Deck 20: Enzymes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/88
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Enzymes
1
Which of the following is a common function of many vitamins in the body?
A) substrates
B) apoenzymes
C) coenzymes
D) activators
A) substrates
B) apoenzymes
C) coenzymes
D) activators
coenzymes
2
The theory that proposes a somewhat flexible enzyme conformation is the
A) lock-and-key theory.
B) induced-fit theory.
C) physically-fit theory.
D) expanding-fit theory.
A) lock-and-key theory.
B) induced-fit theory.
C) physically-fit theory.
D) expanding-fit theory.
induced-fit theory.
3
Which statement does not apply to the lock and key theory?
A) It explains the functioning of enzymes.
B) It explains the need for a specific three dimensional structure found in proteins.
C) It explains the reason why a particular enzyme is involved with one substrate.
D) It explains why a substrate-enzyme complex is so difficult to separate.
A) It explains the functioning of enzymes.
B) It explains the need for a specific three dimensional structure found in proteins.
C) It explains the reason why a particular enzyme is involved with one substrate.
D) It explains why a substrate-enzyme complex is so difficult to separate.
It explains why a substrate-enzyme complex is so difficult to separate.
4
The general term which refers to the catalytic ability of an enzyme is
A) enzyme turnover.
B) enzyme activity.
C) catalytic turnover.
D) catalytic speed.
A) enzyme turnover.
B) enzyme activity.
C) catalytic turnover.
D) catalytic speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The substrate for the digestive enzyme named sucrase is _____ .
A) glucose
B) fructose
C) sucrose
D) more than one response is correct
A) glucose
B) fructose
C) sucrose
D) more than one response is correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The catalytically inactive form of an enzyme is called a(n)_____ .
A) cofactor
B) proenzyme
C) apoenzyme
D) activator
A) cofactor
B) proenzyme
C) apoenzyme
D) activator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An enzyme is known to catalyze the conversion of proteins to amino acids.Which of the following would be a correct designation for the enzyme?
A) transferase
B) oxidoreductase
C) hydrolase
D) lyase
A) transferase
B) oxidoreductase
C) hydrolase
D) lyase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The region of an enzyme where the substrate molecule fits is called the
A) active site.
B) substrate site.
C) substrate bond.
D) primary site.
A) active site.
B) substrate site.
C) substrate bond.
D) primary site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following terms can be used correctly to fill the blank in the following equation? apoenzyme + ____ active enzyme
A) zymogen
B) cofactor
C) isozyme
D) substrate
A) zymogen
B) cofactor
C) isozyme
D) substrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
____ is an example of a cofactor required by an enzyme.
A) Acetyl coenzyme A
B) The ferrous (Fe2+)ion
C) Lipoamide
D) The sodium ion
A) Acetyl coenzyme A
B) The ferrous (Fe2+)ion
C) Lipoamide
D) The sodium ion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which statement about enzymes is incorrect?
A) Enzymes can either speed up or slow down a chemical reaction.
B) Enzymes are not used up during the reaction in which they are involved.
C) Enzymes are proteins that are capable of reducing the activation energy.
D) There are enzymes that interact with one enantiomer,but not the other.
A) Enzymes can either speed up or slow down a chemical reaction.
B) Enzymes are not used up during the reaction in which they are involved.
C) Enzymes are proteins that are capable of reducing the activation energy.
D) There are enzymes that interact with one enantiomer,but not the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Salivary amylase behaves as an enzyme only in the presence of chloride ions.Which of the following terms describes the function of the chloride ion?
A) coenzyme
B) zymogen
C) activator
D) active site
A) coenzyme
B) zymogen
C) activator
D) active site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a metal ion is required to activate an enzyme,it would be considered a ____.
A) cofactor
B) protoenzyme
C) coenzyme
D) zymogen
A) cofactor
B) protoenzyme
C) coenzyme
D) zymogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which disease is attributed to the lack of enzyme?
A) hypertension
B) susceptibility to the cold viruses
C) Tay-Sachs disease
D) all of them
A) hypertension
B) susceptibility to the cold viruses
C) Tay-Sachs disease
D) all of them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Enzymes increase the rates of only certain reactions involving certain substances.This general characteristic is called ____.
A) selectivity
B) enzyme regulation
C) specificity
D) catalytic efficiency
A) selectivity
B) enzyme regulation
C) specificity
D) catalytic efficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The number of substrate molecules acted upon per minute by one molecule of enzyme is referred to as the
A) optimum number.
B) optimum rate.
C) international unit.
D) turnover number.
A) optimum number.
B) optimum rate.
C) international unit.
D) turnover number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When enzyme activity is graphed versus the following,which graph is a straight line?
A) substrate concentration
B) enzyme concentration
C) pH
D) temperature
A) substrate concentration
B) enzyme concentration
C) pH
D) temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following terms is a general definition of an enzyme?
A) catalyst
B) lipid
C) carbohydrate
D) activator
A) catalyst
B) lipid
C) carbohydrate
D) activator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
____ would be considered as a common rate of chemical reaction measure per minute due to the presence of an enzyme.
A) 100
B) 1,000
C) 10,000
D) 100,000
A) 100
B) 1,000
C) 10,000
D) 100,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following enzyme properties is explained by the lock-and-key model?
A) specificity
B) high turnover rate
C) high molecular weight
D) susceptibility to denaturation
A) specificity
B) high turnover rate
C) high molecular weight
D) susceptibility to denaturation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A zymogen is correctly classified as a(n)
A) organic cofactor for an enzyme.
B) inorganic cofactor for an enzyme.
C) coenzyme.
D) inactive form of an enzyme.
A) organic cofactor for an enzyme.
B) inorganic cofactor for an enzyme.
C) coenzyme.
D) inactive form of an enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The optimum temperature for most enzymes is in the range of ____.
A) 25-40 C
B) 0-25 C
C) 50-70 C
D) 40-60 C
A) 25-40 C
B) 0-25 C
C) 50-70 C
D) 40-60 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An enzyme is operating at its optimum pH.If the pH were increased,how would the rate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction change?
A) increase
B) decrease
C) could increase or decrease
D) would not change
A) increase
B) decrease
C) could increase or decrease
D) would not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Enzymes which are affected by the binding of modulators are called
A) induced enzymes.
B) proenzymes.
C) allosteric enzymes.
D) controlled enzymes.
A) induced enzymes.
B) proenzymes.
C) allosteric enzymes.
D) controlled enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Heavy metal ions are believed to act as ____ inhibitors.
A) reversible
B) irreversible
C) competitive
D) noncompetitive
A) reversible
B) irreversible
C) competitive
D) noncompetitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An enzyme useful in diagnosing leukemia is _____ .
A) CK
B) acid phosphatase
C) lysozyme
D) LDH
A) CK
B) acid phosphatase
C) lysozyme
D) LDH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The toxicity of cyanide is due to its affinity for the
A) (-SH groups of enzymes.)
B) carboxyl groups of active sites.
C) iron atoms of cytochrome oxidase.
D) amino groups of hemoglobin.
A) (-SH groups of enzymes.)
B) carboxyl groups of active sites.
C) iron atoms of cytochrome oxidase.
D) amino groups of hemoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the general effect of increasing the substrate concentration in a reaction?
A) The rate of the reaction will increase significantly.
B) The rate of the reaction will increase eventually leveling off.
C) The rate of the reaction will decrease significantly.
D) The substrate concentration cannot be changed in any chemical reaction.
A) The rate of the reaction will increase significantly.
B) The rate of the reaction will increase eventually leveling off.
C) The rate of the reaction will decrease significantly.
D) The substrate concentration cannot be changed in any chemical reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the reason for performing an enzyme assay?
A) to determine the number of enzyme molecules per liter
B) to determine the number of enzyme molecules per mL
C) to determine the activity of an enzyme
D) to determine the number of enzymes present
A) to determine the number of enzyme molecules per liter
B) to determine the number of enzyme molecules per mL
C) to determine the activity of an enzyme
D) to determine the number of enzymes present

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An enzyme valuable in diagnosing heart attacks is _____ .
A) LDH
B) GPT
C) lipase
D) lysozyme
A) LDH
B) GPT
C) lipase
D) lysozyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the function of an inhibitor?
A) slow down the rate of reaction
B) inhibit the effect of temperature and pH changes on enzyme activity
C) inhibit substrate effects on other chemicals in the reaction environment
D) slow down the interaction between the solvent and the substrate
A) slow down the rate of reaction
B) inhibit the effect of temperature and pH changes on enzyme activity
C) inhibit substrate effects on other chemicals in the reaction environment
D) slow down the interaction between the solvent and the substrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Substances that can bind to an enzyme and increase its activity are called
A) positive modulators.
B) negative modulators.
C) allosteric regulators.
D) positive regulators.
A) positive modulators.
B) negative modulators.
C) allosteric regulators.
D) positive regulators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following enzyme types have proven especially useful in diagnostic medicine?
A) allosteric enzyme
B) proenzymes
C) isoenzymes
D) induced enzymes
A) allosteric enzyme
B) proenzymes
C) isoenzymes
D) induced enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The conditions required for maximum enzyme function are called
A) room conditions.
B) standard conditions.
C) optimum conditions.
D) low pressure,high temperature.
A) room conditions.
B) standard conditions.
C) optimum conditions.
D) low pressure,high temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is true of a noncompetitive inhibitor?
A) resembles the substrate
B) binds at a site other than the active site
C) can be reversed by adding more substrate
D) more than one response is correct
A) resembles the substrate
B) binds at a site other than the active site
C) can be reversed by adding more substrate
D) more than one response is correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Sulfa drugs prevent bacterial growth by acting as ____ inhibitors.
A) competitive
B) noncompetitive
C) irreversible
D) more than one response is correct
A) competitive
B) noncompetitive
C) irreversible
D) more than one response is correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Under saturation conditions,an enzyme-catalyzed reaction had a velocity V.Which of the following would increase the rate of the reaction?
A) a decrease in the substrate concentration
B) an increase in the substrate concentration
C) a decrease in the enzyme concentration
D) an increase in the enzyme concentration
A) a decrease in the substrate concentration
B) an increase in the substrate concentration
C) a decrease in the enzyme concentration
D) an increase in the enzyme concentration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which modification of the reaction environment will increase the rate of reaction in which an enzyme participates?
A) increase the temperature to the boiling point of water
B) increase the concentration of the product to saturation
C) increase the concentration of the enzyme
D) increase the amount of water in the solution
A) increase the temperature to the boiling point of water
B) increase the concentration of the product to saturation
C) increase the concentration of the enzyme
D) increase the amount of water in the solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The use of antibiotic creams and ointments should be restricted.Why?
A) The excessive use will affect the flexibility of the skin in the immediate area.
B) There is a possibility that the antibiotic will cause the skin to become dry.
C) There is a possibility that antibiotic immune strains of bacteria will develop.
D) There is more than one correct response.
A) The excessive use will affect the flexibility of the skin in the immediate area.
B) There is a possibility that the antibiotic will cause the skin to become dry.
C) There is a possibility that antibiotic immune strains of bacteria will develop.
D) There is more than one correct response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The synthesis of an enzyme in response to a cellular need is called
A) allosteric production.
B) enzyme induction.
C) feedback control.
D) biofeedback.
A) allosteric production.
B) enzyme induction.
C) feedback control.
D) biofeedback.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
How does a zymogen differ from an apoenzyme?
A) An apoenzyme is deactivated by a cofactor.
B) A zymogen is initially lacking an active site.
C) A zymogen is activated by removing part of its structure.
D) An apoenzyme is produced from a holoenzyme + coenzyme
A) An apoenzyme is deactivated by a cofactor.
B) A zymogen is initially lacking an active site.
C) A zymogen is activated by removing part of its structure.
D) An apoenzyme is produced from a holoenzyme + coenzyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following accurately describes how an enzyme functions?
A) Reduces the enthalpy difference for the reactants and products.
B) Allows for the exothermic reaction of materials that are usually endothermic.
C) Changes the reaction mechanism,effectively reducing the activation energy.
D) Shifts the equilibrium for the reaction.
A) Reduces the enthalpy difference for the reactants and products.
B) Allows for the exothermic reaction of materials that are usually endothermic.
C) Changes the reaction mechanism,effectively reducing the activation energy.
D) Shifts the equilibrium for the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The following represents the results of an experiment on a metabolic enzyme.What is the optimum pH of this enzyme? 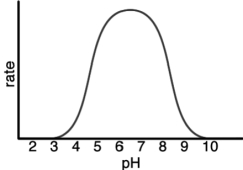
A) 3.0
B) 5.5
C) 6.5
D) 9.5

A) 3.0
B) 5.5
C) 6.5
D) 9.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Enzyme concentration has what effect on the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction?
A) increases
B) decreases
C) no effect
D) increases until reaching a maximum
A) increases
B) decreases
C) no effect
D) increases until reaching a maximum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following disorders results from a deficiency of the enzyme tyroinase?
A) Albinism
B) Galactosemia
C) Phenylketonuria
D) Homocystinuria
A) Albinism
B) Galactosemia
C) Phenylketonuria
D) Homocystinuria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A type of enzyme regulation,where a product acts as an inhibitor molecule,is called ___ inhibition.
A) feedback
B) end product
C) competitive
D) zymogenic
A) feedback
B) end product
C) competitive
D) zymogenic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In an enzyme assay,4.5 mol of substrate was consumed in 3.166 min.What is the enzyme activity expressed in IU?
A) 4.5 IU
B) 14 IU
C) 0.70 IU
D) 1.4 IU
A) 4.5 IU
B) 14 IU
C) 0.70 IU
D) 1.4 IU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the diagram,which number would represent Vmax? 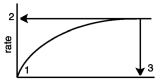
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) either 2 or 3

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) either 2 or 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Chymotrypsin,an enzyme that cleaves peptide linkages,would be classified as a(n)_____ .
A) hydrolase
B) oxioreductase
C) isomerase
D) transferase
A) hydrolase
B) oxioreductase
C) isomerase
D) transferase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What type of enzyme would catalyze the following reaction? 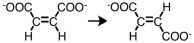
A) ligase
B) oxidoreductase
C) isomerase
D) transferase

A) ligase
B) oxidoreductase
C) isomerase
D) transferase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following describes the significance of the term Vmax ?
A) how rapidly a substrate molecule can travel to an enzyme
B) the maximum rate that an enzyme can process substrate species
C) the velocity at which the enzyme and substrate must collide for activation
D) the maximum speed at which product molecules leave the binding site.
A) how rapidly a substrate molecule can travel to an enzyme
B) the maximum rate that an enzyme can process substrate species
C) the velocity at which the enzyme and substrate must collide for activation
D) the maximum speed at which product molecules leave the binding site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider the following reaction. 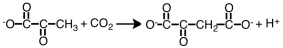
The enzyme that would be placed over the arrow is a _____ .
A) ligase
B) lyase
C) hydrolase
D) transferase

The enzyme that would be placed over the arrow is a _____ .
A) ligase
B) lyase
C) hydrolase
D) transferase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is (are)active enzyme(s)?
A) pepsinogen
B) proelastase
C) trypsin
D) all are active enzymes
A) pepsinogen
B) proelastase
C) trypsin
D) all are active enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is a (are)zymogen(s)?
A) pepsin
B) chymotrypsinogen
C) carboxypeptidase
D) all are zymogens
A) pepsin
B) chymotrypsinogen
C) carboxypeptidase
D) all are zymogens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A neighbor comes to you having just moments ago ingested an unknown amount of antifreeze.You are miles from the nearest hospital.Which of the following is your best course of action after calling 911?
A) To make their last moments as pleasant as possible.
B) Give them enough whiskey to nearly get them intoxicated.
C) Give them methanol to detoxify the antifreeze.
D) Do nothing because antifreeze is not toxic to people.
A) To make their last moments as pleasant as possible.
B) Give them enough whiskey to nearly get them intoxicated.
C) Give them methanol to detoxify the antifreeze.
D) Do nothing because antifreeze is not toxic to people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Substrate concentration has what effect on the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction?
A) increases
B) decreases
C) no effect
D) increases until reaching a maximum
A) increases
B) decreases
C) no effect
D) increases until reaching a maximum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The cyanide ion is very toxic to humans because it binds with iron (Fe3+)in what enzyme to form a stable complex that stops cellular respiration.
A) cytochrome reductase
B) cytochrome kinase
C) cytochrome oxidase
D) elastase
A) cytochrome reductase
B) cytochrome kinase
C) cytochrome oxidase
D) elastase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The EC name of an enzyme is alanine transaminase.This indicates that
A) the substrate is alanine.
B) the functional group is an amine.
C) the type of reaction is a transfer.
D) All of the above.
A) the substrate is alanine.
B) the functional group is an amine.
C) the type of reaction is a transfer.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A substance that when added to a reaction causes the production of more product is called a _____ .
A) catalyst
B) substrate
C) inhibitor
D) none of the choices
A) catalyst
B) substrate
C) inhibitor
D) none of the choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The enzyme model that accounts for molecule flexibility is
A) lock and key.
B) induced fit.
C) allosteric effects.
D) More than one answer is correct.
A) lock and key.
B) induced fit.
C) allosteric effects.
D) More than one answer is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The conversion of a zymogen into an enzyme usually involves another enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Enzymes are proteins that speed up a chemical reaction;inhibitors slow down chemical reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Feedback inhibition is a type of allosteric regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Enzyme assays are reported in international units (IU).By the definition of an IU,the quantity of enzyme present is measured,not the chemical activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Sulfanilamide prevents bacterial growth because it functions as a competitive inhibitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Inhibition is the irreversible process by which enzymes are rendered nonfunctional.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Cofactors and enzymes form a tightly bound complex without which enzymes will not function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Trypsin is an example of a proenzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The measurement of various enzymes in the blood have been found to be useful for diagnosing pathological conditions.Which of the following enzymes is used to detect bone disease?
A) creatine kinase
B) aspartate transaminase
C) lactate dehydrogenase
D) alkaline phosphatase
A) creatine kinase
B) aspartate transaminase
C) lactate dehydrogenase
D) alkaline phosphatase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Noncompetitive inhibitors bind strongly to the active site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Consider the following figure.The step labeled A is known to reduce the activity of Enzyme 1.This would be described as what type of enzyme regulation? 
A) end product inhibition
B) feedback inhibition
C) allosteric inhibition
D) competitive inhibition

A) end product inhibition
B) feedback inhibition
C) allosteric inhibition
D) competitive inhibition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Enzymes have specific temperature and pH ranges within which they function best.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Noncompetitive inhibitors often resemble the natural substrate in structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The lock-and-key theory is the explanation of how a coenzyme functions to modify the substrate which provides a specific product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Many drugs act as competitive inhibitors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Zymogen is another term for cofactor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An irreversible inhibitor usually forms a covalent bond with the enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Enzymes,being proteins,are sensitive to the temperature and will be denatured by high temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
All enzymes catalyze specific reactions which makes it simpler to understand the chemistry of the living cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Pepsin is named because it catalyzes a hydrolysis reaction,and the IEC uses "in" as the word ending to indicate hydrolysis reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



