Deck 14: Introduction to Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Introduction to Metabolism
1
Consider the following metabolic reaction:
Succinyl-CoA + Acetoacetate Acetoacetyl-CoA + Succinate G°' = -1.25 kJ/mol
What is the Keq for this reaction at 25°C?
A)1.66
B)0.602
C)1.00
D)4.22 x 102
E)3.21
Succinyl-CoA + Acetoacetate Acetoacetyl-CoA + Succinate G°' = -1.25 kJ/mol
What is the Keq for this reaction at 25°C?
A)1.66
B)0.602
C)1.00
D)4.22 x 102
E)3.21
1.66
2
Matching
Prokaryotes that are able to synthesize all of their cellular components from simple molecules such as CO2, H2O, NH3, and H2S are called ______.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)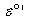
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’
Prokaryotes that are able to synthesize all of their cellular components from simple molecules such as CO2, H2O, NH3, and H2S are called ______.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)
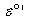
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’
autotrophs
3
Consider the following metabolic reaction:
2-Phosphoglycerate 3-Phosphoglycerate G°' = −4.40 kJ/mol
What can be said about this reaction when the concentration of 2-phosphoglycerate is 0.490 mM and the concentration of 3-phosphoglycerate is 2.90 mM at 25°C?
I.This reaction is endergonic under these conditions.
II.This reaction is exergonic under these conditions.
III.This reaction is at equilibrium under these conditions.
IV.This reaction is not favorable under standard conditions.
A)I, IV
B)II only
C)III only
D)IV only
E)None of the above
2-Phosphoglycerate 3-Phosphoglycerate G°' = −4.40 kJ/mol
What can be said about this reaction when the concentration of 2-phosphoglycerate is 0.490 mM and the concentration of 3-phosphoglycerate is 2.90 mM at 25°C?
I.This reaction is endergonic under these conditions.
II.This reaction is exergonic under these conditions.
III.This reaction is at equilibrium under these conditions.
IV.This reaction is not favorable under standard conditions.
A)I, IV
B)II only
C)III only
D)IV only
E)None of the above
III only
4
Consider the following metabolic reaction:
Succinyl-CoA + Acetoacetate Acetoacetyl-CoA + Succinate G°' = -1.25 kJ/mol
This reaction is
A)favorable under standard conditions.
B)not favorable under standard conditions.
C)nonspontaneous as written regardless of reactant concentrations
D)spontaneous as written only when [succinate] and [acetoacetyl-CoA] are high.
E)favorability of this reaction as written depends on temperature and reactant concentrations
Succinyl-CoA + Acetoacetate Acetoacetyl-CoA + Succinate G°' = -1.25 kJ/mol
This reaction is
A)favorable under standard conditions.
B)not favorable under standard conditions.
C)nonspontaneous as written regardless of reactant concentrations
D)spontaneous as written only when [succinate] and [acetoacetyl-CoA] are high.
E)favorability of this reaction as written depends on temperature and reactant concentrations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Given that the standard reduction potential of oxaloacetate is -0.166 V and the standard reduction potential of NAD+ is -0.315 V.What is the °' for the oxidation of malate by NAD+:
Malate + NAD+ Oxaloacetate + NADH + H+
A)-4.81 V
B)+ 4.81 V
C)-0.149 V
D)+0.149 V
E)+0.052 V
Malate + NAD+ Oxaloacetate + NADH + H+
A)-4.81 V
B)+ 4.81 V
C)-0.149 V
D)+0.149 V
E)+0.052 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Matching
The standard reduction potential under biochemical standard state conditions is symbolized as ______.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)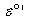
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’
The standard reduction potential under biochemical standard state conditions is symbolized as ______.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)
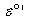
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the numbered arrows in the figure points toward a high-energy phosphoanhydride bond? 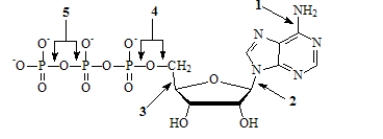
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Matching
A metabolic reaction resulting in the formation of FADH2 is an example of a(n)___ reaction.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)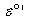
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’
A metabolic reaction resulting in the formation of FADH2 is an example of a(n)___ reaction.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)
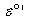
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the choices correctly ranks the following compounds from lowest level of oxidation to highest level of oxidation? 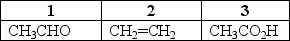
A)1< 2< 3
B)2< 1< 3
C)1< 3< 2
D)3< 2< 1
E)2< 3< 1
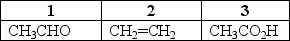
A)1< 2< 3
B)2< 1< 3
C)1< 3< 2
D)3< 2< 1
E)2< 3< 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Matching
The enzyme ______ catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP to AMP.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)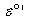
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’
The enzyme ______ catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP to AMP.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)
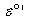
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider the following metabolic reaction: Succinyl-CoA + Acetoacetate Acetoacetyl-CoA + Succinate G°' = -1.25 kJ/mol
The G°' for the hydrolysis of Succinyl-CoA is -33.9 kJ/mol.What is the G°' for the hydrolysis of Acetoacetyl-CoA: Acetoacetyl-CoA Acetoacetate + CoA
A)-35.2 kJ/mol
B)-32.7 kJ/mol
C)+32.7 kJ/mol
D)+35.2 kJ/mol
E)none of the above
The G°' for the hydrolysis of Succinyl-CoA is -33.9 kJ/mol.What is the G°' for the hydrolysis of Acetoacetyl-CoA: Acetoacetyl-CoA Acetoacetate + CoA
A)-35.2 kJ/mol
B)-32.7 kJ/mol
C)+32.7 kJ/mol
D)+35.2 kJ/mol
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Matching
Organisms that require oxygen for nutrient breakdown are called ______.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)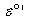
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’
Organisms that require oxygen for nutrient breakdown are called ______.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)
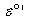
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Matching
The study of the complete set of proteins synthesized in the cell in response to changing conditions is called ______.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)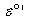
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’
The study of the complete set of proteins synthesized in the cell in response to changing conditions is called ______.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)
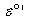
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The Keq is 0.503 at 25°C for the following reaction.What is the G°' for this reaction?
D-Glucose-6-phosphate D-Fructose-6-phosphate G°'= ?
A)-2.87 × 103 J/mol
B)+1.70 kJ/mol
C)+143 J/mol
D)The G°' cannot be determined with the given information.
E)The G°' can be determined with the given information but the correct answer is not shown.
D-Glucose-6-phosphate D-Fructose-6-phosphate G°'= ?
A)-2.87 × 103 J/mol
B)+1.70 kJ/mol
C)+143 J/mol
D)The G°' cannot be determined with the given information.
E)The G°' can be determined with the given information but the correct answer is not shown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Matching
-The enzyme ______ catalyzes the reaction, PPi 2 Pi.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)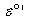
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’
-The enzyme ______ catalyzes the reaction, PPi 2 Pi.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)
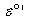
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Matching
-The reaction NADH NAD+ is an example of _____.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)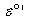
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’
-The reaction NADH NAD+ is an example of _____.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)
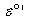
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Matching
Biomolecules are synthesized from simpler components in ______ pathways.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)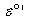
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’
Biomolecules are synthesized from simpler components in ______ pathways.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)
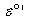
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Organisms that can grow in either the presence or absence of oxygen are classified as
A)obligate aerobes
B)facultative anaerobes
C)autotrophs
D)heterotrophs
E)obligate anaerobes
A)obligate aerobes
B)facultative anaerobes
C)autotrophs
D)heterotrophs
E)obligate anaerobes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Consider the following metabolic reaction:
3-Phosphoglycerate 2-Phosphoglycerate G°' = +4.40 kJ/mol
What is the G for this reaction when the concentration of 2-phosphoglycerate is 0.290 mM and the concentration of 3-phosphoglycerate is 2.90 mM at 37°C?
A)+10.3 kJ/mol
B)-1.53 kJ/mol
C)-1.30 kJ/mol
D)-5.93 kJ/mol
E)-4.40 kJ/mol
3-Phosphoglycerate 2-Phosphoglycerate G°' = +4.40 kJ/mol
What is the G for this reaction when the concentration of 2-phosphoglycerate is 0.290 mM and the concentration of 3-phosphoglycerate is 2.90 mM at 37°C?
A)+10.3 kJ/mol
B)-1.53 kJ/mol
C)-1.30 kJ/mol
D)-5.93 kJ/mol
E)-4.40 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Matching
1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate is an example of a(n)______.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)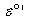
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’
1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate is an example of a(n)______.
A)anabolic
B)adenylate kinase
C)
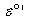
D)catabolic
E)phosphorylase kinase
F)obligate aerobes
G)acyl phosphate
H)proteomics
I)reduction
J)pyrophosphatase
K)autotrophs
L)oxidation
M)ΔG°’

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which compound is in the highest oxidation state?
A)carbon monoxide
B)carbon dioxide
C)ethanol
D)A, B, and C are equal
E)A and B are equal
A)carbon monoxide
B)carbon dioxide
C)ethanol
D)A, B, and C are equal
E)A and B are equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The conversion of triacylglycerides into fatty acids for the purpose of energy generation is an example of which of the following?
A)heterotropism
B)anaerobism
C)catabolism
D)anabolism
E)glycolysis
A)heterotropism
B)anaerobism
C)catabolism
D)anabolism
E)glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is (are)true regarding vitamins?
I.They are essential organic molecules an organism is unable to synthesize.
II.Some water soluble vitamins mediate electron-transfer reactions.
III.In humans, the water soluble vitamins converted into organic coenzymes.
IV.In humans, the fat soluble vitamins mediate group transfer reactions.
A)I, II, III, IV
B)I, II, III
C)II, III, IV
D)I only
E)II, IV
I.They are essential organic molecules an organism is unable to synthesize.
II.Some water soluble vitamins mediate electron-transfer reactions.
III.In humans, the water soluble vitamins converted into organic coenzymes.
IV.In humans, the fat soluble vitamins mediate group transfer reactions.
A)I, II, III, IV
B)I, II, III
C)II, III, IV
D)I only
E)II, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In eukaryotes, glycolysis typically occurs in the
A)mitochondrion.
B)cytosol.
C)lysosome.
D)rough endoplasmic reticulum.
E)smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
A)mitochondrion.
B)cytosol.
C)lysosome.
D)rough endoplasmic reticulum.
E)smooth endoplasmic reticulum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
______ is the most reliable systems biology approach to assess gene expression.
A)genomics
B)transcriptomics
C)proteomics
D)metabolmics
E)none of the above
A)genomics
B)transcriptomics
C)proteomics
D)metabolmics
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The enzyme inorganic pyrophosphatase catalyzes the hydrolysis of bonds in ___.
A)ATP
B)ADP
C)AMP
D)PPi
E)phosphate
A)ATP
B)ADP
C)AMP
D)PPi
E)phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the catabolic pathway major nutrients are _________ broken down resulting in the synthesis of __________ .
A)exergonically; ADP
B)endergonically; ADP
C)exergonically; ATP
D)endergonically; NADP+
E)endergonically; ATP
A)exergonically; ADP
B)endergonically; ADP
C)exergonically; ATP
D)endergonically; NADP+
E)endergonically; ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In redox half-reactions, a more positive standard reduction potential means
I.the oxidized form has a higher affinity for electrons.
II.the oxidized form has a lower affinity for electrons.
III.the reduced form has a higher affinity for electrons.
IV.the greater the tendency for the oxidized form to accept electrons.
A)I only
B)II only
C)II, III
D)I, IV
E)II, IV
I.the oxidized form has a higher affinity for electrons.
II.the oxidized form has a lower affinity for electrons.
III.the reduced form has a higher affinity for electrons.
IV.the greater the tendency for the oxidized form to accept electrons.
A)I only
B)II only
C)II, III
D)I, IV
E)II, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
While ____ is always involved in reactions that require the transfer of 2 electrons, ____ can participate in reactions that transfer either 1 or 2 electrons.
A)O2; NAD+
B)NAD+; FAD
C)NAD+; O2
D)flavin; niacin
E)FAD; NAD+
A)O2; NAD+
B)NAD+; FAD
C)NAD+; O2
D)flavin; niacin
E)FAD; NAD+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The ______ is equal to the rate of synthesis minus the rate of breakdown of the metabolic intermediates.
A)metabolic rate
B)Keq
C)rate determining step
D)flux
E)none of the above
A)metabolic rate
B)Keq
C)rate determining step
D)flux
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Obligate aerobes
A)perish under conditions with O2.
B)use oxidizing agents such as sulfate or nitrate as a primary food source.
C)resemble the earliest life forms.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)perish under conditions with O2.
B)use oxidizing agents such as sulfate or nitrate as a primary food source.
C)resemble the earliest life forms.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
ATP contains ________ bonds.
A)one phosphoanhydride and two phosphoester
B)two phosphoester and one glycosidic
C)three phosphoanhydride
D)one amide and three phosphoanhydride
E)one phosphoester and two phosphoanhydride
A)one phosphoanhydride and two phosphoester
B)two phosphoester and one glycosidic
C)three phosphoanhydride
D)one amide and three phosphoanhydride
E)one phosphoester and two phosphoanhydride

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The term "Nutrition" involves which of the following components?
I.food intake
II.metabolic utilization of food
III.the intake requirement of oxygen
IV.the control of metabolic flux
A)I only
B)II only
C)I, II
D)I, II, III
E)I, II, III, IV
I.food intake
II.metabolic utilization of food
III.the intake requirement of oxygen
IV.the control of metabolic flux
A)I only
B)II only
C)I, II
D)I, II, III
E)I, II, III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Cells control or regulate the flux through metabolic pathways by means of
I.allosteric control of enzymes.
II.covalent modification of enzymes.
III.genetic control of the concentrations of enzymes.
IV.genetic expression of allosteric effectors.
A)I, II, III, IV
B)II, III
C)I, II, IV
D)I, II, III
E)I, IV
I.allosteric control of enzymes.
II.covalent modification of enzymes.
III.genetic control of the concentrations of enzymes.
IV.genetic expression of allosteric effectors.
A)I, II, III, IV
B)II, III
C)I, II, IV
D)I, II, III
E)I, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The vitamin ______ is one of the components of coenzyme A, which is involved in _____.
A)pantothenic acid; carboxylation
B)pantothenic acid; acyl transfer
C)cobalamin; acyl transfer
D)riboflavin; carboxylation
E)niacin; electron transfer
A)pantothenic acid; carboxylation
B)pantothenic acid; acyl transfer
C)cobalamin; acyl transfer
D)riboflavin; carboxylation
E)niacin; electron transfer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Consider the following metabolic reaction important in muscle and nerve cells:
ATP + creatine phosphocreatine + ADP G°' = +12.6 kJ/mol
Under intracellular conditions, the G for the reaction, which is catalyzed by the enzyme creatine kinase, is ~0 kJ/mol.From this information we can conclude that
A)creatine kinase catalysis would not be necessary under intracellular conditions.
B)ATP has a greater phosphoryl group transfer potential compared to phosphocreatine.
C)at equilibrium, most intracellular creatine is phosphorylated.
D)the reaction operates close to equilibrium in cells.
E)None of the above is a correct conclusion.
ATP + creatine phosphocreatine + ADP G°' = +12.6 kJ/mol
Under intracellular conditions, the G for the reaction, which is catalyzed by the enzyme creatine kinase, is ~0 kJ/mol.From this information we can conclude that
A)creatine kinase catalysis would not be necessary under intracellular conditions.
B)ATP has a greater phosphoryl group transfer potential compared to phosphocreatine.
C)at equilibrium, most intracellular creatine is phosphorylated.
D)the reaction operates close to equilibrium in cells.
E)None of the above is a correct conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Acetyl-CoA contains a ____ bond which often provides the energy required for substrate-level phosphorylation.
A)phosphoester
B)phosphoanhydride
C)phosphothioester
D)ester
E)thioester
A)phosphoester
B)phosphoanhydride
C)phosphothioester
D)ester
E)thioester

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Acyl phosphates such as 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate have a ______ phosphoryl group transfer potential compared to ATP, which can be recognized by the _______ G°' values for hydrolysis.
A)greater; more positive
B)greater; more negative
C)lower; more positive
D)lower; more negative
E)none of the above
A)greater; more positive
B)greater; more negative
C)lower; more positive
D)lower; more negative
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The terminal electron acceptor in an aerobic organisms is
A)CO2.
B)NAD+.
C)FAD.
D)O2.
E)H2O.
A)CO2.
B)NAD+.
C)FAD.
D)O2.
E)H2O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following are factors that contribute to the large negative standard free energy change for the reaction shown below?
ATP ADP + Pi
A)the increase in resonance stabilization in the reactants compare to the products
B)the precipitation of the insoluble Pi
C)the addition of a water molecule to the hydrophilic ATP molecule
D)the decrease in negative charge repulsion in the products compared to reactants
E)all of the above
ATP ADP + Pi
A)the increase in resonance stabilization in the reactants compare to the products
B)the precipitation of the insoluble Pi
C)the addition of a water molecule to the hydrophilic ATP molecule
D)the decrease in negative charge repulsion in the products compared to reactants
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use the table below to rank the redox centers in order of increasing ability to produce a favorable electron flow. 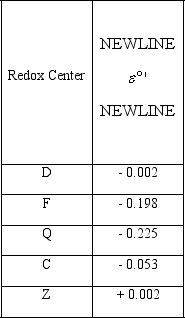
A)D, Q, F, C, Z
B)Q, F, C, D, Z
C)Z, Q, F, C, D
D)Z, F, C, D, Q
E)Z, Q, C, Q, D

A)D, Q, F, C, Z
B)Q, F, C, D, Z
C)Z, Q, F, C, D
D)Z, F, C, D, Q
E)Z, Q, C, Q, D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Negative feedback inhibition is one type of _______ metabolic control.
A)allosteric
B)hormonal
C)covalent modification
D)genetic
E)signal transduction
A)allosteric
B)hormonal
C)covalent modification
D)genetic
E)signal transduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the diagram below represents a catabolic pathway, and enzyme 1 requires NAD+, what type of reaction does enzyme 1 catalyze? 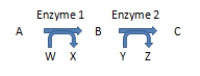
A)reduction
B)oxidation
C)isomerization
D)any of the above
E)none of the above

A)reduction
B)oxidation
C)isomerization
D)any of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A researcher is interested in determining if a long term change in the carbohydrate content of an individual's diet alters the levels of expression of carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes.Which of the following would address this question?
A)proteomics
B)DNA microarrays
C)genomics
D)lipidomics
E)none of the above
A)proteomics
B)DNA microarrays
C)genomics
D)lipidomics
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What are the correct coenzyme forms that correspond to X and Y in the following reaction as catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase?
Pyruvate + X → Lactate + Y
A)X = NADH , Y = NAD+
B)X = NADPH , Y = NADP+
C)X = NAD+ , Y = NADH
D)X = FAD , Y = FADH2
E)X = NADH , Y = NADP+
Pyruvate + X → Lactate + Y
A)X = NADH , Y = NAD+
B)X = NADPH , Y = NADP+
C)X = NAD+ , Y = NADH
D)X = FAD , Y = FADH2
E)X = NADH , Y = NADP+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following increase the phosphate transfer potential of compound?
I.electrostatic repulsion between charged groups on the reactant
II.resonance stabilization of the hydrolysis products
III.greater energy of solvation of the hydrolysis products
IV.the presence of a enol group in the reactants
A)I, II
B)I, IV
C)I, II, IV
D)II, IV
E)I, II, III, IV
I.electrostatic repulsion between charged groups on the reactant
II.resonance stabilization of the hydrolysis products
III.greater energy of solvation of the hydrolysis products
IV.the presence of a enol group in the reactants
A)I, II
B)I, IV
C)I, II, IV
D)II, IV
E)I, II, III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Compound "K" is the ultimate product of a linear metabolic pathway consisting of ten enzymatically catalyzed reactions as shown below.
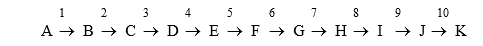
Complete the following description.
If "K" inhibits activity of enzyme "5", then enzyme "5" is under ___ control.If enzyme "3" becomes activated in response to activity of protein kinase A only when compound "A" is present, then enzyme "3" is under ___ control.If enzyme "2" is only expressed in the presence of high concentrations of "A," then enzyme "2" is under ___ control.If all of these are true, high concentrations of "__" will decrease the flux through the pathway.
A)covalent modification; allosteric; genetic; A
B)allosteric; covalent modification; genetic; K
C)genetic; allosteric; genetic; K
D)allosteric; genetic; genetic; K
E)allosteric; genetic; genetic; A
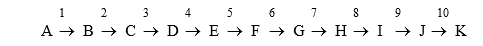
Complete the following description.
If "K" inhibits activity of enzyme "5", then enzyme "5" is under ___ control.If enzyme "3" becomes activated in response to activity of protein kinase A only when compound "A" is present, then enzyme "3" is under ___ control.If enzyme "2" is only expressed in the presence of high concentrations of "A," then enzyme "2" is under ___ control.If all of these are true, high concentrations of "__" will decrease the flux through the pathway.
A)covalent modification; allosteric; genetic; A
B)allosteric; covalent modification; genetic; K
C)genetic; allosteric; genetic; K
D)allosteric; genetic; genetic; K
E)allosteric; genetic; genetic; A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Identify the structure pictured below. 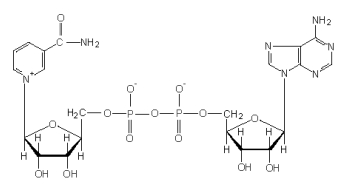
A)NAD+
B)NADH
C)FAD
D)FADH2
E)Coenzyme A (CoA)

A)NAD+
B)NADH
C)FAD
D)FADH2
E)Coenzyme A (CoA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What type of metabolic control is described in the figure below? 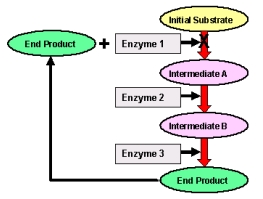
A)feed forward activation
B)product Inhibition
C)feedback Inhibition
D)hormonal control
E)signal transduction control

A)feed forward activation
B)product Inhibition
C)feedback Inhibition
D)hormonal control
E)signal transduction control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
NADH is a derivative of
A)niacin.
B)riboflavin.
C)lipoic acid.
D)thiamine.
E)vitamin A.
A)niacin.
B)riboflavin.
C)lipoic acid.
D)thiamine.
E)vitamin A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If Z = ATP formed via substrate level phosphorylation in the diagram below, which of the following compounds (represented by an uppercase letter)contains a high-energy bond? 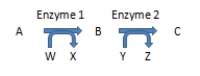
A)Compound A
B)Compound B
C)Compound C
D)All have equally high energy.
E)All have equally low energy.

A)Compound A
B)Compound B
C)Compound C
D)All have equally high energy.
E)All have equally low energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
I have discovered a new metabolic enzyme which utilizes NAD+ as a coenzyme.Which of the following could be true based on this information?
A)It is involved in a catabolic pathway.
B)It is involved in an anabolic pathway.
C)It performs acyl group transfer.
D)It catalyzes a hydrolytic cleavage.
E)It catalyzes the reduction of the enzyme's substrate.
A)It is involved in a catabolic pathway.
B)It is involved in an anabolic pathway.
C)It performs acyl group transfer.
D)It catalyzes a hydrolytic cleavage.
E)It catalyzes the reduction of the enzyme's substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



