Deck 43: Physiology of Ventilatory Support
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/90
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 43: Physiology of Ventilatory Support
1
Which of the following is FALSE about pressure-limited modes of ventilatory?
A)The volume delivered at a given pressure must decrease as compliance falls.
B)The inspiratory flow varies with patient effort and lung mechanics.
C)Active effort by the patient against inspiration will decrease delivered volume.
D)The volume delivered at a given pressure must decrease as Raw rises.
A)The volume delivered at a given pressure must decrease as compliance falls.
B)The inspiratory flow varies with patient effort and lung mechanics.
C)Active effort by the patient against inspiration will decrease delivered volume.
D)The volume delivered at a given pressure must decrease as Raw rises.
D
2
Mean airway pressure may be increased by all of the following adjustments, except increasing the:
A)inspiratory time
B)frequency
C)positive end-expiratory pressure level
D)FIO2
A)inspiratory time
B)frequency
C)positive end-expiratory pressure level
D)FIO2
D
3
Which of the following statements is false about positive-pressure ventilation (PPV)?
A)During inspiration, pleural pressure decreases.
B)During inspiration, pressure in the alveoli increases.
C)The pressure gradients of normal breathing are reversed.
D)During inspiration, alveolar pressure exceeds pleural pressure.
A)During inspiration, pleural pressure decreases.
B)During inspiration, pressure in the alveoli increases.
C)The pressure gradients of normal breathing are reversed.
D)During inspiration, alveolar pressure exceeds pleural pressure.
A
4
Administration of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is associated with all of the following benefits except maintaining:
A)alveoli open
B)alveoli stable
C)fluid-filled alveoli open
D)surfactant-depleted alveoli closed
A)alveoli open
B)alveoli stable
C)fluid-filled alveoli open
D)surfactant-depleted alveoli closed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is the explanation for the increased ratio when excessive positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) is used?
A)diversion of blood from ventilated alveoli to hypoventilated alveoli
B)diversion of blood from hypoventilated alveoli to ventilated alveoli
C)shunt-like effect
D)hyperexpansion
A)diversion of blood from ventilated alveoli to hypoventilated alveoli
B)diversion of blood from hypoventilated alveoli to ventilated alveoli
C)shunt-like effect
D)hyperexpansion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In which of the following types of ventilation is alveolar expansion during inspiration due to a decrease in pleural pressure?
I. positive-pressure ventilation (PPV)
II. negative-pressure ventilation (NPV)
III. spontaneous ventilation
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III
I. positive-pressure ventilation (PPV)
II. negative-pressure ventilation (NPV)
III. spontaneous ventilation
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following are considered safe settings for a recruitment maneuver?
I)pressures up to 50 cm H2O
II)pressures up to 35 cm H2O
III)pressures applied for 5 to 10 minutes
IV)pressures applied for 1 to 3 minutes
A)I and III
B)I and IV
C)II and III
D)II and IV
I)pressures up to 50 cm H2O
II)pressures up to 35 cm H2O
III)pressures applied for 5 to 10 minutes
IV)pressures applied for 1 to 3 minutes
A)I and III
B)I and IV
C)II and III
D)II and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In which of the following types of ventilation is alveolar expansion during inspiration due to an increase in alveolar pressure?
I)negative-pressure ventilation
II)positive-pressure ventilation
III)spontaneous ventilation
A)I and II
B)II and III
C)II
D)I, II, and III
I)negative-pressure ventilation
II)positive-pressure ventilation
III)spontaneous ventilation
A)I and II
B)II and III
C)II
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The volume delivered by a pressure-limited ventilator will decrease under all of the following conditions except:
A)the patient's lung or thoracic (chest wall) compliance falls.
B)airway resistances rises (inspiratory time less than 3 times the time constant).
C)the patient tenses the respiratory muscles during inspiration.
D)airway resistances rises (inspiratory time greater than 3 times the time constant).
A)the patient's lung or thoracic (chest wall) compliance falls.
B)airway resistances rises (inspiratory time less than 3 times the time constant).
C)the patient tenses the respiratory muscles during inspiration.
D)airway resistances rises (inspiratory time greater than 3 times the time constant).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements are TRUE about negative-pressure ventilation (NPV)?
I. NPV is similar to spontaneous breathing.
II. Airway (mouth) pressure during NPV is zero.
III. Expiration during NPV is by passive recoil.
IV. NPV decreases pressure at the body surface.
A)II and IV
B)I, II, III, and IV
C)III and IV
D)I, III, and IV
I. NPV is similar to spontaneous breathing.
II. Airway (mouth) pressure during NPV is zero.
III. Expiration during NPV is by passive recoil.
IV. NPV decreases pressure at the body surface.
A)II and IV
B)I, II, III, and IV
C)III and IV
D)I, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following conditions is associated with a lack of response to increased FIO2 in patients receiving positive-pressure ventilation?
A)dead space
B)shunt
C)hypoxemia
D)hypoventilation
A)dead space
B)shunt
C)hypoxemia
D)hypoventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following conditions does not require high mechanical respiratory rates?
A)metabolic alkalosis
B)ARDS
C)increased intracranial pressure
D)metabolic acidosis
A)metabolic alkalosis
B)ARDS
C)increased intracranial pressure
D)metabolic acidosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In which of the following types of ventilation can pleural pressure become positive during inspiration?
I)positive-pressure ventilation
II)spontaneous ventilation
III)negative-pressure ventilation
A)II and III
B)I and II
C)I, II, and III
D)I
I)positive-pressure ventilation
II)spontaneous ventilation
III)negative-pressure ventilation
A)II and III
B)I and II
C)I, II, and III
D)I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
On what does volume delivered depend during pressure-targeted modes of ventilatory support?
I)set pressure limit
II)patient lung mechanics
III)patient effort
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III
I)set pressure limit
II)patient lung mechanics
III)patient effort
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In which of the following modes of ventilatory support would the patient's work of breathing be greatest?
A)continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
B)pressure-supported ventilation (PSV)
C)intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV)
D)continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV)
A)continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
B)pressure-supported ventilation (PSV)
C)intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV)
D)continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The magnitude of WOBpt depends on which of the following?
I)compliance
II)resistance
III)ventilatory drive
IV)trigger sensitivity
V)peak flow
A)I and III
B)I, II, and IV
C)I, II, III, IV, and V
D)I, II, and V
I)compliance
II)resistance
III)ventilatory drive
IV)trigger sensitivity
V)peak flow
A)I and III
B)I, II, and IV
C)I, II, III, IV, and V
D)I, II, and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is the recommended tidal volume for mechanical ventilation in acute respiratory failure?
A)4 to 8 ml/kg
B)3 to 5 ml/kg
C)6 to 10 ml/kg
D)10 to 12 ml/kg
A)4 to 8 ml/kg
B)3 to 5 ml/kg
C)6 to 10 ml/kg
D)10 to 12 ml/kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is considered a normal spontaneous tidal volume?
A)3 to 5 ml/kg
B)5 to 7 ml/kg
C)7 to 9 ml/kg
D)10 to 12 ml/kg
A)3 to 5 ml/kg
B)5 to 7 ml/kg
C)7 to 9 ml/kg
D)10 to 12 ml/kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is the consequence of decreased resistance and compliance?
A)It takes more time to fill the alveoli.
B)It takes more time to empty the alveoli.
C)It takes less time to fill and more time to empty the alveoli.
D)It takes less time to fill and empty the alveoli.
A)It takes more time to fill the alveoli.
B)It takes more time to empty the alveoli.
C)It takes less time to fill and more time to empty the alveoli.
D)It takes less time to fill and empty the alveoli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following strategies are useful in the management of shunt?
I)positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)II.permissive hypercapnia
III)control of membrane permeability
A)II and III
B)I and III
C)I, II, and III
D)I
I)positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)II.permissive hypercapnia
III)control of membrane permeability
A)II and III
B)I and III
C)I, II, and III
D)I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Detrimental effects of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) include all of the following except:
A)increased incidence of barotrauma
B)decreased venous return or cardiac output
C)increased pulmonary vascular resistance
D)increased CL
A)increased incidence of barotrauma
B)decreased venous return or cardiac output
C)increased pulmonary vascular resistance
D)increased CL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When bedside work of breathing measures are unavailable, you should adjust the level of pressure-supported ventilation (PSV) to which of the following breathing patterns?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Beneficial physiological effects of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) include which of the following?
I)increased PaO2 for given FIO2
II)increased lung compliance (CL)III.decreased shunt fraction
IV)increased functional residual capacity
A)I, II, III, and IV
B)III and IV
C)II, III, and IV
D)II and IV
I)increased PaO2 for given FIO2
II)increased lung compliance (CL)III.decreased shunt fraction
IV)increased functional residual capacity
A)I, II, III, and IV
B)III and IV
C)II, III, and IV
D)II and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What are some key causes of patient-ventilator asynchrony and increased work of breathing during pressure-triggered volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation?
I)improper trigger setting
II)insufficient inspiratory flow
III)high peak airway pressures
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III
I)improper trigger setting
II)insufficient inspiratory flow
III)high peak airway pressures
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Primary indications for using positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) in conjunction with mechanical ventilation include which of the following?
I)when dynamic hyperinflation occurs in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients
II)when the imposed work of breathing is excessive
III)when acute lung injury causes refractory hypoxemia
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III
I)when dynamic hyperinflation occurs in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients
II)when the imposed work of breathing is excessive
III)when acute lung injury causes refractory hypoxemia
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In which of the following patients is positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) most indicated?
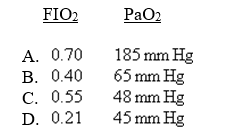


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the following factors would tend to increase mean airway pressure except:
A)short inspiratory times
B)increased mandatory breaths
C)increased levels of positive inspiratory pressure (PIP)
D)increased levels of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)
A)short inspiratory times
B)increased mandatory breaths
C)increased levels of positive inspiratory pressure (PIP)
D)increased levels of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Contraindications for using positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) in conjunction with mechanical ventilation include which of the following?
I)untreated bronchopleural fistula
II)chronic airway obstruction
III)untreated pneumothorax
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III
I)untreated bronchopleural fistula
II)chronic airway obstruction
III)untreated pneumothorax
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In which of the following modes of ventilatory support is muscle atrophy most likely to occur?
A)volume-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
B)(volume-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation) + pressure-supported ventilation
C)volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation
D)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
A)volume-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
B)(volume-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation) + pressure-supported ventilation
C)volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation
D)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following modes of ventilatory support would result in the highest mean airway pressure?
A)volume-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
B)(volume-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation) + pressure-supported ventilation
C)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
D)volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation
A)volume-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
B)(volume-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation) + pressure-supported ventilation
C)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
D)volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In which of the following modes does the clinician have the most control over the patient's ventilatory pattern, PaO2, PaCO2, and acid-base balance?
A)volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation
B)volume-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
C)pressure-supported ventilation
D)pressure-controlled inspiratory reserve volume
A)volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation
B)volume-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
C)pressure-supported ventilation
D)pressure-controlled inspiratory reserve volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Inspection of the airway pressure waveform of a patient receiving volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation assist-control with constant flow reveals a large dip or drop in pressure at the beginning of inspiration. Which of the following problems is most likely?
A)The trigger setting is improper.
B)The inspiratory flow is inadequate.
C)The set volume is too large.
D)The pressure limit is too low.
A)The trigger setting is improper.
B)The inspiratory flow is inadequate.
C)The set volume is too large.
D)The pressure limit is too low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In which of the following modes of ventilatory support would the patient's work of breathing be least?
A)continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
B)pressure-supported ventilation (PSV)
C)intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV)
D)continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV)
A)continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
B)pressure-supported ventilation (PSV)
C)intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV)
D)continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Physiological effects of adding a volume-limited inflation hold to mandatory breaths include which of the following?
I)decreased PaCO2
II)increased inspiratory time
III)decreased VD/VT
IV)Longer expiratory times
A)II and IV
B)I, II, III, and IV
C)III and IV
D)I, II, and III
I)decreased PaCO2
II)increased inspiratory time
III)decreased VD/VT
IV)Longer expiratory times
A)II and IV
B)I, II, III, and IV
C)III and IV
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which level of plateau pressure increases the likelihood of causing lung injury?
A)> 15 cm H2O
B)> 25 cm H2O
C)> 30 cm H2O
D)It doesn't matter as long as positive inspiratory pressure is less than 50 cm H2O.
A)> 15 cm H2O
B)> 25 cm H2O
C)> 30 cm H2O
D)It doesn't matter as long as positive inspiratory pressure is less than 50 cm H2O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is a benefit of high inspiratory flows during positive-pressure ventilation?
A)improved gas exchange
B)higher peak pressures
C)reduced air trapping
D)higher work of breathing
A)improved gas exchange
B)higher peak pressures
C)reduced air trapping
D)higher work of breathing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following modes of support provides all of the patient's minute ventilation (VE) as mandatory volume-controlled (VC) breaths?
A)VC continuous mandatory ventilation
B)VC intermittent mandatory ventilation
C)pressure-supported ventilation
D)continuous positive airway pressure
A)VC continuous mandatory ventilation
B)VC intermittent mandatory ventilation
C)pressure-supported ventilation
D)continuous positive airway pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Volume-controlled (VC) modes of mechanical ventilation include which of the following?
I)VC continuous mandatory ventilation
II)VC intermittent mandatory ventilation
III)volume-assured, pressure-controlled
IV)bilevel positive airway pressure
A)II and IV
B)I, II, III, and IV
C)I and II
D)I, III, and IV
I)VC continuous mandatory ventilation
II)VC intermittent mandatory ventilation
III)volume-assured, pressure-controlled
IV)bilevel positive airway pressure
A)II and IV
B)I, II, III, and IV
C)I and II
D)I, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
To prevent muscle fatigue or atrophy, the level of PSV should be adjusted to achieve what work load?
A)0 J/L
B)0.6 to 0.8 J/L
C)0 to 0.5 J/L
D)>0.8 J/L
A)0 J/L
B)0.6 to 0.8 J/L
C)0 to 0.5 J/L
D)>0.8 J/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Compared with a square wave flow pattern, a decelerating flow waveform has all of the following potential benefits except:
A)reduced peak pressure
B)improved cardiac output
C)less inspiratory work
D)decreased volume of dead space-to-tidal volume ratio (VD/VT)
A)reduced peak pressure
B)improved cardiac output
C)less inspiratory work
D)decreased volume of dead space-to-tidal volume ratio (VD/VT)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Pressure-controlled (PC) modes of ventilatory support include all of the following except:
A)pressure-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation (PC-CMV)
B)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
C)volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation
D)volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation (VAPSV)
A)pressure-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation (PC-CMV)
B)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
C)volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation
D)volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation (VAPSV)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following modes of ventilatory support is used to help decrease airway and alveolar pressures?
A)pressure-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation
B)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
C)volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation
D)volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation
A)pressure-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation
B)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
C)volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation
D)volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What spontaneous pressure-controlled breath mode allows separate regulation of the inspiratory and expiratory pressures?
A)bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP)
B)continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
C)pressure-supported ventilation
D)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
A)bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP)
B)continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
C)pressure-supported ventilation
D)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For patients with respiratory insufficiency, pressure-supported ventilation (PSV) has all of the following advantages over spontaneous breathing except:
A)decreased respiratory rate
B)increased VT
C)decreased O2 consumption
D)increased muscle activity
A)decreased respiratory rate
B)increased VT
C)decreased O2 consumption
D)increased muscle activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following modes of ventilatory support combines the advantages of pressure-controlled and volume-controlled ventilation?
A)volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation
B)pressure-supported ventilation
C)bilevel positive airway pressure
D)airway pressure release ventilation
A)volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation
B)pressure-supported ventilation
C)bilevel positive airway pressure
D)airway pressure release ventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The volume of gas actually delivered to a patient by most positive-pressure ventilation is always less than that expelled from the machine. Which of the following factors help to explain this finding?
I)gas compression under pressure
II)presence of built-in leaks
III)expansion of the ventilator circuitry
A)II and III
B)I and II
C)I, II, and III
D)I and III
I)gas compression under pressure
II)presence of built-in leaks
III)expansion of the ventilator circuitry
A)II and III
B)I and II
C)I, II, and III
D)I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What mode of pressure-controlled ventilation is designed to prevent alveoli with short time constants from collapsing, thereby improving oxygenation?
A)pressure-controlled inverse ration ventilation
B)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
C)volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation
D)bilevel positive airway pressure
A)pressure-controlled inverse ration ventilation
B)pressure-controlled intermittent mandatory ventilation
C)volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation
D)bilevel positive airway pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) is used for all of the following purposes except:
A)nocturnal ventilatory support of chronic disease patients
B)preventing intubation of patients with acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
C)treatment of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in the home
D)providing ventilatory support for patients with status asthmaticus
A)nocturnal ventilatory support of chronic disease patients
B)preventing intubation of patients with acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
C)treatment of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in the home
D)providing ventilatory support for patients with status asthmaticus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
During volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation, if the desired VT is not reached or exceeded at the preset pressure support level, what happens?
A)Flow continues at a constant rate until the desired volume is achieved.
B)The breath terminates when a predetermined low flow is achieved.
C)Flow decreases exponentially until the desired volume is achieved.
D)Flow increases linearly until the desired volume is achieved.
A)Flow continues at a constant rate until the desired volume is achieved.
B)The breath terminates when a predetermined low flow is achieved.
C)Flow decreases exponentially until the desired volume is achieved.
D)Flow increases linearly until the desired volume is achieved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following actions can you use to decrease compressed volume loss during mechanical ventilation?
I)low-volume, low-compliance tubing
II)ventilator with minimal internal volume
III)low-volume humidifier or heat-moisture exchanger
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III
I)low-volume, low-compliance tubing
II)ventilator with minimal internal volume
III)low-volume humidifier or heat-moisture exchanger
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
During volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation, the breath will be pressure-limited under what conditions?
A)The delivered tidal volume (VT) is greater than the preset minimum VT.
B)The patient's lung or thoracic compliance decreases from the baseline.
C)The delivered VT is less than the preset minimum VT.
D)The patient's Raw increases from baseline.
A)The delivered tidal volume (VT) is greater than the preset minimum VT.
B)The patient's lung or thoracic compliance decreases from the baseline.
C)The delivered VT is less than the preset minimum VT.
D)The patient's Raw increases from baseline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What are some physiological advantages of volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation?
I)improved patient-ventilator synchrony
II)increased pressure-time product
III)decreased work of breathing
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III
I)improved patient-ventilator synchrony
II)increased pressure-time product
III)decreased work of breathing
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A patient switched from pressure-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV) with positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) to pressure-controlled inverse ratio ventilation (PC-IRV) shows a good improvement in PaO2 but a decrease in tissue oxygenation. Which of the following best explains this observation?
A)High mean pressures caused by PC-IRV decreased pulmonary blood flow.
B)Intrinsic PEEP caused by PC-IRV resulted in increased alveolar recruitment.
C)High mean pressures caused by PC-IRV decreased cardiac output.
D)Intrinsic PEEP caused by PC-IRV compressed the pulmonary capillaries.
A)High mean pressures caused by PC-IRV decreased pulmonary blood flow.
B)Intrinsic PEEP caused by PC-IRV resulted in increased alveolar recruitment.
C)High mean pressures caused by PC-IRV decreased cardiac output.
D)Intrinsic PEEP caused by PC-IRV compressed the pulmonary capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is FALSE about permissive hypercapnia?
A)It lowers intrathoracic and alveolar pressures.
B)It can reduce the incidence of barotrauma.
C)It does not reduce systemic oxygenation.
D)It increases pulmonary vascular resistance.
A)It lowers intrathoracic and alveolar pressures.
B)It can reduce the incidence of barotrauma.
C)It does not reduce systemic oxygenation.
D)It increases pulmonary vascular resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is FALSE about continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)?
A)It maintains alveoli at greater inflation volumes.
B)It holds airway pressure essentially constant.
C)It provides the pressure gradient needed for ventilation.
D)It has side effects similar to those of positive pressure ventilation.
A)It maintains alveoli at greater inflation volumes.
B)It holds airway pressure essentially constant.
C)It provides the pressure gradient needed for ventilation.
D)It has side effects similar to those of positive pressure ventilation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
After accounting for the compressed volume loss on a stable adult patient receiving volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation at a preset volume of 700 ml, you still note a 150-ml difference between the expected and the actual delivered volume. Which of the following is most likely causing this problem?
A)gas absorption across the alveolar membrane
B)increase in the respiratory quotient
C)bronchopleural fistula or pneumothorax
D)leak in the patient-ventilator system
A)gas absorption across the alveolar membrane
B)increase in the respiratory quotient
C)bronchopleural fistula or pneumothorax
D)leak in the patient-ventilator system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What are some primary uses for pressure-supported ventilation (PSV)?
I)recruiting collapsed alveoli and improving oxygenation
II)augmenting patient's spontaneous VT
III)overcoming the imposed work of breathing
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III
I)recruiting collapsed alveoli and improving oxygenation
II)augmenting patient's spontaneous VT
III)overcoming the imposed work of breathing
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What does pressure-supported ventilation consist of?
A)patient-triggered, pressure-limited, flow-cycled breaths
B)machine-triggered, pressure-limited, flow-cycled breaths
C)patient-triggered, pressure-limited, time-cycled breaths
D)machine-triggered, flow-limited, pressure-cycled breaths
A)patient-triggered, pressure-limited, flow-cycled breaths
B)machine-triggered, pressure-limited, flow-cycled breaths
C)patient-triggered, pressure-limited, time-cycled breaths
D)machine-triggered, flow-limited, pressure-cycled breaths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
During volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation, should either compliance decrease or airway resistance (Raw) increase, what will happen?
A)The peak airway pressure will decrease.
B)The inspiratory flow will increase.
C)The peak airway pressure will increase.
D)The inspiratory time will decrease.
A)The peak airway pressure will decrease.
B)The inspiratory flow will increase.
C)The peak airway pressure will increase.
D)The inspiratory time will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In which mode of ventilatory support does the patient breathe spontaneously at an elevated airway pressure, with short, intermittent decreases in pressure to a lower level?
A)volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation
B)pressure-controlled inverse ratio ventilation (PC-IRV)
C)bilevel positive airway pressure
D)airway pressure release ventilation (APRV)
A)volume-assured pressure-supported ventilation
B)pressure-controlled inverse ratio ventilation (PC-IRV)
C)bilevel positive airway pressure
D)airway pressure release ventilation (APRV)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following variables determine the level of support achieved with adaptive support ventilation?
I)patient effort
II)flow
III)time constant
A)I and III
B)II
C)I
D)I, II, and III
I)patient effort
II)flow
III)time constant
A)I and III
B)II
C)I
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is traumatic injury to lung tissue caused by excessive pressure called?
A)pulmonary barotrauma
B)pulmonary hemorrhage
C)pulmonary infarction
D)pulmonary embolism
A)pulmonary barotrauma
B)pulmonary hemorrhage
C)pulmonary infarction
D)pulmonary embolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following gastrointestinal conditions are commonly associated with long-term positive-pressure ventilation (PPV)?
I)bleeding
II)ulceration
III)diarrhea
A)I and II
B)II and III
C)I and III
D)I, II, and III
I)bleeding
II)ulceration
III)diarrhea
A)I and II
B)II and III
C)I and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A patient receiving long-term positive-pressure ventilation support exhibits a progressive weight gain and a reduction in the hematocrit. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this problem?
A)pulmonary hemorrhage
B)water retention
C)hypovolemia
D)hyponatremia
A)pulmonary hemorrhage
B)water retention
C)hypovolemia
D)hyponatremia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Positive-pressure ventilation (PPV) can reduce urinary output by how much?
A)10% to 20%
B)30% to 50%
C)60% to 70%
D)80% to 90%
A)10% to 20%
B)30% to 50%
C)60% to 70%
D)80% to 90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following variables determine the level of support achieved with proportional assist ventilation?
I)patient effort
II)elastance
III)resistance
A)I and III
B)II
C)I
D)I, II, and III
I)patient effort
II)elastance
III)resistance
A)I and III
B)II
C)I
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following variables determine the level of support achieved with adaptive support ventilation?
I)patient effort
II)elastance
III)resistance of the endotracheal tube
A)I and III
B)II
C)I
D)I, II, and III
I)patient effort
II)elastance
III)resistance of the endotracheal tube
A)I and III
B)II
C)I
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Assuming a constant rate of breathing, which of the following inspiratory/expiratory ratios (I:E) would tend to most greatly impair a patient's systemic diastolic pressure?
A)1:4
B)1:3
C)1:2
D)1:1
A)1:4
B)1:3
C)1:2
D)1:1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following parameters are set when volume-supported ventilation (VSV) is used?
I)tidal volume
II)maximum peak pressure
III)positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)IV.flow
A)I and III
B)II
C)I, II, III, and IV
D)I, II, and III
I)tidal volume
II)maximum peak pressure
III)positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)IV.flow
A)I and III
B)II
C)I, II, III, and IV
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Potential effects of hyperventilation on the central nervous system include which of the following?
I)increased O2 consumption
II)increased cerebral vascular resistance (CVR)III.increased intracranial pressure (ICP)
A)I and II
B)II and III
C)I and III
D)I, II, and III
I)increased O2 consumption
II)increased cerebral vascular resistance (CVR)III.increased intracranial pressure (ICP)
A)I and II
B)II and III
C)I and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Hyperventilation should generally be avoided during mechanical ventilatory support. Exceptions to this rule include:
I)trying to calm an agitated patient.II.failure of other methods to reduce intracranial pressure
III)hypokalemia causing cardiac arrhythmias
A)II and III
B)I and III
C)II
D)I and II
I)trying to calm an agitated patient.II.failure of other methods to reduce intracranial pressure
III)hypokalemia causing cardiac arrhythmias
A)II and III
B)I and III
C)II
D)I and II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following mechanisms explains the impaired renal function seen in patients receiving ventilatory support with positive pressure?
I)decreased secretion of aldosterone
II)decreased intravascular volume
III)increased secretion of vasopressin
A)I
B)II
C)I and III
D)I, II, and III
I)decreased secretion of aldosterone
II)decreased intravascular volume
III)increased secretion of vasopressin
A)I
B)II
C)I and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What factor primarily determines the effect of positive-pressure ventilation (PPV) on the cardiac output?
A)peak airway pressure
B)mean pleural pressure
C)CO2
D)expiratory time
A)peak airway pressure
B)mean pleural pressure
C)CO2
D)expiratory time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Physical assessment indicating the presence of a tension pneumothorax includes all of the following except:
A)unequal chest excursion
B)hyperresonance upon chest percussion
C)absent breath sounds
D)loud breath sounds
A)unequal chest excursion
B)hyperresonance upon chest percussion
C)absent breath sounds
D)loud breath sounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following mechanisms explains the hepatic dysfunction in patients receiving positive-pressure ventilation (PPV)?
A)decreased hepatic blood flow
B)increased portal venous pressure
C)hepatic congestion
D)increased bilirubin conjugation
A)decreased hepatic blood flow
B)increased portal venous pressure
C)hepatic congestion
D)increased bilirubin conjugation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Ventricular dysfunction occurs in patients receiving positive-pressure ventilation for all of the following reasons except:
A)hypovolemia
B)excessive tidal volume
C)receiving more than optimal positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)
D)hypervolemia
A)hypovolemia
B)excessive tidal volume
C)receiving more than optimal positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)
D)hypervolemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following are potential effects of positive-pressure ventilation on the cardiovascular system?
I)decreased venous return
II)decreased cranial perfusion pressures
III)increased pulmonary blood flow
IV)decreased ventricular stroke volume
A)II and IV
B)I and IV
C)III and IV
D)I, II, III, and IV
I)decreased venous return
II)decreased cranial perfusion pressures
III)increased pulmonary blood flow
IV)decreased ventricular stroke volume
A)II and IV
B)I and IV
C)III and IV
D)I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Moderate rises in pleural pressure during positive-pressure ventilation have a minimal effect on cardiac output in normal subjects. What are some reasons for this lack of effect?
I)compensatory dilation of the large arteries
II)compensatory increase in venomotor tone
III)compensatory increase in the cardiac rate
A)II and III
B)I and II
C)I, II, and III
D)I and III
I)compensatory dilation of the large arteries
II)compensatory increase in venomotor tone
III)compensatory increase in the cardiac rate
A)II and III
B)I and II
C)I, II, and III
D)I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Types of damage associated with pulmonary barotrauma include all of the following except:
A)pneumoconiosis
B)pneumomediastinum
C)pneumothorax
D)subcutaneous emphysema
A)pneumoconiosis
B)pneumomediastinum
C)pneumothorax
D)subcutaneous emphysema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is the best explanation for the decreased levels of atrial natriuretic hormone commonly observed among patients receiving positive-pressure ventilation?
A)stimulation of the pulmonary stretch receptors
B)inhibition of posterior pituitary function
C)inhibition of the cortex of the adrenal gland
D)decreased right atrial transmural pressure
A)stimulation of the pulmonary stretch receptors
B)inhibition of posterior pituitary function
C)inhibition of the cortex of the adrenal gland
D)decreased right atrial transmural pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



