Deck 27: Translation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 27: Translation
1
Codons that do not specify amino acids but signal the ribosome to terminate polypeptide chain elongation are termed
A)frameshifts.
B)anticodon.
C)Stop codons.
D)suppressors.
E)terminators.
A)frameshifts.
B)anticodon.
C)Stop codons.
D)suppressors.
E)terminators.
Stop codons.
2
Matching
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
The start codon is usually ______.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
The start codon is usually ______.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
AUG
3
Matching
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
At low concentrations the antibiotic ______ causes misreading of the mRNA.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
At low concentrations the antibiotic ______ causes misreading of the mRNA.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
streptomycin
4
Which of the following is a ribonucleoprotein required for the delivery of membrane and secretory proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum?
A)protein-conducting channel (PCC)
B)small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO)
C)trigger factor
D)calnexin
E)signal recognition particles (SRP)
A)protein-conducting channel (PCC)
B)small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO)
C)trigger factor
D)calnexin
E)signal recognition particles (SRP)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Matching
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
The fidelity of amino acid attachment to a tRNA is enhanced by the ______ ability of the corresponding aaRS.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
The fidelity of amino acid attachment to a tRNA is enhanced by the ______ ability of the corresponding aaRS.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Matching
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
A mutation that converts an aminoacyl-coding codon to a Stop codon is known as a ______ mutation.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
A mutation that converts an aminoacyl-coding codon to a Stop codon is known as a ______ mutation.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In E.coli, base-pairing between an mRNA's ______ and the 3 end of the 16S rRNA permits the ribosome to select the proper initiation codon, thus minimizing ______.
A)start codon; abortive initiation
B)Shine-Dalgarno sequence; abortive initiation
C)start codon; frameshift mutations
D)Shine-Dalgarno sequence; frameshift mutations
E)none of the above
A)start codon; abortive initiation
B)Shine-Dalgarno sequence; abortive initiation
C)start codon; frameshift mutations
D)Shine-Dalgarno sequence; frameshift mutations
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In E.coli, which of the following factors function to ensure the proper binding of tRNAfMet during mRNA binding and ribosomal subunit assembly?
I.IF-1
II.IF-2
III.IF-3
IV.EF-Ts
A)I only
B)I, II
C)I, III
D)II, IV
E)I, II, III
I.IF-1
II.IF-2
III.IF-3
IV.EF-Ts
A)I only
B)I, II
C)I, III
D)II, IV
E)I, II, III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Insertions or deletions of one or two nucleotides can cause
A)frameshift mutations.
B)degenerate mutations.
C)synonymous mutations.
D)wobble codons.
E)transpeptidation.
A)frameshift mutations.
B)degenerate mutations.
C)synonymous mutations.
D)wobble codons.
E)transpeptidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Matching
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
EF-Tu binds all ______ aminoacyl tRNAs but that of tRNAsec.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
EF-Tu binds all ______ aminoacyl tRNAs but that of tRNAsec.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Proteins are properly folded with the assistance of
A)protein-conducting channels (PCCs).
B)small ubiquitin-related modifiers (SUMOs).
C)trigger factors.
D)chaperones.
E)signal recognition particles (SRPs).
A)protein-conducting channels (PCCs).
B)small ubiquitin-related modifiers (SUMOs).
C)trigger factors.
D)chaperones.
E)signal recognition particles (SRPs).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Matching
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
Some proteins are synthesized as inactive precursors called ______.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
Some proteins are synthesized as inactive precursors called ______.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The thermodynamic requirement for proofreading is met by
A)aminoacyl-tRNA binding to the ribosomal A site.
B)hydrolysis of GTP by EF-Tu
C)transpeptidation mediated by IF-2.
D)transpeptidation mediated by RF-3
E)none of the above.
A)aminoacyl-tRNA binding to the ribosomal A site.
B)hydrolysis of GTP by EF-Tu
C)transpeptidation mediated by IF-2.
D)transpeptidation mediated by RF-3
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Matching
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
Almost all known tRNAs can be arranged in the so-called ______ secondary structure.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
Almost all known tRNAs can be arranged in the so-called ______ secondary structure.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Inhibitors of translation may be effective as
A)antibiotics.
B)anticancer agents.
C)research on translation.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)antibiotics.
B)anticancer agents.
C)research on translation.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Matching
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
Translation termination requires ______ that recognize Stop codons.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
Translation termination requires ______ that recognize Stop codons.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The correct amino acid is covalently attached to a tRNA by the corresponding ______ which is specific for each ______.
A)aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS); amino acid
B)aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS); species
C)elongation factor; amino acid
D)elongation factor; species
E)none of the above
A)aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS); amino acid
B)aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS); species
C)elongation factor; amino acid
D)elongation factor; species
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Matching
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
Codons that specify the same amino acid are called ______.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
Codons that specify the same amino acid are called ______.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Matching
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
The ______ is composed of three-nucleotide codons that do not overlap and are read sequentially by the protein-synthesizing machinery.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf
Choose the correct answer from the list. Not all the answers will be used.
The ______ is composed of three-nucleotide codons that do not overlap and are read sequentially by the protein-synthesizing machinery.
A)AUG
B)sense
C)release factors
D)noninitiator
E)hairpin
F)preproteins
G)genetic code
H)penicillin
I)proproteins
J)proofreading
K)UUA
L)synonyms
M)nucleotide cypher
N)streptomycin
O)nonsense
P)revising
Q)cloverleaf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The structural similarities of EF-G and the EF-Tu·tRNA complex indicate
A)EF-G may be used as a substitute for EF-Tu.
B)EF-G may play a role in displacing the tRNA growing peptide.
C)EF-G may mediate a change in conformation that facilitates EF-Tu binding.
D)EF-G may be involved in facilitating binding of initiation factors.
E)EF-G and EF-Tu are both required for proper initiation.
A)EF-G may be used as a substitute for EF-Tu.
B)EF-G may play a role in displacing the tRNA growing peptide.
C)EF-G may mediate a change in conformation that facilitates EF-Tu binding.
D)EF-G may be involved in facilitating binding of initiation factors.
E)EF-G and EF-Tu are both required for proper initiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the Shine-Dalgarno sequence?
A)It functions as a promoter sequence which recognizes and bonds the sigma factor.
B)It is part of the operator sequence used to control translation.
C)It is a nucleotide sequence involved in initiation of translation.
D)It is a nucleotide sequence involved in termination of translation.
E)none of the above
A)It functions as a promoter sequence which recognizes and bonds the sigma factor.
B)It is part of the operator sequence used to control translation.
C)It is a nucleotide sequence involved in initiation of translation.
D)It is a nucleotide sequence involved in termination of translation.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of following describes proofreading for the addition of amino acids (AAs)to the growing peptide?
A)An RNA component of the ribosome ensures that the correct AA is associated with the A site before addition occurs.
B)An RNA component of the ribosome ensures that the correct AA has been added, but before the peptidyl-tRNA is shifted to the P site.
C)The EF-Tu • GTP complex ensures that the correct AA is associated with the A site before addition occurs.
D)EF-G ensures that the correct AA has been added, but before the peptidyl-tRNA is shifted to the P -site.
E)No proofreading of this process occurs.
A)An RNA component of the ribosome ensures that the correct AA is associated with the A site before addition occurs.
B)An RNA component of the ribosome ensures that the correct AA has been added, but before the peptidyl-tRNA is shifted to the P site.
C)The EF-Tu • GTP complex ensures that the correct AA is associated with the A site before addition occurs.
D)EF-G ensures that the correct AA has been added, but before the peptidyl-tRNA is shifted to the P -site.
E)No proofreading of this process occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is NOT a feature of tRNA structure?
A)acceptor or amino acid stem
B)D arm
C)anticodon loop
D)3 terminal phosphate arm
E)variable arm
A)acceptor or amino acid stem
B)D arm
C)anticodon loop
D)3 terminal phosphate arm
E)variable arm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Class I and Class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases differ in their
I.structural motifs.
II.anticodon recognition.
III.site of aminoacylation.
IV.amino acid specificity.
A)I only
B)II, III
C)II, IV
D)II only
E)I, II, III, IV
I.structural motifs.
II.anticodon recognition.
III.site of aminoacylation.
IV.amino acid specificity.
A)I only
B)II, III
C)II, IV
D)II only
E)I, II, III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which linkage best describes the covalent bond between an amino acid (AA)and its cognate tRNA?
A)amino group of AA linked to 5' -OH of tRNA
B)amino group of AA linked to 5' phosphate of tRNA
C)carboxyl group of AA linked to 3' -OH of tRNA
D)carboxyl group of AA linked to 3' phosphate of tRNA
E)none of the above
A)amino group of AA linked to 5' -OH of tRNA
B)amino group of AA linked to 5' phosphate of tRNA
C)carboxyl group of AA linked to 3' -OH of tRNA
D)carboxyl group of AA linked to 3' phosphate of tRNA
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
During translation, translocation of the ribosome is driven by which of the following?
A)ATP → ADP + Pi
B)ATP → AMP + PPi
C)GTP → GDP + Pi
D)GTP → GMP + PPi
E)Release of the tRNA in the P site
A)ATP → ADP + Pi
B)ATP → AMP + PPi
C)GTP → GDP + Pi
D)GTP → GMP + PPi
E)Release of the tRNA in the P site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Polypeptide synthesis
A)proceeds from the C-terminus to the N-terminus.
B)proceeds from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
C)proceeds in both directions simultaneously.
D)proceeds in either direction once initiated.
E)proceeds randomly.
A)proceeds from the C-terminus to the N-terminus.
B)proceeds from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
C)proceeds in both directions simultaneously.
D)proceeds in either direction once initiated.
E)proceeds randomly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is NOT associated with eukaryotic translation initiation?
A)Shine-Dalgarno sequence
B)a formylated Met−tRNAfmet
C)base pairing between the mRNA and 16S rRNA
D)initiation factors IF-1, IF-2, and IF-3
E)all of the above
A)Shine-Dalgarno sequence
B)a formylated Met−tRNAfmet
C)base pairing between the mRNA and 16S rRNA
D)initiation factors IF-1, IF-2, and IF-3
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The signal recognition particle (SRP)is a _____, and its function is to ______.
A)DNA:protein complex, transport proteins into the eukaryotic nucleus
B)multisubunit protein, modify proteins
C)ribosome complex, catalyze posttranslational modification
D)ribonucleoprotein, bind the N-terminal end of growing polypeptides for membrane translocation
E)none of the above
A)DNA:protein complex, transport proteins into the eukaryotic nucleus
B)multisubunit protein, modify proteins
C)ribosome complex, catalyze posttranslational modification
D)ribonucleoprotein, bind the N-terminal end of growing polypeptides for membrane translocation
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The steps required for peptide elongation at the ribosome are, respectively,
A)initiation, elongation and termination.
B)decoding, transpeptidation, and translocation.
C)initiation, elongation, and release.
D)aa-tRNA binding, GTP-peptidation, and translocation.
E)none of the above
A)initiation, elongation and termination.
B)decoding, transpeptidation, and translocation.
C)initiation, elongation, and release.
D)aa-tRNA binding, GTP-peptidation, and translocation.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following best describes the method used for error minimization or proofreading to ensure the correct charging of the tRNAs?
A)The enzymes catalyzing the addition always proofread after the first step.
B)The enzymes catalyzing the addition always proofread after the second step.
C)Some of the enzymes catalyzing the addition proofread after the first step, some after the second.
D)Ribosomes themselves proofread the linkage when the AA-tRNA reaches the A site.
E)No proofreading of this process occurs.
A)The enzymes catalyzing the addition always proofread after the first step.
B)The enzymes catalyzing the addition always proofread after the second step.
C)Some of the enzymes catalyzing the addition proofread after the first step, some after the second.
D)Ribosomes themselves proofread the linkage when the AA-tRNA reaches the A site.
E)No proofreading of this process occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The triplet code allows many amino acids to be specified by more than one codon.Such a code is said to be
A)replicative.
B)synonymous.
C)duplicative.
D)universal.
E)degenerate.
A)replicative.
B)synonymous.
C)duplicative.
D)universal.
E)degenerate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following best describes the preparation of fMet-tRNAfmet for translation in prokaryotes?
A)Met is first formylated, then added to a tRNA specific for the start codon that differs from that designed to carry Met.
B)Met is first added to a tRNA specific for the start codon that differs from that designed to carry Met, then is formylated.
C)Met is first formylated, then added to a "regular" tRNA; the fact that it has the formyl group allows use in the initiation codon.
D)Met is first added to a "regular" tRNA, then is formylated; the fact that it has the formyl group allows use in the initiation codon.
E)f-Met isn't used in prokaryotes, only in eukaryotes.
A)Met is first formylated, then added to a tRNA specific for the start codon that differs from that designed to carry Met.
B)Met is first added to a tRNA specific for the start codon that differs from that designed to carry Met, then is formylated.
C)Met is first formylated, then added to a "regular" tRNA; the fact that it has the formyl group allows use in the initiation codon.
D)Met is first added to a "regular" tRNA, then is formylated; the fact that it has the formyl group allows use in the initiation codon.
E)f-Met isn't used in prokaryotes, only in eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Posttranslational modifications to proteins include all of the following, except
A)glycosylation.
B)phosphorylation.
C)amino acid derivatization.
D)peptide joining.
E)proteolysis.
A)glycosylation.
B)phosphorylation.
C)amino acid derivatization.
D)peptide joining.
E)proteolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of following best describes the process for attachment of amino acid to the appropriate tRNAs? (Note: AA = amino acid, Pi = phosphate, PPi = pyrophosphate)
A)AA + ATP → AA-P + ADP then AA-P + tRNA → AA-tRNA + Pi
B)AA + ATP → AA-AMP + PPi thenAA-AMP + tRNA → AA-tRNA + AMP
C)tRNA + ATP → tRNA-P + ADP then tRNA-P + AA → AA-tRNA + Pi
D)tRNA + ATP → tRNA-AMP + PPi then tRNA-AMP + AA → AA-tRNA + AMP
E)AA + GTP → AA-GMP + PPi then AA-GMP + tRNA → AA-tRNA + GMP
A)AA + ATP → AA-P + ADP then AA-P + tRNA → AA-tRNA + Pi
B)AA + ATP → AA-AMP + PPi thenAA-AMP + tRNA → AA-tRNA + AMP
C)tRNA + ATP → tRNA-P + ADP then tRNA-P + AA → AA-tRNA + Pi
D)tRNA + ATP → tRNA-AMP + PPi then tRNA-AMP + AA → AA-tRNA + AMP
E)AA + GTP → AA-GMP + PPi then AA-GMP + tRNA → AA-tRNA + GMP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Based on the structure shown below, which of the following correctly represents the sequence that would be present at the "XYZ" position? 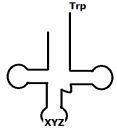
A)UGG
B)TGG
C)ACC
D)Cannot be determined from the given data.
E)None of the above is the correct sequence.

A)UGG
B)TGG
C)ACC
D)Cannot be determined from the given data.
E)None of the above is the correct sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following correctly describes the sequence of events in formation of the ribosome assembly and associated RNAs and proteins?
A)small ribosome subunit associates with large subunit; mRNA associates next; IF with bound NTP brings in first f-Met-tRNA; IF then hydrolyses bound NTP.
B)IF with bound NTP binds f-Met-tRNA; small ribosome subunit associates next; mRNA associates next; then large subunit; IF then hydrolyses bound NTP.
C)small subunit associates with mRNA; IF w/ bound NTP brings in first f-Met-tRNA; IF then hydrolyses bound NTP; large subunit associates
D)large subunit associates with mRNA; IF w/ bound NTP brings in first f-Met-tRNA; small subunit associates; IF then hydrolyses bound NTP.
E)none of the above
A)small ribosome subunit associates with large subunit; mRNA associates next; IF with bound NTP brings in first f-Met-tRNA; IF then hydrolyses bound NTP.
B)IF with bound NTP binds f-Met-tRNA; small ribosome subunit associates next; mRNA associates next; then large subunit; IF then hydrolyses bound NTP.
C)small subunit associates with mRNA; IF w/ bound NTP brings in first f-Met-tRNA; IF then hydrolyses bound NTP; large subunit associates
D)large subunit associates with mRNA; IF w/ bound NTP brings in first f-Met-tRNA; small subunit associates; IF then hydrolyses bound NTP.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The site on the ribosome complex which binds the new incoming amino acid- tRNA is called the
A)P site.
B)A site.
C)E site.
D)50 S site.
E)30 S site.
A)P site.
B)A site.
C)E site.
D)50 S site.
E)30 S site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
During translation, the reaction catalyzed by peptidyl transferase is coupled to which of the following?
A)ATP → ADP + Pi
B)ATP → AMP + PPi
C)GTP → GDP + Pi
D)GTP → GMP + PPi
E)Release of the tRNA in the P site
A)ATP → ADP + Pi
B)ATP → AMP + PPi
C)GTP → GDP + Pi
D)GTP → GMP + PPi
E)Release of the tRNA in the P site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What happens when a stop codon is reached by a ribosome?
A)A termination tRNAter binds to the codon and is used to release the growing peptide from the P site tRNA.The ribosome then is likely to dissociate.
B)A termination tRNAter binds to the codon and the growing peptide is transferred to it.When the peptidyl-tRNAter reaches the P site, the ribosome is signaled to release the protein.The ribosome then is likely to dissociate.
C)A termination tRNAter binds to the codon and the growing peptide is transferred to it.When the peptidyl-tRNAter reaches the P site, the ribosome dissociates.A separate peptidyl transferase then releases the protein from tRNAter.
D)A release factor binds to the codon and is used to release the growing peptide from the P site tRNA.
E)A release factor binds to the codon and the ribosome dissociates.A separate peptidyl transferase then releases the protein from the last tRNA to which was attached.
A)A termination tRNAter binds to the codon and is used to release the growing peptide from the P site tRNA.The ribosome then is likely to dissociate.
B)A termination tRNAter binds to the codon and the growing peptide is transferred to it.When the peptidyl-tRNAter reaches the P site, the ribosome is signaled to release the protein.The ribosome then is likely to dissociate.
C)A termination tRNAter binds to the codon and the growing peptide is transferred to it.When the peptidyl-tRNAter reaches the P site, the ribosome dissociates.A separate peptidyl transferase then releases the protein from tRNAter.
D)A release factor binds to the codon and is used to release the growing peptide from the P site tRNA.
E)A release factor binds to the codon and the ribosome dissociates.A separate peptidyl transferase then releases the protein from the last tRNA to which was attached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A mutation in the DNA sequence prior to (on the 5ꞌside of)the ATG start site will result in which of the following?
I.decreased binding efficiency of the TATA binding protein
II.decreased promoter efficiency
III.frameshift mutation
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)I, II
E)I, II, III
I.decreased binding efficiency of the TATA binding protein
II.decreased promoter efficiency
III.frameshift mutation
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)I, II
E)I, II, III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following best describes the wobble hypothesis?
I.The degree of variance in base pairing is greater at the 5' end of the anticodon, thus accounting for more than one codon.
II.The degree of variance in base pairing is greater at the 3' end of the anticodon, thus accounting for more than one codon
III.Non-Watson-Crick base pairing is sometimes allowed in the last position of the anticodon-codon pairing.
A)I only
B)II only
C)I and III
D)II and III
E)III only
I.The degree of variance in base pairing is greater at the 5' end of the anticodon, thus accounting for more than one codon.
II.The degree of variance in base pairing is greater at the 3' end of the anticodon, thus accounting for more than one codon
III.Non-Watson-Crick base pairing is sometimes allowed in the last position of the anticodon-codon pairing.
A)I only
B)II only
C)I and III
D)II and III
E)III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Structural studies of the bacterial ribosome indicate which of the following important points regarding function?
A)The domains of the 30S subunit appear flexible during protein synthesis.
B)The large subunit of the ribosome appears to undergo domain motion during protein synthesis.
C)The small and large subunits of the ribosome appear static throughout protein synthesis.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)The domains of the 30S subunit appear flexible during protein synthesis.
B)The large subunit of the ribosome appears to undergo domain motion during protein synthesis.
C)The small and large subunits of the ribosome appear static throughout protein synthesis.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is(are)used to assist in protein folding?
I.calnexin
II.calreticulin
III.DnaK
IV.GroEL
A)I, II
B)III, IV
C)II, IV
D)I, III
E)I, II, III, IV
I.calnexin
II.calreticulin
III.DnaK
IV.GroEL
A)I, II
B)III, IV
C)II, IV
D)I, III
E)I, II, III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The Shine-Dalgarno sequence is
A)used to align ribosome subunits and initiation translation.
B)functions as a stop codon.
C)is used to align RNA polymerase.
D)is used during transcription termination.
E)all of the above
A)used to align ribosome subunits and initiation translation.
B)functions as a stop codon.
C)is used to align RNA polymerase.
D)is used during transcription termination.
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A silent mutation occurs when a nucleotide mutation results in the identical amino acid in place upon completion of translation.If the original sequence is as follows, which example below represents a silent mutation?
GUACAAGCAUGAAGUUUGGUAAGCG
A)GUGCAAGCAUGAAGUUUGGUAAGCG
B)GUACAAGCAUGAAAUUUGGUAAGCG
C)GUACAAGCAUGAAGUUGGGUAAGCG
D)GUACAGGCAUGAAGUUUGGUAAGCG
E)GUACAAGCAUGAAGUUUGGUAACCG
GUACAAGCAUGAAGUUUGGUAAGCG
A)GUGCAAGCAUGAAGUUUGGUAAGCG
B)GUACAAGCAUGAAAUUUGGUAAGCG
C)GUACAAGCAUGAAGUUGGGUAAGCG
D)GUACAGGCAUGAAGUUUGGUAAGCG
E)GUACAAGCAUGAAGUUUGGUAACCG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Considering elongation of peptides via ribosome-mediated peptide synthesis, how many ATP equivalents are required for addition of on amino acid to the growing peptide chain and translocation such that the assembly is prepared for the subsequent addition of another amino acid?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The sequence steps involved in elongation of the newly synthesized protein are ordered as follows: (Note: AA=amino acid)
A)AA-tRNA binding, peptide bond formation, translocation, tRNA release.
B)translocation, AA-tRNA binding, tRNA release, peptide bond formation.
C)tRNA release, AA-tRNA binding, translocation, peptide bond formation.
D)translocation, peptide bond formation, AA-tRNA binding, tRNA release.
E)peptide bond formation, tRNA release, AA-tRNA binding, translocation.
A)AA-tRNA binding, peptide bond formation, translocation, tRNA release.
B)translocation, AA-tRNA binding, tRNA release, peptide bond formation.
C)tRNA release, AA-tRNA binding, translocation, peptide bond formation.
D)translocation, peptide bond formation, AA-tRNA binding, tRNA release.
E)peptide bond formation, tRNA release, AA-tRNA binding, translocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is a function of the ribosome?
I.bind mRNA and allow codon recognition
II.mediate the binding of proteins necessary for initiation, elongation, and termination
III.catalyze synthesis of peptide bonds
IV.translocates such that multiple codons can be read
A)I only
B)I, II
C)I, IV
D)II only
E)I, II, III, IV
I.bind mRNA and allow codon recognition
II.mediate the binding of proteins necessary for initiation, elongation, and termination
III.catalyze synthesis of peptide bonds
IV.translocates such that multiple codons can be read
A)I only
B)I, II
C)I, IV
D)II only
E)I, II, III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



