Deck 7: Protein Function Part I: Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/74
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Protein Function Part I: Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
1
Which of the following statements does not apply to the K value in the equation for the oxygen binding curve of myoglobin?
A)It is numerically equal to p50.
B)It is defined as that oxygen partial pressure at which half of the oxygen binding sites are occupied.
C)It is a measure of the affinity of myoglobin for oxygen.
D)If Y > K, then myoglobin is less than 50% saturated with oxygen.
E)It is the value of pO2 at which Y = 0.5.
A)It is numerically equal to p50.
B)It is defined as that oxygen partial pressure at which half of the oxygen binding sites are occupied.
C)It is a measure of the affinity of myoglobin for oxygen.
D)If Y > K, then myoglobin is less than 50% saturated with oxygen.
E)It is the value of pO2 at which Y = 0.5.
If Y > K, then myoglobin is less than 50% saturated with oxygen.
2
Matching
The ______ model of allosterism requires subunits to change conformation simultaneously.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
The ______ model of allosterism requires subunits to change conformation simultaneously.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
symmetry
3
Matching
The conversion of hemoglobin from the T to the R state requires breaking of ______ involving C-terminal residues.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
The conversion of hemoglobin from the T to the R state requires breaking of ______ involving C-terminal residues.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
ion pairs
4
Hemoglobin is a heterotetramer.How many protomers are present in hemoglobin?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Matching
The absence of 2,3-BPG causes hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen to______.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
The absence of 2,3-BPG causes hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen to______.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Matching
An increase in pCO2 causes hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen to ______.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
An increase in pCO2 causes hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen to ______.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Myoglobin's primary physiological role is to facilitate oxygen ________.
A)storage
B)metabolism
C)binding
D)reduction
E)diffusion
A)storage
B)metabolism
C)binding
D)reduction
E)diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If the gene for myoglobin is "knocked out" in mice, the mice:
A)have larger lungs.
B)respire extremely rapidly.
C)have dark brown muscle tissue.
D)appear normal, with lighter colored muscle tissue.
E)have their growth stunted.
A)have larger lungs.
B)respire extremely rapidly.
C)have dark brown muscle tissue.
D)appear normal, with lighter colored muscle tissue.
E)have their growth stunted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Matching
In the ______ state of hemoglobin, the iron ion is out of the plane of the porphyrin ring.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
In the ______ state of hemoglobin, the iron ion is out of the plane of the porphyrin ring.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Myoglobin and a single chain of hemoglobin have similar ______ structures.
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary
E)none of the above
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Myoglobin's secondary structure is primarily composed of ______________.
A)parallel -sheets
B)antiparallel -sheets
C)( -helices)
D)( -loops)
E)polyproline helices
A)parallel -sheets
B)antiparallel -sheets
C)( -helices)
D)( -loops)
E)polyproline helices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Matching
When unstable hemoglobin is degraded; degradation products often cause cell lysis, leading to a condition called ______.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
When unstable hemoglobin is degraded; degradation products often cause cell lysis, leading to a condition called ______.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which gas does not bind to the porphyrin ring Fe(II)ion in myoglobin?
A)NO
B)CO
C)CO2
D)O2
E)H2S
A)NO
B)CO
C)CO2
D)O2
E)H2S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is not a ligand to the porphyrin ring Fe(II) ion in oxymyoglobin?
A)His E7
B)His F8
C)Nitrogen atoms in the porphyrin ring
D)Oxygen
E)all are ligands
A)His E7
B)His F8
C)Nitrogen atoms in the porphyrin ring
D)Oxygen
E)all are ligands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Carbon monoxide binds to heme:
A)with a higher affinity than oxygen.
B)resulting in the oxidation of the Fe(II)to Fe(III)
C)in a manner that displaces carbon dioxide, causing CO2 poisoning.
D)from the side opposite oxygen, resulting in a brown colored heme.
E)with a lower affinity than oxygen.
A)with a higher affinity than oxygen.
B)resulting in the oxidation of the Fe(II)to Fe(III)
C)in a manner that displaces carbon dioxide, causing CO2 poisoning.
D)from the side opposite oxygen, resulting in a brown colored heme.
E)with a lower affinity than oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The primary structure of mammalian hemoglobin, an 2 2 tetramer, is approximately _____ identical to myoglobin.
A)2%
B)18%
C)50%
D)78%
E)98%
A)2%
B)18%
C)50%
D)78%
E)98%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Matching
Hemoglobin's subunits bind oxygen in a ______ manner.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
Hemoglobin's subunits bind oxygen in a ______ manner.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Matching
Sickle cell hemoglobin does not form fibers in the ______ form.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
Sickle cell hemoglobin does not form fibers in the ______ form.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Matching
When oxygen binds to heme, the oxygen forms a hydrogen bond with ______.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
When oxygen binds to heme, the oxygen forms a hydrogen bond with ______.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Matching
Mutations that favor the oxidation of the heme iron(II)to iron(III)can cause ______.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial
Mutations that favor the oxidation of the heme iron(II)to iron(III)can cause ______.
A)positively cooperative
B)cyanosis
C)His E7
D)decrease
E)R
F)hydrogen bonds
G)increase
H)symmetry
I)His F8
J)ion pairs
K)T
L)hemolytic anemia
M)sequencial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Some abnormal hemoglobins have Hill coefficients that are ______ that of normal hemoglobin, indicating that their ability to bind oxygen cooperatively has been compromised.
A)less than
B)greater than
C)much greater than
D)about equal to
E)The correct answer cannot be determined from the information given.
A)less than
B)greater than
C)much greater than
D)about equal to
E)The correct answer cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the type of symmetry that relates the protomers in hemoglobin with respect to each other?
A)C2
B)C4
C)D2
D)D4
E)Tetrahedral symmetry
A)C2
B)C4
C)D2
D)D4
E)Tetrahedral symmetry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The rearrangement of T state hemoglobin to the R state
A)occurs in each protein subunit independently when its heme binds oxygen.
B)requires the binding of at least three oxygen molecules.
C)increases the ion pairing interactions of the C-terminal amino acids.
D)involves the movement of the Fe(II)into the heme plane.
E)opens a central cavity for BPG binding.
A)occurs in each protein subunit independently when its heme binds oxygen.
B)requires the binding of at least three oxygen molecules.
C)increases the ion pairing interactions of the C-terminal amino acids.
D)involves the movement of the Fe(II)into the heme plane.
E)opens a central cavity for BPG binding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
During the T to R conformational shift, Fe(II)drags the F-helix via a bond to the side chain of ________.
A)Leu F7
B)Leu F4
C)His F8
D)Leu FG3
E)Val FG5
A)Leu F7
B)Leu F4
C)His F8
D)Leu FG3
E)Val FG5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The oxygen binding by hemocyanins is mediated by
A)an iron ion
B)a pair of iron ions
C)a heme group
D)a copper atom
E)a pair of copper atoms
A)an iron ion
B)a pair of iron ions
C)a heme group
D)a copper atom
E)a pair of copper atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
BPG stands for
A)biphenylglycine.
B)boronylphenylglutamate.
C)bisphosphoglycerate.
D)bisphenylglycerol.
E)betapropylglutamine.
A)biphenylglycine.
B)boronylphenylglutamate.
C)bisphosphoglycerate.
D)bisphenylglycerol.
E)betapropylglutamine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The value of n, the Hill constant (coefficient), for hemoglobin is about ______ as great as the value for myoglobin.
A)half
B)twice
C)three times
D)five times
E)ten times
A)half
B)twice
C)three times
D)five times
E)ten times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The most rapid way that erythrocytes adapt to high altitudes is
A)by producing genetically altered hemoglobins that have higher O2-binding affinities.
B)by adopting the symmetry model of allosterism.
C)by increasing the concentration of hemoglobin.
D)by relying upon the simpler protein myoglobin.
E)by increasing the intracellular concentration of BPG.
A)by producing genetically altered hemoglobins that have higher O2-binding affinities.
B)by adopting the symmetry model of allosterism.
C)by increasing the concentration of hemoglobin.
D)by relying upon the simpler protein myoglobin.
E)by increasing the intracellular concentration of BPG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Bohr effect refers to
A)the decrease in affinity of Hb for O2 when the pH goes down
B)the decrease in affinity of Hb for O2 when the pH goes up
C)the increase in the affinity of Hb for O2 when the O2 concentration goes up
D)the decrease in affinity of Hb for O2 when the BPG concentration goes up
E)the decrease in affinity of Hb for O2 when the BPG concentration goes down
A)the decrease in affinity of Hb for O2 when the pH goes down
B)the decrease in affinity of Hb for O2 when the pH goes up
C)the increase in the affinity of Hb for O2 when the O2 concentration goes up
D)the decrease in affinity of Hb for O2 when the BPG concentration goes up
E)the decrease in affinity of Hb for O2 when the BPG concentration goes down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When the partial pressure of O2 in venous blood is 30 torr, the saturation of myoglobin with O2 is ______ while the saturation of hemoglobin with O2 is ______.
A)0.55, 0.91
B)0.91, 0.55
C)2.8 torr, 26 torr
D)0.91, 0.97
E)none of the above
A)0.55, 0.91
B)0.91, 0.55
C)2.8 torr, 26 torr
D)0.91, 0.97
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The reaction of carbonic anhydrase catalyzes
A)the formation of carbamates with the concomitant release of protons.
B)the hydration of bicarbonate, resulting in the formation of carbonic acid.
C)the reduction of carbon dioxide with the concomitant consumption of protons.
D)the hydration of carbon dioxide, forming bicarbonate and protons.
E)the hydrolysis of carbamates with the concomitant consumption of protons.
A)the formation of carbamates with the concomitant release of protons.
B)the hydration of bicarbonate, resulting in the formation of carbonic acid.
C)the reduction of carbon dioxide with the concomitant consumption of protons.
D)the hydration of carbon dioxide, forming bicarbonate and protons.
E)the hydrolysis of carbamates with the concomitant consumption of protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why is the decreased affinity of fetal hemoglobin for BPG advantageous?
A)With fewer BPG molecules bound there are more heme residues available for O2 binding.
B)Decreased BPG binding biases the fetal hemoglobin toward the R state.
C)More free BPG is available to bind to adult hemoglobin, resulting in a shift to the R state.
D)BPG is available to bind to fetal myoglobin, helping to release O2 in fetal muscle tissue.
E)none of the above
A)With fewer BPG molecules bound there are more heme residues available for O2 binding.
B)Decreased BPG binding biases the fetal hemoglobin toward the R state.
C)More free BPG is available to bind to adult hemoglobin, resulting in a shift to the R state.
D)BPG is available to bind to fetal myoglobin, helping to release O2 in fetal muscle tissue.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following increases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2?
A)an increase in BPG concentration
B)the formation of N-terminal carbamates
C)an increase in pH
D)a decrease in pH
E)an increase in CO2 concentration
A)an increase in BPG concentration
B)the formation of N-terminal carbamates
C)an increase in pH
D)a decrease in pH
E)an increase in CO2 concentration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Hill plot shows that the fourth oxygen binds to hemoglobin with a ______-fold greater affinity than the first.
A)2
B)5
C)10
D)20
E)100
A)2
B)5
C)10
D)20
E)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider a hypothetical hemoglobin-like molecule with a Hill coefficient (constant)of 1 and the same p50 value as normal hemoglobin.Choose the statement below that best describes the two proteins.
A)There is a cooperative interaction between oxygen-binding sites in both the hypothetical and normal hemoglobins.
B)The hypothetical hemoglobin has a greater oxygen affinity than normal hemoglobin.
C)The oxygen binding curve for the hypothetical hemoglobin is hyperbolic, and the curve for normal hemoglobin is sigmoidal.
D)The two hemoglobins would be able to deliver about the same amount of oxygen to the tissues.
E)At pO2 less than p50, normal hemoglobin has a greater YO2 value.
A)There is a cooperative interaction between oxygen-binding sites in both the hypothetical and normal hemoglobins.
B)The hypothetical hemoglobin has a greater oxygen affinity than normal hemoglobin.
C)The oxygen binding curve for the hypothetical hemoglobin is hyperbolic, and the curve for normal hemoglobin is sigmoidal.
D)The two hemoglobins would be able to deliver about the same amount of oxygen to the tissues.
E)At pO2 less than p50, normal hemoglobin has a greater YO2 value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Hemerythrin and hemocyanin are:
A)human mutant hemoglobins with decreased oxygen affinity.
B)hemoglobin variants that are found in animals at high altitude.
C)synthetic derivatives of hemoglobin's heme group used in artificial blood substitutes.
D)oxygen transport proteins found in invertebrates.
E)tetrameric hemoglobin derivatives containing only -chains ( 4 tetramers).
A)human mutant hemoglobins with decreased oxygen affinity.
B)hemoglobin variants that are found in animals at high altitude.
C)synthetic derivatives of hemoglobin's heme group used in artificial blood substitutes.
D)oxygen transport proteins found in invertebrates.
E)tetrameric hemoglobin derivatives containing only -chains ( 4 tetramers).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Hemoglobin's p50 value is about ______ as great as myoglobin's p50 value.
A)one-tenth
B)half
C)twice
D)ten times
E)twenty times
A)one-tenth
B)half
C)twice
D)ten times
E)twenty times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements about the symmetry model of allosterism is not true?
A)the protein is an oligomer of symmetrically (or pseudosymmetrically)related subunits.
B)the oligomer can exist in two conformational states, which are in equilibrium.
C)the ligand can bind to a subunit in either conformation.
D)the molecular symmetry of the protein is conserved during the conformational change.
E)none of the above.
A)the protein is an oligomer of symmetrically (or pseudosymmetrically)related subunits.
B)the oligomer can exist in two conformational states, which are in equilibrium.
C)the ligand can bind to a subunit in either conformation.
D)the molecular symmetry of the protein is conserved during the conformational change.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
While the binding of O2 to myoglobin as a function of pO2 is described by a simple __________ curve, the binding to hemoglobin is described by a more complex ______ curve.
A)sigmoidal; hyperbolic
B)hyperbolic; sigmoidal
C)exponential; hyperbolic
D)sigmoidal; bell-shaped
E)hyperbolic; concave
A)sigmoidal; hyperbolic
B)hyperbolic; sigmoidal
C)exponential; hyperbolic
D)sigmoidal; bell-shaped
E)hyperbolic; concave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Max Perutz's investigation of the structure of hemoglobin primarily utilized_____.
A)X-ray crystallography
B)NMR spectroscopy
C)genomics
D)mass spectrometry
E)genetic engineering
A)X-ray crystallography
B)NMR spectroscopy
C)genomics
D)mass spectrometry
E)genetic engineering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which statement about actin is not true?
A)There are two actin genes, one for F-actin and one for G-actin.
B)Monomeric G-actin polymerizes to form F-actin.
C)Actin filaments are polar (the ends can be distinguished).
D)Actin can bind ATP.
E)Actin is a common protein in nonmuscle cells.
A)There are two actin genes, one for F-actin and one for G-actin.
B)Monomeric G-actin polymerizes to form F-actin.
C)Actin filaments are polar (the ends can be distinguished).
D)Actin can bind ATP.
E)Actin is a common protein in nonmuscle cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Hemoglobin S, the variant responsible for the misshapen red blood cells characteristic of the disease sickle-cell anemia, is potentially advantageous to heterozygotes because it confers some level of resistance to the disease _________.
A)rickets
B)AIDS
C)cyanosis
D)polycythemia
E)malaria
A)rickets
B)AIDS
C)cyanosis
D)polycythemia
E)malaria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Muscle contraction is directly caused by
A)structural changes in actin.
B)structural changes in myosin.
C)structural changes in the A band.
D)structural changes in the Z disk.
E)None of the above is correct.
A)structural changes in actin.
B)structural changes in myosin.
C)structural changes in the A band.
D)structural changes in the Z disk.
E)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Humoral immunity refers to that part of the immune response that is mediated by
A)T lymphocytes.
B)antibodies.
C)antigens.
D)the thymus.
E)the skin.
A)T lymphocytes.
B)antibodies.
C)antigens.
D)the thymus.
E)the skin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which statement about actin is correct?
A)Actin is expressed only in muscle.
B)Actin is expressed at low levels in most cells.
C)No known function has been described for actin in nonmuscle cells.
D)Nonmuscle cells only contain G actin.
E)Actin is the most abundant cytoplasmic protein in many cell types.
A)Actin is expressed only in muscle.
B)Actin is expressed at low levels in most cells.
C)No known function has been described for actin in nonmuscle cells.
D)Nonmuscle cells only contain G actin.
E)Actin is the most abundant cytoplasmic protein in many cell types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the statements about muscle contraction is not true?
A)During muscle contraction the sarcomere becomes shorter.
B)During muscle contraction the I band becomes shorter.
C)During muscle contraction the H zone becomes shorter.
D)During muscle contraction the A band becomes shorter
E)During muscle contraction the distance between the Z disk and the M disk becomes shorter.
A)During muscle contraction the sarcomere becomes shorter.
B)During muscle contraction the I band becomes shorter.
C)During muscle contraction the H zone becomes shorter.
D)During muscle contraction the A band becomes shorter
E)During muscle contraction the distance between the Z disk and the M disk becomes shorter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Treadmilling refers to
A)myosin heads walking along actin microfilaments.
B)actin and myosin filaments sliding along each other.
C)actin monomers moving through a microfilament from the + end to the - end.
D)synthesis and degradation of actin monomers.
E)the interactions between actin and tropomyosin.
A)myosin heads walking along actin microfilaments.
B)actin and myosin filaments sliding along each other.
C)actin monomers moving through a microfilament from the + end to the - end.
D)synthesis and degradation of actin monomers.
E)the interactions between actin and tropomyosin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements about actin is not true?
A)Actin is the most abundant cytoplasmic protein in many cell types.
B)Actin forms microfilaments in many cell types.
C)Actin plays an important role in endocytosis.
D)Actin is present only as monomers in nonmuscle cells.
E)Actin filaments are dynamic, they grow at one end and they lose subunits at the other end.
A)Actin is the most abundant cytoplasmic protein in many cell types.
B)Actin forms microfilaments in many cell types.
C)Actin plays an important role in endocytosis.
D)Actin is present only as monomers in nonmuscle cells.
E)Actin filaments are dynamic, they grow at one end and they lose subunits at the other end.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the statements about muscle contraction is correct?
A)During muscle contraction the sarcomere becomes shorter.
B)During muscle contraction the I band becomes shorter.
C)During muscle contraction the H zone becomes shorter.
D)During muscle contraction the distance between the Z disk and the M disk becomes shorter.
E)All of the answers above are correct.
A)During muscle contraction the sarcomere becomes shorter.
B)During muscle contraction the I band becomes shorter.
C)During muscle contraction the H zone becomes shorter.
D)During muscle contraction the distance between the Z disk and the M disk becomes shorter.
E)All of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In sickle-cell anemia, the negatively charged glutamic acid residue is replaced by the neutral amino acid ____________.
A)tyrosine
B)lysine
C)valine
D)adenosine
E)glycine
A)tyrosine
B)lysine
C)valine
D)adenosine
E)glycine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
During muscle contraction
A)myosin pulls actin filaments toward the M disk.
B)myosin pushes actin filaments toward the Z disk.
C)actin pulls myosin toward the Z disk.
D)actin pushes myosin toward the M disk.
E)All of the answers above are correct.
A)myosin pulls actin filaments toward the M disk.
B)myosin pushes actin filaments toward the Z disk.
C)actin pulls myosin toward the Z disk.
D)actin pushes myosin toward the M disk.
E)All of the answers above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What are the main bonds or forces that stabilize the dimer formed by two myosin heavy chains?
A)hydrophobic interactions
B)hydrogen-bonds
C)ionic interactions
D)disulfide bonds
E)isopeptide bonds
A)hydrophobic interactions
B)hydrogen-bonds
C)ionic interactions
D)disulfide bonds
E)isopeptide bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Muscle contraction is triggered
A)in response to an increase in the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration.
B)in response to a decrease in the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration.
C)in response to an increase in the cytoplasmic cAMP concentration.
D)in response to a decrease in the cytoplasmic cAMP concentration.
E)in response to an increase in the cytoplasmic titin concentration.
A)in response to an increase in the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration.
B)in response to a decrease in the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration.
C)in response to an increase in the cytoplasmic cAMP concentration.
D)in response to a decrease in the cytoplasmic cAMP concentration.
E)in response to an increase in the cytoplasmic titin concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Humoral immunity is mediated by soluble molecules.Which cell type produces the soluble molecules that carry out the humoral immunity?
A)T cells
B)B cells
C)macrophages
D)neutrophils
E)monocytes
A)T cells
B)B cells
C)macrophages
D)neutrophils
E)monocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which statement about myosin is not true?
A)Myosin is a heterohexamer.
B)Myosin contains two globular heads.
C)Myosin contains six different polypeptides
D)Myosin aggregates to form thick filaments
E)All of the answers above are true of myosin.
A)Myosin is a heterohexamer.
B)Myosin contains two globular heads.
C)Myosin contains six different polypeptides
D)Myosin aggregates to form thick filaments
E)All of the answers above are true of myosin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The energy needed to drive muscle contraction comes from ATP hydrolysis that is carried out by
A)G-actin.
B)F-actin.
C)myosin heads.
D)myosin tails.
E)tropomyosin.
A)G-actin.
B)F-actin.
C)myosin heads.
D)myosin tails.
E)tropomyosin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How many different classes of antibodies are produced by the human immune system?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
______of the world's human population carries an inherited variant hemoglobin gene.
A)5%
B)25%
C)50%
D)75%
E)90%
A)5%
B)25%
C)50%
D)75%
E)90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
During muscle contraction myosin heads
A)walk along thick filaments toward the M disk.
B)walk along thick filaments toward the Z disk.
C)walk along thin filaments toward the M disk.
D)walk along the thin filaments toward the H zone.
E)walk along the thin filaments toward the Z disk.
A)walk along thick filaments toward the M disk.
B)walk along thick filaments toward the Z disk.
C)walk along thin filaments toward the M disk.
D)walk along the thin filaments toward the H zone.
E)walk along the thin filaments toward the Z disk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Muscle contraction is directly caused by
A)structural changes in actin.
B)structural changes in myosin.
C)thick and thin filaments sliding past each other.
D)structural changes in the Z disk.
E)None of the above is correct.
A)structural changes in actin.
B)structural changes in myosin.
C)thick and thin filaments sliding past each other.
D)structural changes in the Z disk.
E)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Fab fragments can be generated by
A)reduction of IgG molecules.
B)oxidation of IgG molecules.
C)limited digestion of IgG molecules with papain.
D)combining two light chains.
E)combining two heavy chains.
A)reduction of IgG molecules.
B)oxidation of IgG molecules.
C)limited digestion of IgG molecules with papain.
D)combining two light chains.
E)combining two heavy chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which statement about antigen-binding sites in antibodies is false?
A)An antigen-binding site on an IgG is formed by the amino-terminal ~110 amino acids of a light chain and the amino terminal ~110 amino acids of a heavy chain.
B)An antigen-binding site on an IgG is formed by the variable region of a light chain and the variable region of a heavy chain.
C)The antigen-binding site is composed of two Ig folds.
D)Antigen-binding specificity is determined by the sequences of the hypervariable sequences in both the light chain and the heavy chain.
E)Antigen binding specificity is determined exclusively by the sequences in the carboxy-terminal ~110 amino acids in the light chain and the heavy chain.
A)An antigen-binding site on an IgG is formed by the amino-terminal ~110 amino acids of a light chain and the amino terminal ~110 amino acids of a heavy chain.
B)An antigen-binding site on an IgG is formed by the variable region of a light chain and the variable region of a heavy chain.
C)The antigen-binding site is composed of two Ig folds.
D)Antigen-binding specificity is determined by the sequences of the hypervariable sequences in both the light chain and the heavy chain.
E)Antigen binding specificity is determined exclusively by the sequences in the carboxy-terminal ~110 amino acids in the light chain and the heavy chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Myoglobin is an oxygen binding protein in muscle.Describe in one sentence the overall structure of myoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Mammals and other animals have a circulatory system because diffusion is to slow to supply the tissues with oxygen in animals that are larger than 2 millimeter.Explain in one sentence why these circulatory systems contain hemoglobin or other oxygen binding proteins?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
IgG is one of five classes of antibodies that can be produced by our immune system.IgGs have a molecular mass of approximately 150 kDa, what is their subunit composition?
A)2 light chains and 2 heavy chains
B)2 light chains, 2 heavy chains, and a J chain
C)4 light chains, 4 heavy chains, and a J chain
D)6 light chains, 6 heavy chains, and a J chain
E)10 light chains, 10 heavy chains , and a J chain.
A)2 light chains and 2 heavy chains
B)2 light chains, 2 heavy chains, and a J chain
C)4 light chains, 4 heavy chains, and a J chain
D)6 light chains, 6 heavy chains, and a J chain
E)10 light chains, 10 heavy chains , and a J chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
It appears that the heme group in myoglobin binds the O2.What is the function of the polypeptide?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The Ig fold can be described as a
A)globular fold composed of helices.
B)a globular fold composed of a four helix bundle.
C)a globular fold composed of a sandwich.
D)a globular fold composed of barrel.
E)a coiled-coil.
A)globular fold composed of helices.
B)a globular fold composed of a four helix bundle.
C)a globular fold composed of a sandwich.
D)a globular fold composed of barrel.
E)a coiled-coil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How many antigen-binding sites are present on an IgM molecule?
A)2
B)4
C)10
D)16
E)25
A)2
B)4
C)10
D)16
E)25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The graph below shows the O2-binding curves for myoglobin (Mb)and hemoglobin (Hb).
a.Label the two curves (indicate which one represents Mb and which one represents Hb).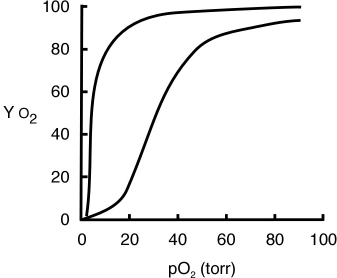 b.Use the graph to determine the Kd of myoglobin for O2 (show your approach).
b.Use the graph to determine the Kd of myoglobin for O2 (show your approach).
c.What is the difference between myoglobin and hemoglobin that cause the O2-binding curves to so be different?
d.Why is it important that hemoglobin has these particular O2-binding characteristics?
a.Label the two curves (indicate which one represents Mb and which one represents Hb).
 b.Use the graph to determine the Kd of myoglobin for O2 (show your approach).
b.Use the graph to determine the Kd of myoglobin for O2 (show your approach).c.What is the difference between myoglobin and hemoglobin that cause the O2-binding curves to so be different?
d.Why is it important that hemoglobin has these particular O2-binding characteristics?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the primary physiological function of myoglobin in most mammals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
How many antigen-binding sites are present on an IgG molecule?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
You have been studying O2 binding to a hemerythrin-like protein isolated from an exotic marine worm.Your O2-binding data are shown in the table below.
a.Use the data to generate an O2-binding curve (do not forget to mark the axes).
b.Use the curve to estimate the Kd for the interaction.
c.Is there any evidence from your data that this hemoglobin-like protein binds O2 in a cooperative manner (briefly explain your answer)?
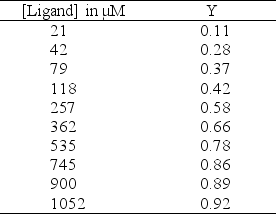
a.Use the data to generate an O2-binding curve (do not forget to mark the axes).
b.Use the curve to estimate the Kd for the interaction.
c.Is there any evidence from your data that this hemoglobin-like protein binds O2 in a cooperative manner (briefly explain your answer)?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
IgG is the most common immunoglobulin in the circulatory system and in the extravascular fluid.It is composed of two light chains and two heavy chains.What is the approximate molecular mass of an IgG molecule?
A)23 kDa
B)75 kDa
C)150 kDa
D)360 kDa
E)950 kDa
A)23 kDa
B)75 kDa
C)150 kDa
D)360 kDa
E)950 kDa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which class of antibodies has been implicated in allergic reactions?
A)IgA
B)IgD
C)IgE
D)IgG
E)IgM
A)IgA
B)IgD
C)IgE
D)IgG
E)IgM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



