Deck 10: Macroeconomic Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Macroeconomic Policy
1
The key policy rate and the prime business rate are examples of
A) interest rate spreads.
B) basis point balances.
C) deposit rates.
D) inflation rates.
E) benchmark rates.
A) interest rate spreads.
B) basis point balances.
C) deposit rates.
D) inflation rates.
E) benchmark rates.
benchmark rates.
2
The Bank of Canada sets
A) potential output.
B) the money supply.
C) the government purchases.
D) the exchange rate.
E) the key policy ratE.
A) potential output.
B) the money supply.
C) the government purchases.
D) the exchange rate.
E) the key policy ratE.
the key policy ratE.
3
While ________ are the two major types of stabilization policy,________ is used most often to help stabilize the economy.
A) fiscal policy and monetary policy;monetary policy
B) fiscal policy and monetary policy;fiscal policy
C) tax policy and spending policy;tax policy
D) tax policy and spending policy;spending policy
E) monetary policy and structural policy;monetary policy
A) fiscal policy and monetary policy;monetary policy
B) fiscal policy and monetary policy;fiscal policy
C) tax policy and spending policy;tax policy
D) tax policy and spending policy;spending policy
E) monetary policy and structural policy;monetary policy
fiscal policy and monetary policy;monetary policy
4
Holding all else constant,lower real interest rates promote ________ spending in the economy and result in ________ inflation.
A) less;lower
B) less;higher
C) more;higher
D) more;lower
E) no change in;lower
A) less;lower
B) less;higher
C) more;higher
D) more;lower
E) no change in;lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The core CPI differs from total CPI because it
A) excludes the most volatile components of the total CPI.
B) includes the most volatile components of the total CPI.
C) excludes exported and imported goods.
D) includes exported and imported goods.
E) excludes all transfer payments.
A) excludes the most volatile components of the total CPI.
B) includes the most volatile components of the total CPI.
C) excludes exported and imported goods.
D) includes exported and imported goods.
E) excludes all transfer payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Bank of Canada's inflation-control target is to keep annual inflation between __________ percent.
A) zero and two
B) one and three
C) two and four
D) three and five
E) four and six
A) zero and two
B) one and three
C) two and four
D) three and five
E) four and six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Core CPI inflation is _________ than total CPI inflation in the _________ term.
A) more volatile;short
B) more volatile;long
C) more volatile;medium
D) less volatile;short
E) less volatile;long
A) more volatile;short
B) more volatile;long
C) more volatile;medium
D) less volatile;short
E) less volatile;long

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to the modern central banking theory,the central bank changes the nominal interest rate directly by changing its key policy rate,and any value of the nominal interest rate chosen by the central bank implies a specific value for
A) potential output.
B) net exports.
C) government purchases.
D) the budget deficit.
E) the money supply.
A) potential output.
B) net exports.
C) government purchases.
D) the budget deficit.
E) the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Although the Bank of Canada Act lists several intended objectives of the Bank of Canada,the Bank of Canada's stated sole policy objective since the early 1990s has been
A) economic growth.
B) exchange rate stability.
C) low unemployment.
D) low inflation.
E) government budget surpluses.
A) economic growth.
B) exchange rate stability.
C) low unemployment.
D) low inflation.
E) government budget surpluses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The Bank of Canada's inflation-control target is to keep annual inflation at __________ percent.
A) zero
B) one
C) two.
D) three.
E) four.
A) zero
B) one
C) two.
D) three.
E) four.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The key policy instrument employed by the Bank of Canada is control over
A) tax rates.
B) spending rates.
C) GDP growth rates.
D) population growth rates.
E) interest rates.
A) tax rates.
B) spending rates.
C) GDP growth rates.
D) population growth rates.
E) interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Bank of Canada is based in ________ and its policies are determined with a high degree of ________ the government.
A) Toronto;independence from
B) Toronto;dependence on
C) Ottawa;independence from
D) Ottawa;dependence on
E) Vancouver;independence from
A) Toronto;independence from
B) Toronto;dependence on
C) Ottawa;independence from
D) Ottawa;dependence on
E) Vancouver;independence from

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is NOT stated in the Bank of Canada Act as a policy objective of the Bank of Canada?
A) Regulate credit.
B) Regulate currency.
C) Mitigate fluctuations in prices.
D) Mitigate fluctuations in employment.
E) Promote government budget surpluses.
A) Regulate credit.
B) Regulate currency.
C) Mitigate fluctuations in prices.
D) Mitigate fluctuations in employment.
E) Promote government budget surpluses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The _________ excludes the most volatile components of the Consumer Price Index.
A) total CPI
B) total GNE
C) core CPI
D) core GNE
E) core GNI
A) total CPI
B) total GNE
C) core CPI
D) core GNE
E) core GNI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Each of the following is an international counterpart to the Bank of Canada,EXCEPT
A) the Federal Reserve.
B) the Bank of America.
C) the European Central Bank.
D) the Bank of England.
E) the Bank of Japan.
A) the Federal Reserve.
B) the Bank of America.
C) the European Central Bank.
D) the Bank of England.
E) the Bank of Japan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The Bank of Canada is responsible for ________ policy and it uses ________ to achieve its objectives.
A) fiscal;tax rates
B) fiscal;government purchases
C) monetary;interest rates
D) monetary;the money supply
E) structural;the legal system
A) fiscal;tax rates
B) fiscal;government purchases
C) monetary;interest rates
D) monetary;the money supply
E) structural;the legal system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The Bank of Canada makes announcements about interest rate changes
A) every morning.
B) every Monday morning.
C) every Wednesday at noon.
D) on the first day of each month.
E) eight times a year.
A) every morning.
B) every Monday morning.
C) every Wednesday at noon.
D) on the first day of each month.
E) eight times a year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The tools or techniques that a central bank employs to achieve its monetary policy objectives are called
A) monetary policy instruments.
B) monetary policy targets.
C) settlement balances.
D) benchmark rates.
E) large value transfers.
A) monetary policy instruments.
B) monetary policy targets.
C) settlement balances.
D) benchmark rates.
E) large value transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Total CPI inflation is _________ than core CPI inflation in the _________ term.
A) more volatile;short
B) more volatile;long
C) more volatile;medium
D) less volatile;short
E) less volatile;long
A) more volatile;short
B) more volatile;long
C) more volatile;medium
D) less volatile;short
E) less volatile;long

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Holding all else constant,higher real interest rates promote ________ spending in the economy and result in ________ inflation.
A) less;lower
B) less;higher
C) more;higher
D) more;lower
E) no change in;lower
A) less;lower
B) less;higher
C) more;higher
D) more;lower
E) no change in;lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The prime business rate refers to
A) the interest rate that commercial banks charge to their least risky business borrowers.
B) the market interest rate that financial institutions charge each other for overnight loans.
C) a term used to describe the range of possible overnight interest rates.
D) the interest rate that the Bank of Canada charges commercial banks for overnight loans.
E) accounts held at the Bank of Canada by financial institutions for the purpose of settling their net payment obligations to one another.
A) the interest rate that commercial banks charge to their least risky business borrowers.
B) the market interest rate that financial institutions charge each other for overnight loans.
C) a term used to describe the range of possible overnight interest rates.
D) the interest rate that the Bank of Canada charges commercial banks for overnight loans.
E) accounts held at the Bank of Canada by financial institutions for the purpose of settling their net payment obligations to one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When the Bank of Canada wants to lower the real interest rate in Canada,it announces a ________ overnight rate target (and the entire operating band around the overnight rate target shifts ______).In response,the commercial banks ________ the market interest rates,particularly,the short-term rates,by a similar amount.
A) higher;down;raise
B) lower;up;lower
C) lower;down;lower
D) higher;up;raise
E) lower;down;up
A) higher;down;raise
B) lower;up;lower
C) lower;down;lower
D) higher;up;raise
E) lower;down;up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The interest rate that commercial banks charge their least risky customers is called the
A) prime business rate.
B) overnight rate target.
C) bank rate.
D) market rate.
E) equilibrium ratE.
A) prime business rate.
B) overnight rate target.
C) bank rate.
D) market rate.
E) equilibrium ratE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When the Bank of Canada wants to raise the real interest rate in Canada,it announces a ________ overnight rate target (and the entire operating band around the overnight rate target shifts ________).In response,the commercial banks ________ the market interest rates,particularly,the short-term rates,by a similar amount.
A) higher;down;raise
B) lower;up;lower
C) higher;up;lower
D) higher;up;raise
E) lower;down;up
A) higher;down;raise
B) lower;up;lower
C) higher;up;lower
D) higher;up;raise
E) lower;down;up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The interest rate that the Bank of Canada pays commercial banks for overnight deposits is the
A) prime business rate.
B) overnight rate target.
C) deposit rate.
D) bank rate.
E) equilibrium ratE.
A) prime business rate.
B) overnight rate target.
C) deposit rate.
D) bank rate.
E) equilibrium ratE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The interest rate that the Bank of Canada charges commercial banks for overnight loans is called the
A) prime business rate.
B) overnight rate target.
C) bank rate.
D) market rate.
E) equilibrium ratE.
A) prime business rate.
B) overnight rate target.
C) bank rate.
D) market rate.
E) equilibrium ratE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The Bank of Canada's official interest rate is the _______.This is the interest rate that prevails in the _______,and the rate at which commercial banks lend and borrow _______ funds from each other.
A) overnight rate target;overnight loans market;overnight
B) prime business rate;money markets;short term
C) overnight rate target;money markets;long term
D) prime business rate;overnight loans market;long term
E) bank rate;money markets;overnight
A) overnight rate target;overnight loans market;overnight
B) prime business rate;money markets;short term
C) overnight rate target;money markets;long term
D) prime business rate;overnight loans market;long term
E) bank rate;money markets;overnight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Under its current operating procedure,the Bank of Canada implements monetary policy by announcing a target for the ________,and then intervenes (if necessary)in the _______ in order to maintain this rate within a _______ percentage-point operating band above and below this target.
A) overnight rate;overnight loan market;
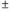 0.50
0.50
B) prime business rate;money markets;
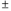 0.25
0.25
C) overnight rate;money markets;
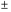 0.25
0.25
D) overnight rate;overnight loan market;
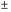 0.25
0.25
E) overnight rate;money markets;0.50
A) overnight rate;overnight loan market;
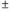 0.50
0.50B) prime business rate;money markets;
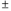 0.25
0.25C) overnight rate;money markets;
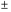 0.25
0.25D) overnight rate;overnight loan market;
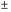 0.25
0.25E) overnight rate;money markets;0.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If overnight funds in the overnight loans market are trading above the overnight rate target,then the Bank of Canada will _______ Government of Canada bonds,driving the overnight market rate ______;conversely,if overnight funds are trading below the overnight target rate,then the Bank will _______ Government of Canada bonds,driving the overnight interest rate _______.
A) sell;up;buy;down
B) buy;down;sell;up
C) sell;down;buy;down
D) buy;up;buy;down
E) buy;up;sell;up
A) sell;up;buy;down
B) buy;down;sell;up
C) sell;down;buy;down
D) buy;up;buy;down
E) buy;up;sell;up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The overnight rate refers to
A) the interest rate that commercial banks charge to their least risky business borrowers.
B) the market interest rate that financial institutions charge each other for overnight loans.
C) a term used to describe the range of possible overnight interest rates.
D) the interest rate that the Bank of Canada charges commercial banks for overnight loans.
E) accounts held at the Bank of Canada by financial institutions for the purpose of settling their net payment obligations to one another.
A) the interest rate that commercial banks charge to their least risky business borrowers.
B) the market interest rate that financial institutions charge each other for overnight loans.
C) a term used to describe the range of possible overnight interest rates.
D) the interest rate that the Bank of Canada charges commercial banks for overnight loans.
E) accounts held at the Bank of Canada by financial institutions for the purpose of settling their net payment obligations to one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The bank rate refers to
A) the interest rate that commercial banks charge to their least risky business borrowers.
B) the market interest rate that financial institutions charge each other for overnight loans.
C) a term used to describe the range of possible overnight interest rates.
D) the interest rate that the Bank of Canada charges commercial banks for overnight loans.
E) accounts held at the Bank of Canada by financial institutions for the purpose of settling their net payment obligations to one another.
A) the interest rate that commercial banks charge to their least risky business borrowers.
B) the market interest rate that financial institutions charge each other for overnight loans.
C) a term used to describe the range of possible overnight interest rates.
D) the interest rate that the Bank of Canada charges commercial banks for overnight loans.
E) accounts held at the Bank of Canada by financial institutions for the purpose of settling their net payment obligations to one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The lowest feasible level for a central bank's key policy rate is called the
A) minimum prime business rate.
B) minimum overnight lending rate.
C) benchmark rate.
D) lowest official interest rate.
E) effective lower bound
A) minimum prime business rate.
B) minimum overnight lending rate.
C) benchmark rate.
D) lowest official interest rate.
E) effective lower bound

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Bank of Canada ensures that the overnight rate stays within an operating band of ________ percentage points of its overnight rate target.
A) ± 0.1
B) ± 0.25
C) ± 0.50
D) ± 0.75
E) ± 1.00
A) ± 0.1
B) ± 0.25
C) ± 0.50
D) ± 0.75
E) ± 1.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Financial markets pay close attention to changes in the overnight rate target because these changes
A) directly affect a large volume of loans.
B) indicate the Bank of Canada's plans for monetary policy.
C) indicate commercial bank lending policies.
D) directly affect the interest payments on the national debt.
E) directly impact consumer interest burdens.
A) directly affect a large volume of loans.
B) indicate the Bank of Canada's plans for monetary policy.
C) indicate commercial bank lending policies.
D) directly affect the interest payments on the national debt.
E) directly impact consumer interest burdens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The interest rate that the Bank of Canada pays commercial banks for overnight deposits is the
A) prime business rate.
B) overnight rate target.
C) deposit rate.
D) bank rate.
E) equilibrium ratE.
A) prime business rate.
B) overnight rate target.
C) deposit rate.
D) bank rate.
E) equilibrium ratE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Proponents of the modern central banking theory of interest rate determination agree that central banks can control
A) short-term market interest rates.
B) medium-term market interest rates.
C) long-term market interest rates.
D) long-term real interest rates.
E) medium-term real interest rates.
A) short-term market interest rates.
B) medium-term market interest rates.
C) long-term market interest rates.
D) long-term real interest rates.
E) medium-term real interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When the Bank of Canada changes its key official interest rate,in response the commercial banks in the country
A) change market interest rates (particularly short-term ones)by the same amount and in the same direction.
B) change market interest rates (particularly short-term ones)by the same amount in the opposite direction.
C) leave market interest rates unchanged (particularly short-term ones).
D) change only the prime business rate they charge their least risky customers.
E) leave the prime business rate unchanged.
A) change market interest rates (particularly short-term ones)by the same amount and in the same direction.
B) change market interest rates (particularly short-term ones)by the same amount in the opposite direction.
C) leave market interest rates unchanged (particularly short-term ones).
D) change only the prime business rate they charge their least risky customers.
E) leave the prime business rate unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A "basis point" is a term often used in describing interest rates and 100 basis points is the equivalent to a __________ percent change in the interest rate.
A) 0.01
B) 0.1
C) 1.0
D) 10
E) 100
A) 0.01
B) 0.1
C) 1.0
D) 10
E) 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The conduct of monetary policy in Canada is a real-world application of the modern central banking theory.Thus,the Bank of Canada's main monetary policy tool is
A) the money supply.
B) the bank rate.
C) the key policy rate.
D) the prime business rate.
E) potential output.
A) the money supply.
B) the bank rate.
C) the key policy rate.
D) the prime business rate.
E) potential output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The Bank of Canada's overnight rate target corresponds closely to the
A) bank rate.
B) prime business rate.
C) federal funds rate in the U.S.
D) market rate.
E) T-bill ratE.
A) bank rate.
B) prime business rate.
C) federal funds rate in the U.S.
D) market rate.
E) T-bill ratE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The ________ interest rate is defined as the ________ interest rate minus inflation,and it is the ________ interest rate that matters for consumption and investment decisions.
A) nominal;real;nominal
B) real;nominal;nominal
C) nominal;real;real
D) real;nominal;real
E) prime business;overnight;overnight
A) nominal;real;nominal
B) real;nominal;nominal
C) nominal;real;real
D) real;nominal;real
E) prime business;overnight;overnight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Bank of Canada has a great deal of control over the ________,but has less control over the ________ or the ________.
A) long-term government bond rate;overnight rate;rate on bonds issued by corporations
B) rate on bonds issued by corporations;overnight rate;long-term government bond rate
C) overnight rate;long-term government bond rate;rate on bonds issued by corporations
D) overnight rate;bank rate;prime business rate
E) prime business rate;overnight rate;bank rate
A) long-term government bond rate;overnight rate;rate on bonds issued by corporations
B) rate on bonds issued by corporations;overnight rate;long-term government bond rate
C) overnight rate;long-term government bond rate;rate on bonds issued by corporations
D) overnight rate;bank rate;prime business rate
E) prime business rate;overnight rate;bank rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
While a central bank has the power to control the economy's ________ interest rate,decisions regarding consumption and investment depend on the ________ interest rate.
A) real;nominal
B) nominal;real
C) prime business;nominal
D) nominal;overnight
E) real;overnight
A) real;nominal
B) nominal;real
C) prime business;nominal
D) nominal;overnight
E) real;overnight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Because inflation tends to change relatively ________,action by the Bank of Canada to change the ________ interest rate causes the ________ interest rate to change by about the same amount.
A) quickly;nominal;real
B) quickly;real;nominal
C) slowly;nominal;real
D) slowly;real;nominal
E) slowly;prime business;overnight
A) quickly;nominal;real
B) quickly;real;nominal
C) slowly;nominal;real
D) slowly;real;nominal
E) slowly;prime business;overnight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The interest rate spread is the difference between
A) a nominal rate and a real rate of interest.
B) a benchmark rate and the effective lower bound.
C) a benchmark rate and a related market interest rate.
D) the key policy rate and the official interest rate
E) the upper and lower bound of the operating band.
A) a nominal rate and a real rate of interest.
B) a benchmark rate and the effective lower bound.
C) a benchmark rate and a related market interest rate.
D) the key policy rate and the official interest rate
E) the upper and lower bound of the operating band.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The Bank of Canada keeps the overnight rate within the operating band by standing ready to ________ funds at the lower limit of the band and to ________ funds at the upper limit.
A) lend;borrow
B) lend;lend
C) borrow;lend
D) borrow;borrow
E) give away;take
A) lend;borrow
B) lend;lend
C) borrow;lend
D) borrow;borrow
E) give away;take

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Accounts held at the Bank of Canada by financial institutions for the purpose of settling their net payment obligations to one another are called
A) transfer accounts.
B) payment accounts.
C) financial balances.
D) settlement balances.
E) institutional balances.
A) transfer accounts.
B) payment accounts.
C) financial balances.
D) settlement balances.
E) institutional balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If inflation does not adjust rapidly,then when the Bank of Canada decreases the nominal interest rate,the real interest rate in the short run will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) equal the nominal interest rate.
E) be determined by saving and investment decisions.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) equal the nominal interest rate.
E) be determined by saving and investment decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When the Bank of Canada raises its key policy rate,it sends a signal to financial intermediaries that it wants them to
A) raise their short-term interest rates.
B) lower their short-term interest rates.
C) raise the money supply.
D) lower the money supply.
E) lower their long-term interest rates.
A) raise their short-term interest rates.
B) lower their short-term interest rates.
C) raise the money supply.
D) lower the money supply.
E) lower their long-term interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Macroeconomists typically assume that most market interest rates move in tandem with the central bank's official interest rate.While this assumption allows them to speak of "the" interest rate,it is a simplification of the fact that central banks generally have better control over _______ than over _______.
A) short-term nominal interest rates;long-term nominal interest rates
B) short-term real interest rates;short-term nominal interest rates
C) long-term nominal interest rates;short-term nominal interest rates
D) long-term mortgage rates;short-term mortgage rates
E) the prime business rate;the overnight rate
A) short-term nominal interest rates;long-term nominal interest rates
B) short-term real interest rates;short-term nominal interest rates
C) long-term nominal interest rates;short-term nominal interest rates
D) long-term mortgage rates;short-term mortgage rates
E) the prime business rate;the overnight rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If inflation does not adjust rapidly,then when the Bank of Canada increases the nominal interest rate,the real interest rate in the short run will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) equal the nominal interest rate.
E) be determined by saving and investment decisions.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) equal the nominal interest rate.
E) be determined by saving and investment decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When the Bank of Canada changes the overnight rate by a certain amount,
A) all interest rates in the economy change by exactly that amount.
B) short-term interest rates usually change by that amount,but long-term interest rates may or may not change by the same amount.
C) long-term interest rates usually increase by that amount,but short-term interest rates may or may not change by the same amount.
D) interest rates on both 30-year and 1-year Government of Canada bonds usually increase by that amount.
E) interest rates on bonds issued by corporations usually increase by that amount,but the prime business rate may or may not change by the same amount.
A) all interest rates in the economy change by exactly that amount.
B) short-term interest rates usually change by that amount,but long-term interest rates may or may not change by the same amount.
C) long-term interest rates usually increase by that amount,but short-term interest rates may or may not change by the same amount.
D) interest rates on both 30-year and 1-year Government of Canada bonds usually increase by that amount.
E) interest rates on bonds issued by corporations usually increase by that amount,but the prime business rate may or may not change by the same amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The fact that central banks are able to influence _________ implies that they can also influence _________ in the desired direction,because ________ is slow to adjust.
A) short-term market interest rates;long-term real interest rates;output
B) short-term market interest rates;short-term real interest rates;output
C) short-term market interest rates;short-term real interest rates;inflation
D) long-term market interest rates;long-term real interest rates;output
E) long-term market interest rates;long-term real interest rates;inflation
A) short-term market interest rates;long-term real interest rates;output
B) short-term market interest rates;short-term real interest rates;output
C) short-term market interest rates;short-term real interest rates;inflation
D) long-term market interest rates;long-term real interest rates;output
E) long-term market interest rates;long-term real interest rates;inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
At the end of each working day,any bank with a surplus of funds will use the ________ to lend funds to another bank that is short of funds,charging the ________ rate.
A) Large Value Payment System;overnight
B) Large Value Transfer System;overnight
C) Large Value Wire System;bank
D) Financial Wire System;bank
E) Transfer Payment System;prime business
A) Large Value Payment System;overnight
B) Large Value Transfer System;overnight
C) Large Value Wire System;bank
D) Financial Wire System;bank
E) Transfer Payment System;prime business

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The electronic wire system overseen by the Bank of Canada that allows major financial institutions operating in Canada to send large payments back and forth to each other is called the
A) Large Value Payment System.
B) Large Value Transfer System.
C) Large Value Wire System.
D) Financial Wire System.
E) Transfer Payment System.
A) Large Value Payment System.
B) Large Value Transfer System.
C) Large Value Wire System.
D) Financial Wire System.
E) Transfer Payment System.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When the Bank of Canada raises the overnight rate target,the ________ rate and the ________ rate usually go up by the exact same amount,but the ________ rate may or may not go up by the same amount.
A) overnight;prime business;long-term government bond
B) overnight;long-term government bond;prime business
C) overnight;prime business;bank
D) bank;long-term government bond;overnight
E) bank;long-term government bond;prime business
A) overnight;prime business;long-term government bond
B) overnight;long-term government bond;prime business
C) overnight;prime business;bank
D) bank;long-term government bond;overnight
E) bank;long-term government bond;prime business

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When the overnight rate exceeds the overnight rate target,settlement balances are in ________ and the Bank of Canada will ________ Government of Canada bonds and ________ them at a predetermined price the next business day.
A) deficit;buy;sell
B) deficit;sell;buy
C) surplus;buy;sell
D) surplus;sell;buy
E) equilibrium;buy;sell
A) deficit;buy;sell
B) deficit;sell;buy
C) surplus;buy;sell
D) surplus;sell;buy
E) equilibrium;buy;sell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When the Bank of Canada cuts its key policy rate,it sends a signal to financial intermediaries that it wants them to
A) raise their short-term interest rates.
B) lower their short-term interest rates.
C) raise the money supply.
D) lower the money supply.
E) lower their long-term interest rates.
A) raise their short-term interest rates.
B) lower their short-term interest rates.
C) raise the money supply.
D) lower the money supply.
E) lower their long-term interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If interest rate spreads widen,central banks may have to ___________ to offset the rise interest rate spreads
A) increase their key policy rates
B) decrease their key policy rates
C) increase the operating band
D) decrease the operating band
E) increase the effective lower bound
A) increase their key policy rates
B) decrease their key policy rates
C) increase the operating band
D) decrease the operating band
E) increase the effective lower bound

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When the overnight rate is less than the overnight rate target,settlement balances are in ________ and the Bank of Canada will ________ Government of Canada bonds and ________ them at a predetermined price the next business day.
A) deficit;buy;sell
B) deficit;sell;buy
C) surplus;buy;sell
D) surplus;sell;buy
E) equilibrium;buy;sell
A) deficit;buy;sell
B) deficit;sell;buy
C) surplus;buy;sell
D) surplus;sell;buy
E) equilibrium;buy;sell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In Econland,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 500 + 0.75(Y - T)- 500r
I = 300 - 500r
G = 400
NX = 30
If net taxes equal 40 and the central bank sets the interest rate at 0.04 (4%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 4,520.
B) 4,560.
C) 4,600.
D) 4,640.
E) 4,680.
C = 500 + 0.75(Y - T)- 500r
I = 300 - 500r
G = 400
NX = 30
If net taxes equal 40 and the central bank sets the interest rate at 0.04 (4%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 4,520.
B) 4,560.
C) 4,600.
D) 4,640.
E) 4,680.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If potential output equals 4,000 and short-run equilibrium output equals 3,500,there is a ______ gap and the Bank of Canada must ________ real interest rates in order to close the gap.
A) recessionary;raise
B) recessionary;lower
C) recessionary;not change
D) expansionary;raise
E) expansionary;lower
A) recessionary;raise
B) recessionary;lower
C) recessionary;not change
D) expansionary;raise
E) expansionary;lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A higher real interest rate _________ private-sector investment spending and _________ consumption spending.
A) increases;increases
B) increases;decreases
C) does not change;does not change
D) decreases;increases
E) decreases;decreases
A) increases;increases
B) increases;decreases
C) does not change;does not change
D) decreases;increases
E) decreases;decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In Econland,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 500 + 0.75(Y - T)- 500r
I = 300 - 500r
G = 400
NX = 30
If net taxes equal 40 and the central bank sets the interest rate at 0.06 (6%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 4,520.
B) 4,560.
C) 4,600.
D) 4,640.
E) 4,680.
C = 500 + 0.75(Y - T)- 500r
I = 300 - 500r
G = 400
NX = 30
If net taxes equal 40 and the central bank sets the interest rate at 0.06 (6%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 4,520.
B) 4,560.
C) 4,600.
D) 4,640.
E) 4,680.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A lower real interest rate _________ private-sector investment spending and _________ consumption spending.
A) increases;increases
B) increases;decreases
C) does not change;does not change
D) decreases;increases
E) decreases;decreases
A) increases;increases
B) increases;decreases
C) does not change;does not change
D) decreases;increases
E) decreases;decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In Macroland,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 100 + 0.9(Y - T)- 500r
I = 150 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If potential output equals 3,500,net taxes equal 100,and the central bank sets the interest rate to equal 0.05 (5%),then at the short-run equilibrium,there is a(n)_________ gap of ________.
A) expansionary;100
B) expansionary;150
C) recessionary;50
D) recessionary;100
E) recessionary;150
C = 100 + 0.9(Y - T)- 500r
I = 150 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If potential output equals 3,500,net taxes equal 100,and the central bank sets the interest rate to equal 0.05 (5%),then at the short-run equilibrium,there is a(n)_________ gap of ________.
A) expansionary;100
B) expansionary;150
C) recessionary;50
D) recessionary;100
E) recessionary;150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the short run,if the Bank of Canada decreases interest rates,then consumption and investment ______,planned aggregate expenditure ______,and short-run equilibrium output _______.
A) increase;increases;increases
B) increase;increases;decreases
C) increase;decreases;decreases
D) decrease;decreases;increases
E) decrease;decreases;decreases
A) increase;increases;increases
B) increase;increases;decreases
C) increase;decreases;decreases
D) decrease;decreases;increases
E) decrease;decreases;decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In Macroland,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 100 + 0.9(Y - T)- 500r
I = 150 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate to equal 0.05 (5%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 3,200.
B) 3,350.
C) 3,500.
D) 3,650.
E) 3,800.
C = 100 + 0.9(Y - T)- 500r
I = 150 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate to equal 0.05 (5%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 3,200.
B) 3,350.
C) 3,500.
D) 3,650.
E) 3,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In a certain economy,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 60 + 0.6(Y - T)- 1,000r
I = 200 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate equal to 0.04 (4%),short-run equilibrium output equals
A) 825.
B) 875.
C) 925.
D) 975.
E) 1,025.
C = 60 + 0.6(Y - T)- 1,000r
I = 200 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate equal to 0.04 (4%),short-run equilibrium output equals
A) 825.
B) 875.
C) 925.
D) 975.
E) 1,025.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In Macroland,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 100 + 0.9(Y - T)- 500r
I = 150 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate to equal 0.04 (4%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 3,200.
B) 3,350.
C) 3,500.
D) 3,650.
E) 3,800.
C = 100 + 0.9(Y - T)- 500r
I = 150 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate to equal 0.04 (4%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 3,200.
B) 3,350.
C) 3,500.
D) 3,650.
E) 3,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In Econland,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 500 + 0.75(Y - T)- 500 r
I = 300 - 500r
G = 400
NX = 30
If potential output equals 4,640,net taxes equal 40 and the central bank sets the interest rate at 0.05 (5%),then at the short-run equilibrium,there is a(n)_______ gap of _____.
A) expansionary;40
B) expansionary;100
C) recessionary;100
D) recessionary;80
E) recessionary;40
C = 500 + 0.75(Y - T)- 500 r
I = 300 - 500r
G = 400
NX = 30
If potential output equals 4,640,net taxes equal 40 and the central bank sets the interest rate at 0.05 (5%),then at the short-run equilibrium,there is a(n)_______ gap of _____.
A) expansionary;40
B) expansionary;100
C) recessionary;100
D) recessionary;80
E) recessionary;40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A higher real interest rate _________ saving and __________ consumption spending.
A) increases;increases
B) increases;decreases
C) does not change;does not change
D) decreases;increases
E) decreases;decreases
A) increases;increases
B) increases;decreases
C) does not change;does not change
D) decreases;increases
E) decreases;decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In a certain economy,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 60 + 0.6(Y - T)- 1,000r
I = 200 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate equal to 0.06 (6%),short-run equilibrium output equals
A) 825.
B) 875.
C) 925.
D) 975.
E) 1,025.
C = 60 + 0.6(Y - T)- 1,000r
I = 200 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate equal to 0.06 (6%),short-run equilibrium output equals
A) 825.
B) 875.
C) 925.
D) 975.
E) 1,025.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In the short run,if the Bank of Canada increases interest rates,then consumption and investment ______,planned aggregate expenditure ______,and short-run equilibrium output _______.
A) increase;increases;increases
B) increase;increases;decreases
C) increase;decreases;decreases
D) decrease;decreases;increases
E) decrease;decreases;decreases
A) increase;increases;increases
B) increase;increases;decreases
C) increase;decreases;decreases
D) decrease;decreases;increases
E) decrease;decreases;decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If potential output equals 10,000 and short-run equilibrium output equals 8,500,there is a ______ gap and the Bank of Canada must ________ real interest rates in order to close the gap.
A) recessionary;raise
B) recessionary;lower
C) recessionary;not change
D) expansionary;raise
E) expansionary;lower
A) recessionary;raise
B) recessionary;lower
C) recessionary;not change
D) expansionary;raise
E) expansionary;lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In a certain economy,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 60 + 0.6(Y - T)- 1,000r
I = 200 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate equal to 0.05 (5%),short-run equilibrium output equals
A) 825.
B) 875.
C) 925.
D) 975.
E) 1,025.
C = 60 + 0.6(Y - T)- 1,000r
I = 200 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate equal to 0.05 (5%),short-run equilibrium output equals
A) 825.
B) 875.
C) 925.
D) 975.
E) 1,025.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In Macroland,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 100 + 0.9(Y - T)- 500r
I = 150 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate to equal 0.06 (6%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 3,200.
B) 3,350.
C) 3,500.
D) 3,650.
E) 3,800.
C = 100 + 0.9(Y - T)- 500r
I = 150 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate to equal 0.06 (6%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 3,200.
B) 3,350.
C) 3,500.
D) 3,650.
E) 3,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In a certain economy,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 60 + 0.6 (Y - T)- 1,000r
I = 200 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If potential output equals 925,net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate equal to 0.05 (5%),then at the short-run equilibrium,there is a(n)________ gap of ________.
A) expansionary;50
B) expansionary;100
C) recessionary;150
D) recessionary;100
E) recessionary;50
C = 60 + 0.6 (Y - T)- 1,000r
I = 200 - 1,000r
G = 200
NX = 50
If potential output equals 925,net taxes equal 100 and the central bank sets the interest rate equal to 0.05 (5%),then at the short-run equilibrium,there is a(n)________ gap of ________.
A) expansionary;50
B) expansionary;100
C) recessionary;150
D) recessionary;100
E) recessionary;50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In Econland,the components of planned aggregate expenditure are given by:
C = 500 + 0.75(Y - T)- 500r
I = 300 - 500r
G = 400
NX = 30
If net taxes equal 40 and the central bank sets the interest rate at 0.05 (5%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 4,520.
B) 4,560.
C) 4,600.
D) 4,640.
E) 4,680.
C = 500 + 0.75(Y - T)- 500r
I = 300 - 500r
G = 400
NX = 30
If net taxes equal 40 and the central bank sets the interest rate at 0.05 (5%),what is short-run equilibrium output?
A) 4,520.
B) 4,560.
C) 4,600.
D) 4,640.
E) 4,680.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A lower real interest rate __________ saving and __________ consumption spending.
A) increases;increases
B) increases;decreases
C) does not change;does not change
D) decreases;increases
E) decreases;decreases
A) increases;increases
B) increases;decreases
C) does not change;does not change
D) decreases;increases
E) decreases;decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



