Deck 10: Capital Budgeting Decisions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Capital Budgeting Decisions
1
A follow-up evaluation of capital-budgeting decisions is called a postaudit.
True
2
Alpha Company has the following information:
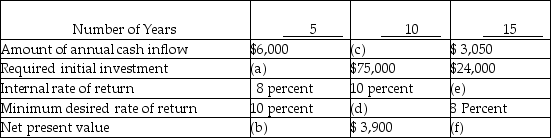
What is (a)?
A) $23,958
B) $22,746
C) $ 8,811
D) $ 9,662

What is (a)?
A) $23,958
B) $22,746
C) $ 8,811
D) $ 9,662
A
3
The cash outflow for the purchase of equipment is an example of an operating cash flow.
False
4
The cost of assets is recognized by the initial outlay, not by depreciation as computed under accrual accounting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Two common methods for comparing alternatives are (1) the total project approach and (2) the conversion approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Alpha Company has the following information:

What is (f)?
A) $2,105
B) $26,105
C) $3,050
D) $(4,510)

What is (f)?
A) $2,105
B) $26,105
C) $3,050
D) $(4,510)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The differential approach is limited to cases in which no more than four alternatives are being examined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Alpha Company has the following information:

What is (e)?
A) Below 6 percent
B) Between 6 and 8 percent
C) Between 8 and 10 percent
D) Between 10 and 12 percent

What is (e)?
A) Below 6 percent
B) Between 6 and 8 percent
C) Between 8 and 10 percent
D) Between 10 and 12 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
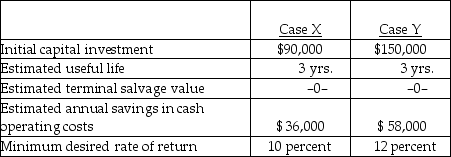
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
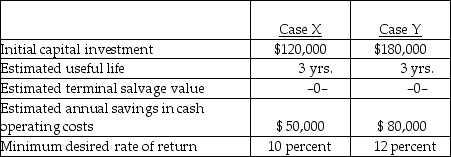
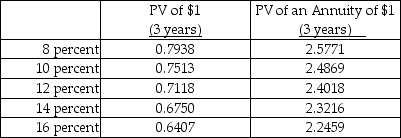
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The net present value in case X is
A) $4,345.
B) $82,435.
C) $50,000.
D) $90.


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The net present value in case X is
A) $4,345.
B) $82,435.
C) $50,000.
D) $90.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The payback model measures profitability as well as how quickly investment dollars may be recouped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
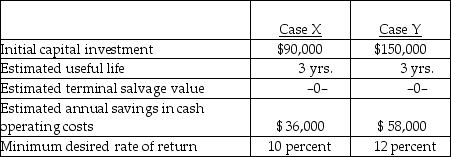
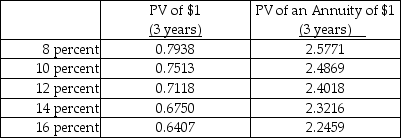
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The net present value in case B is
A) $8,000.
B) $(8,000).
C) $(10,696).
D) $(8,716).


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The net present value in case B is
A) $8,000.
B) $(8,000).
C) $(10,696).
D) $(8,716).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Alpha Company has the following information:

What is (b)?
A) $ -0-
B) $(1,212)
C) $16,359
D) $14,296

What is (b)?
A) $ -0-
B) $(1,212)
C) $16,359
D) $14,296

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Alpha Company has the following information:

What is (d)?
A) Less than 6 percent
B) Between 6 and 8 percent
C) Between 8 and 10 percent
D) Between 10 and 12 percent

What is (d)?
A) Less than 6 percent
B) Between 6 and 8 percent
C) Between 8 and 10 percent
D) Between 10 and 12 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Alpha Company has the following information:

What is (c)?
A) $28,950
B) $71,100
C) $12,205
D) $ 3,900

What is (c)?
A) $28,950
B) $71,100
C) $12,205
D) $ 3,900

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Both the payback and the accounting rate-of-return models are attempts to approach capital budgeting systematically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When no revenue is involved, organizations try to choose projects with the least cost for any given set of objectives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Below are two potential investment alternatives:


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The net present value in case Y is
A) $80,000.
B) $12,144.
C) $(328).
D) $123,056.


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The net present value in case Y is
A) $80,000.
B) $12,144.
C) $(328).
D) $123,056.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Below are two potential investment alternatives:


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The net present value in case A is
A) $54,000.
B) $( 472).
C) $ 6,000.
D) $(6,000).


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The net present value in case A is
A) $54,000.
B) $( 472).
C) $ 6,000.
D) $(6,000).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
One purpose of a postaudit is to evaluate the continuation of the project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The net present value model expresses all amounts in today's monetary units at time zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Beta Company has the following information:
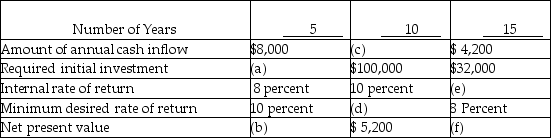
What is (c)?
A) $38,599
B) $94,800
C) $16,273
D) $ 5,200

What is (c)?
A) $38,599
B) $94,800
C) $16,273
D) $ 5,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Beta Company has the following information:

What is (a)?
A) $31,944
B) $30,328
C) $11,747
D) $12,882

What is (a)?
A) $31,944
B) $30,328
C) $11,747
D) $12,882

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
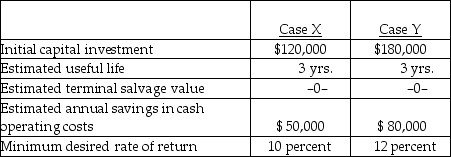
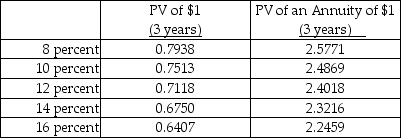
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The internal rate of return in case Y is approximately
A) 10 percent.
B) 12 percent.
C) 14 percent.
D) 16 percent.


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The internal rate of return in case Y is approximately
A) 10 percent.
B) 12 percent.
C) 14 percent.
D) 16 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Beta Company has the following information:

What is (f)?
A) $ 3,948
B) $35,948
C) $ 4,200
D) $(6,013)

What is (f)?
A) $ 3,948
B) $35,948
C) $ 4,200
D) $(6,013)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Beta Company has the following information:

What is (d)?
A) Less than 6 percent
B) Between 6 and 8 percent
C) Between 8 and 10 percent
D) Between 10 and 12 percent

What is (d)?
A) Less than 6 percent
B) Between 6 and 8 percent
C) Between 8 and 10 percent
D) Between 10 and 12 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
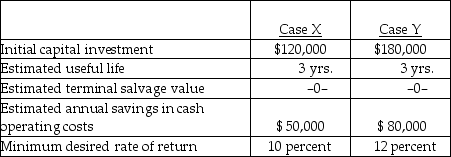 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
The accounting rate of return based on INITIAL investment in case X is
A) 41.67 percent.
B) 8.33 percent.
C) 16.67 percent.
D) 33.33 percent.
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.The accounting rate of return based on INITIAL investment in case X is
A) 41.67 percent.
B) 8.33 percent.
C) 16.67 percent.
D) 33.33 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
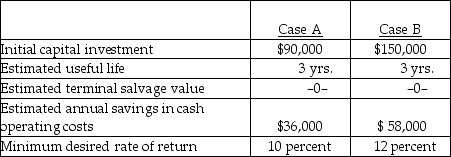 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
In capital budgeting, the relevant tax rate to consider is the
A) prior year tax rate.
B) average rate expected for the company.
C) marginal rate expected for the company.
D) highest rate that applies to U.S. corporations.
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.In capital budgeting, the relevant tax rate to consider is the
A) prior year tax rate.
B) average rate expected for the company.
C) marginal rate expected for the company.
D) highest rate that applies to U.S. corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
The accounting rate of return based on INITIAL investment in case A is
A) 6.67 percent.
B) 5.56 percent.
C) 2.49 percent.
D) 40.00 percent.
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.The accounting rate of return based on INITIAL investment in case A is
A) 6.67 percent.
B) 5.56 percent.
C) 2.49 percent.
D) 40.00 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
The payback period in case X is
A) 3.0 years.
B) 0.4 years.
C) 2.5 years.
D) 2.4 years.
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.The payback period in case X is
A) 3.0 years.
B) 0.4 years.
C) 2.5 years.
D) 2.4 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
The payback period for case Y is
A) 0.44 years.
B) 3.00 years.
C) 2.25 years.
D) 2.40 years.
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.The payback period for case Y is
A) 0.44 years.
B) 3.00 years.
C) 2.25 years.
D) 2.40 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
The accounting rate of return based on INITIAL investment in case Y is
A) 11.11 percent.
B) 44.44 percent.
C) 33.33 percent.
D) 22.22 percent.
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.The accounting rate of return based on INITIAL investment in case Y is
A) 11.11 percent.
B) 44.44 percent.
C) 33.33 percent.
D) 22.22 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Beta Company has the following information:

What is (b)?
A) $-0-
B) $(1,616)
C) $20,197
D) $19,062

What is (b)?
A) $-0-
B) $(1,616)
C) $20,197
D) $19,062

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
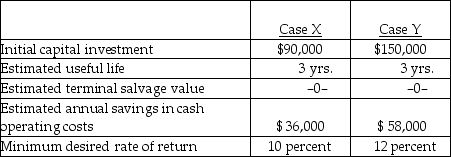
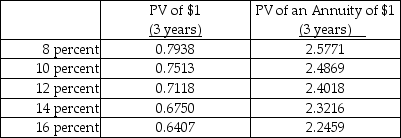
There are two key aspects of capital budgeting: (1) investing decisions and (2)
A) accounting decisions.
B) financing decisions.
C) discount decisions.
D) payback decisions.


There are two key aspects of capital budgeting: (1) investing decisions and (2)
A) accounting decisions.
B) financing decisions.
C) discount decisions.
D) payback decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
The accounting rate of return based on INITIAL investment in case B is
A) 38.67 percent.
B) 2.59 percent.
C) 5.33 percent.
D) 2.40 percent.
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.The accounting rate of return based on INITIAL investment in case B is
A) 38.67 percent.
B) 2.59 percent.
C) 5.33 percent.
D) 2.40 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Below are two potential investment alternatives:


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The internal rate of return in case X is approximately
A) 8 percent.
B) 10 percent.
C) 12 percent.
D) 14 percent.


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The internal rate of return in case X is approximately
A) 8 percent.
B) 10 percent.
C) 12 percent.
D) 14 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Beta Company has the following information:

What is (e)?
A) Below 6 percent
B) Between 6 and 8 percent
C) Between 8 and 10 percent
D) Between 10 and 12 percent

What is (e)?
A) Below 6 percent
B) Between 6 and 8 percent
C) Between 8 and 10 percent
D) Between 10 and 12 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
The payback period in case A is
A) 0.4 years.
B) 2.5 years.
C) 3.3 years.
D) 3.0 years.
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.The payback period in case A is
A) 0.4 years.
B) 2.5 years.
C) 3.3 years.
D) 3.0 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Below are two potential investment alternatives:


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The internal rate of return in case A is approximately
A) 8 percent.
B) 10 percent.
C) 12 percent.
D) 14 percent.


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The internal rate of return in case A is approximately
A) 8 percent.
B) 10 percent.
C) 12 percent.
D) 14 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The internal rate of return in case B is approximately
A) 14 percent.
B) 12 percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) 8 percent.


Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes. The internal rate of return in case B is approximately
A) 14 percent.
B) 12 percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) 8 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
The payback period in case B is
A) 3.63 years.
B) 3.00 years.
C) 3.87 years.
D) 2.59 years.
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.The payback period in case B is
A) 3.63 years.
B) 3.00 years.
C) 3.87 years.
D) 2.59 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Inflation is
A) not a factor in most capital-budgeting decisions because it tends to be very low in Canada.
B) equal to the amount of interest (or nominal rate) charged for most loans.
C) the increase in the general purchasing power of the monetary unit.
D) the decrease in the general purchasing power of the monetary unit.
A) not a factor in most capital-budgeting decisions because it tends to be very low in Canada.
B) equal to the amount of interest (or nominal rate) charged for most loans.
C) the increase in the general purchasing power of the monetary unit.
D) the decrease in the general purchasing power of the monetary unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If a company pays taxes of 15 percent on their first $25,000 of pretax income, and 30 percent on any taxable income in excess of $25,000, what is the marginal tax rate if current pretax income is $40,000?
A) 15.00 percent
B) 20.63 percent
C) 30.00 percent
D) 22.50 percent
A) 15.00 percent
B) 20.63 percent
C) 30.00 percent
D) 22.50 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If a company pays taxes of 20 percent on their first $20,000 of pretax income, and 30 percent on any taxable income in excess of $20,000, what is the marginal tax rate if current pretax income is $45,000?
A) 20 percent
B) 30 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 39 percent
A) 20 percent
B) 30 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 39 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A company with pretax income of $45,000 is required to pay taxes of 20 percent on all income up to $15,000 and 32 percent on any income in excess of $15,000. The company's average tax rate is
A) 28 percent.
B) 32 percent.
C) 26 percent.
D) higher than its marginal rate.
A) 28 percent.
B) 32 percent.
C) 26 percent.
D) higher than its marginal rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Below are two potential investment alternatives:
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
The marginal tax rate is
A) the average rate for the company.
B) the highest possible rate the company might be expected to pay.
C) the lowest tax rate applicable to the company.
D) the rate paid on additional amounts of pretax income.
 Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.
Assume straight-line amortization in all computations, and ignore income taxes.The marginal tax rate is
A) the average rate for the company.
B) the highest possible rate the company might be expected to pay.
C) the lowest tax rate applicable to the company.
D) the rate paid on additional amounts of pretax income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is not true about CCA expense?
A) It is sometimes called a tax shield.
B) It usually causes an increase in taxes.
C) Businesses usually want the largest possible CCA deduction.
D) The expense deduction results from a cash expenditure.
A) It is sometimes called a tax shield.
B) It usually causes an increase in taxes.
C) Businesses usually want the largest possible CCA deduction.
D) The expense deduction results from a cash expenditure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is NOT usually considered when a company establishes its minimum desired rate of return?
A) A risk-free element of interest
B) A business-risk element
C) An inflation element
D) A political-risk element
A) A risk-free element of interest
B) A business-risk element
C) An inflation element
D) A political-risk element

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When making capital-budgeting decisions, the effects of inflation
A) should be ignored since it is impossible to know what future inflation rates will be.
B) are important, but it is impossible to estimate their effects on capital-budgeting decisions.
C) act to reduce the minimum desired rate of return on projects.
D) act to increase the minimum desired rate of return on projects.
A) should be ignored since it is impossible to know what future inflation rates will be.
B) are important, but it is impossible to estimate their effects on capital-budgeting decisions.
C) act to reduce the minimum desired rate of return on projects.
D) act to increase the minimum desired rate of return on projects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A company is considering the purchase of some equipment that in the second year of operation should cause an increase in sales of $200,000, an increase in cash expenses of $120,000, and a depreciation deduction of $60,000. If the appropriate tax rate is 40 percent, what will be the after-tax effect of this equipment on cash flows in year two?
A) No effect
B) Net after-tax cash inflows will be $72,000.
C) Net after-tax cash inflows will be $12,000.
D) Net after-tax cash inflows will be $20,000.
A) No effect
B) Net after-tax cash inflows will be $72,000.
C) Net after-tax cash inflows will be $12,000.
D) Net after-tax cash inflows will be $20,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A company with pretax income of $60,000 is required to pay taxes of 20 percent on all income up to $20,000 and 32 percent on any income in excess of $20,000. The company's average tax rate is
A) 20 percent.
B) 28 percent.
C) 32 percent.
D) higher than its marginal rate.
A) 20 percent.
B) 28 percent.
C) 32 percent.
D) higher than its marginal rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In making capital-budgeting decisions, it is relevant to consider
A) future data that will differ among competing alternatives.
B) the cash outflows caused by future depreciation deductions.
C) the book value of equipment.
D) the original cost of currently owned equipment.
A) future data that will differ among competing alternatives.
B) the cash outflows caused by future depreciation deductions.
C) the book value of equipment.
D) the original cost of currently owned equipment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Fagen Grocery Store is considering the purchase of a new $45,000 delivery truck. The truck will have a useful life of 5 years, no terminal salvage value, and tax amortization will be calculated using the straight-line method.
If the truck is purchased, the company will be able to increase annual revenues by $90,000 per year for the life of the truck, but out-of-pocket expenses will also increase by $67,500 per year.
Assume a tax rate of 30 percent and a required after-tax rate of return equal to 10 percent.
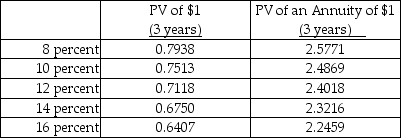
Time value factors are given below for 5 years and an interest rate of 10 percent.

What is the net present value of the tax savings from depreciation?
A) $3,912
B) $23,881
C) $10,235
D) $1,677
If the truck is purchased, the company will be able to increase annual revenues by $90,000 per year for the life of the truck, but out-of-pocket expenses will also increase by $67,500 per year.
Assume a tax rate of 30 percent and a required after-tax rate of return equal to 10 percent.
Time value factors are given below for 5 years and an interest rate of 10 percent.

What is the net present value of the tax savings from depreciation?
A) $3,912
B) $23,881
C) $10,235
D) $1,677

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Fagen Grocery Store is considering the purchase of a new $45,000 delivery truck. The truck will have a useful life of 5 years, no terminal salvage value, and tax amortization will be calculated using the straight-line method.
If the truck is purchased, the company will be able to increase annual revenues by $90,000 per year for the life of the truck, but out-of-pocket expenses will also increase by $67,500 per year.
Assume a tax rate of 30 percent and a required after-tax rate of return equal to 10 percent.
Time value factors are given below for 5 years and an interest rate of 10 percent.

What is the total net present value of the investment?
A) $69,941
B) $24,941
C) $42,000
D) $(33,545)
If the truck is purchased, the company will be able to increase annual revenues by $90,000 per year for the life of the truck, but out-of-pocket expenses will also increase by $67,500 per year.
Assume a tax rate of 30 percent and a required after-tax rate of return equal to 10 percent.
Time value factors are given below for 5 years and an interest rate of 10 percent.

What is the total net present value of the investment?
A) $69,941
B) $24,941
C) $42,000
D) $(33,545)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The cash inflow effect of a disposal at a loss is equal to the
A) amount of the loss plus the tax savings.
B) amount of the loss minus the tax savings.
C) selling price plus the tax savings.
D) selling price minus the tax savings.
A) amount of the loss plus the tax savings.
B) amount of the loss minus the tax savings.
C) selling price plus the tax savings.
D) selling price minus the tax savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Another term for market interest rate is
A) risk-free interest rate.
B) real rate.
C) nominal rate.
D) marginal rate.
A) risk-free interest rate.
B) real rate.
C) nominal rate.
D) marginal rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The "inflation element" refers to the
A) future increase in the general purchasing power of the monetary unit.
B) future deterioration of the general purchasing power of the monetary unit.
C) impact that future price increases will have on the original cost of a piece of equipment.
D) fact that the real purchasing power of a monetary unit usually increases over time.
A) future increase in the general purchasing power of the monetary unit.
B) future deterioration of the general purchasing power of the monetary unit.
C) impact that future price increases will have on the original cost of a piece of equipment.
D) fact that the real purchasing power of a monetary unit usually increases over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements about depreciation is TRUE?
A) The amortization method chosen does not affect cash inflows from operations.
B) The amortization method chosen for taxes will not affect cash outflows.
C) The total amount of amortization over the life of the assets differs with different amortization methods.
D) Since amortization does not involve a cash expenditure, it can be ignored in capital-budgeting decisions.
A) The amortization method chosen does not affect cash inflows from operations.
B) The amortization method chosen for taxes will not affect cash outflows.
C) The total amount of amortization over the life of the assets differs with different amortization methods.
D) Since amortization does not involve a cash expenditure, it can be ignored in capital-budgeting decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Fagen Grocery Store is considering the purchase of a new $45,000 delivery truck. The truck will have a useful life of 5 years, no terminal salvage value, and tax amortization will be calculated using the straight-line method.
If the truck is purchased, the company will be able to increase annual revenues by $90,000 per year for the life of the truck, but out-of-pocket expenses will also increase by $67,500 per year.
Assume a tax rate of 30 percent and a required after-tax rate of return equal to 10 percent.
Time value factors are given below for 5 years and an interest rate of 10 percent.

What is the present value of the after-tax cash flows from operations, exclusive of depreciation?
A) $85,293
B) $13,971
C) $ 9,778
D) $59,705
If the truck is purchased, the company will be able to increase annual revenues by $90,000 per year for the life of the truck, but out-of-pocket expenses will also increase by $67,500 per year.
Assume a tax rate of 30 percent and a required after-tax rate of return equal to 10 percent.
Time value factors are given below for 5 years and an interest rate of 10 percent.

What is the present value of the after-tax cash flows from operations, exclusive of depreciation?
A) $85,293
B) $13,971
C) $ 9,778
D) $59,705

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If the appropriate tax rate is 35%, the after-tax effect of a single CCA deduction of $30,000 is
A) $19,500 net after-tax cash outflow.
B) $19,500 net after-tax cash inflow.
C) $10,500 net after-tax cash outflow.
D) $10,500 net after-tax cash inflow.
A) $19,500 net after-tax cash outflow.
B) $19,500 net after-tax cash inflow.
C) $10,500 net after-tax cash outflow.
D) $10,500 net after-tax cash inflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If a company pays taxes of 15 percent on their first $25,000 of pretax income, and 30 percent on any taxable income in excess of $25,000, what is the average tax rate if current pretax income is $40,000?
A) 15.00 percent
B) 20.63 percent
C) 30.00 percent
D) 22.50 percent
A) 15.00 percent
B) 20.63 percent
C) 30.00 percent
D) 22.50 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The present value of 5-year annuity of $10,000, earning an annual return of 8 percent is
A) $31,700.
B) $34,700.
C) $37,910.
D) $39,930.
A) $31,700.
B) $34,700.
C) $37,910.
D) $39,930.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following statements about the riskiness of an investment is true?
A) The lower the risk, the higher the discount rate.
B) The higher the risk, the higher the discount rate.
C) The higher the risk, the lower the cost of capital.
D) The higher the risk, the higher the minimum desired rate of return.
A) The lower the risk, the higher the discount rate.
B) The higher the risk, the higher the discount rate.
C) The higher the risk, the lower the cost of capital.
D) The higher the risk, the higher the minimum desired rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following information to answer the next question(s).
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
Payback for the project is
A) 6.11 years.
B) 6.25 years.
C) 7.96 years.
D) 8.33 years.
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
Payback for the project is
A) 6.11 years.
B) 6.25 years.
C) 7.96 years.
D) 8.33 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following methods determines the interest rate which equates the present value of the future cash flows with the investment outlay?
A) Payback
B) Accounting rate of return
C) Internal rate of return
D) Net present value
A) Payback
B) Accounting rate of return
C) Internal rate of return
D) Net present value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following information to answer the next question(s).
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
If the depreciation is $25,000 per year, the accounting rate of return based on the initial investment is
A) 11%.
B) 12%.
C) 16%.
D) 17.2%.
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
If the depreciation is $25,000 per year, the accounting rate of return based on the initial investment is
A) 11%.
B) 12%.
C) 16%.
D) 17.2%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the following information regarding a production asset to answer the next question(s).
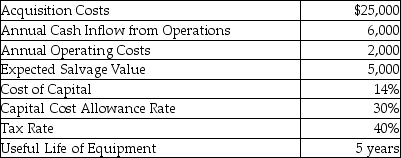
The annual after-tax operation costs would be
A) $1,000.
B) $1,200.
C) $1,500.
D) $2.000.

The annual after-tax operation costs would be
A) $1,000.
B) $1,200.
C) $1,500.
D) $2.000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following information regarding a production asset to answer the next question(s).

The annual after-tax cash inflow from operations would be
A) $1,200.
B) $2,400.
C) $2,800.
D) $3,600.

The annual after-tax cash inflow from operations would be
A) $1,200.
B) $2,400.
C) $2,800.
D) $3,600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following information regarding a production asset to answer the next question(s).

The capital cost allowance for the first year would be
A) $3,750.
B) $6,375.
C) $7,500.
D) $4,463.

The capital cost allowance for the first year would be
A) $3,750.
B) $6,375.
C) $7,500.
D) $4,463.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following statements about depreciation is TRUE?
A) The tax effects of depreciation are not adjusted for inflation.
B) The tax effects of depreciation must be adjusted for inflation.
C) Canadian tax laws allow for inflation adjustments to depreciation each year.
D) Capital investment is encouraged by not allowing depreciation to be adjusted for the effect of inflation.
A) The tax effects of depreciation are not adjusted for inflation.
B) The tax effects of depreciation must be adjusted for inflation.
C) Canadian tax laws allow for inflation adjustments to depreciation each year.
D) Capital investment is encouraged by not allowing depreciation to be adjusted for the effect of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following information to answer the next question(s).
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
Miller Manufacturing has acquired a new parcel van to transport packages from the airport to its sales offices for $20,000. The van is a class 10 item which has a capital cost allowance rate of 30%. The company plans to use the van for five years and then sell it for an expected salvage value of $4,000. The capital cost allowance for the first year would be
A) $3,000.
B) $6,000.
C) $5,100.
D) $3,500.
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
Miller Manufacturing has acquired a new parcel van to transport packages from the airport to its sales offices for $20,000. The van is a class 10 item which has a capital cost allowance rate of 30%. The company plans to use the van for five years and then sell it for an expected salvage value of $4,000. The capital cost allowance for the first year would be
A) $3,000.
B) $6,000.
C) $5,100.
D) $3,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following information to answer the next question(s).
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
The cost of capital for the firm is
A) 8%.
B) 6%.
C) 10%.
D) 12%.
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
The cost of capital for the firm is
A) 8%.
B) 6%.
C) 10%.
D) 12%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following methods determines the interest rate which equates the present value of the future cash flows with the investment outlay?
A) Payback
B) Accounting rate of return
C) Internal rate of return
D) Net present value
A) Payback
B) Accounting rate of return
C) Internal rate of return
D) Net present value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The discount rate is
A) the rate used to compute payback.
B) the rate used to compute the accounting rate of return.
C) the rate used to compute the internal rate of return.
D) the rate used to compute NPV.
A) the rate used to compute payback.
B) the rate used to compute the accounting rate of return.
C) the rate used to compute the internal rate of return.
D) the rate used to compute NPV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following information to answer the next question(s).
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
The amount of the capital cost allowance for the second year for Mike Manufacturing would be
A) $3,000.
B) $6,000.
C) $5,100.
D) $3,500.
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
The amount of the capital cost allowance for the second year for Mike Manufacturing would be
A) $3,000.
B) $6,000.
C) $5,100.
D) $3,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The present value of $10,000 to be received 5 years from now and earning an annual return of 8 percent is
A) $6,210.
B) $6,810.
C) $4,000.
D) $4,693.
A) $6,210.
B) $6,810.
C) $4,000.
D) $4,693.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following information to answer the next question(s).
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
The approximate internal rate of return of the project is
A) 8%.
B) 12%.
C) 12.5%.
D) 14%.
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
The approximate internal rate of return of the project is
A) 8%.
B) 12%.
C) 12.5%.
D) 14%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following information to answer the next question(s).
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
Using the cost capital as the discount rate, the net present value of the project is
A) $89,360.
B) $108,480.
C) $114,680.
D) $228,180.
Sunny Flowers is considering the purchase of a small business that costs $500,000. Sunny plans to sell stock valued at $250,000. The stock would pay dividends of $20,000 per year. Sunny would borrow the remaining $250,000 from a local bank at 12 percent interest.
The business is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $80,000. Duane plans to operate the business for 15 years and then turn it over to his son.
Using the cost capital as the discount rate, the net present value of the project is
A) $89,360.
B) $108,480.
C) $114,680.
D) $228,180.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Discounting
A) is the process of determining value at a future time.
B) is the process of converting future cash flows to their present value.
C) is a process that doers not consider the time value of money.
D) is a process that can only be used for a single amount (not annuities).
A) is the process of determining value at a future time.
B) is the process of converting future cash flows to their present value.
C) is a process that doers not consider the time value of money.
D) is a process that can only be used for a single amount (not annuities).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Use the following information regarding a production asset to answer the next question(s).

The present value of equipment salvage value at the end of the five years would be
A) $4,000.
B) $5,000,
C) $2,076,
D) $2,595,

The present value of equipment salvage value at the end of the five years would be
A) $4,000.
B) $5,000,
C) $2,076,
D) $2,595,

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use the following information regarding a production asset to answer the next question(s).

The tax savings from the capital cost allowance in the second year would be
A) $1,500.
B) $2,550.
C) $3,000.
D) $2,000.

The tax savings from the capital cost allowance in the second year would be
A) $1,500.
B) $2,550.
C) $3,000.
D) $2,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



