Deck 23: Insurance and Risk Management
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/38
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Insurance and Risk Management
1
To protect the firm against the loss of earnings if the business operations are disrupted due to fire, accident or some other insured peril, a firm would purchase
A)business interruption insurance.
B)property insurance.
C)business liability insurance.
D)key personnel insurance.
A)business interruption insurance.
B)property insurance.
C)business liability insurance.
D)key personnel insurance.
business interruption insurance.
2
To insure their assets against hazards such as fire, storm damage, vandalism, earthquakes and other natural and environmental risks, firms commonly purchase
A)key personnel insurance.
B)business interruption insurance.
C)business liability insurance.
D)property insurance.
A)key personnel insurance.
B)business interruption insurance.
C)business liability insurance.
D)property insurance.
property insurance.
3
Use the information for the question(s)below.
Your firm faces an 8% chance of a potential loss of $50 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $250 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
Assuming that your firm will purchase insurance, what is the minimum-size deductible that would leave your firm with an incentive to implement the new safety policies? Show your calculations.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Your firm faces an 8% chance of a potential loss of $50 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $250 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
Assuming that your firm will purchase insurance, what is the minimum-size deductible that would leave your firm with an incentive to implement the new safety policies? Show your calculations.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
If the firm is fully insured (no deductible), the insurance company will pay for the loss regardless of whether the safety program is in force or not. Therefore, the end-of-period cash flows will be identical with or without the program and the NPV is -$250 000 reflecting the cost of the safety program.
In order to give the firm the incentive to buy the insurance, the NPV of the safety program must be positive.
Another way of looking at this is to find the point where the PV of the expected deductible equals the cost of the safety program. Mathematically, we have:
(0.08 - 0.03)= $250 000, solving for the Deductible = = $5 250 000
To show that this indeed is the correct answer:
(0.08)= (0.03)- $250 000
In order to give the firm the incentive to buy the insurance, the NPV of the safety program must be positive.
Another way of looking at this is to find the point where the PV of the expected deductible equals the cost of the safety program. Mathematically, we have:
(0.08 - 0.03)= $250 000, solving for the Deductible = = $5 250 000
To show that this indeed is the correct answer:
(0.08)= (0.03)- $250 000
4
Use the information for the question(s)below.
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
Insurance for large risks that cannot be well diversified has a(n)________, which increases its cost.
A)negative beta
B)moral hazard clause
C)actuarially biased risk
D)positive beta
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
Insurance for large risks that cannot be well diversified has a(n)________, which increases its cost.
A)negative beta
B)moral hazard clause
C)actuarially biased risk
D)positive beta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Insurance that compensates for the loss or unavoidable absence of crucial employees in the firm is called
A)business liability insurance.
B)business interruption insurance.
C)property insurance.
D)key personnel insurance.
A)business liability insurance.
B)business interruption insurance.
C)property insurance.
D)key personnel insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A)Firms generally do not possess better information than outside investors regarding the risk of future commodity price changes, nor can they influence that risk through their actions.
B)The firm may speculate by entering into contracts that do not offset its actual risks.
C)Cash flows are exchanged on a monthly basis, rather than waiting until the end of the contract, through a procedure called 'marking to market'.
D)When a firm authorises managers to trade contracts to hedge, it opens the door to the possibility of speculation.
A)Firms generally do not possess better information than outside investors regarding the risk of future commodity price changes, nor can they influence that risk through their actions.
B)The firm may speculate by entering into contracts that do not offset its actual risks.
C)Cash flows are exchanged on a monthly basis, rather than waiting until the end of the contract, through a procedure called 'marking to market'.
D)When a firm authorises managers to trade contracts to hedge, it opens the door to the possibility of speculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A)Not all insurable risks have a beta of zero. Some risks, such as hurricanes and earthquakes, create losses of tens of billions of dollars and may be difficult to diversify completely.
B)By its very nature, insurance for no diversifiable hazards is generally a positive beta asset; the insurance payment to the firm tends to be larger when total losses are low and the market portfolio is high.
C)Because insurance provides cash to the firm to offset losses, it can reduce the firm's need for external capital and thus reduce issuance costs.
D)When a firm buys insurance, it transfers the risk of the loss to an insurance company. The insurance company charges an upfront premium to take on that risk.
A)Not all insurable risks have a beta of zero. Some risks, such as hurricanes and earthquakes, create losses of tens of billions of dollars and may be difficult to diversify completely.
B)By its very nature, insurance for no diversifiable hazards is generally a positive beta asset; the insurance payment to the firm tends to be larger when total losses are low and the market portfolio is high.
C)Because insurance provides cash to the firm to offset losses, it can reduce the firm's need for external capital and thus reduce issuance costs.
D)When a firm buys insurance, it transfers the risk of the loss to an insurance company. The insurance company charges an upfront premium to take on that risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the information for the question(s)below.
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
If your firm is fully insured, the NPV of implementing the new safety policies is closest to:
A)$2.15 million
B)$-2.25 million
C)$2.5 million
D)-$.35 million
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
If your firm is fully insured, the NPV of implementing the new safety policies is closest to:
A)$2.15 million
B)$-2.25 million
C)$2.5 million
D)-$.35 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the information for the question(s)below.
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
If your firm is uninsured, the NPV of implementing the new safety policies is closest to:
A)$2.25 million
B)-$0.25 million
C)$0.94 million
D)$1.95 million
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
If your firm is uninsured, the NPV of implementing the new safety policies is closest to:
A)$2.25 million
B)-$0.25 million
C)$0.94 million
D)$1.95 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The risk that arises because the value of the futures contract will not be perfectly correlated with the firm's exposure is called
A)speculation risk.
B)liquidity risk.
C)basis risk.
D)commodity price risk.
A)speculation risk.
B)liquidity risk.
C)basis risk.
D)commodity price risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Use the information for the question(s)below.
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
What is the actuarially fair cost of full insurance?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
What is the actuarially fair cost of full insurance?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In reality, market imperfections exist that can raise the cost of insurance above the actuarially fair price and offset some of these benefits. These insurance market imperfections include all of the following EXCEPT:
A)taxation of insurance payments
B)agency costs
C)adverse selection
D)administrative and overhead costs
A)taxation of insurance payments
B)agency costs
C)adverse selection
D)administrative and overhead costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A)In a perfect market without other frictions, insurance companies should compete until they are just earning a fair return and the NPV from selling insurance is zero. The NPV is zero if the price of insurance equals the present value of the expected payment; in that case, we say the price is 'actuarially fair'.
B)Because insurance reduces the risk of financial distress, it can relax this trade-off and allow the firm to increase its use of debt financing.
C)When a firm is subject to graduated income tax rates, insurance can produce a tax saving if the firm is in a higher tax bracket when it pays the premium than the tax bracket it is in when it receives the insurance payment in the event of a loss.
D)By lowering the volatility of the shares, insurance discourages concentrated ownership by an outside director or investor who will monitor the firm and its management.
A)In a perfect market without other frictions, insurance companies should compete until they are just earning a fair return and the NPV from selling insurance is zero. The NPV is zero if the price of insurance equals the present value of the expected payment; in that case, we say the price is 'actuarially fair'.
B)Because insurance reduces the risk of financial distress, it can relax this trade-off and allow the firm to increase its use of debt financing.
C)When a firm is subject to graduated income tax rates, insurance can produce a tax saving if the firm is in a higher tax bracket when it pays the premium than the tax bracket it is in when it receives the insurance payment in the event of a loss.
D)By lowering the volatility of the shares, insurance discourages concentrated ownership by an outside director or investor who will monitor the firm and its management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A)Horizontal integration entails the merger of a firm and its supplier or a firm and its customer.
B)Because an increase in the price of the commodity raises the firm's costs and the supplier's revenues, these firms can offset their risks by merging.
C)For many firms, changes in the market prices of the raw materials they use and the goods they produce may be the most important source of risk to their profitability.
D)Like insurance, hedging involves contracts or transactions that provide the firm with cash flows that offset its losses from price changes.
A)Horizontal integration entails the merger of a firm and its supplier or a firm and its customer.
B)Because an increase in the price of the commodity raises the firm's costs and the supplier's revenues, these firms can offset their risks by merging.
C)For many firms, changes in the market prices of the raw materials they use and the goods they produce may be the most important source of risk to their profitability.
D)Like insurance, hedging involves contracts or transactions that provide the firm with cash flows that offset its losses from price changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
'Liquidity risk' is the risk that the firm will not have, or be able to raise, the cash required to meet the margin calls on its hedges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Use the information for the question(s)below.
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
An operator of an oil rig has a 0.5% chance of experiencing a catastrophic failure. This failure will cost the operator $500 million. If the risk-free rate is 2%, the expected return on the market is 8%, and the beta of the risk is -1.2, what is the actuarially fair insurance premium?
A)$2 550 000
B)$2 500 000
C)$2 637 131
D)$2 753 304
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
An operator of an oil rig has a 0.5% chance of experiencing a catastrophic failure. This failure will cost the operator $500 million. If the risk-free rate is 2%, the expected return on the market is 8%, and the beta of the risk is -1.2, what is the actuarially fair insurance premium?
A)$2 550 000
B)$2 500 000
C)$2 637 131
D)$2 753 304

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Use the information for the question(s)below.
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
An operator of an oil rig has a 0.5% chance of experiencing a catastrophic failure. This failure will cost the operator $500 million. If the risk-free rate is 2%, the expected return on the market is 8%, and the beta of the risk is 0, what is the actuarially fair insurance premium?
A)$2 314 815
B)$2 550 000
C)$2 450 980
D)$2 500 000
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
An operator of an oil rig has a 0.5% chance of experiencing a catastrophic failure. This failure will cost the operator $500 million. If the risk-free rate is 2%, the expected return on the market is 8%, and the beta of the risk is 0, what is the actuarially fair insurance premium?
A)$2 314 815
B)$2 550 000
C)$2 450 980
D)$2 500 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
To cover the costs that result if some aspect of the business causes harm to a third party or someone else's property, a firm would purchase
A)business liability insurance.
B)business interruption insurance.
C)property insurance.
D)key personnel insurance.
A)business liability insurance.
B)business interruption insurance.
C)property insurance.
D)key personnel insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Use the information for the question(s)below.
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
The value of insurance comes from its ability to reduce the cost of ________ for the firm.
A)market imperfections
B)overhead
C)adverse selection
D)vertical integration
Your firm faces a 6% chance of a potential loss of $45 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $350 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
The value of insurance comes from its ability to reduce the cost of ________ for the firm.
A)market imperfections
B)overhead
C)adverse selection
D)vertical integration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use the information for the question(s)below.
Your firm faces an 8% chance of a potential loss of $50 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $250 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
Farmville Industries is a major agricultural firm and is concerned about the possibility of drought impacting wheat production. In the event of a drought, Farmville Industries anticipates a loss of $75 million. Suppose the likelihood of a drought is 10% per year, and the beta associated with such a loss is 0.4. If the risk-free interest rate is 5% and the expected return on the market is 10%, then what is the actuarially fair insurance premium? Show your calculations.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Your firm faces an 8% chance of a potential loss of $50 million next year. If your firm implements new safety policies, it can reduce the chance of this loss to 3%, but the new safety policies have an upfront cost of $250 000. Suppose that the beta of the loss is 0 and the risk-free rate of interest is 5%.
Farmville Industries is a major agricultural firm and is concerned about the possibility of drought impacting wheat production. In the event of a drought, Farmville Industries anticipates a loss of $75 million. Suppose the likelihood of a drought is 10% per year, and the beta associated with such a loss is 0.4. If the risk-free interest rate is 5% and the expected return on the market is 10%, then what is the actuarially fair insurance premium? Show your calculations.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The duration of a five-year bond with 7% annual coupons and a yield-to-maturity of 8% is closest to:
A)6.2 years
B)2.5 years
C)4.4 years
D)5.0 years
A)6.2 years
B)2.5 years
C)4.4 years
D)5.0 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A)An interest rate that adjusts to current market conditions is called a 'floating rate'.
B)When interest rates rise, the swap's value will rise for the party receiving the fixed rate; conversely, it will fall for the party paying the fixed rate.
C)Corporations use interest rate swaps routinely to alter their exposure to interest rate fluctuations.
D)The value of a swap, while initially zero, will fluctuate over time as interest rates change.
A)An interest rate that adjusts to current market conditions is called a 'floating rate'.
B)When interest rates rise, the swap's value will rise for the party receiving the fixed rate; conversely, it will fall for the party paying the fixed rate.
C)Corporations use interest rate swaps routinely to alter their exposure to interest rate fluctuations.
D)The value of a swap, while initially zero, will fluctuate over time as interest rates change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements regarding long-term supply contracts is FALSE?
A)Long-term supply contracts are designed to eliminate credit risk.
B)Long-term supply contracts insulate the firms from commodity price risk.
C)Long-term supply contracts are bilateral contracts negotiated by a buyer and a seller.
D)The market value of the contract at any point in time may not be easy to determine, making it difficult to track gains and losses.
A)Long-term supply contracts are designed to eliminate credit risk.
B)Long-term supply contracts insulate the firms from commodity price risk.
C)Long-term supply contracts are bilateral contracts negotiated by a buyer and a seller.
D)The market value of the contract at any point in time may not be easy to determine, making it difficult to track gains and losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the duration of a four-year zero-coupon bond?
A)1 year
B)4 years
C)2.5 years
D)0 years
A)1 year
B)4 years
C)2.5 years
D)0 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A floating interest rate adjusts to current market conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A)A 'futures contract' is an agreement to trade an asset on some future date, at a price that is locked in today.
B)Long-term supply contracts are unilateral contracts offered by a seller.
C)Long-term supply contracts cannot be entered into anonymously; the buyer and seller know each other's identity. This lack of anonymity may have strategic disadvantages.
D)An alternative to vertical integration or storage is a long-term supply contract.
A)A 'futures contract' is an agreement to trade an asset on some future date, at a price that is locked in today.
B)Long-term supply contracts are unilateral contracts offered by a seller.
C)Long-term supply contracts cannot be entered into anonymously; the buyer and seller know each other's identity. This lack of anonymity may have strategic disadvantages.
D)An alternative to vertical integration or storage is a long-term supply contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A steel maker needs 5 000 000 tonnes of coal next year. The current market price for coal is $70.00 per tonne. At this price, the firm expects its EBIT to be $500 million. What will be the firm's EBIT if the firm enters into a supply contract for coal for a fixed price of $72.00 per tonne?
A)$350 million
B)$490 million
C)$510 million
D)$500 million
A)$350 million
B)$490 million
C)$510 million
D)$500 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A)When the durations of a firm's assets and liabilities are significantly different, the firm has a duration mismatch.
B)Adjusting a portfolio to make its duration neutral is sometimes referred to as 'immunising the portfolio', a term that indicates it is being protected against interest rate changes.
C)As interest rates change, the market values of the securities and cash flows in the portfolio change as well, which in turn alters the weights used when computing the duration as the value-weighted average maturity.
D)The duration of a portfolio of investments is the simple average of the durations of each investment in the portfolio.
A)When the durations of a firm's assets and liabilities are significantly different, the firm has a duration mismatch.
B)Adjusting a portfolio to make its duration neutral is sometimes referred to as 'immunising the portfolio', a term that indicates it is being protected against interest rate changes.
C)As interest rates change, the market values of the securities and cash flows in the portfolio change as well, which in turn alters the weights used when computing the duration as the value-weighted average maturity.
D)The duration of a portfolio of investments is the simple average of the durations of each investment in the portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What are some of the disadvantages of long-term supply contracts?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is an agreement to trade an asset on some future date, at a price that is fixed today?
A)notional contract
B)margin
C)interest rate swap
D)futures contract
A)notional contract
B)margin
C)interest rate swap
D)futures contract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A)A firm's market capitalisation is determined by the difference in the market value of its assets and its liabilities.
B)We can measure a firm's sensitivity to interest rates by computing the duration of its balance sheet.
C)Just as the interest rate sensitivity of a single cash flow increases with its maturity, the interest rate sensitivity of a stream of cash flows increases with its duration.
D)By restructuring the balance sheet to increase its duration, we can hedge the firm's interest rate risk.
A)A firm's market capitalisation is determined by the difference in the market value of its assets and its liabilities.
B)We can measure a firm's sensitivity to interest rates by computing the duration of its balance sheet.
C)Just as the interest rate sensitivity of a single cash flow increases with its maturity, the interest rate sensitivity of a stream of cash flows increases with its duration.
D)By restructuring the balance sheet to increase its duration, we can hedge the firm's interest rate risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements regarding futures contracts is FALSE?
A)Traders are required to post collateral, called 'margin', when buying or selling commodities using futures contracts.
B)Futures contracts are traded anonymously on an exchange at a publicly observed market price and are generally very illiquid.
C)Futures prices are not prices that are paid today. Rather, they are prices agreed to today, to be paid in the future.
D)Both the buyer and the seller can get out of the contract at any time by selling it to a third party at the current market price.
A)Traders are required to post collateral, called 'margin', when buying or selling commodities using futures contracts.
B)Futures contracts are traded anonymously on an exchange at a publicly observed market price and are generally very illiquid.
C)Futures prices are not prices that are paid today. Rather, they are prices agreed to today, to be paid in the future.
D)Both the buyer and the seller can get out of the contract at any time by selling it to a third party at the current market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A)The swap contract - like forward and futures contracts - is typically structured as a 'zero-cost' security.
B)If short-term interest rates were to fall while long-term rates remained stable, then short-term securities would fall in value relative to long-term securities, despite their shorter duration.
C)An 'interest rate swap' is a contract entered into with a bank, much like a forward contract, in which the firm and the bank agree to exchange the coupons from two different types of loans.
D)In a standard interest rate swap, one party agrees to pay coupons based on a fixed interest rate in exchange for receiving coupons based on the prevailing market interest rate during each coupon period.
A)The swap contract - like forward and futures contracts - is typically structured as a 'zero-cost' security.
B)If short-term interest rates were to fall while long-term rates remained stable, then short-term securities would fall in value relative to long-term securities, despite their shorter duration.
C)An 'interest rate swap' is a contract entered into with a bank, much like a forward contract, in which the firm and the bank agree to exchange the coupons from two different types of loans.
D)In a standard interest rate swap, one party agrees to pay coupons based on a fixed interest rate in exchange for receiving coupons based on the prevailing market interest rate during each coupon period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Firms use all of the following for reducing their exposure to commodity price movements EXCEPT:
A)long-term storage of inventory
B)futures contracts
C)vertical integration
D)horizontal integration
A)long-term storage of inventory
B)futures contracts
C)vertical integration
D)horizontal integration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A manufacturer of breakfast cereal is concerned about corn prices. The firm anticipates needing 1 million bushels of corn in one month. The current price of corn is $6.60 per bushel and the futures price for delivery in one month is $7.25 per bushel. The cost to store the corn for 1 month is $150 000. What should the firm do?
A)Hedge with futures for a total cost of $6 600 000.
B)Hedge with futures for a total cost of $7 250 000.
C)Buy the corn now and store for 1 month, for a total cost of $6 750 000.
D)Buy the corn now and store for 1 month, for a total cost of $6 500 000.
A)Hedge with futures for a total cost of $6 600 000.
B)Hedge with futures for a total cost of $7 250 000.
C)Buy the corn now and store for 1 month, for a total cost of $6 750 000.
D)Buy the corn now and store for 1 month, for a total cost of $6 500 000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Luther Industries needs to borrow $50 million in cash. Currently long-term AAA rates are 9%. Luther can borrow at 9.75% given its current credit rating. Luther is expecting interest rates to fall over the next few years, so it would prefer to borrow at the short-term rates and refinance after rates have dropped. Luther management is afraid, however, that its credit rating may fall which could greatly increase the spread the firm must pay on new borrowings. How can Luther benefit from the expected decline in future interest rates without exposure to the risk of the potential future changes to its credit ratings?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A portfolio with a negative duration is called a 'duration-neutral portfolio' or an 'immunised portfolio', which means that if small interest rate fluctuations occur, the value of equity should remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Your oil refinery will need to buy 250 000 barrels of crude oil in one week and you are worried about crude oil prices. Suppose you take on a long position in 250 crude oil futures contracts, each for 1 000 barrels of crude oil, at the current futures price of $68 per barrel. Suppose futures prices change each day over the next week as follows:
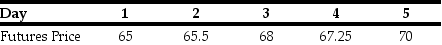 What is the daily and cumulative mark to market profit or loss (in dollars)that you will have on each of the next five days?
What is the daily and cumulative mark to market profit or loss (in dollars)that you will have on each of the next five days?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
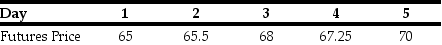 What is the daily and cumulative mark to market profit or loss (in dollars)that you will have on each of the next five days?
What is the daily and cumulative mark to market profit or loss (in dollars)that you will have on each of the next five days?_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



