Deck 31: International Corporate Finance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 31: International Corporate Finance
1
Consider the following equation: 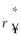 =
= 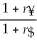 (1 +
(1 + 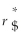 )- 1 The term
)- 1 The term 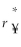 in this equation refers to
in this equation refers to
A) the risk-free rate of interest on the dollar.
B) the risk-free rate of interest on the yen.
C) the cost of capital for the firm in terms of yen.
D) the cost of capital in terms of dollars.
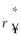 =
= 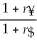 (1 +
(1 + 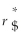 )- 1 The term
)- 1 The term 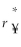 in this equation refers to
in this equation refers toA) the risk-free rate of interest on the dollar.
B) the risk-free rate of interest on the yen.
C) the cost of capital for the firm in terms of yen.
D) the cost of capital in terms of dollars.
the cost of capital for the firm in terms of yen.
2
Consider the following equation: 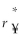 =
= 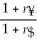 (1 +
(1 + 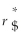 )- 1 The term r$ in this equation refers to
)- 1 The term r$ in this equation refers to
A) the cost of capital for the firm in terms of yen.
B) the cost of capital in terms of dollars.
C) the risk-free rate of interest on the dollar.
D) the risk-free rate of interest on the yen.
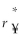 =
= 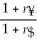 (1 +
(1 + 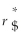 )- 1 The term r$ in this equation refers to
)- 1 The term r$ in this equation refers toA) the cost of capital for the firm in terms of yen.
B) the cost of capital in terms of dollars.
C) the risk-free rate of interest on the dollar.
D) the risk-free rate of interest on the yen.
the risk-free rate of interest on the dollar.
3
Use the information for the question(s) below.
You are a Canadian Investor who is trying to calculate the present value of £5 million cash inflow that will occur one year in the future. The spot exchange rate is S = $1.8839/£ and the forward rate is F1 = $1.8862/£. The appropriate dollar discount rate for this cash flow is 5.32% and the appropriate £ discount rate is 5.24%.
The present value of the £5 million cash inflow computed by first discounting the £s and then converting into dollars is closest to:
A) $8,961,420
B) $8,950,495
C) $8,954,615
D) $8,943,695
You are a Canadian Investor who is trying to calculate the present value of £5 million cash inflow that will occur one year in the future. The spot exchange rate is S = $1.8839/£ and the forward rate is F1 = $1.8862/£. The appropriate dollar discount rate for this cash flow is 5.32% and the appropriate £ discount rate is 5.24%.
The present value of the £5 million cash inflow computed by first discounting the £s and then converting into dollars is closest to:
A) $8,961,420
B) $8,950,495
C) $8,954,615
D) $8,943,695
$8,950,495
4
Which of the following statements regarding international projects is false?
A) Interest rates and costs of capital will likely be different in the foreign country as a result of the macroeconomic environment.
B) The project will most likely generate foreign currency cash flows, and the firm cares about the foreign currency value of the project.
C) Under internationally integrated capital markets, the value of an investment does not depend on the currency we use in the analysis.
D) The firm will probably face a different tax rate in the foreign country and will be subject to both foreign and domestic tax codes.
A) Interest rates and costs of capital will likely be different in the foreign country as a result of the macroeconomic environment.
B) The project will most likely generate foreign currency cash flows, and the firm cares about the foreign currency value of the project.
C) Under internationally integrated capital markets, the value of an investment does not depend on the currency we use in the analysis.
D) The firm will probably face a different tax rate in the foreign country and will be subject to both foreign and domestic tax codes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the following equation: 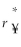 =
= 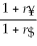 (1 +
(1 + 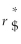 )- 1 The term r¥ in this equation refers to
)- 1 The term r¥ in this equation refers to
A) the cost of capital for the firm in terms of yen.
B) the risk-free rate of interest on the dollar.
C) the cost of capital in terms of dollars.
D) the risk-free rate of interest on the yen.
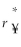 =
= 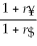 (1 +
(1 + 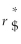 )- 1 The term r¥ in this equation refers to
)- 1 The term r¥ in this equation refers toA) the cost of capital for the firm in terms of yen.
B) the risk-free rate of interest on the dollar.
C) the cost of capital in terms of dollars.
D) the risk-free rate of interest on the yen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Use the information for the question(s) below.
Luther Industries, a Canadian Corporation, is considering a new project located in Great Britain. The expected free cash flows from the project are detailed below:
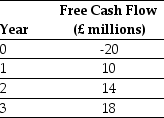 You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.
You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.
Calculate the pound denominated cost of capital for Luther's project.
Luther Industries, a Canadian Corporation, is considering a new project located in Great Britain. The expected free cash flows from the project are detailed below:
 You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.
You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.Calculate the pound denominated cost of capital for Luther's project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Under the condition of internationally integrated capital markets,the value of an investment ________ we use in the analysis because of ________.
A) depends on the currency; the Law of One Price
B) depends on the currency; the exchange rate between two currencies
C) does not depend on the currency; the Law of One Price
D) does not depend on the currency; the exchange rate between two currencies
A) depends on the currency; the Law of One Price
B) depends on the currency; the exchange rate between two currencies
C) does not depend on the currency; the Law of One Price
D) does not depend on the currency; the exchange rate between two currencies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Luther Industries,a Canadian firm,is considering an investment in Japan.The dollar cost of equity for Luther is 12%.The risk-free interest rates on dollars and yen are r$ = 5.5% and r¥ = 1.5% respectively.Luther Industries is willing to assume that capital markets are internationally integrated.Luther Industries needs to know the comparable cost of equity in Japanese yen for a project with free cash flows that are uncorrelated with spot exchange rates.The yen cost of equity for Luther Industries is closest to:
A) 14.0%
B) 12.3%
C) 7.8%
D) 18.5%
A) 14.0%
B) 12.3%
C) 7.8%
D) 18.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the information for the question(s) below.
You are a Canadian Investor who is trying to calculate the present value of £5 million cash inflow that will occur one year in the future. The spot exchange rate is S = $1.8839/£ and the forward rate is F1 = $1.8862/£. The appropriate dollar discount rate for this cash flow is 5.32% and the appropriate £ discount rate is 5.24%.
The present value of the £5 million cash inflow computed by first converting into dollars and then discounting is closest to:
A) $8,950,495
B) $8,954,615
C) $8,943,695
D) $8,961,420
You are a Canadian Investor who is trying to calculate the present value of £5 million cash inflow that will occur one year in the future. The spot exchange rate is S = $1.8839/£ and the forward rate is F1 = $1.8862/£. The appropriate dollar discount rate for this cash flow is 5.32% and the appropriate £ discount rate is 5.24%.
The present value of the £5 million cash inflow computed by first converting into dollars and then discounting is closest to:
A) $8,950,495
B) $8,954,615
C) $8,943,695
D) $8,961,420

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Consider the following equation: S × 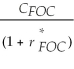 =
= 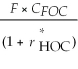 The term F in this equation is
The term F in this equation is
A) the future spot exchange rate.
B) the current spot exchange rate.
C) the amount of foreign currency.
D) the forward exchange rate.
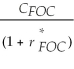 =
= 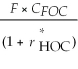 The term F in this equation is
The term F in this equation isA) the future spot exchange rate.
B) the current spot exchange rate.
C) the amount of foreign currency.
D) the forward exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider the following equation: S × 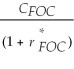 =
= 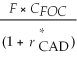 The term
The term 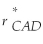 in this equation is
in this equation is
A) the appropriate cost of capital from the standpoint of a Canadian investor.
B) the risk-free rate for a foreign investor.
C) the risk-free rate for a Canadian investor.
D) the appropriate cost of capital from the standpoint of a foreign investor.
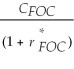 =
= 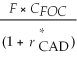 The term
The term 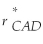 in this equation is
in this equation isA) the appropriate cost of capital from the standpoint of a Canadian investor.
B) the risk-free rate for a foreign investor.
C) the risk-free rate for a Canadian investor.
D) the appropriate cost of capital from the standpoint of a foreign investor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The risk of the foreign project is ________ the risk of Canadian domestic projects because the foreign project contains ________ that the domestic projects often do not contain.
A) likely to be the same as; residual exchange rate risk
B) unlikely to be exactly the same as; residual exchange rate risk
C) likely to be the same as; residual inflation risk
D) unlikely to be exactly the same as; residual inflation risk
A) likely to be the same as; residual exchange rate risk
B) unlikely to be exactly the same as; residual exchange rate risk
C) likely to be the same as; residual inflation risk
D) unlikely to be exactly the same as; residual inflation risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the following equation: 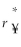 =
= 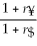 (1 +
(1 + 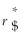 )- 1 The term
)- 1 The term 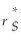 in this equation refers to
in this equation refers to
A) the cost of capital in terms of dollars.
B) the risk-free rate of interest on the yen.
C) the risk-free rate of interest on the dollar.
D) the cost of capital for the firm in terms of yen.
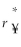 =
= 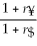 (1 +
(1 + 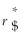 )- 1 The term
)- 1 The term 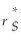 in this equation refers to
in this equation refers toA) the cost of capital in terms of dollars.
B) the risk-free rate of interest on the yen.
C) the risk-free rate of interest on the dollar.
D) the cost of capital for the firm in terms of yen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements is false?
A) If the foreign project is owned by a domestic corporation, managers and shareholders need to determine the home currency value of the foreign currency cash flows.
B) The most obvious difference between a domestic project and a foreign project is that the foreign project will most likely generate cash flows in a foreign currency.
C) The risk of the foreign project is unlikely to be exactly the same as the risk of domestic projects (or the firm as a whole), because the foreign project contains residual exchange rate risk that the domestic projects often do not contain.
D) In an internationally integrated capital market, two equivalent methods are available for calculating the NPV of a foreign project: either we can calculate the NPV in the foreign country and convert it to the local currency at the forward rate, or we can convert the cash flows of the foreign project into the local currency and then calculate the NPV of these cash flows.
A) If the foreign project is owned by a domestic corporation, managers and shareholders need to determine the home currency value of the foreign currency cash flows.
B) The most obvious difference between a domestic project and a foreign project is that the foreign project will most likely generate cash flows in a foreign currency.
C) The risk of the foreign project is unlikely to be exactly the same as the risk of domestic projects (or the firm as a whole), because the foreign project contains residual exchange rate risk that the domestic projects often do not contain.
D) In an internationally integrated capital market, two equivalent methods are available for calculating the NPV of a foreign project: either we can calculate the NPV in the foreign country and convert it to the local currency at the forward rate, or we can convert the cash flows of the foreign project into the local currency and then calculate the NPV of these cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the information for the question(s) below.
Luther Industries, a Canadian Corporation, is considering a new project located in Great Britain. The expected free cash flows from the project are detailed below:
 You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.
You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.
What is the pound present value of the project?
Luther Industries, a Canadian Corporation, is considering a new project located in Great Britain. The expected free cash flows from the project are detailed below:
 You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.
You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.What is the pound present value of the project?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Because obtaining forward rate quotes for as long as four years in the future is difficult,managers normally use the covered ________ to compute ________.
A) interest rate parity; the forward rates
B) price parity; the forward rates
C) interest rate parity; the spot rates
D) price parity; the spot rates
A) interest rate parity; the forward rates
B) price parity; the forward rates
C) interest rate parity; the spot rates
D) price parity; the spot rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Consider the following equation: S × 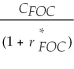 =
= 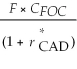 The term
The term 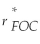 in this equation is
in this equation is
A) the risk-free rate for a foreign investor.
B) the risk-free rate for a Canadian investor.
C) the appropriate cost of capital from the standpoint of a foreign investor.
D) the appropriate cost of capital from the standpoint of a Canadian investor.
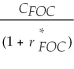 =
= 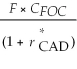 The term
The term 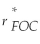 in this equation is
in this equation isA) the risk-free rate for a foreign investor.
B) the risk-free rate for a Canadian investor.
C) the appropriate cost of capital from the standpoint of a foreign investor.
D) the appropriate cost of capital from the standpoint of a Canadian investor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consider the following equation: S × 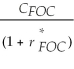 =
= 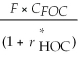 The term S in this equation is
The term S in this equation is
A) the forward exchange rate.
B) the amount of foreign currency.
C) the future spot exchange rate.
D) the current spot exchange rate.
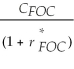 =
= 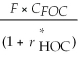 The term S in this equation is
The term S in this equation isA) the forward exchange rate.
B) the amount of foreign currency.
C) the future spot exchange rate.
D) the current spot exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The current spot exchange rate, S, is $1.8862/£. Suppose that the yield curve in both countries is flat. The risk-free rate on dollars, r$, is 5.35% and the risk-free interest rate on pounds, r£, is 4.80%.
Using the covered interest parity condition,the calculated three-year forward rate F3 is closest to:
A) $1.8568/£
B) $1.9161/£
C) $1.8961/£
D) $1.8764/£
The current spot exchange rate, S, is $1.8862/£. Suppose that the yield curve in both countries is flat. The risk-free rate on dollars, r$, is 5.35% and the risk-free interest rate on pounds, r£, is 4.80%.
Using the covered interest parity condition,the calculated three-year forward rate F3 is closest to:
A) $1.8568/£
B) $1.9161/£
C) $1.8961/£
D) $1.8764/£

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The current spot exchange rate, S, is $1.8862/£. Suppose that the yield curve in both countries is flat. The risk-free rate on dollars, r$, is 5.35% and the risk-free interest rate on pounds, r£, is 4.80%.
Using the covered interest parity condition,the calculated one-year forward rate F1 is closest to:
A) $1.8568/£
B) $1.8764/£
C) $1.9161/£
D) $1.8961/£
The current spot exchange rate, S, is $1.8862/£. Suppose that the yield curve in both countries is flat. The risk-free rate on dollars, r$, is 5.35% and the risk-free interest rate on pounds, r£, is 4.80%.
Using the covered interest parity condition,the calculated one-year forward rate F1 is closest to:
A) $1.8568/£
B) $1.8764/£
C) $1.9161/£
D) $1.8961/£

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
For Canadian companies,if the foreign project is a separately incorporated subsidiary of the parent,the amount of taxes a company pays generally depends on the amount of profits ________.
A) received in Canada
B) earned in Canada
C) earned in the host country
D) received in the host country
A) received in Canada
B) earned in Canada
C) earned in the host country
D) received in the host country

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Many countries regulate or limit capital inflows or outflows, and many do not allow their currencies to be freely converted into dollars, thereby creating capital market segmentation.
B) The existence of internationally integrated capital markets makes many decisions in international corporate finance more complicated but potentially more lucrative for a firm that is well positioned to exploit the market segmentation.
C) Political, legal, social, and cultural characteristics that differ across countries may require compensation in the form of a country risk premium.
D) Swaps allow firms to mitigate their exchange rate risk exposure between assets and liabilities, while still making investments and raising funds in the most attractive locales.
A) Many countries regulate or limit capital inflows or outflows, and many do not allow their currencies to be freely converted into dollars, thereby creating capital market segmentation.
B) The existence of internationally integrated capital markets makes many decisions in international corporate finance more complicated but potentially more lucrative for a firm that is well positioned to exploit the market segmentation.
C) Political, legal, social, and cultural characteristics that differ across countries may require compensation in the form of a country risk premium.
D) Swaps allow firms to mitigate their exchange rate risk exposure between assets and liabilities, while still making investments and raising funds in the most attractive locales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements is false?
A) When the foreign tax rate is less than the Canadian tax rate, deferral can provide significant benefits.
B) The Canadian tax liability is not incurred until the profits are brought back home if the foreign operation is set up as a foreign branch rather than as a separately incorporated subsidiary.
C) If a company chooses not to repatriate £12.5 million in pre-tax earnings, for example, it effectively reinvests those earnings abroad and defers its Canadian tax liability.
D) When the foreign tax rates exceed the Canadian tax rates, there are no benefits to deferral because in such a case there is no additional Canadian tax liability.
A) When the foreign tax rate is less than the Canadian tax rate, deferral can provide significant benefits.
B) The Canadian tax liability is not incurred until the profits are brought back home if the foreign operation is set up as a foreign branch rather than as a separately incorporated subsidiary.
C) If a company chooses not to repatriate £12.5 million in pre-tax earnings, for example, it effectively reinvests those earnings abroad and defers its Canadian tax liability.
D) When the foreign tax rates exceed the Canadian tax rates, there are no benefits to deferral because in such a case there is no additional Canadian tax liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The amount of the taxes paid in dollars for the Japanese operations is closest to:
A) $29.5 million
B) $5.1 million
C) $50.0 million
D) $20.5 million
A) $29.5 million
B) $5.1 million
C) $50.0 million
D) $20.5 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the foreign tax rate is ________ the Canadian tax rate,the company pays total taxes ________ the Canadian tax rate on its foreign earnings.
A) greater than; equal to
B) greater than; more than
C) less than; equal to
D) less than; less than
A) greater than; equal to
B) greater than; more than
C) less than; equal to
D) less than; less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements is false?
A) If the foreign tax rate exceeds the Canadian tax rate, companies must pay this higher rate on foreign earnings.
B) Canadian tax policy allows companies to apply the part of the tax credit that is not used to offset domestic taxes owed, so this extra tax credit is not wasted.
C) If the foreign tax rate is less than the Canadian tax rate, the company pays total taxes equal to the Canadian tax rate on its foreign earnings.
D) A full tax credit is given for foreign taxes paid up to the amount of the Canadian tax liability.
A) If the foreign tax rate exceeds the Canadian tax rate, companies must pay this higher rate on foreign earnings.
B) Canadian tax policy allows companies to apply the part of the tax credit that is not used to offset domestic taxes owed, so this extra tax credit is not wasted.
C) If the foreign tax rate is less than the Canadian tax rate, the company pays total taxes equal to the Canadian tax rate on its foreign earnings.
D) A full tax credit is given for foreign taxes paid up to the amount of the Canadian tax liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Differential access to national capital markets is common enough that it provides the best explanation for the existence of currency swaps, which are like the interest rate swap contracts, but with the holder receiving coupons in one currency and paying coupons denominated in a different currency.
B) Currency swaps generally also have final face value payments, also in different currencies.
C) Using a currency swap, a firm can borrow in the market where it has the best access to capital, and then "swap" the coupon and principal payments to whichever currency it would prefer to make payments in.
D) With differential access to national markets, to maximize shareholder value, the firm should raise capital in the foreign market; the method of valuing the foreign project as if it were a domestic project would then provide the correct NPV.
A) Differential access to national capital markets is common enough that it provides the best explanation for the existence of currency swaps, which are like the interest rate swap contracts, but with the holder receiving coupons in one currency and paying coupons denominated in a different currency.
B) Currency swaps generally also have final face value payments, also in different currencies.
C) Using a currency swap, a firm can borrow in the market where it has the best access to capital, and then "swap" the coupon and principal payments to whichever currency it would prefer to make payments in.
D) With differential access to national markets, to maximize shareholder value, the firm should raise capital in the foreign market; the method of valuing the foreign project as if it were a domestic project would then provide the correct NPV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the information for the question(s) below.
Luther Industries, a Canadian Corporation, is considering a new project located in Great Britain. The expected free cash flows from the project are detailed below:
 You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.
You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.
What is the dollar present value of the project?
Luther Industries, a Canadian Corporation, is considering a new project located in Great Britain. The expected free cash flows from the project are detailed below:
 You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.
You know that the spot exchange rate is S = 1.8862/£. In addition, the risk-free interest rate on dollars and pounds is 5.4% and 4.6% respectively. Assume that these markets are internationally integrated and the uncertainty in the free cash flow is not correlated with uncertainty in the exchange rate. You have determined that the dollar WACC for these cash flows is 10.2%.What is the dollar present value of the project?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Canadian tax policy ________ companies to apply the part of the tax credit that is not used to offset domestic taxes owed.
A) does not allow
B) allows
C) encourages
D) discourages
A) does not allow
B) allows
C) encourages
D) discourages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements is false?
A) In some countries, especially in the developing world, all investors do not have equal access to financial securities.
B) Firms may face differential access to markets if there is any kind of asymmetry with respect to information about them.
C) In some cases, a country's risk-free securities are internationally integrated but markets for a specific firm's securities are not.
D) When countries' capital markets are not integrated we call them disintegrated capital markets.
A) In some countries, especially in the developing world, all investors do not have equal access to financial securities.
B) Firms may face differential access to markets if there is any kind of asymmetry with respect to information about them.
C) In some cases, a country's risk-free securities are internationally integrated but markets for a specific firm's securities are not.
D) When countries' capital markets are not integrated we call them disintegrated capital markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Use the information for the question(s) below.
KT Enterprises, a Canadian import-export trading company, is considering its international tax situation. Currently KT's Canadian tax rate is 35%. KT has significant operations in both Japan and Ireland. In Japan the current exchange rate is ¥118.4/$ and earnings in Japan are taxed at 41%. In Ireland the current exchange rate is $1.27/€ and earnings in Ireland are taxed at 12.5%. KT's profits, which are fully and immediately repatriated, and foreign taxes paid for the current year are shown here (in millions):
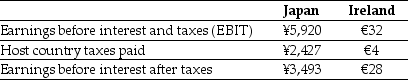
After the Japanese taxes are paid,the amount of the earnings before interest and after taxes in dollars from the Japanese operations is closest to:
A) $20.5 million
B) $29.5 million
C) $5.1 million
D) $50.0 million
KT Enterprises, a Canadian import-export trading company, is considering its international tax situation. Currently KT's Canadian tax rate is 35%. KT has significant operations in both Japan and Ireland. In Japan the current exchange rate is ¥118.4/$ and earnings in Japan are taxed at 41%. In Ireland the current exchange rate is $1.27/€ and earnings in Ireland are taxed at 12.5%. KT's profits, which are fully and immediately repatriated, and foreign taxes paid for the current year are shown here (in millions):

After the Japanese taxes are paid,the amount of the earnings before interest and after taxes in dollars from the Japanese operations is closest to:
A) $20.5 million
B) $29.5 million
C) $5.1 million
D) $50.0 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Canadian tax policy requires Canadian corporations to pay taxes on their foreign income at the same rate as profits earned in Canada.
B) The home government gets an opportunity to tax the income from a foreign project to the domestic firm.
C) The general international arrangement prevailing with respect to taxation of corporate profits is that the home country gets the first opportunity to tax income.
D) The home government must establish a tax policy specifying its treatment of foreign income and foreign taxes paid on that income.
A) Canadian tax policy requires Canadian corporations to pay taxes on their foreign income at the same rate as profits earned in Canada.
B) The home government gets an opportunity to tax the income from a foreign project to the domestic firm.
C) The general international arrangement prevailing with respect to taxation of corporate profits is that the home country gets the first opportunity to tax income.
D) The home government must establish a tax policy specifying its treatment of foreign income and foreign taxes paid on that income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Use the information for the question(s) below.
KT Enterprises, a Canadian import-export trading company, is considering its international tax situation. Currently KT's Canadian tax rate is 35%. KT has significant operations in both Japan and Ireland. In Japan the current exchange rate is ¥118.4/$ and earnings in Japan are taxed at 41%. In Ireland the current exchange rate is $1.27/€ and earnings in Ireland are taxed at 12.5%. KT's profits, which are fully and immediately repatriated, and foreign taxes paid for the current year are shown here (in millions):

After the Irish taxes are paid,the amount of the earnings before interest and after taxes in dollars from the Ireland operations is closest to:
A) $5.1 million
B) $20.5 million
C) $35.6 million
D) $29.5 million
KT Enterprises, a Canadian import-export trading company, is considering its international tax situation. Currently KT's Canadian tax rate is 35%. KT has significant operations in both Japan and Ireland. In Japan the current exchange rate is ¥118.4/$ and earnings in Japan are taxed at 41%. In Ireland the current exchange rate is $1.27/€ and earnings in Ireland are taxed at 12.5%. KT's profits, which are fully and immediately repatriated, and foreign taxes paid for the current year are shown here (in millions):

After the Irish taxes are paid,the amount of the earnings before interest and after taxes in dollars from the Ireland operations is closest to:
A) $5.1 million
B) $20.5 million
C) $35.6 million
D) $29.5 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the foreign tax rate ________ the Canadian tax rate,companies must pay ________ on foreign earnings.
A) exceeds; this higher rate
B) exceeds; an extra rate
C) exceeds; the same as the Canadian tax rate
D) exceeds; a lower rate in Canada
A) exceeds; this higher rate
B) exceeds; an extra rate
C) exceeds; the same as the Canadian tax rate
D) exceeds; a lower rate in Canada

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The amount of the taxes paid in dollars for the Irish operations is closest to:
A) $20.5 million
B) $5.1 million
C) $29.5 million
D) $50.0 million
A) $20.5 million
B) $5.1 million
C) $29.5 million
D) $50.0 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Luther Industries,a Canadian firm,has a subsidiary in the United Kingdom.This year,the subsidiary reported and repatriated earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT)of £45 million.The current exchange rate is $1.86/£.The tax rate in the U.K.for this activity is 28%.Under Canadian tax codes,Luther is facing a 35% corporate tax rate on their earnings.What is Luther's Canadian tax liability on its U.K.subsidiary?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Other benefits from deferral arise because the firm effectively gains a real option to repatriate income at times when repatriation might be cheaper.
B) By pooling foreign income, the firm effectively pays the combined tax rate on all foreign income.
C) In years in which the Canadian tax rate exceeds the combined tax rate on all foreign income, the repatriation of additional income does not incur an additional Canadian tax liability, so the earnings can be repatriated tax-free.
D) Deferring repatriation of earnings lowers the overall tax burden in much the same way that deferring capital gains lowers the tax burden imposed by the capital gains tax.
A) Other benefits from deferral arise because the firm effectively gains a real option to repatriate income at times when repatriation might be cheaper.
B) By pooling foreign income, the firm effectively pays the combined tax rate on all foreign income.
C) In years in which the Canadian tax rate exceeds the combined tax rate on all foreign income, the repatriation of additional income does not incur an additional Canadian tax liability, so the earnings can be repatriated tax-free.
D) Deferring repatriation of earnings lowers the overall tax burden in much the same way that deferring capital gains lowers the tax burden imposed by the capital gains tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements is false?
A) If the Canadian tax rate exceeds the combined tax rate on all foreign income, it is valid to assume that the firm pays the same tax rate on all income no matter where it is earned.
B) Firms can lower their taxes by pooling multiple foreign projects and accelerating the repatriation of earnings.
C) Under Canadian tax law, multinational corporations may use any excess tax credits generated in high-tax foreign countries to offset their net Canadian tax liabilities on earnings in low-tax foreign countries.
D) If the foreign tax rate exceeds the Canadian tax rate, because the Canadian tax credit exceeds the amount of Canadian taxes owed, no tax is owed in Canada.
A) If the Canadian tax rate exceeds the combined tax rate on all foreign income, it is valid to assume that the firm pays the same tax rate on all income no matter where it is earned.
B) Firms can lower their taxes by pooling multiple foreign projects and accelerating the repatriation of earnings.
C) Under Canadian tax law, multinational corporations may use any excess tax credits generated in high-tax foreign countries to offset their net Canadian tax liabilities on earnings in low-tax foreign countries.
D) If the foreign tax rate exceeds the Canadian tax rate, because the Canadian tax credit exceeds the amount of Canadian taxes owed, no tax is owed in Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Currency swaps allow firms to mitigate their exchange rate risk exposure between ________,while still making investments and raising funds in the most attractive locales.
A) assets and liabilities
B) long-term liabilities and equity
C) assets and equity
D) equity and liabilities
A) assets and liabilities
B) long-term liabilities and equity
C) assets and equity
D) equity and liabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Canadian tax policy requires that a ________ is given for foreign taxes paid up to the amount of the ________.
A) 50 percent tax credit; Canadian tax liability
B) full tax credit; Canadian tax liability
C) 50 percent tax credit; foreign tax liability
D) full tax credit; foreign tax liability
A) 50 percent tax credit; Canadian tax liability
B) full tax credit; Canadian tax liability
C) 50 percent tax credit; foreign tax liability
D) full tax credit; foreign tax liability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What conditions cause the cash flows of a foreign project to be affected by exchange rate risk?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Whenever a project has cash flows that depend on the values of ________,the most convenient approach is to ________ the cash flows according to the currency they depend on.
A) multiple currencies; separate
B) multiple currencies; consolidate
C) single currency; separate
D) single currency; combine
A) multiple currencies; separate
B) multiple currencies; consolidate
C) single currency; separate
D) single currency; combine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Suppose the interest rate on Russian government bonds is 7.8%,and the current exchange rate is 26.8 rubles per dollar.If the forward exchange rate is 27.2 rubles per dollar,and the current Canadian risk-free interest rate is 4.6%,what is the implied credit spread for the Russian government bonds?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The rate of interest paid on government bonds or other securities in a country with a tradition of weak enforcement of property rights is likely not really a risk-free rate. Instead, interest rates in the country will reflect a risk premium for the possibility of default, so relations such as covered interest rate parity will likely not hold exactly.
B) If the return difference in a segmented financial market results from a market friction such as capital controls, corporations can exploit this friction by setting up projects and raising capital in the high-return country/currency.
C) Important macroeconomic reasons for segmented capital markets include capital controls and foreign exchange controls that create barriers to international capital flows and thus segment national markets.
D) A segmented financial market has an important implication for international corporate finance: one country or currency has a higher rate of return than another country or currency, when the two rates are compared in the same currency.
A) The rate of interest paid on government bonds or other securities in a country with a tradition of weak enforcement of property rights is likely not really a risk-free rate. Instead, interest rates in the country will reflect a risk premium for the possibility of default, so relations such as covered interest rate parity will likely not hold exactly.
B) If the return difference in a segmented financial market results from a market friction such as capital controls, corporations can exploit this friction by setting up projects and raising capital in the high-return country/currency.
C) Important macroeconomic reasons for segmented capital markets include capital controls and foreign exchange controls that create barriers to international capital flows and thus segment national markets.
D) A segmented financial market has an important implication for international corporate finance: one country or currency has a higher rate of return than another country or currency, when the two rates are compared in the same currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How do we make adjustments when a project has inputs and outputs in different currencies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



