse consists of light at wavelength 5.0 × 10-7 m and has a 25 ms duration. How many photons are emitted in a single pulse?
A)1.0 × 1017
B)2.5 × 1017
C)3.7 × 1017
D)5.0 × 1017
E)7.4 × 1017
A)1.0 × 1017
B)2.5 × 1017
C)3.7 × 1017
D)5.0 × 1017
E)7.4 × 1017

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The figure shows an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. Several transitions are shown and are labeled by letters.  Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Which transition involves the longest wavelength line in the visible portion of the hydrogen spectrum?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
 Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.Which transition involves the longest wavelength line in the visible portion of the hydrogen spectrum?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which one of the following statements best explains why a neon sign does not emit visible light after it is turned off?
A)All of the neon atoms are ionized.
B)Most of the neon atoms are in the ground state.
C)None of the neon atoms are in the n = 2 state.
D)All of the neon atoms have principle quantum number n = 0.
E)Only some of the neon atoms have returned to the n = 1 state.
A)All of the neon atoms are ionized.
B)Most of the neon atoms are in the ground state.
C)None of the neon atoms are in the n = 2 state.
D)All of the neon atoms have principle quantum number n = 0.
E)Only some of the neon atoms have returned to the n = 1 state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The figure shows an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. Several transitions are shown and are labeled by letters.  Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Which transition corresponds to the absorption of the photon with the longest wavelength?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
 Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.Which transition corresponds to the absorption of the photon with the longest wavelength?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The figure shows an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. Several transitions are shown and are labeled by letters.  Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Determine the energy of the photon involved in transition E.
A)1.5 eV
B)1.9 eV
C)3.4 eV
D)10.2 eV
E)12.1 eV
 Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.Determine the energy of the photon involved in transition E.
A)1.5 eV
B)1.9 eV
C)3.4 eV
D)10.2 eV
E)12.1 eV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The figure shows an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. Several transitions are shown and are labeled by letters.  Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Which transition will occur when a hydrogen atom is irradiated with radiation of frequency 1.60 × 1014 Hz?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
 Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.
Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale.Which transition will occur when a hydrogen atom is irradiated with radiation of frequency 1.60 × 1014 Hz?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An electron makes a transition from a higher energy state to a lower one without any external provocation. As a result of the transition, a photon is emitted and moves in a random direction. What is the name of this emission process?
A)stationary emission
B)stimulated emission
C)spectral emission
D)spontaneous emission
E)specular emission
A)stationary emission
B)stimulated emission
C)spectral emission
D)spontaneous emission
E)specular emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Complete the following sentence: Holography is
A)the projection of an image produced by a combination of mirrors and lenses.
B)a photograph of the light produced by a laser.
C)a process for producing three dimensional images using the interference of laser light beams.
D)the name for an imaging process that occurs within a camera when a photograph is taken.
E)the production of a two dimensional image of the three dimensional object.
A)the projection of an image produced by a combination of mirrors and lenses.
B)a photograph of the light produced by a laser.
C)a process for producing three dimensional images using the interference of laser light beams.
D)the name for an imaging process that occurs within a camera when a photograph is taken.
E)the production of a two dimensional image of the three dimensional object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



