Deck 16: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/101
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Chemical Equilibrium
1
In the following equilibrium,when chloride ion is added,the concentration of sodium ion will NaCl(s) 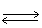 Na+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)
Na+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)
A)Increase
B)Decrease
C)Remain the same
 Na+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)
Na+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)A)Increase
B)Decrease
C)Remain the same
Decrease
2
In the following equilibrium,when Fe+3 ion is added,the concentration of Fe(SCN)+2 ion will Fe+3 + SCN-1 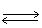 Fe(SCN)+2
Fe(SCN)+2
A)Increase
B)Decrease
C)Remain the same
 Fe(SCN)+2
Fe(SCN)+2A)Increase
B)Decrease
C)Remain the same
Increase
3
The addition of a catalyst to a chemical reaction would change the
A)heat of reaction.
B)enthalpy of the reactants.
C)enthalpy of the products.
D)activation energy.
A)heat of reaction.
B)enthalpy of the reactants.
C)enthalpy of the products.
D)activation energy.
activation energy.
4
A solution in which equilibrium is reached between dissolved and undissolved solute is
A)saturated.
B)unsaturated.
C)supersaturated.
A)saturated.
B)unsaturated.
C)supersaturated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the following equilibrium,when sodium ion is removed,the concentration of chloride ion will Na+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq) 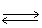 NaCl (s)
NaCl (s)
A)Increase
B)Decrease
C)Remain the same
 NaCl (s)
NaCl (s)A)Increase
B)Decrease
C)Remain the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In which direction will the point of equilibrium shift when the pressure is increased in the following equilibrium? N2 (g)+ 3 H2 (g) 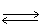 2 NH3 (g)
2 NH3 (g)
A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift
 2 NH3 (g)
2 NH3 (g)A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In which direction will the point of equilibrium shift when temperature is increased in the following equilibrium? 2 SO3 (g)+ 188 kJ 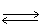 2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)
A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift
 2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In which direction will the point of equilibrium shift when the pressure is decreased in the following equilibrium?
H2 (g)+ Cl2 (g)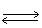 2 HCl (g)
2 HCl (g)
A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift
H2 (g)+ Cl2 (g)
 2 HCl (g)
2 HCl (g)A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In which direction will the point of equilibrium shift when the volume of the reaction vessel increases in the following equilibrium? 2 CO2 (g) 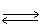 2 CO (g)+ O2 (g)
2 CO (g)+ O2 (g)
A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift
 2 CO (g)+ O2 (g)
2 CO (g)+ O2 (g)A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In which direction will the point of equilibrium shift when a catalyst is added to thefollowing equilibrium system? KNO3 + 34.7 kJ 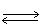 K+1 (aq)+ NO3-1 (aq)
K+1 (aq)+ NO3-1 (aq)
A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift
 K+1 (aq)+ NO3-1 (aq)
K+1 (aq)+ NO3-1 (aq)A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which is the common ion when hydrochloric acid is added to a saturated solution of sodium chloride?
A)Hydrogen ion
B)Chloride ion
C)Sodium ion
D)Hydroxide ion
A)Hydrogen ion
B)Chloride ion
C)Sodium ion
D)Hydroxide ion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In which direction will the point of equilibrium shift when the concentration of iron(III)ion decreases in the following equilibrium? Fe+3 (aq)+ SCN-1 (aq) 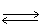 Fe(SCN)+2 (aq)
Fe(SCN)+2 (aq)
A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift
 Fe(SCN)+2 (aq)
Fe(SCN)+2 (aq)A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to Le Châtelier's Principle,decreasing the temperature at which the following reaction takes place will N2O4 + 58.6 kJ  2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
A)shift the equilibrium to the left.
B)shift the equilibrium to the right.
C)have no effect on the equilibrium.
 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)A)shift the equilibrium to the left.
B)shift the equilibrium to the right.
C)have no effect on the equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In which direction will the point of equilibrium shift when the volume of the reaction vessel decreases in the following equilibrium? 2 SO3 (g) 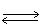 2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)
A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift
 2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g)+ O2 (g)A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Equilibrium is reached in a chemical reaction when
A)the reactants are completely consumed.
B)the concentrations of all reactants and products become equal.
C)the rates of the opposing reactions become equal.
D)the forward and reverse reactions stop.
A)the reactants are completely consumed.
B)the concentrations of all reactants and products become equal.
C)the rates of the opposing reactions become equal.
D)the forward and reverse reactions stop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In which direction will the point of equilibrium shift when temperature is decreased in the following equilibrium? 2 NO (g)+ O2 (g) 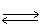 2 NO2 (g)+ 113 kJ
2 NO2 (g)+ 113 kJ
A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift
 2 NO2 (g)+ 113 kJ
2 NO2 (g)+ 113 kJA)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In which direction will the point of equilibrium shift when a catalyst is added to thefollowing equilibrium system? 2 C (s)+ O2 (g) 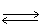 2 CO (g)+ 110 kJ
2 CO (g)+ 110 kJ
A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift
 2 CO (g)+ 110 kJ
2 CO (g)+ 110 kJA)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In which direction will the point of equilibrium shift when pressure is increased in the following equilibrium? KCl(s) 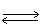 K+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)
K+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)
A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift
 K+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)
K+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The main reason for the increase in the rate of reaction as temperature increases is
A)molecules can be closer together to react.
B)the number or frequency of collisions between molecules increases.
C)molecules have less energy to move away from each other.
D)more energy is available to overcome the activation energy.
A)molecules can be closer together to react.
B)the number or frequency of collisions between molecules increases.
C)molecules have less energy to move away from each other.
D)more energy is available to overcome the activation energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In which direction will the point of equilibrium shift when the concentration of chloride ion increases in the following equilibrium?
NaCl (s)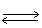 Na+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)
Na+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)
A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift
NaCl (s)
 Na+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)
Na+1 (aq)+ Cl-1 (aq)A)Shift to the right
B)Shift to the left
C)No shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which acid ionization constant would indicate the weakest acid?
A)3.5 10-4
10-4
B)1.8 10-5
10-5
C)4.6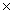 10-4
10-4
D)1.5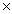 10-2
10-2
A)3.5
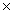 10-4
10-4B)1.8
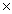 10-5
10-5C)4.6
 10-4
10-4D)1.5
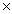 10-2
10-2
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the following equilibrium;as I2 (g)is added,the concentration of H2 (g)will H2 (g)+ I2 (g) 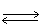 2 HI (g)
2 HI (g)
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.
 2 HI (g)
2 HI (g)A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Calculate the value of Keq for the following equilibrium when [ H2 ] = 0.228 M, [ I2 ] = 0.228 M,and [ HI ] =1.544 M.
H2 (g)+ I2 (g)![<strong>Calculate the value of K<sub>eq</sub> for the following equilibrium when [ H<sub>2</sub> ] = 0.228 M, [ I<sub>2</sub> ] = 0.228 M,and [ HI ] =1.544 M. H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ I<sub>2</sub> (g) 2 HI (g)</strong> A)29.7 B)0.0337 C)0.0219 D)45.9](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_163e_9ecd_c5494f9b5322_TB4036_11.jpg) 2 HI (g)
2 HI (g)
A)29.7
B)0.0337
C)0.0219
D)45.9
H2 (g)+ I2 (g)
![<strong>Calculate the value of K<sub>eq</sub> for the following equilibrium when [ H<sub>2</sub> ] = 0.228 M, [ I<sub>2</sub> ] = 0.228 M,and [ HI ] =1.544 M. H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ I<sub>2</sub> (g) 2 HI (g)</strong> A)29.7 B)0.0337 C)0.0219 D)45.9](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_163e_9ecd_c5494f9b5322_TB4036_11.jpg) 2 HI (g)
2 HI (g)A)29.7
B)0.0337
C)0.0219
D)45.9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which solubility product constant indicates the least soluble salt?
A)2.8 10-13
10-13
B)9.1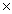 10-6
10-6
C)5.0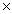 10-13
10-13
D)1.1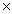 10-10
10-10
A)2.8
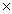 10-13
10-13B)9.1
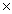 10-6
10-6C)5.0
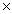 10-13
10-13D)1.1
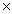 10-10
10-10
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the [OH-1] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?
A)1![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_8b7b_9ecd_2d83ed103086_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-2 M
10-2 M
B)1![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_8b7c_9ecd_4780632ac02e_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-14 M
10-14 M
C)1![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_b28d_9ecd_e1318f7d8dc7_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M
D)1![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_b28e_9ecd_7da14b835864_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-12 M
10-12 M
A)1
![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_8b7b_9ecd_2d83ed103086_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-2 M
10-2 MB)1
![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_8b7c_9ecd_4780632ac02e_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-14 M
10-14 MC)1
![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_b28d_9ecd_e1318f7d8dc7_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 MD)1
![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_b28e_9ecd_7da14b835864_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-12 M
10-12 M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which solubility product constant indicates the most soluble salt?
A)5.0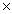 10-13
10-13
B)7.1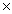 10-9
10-9
C)8.3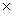 10-17
10-17
D)2.5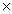 10-2
10-2
A)5.0
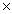 10-13
10-13B)7.1
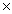 10-9
10-9C)8.3
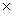 10-17
10-17D)2.5
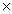 10-2
10-2
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which Keq value indicates the greatest concentration of reactants at equilibrium?
A)6.7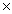 105
105
B)3.2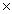 109
109
C)1.4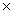 10-3
10-3
D)3.2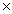 10-7
10-7
A)6.7
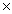 105
105B)3.2
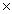 109
109C)1.4
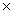 10-3
10-3D)3.2
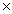 10-7
10-7
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the following equilibrium,as volume of the reaction vessel decreases,the point of equilibrium will N2O4 (g) 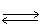 2 NO2 (g)
2 NO2 (g)
A)shift to the right.
B)shift to the left.
C)not shift.
 2 NO2 (g)
2 NO2 (g)A)shift to the right.
B)shift to the left.
C)not shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the [OH-1] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?
A)1![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup> <sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M<sup> </sup> B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_6463_9ecd_41cb24fc19aa_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-14 M
10-14 M
B)1![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup> <sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M<sup> </sup> B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_6464_9ecd_49b1bc74031d_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-10 M
10-10 M
C)1![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup> <sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M<sup> </sup> B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_6465_9ecd_8f878db98d8d_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M
10-4 M
D)1![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup> <sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M<sup> </sup> B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_6466_9ecd_8371cd8ab021_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M
A)1
![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup> <sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M<sup> </sup> B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_6463_9ecd_41cb24fc19aa_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-14 M
10-14 M B)1
![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup> <sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M<sup> </sup> B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_6464_9ecd_49b1bc74031d_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-10 M
10-10 M C)1
![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup> <sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M<sup> </sup> B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_6465_9ecd_8f878db98d8d_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M
10-4 MD)1
![<strong>What is the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup> <sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M<sup> </sup> B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_6466_9ecd_8371cd8ab021_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which acid ionization constant would indicate the strongest acid?
A)3.5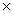 10-4
10-4
B)9.5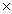 10-8
10-8
C)1.5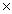 10-2
10-2
D)1.3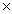 10-13
10-13
A)3.5
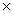 10-4
10-4B)9.5
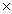 10-8
10-8C)1.5
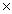 10-2
10-2D)1.3
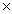 10-13
10-13
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which Keq value indicates the greatest concentration of products at equilibrium?
A)6.7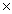 105
105
B)3.2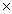 109
109
C)1.4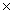 10-3
10-3
D)3.2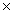 10-7
10-7
A)6.7
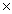 105
105B)3.2
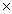 109
109C)1.4
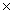 10-3
10-3D)3.2
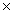 10-7
10-7
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the [H+1] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?
A)1![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?<sup></sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_6467_9ecd_a50caf1721c8_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-2 M
10-2 M
B)1![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?<sup></sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_8b78_9ecd_7ff6d540b7d2_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-14 M
10-14 M
C)1![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?<sup></sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_8b79_9ecd_99b9b9df8671_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M
D)1![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?<sup></sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_8b7a_9ecd_6fc09781b771_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-12 M
10-12 M
A)1
![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?<sup></sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_6467_9ecd_a50caf1721c8_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-2 M
10-2 MB)1
![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?<sup></sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_8b78_9ecd_7ff6d540b7d2_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-14 M
10-14 MC)1
![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?<sup></sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_8b79_9ecd_99b9b9df8671_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 MD)1
![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.01 M KOH solution?<sup></sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-12</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_8b7a_9ecd_6fc09781b771_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-12 M
10-12 M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
For the following reaction: 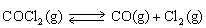 Keq =
Keq = 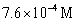 .COCl2 is introduced in a closed container until its concentration is 0.890 M.What will be the concentration of Cl2(g)once the reaction has reached equilibrium?
.COCl2 is introduced in a closed container until its concentration is 0.890 M.What will be the concentration of Cl2(g)once the reaction has reached equilibrium?
A)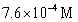
B)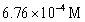
C)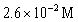
D)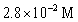
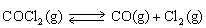 Keq =
Keq = 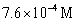 .COCl2 is introduced in a closed container until its concentration is 0.890 M.What will be the concentration of Cl2(g)once the reaction has reached equilibrium?
.COCl2 is introduced in a closed container until its concentration is 0.890 M.What will be the concentration of Cl2(g)once the reaction has reached equilibrium?A)
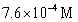
B)
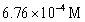
C)
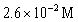
D)
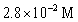

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the following equilibrium,as HNO3 is added,the concentration of CrO4-2 ion will 2 CrO4-2 (aq)+ 2 H+1 (aq) 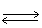 Cr2O7-2 (aq)+ H2O (l)
Cr2O7-2 (aq)+ H2O (l)
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.
 Cr2O7-2 (aq)+ H2O (l)
Cr2O7-2 (aq)+ H2O (l)A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An aqueous solution of sodium sulfate will be:
A)acidic
B)neutral
C)basic
A)acidic
B)neutral
C)basic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the following equilibrium;as H2 (g)is removed,the concentration of HI (g)will
H2 (g)+ I2 (g)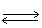 2 HI (g)
2 HI (g)
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.
H2 (g)+ I2 (g)
 2 HI (g)
2 HI (g)A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the following equilibrium,as the concentration of CrO4-2 ion increases,the concentration of Cr2O7-2 ion 2 CrO4-2(aq)+ 2 H+1(aq) 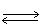 Cr2O7-2(aq)+ H2O (l)
Cr2O7-2(aq)+ H2O (l)
A)increases
B)decreases
C)remains the same
 Cr2O7-2(aq)+ H2O (l)
Cr2O7-2(aq)+ H2O (l)A)increases
B)decreases
C)remains the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the following equilibrium,as temperature increases,the point of equilibrium will CO2 (g)+ 2 H2O (g)+ 890 kJ 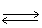 CH4 (g)+ 2 O2 (g)
CH4 (g)+ 2 O2 (g)
A)shift to the right.
B)shift to the left.
C)not shift.
 CH4 (g)+ 2 O2 (g)
CH4 (g)+ 2 O2 (g)A)shift to the right.
B)shift to the left.
C)not shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the [H+1] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?
A)1![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_3d4f_9ecd_796b7fb73667_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-14 M
10-14 M
B)1![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_3d50_9ecd_c9a29e663e8e_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-10 M
10-10 M
C)1![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_3d51_9ecd_ff5b18f6a632_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M
10-4 M
D)1![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_3d52_9ecd_b19fbc062848_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M
A)1
![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_3d4f_9ecd_796b7fb73667_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-14 M
10-14 MB)1
![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_3d50_9ecd_c9a29e663e8e_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-10 M
10-10 MC)1
![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_3d51_9ecd_ff5b18f6a632_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M
10-4 MD)1
![<strong>What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.0001 M solution of HCl?<sup> </sup></strong> A)1 10<sup>-14</sup> M B)1 10<sup>-10</sup> M C)1 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_3d52_9ecd_b19fbc062848_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In the following equilibrium,as volume of the reaction vessel increases,the point of equilibrium will 2 HF (g) 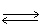 H2 (g)+ F2 (g)
H2 (g)+ F2 (g)
A)shift to the right.
B)shift to the left.
C)not shift.
 H2 (g)+ F2 (g)
H2 (g)+ F2 (g)A)shift to the right.
B)shift to the left.
C)not shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the pH of a 0.140 M HCl solution?
A)0.854
B)13.2
C)0.140
D)3.66
A)0.854
B)13.2
C)0.140
D)3.66

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the pH of a 0.10 M KOH solution?
A)1
B)7
C)13
D)14
A)1
B)7
C)13
D)14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
AgNO3 is added to a saturated AgI solution until the [Ag+1] is 0.050 M.What is the [I-1] remaining in the solution? The Ksp of AgI is 8.3 ![<strong>AgNO<sub>3</sub> is added to a saturated AgI solution until the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>] is 0.050 M.What is the [I<sup>-1</sup>] remaining in the solution? The Ksp of AgI is 8.3 10<sup>-17</sup>.</strong> A)0.050 M B)4.2 10<sup>-18</sup> M C)1.7 10<sup>-15</sup> M D)8.3 10<sup>-17</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_9d08_9ecd_b78630365fa4_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-17.
10-17.
A)0.050 M
B)4.2![<strong>AgNO<sub>3</sub> is added to a saturated AgI solution until the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>] is 0.050 M.What is the [I<sup>-1</sup>] remaining in the solution? The Ksp of AgI is 8.3 10<sup>-17</sup>.</strong> A)0.050 M B)4.2 10<sup>-18</sup> M C)1.7 10<sup>-15</sup> M D)8.3 10<sup>-17</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_9d09_9ecd_318c06267d8c_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-18 M
10-18 M
C)1.7![<strong>AgNO<sub>3</sub> is added to a saturated AgI solution until the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>] is 0.050 M.What is the [I<sup>-1</sup>] remaining in the solution? The Ksp of AgI is 8.3 10<sup>-17</sup>.</strong> A)0.050 M B)4.2 10<sup>-18</sup> M C)1.7 10<sup>-15</sup> M D)8.3 10<sup>-17</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_9d0a_9ecd_7fd5a8b1a6dc_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-15 M
10-15 M
D)8.3![<strong>AgNO<sub>3</sub> is added to a saturated AgI solution until the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>] is 0.050 M.What is the [I<sup>-1</sup>] remaining in the solution? The Ksp of AgI is 8.3 10<sup>-17</sup>.</strong> A)0.050 M B)4.2 10<sup>-18</sup> M C)1.7 10<sup>-15</sup> M D)8.3 10<sup>-17</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_9d0b_9ecd_f7e9e9a2a15c_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-17 M
10-17 M
![<strong>AgNO<sub>3</sub> is added to a saturated AgI solution until the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>] is 0.050 M.What is the [I<sup>-1</sup>] remaining in the solution? The Ksp of AgI is 8.3 10<sup>-17</sup>.</strong> A)0.050 M B)4.2 10<sup>-18</sup> M C)1.7 10<sup>-15</sup> M D)8.3 10<sup>-17</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_9d08_9ecd_b78630365fa4_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-17.
10-17.A)0.050 M
B)4.2
![<strong>AgNO<sub>3</sub> is added to a saturated AgI solution until the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>] is 0.050 M.What is the [I<sup>-1</sup>] remaining in the solution? The Ksp of AgI is 8.3 10<sup>-17</sup>.</strong> A)0.050 M B)4.2 10<sup>-18</sup> M C)1.7 10<sup>-15</sup> M D)8.3 10<sup>-17</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_9d09_9ecd_318c06267d8c_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-18 M
10-18 MC)1.7
![<strong>AgNO<sub>3</sub> is added to a saturated AgI solution until the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>] is 0.050 M.What is the [I<sup>-1</sup>] remaining in the solution? The Ksp of AgI is 8.3 10<sup>-17</sup>.</strong> A)0.050 M B)4.2 10<sup>-18</sup> M C)1.7 10<sup>-15</sup> M D)8.3 10<sup>-17</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_9d0a_9ecd_7fd5a8b1a6dc_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-15 M
10-15 MD)8.3
![<strong>AgNO<sub>3</sub> is added to a saturated AgI solution until the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>] is 0.050 M.What is the [I<sup>-1</sup>] remaining in the solution? The Ksp of AgI is 8.3 10<sup>-17</sup>.</strong> A)0.050 M B)4.2 10<sup>-18</sup> M C)1.7 10<sup>-15</sup> M D)8.3 10<sup>-17</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_9d0b_9ecd_f7e9e9a2a15c_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-17 M
10-17 M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In aqueous solution the [H+1] is 1.4 ![<strong>In aqueous solution the [H<sup>+1</sup>] is 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.4 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1.4 10<sup>-7</sup> M C)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M <sup> </sup> D)7.1 10<sup>-11</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb30_9ecd_87858265330c_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M.The [OH-1] in the same solution is
10-4 M.The [OH-1] in the same solution is
A)1.4![<strong>In aqueous solution the [H<sup>+1</sup>] is 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.4 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1.4 10<sup>-7</sup> M C)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M <sup> </sup> D)7.1 10<sup>-11</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb31_9ecd_c7fd561338e2_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-2 M
10-2 M
B)1.4![<strong>In aqueous solution the [H<sup>+1</sup>] is 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.4 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1.4 10<sup>-7</sup> M C)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M <sup> </sup> D)7.1 10<sup>-11</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb32_9ecd_a303930c5673_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M
C)1.0![<strong>In aqueous solution the [H<sup>+1</sup>] is 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.4 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1.4 10<sup>-7</sup> M C)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M <sup> </sup> D)7.1 10<sup>-11</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb33_9ecd_75dcbd5881a0_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M
D)7.1![<strong>In aqueous solution the [H<sup>+1</sup>] is 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.4 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1.4 10<sup>-7</sup> M C)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M <sup> </sup> D)7.1 10<sup>-11</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb34_9ecd_b7c3ddbeb619_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-11 M
10-11 M
![<strong>In aqueous solution the [H<sup>+1</sup>] is 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.4 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1.4 10<sup>-7</sup> M C)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M <sup> </sup> D)7.1 10<sup>-11</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb30_9ecd_87858265330c_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M.The [OH-1] in the same solution is
10-4 M.The [OH-1] in the same solution isA)1.4
![<strong>In aqueous solution the [H<sup>+1</sup>] is 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.4 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1.4 10<sup>-7</sup> M C)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M <sup> </sup> D)7.1 10<sup>-11</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb31_9ecd_c7fd561338e2_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-2 M
10-2 MB)1.4
![<strong>In aqueous solution the [H<sup>+1</sup>] is 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.4 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1.4 10<sup>-7</sup> M C)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M <sup> </sup> D)7.1 10<sup>-11</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb32_9ecd_a303930c5673_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 MC)1.0
![<strong>In aqueous solution the [H<sup>+1</sup>] is 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.4 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1.4 10<sup>-7</sup> M C)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M <sup> </sup> D)7.1 10<sup>-11</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb33_9ecd_75dcbd5881a0_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M D)7.1
![<strong>In aqueous solution the [H<sup>+1</sup>] is 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The [OH<sup>-1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.4 10<sup>-2</sup> M B)1.4 10<sup>-7</sup> M C)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M <sup> </sup> D)7.1 10<sup>-11</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb34_9ecd_b7c3ddbeb619_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-11 M
10-11 M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A solution of NaNO3 would be
A)acidic.
B)basic.
C)neutral.
A)acidic.
B)basic.
C)neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A solution of K2SO3 would be
A)acidic.
B)basic.
C)neutral.
A)acidic.
B)basic.
C)neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which salt would produce a neutral solution?
A)KNO2
B)NH4Cl
C)Na2S
D)KCl
A)KNO2
B)NH4Cl
C)Na2S
D)KCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the pH of a 0.0010 M HCl solution?
A)1.0 X 10-3
B)3.0
C)11
D)4.0
A)1.0 X 10-3
B)3.0
C)11
D)4.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose Ka value is 4.0 ![<strong>Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 4.0 10<sup>-10</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-4</sup> B)6.3 10<sup>-</sup><sup>6</sup> C)4.0 10<sup>-</sup><sup>9</sup> D)1.0 10<sup>-11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_b28f_9ecd_779e914a3a0f_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-10.What is the [H+1] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?
10-10.What is the [H+1] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?
A)1![<strong>Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 4.0 10<sup>-10</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-4</sup> B)6.3 10<sup>-</sup><sup>6</sup> C)4.0 10<sup>-</sup><sup>9</sup> D)1.0 10<sup>-11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_d9a0_9ecd_f9973cf68aaf_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4
10-4
B)6.3![<strong>Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 4.0 10<sup>-10</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-4</sup> B)6.3 10<sup>-</sup><sup>6</sup> C)4.0 10<sup>-</sup><sup>9</sup> D)1.0 10<sup>-11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_d9a1_9ecd_03e42498de41_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-6
10-6
C)4.0![<strong>Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 4.0 10<sup>-10</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-4</sup> B)6.3 10<sup>-</sup><sup>6</sup> C)4.0 10<sup>-</sup><sup>9</sup> D)1.0 10<sup>-11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_d9a2_9ecd_df7931710b5b_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-9
10-9
D)1.0![<strong>Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 4.0 10<sup>-10</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-4</sup> B)6.3 10<sup>-</sup><sup>6</sup> C)4.0 10<sup>-</sup><sup>9</sup> D)1.0 10<sup>-11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_d9a3_9ecd_1d5606dba870_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-11
10-11
![<strong>Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 4.0 10<sup>-10</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-4</sup> B)6.3 10<sup>-</sup><sup>6</sup> C)4.0 10<sup>-</sup><sup>9</sup> D)1.0 10<sup>-11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_b28f_9ecd_779e914a3a0f_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-10.What is the [H+1] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?
10-10.What is the [H+1] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?A)1
![<strong>Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 4.0 10<sup>-10</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-4</sup> B)6.3 10<sup>-</sup><sup>6</sup> C)4.0 10<sup>-</sup><sup>9</sup> D)1.0 10<sup>-11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_d9a0_9ecd_f9973cf68aaf_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4
10-4B)6.3
![<strong>Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 4.0 10<sup>-10</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-4</sup> B)6.3 10<sup>-</sup><sup>6</sup> C)4.0 10<sup>-</sup><sup>9</sup> D)1.0 10<sup>-11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_d9a1_9ecd_03e42498de41_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-6
10-6C)4.0
![<strong>Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 4.0 10<sup>-10</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-4</sup> B)6.3 10<sup>-</sup><sup>6</sup> C)4.0 10<sup>-</sup><sup>9</sup> D)1.0 10<sup>-11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_d9a2_9ecd_df7931710b5b_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-9
10-9D)1.0
![<strong>Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 4.0 10<sup>-10</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN?</strong> A)1 10<sup>-4</sup> B)6.3 10<sup>-</sup><sup>6</sup> C)4.0 10<sup>-</sup><sup>9</sup> D)1.0 10<sup>-11</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea4_d9a3_9ecd_1d5606dba870_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-11
10-11
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Hydrocyanic acid,HCN,is a weak acid whose Ka value is 4.0  10-10.What is the pH of a 0.10 M solution of HCN?
10-10.What is the pH of a 0.10 M solution of HCN?
A)1.0
B)5.2
C)9.4
D)10.
 10-10.What is the pH of a 0.10 M solution of HCN?
10-10.What is the pH of a 0.10 M solution of HCN? A)1.0
B)5.2
C)9.4
D)10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which salt would produce an acidic solution?
A)NaCl
B)NH4Cl
C)KNO3
D)NaI
A)NaCl
B)NH4Cl
C)KNO3
D)NaI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In aqueous solution the [OH-1] is 3.0 ![<strong>In aqueous solution the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] is 3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M.The [H<sup>+1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M B)3.3 10<sup>-9</sup> M C)3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M D)3.0 10<sup>8</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_1245_9ecd_5fc976ef1778_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-6 M.The [H+1] in the same solution is
10-6 M.The [H+1] in the same solution is
A)1.0![<strong>In aqueous solution the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] is 3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M.The [H<sup>+1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M B)3.3 10<sup>-9</sup> M C)3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M D)3.0 10<sup>8</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_1246_9ecd_35101bc7d65c_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M
B)3.3![<strong>In aqueous solution the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] is 3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M.The [H<sup>+1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M B)3.3 10<sup>-9</sup> M C)3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M D)3.0 10<sup>8</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_1247_9ecd_81e69a653db2_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-9 M
10-9 M
C)3.0![<strong>In aqueous solution the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] is 3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M.The [H<sup>+1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M B)3.3 10<sup>-9</sup> M C)3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M D)3.0 10<sup>8</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_1248_9ecd_b54e32b20cdb_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-6 M
10-6 M
D)3.0![<strong>In aqueous solution the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] is 3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M.The [H<sup>+1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M B)3.3 10<sup>-9</sup> M C)3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M D)3.0 10<sup>8</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_1249_9ecd_7b672b4410dc_TB4036_11.jpg) 108 M
108 M
![<strong>In aqueous solution the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] is 3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M.The [H<sup>+1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M B)3.3 10<sup>-9</sup> M C)3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M D)3.0 10<sup>8</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_1245_9ecd_5fc976ef1778_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-6 M.The [H+1] in the same solution is
10-6 M.The [H+1] in the same solution isA)1.0
![<strong>In aqueous solution the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] is 3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M.The [H<sup>+1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M B)3.3 10<sup>-9</sup> M C)3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M D)3.0 10<sup>8</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_1246_9ecd_35101bc7d65c_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 MB)3.3
![<strong>In aqueous solution the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] is 3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M.The [H<sup>+1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M B)3.3 10<sup>-9</sup> M C)3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M D)3.0 10<sup>8</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_1247_9ecd_81e69a653db2_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-9 M
10-9 MC)3.0
![<strong>In aqueous solution the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] is 3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M.The [H<sup>+1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M B)3.3 10<sup>-9</sup> M C)3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M D)3.0 10<sup>8</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_1248_9ecd_b54e32b20cdb_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-6 M
10-6 MD)3.0
![<strong>In aqueous solution the [OH<sup>-1</sup>] is 3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M.The [H<sup>+1</sup>] in the same solution is</strong> A)1.0 10<sup>-7</sup> M B)3.3 10<sup>-9</sup> M C)3.0 10<sup>-6</sup> M D)3.0 10<sup>8</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_1249_9ecd_7b672b4410dc_TB4036_11.jpg) 108 M
108 M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Ksp of silver iodide is 8.3  10-17.What is the solubility of silver iodide in g/L?
10-17.What is the solubility of silver iodide in g/L?
A)1.5 10-6
10-6
B)1.6 10-30
10-30
C)1.9 10-14
10-14
D)6.1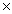 10-21
10-21
 10-17.What is the solubility of silver iodide in g/L?
10-17.What is the solubility of silver iodide in g/L?A)1.5
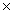 10-6
10-6B)1.6
 10-30
10-30C)1.9
 10-14
10-14D)6.1
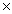 10-21
10-21
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Hydrosulfuric acid,H2S,is a weak acid whose Ka value is 9.5 ![<strong>Hydrosulfuric acid,H<sub>2</sub>S,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 9.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 4.0 M solution of H<sub>2</sub>S?</strong> A)6.0 10<sup>-1</sup> M B)6.2 10<sup>-4</sup> M C)4.0 M <sup> </sup> D)3.8 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_00b5_9ecd_4b25bfe49dc7_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8.What is the [H+1] in a 4.0 M solution of H2S?
10-8.What is the [H+1] in a 4.0 M solution of H2S?
A)6.0![<strong>Hydrosulfuric acid,H<sub>2</sub>S,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 9.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 4.0 M solution of H<sub>2</sub>S?</strong> A)6.0 10<sup>-1</sup> M B)6.2 10<sup>-4</sup> M C)4.0 M <sup> </sup> D)3.8 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_00b6_9ecd_95fb0f92c196_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-1 M
10-1 M
B)6.2![<strong>Hydrosulfuric acid,H<sub>2</sub>S,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 9.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 4.0 M solution of H<sub>2</sub>S?</strong> A)6.0 10<sup>-1</sup> M B)6.2 10<sup>-4</sup> M C)4.0 M <sup> </sup> D)3.8 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_00b7_9ecd_d7751ffab767_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M
10-4 M
C)4.0 M
D)3.8![<strong>Hydrosulfuric acid,H<sub>2</sub>S,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 9.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 4.0 M solution of H<sub>2</sub>S?</strong> A)6.0 10<sup>-1</sup> M B)6.2 10<sup>-4</sup> M C)4.0 M <sup> </sup> D)3.8 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_00b8_9ecd_03bd87163c19_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M
![<strong>Hydrosulfuric acid,H<sub>2</sub>S,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 9.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 4.0 M solution of H<sub>2</sub>S?</strong> A)6.0 10<sup>-1</sup> M B)6.2 10<sup>-4</sup> M C)4.0 M <sup> </sup> D)3.8 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_00b5_9ecd_4b25bfe49dc7_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8.What is the [H+1] in a 4.0 M solution of H2S?
10-8.What is the [H+1] in a 4.0 M solution of H2S?A)6.0
![<strong>Hydrosulfuric acid,H<sub>2</sub>S,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 9.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 4.0 M solution of H<sub>2</sub>S?</strong> A)6.0 10<sup>-1</sup> M B)6.2 10<sup>-4</sup> M C)4.0 M <sup> </sup> D)3.8 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_00b6_9ecd_95fb0f92c196_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-1 M
10-1 MB)6.2
![<strong>Hydrosulfuric acid,H<sub>2</sub>S,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 9.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 4.0 M solution of H<sub>2</sub>S?</strong> A)6.0 10<sup>-1</sup> M B)6.2 10<sup>-4</sup> M C)4.0 M <sup> </sup> D)3.8 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_00b7_9ecd_d7751ffab767_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M
10-4 MC)4.0 M
D)3.8
![<strong>Hydrosulfuric acid,H<sub>2</sub>S,is a weak acid whose K<sub>a</sub> value is 9.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.What is the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 4.0 M solution of H<sub>2</sub>S?</strong> A)6.0 10<sup>-1</sup> M B)6.2 10<sup>-4</sup> M C)4.0 M <sup> </sup> D)3.8 10<sup>-7</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_00b8_9ecd_03bd87163c19_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-7 M
10-7 M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The pH of an aqueous solution is 3.2.What is the [ ![<strong>The pH of an aqueous solution is 3.2.What is the [ ] in the same solution?</strong> A) M B) M C) M D)10.8 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_c41c_9ecd_d5c2e9ac3aea_TB4036_11.jpg) ] in the same solution?
] in the same solution?
A)![<strong>The pH of an aqueous solution is 3.2.What is the [ ] in the same solution?</strong> A) M B) M C) M D)10.8 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_c41d_9ecd_61364e318e9c_TB4036_11.jpg) M
M
B)![<strong>The pH of an aqueous solution is 3.2.What is the [ ] in the same solution?</strong> A) M B) M C) M D)10.8 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_c41e_9ecd_8969bb8b97e6_TB4036_11.jpg) M
M
C)![<strong>The pH of an aqueous solution is 3.2.What is the [ ] in the same solution?</strong> A) M B) M C) M D)10.8 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb2f_9ecd_e3db8bf23f96_TB4036_11.jpg) M
M
D)10.8 M
![<strong>The pH of an aqueous solution is 3.2.What is the [ ] in the same solution?</strong> A) M B) M C) M D)10.8 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_c41c_9ecd_d5c2e9ac3aea_TB4036_11.jpg) ] in the same solution?
] in the same solution?A)
![<strong>The pH of an aqueous solution is 3.2.What is the [ ] in the same solution?</strong> A) M B) M C) M D)10.8 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_c41d_9ecd_61364e318e9c_TB4036_11.jpg) M
MB)
![<strong>The pH of an aqueous solution is 3.2.What is the [ ] in the same solution?</strong> A) M B) M C) M D)10.8 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_c41e_9ecd_8969bb8b97e6_TB4036_11.jpg) M
MC)
![<strong>The pH of an aqueous solution is 3.2.What is the [ ] in the same solution?</strong> A) M B) M C) M D)10.8 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_eb2f_9ecd_e3db8bf23f96_TB4036_11.jpg) M
MD)10.8 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The Ksp of silver bromide is 5.0 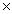 10-13.What is the solubility of silver bromide in g/L?
10-13.What is the solubility of silver bromide in g/L?
A)4.7 10-23
10-23
B)3.0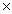 10-11
10-11
C)1.3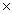 10-4
10-4
D)9.4 10-11
10-11
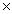 10-13.What is the solubility of silver bromide in g/L?
10-13.What is the solubility of silver bromide in g/L?A)4.7
 10-23
10-23B)3.0
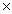 10-11
10-11C)1.3
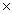 10-4
10-4D)9.4
 10-11
10-11
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
HCl is added to a saturated AgCl solution until the [Cl-1] is 0.010 M.What is the [Ag+1] remaining in the solution? The Ksp of AgCl is 1.8 ![<strong>HCl is added to a saturated AgCl solution until the [Cl<sup>-1</sup>] is 0.010 M.What is the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>]<sup></sup> remaining in the solution? The K<sub>sp</sub> of AgCl is 1.8 10<sup>-10</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-10</sup> M B)1.8 10<sup>-8 </sup>M C)1.8 10<sup>-12</sup> M D)0.010 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_75f4_9ecd_0b02b8af41cc_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-10.
10-10.
A)1.8![<strong>HCl is added to a saturated AgCl solution until the [Cl<sup>-1</sup>] is 0.010 M.What is the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>]<sup></sup> remaining in the solution? The K<sub>sp</sub> of AgCl is 1.8 10<sup>-10</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-10</sup> M B)1.8 10<sup>-8 </sup>M C)1.8 10<sup>-12</sup> M D)0.010 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_75f5_9ecd_f792724b357a_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-10 M
10-10 M
B)1.8![<strong>HCl is added to a saturated AgCl solution until the [Cl<sup>-1</sup>] is 0.010 M.What is the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>]<sup></sup> remaining in the solution? The K<sub>sp</sub> of AgCl is 1.8 10<sup>-10</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-10</sup> M B)1.8 10<sup>-8 </sup>M C)1.8 10<sup>-12</sup> M D)0.010 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_75f6_9ecd_d7ba38a18884_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8 M
10-8 M
C)1.8![<strong>HCl is added to a saturated AgCl solution until the [Cl<sup>-1</sup>] is 0.010 M.What is the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>]<sup></sup> remaining in the solution? The K<sub>sp</sub> of AgCl is 1.8 10<sup>-10</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-10</sup> M B)1.8 10<sup>-8 </sup>M C)1.8 10<sup>-12</sup> M D)0.010 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_75f7_9ecd_55ce0b85883e_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-12 M
10-12 M
D)0.010 M
![<strong>HCl is added to a saturated AgCl solution until the [Cl<sup>-1</sup>] is 0.010 M.What is the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>]<sup></sup> remaining in the solution? The K<sub>sp</sub> of AgCl is 1.8 10<sup>-10</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-10</sup> M B)1.8 10<sup>-8 </sup>M C)1.8 10<sup>-12</sup> M D)0.010 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_75f4_9ecd_0b02b8af41cc_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-10.
10-10.A)1.8
![<strong>HCl is added to a saturated AgCl solution until the [Cl<sup>-1</sup>] is 0.010 M.What is the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>]<sup></sup> remaining in the solution? The K<sub>sp</sub> of AgCl is 1.8 10<sup>-10</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-10</sup> M B)1.8 10<sup>-8 </sup>M C)1.8 10<sup>-12</sup> M D)0.010 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_75f5_9ecd_f792724b357a_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-10 M
10-10 MB)1.8
![<strong>HCl is added to a saturated AgCl solution until the [Cl<sup>-1</sup>] is 0.010 M.What is the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>]<sup></sup> remaining in the solution? The K<sub>sp</sub> of AgCl is 1.8 10<sup>-10</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-10</sup> M B)1.8 10<sup>-8 </sup>M C)1.8 10<sup>-12</sup> M D)0.010 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_75f6_9ecd_d7ba38a18884_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8 M
10-8 MC)1.8
![<strong>HCl is added to a saturated AgCl solution until the [Cl<sup>-1</sup>] is 0.010 M.What is the [Ag<sup>+1</sup>]<sup></sup> remaining in the solution? The K<sub>sp</sub> of AgCl is 1.8 10<sup>-10</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-10</sup> M B)1.8 10<sup>-8 </sup>M C)1.8 10<sup>-12</sup> M D)0.010 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea5_75f7_9ecd_55ce0b85883e_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-12 M
10-12 MD)0.010 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is the pH of a 0.0500 M NaOH solution?
A)1.30
B)-1.30
C)12.7
D)0.0500
A)1.30
B)-1.30
C)12.7
D)0.0500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which salt would produce a basic solution?
A)KBr
B)NaNO2
C)CuCl
D)NH4Cl
A)KBr
B)NaNO2
C)CuCl
D)NH4Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Hydrosulfuric acid,H2S,is a weak acid whose Ka value is 9.5 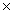 10-8.What is the pH of a 4.0 M solution of H2S?
10-8.What is the pH of a 4.0 M solution of H2S?
A)0.60
B)6.2
C)3.5
D)3.2
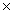 10-8.What is the pH of a 4.0 M solution of H2S?
10-8.What is the pH of a 4.0 M solution of H2S? A)0.60
B)6.2
C)3.5
D)3.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The equilibrium constant can change significantly with a change in
A)concentration.
B)catalyst.
C)temperature.
D)pressure.
A)concentration.
B)catalyst.
C)temperature.
D)pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Calculate the pH of a 0.250 M aqueous solution of HNO2.The acid dissociation constant,Ka,for HNO2 is 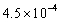 .
.
A)1.97
B)2.74
C)3.35
D)3.95
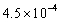 .
.A)1.97
B)2.74
C)3.35
D)3.95

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The magnitude of Keq depends on
A)initial concentration of reactants.
B)presence of a catalyst.
C)temperature.
D)volume of reaction vessel.
A)initial concentration of reactants.
B)presence of a catalyst.
C)temperature.
D)volume of reaction vessel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Calculate the percent ionization of a 0.200 M aqueous solution of HNO2 having a pH of 2.80.
A)7.1%
B)1.4%
C)2.0%
D)0.79%
A)7.1%
B)1.4%
C)2.0%
D)0.79%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A 0.50 M solution of hydrofluoric acid,HF,is 3.6% ionized.The acid ionization constant, Ka,for hydrofluoric acid is
A)3.6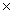 10-2
10-2
B)1.8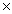 10-2
10-2
C)3.2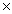 10-4
10-4
D)6.5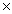 10-4
10-4
A)3.6
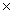 10-2
10-2B)1.8
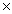 10-2
10-2C)3.2
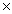 10-4
10-4D)6.5
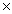 10-4
10-4
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Calculate the percent ionization of a 0.050 M aqueous solution of HF having a pH of 3.15.
A)1.4%
B)4.9%
C)1.6%
D)6.3%
A)1.4%
B)4.9%
C)1.6%
D)6.3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which solution has the highest pH?
A)0.1 M HNO2
B)0.1 M HCl
C)0.1 M KOH
D)0.1 M NH4Cl
A)0.1 M HNO2
B)0.1 M HCl
C)0.1 M KOH
D)0.1 M NH4Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which solution has the lowest pH?
A)0.1 M HNO2
B)0.1 M HCl
C)0.1 M KOH
D)0.1 M NH4OH
A)0.1 M HNO2
B)0.1 M HCl
C)0.1 M KOH
D)0.1 M NH4OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What will be the [H+1] in a 0.50 M solution of HClO? The Ka of HClO = 3.5 ![<strong>What will be the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.50 M solution of HClO? The K<sub>a</sub> of HClO = 3.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-8</sup> M B)7.0 10<sup>-8</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1.3 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1.9 10<sup>-4</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_ae97_9ecd_7f585b9599e5_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8.
10-8.
A)1.8![<strong>What will be the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.50 M solution of HClO? The K<sub>a</sub> of HClO = 3.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-8</sup> M B)7.0 10<sup>-8</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1.3 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1.9 10<sup>-4</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_ae98_9ecd_2d14518b94fa_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8 M
10-8 M
B)7.0![<strong>What will be the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.50 M solution of HClO? The K<sub>a</sub> of HClO = 3.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-8</sup> M B)7.0 10<sup>-8</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1.3 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1.9 10<sup>-4</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_d5a9_9ecd_8d96e1e97615_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8 M
10-8 M
C)1.3![<strong>What will be the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.50 M solution of HClO? The K<sub>a</sub> of HClO = 3.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-8</sup> M B)7.0 10<sup>-8</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1.3 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1.9 10<sup>-4</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_d5aa_9ecd_a15cbfacb676_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M
10-4 M
D)1.9![<strong>What will be the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.50 M solution of HClO? The K<sub>a</sub> of HClO = 3.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-8</sup> M B)7.0 10<sup>-8</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1.3 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1.9 10<sup>-4</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_d5ab_9ecd_fd8a4faa64f6_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M
10-4 M
![<strong>What will be the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.50 M solution of HClO? The K<sub>a</sub> of HClO = 3.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-8</sup> M B)7.0 10<sup>-8</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1.3 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1.9 10<sup>-4</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_ae97_9ecd_7f585b9599e5_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8.
10-8.A)1.8
![<strong>What will be the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.50 M solution of HClO? The K<sub>a</sub> of HClO = 3.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-8</sup> M B)7.0 10<sup>-8</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1.3 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1.9 10<sup>-4</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_ae98_9ecd_2d14518b94fa_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8 M
10-8 MB)7.0
![<strong>What will be the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.50 M solution of HClO? The K<sub>a</sub> of HClO = 3.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-8</sup> M B)7.0 10<sup>-8</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1.3 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1.9 10<sup>-4</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_d5a9_9ecd_8d96e1e97615_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8 M
10-8 M C)1.3
![<strong>What will be the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.50 M solution of HClO? The K<sub>a</sub> of HClO = 3.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-8</sup> M B)7.0 10<sup>-8</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1.3 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1.9 10<sup>-4</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_d5aa_9ecd_a15cbfacb676_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M
10-4 MD)1.9
![<strong>What will be the [H<sup>+1</sup>] in a 0.50 M solution of HClO? The K<sub>a</sub> of HClO = 3.5 10<sup>-8</sup>.</strong> A)1.8 10<sup>-8</sup> M B)7.0 10<sup>-8</sup> M<sup> </sup> C)1.3 10<sup>-4</sup> M D)1.9 10<sup>-4</sup> M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_d5ab_9ecd_fd8a4faa64f6_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M
10-4 M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The mathematical expression for the equilibrium constant of the following reaction is: 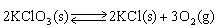
A)
B)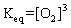
C)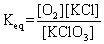
D)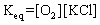
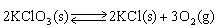
A)

B)
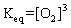
C)
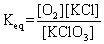
D)
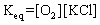

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The sodium salts of all anions listed below yield basic solutions when dissolved in water except
A)fluoride
B)chloride
C)cyanide
D)nitrite
A)fluoride
B)chloride
C)cyanide
D)nitrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the pH of a 0.00500 M solution of barium hydroxide?
A)11.7
B)12.0
C)2.00
D)2.30
A)11.7
B)12.0
C)2.00
D)2.30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The concentration of hydroxide ions, 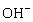 ,in an aqueous solution is
,in an aqueous solution is 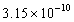 M.The pH of the solution is:
M.The pH of the solution is:
A)1.00
B)4.50
C)9.50
D)3.17
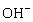 ,in an aqueous solution is
,in an aqueous solution is 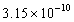 M.The pH of the solution is:
M.The pH of the solution is:A)1.00
B)4.50
C)9.50
D)3.17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The solubility of silver bromide is 7.1 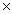 10-7 M.The Ksp of silver bromide is
10-7 M.The Ksp of silver bromide is
A)7.1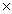 10-5
10-5
B)5.0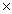 10 -5
10 -5
C)5.0 10-13
10-13
D)5.0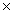 10-15
10-15
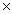 10-7 M.The Ksp of silver bromide is
10-7 M.The Ksp of silver bromide isA)7.1
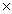 10-5
10-5B)5.0
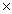 10 -5
10 -5C)5.0
 10-13
10-13D)5.0
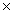 10-15
10-15
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The solubility of CaF2 is 2.14  10-4 M.The Ksp of CaF2 is
10-4 M.The Ksp of CaF2 is
A)3.92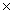 10-11
10-11
B)4.58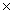 10 -8
10 -8
C)9.80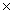 10-12
10-12
D)2.14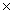 10-8
10-8
 10-4 M.The Ksp of CaF2 is
10-4 M.The Ksp of CaF2 isA)3.92
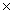 10-11
10-11B)4.58
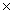 10 -8
10 -8C)9.80
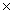 10-12
10-12D)2.14
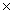 10-8
10-8
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A 0.20 M solution of the weak acid HA has a [H+1] = 1.4 ![<strong>A 0.20 M solution of the weak acid HA has a [H<sup>+1</sup>] = 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The acid ionization constant,K<sub>a</sub>,for this acid is <sup> </sup></strong> A)9.8 10<sup>-8</sup> B)1.8 10<sup>-5</sup> C)2.0 10<sup>-8</sup> D)7.0 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_8782_9ecd_396a87e5e0d4_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M.The acid ionization constant,Ka,for this acid is
10-4 M.The acid ionization constant,Ka,for this acid is
A)9.8![<strong>A 0.20 M solution of the weak acid HA has a [H<sup>+1</sup>] = 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The acid ionization constant,K<sub>a</sub>,for this acid is <sup> </sup></strong> A)9.8 10<sup>-8</sup> B)1.8 10<sup>-5</sup> C)2.0 10<sup>-8</sup> D)7.0 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_8783_9ecd_15cabe24dcba_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8
10-8
B)1.8![<strong>A 0.20 M solution of the weak acid HA has a [H<sup>+1</sup>] = 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The acid ionization constant,K<sub>a</sub>,for this acid is <sup> </sup></strong> A)9.8 10<sup>-8</sup> B)1.8 10<sup>-5</sup> C)2.0 10<sup>-8</sup> D)7.0 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_8784_9ecd_354f4a697c88_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-5
10-5
C)2.0![<strong>A 0.20 M solution of the weak acid HA has a [H<sup>+1</sup>] = 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The acid ionization constant,K<sub>a</sub>,for this acid is <sup> </sup></strong> A)9.8 10<sup>-8</sup> B)1.8 10<sup>-5</sup> C)2.0 10<sup>-8</sup> D)7.0 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_8785_9ecd_25d2932d8638_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8
10-8
D)7.0![<strong>A 0.20 M solution of the weak acid HA has a [H<sup>+1</sup>] = 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The acid ionization constant,K<sub>a</sub>,for this acid is <sup> </sup></strong> A)9.8 10<sup>-8</sup> B)1.8 10<sup>-5</sup> C)2.0 10<sup>-8</sup> D)7.0 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_8786_9ecd_09ebaefdf7eb_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4
10-4
![<strong>A 0.20 M solution of the weak acid HA has a [H<sup>+1</sup>] = 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The acid ionization constant,K<sub>a</sub>,for this acid is <sup> </sup></strong> A)9.8 10<sup>-8</sup> B)1.8 10<sup>-5</sup> C)2.0 10<sup>-8</sup> D)7.0 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_8782_9ecd_396a87e5e0d4_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4 M.The acid ionization constant,Ka,for this acid is
10-4 M.The acid ionization constant,Ka,for this acid is A)9.8
![<strong>A 0.20 M solution of the weak acid HA has a [H<sup>+1</sup>] = 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The acid ionization constant,K<sub>a</sub>,for this acid is <sup> </sup></strong> A)9.8 10<sup>-8</sup> B)1.8 10<sup>-5</sup> C)2.0 10<sup>-8</sup> D)7.0 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_8783_9ecd_15cabe24dcba_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8
10-8B)1.8
![<strong>A 0.20 M solution of the weak acid HA has a [H<sup>+1</sup>] = 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The acid ionization constant,K<sub>a</sub>,for this acid is <sup> </sup></strong> A)9.8 10<sup>-8</sup> B)1.8 10<sup>-5</sup> C)2.0 10<sup>-8</sup> D)7.0 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_8784_9ecd_354f4a697c88_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-5
10-5C)2.0
![<strong>A 0.20 M solution of the weak acid HA has a [H<sup>+1</sup>] = 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The acid ionization constant,K<sub>a</sub>,for this acid is <sup> </sup></strong> A)9.8 10<sup>-8</sup> B)1.8 10<sup>-5</sup> C)2.0 10<sup>-8</sup> D)7.0 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_8785_9ecd_25d2932d8638_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-8
10-8D)7.0
![<strong>A 0.20 M solution of the weak acid HA has a [H<sup>+1</sup>] = 1.4 10<sup>-4</sup> M.The acid ionization constant,K<sub>a</sub>,for this acid is <sup> </sup></strong> A)9.8 10<sup>-8</sup> B)1.8 10<sup>-5</sup> C)2.0 10<sup>-8</sup> D)7.0 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4036/11ea7f51_1ea6_8786_9ecd_09ebaefdf7eb_TB4036_11.jpg) 10-4
10-4
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What is the pH of 0.50 M HClO? The Ka of HClO is 3.5 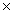 10-8.
10-8.
A)0.30
B)7.5
C)7.8
D)3.9
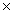 10-8.
10-8.A)0.30
B)7.5
C)7.8
D)3.9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the following equilibrium;as the pressure is increased,the amount of NO2 formed will N2 (g)+ 2 O2 (g) 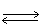 2 NO2 (g)
2 NO2 (g)
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.
 2 NO2 (g)
2 NO2 (g)A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If HCl (aq)is added to a saturated NaCl solution,the [Na+1] will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A 0.30 M solution of formic acid,HCHO2,is 2.4% ionized.The acid ionization constant, Ka,for formic acid is
A)1.7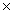 10-4
10-4
B)7.2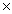 10-3
10-3
C)2.4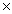 10-2
10-2
D)1.6 10-5
10-5
A)1.7
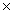 10-4
10-4B)7.2
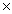 10-3
10-3C)2.4
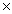 10-2
10-2D)1.6
 10-5
10-5
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



