Deck 2: Demand and Supply Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Demand and Supply Analysis
1
Which of the following statements best illustrates the law of supply?
A) When the price of oil rises, the supply of automobiles falls.
B) When the price of steel falls, the supply of automobiles rises.
C) When the price of computers rises, the quantity supplied of computers rises.
D) When the price of televisions rises, the quantity supplied of televisions falls.
A) When the price of oil rises, the supply of automobiles falls.
B) When the price of steel falls, the supply of automobiles rises.
C) When the price of computers rises, the quantity supplied of computers rises.
D) When the price of televisions rises, the quantity supplied of televisions falls.
C
2
Factors that could cause a demand curve to shift to the left include all of the following except
A) a change in preferences away from the product in question.
B) an increase in the price of substitute products.
C) a growing awareness of a health risk associated with the product.
D) a decrease in the general level of income in the country.
A) a change in preferences away from the product in question.
B) an increase in the price of substitute products.
C) a growing awareness of a health risk associated with the product.
D) a decrease in the general level of income in the country.
B
3
Suppose demand is given by Qd = 400 - 15P + I, where Qd is quantity demanded, P is price and I is income. Supply is given by Qs = 5P, where Qs is quantity supplied. When I = 200, equilibrium price is
A) 15
B) 20
C) 25
D) 30
A) 15
B) 20
C) 25
D) 30
D
4
The linear demand curve is represented by the equation
A) P=Q - aP
B) Q=a - bP
C) Q=a - bP2
D) Q = AP-b
A) P=Q - aP
B) Q=a - bP
C) Q=a - bP2
D) Q = AP-b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is not a factor held constant when deriving a supply curve for ski boots?
A) The price of ski lift tickets.
B) The price of ski boots.
C) The wages of workers who make ski boots.
D) The price of skis.
A) The price of ski lift tickets.
B) The price of ski boots.
C) The wages of workers who make ski boots.
D) The price of skis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose demand is given by Qd = 500 - 15P and supply is given by Qs = 5P. If the government imposes a $30 price floor, the excess supply will be
A) 25
B) 50
C) 100
D) 150
A) 25
B) 50
C) 100
D) 150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the difference between a derived demand curve and a direct demand curve?
A) Derived demand is unknown, whereas direct demand is known.
B) Derived demand is unobservable, whereas direct demand is observable.
C) Derived demand is demand determined by the demand for another good, whereas direct demand is demand for a good itself.
D) Derived and direct demand are both terms referring to the same thing.
A) Derived demand is unknown, whereas direct demand is known.
B) Derived demand is unobservable, whereas direct demand is observable.
C) Derived demand is demand determined by the demand for another good, whereas direct demand is demand for a good itself.
D) Derived and direct demand are both terms referring to the same thing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Factors that could cause a supply curve to shift to the right include all of the following except
A) a drop in the price of inputs to the supply process.
B) an increase in the number of firms in the industry.
C) an increase in demand for the product.
D) a technological innovation that makes it cheaper to produce the product.
A) a drop in the price of inputs to the supply process.
B) an increase in the number of firms in the industry.
C) an increase in demand for the product.
D) a technological innovation that makes it cheaper to produce the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose demand is given by Qd = 400 - 15P + I, where Qd is quantity demanded, P is price and I is income. Supply is given by Qs = 5P, where Qs is quantity supplied. When I = 100, equilibrium price is
A) 15
B) 20
C) 25
D) 30
A) 15
B) 20
C) 25
D) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A relationship that shows the quantity of goods that consumers are willing to buy at different prices is the
A) elasticity
B) market demand curve
C) market supply curve
D) market equilibrium
A) elasticity
B) market demand curve
C) market supply curve
D) market equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose that the market for computers is initially in equilibrium. Further suppose that there is an increase in the price of computer software. Which of the following accurately describes the new equilibrium in the computer market?
A) The equilibrium price will rise; the equilibrium quantity will fall.
B) The equilibrium price will rise; the equilibrium quantity will rise.
C) The equilibrium price will fall; the equilibrium quantity will fall.
D) The equilibrium price will fall; the equilibrium quantity will rise.
A) The equilibrium price will rise; the equilibrium quantity will fall.
B) The equilibrium price will rise; the equilibrium quantity will rise.
C) The equilibrium price will fall; the equilibrium quantity will fall.
D) The equilibrium price will fall; the equilibrium quantity will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following would cause an unambiguous decrease in the equilibrium quantity in a market?
A) a rightward shift in supply and a rightward shift in demand.
B) a rightward shift in supply and a leftward shift in demand.
C) a leftward shift in supply and a rightward shift in demand.
D) a leftward shift in supply and a leftward shift in demand.
A) a rightward shift in supply and a rightward shift in demand.
B) a rightward shift in supply and a leftward shift in demand.
C) a leftward shift in supply and a rightward shift in demand.
D) a leftward shift in supply and a leftward shift in demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A curve that shows us the total quantity of goods that their suppliers are willing to sell at different prices is
A) Market supply curve
B) Law of supply
C) Demand curve
D) Market demand curve
A) Market supply curve
B) Law of supply
C) Demand curve
D) Market demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is not typically a factor held constant when deriving a demand curve for clothing?
A) consumer income.
B) the price of clothing.
C) the price of other goods.
D) consumer tastes.
A) consumer income.
B) the price of clothing.
C) the price of other goods.
D) consumer tastes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Suppose that the supply of apples can be represented by the following equation: Qs = 2P + 500. Further suppose that the demand for apples can be represented by the following equation: Qd = 900 - 3P. Which of the following is the equilibrium price in the market for apples?
A) 10
B) 50
C) 80
D) 100
A) 10
B) 50
C) 80
D) 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose in a market with Qd = 100 - 5P and Qs = 5P, the government imposes a price floor of $15. If the government is required to purchase any excess supply at the price floor, how much will the government have to pay to purchase the excess in this market?
A) Nothing; there is no surplus
B) $1,000
C) $1,500
D) $750
A) Nothing; there is no surplus
B) $1,000
C) $1,500
D) $750

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements best illustrates the law of demand?
A) When the price of pepperoni rises, the demand for pizza falls.
B) When the weather gets hotter, the quantity demanded of ice cream rises.
C) When the price of lemons falls, the demand for lemonade rises.
D) When the price of eggs rises, the quantity demanded of eggs falls.
A) When the price of pepperoni rises, the demand for pizza falls.
B) When the weather gets hotter, the quantity demanded of ice cream rises.
C) When the price of lemons falls, the demand for lemonade rises.
D) When the price of eggs rises, the quantity demanded of eggs falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the quantity of televisions demanded per year when the average price of a television is $100 per unit and the demand curve for televisions is represented by Qd = 3.5million - 5000P?
A) 2.5 million televisions
B) 3.0 million televisions
C) 3.2 million televisions
D) 4.0 million televisions
A) 2.5 million televisions
B) 3.0 million televisions
C) 3.2 million televisions
D) 4.0 million televisions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The law of demand states :
A) that price and quantity demanded are inversely related.
B) that price and quantity demanded are inversely related, holding all other factors that influence demand fixed.
C) that demand for a good comes from the desire of buyers to directly consume the good itself.
D) an increase in demand results in an increase in price.
A) that price and quantity demanded are inversely related.
B) that price and quantity demanded are inversely related, holding all other factors that influence demand fixed.
C) that demand for a good comes from the desire of buyers to directly consume the good itself.
D) an increase in demand results in an increase in price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose demand is given by Qd = 500 - 15P and supply is given by Qs = 5P. If the government imposes a $15 price ceiling, the excess demand will be
A) 200
B) 225
C) 250
D) 275
A) 200
B) 225
C) 250
D) 275

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose that the market for soybeans is initially in equilibrium. Further suppose that there is a decrease in the price of fertilizer. Which of the following accurately describes the new equilibrium?
A) The equilibrium price will rise; the equilibrium quantity will fall.
B) The equilibrium price will rise; the equilibrium quantity will rise.
C) The equilibrium price will fall; the equilibrium quantity will fall.
D) The equilibrium price will fall; the equilibrium quantity will rise.
A) The equilibrium price will rise; the equilibrium quantity will fall.
B) The equilibrium price will rise; the equilibrium quantity will rise.
C) The equilibrium price will fall; the equilibrium quantity will fall.
D) The equilibrium price will fall; the equilibrium quantity will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following would cause an unambiguous increase in the equilibrium price in a market?
A) a rightward shift in supply and a rightward shift in demand.
B) a rightward shift in supply and a leftward shift in demand.
C) a leftward shift in supply and a rightward shift in demand.
D) a leftward shift in supply and a leftward shift in demand.
A) a rightward shift in supply and a rightward shift in demand.
B) a rightward shift in supply and a leftward shift in demand.
C) a leftward shift in supply and a rightward shift in demand.
D) a leftward shift in supply and a leftward shift in demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose that demand is linear, Qd = 100 - 12P. At P = 5 and Q = 40, the price elasticity of demand is:
A) -2/3
B) -2
C) -12
D) -3/2
A) -2/3
B) -2
C) -12
D) -3/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose that when the price of a good is $15, the quantity demanded is 40 units, and when the price falls to $6, the quantity increases to 60 units. The price elasticity of demand near a price of $6 and a quantity of 60 can be calculated as:
A) -5/6
B) -2
C) -2/9
D) -9/2
A) -5/6
B) -2
C) -2/9
D) -9/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A measure of the rate of percentage change of quantity demanded with respect to price, holding all other determinants of demand constant is
A) Price elasticity of market equilibrium
B) Price elasticity of demand
C) Price elasticity of supply
D) Price elasticity equilibrium
A) Price elasticity of market equilibrium
B) Price elasticity of demand
C) Price elasticity of supply
D) Price elasticity equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose that the market for newspaper is initially in equilibrium. Further suppose that there is both an increase in the price of ink and a decrease in the price of magazines, which people may read in place of a newspaper. Which of the following accurately describes the new equilibrium?
A) The equilibrium price will rise; the equilibrium quantity is ambiguous.
B) The equilibrium price is ambiguous; the equilibrium quantity will fall.
C) The equilibrium price will fall; the equilibrium quantity is ambiguous.
D) The equilibrium price is ambiguous; the equilibrium quantity will rise.
A) The equilibrium price will rise; the equilibrium quantity is ambiguous.
B) The equilibrium price is ambiguous; the equilibrium quantity will fall.
C) The equilibrium price will fall; the equilibrium quantity is ambiguous.
D) The equilibrium price is ambiguous; the equilibrium quantity will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The choke price is
A) the price at which quantity supplied falls to zero.
B) the price at which quantity demanded falls to zero.
C) the price at which quantity supplied is maximized.
D) the price at which quantity demanded is maximized.
A) the price at which quantity supplied falls to zero.
B) the price at which quantity demanded falls to zero.
C) the price at which quantity supplied is maximized.
D) the price at which quantity demanded is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Indicate whether each of the following events will shift the monthly demand curve for the Ford Taurus (a midsize car) to the right, to the left, or not at all: (a) GM introduces a new line of small, fuel-efficient cars; (b) Following an agreement between the US and Japan, Japanese car manufacturers will ''voluntarily'' reduce their exports of medium sized cars to the US; (c) The cost of steel increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Eggs would typically have a
A) low elasticity of demand, probably between -1 and -2
B) low elasticity of demand, probably between 0 and -1
C) high elasticity of demand , probably between -2 and -3
D) low elasticity of demand, probably between -2 and -3
A) low elasticity of demand, probably between -1 and -2
B) low elasticity of demand, probably between 0 and -1
C) high elasticity of demand , probably between -2 and -3
D) low elasticity of demand, probably between -2 and -3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is False?
A) Rightward shift in demand + unchanged supply curve = higher equilibrium price and larger equilibrium quantity
B) Rightward shift in demand + Rightward shift in supply curve = lower equilibrium price and smaller equilibrium quantity
C) Leftward shift in supply + unchanged demand curve = higher equilibrium price and smaller equilibrium quantity
D) Leftward shift in demand + unchanged supply curve = lower equilibrium price and smaller equilibrium quantity
E) Rightward shift in supply + unchanged demand curve = lower equilibrium price and larger equilibrium quantity
A) Rightward shift in demand + unchanged supply curve = higher equilibrium price and larger equilibrium quantity
B) Rightward shift in demand + Rightward shift in supply curve = lower equilibrium price and smaller equilibrium quantity
C) Leftward shift in supply + unchanged demand curve = higher equilibrium price and smaller equilibrium quantity
D) Leftward shift in demand + unchanged supply curve = lower equilibrium price and smaller equilibrium quantity
E) Rightward shift in supply + unchanged demand curve = lower equilibrium price and larger equilibrium quantity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A simultaneous shift to the right of both supply and demand will
A) increase the equilibrium price
B) decrease the equilibrium price
C) increase the equilibrium quantity
D) decrease the equilibrium quantity
A) increase the equilibrium price
B) decrease the equilibrium price
C) increase the equilibrium quantity
D) decrease the equilibrium quantity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose that demand and supply for cookies can be written as:
Qd = 50 - P; Qs = P. Compute the equilibrium price and quantity. Now, suppose that a change in the price of cake causes demand for cookies to become:
Qd = 100 - P. Compute the new equilibrium price and quantity. What has changed?
Qd = 50 - P; Qs = P. Compute the equilibrium price and quantity. Now, suppose that a change in the price of cake causes demand for cookies to become:
Qd = 100 - P. Compute the new equilibrium price and quantity. What has changed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Price elasticity of demand measures
A) the shift in demand as price changes.
B) the sensitivity of quantity demanded to price.
C) the slope of the demand curve.
D) the relationship of percentages to price.
A) the shift in demand as price changes.
B) the sensitivity of quantity demanded to price.
C) the slope of the demand curve.
D) the relationship of percentages to price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider the demand curve Qd = 1000 - 20P - 6r. If the value of r falls, the demand curve will
A) shift to the left
B) shift to the right
C) remain unchanged
D) rotate along the quantity axis
A) shift to the left
B) shift to the right
C) remain unchanged
D) rotate along the quantity axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the demand curve Qd = 40 - 2P + 6i. If the value of i rises, the demand curve will
A) not shift at all
B) shift to the right
C) shift to the left
D) rotate so it becomes upward sloping
A) not shift at all
B) shift to the right
C) shift to the left
D) rotate so it becomes upward sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Consider the supply curve Qs = 2P and the demand curve Qd = 90 - P. Which expression best shows how you would calculate the elasticity of demand when P increases by 1 along the demand curve from its equilibrium value?
A) [(59 - 60)/ (31 - 30)] x (30/60)
B) [(56 - 60)/ (31 - 30)] x (30/60)
C) [(59 - 61)/ (31 - 30)] x (30/60)
D) [(59 - 62)/ (32 - 30)] x (30/60)
A) [(59 - 60)/ (31 - 30)] x (30/60)
B) [(56 - 60)/ (31 - 30)] x (30/60)
C) [(59 - 61)/ (31 - 30)] x (30/60)
D) [(59 - 62)/ (32 - 30)] x (30/60)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider the supply curve Qs = 40 + 2P + 6i. If the value of i rises, the supply curve will
A) not shift at all
B) shift to the right
C) shift to the left
D) rotate so it becomes upward sloping
A) not shift at all
B) shift to the right
C) shift to the left
D) rotate so it becomes upward sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A higher consumer income increases the demand for a particular good. The effect of this income on market demand usually is illustrated by
A) a rightward shift in the demand curve
B) a leftward shift in the demand curve
C) a rightward movement along the demand curve
D) a leftward movement along the demand curve.
A) a rightward shift in the demand curve
B) a leftward shift in the demand curve
C) a rightward movement along the demand curve
D) a leftward movement along the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose we postulate a linear demand curve and observe, through supply shifts, two points on the demand curve. At point A, PA = 2 and QdA = 6. At point B, PB = 4 and QdB = 2. The choke price for this demand curve is
A) 10
B) 2
C) 5
D) -2
A) 10
B) 2
C) 5
D) -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the demand curve Qd = 500P -2. If the price is 1, the elasticity of demand is
A) -0.50
B) -2
C) 500
D) -500
A) -0.50
B) -2
C) 500
D) -500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in
A) price.
B) income.
C) demand substitutes.
D) demand complements.
A) price.
B) income.
C) demand substitutes.
D) demand complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
All else equal, an increase in the price of bicycle helmets, would tend to
A) reduce the demand for cars
B) increase the demand for bicycles
C) reduce the demand for bicycles
D) cause more riders to walk to work.
A) reduce the demand for cars
B) increase the demand for bicycles
C) reduce the demand for bicycles
D) cause more riders to walk to work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The price elasticity of demand is positive when there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
B) A positive income elasticity indicates that demand for a good rises as consumer income falls.
C) A positive cross-price elasticity for two goods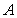 and
and
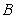 would arise if
would arise if
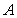 and
and
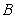 were demand complements.
were demand complements.
D) A negative cross-price elasticity for two goods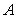 and
and
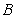 would arise if
would arise if
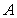 and
and
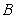 were demand complements.
were demand complements.
A) The price elasticity of demand is positive when there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
B) A positive income elasticity indicates that demand for a good rises as consumer income falls.
C) A positive cross-price elasticity for two goods
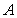 and
and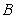 would arise if
would arise if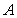 and
and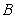 were demand complements.
were demand complements.D) A negative cross-price elasticity for two goods
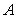 and
and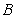 would arise if
would arise if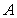 and
and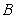 were demand complements.
were demand complements.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the elasticity of the following demand curve? QP2 = 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A cross price elasticity of demand for product with respect to the price of product of 0.3 means that
A) an increase in the price of A by 10 percent gives rise to an increase in quantity demanded of B by 3 percent.
B) an increase in the price of B by 10 percent gives rise to an increase in the quantity demanded of A by 3 percent.
C) an increase in the price of B by 10 percent gives rise to a decrease in the quantity demanded of A by 3 percent.
D) an increase in the price of A by 10 percent gives rise to a decrease in the quantity demanded of B by 3 percent.
A) an increase in the price of A by 10 percent gives rise to an increase in quantity demanded of B by 3 percent.
B) an increase in the price of B by 10 percent gives rise to an increase in the quantity demanded of A by 3 percent.
C) an increase in the price of B by 10 percent gives rise to a decrease in the quantity demanded of A by 3 percent.
D) an increase in the price of A by 10 percent gives rise to a decrease in the quantity demanded of B by 3 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suppose the cross-price elasticity for two goods is positive. The two goods are
A) normal goods
B) substitutes
C) complements
D) inferior goods
A) normal goods
B) substitutes
C) complements
D) inferior goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Along a linear demand curve, as price falls,
A) the price elasticity of demand is constant, but the slope of demand falls.
B) the price elasticity of demand approaches zero, but the slope is constant.
C) the price elasticity of demand moves away from zero.
D) the price elasticity is the same as the slope of the demand curve.
A) the price elasticity of demand is constant, but the slope of demand falls.
B) the price elasticity of demand approaches zero, but the slope is constant.
C) the price elasticity of demand moves away from zero.
D) the price elasticity is the same as the slope of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The following equations represent demand curves for a commodity, q: (i) q = 100 - p; (ii) q = 10 + p; (iii) q = 50. For each of these demands, calculate the choke price, the slope, and the price elasticities of demand in the neighborhood of q = 100 and q = 50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider the demand curve Qd = 5P -1. The elasticity of demand along this demand curve
A) is inelastic
B) is elastic
C) is unitary elastic
D) falls as the price falls
A) is inelastic
B) is elastic
C) is unitary elastic
D) falls as the price falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Why are long-run demand curves likely to be more elastic than short-run demand curves?
A) Prices tend to rise in the long-run.
B) Prices tend to be stable in the long-run.
C) Consumers have more time to adjust their purchase decisions in response to a change in price.
D) Supply tends to adjust in the long run.
A) Prices tend to rise in the long-run.
B) Prices tend to be stable in the long-run.
C) Consumers have more time to adjust their purchase decisions in response to a change in price.
D) Supply tends to adjust in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If demand is elastic, an increase in price
A) will increase total revenue
B) will decrease total revenue
C) will have an indeterminate effect on total revenue
D) will decrease total profit
A) will increase total revenue
B) will decrease total revenue
C) will have an indeterminate effect on total revenue
D) will decrease total profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Identify the truthfulness of the following statements. I. Demand tends to be more price inelastic when few substitutes for a product exist.
II) Demand tends to be more price elastic when a consumer's expenditure on the product is small.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) Both I and II are false.
C) I is true; II is false.
D) I is false; II is true.
II) Demand tends to be more price elastic when a consumer's expenditure on the product is small.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) Both I and II are false.
C) I is true; II is false.
D) I is false; II is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose that the government wishes to encourage the manufacture and sale of small cars. The current supply and demand of small cars are: Qs = - 10/9 + (1/9)P; Qd = 100 - P, where Q is in millions of cars and P is in hundreds of dollars. What is the current equilibrium price and quantity of cars sold? Now, suppose that the government is considering two alternative plans for encouraging small car sales. Under Plan A, every car manufacturer will receive a $500 rebate from the government for each car sold. Under plan B, every purchaser of a small car will receive a $500 rebate from the government. Which plan, A or B, is more effective? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An income elasticity of demand for milk of 0.1 could mean that
A) as income rises by 10 percent, quantity demanded rises by 1 percent.
B) as income rises by 100 percent, quantity demanded rises by 1 percent.
C) as income rises by 20 percent, quantity demanded rises by 10 percent.
D) as income rises by 50 percent, quantity demanded rises by 25 percent.
A) as income rises by 10 percent, quantity demanded rises by 1 percent.
B) as income rises by 100 percent, quantity demanded rises by 1 percent.
C) as income rises by 20 percent, quantity demanded rises by 10 percent.
D) as income rises by 50 percent, quantity demanded rises by 25 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose demand is given by Qd = 1000 - 25P and supply is given by Qs = 75P. At the equilibrium price and quantity, the price elasticity of demand is
A) -3
B) -25
C) -1/3
D) -10
A) -3
B) -25
C) -1/3
D) -10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Of the following choices, which good should have the most inelastic price elasticity of demand?
A) Gasoline to a car owner.
B) Cigarettes to a smoker.
C) Insulin to an insulin-dependent diabetic.
D) Apples to a vegetarian.
A) Gasoline to a car owner.
B) Cigarettes to a smoker.
C) Insulin to an insulin-dependent diabetic.
D) Apples to a vegetarian.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The current price in the market for bananas is $0.10 per pound. At this price, 1 million pounds are sold per year in Small-town, U.S.A. Suppose that the price elasticity of demand is -5 and the short run price elasticity of supply is 0.05. Solve for the equations of demand and supply, assuming that demand and supply are linear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The constant elasticity demand curve is represented by the equation
A) P = Q - aP
B) Q = a - bP
C) Q = a - bP2
D) Q = AP-b
A) P = Q - aP
B) Q = a - bP
C) Q = a - bP2
D) Q = AP-b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose the cross-price elasticity for two goods is negative. The two goods are
A) normal goods
B) substitutes
C) complements
D) inferior goods
A) normal goods
B) substitutes
C) complements
D) inferior goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider the following demand and supply curves: Qd = 100 - 2P, and Qs = ½ P, calculate the equilibrium P and Q for this initial situation and assuming the demand curve changes to Qd = 100 - P. Which of the following is correct?
A) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the demand curve shifts left.
B) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the new equilibrium is P = 36, Q = 28.
C) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the new equilibrium is P = 66 2/3 and Q = 33 1/3.
D) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the demand curve shifts right.
A) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the demand curve shifts left.
B) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the new equilibrium is P = 36, Q = 28.
C) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the new equilibrium is P = 66 2/3 and Q = 33 1/3.
D) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the demand curve shifts right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between short-run supply elasticity and long-run supply elasticity?
A) For many products, long-run supply is likely to be more price elastic than short-run supply.
B) For products that can be recycled, long-run supply is likely to be more price elastic than short-run supply.
C) For many products, long-run supply is likely to be less price elastic than short-run supply.
D) Both a) and b) are generally true, but c) is generally false.
A) For many products, long-run supply is likely to be more price elastic than short-run supply.
B) For products that can be recycled, long-run supply is likely to be more price elastic than short-run supply.
C) For many products, long-run supply is likely to be less price elastic than short-run supply.
D) Both a) and b) are generally true, but c) is generally false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose that demand and supply in the market for Brazil nuts is linear, with a historic market price of $.50 per pound and 10 million pounds sold. In 2004, a news item raised health fears about the nuts. That year, the market price fell to $.45 per pound and only 8 million pounds traded. An estimate for the equation of the supply of Brazil nuts (where QS is in millions of pounds and P is in dollars) would be:
A) This information only relates to demand, and so cannot be used to generate a supply equation.
B) Qs = 30 + 40P
C) Qs = 40P
D) Qs = -10 + 40P
A) This information only relates to demand, and so cannot be used to generate a supply equation.
B) Qs = 30 + 40P
C) Qs = 40P
D) Qs = -10 + 40P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between short-run demand elasticity and long-run demand elasticity?
A) For many products, long-run demand is likely to be more price elastic than short-run demand.
B) For durable goods, long-run demand is likely to be more price elastic than short-run demand.
C) For many products, long-run demand is likely to be more price inelastic than short-run demand.
D) For most products, long-run and short-run demand elasticities are the same.
A) For many products, long-run demand is likely to be more price elastic than short-run demand.
B) For durable goods, long-run demand is likely to be more price elastic than short-run demand.
C) For many products, long-run demand is likely to be more price inelastic than short-run demand.
D) For most products, long-run and short-run demand elasticities are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
To identify a demand curve we must observe
A) many years of data.
B) shifts in the demand curve.
C) shifts in the supply curve.
D) many different markets simultaneously.
A) many years of data.
B) shifts in the demand curve.
C) shifts in the supply curve.
D) many different markets simultaneously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Consider the following demand and supply curves: Qd = 100 - 2P, and Qs = ½ P, calculate the equilibrium P and Q for this initial situation and assuming the supply curve changes to Qs = ½ P + 10. Which of the following is correct?
A) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the supply curve shifts left.
B) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the new equilibrium is P = 36, Q = 28.
C) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the new equilibrium remains the same.
D) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the new equilibrium is P = 38, Q = 28.
A) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the supply curve shifts left.
B) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the new equilibrium is P = 36, Q = 28.
C) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the new equilibrium remains the same.
D) the initial equilibrium is P = 40, Q = 20 and the new equilibrium is P = 38, Q = 28.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Let the price elasticity of demand for a soft drink be - 2. In the year 2005, the per capita consumption of soft drinks was about 500 cans per person, and the average price was $1.00 per can. If we suppose that demand for the soft drink is linear, Qd = a - bP, where a and b are constants, Qd is quantity demanded and P is price, an estimate of the demand equation could be:
A) Qd = 100 - 2P
B) Qd = 1500 - 2P
C) Qd = 1500 - 1000P
D) Qd = 1000 - 1500P
A) Qd = 100 - 2P
B) Qd = 1500 - 2P
C) Qd = 1500 - 1000P
D) Qd = 1000 - 1500P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Gasoline in the long run will generally exhibit
A) greater elasticity of demand than in the short run.
B) greater elasticity of demand that for jewelry.
C) less elasticity of demand than in the short run.
D) less elasticity of demand than with regard to insulin for diabetics.
A) greater elasticity of demand than in the short run.
B) greater elasticity of demand that for jewelry.
C) less elasticity of demand than in the short run.
D) less elasticity of demand than with regard to insulin for diabetics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following explanations supports the statement that long-run supply curves are likely to be more elastic than short-run supply curves?
A) Firms are able to adjust fixed inputs in the long-run but not in the short-run.
B) Firms are able to adjust variable inputs in the short-run.
C) Firms prefer to hire workers rather than capital.
D) Firms have more flexibility in the short-run.
A) Firms are able to adjust fixed inputs in the long-run but not in the short-run.
B) Firms are able to adjust variable inputs in the short-run.
C) Firms prefer to hire workers rather than capital.
D) Firms have more flexibility in the short-run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



