Deck 9: Thermodynamics: the Second and Third Laws
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Thermodynamics: the Second and Third Laws
1
Calculate the change in molar entropy when 2.00 mol of ozone are compressed isothermally to one quarter of its original volume.Treat ozone as an ideal gas.
A)(-23.1 J.K - 1 )
B)(-10.0 J.K - 1 )
C)(-1.39 J.K - 1 )
D)+10.0 J.K - 1
E)+23.1 J.K - 1
A)(-23.1 J.K - 1 )
B)(-10.0 J.K - 1 )
C)(-1.39 J.K - 1 )
D)+10.0 J.K - 1
E)+23.1 J.K - 1
(-23.1 J.K - 1 )
2
The enthalpy of fusion of H2O(s)at its normal melting point is 6.01 kJ.mol-1.The entropy change for freezing 1 mol of water at this temperature is
A)+20.2 J.K-1.mol-1.
B)0 J.K-1.mol-1.
C)(-20.2 J.K-1.mol-1. )
D)+22.0 J.K-1.mol-1.
E)(-22.0 J.K-1.molF-1. )
A)+20.2 J.K-1.mol-1.
B)0 J.K-1.mol-1.
C)(-20.2 J.K-1.mol-1. )
D)+22.0 J.K-1.mol-1.
E)(-22.0 J.K-1.molF-1. )
(-22.0 J.K-1.molF-1. )
3
Use Trouton's constant to estimate the enthalpy of vaporization of diethyl ether,which boils at 309 K.
A)+85 kJ.mol - 1
B)+26 kJ.mol - 1
C)+275 kJ.mol - 1
D)(-85 kJ.mol - 1 )
E)(+3.6 kJ.mol - 1 )
A)+85 kJ.mol - 1
B)+26 kJ.mol - 1
C)+275 kJ.mol - 1
D)(-85 kJ.mol - 1 )
E)(+3.6 kJ.mol - 1 )
+26 kJ.mol - 1
4
What is the change in entropy when the pressure of an ideal gas is increased at constant temperature? Choose from +,0,-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The change in molar entropy for vaporization of all liquids is about the same.True or false?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Calculate the change in molar entropy when the pressure of argon is allowed to double isothermally (assume ideal behavior).
A)+1.39 J.K - 1.mol - 1
B)(-1.39 J.K -- 1.mol - 1 )
C)(-4.16 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
D)(-5.76 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
E)+5.76 J.K - 1.mol - 1
A)+1.39 J.K - 1.mol - 1
B)(-1.39 J.K -- 1.mol - 1 )
C)(-4.16 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
D)(-5.76 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
E)+5.76 J.K - 1.mol - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use Trouton's constant to estimate the enthalpy of condensation of diethyl ether,which boils at 309 K.
A)(-26 kJ.mol - 1 )
B)+26 kJ.mol - 1
C)(-275 kJ.mol - 1 )
D)(-85 kJ.mol - 1 )
E)+85 kJ.mol - 1
A)(-26 kJ.mol - 1 )
B)+26 kJ.mol - 1
C)(-275 kJ.mol - 1 )
D)(-85 kJ.mol - 1 )
E)+85 kJ.mol - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The molar entropy of silver at 298 K is equal to the area under the curve obtained by plotting (from T = 0 to T = 298 K)
A)CP versus T.
B)lnCP versus T.
C)ln(CP/T)versus T.
D)CP/T versus T.
E)CP versus 1/T.
A)CP versus T.
B)lnCP versus T.
C)ln(CP/T)versus T.
D)CP/T versus T.
E)CP versus 1/T.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Calculate the standard entropy of vaporization of ethanol at its boiling point,352 K.The standard molar enthalpy of vaporization of ethanol at its boiling point is 40.5 kJ.mol - 1.
A)+40.5 kJ.K - 1.mol - 1
B)+115 J.K - 1.mol - 1
C)(-40.5 kJ.K - 1.mol - 1 )
D)+513 J.K - 1.mol - 1
E)(-115 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
A)+40.5 kJ.K - 1.mol - 1
B)+115 J.K - 1.mol - 1
C)(-40.5 kJ.K - 1.mol - 1 )
D)+513 J.K - 1.mol - 1
E)(-115 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
All entropies of fusion are positive.True or false?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Calculate the standard entropy of condensation of chloroform at its boiling point,335 K.The standard molar enthalpy of vaporization of chloroform at its boiling point is 31.4 kJ.mol-1.
A)(-31.3 kJ.K-1.mol-1 )
B)+93.7 J.K - 1.mol - 1
C)(-93.7 J.K-1.mol-1 )
D)+31.4 kJ.K-1.mol-1
E)+506 J.K-1.mol-1
A)(-31.3 kJ.K-1.mol-1 )
B)+93.7 J.K - 1.mol - 1
C)(-93.7 J.K-1.mol-1 )
D)+31.4 kJ.K-1.mol-1
E)+506 J.K-1.mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The cooling of a hot metal is accompanied by an increase in entropy.True or false?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the following processes (treat all gases as ideal).
1.The pressure of 1 mole of oxygen gas is allowed to double isothermally.
2.Carbon dioxide is allowed to expand isothermally to 10 times its original volume.
3.The temperature of 1 mol of helium is increased 25 C at constant pressure.
4.Nitrogen gas is compressed isothermally to half its original volume.
"5.A glass of water loses 100 J of energy reversibly at 30 C.
Which of these processes lead(s)to an increase in entropy?"
A)1 and 4
B)5
C)3 and 5
D)2 and 3
E)1 and 2
1.The pressure of 1 mole of oxygen gas is allowed to double isothermally.
2.Carbon dioxide is allowed to expand isothermally to 10 times its original volume.
3.The temperature of 1 mol of helium is increased 25 C at constant pressure.
4.Nitrogen gas is compressed isothermally to half its original volume.
"5.A glass of water loses 100 J of energy reversibly at 30 C.
Which of these processes lead(s)to an increase in entropy?"
A)1 and 4
B)5
C)3 and 5
D)2 and 3
E)1 and 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The molar heat capacity of Cu(s)at 1 atm pressure has been measured over a range of temperatures from close to 0 K to 400 K.Describe how you would obtain the standard molar entropy of Cu(s)at 298 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider the following processes (treat all gases as ideal).
1.The pressure of 1 mol of oxygen gas is allowed to double isothermally.
2.Carbon dioxide is allowed to expand isothermally to 10 times its original volume.
3.The temperature of 1 mol of helium is increased 25 C at constant pressure.
4.Nitrogen gas is compressed isothermally to half its original volume.
"5.A glass of water loses 100 J of energy reversibly at 30 C.
Which of these processes lead(s)to a decrease in entropy?"
A)1 and 2
B)2
C)3 and 4
D)1, 4, and 5
E)1 and 3
1.The pressure of 1 mol of oxygen gas is allowed to double isothermally.
2.Carbon dioxide is allowed to expand isothermally to 10 times its original volume.
3.The temperature of 1 mol of helium is increased 25 C at constant pressure.
4.Nitrogen gas is compressed isothermally to half its original volume.
"5.A glass of water loses 100 J of energy reversibly at 30 C.
Which of these processes lead(s)to a decrease in entropy?"
A)1 and 2
B)2
C)3 and 4
D)1, 4, and 5
E)1 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Calculate the normal boiling point of chloroform,given that the standard entropy and enthalpy of vaporization of chloroform is +93.7 J∙K - 1∙mol - 1 and 31.4 kJ∙mol - 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The temperature of 2.00 mol Ne(g)is increased from 25 C to 200 C at constant pressure.Calculate the change in the entropy of neon (assume ideal behavior).
A)+7.68 J.K - 1
B)+19.2 J.K - 1
C)(-7.68 J.K - 1 )
D)(-19.2 J.K - 1 )
E)+9.60 J.K - 1
A)+7.68 J.K - 1
B)+19.2 J.K - 1
C)(-7.68 J.K - 1 )
D)(-19.2 J.K - 1 )
E)+9.60 J.K - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Calculate the standard entropy of fusion of ethanol at its melting point,159 K.The standard molar enthalpy of fusion of ethanol at its melting point is 5.02 kJ.mol - 1.
A)(-5.02 kJ.K - 1.mol - 1 )
B)(-31.6 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
C)+5.02 kJ.K -1.mol-1
D)+31.6 J.K- 1.mol- 1
E)(-44.0 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
A)(-5.02 kJ.K - 1.mol - 1 )
B)(-31.6 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
C)+5.02 kJ.K -1.mol-1
D)+31.6 J.K- 1.mol- 1
E)(-44.0 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
For a given transfer of energy,a greater change in disorder occurs when the temperature is high.True or false?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Calculate the change in entropy of a large pail of water after 200 J of energy is reversibly transferred to the water at 20 C.
A)(-0.733 J.K - 1 )
B)+0.683 J.K - 1
C)(-0.683 J.K - 1 )
D)+0.733 J.K - 1
E)(-200 J.K - 1 )
A)(-0.733 J.K - 1 )
B)+0.683 J.K - 1
C)(-0.683 J.K - 1 )
D)+0.733 J.K - 1
E)(-200 J.K - 1 )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following quantities is not equal to zero at 298 K?
A)( Hf (H+(aq)))
B)S (H2(g))
C)S (H+(aq))
D)( Gf (H+(aq)))
E)( Hf (H2(g)))
A)( Hf (H+(aq)))
B)S (H2(g))
C)S (H+(aq))
D)( Gf (H+(aq)))
E)( Hf (H2(g)))

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following has the smallest molar entropy?
A)C(diamond)
B)C60(s)
C)CaCO3(s)
D)CO2(s)
E)C(graphite)
A)C(diamond)
B)C60(s)
C)CaCO3(s)
D)CO2(s)
E)C(graphite)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following has the lowest standard molar entropy?
A)C(graphite)
B)P4(s)
C)S8(s)
D)C60(s)
E)C(diamond)
A)C(graphite)
B)P4(s)
C)S8(s)
D)C60(s)
E)C(diamond)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following has the smallest entropy at 298 K?
A)Kr(g)
B)Br2(l)
C)Xe(g)
D)Cl2(g)
E)Br2(g)
A)Kr(g)
B)Br2(l)
C)Xe(g)
D)Cl2(g)
E)Br2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following has the smallest molar entropy at 298 K?
A)Cl2(g)
B)N2(g)
C)He(g)
D)F2(g)
E)Ne(g)
A)Cl2(g)
B)N2(g)
C)He(g)
D)F2(g)
E)Ne(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following reactions has the smallest value of S ?
A)NH3(g)+ HCl(g) NH4Cl(s)
B)2H2(l)+ O2(l) 2H2O(g)
C)N2(g)+ 3H2(g) 2NH3(g)
D)K(s)+ O2(g) KO2(s)
E)BaCl2.2H2O(s) BaCl2(s)+ 2H2O(g)
A)NH3(g)+ HCl(g) NH4Cl(s)
B)2H2(l)+ O2(l) 2H2O(g)
C)N2(g)+ 3H2(g) 2NH3(g)
D)K(s)+ O2(g) KO2(s)
E)BaCl2.2H2O(s) BaCl2(s)+ 2H2O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Use the Boltzmann formula to calculate the entropy at T = 0 of 1.00 mol chlorobenzene,C6H5Cl,where each molecule can be oriented in any of six ways.
A)0 J.K - 1; at T = 0, there is no randomness.
B)(-15 J.K - 1 )
C)(-30 J.K - 1 )
D)+30 J.K - 1
E)+15 J.K - 1
A)0 J.K - 1; at T = 0, there is no randomness.
B)(-15 J.K - 1 )
C)(-30 J.K - 1 )
D)+30 J.K - 1
E)+15 J.K - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The molar entropy of Pb(s)at 298 K is equal to
A)CP × 298.
B)zero.
C)the sum of the integral of CPdT/T from 0 K to 298 K.
A)CP × 298.
B)zero.
C)the sum of the integral of CPdT/T from 0 K to 298 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Calculate Ssurr° at 298 K for the reaction 6C(s)+ 3H2(g) C6H6(l)
Hr° = +49.0 kJ.mol - 1, Sr° = -253 J.K - 1.mol - 1
A)+164 J.K - 1.mol - 1
B)(-417 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
C)+253 J.K - 1.mol - 1
D)(-164 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
E)(-253 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
Hr° = +49.0 kJ.mol - 1, Sr° = -253 J.K - 1.mol - 1
A)+164 J.K - 1.mol - 1
B)(-417 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
C)+253 J.K - 1.mol - 1
D)(-164 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
E)(-253 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is always true for a spontaneous process at constant temperature?
A)( Ssystem + Ssurroundings = q/T)
B)( S > 0)
C)( S = q/T)
D)( Ssystem + Ssurroundings > 0)
E)( S < q/T)
A)( Ssystem + Ssurroundings = q/T)
B)( S > 0)
C)( S = q/T)
D)( Ssystem + Ssurroundings > 0)
E)( S < q/T)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Calculate the standard entropy for the following reaction from standard molar entropies.
NH4ClO4(s)+ Al(s) NH4Cl(s)+ Al2O3(s)
NH4ClO4(s)+ Al(s) NH4Cl(s)+ Al2O3(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The experimental value of the molar entropy of 1 mol NO at 0 K is about 5 J∙K - 1.We can conclude that in the crystal the molecules of NO are arranged randomly.True or false?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following has the largest molar entropy?
A)H2(g)
B)KF(aq)
C)CO2(s)
D)CaO(s)
E)He(l)
A)H2(g)
B)KF(aq)
C)CO2(s)
D)CaO(s)
E)He(l)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following would probably have a positive S value?
A)He(g, 2 atm) He(g, 10 atm)
B)H2(g)+ I2(s) 2HI(g)
C)2Ag(s)+ Br2(l) 2AgBr(s)
D)O2(g) O2(aq)
E)2NO2(g) N2O4(g)
A)He(g, 2 atm) He(g, 10 atm)
B)H2(g)+ I2(s) 2HI(g)
C)2Ag(s)+ Br2(l) 2AgBr(s)
D)O2(g) O2(aq)
E)2NO2(g) N2O4(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
For CO2(g) CO2(aq),is the entropy change positive or negative?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For He(g,10 atm) He(g,1 atm),is the entropy change positive or negative?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Calculate Ssurr at 298 K for the reaction H2(g)+ F2(g) 2HF(g)
Hr° = -546 kJ.mol - 1, Sr° = +14.1 J.K - 1.mol - 1
A)+14.1 J.K - 1.mol- 1
B)+1820 J.K - 1.mol - 1
C)+1830 J.K-1.mol-1
D)(-1830 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
E)(-14.1 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
Hr° = -546 kJ.mol - 1, Sr° = +14.1 J.K - 1.mol - 1
A)+14.1 J.K - 1.mol- 1
B)+1820 J.K - 1.mol - 1
C)+1830 J.K-1.mol-1
D)(-1830 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
E)(-14.1 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Sketch a plot of the molar entropy of oxygen gas from 0 K to 200 K.The normal melting and boiling points of oxygen are 55 K and 90 K,respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Calculate Stotal for the isothermal irreversible free expansion of 1.00 mol of ideal gas from 8.00 L to 20.00 L at 298 K.
A)0
B)+15.2 J.K - 1.molF - 1
C)+7.6 J.K - 1.mol - 1
D)(-15.2 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
E)(-7.6 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
A)0
B)+15.2 J.K - 1.molF - 1
C)+7.6 J.K - 1.mol - 1
D)(-15.2 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )
E)(-7.6 J.K - 1.mol - 1 )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
For the reaction 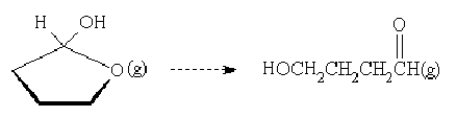 is the entropy change positive or negative?
is the entropy change positive or negative?
 is the entropy change positive or negative?
is the entropy change positive or negative?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The reaction 2Cu(s)+ CO2(g) 2CuO(s)+ C(s)
Is endothermic.Which of the following statements is true?
A)The reaction is not spontaneous at any temperature.
B)The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
C)It is impossible to determine if the reaction is spontaneous without calculations.
D)The reaction will be spontaneous only at low temperatures.
E)The reaction will be spontaneous only at high temperatures.
Is endothermic.Which of the following statements is true?
A)The reaction is not spontaneous at any temperature.
B)The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
C)It is impossible to determine if the reaction is spontaneous without calculations.
D)The reaction will be spontaneous only at low temperatures.
E)The reaction will be spontaneous only at high temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The entropy of fusion of water is +22.0 J.K-1.mol-1 and the enthalpy of fusion of water is +6.01 kJ.mol - 1 at 0 C.At 0 C, Stotal for the melting of ice is
A)(-6010 J.K - 1.mol - 1. )
B)0.
C)(-22.0 J.K - 1.mol - 1. )
D)+6010 J.K - 1.mol - 1.
E)+22.0 J.K - 1.mol - 1.
A)(-6010 J.K - 1.mol - 1. )
B)0.
C)(-22.0 J.K - 1.mol - 1. )
D)+6010 J.K - 1.mol - 1.
E)+22.0 J.K - 1.mol - 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Calculate the standard free energy of formation of mercury(II)oxide at 298 K,given HgO(s)
Hg(l)
O2(g)
-----------
Hf°,kJ.mol - 1
-90.83
-
-
Sm°,J.K - 1.mol - 1
70.29
76.02
205.14
A)+58.5 kJ.mol - 1
B)+117.1 kJ.mol - 1
C)-58.5 kJ.mol - 1
D)-123.1 kJ.mol - 1
E)-117.1 kJ.mol - 1
Hg(l)
O2(g)
-----------
Hf°,kJ.mol - 1
-90.83
-
-
Sm°,J.K - 1.mol - 1
70.29
76.02
205.14
A)+58.5 kJ.mol - 1
B)+117.1 kJ.mol - 1
C)-58.5 kJ.mol - 1
D)-123.1 kJ.mol - 1
E)-117.1 kJ.mol - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For the reaction 2SO3(g) 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)
Hr° = +198 kJ.mol - 1 and Sr° = 190 J.K - 1.mol - 1 at 298 K.The equilibrium constant for this reaction will be greater than 1 at
A)all temperatures.
B)temperatures above 1315 K.
C)temperatures below 1042 K.
D)no temperature.
E)temperatures above 1042 K.
Hr° = +198 kJ.mol - 1 and Sr° = 190 J.K - 1.mol - 1 at 298 K.The equilibrium constant for this reaction will be greater than 1 at
A)all temperatures.
B)temperatures above 1315 K.
C)temperatures below 1042 K.
D)no temperature.
E)temperatures above 1042 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Under what conditions (e.g.,constant P)are the following relations true?
(a) G = H- T S
(b)q = H
(a) G = H- T S
(b)q = H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consider the reaction Cl2(g) 2Cl(g)
Which of the following statement regarding this reaction is true?
A)The reaction is spontaneous at high temperatures.
B)The reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures.
C)The reaction is not spontaneous at any temperature.
D)The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
Which of the following statement regarding this reaction is true?
A)The reaction is spontaneous at high temperatures.
B)The reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures.
C)The reaction is not spontaneous at any temperature.
D)The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The reaction 2C(s)+ 2H2(g) C2H4(g)is endothermic.This reaction will not be spontaneous at any temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Labile is a term that refers to the thermodynamic tendency of a substance to decompose.
B)A thermodynamically unstable compound is a compound with a positive standard free energy of formation.
C)Spontaneous reactions always have Sr > 0.
D)Spontaneous reactions always have Gr > 0.
E)Spontaneous reactions always have Hr < 0.
A)Labile is a term that refers to the thermodynamic tendency of a substance to decompose.
B)A thermodynamically unstable compound is a compound with a positive standard free energy of formation.
C)Spontaneous reactions always have Sr > 0.
D)Spontaneous reactions always have Gr > 0.
E)Spontaneous reactions always have Hr < 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For the reaction 2C(s)+ 2H2(g) C2H4(g)
Hr = +52.3 kJ.mol sup>- 1 and Sr = -53.07 J.K - 1.mol - 1 at 298 K.The reverse reaction will be spontaneous at
A)temperatures below 985 K.
B)temperatures above 985 K.
C)temperatures below 1015 K.
D)all temperatures.
E)no temperatures.
Hr = +52.3 kJ.mol sup>- 1 and Sr = -53.07 J.K - 1.mol - 1 at 298 K.The reverse reaction will be spontaneous at
A)temperatures below 985 K.
B)temperatures above 985 K.
C)temperatures below 1015 K.
D)all temperatures.
E)no temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider the following compounds and their standard free energies of formation: 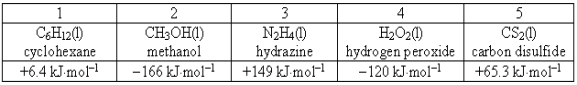 Which of these liquids is (are)thermodynamically stable?
Which of these liquids is (are)thermodynamically stable?
A)2 and 4
B)2 and 3
C)1, 3, and 5
D)1
E)3
 Which of these liquids is (are)thermodynamically stable?
Which of these liquids is (are)thermodynamically stable?A)2 and 4
B)2 and 3
C)1, 3, and 5
D)1
E)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Consider the reaction 2SO3(g) 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)
Which statement is true for this reaction?
A)( S < 0)
B)( S > 0)
C)( S = 0)
D)Smo = 0 for O2(g)
Which statement is true for this reaction?
A)( S < 0)
B)( S > 0)
C)( S = 0)
D)Smo = 0 for O2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The reaction CH3CH2CH2CH3(g) CH3CH(CH3)2(g),is exothermic.This reaction will be spontaneous at high temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The reaction N2(g)+ 3H2(g) 2NH3(g)is exothermic.This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For the reaction 2C(s)+ 2H2(g) C2H4(g)
Hr = +52.3 kJ.mol - 1 and Sr = -53.07 J.K - 1.mol - 1 at 298 K.This reaction will be spontaneous at
A)no temperature.
B)all temperatures.
C)temperatures below 985 K.
D)temperatures above 985 K.
E)temperatures below 1015 K.
Hr = +52.3 kJ.mol - 1 and Sr = -53.07 J.K - 1.mol - 1 at 298 K.This reaction will be spontaneous at
A)no temperature.
B)all temperatures.
C)temperatures below 985 K.
D)temperatures above 985 K.
E)temperatures below 1015 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Calculate Gr for the decomposition of mercury(II)oxide at 298 K. 2HgO(s)
2Hg(l)+
O2(g)
------------
Hf ,kJ.mol - 1
-90.83
Sm ,J.K - 1.mol - 1
70.29
76.02
205.14
A)-117.1 kJ.mol - 1
B)+246.2 kJ.mol - 1
C)-64.5 kJ.mol - 1
D)+117.1 kJ.mol - 1
E)-246.2 kJ.mol - 1
2Hg(l)+
O2(g)
------------
Hf ,kJ.mol - 1
-90.83
Sm ,J.K - 1.mol - 1
70.29
76.02
205.14
A)-117.1 kJ.mol - 1
B)+246.2 kJ.mol - 1
C)-64.5 kJ.mol - 1
D)+117.1 kJ.mol - 1
E)-246.2 kJ.mol - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The standard free energy of formation of benzene,C6H6(l),is +124.3 kJ.mol - 1 at 298 K.This means that at 298 K benzene is thermodynamically unstable even though it can be kept indefinitely without decomposing.Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Consider the following compounds and their standard free energies of formation: 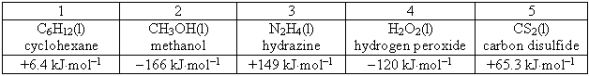 Which of these liquids is (are)thermodynamically unstable?
Which of these liquids is (are)thermodynamically unstable?
A)2
B)1, 3, and 5
C)1 and 4
D)2 and 3
E)2 and 4
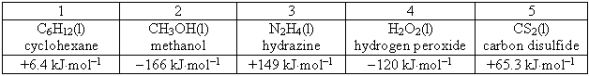 Which of these liquids is (are)thermodynamically unstable?
Which of these liquids is (are)thermodynamically unstable?A)2
B)1, 3, and 5
C)1 and 4
D)2 and 3
E)2 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which one of the following statements is true?
A)Labile is a term that refers to the thermodynamic tendency of a substance to decompose.
B)Spontaneous reactions always have Gr > 0.
C)Spontaneous reactions always have Hr < 0.
D)Spontaneous reactions always have Sr > 0.
E)A thermodynamically stable compound is a compound with a negative standard free energy of formation.
A)Labile is a term that refers to the thermodynamic tendency of a substance to decompose.
B)Spontaneous reactions always have Gr > 0.
C)Spontaneous reactions always have Hr < 0.
D)Spontaneous reactions always have Sr > 0.
E)A thermodynamically stable compound is a compound with a negative standard free energy of formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
For the reaction 2SO3(g) 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)
Hr = +198 kJ.mol - 1 at 298 K.Which statement is true for this reaction?
A)The reaction is driven by the enthalpy.
B)The reaction will not be spontaneous at low temperatures.
C)( Gr will be negative at high temperatures.)
D)The reaction will not be spontaneous at any temperature.
E)( Gr will be positive at high temperatures.)
Hr = +198 kJ.mol - 1 at 298 K.Which statement is true for this reaction?
A)The reaction is driven by the enthalpy.
B)The reaction will not be spontaneous at low temperatures.
C)( Gr will be negative at high temperatures.)
D)The reaction will not be spontaneous at any temperature.
E)( Gr will be positive at high temperatures.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Estimate the minimum temperature at which magnetite can be reduced to iron by graphite. Fe3O4(s)+ 2C(s) 2CO2(g)+ 3Fe(s)
Sr = +351.44 J.K - 1.mol - 1
The standard molar enthalpies of formation of magnetite and CO2(g)are -118.4 and -393.51 kJ.mol - 1,respectively.
A)670 C
B)Magnetite cannot be reduced by carbon at any temperature.
C)787 C
D)943 C
E)1790 C
Sr = +351.44 J.K - 1.mol - 1
The standard molar enthalpies of formation of magnetite and CO2(g)are -118.4 and -393.51 kJ.mol - 1,respectively.
A)670 C
B)Magnetite cannot be reduced by carbon at any temperature.
C)787 C
D)943 C
E)1790 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
U = 0 for the isothermal expansion of an ideal gas and therefore S = -wrev/T = nRln(V2/V1).True or false?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Consider the compounds PCl5(g),HCN(g),CuO(s),NO(g),NH3(g),and SO2(g).
Which compound will have approximately the same stability with respect to its elements if the temperature is raised?
A)CuO(s)
B)NO(g)
C)PCl5(g)
D)HCN(g)
E)NH3(g)
Which compound will have approximately the same stability with respect to its elements if the temperature is raised?
A)CuO(s)
B)NO(g)
C)PCl5(g)
D)HCN(g)
E)NH3(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is true for a spontaneous reaction at constant temperature?
A)( S + H/T < 0)
B)( G° = 0)
C)( Ssystem < q/T)
D)( H -T S < 0)
E)( Ssurr > 0)
A)( S + H/T < 0)
B)( G° = 0)
C)( Ssystem < q/T)
D)( H -T S < 0)
E)( Ssurr > 0)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use tabulated thermodynamic data to calculate the concentration of CO2(aq)in equilibrium with an external pressure of 2.50 atm CO2(g)at 298 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use tabulated thermodynamic data to estimate the temperature at which the vapor pressure of benzene is 1.33 kPa.Hint: Assume that the enthalpy and entropy of the reaction are independent of temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Consider the compounds PCl5(g),HCN(g),CuO(s),NO(g),NH3(g),and SO2(g).
Which compound will become more stable with respect to its elements if the temperature is raised?
A)SO2(g)
B)CuO(s)
C)NH3(g)
D)PCl5(g)
E)NO(g)
Which compound will become more stable with respect to its elements if the temperature is raised?
A)SO2(g)
B)CuO(s)
C)NH3(g)
D)PCl5(g)
E)NO(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The entropy of vaporization of a substance is always larger than its entropy of fusion.True or false?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
All the following compounds become less stable with respect to their elements as the temperature is raised except
A)PCl5(g).
B)C6H12(l).
C)N2H4(l).
D)CuO(s).
E)HCN(g).
A)PCl5(g).
B)C6H12(l).
C)N2H4(l).
D)CuO(s).
E)HCN(g).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
All the halogens exist as diatomic molecules at room temperature and 1 bar.Under these conditions,which of the halogens,F to I,has the smallest molar entropy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When calculating the entropy change as a result of transferring heat reversibly to or from a system,the temperature must be constant.True or false?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
For the reaction 2NH3(g)→ 3H2(g)+ N2(g),KP = 1.47 *10 - 6 at 298 K.Estimate the temperature at which KP = 0.0100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A piece of equipment must be capable of containing water at temperatures well above its normal boiling point.If the piece of equipment withstands an internal pressure of no more than 10.0 atm,calculate the highest temperature at which the system can be safely operated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Calculate G for the process
He(g,1 atm,298 K) He(g,10 atm,298 K)
He(g,1 atm,298 K) He(g,10 atm,298 K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The sublimation of solid carbon dioxide is a spontaneous process.Predict the sign (+,-,or 0)of Gr Hr and Sr ,respectively.
A)(-, 0, +)
B)(-, -, -)
C)(-, +, +)
D)0, +, +
E)(-, +, -)
A)(-, 0, +)
B)(-, -, -)
C)(-, +, +)
D)0, +, +
E)(-, +, -)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
An example of a spontaneous process having H ~ 0 is
A)1 L He(1 atm, 298 K)+ 1 L Ar(1 atm, 298 K) 2 L He/Ar mixture(1 atm, 298 K).
B)evaporation of water at 100 C and 1 atm.
C)a ball rolling from the top of a hill to the bottom of a valley.
D)precipitation of AgBr(s)from a solution of Ag+(aq)and Br - (aq).
E)freezing of water at -10 C.
A)1 L He(1 atm, 298 K)+ 1 L Ar(1 atm, 298 K) 2 L He/Ar mixture(1 atm, 298 K).
B)evaporation of water at 100 C and 1 atm.
C)a ball rolling from the top of a hill to the bottom of a valley.
D)precipitation of AgBr(s)from a solution of Ag+(aq)and Br - (aq).
E)freezing of water at -10 C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When calculating the entropy of vaporization of water at 25 C,the dominant contribution is
A)the molar heat capacity of liquid water.
B)heating the water from 25 C to 100 C.
C)cooling the water from 100 C to 25 C.
D)the entropy of vaporization of water at its normal boiling point.
A)the molar heat capacity of liquid water.
B)heating the water from 25 C to 100 C.
C)cooling the water from 100 C to 25 C.
D)the entropy of vaporization of water at its normal boiling point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Calculate the entropy of vaporization of water at 25 C and 1 bar.The molar heat capacities of the liquid and gas are 75 and 34 J·K - 1·mol - 1,respectively.The molar enthalpy of vaporization of water at its normal boiling point is 40.7 kJ·mol - 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements is true?
A)If a reaction has Gr = -275 kJ.mol - 1, it must proceed rapidly toward equilibrium.
B)All endothermic reactions are nonspontaneous.
C)The value of Gr is not dependent on temperature.
D)A spontaneous reaction for which the entropy change is negative is entropy driven.
E)If a certain reaction is spontaneous, it is not spontaneous in the reverse direction.
A)If a reaction has Gr = -275 kJ.mol - 1, it must proceed rapidly toward equilibrium.
B)All endothermic reactions are nonspontaneous.
C)The value of Gr is not dependent on temperature.
D)A spontaneous reaction for which the entropy change is negative is entropy driven.
E)If a certain reaction is spontaneous, it is not spontaneous in the reverse direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the compounds PCl5(g),HCN(g),CuO(s),NO(g),NH3(g),and SO2(g).
Which compound will become more stable with respect to its elements if the temperature is raised?
A)CuO(s)
B)PCl5(g)
C)NH3(g)
D)NO(g)
E)HCN(g)
Which compound will become more stable with respect to its elements if the temperature is raised?
A)CuO(s)
B)PCl5(g)
C)NH3(g)
D)NO(g)
E)HCN(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following statements is true?
A)The molar entropy does not depend on the structure of the compound.
B)The molar entropy of H2O(l)is about the same as the molar entropy of ice.
C)An isothermal process that leads to a decrease in free energy is spontaneous.
D)If Gr > 0, then the reaction is spontaneous.
E)All processes that give positive changes in energy are spontaneous.
A)The molar entropy does not depend on the structure of the compound.
B)The molar entropy of H2O(l)is about the same as the molar entropy of ice.
C)An isothermal process that leads to a decrease in free energy is spontaneous.
D)If Gr > 0, then the reaction is spontaneous.
E)All processes that give positive changes in energy are spontaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



