Deck 1: Introduction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Introduction
1
Inputs to a quantitative model
A)are a trivial part of the problem solving process.
B)are uncertain for a stochastic model.
C)are uncontrollable for the decision variables.
D)must all be deterministic if the problem is to have a solution.
A)are a trivial part of the problem solving process.
B)are uncertain for a stochastic model.
C)are uncontrollable for the decision variables.
D)must all be deterministic if the problem is to have a solution.
B
2
The volume that results in marginal revenue equaling marginal cost is called the break-even point.A8
False
3
In a multicriteria decision problem
A)it is impossible to select a single decision alternative.
B)the decision maker must evaluate each alternative with respect to each criterion.
C)successive decisions must be made over time.
D)each of the above is true.
A)it is impossible to select a single decision alternative.
B)the decision maker must evaluate each alternative with respect to each criterion.
C)successive decisions must be made over time.
D)each of the above is true.
B
4
The quantitative analysis approach requires
A)the manager's prior experience with a similar problem.
B)a relatively uncomplicated problem.
C)mathematical expressions for the relationships.
D)each of the above is true.
A)the manager's prior experience with a similar problem.
B)a relatively uncomplicated problem.
C)mathematical expressions for the relationships.
D)each of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The process of decision making is more limited than that of problem solving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A physical model that does not have the same physical appearance as the object being modeled is
A)an analog model.
B)an iconic model.
C)a mathematical model.
D)a qualitative model.
A)an analog model.
B)an iconic model.
C)a mathematical model.
D)a qualitative model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
George Dantzig is important in the history of management science because he developed
A)the scientific management revolution.
B)World War II operations research teams.
C)the simplex method for linear programming.
D)powerful digital computers.
A)the scientific management revolution.
B)World War II operations research teams.
C)the simplex method for linear programming.
D)powerful digital computers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identification and definition of a problem
A)cannot be done until alternatives are proposed.
B)is the first step of decision making.
C)is the final step of problem solving.
D)requires consideration of multiple criteria.
A)cannot be done until alternatives are proposed.
B)is the first step of decision making.
C)is the final step of problem solving.
D)requires consideration of multiple criteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The field of management science
A)concentrates on the use of quantitative methods to assist in decision making.
B)approaches decision making rationally,with techniques based on the scientific method.
C)is another name for decision science and for operations research.
D)each of the above is true.
A)concentrates on the use of quantitative methods to assist in decision making.
B)approaches decision making rationally,with techniques based on the scientific method.
C)is another name for decision science and for operations research.
D)each of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The volume that results in total revenue being equal to total cost is the
A)break-even point.
B)marginal volume.
C)marginal cost.
D)profit mix.
A)break-even point.
B)marginal volume.
C)marginal cost.
D)profit mix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The first step in problem solving is
A)determination of the correct analytical solution procedure.
B)definition of decision variables.
C)the identification of a difference between the actual and desired state of affairs.
D)implementation.
A)determination of the correct analytical solution procedure.
B)definition of decision variables.
C)the identification of a difference between the actual and desired state of affairs.
D)implementation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Problem definition
A)includes specific objectives and operating constraints.
B)must occur prior to the quantitative analysis process.
C)must involve the analyst and the user of the results.
D)each of the above is true.
A)includes specific objectives and operating constraints.
B)must occur prior to the quantitative analysis process.
C)must involve the analyst and the user of the results.
D)each of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A model that uses a system of symbols to represent a problem is called
A)mathematical.
B)iconic.
C)analog.
D)constrained.
A)mathematical.
B)iconic.
C)analog.
D)constrained.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When the value of the output cannot be determined even if the value of the controllable input is known,the model is
A)analog.
B)digital.
C)stochastic.
D)deterministic.
A)analog.
B)digital.
C)stochastic.
D)deterministic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Management science and operations research both involve
A)qualitative managerial skills.
B)quantitative approaches to decision making.
C)operational management skills.
D)scientific research as opposed to applications.
A)qualitative managerial skills.
B)quantitative approaches to decision making.
C)operational management skills.
D)scientific research as opposed to applications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The terms 'stochastic' and 'deterministic' have the same meaning in quantitative analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Problem solving encompasses both the identification of a problem and the action to resolve it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Decision alternatives
A)should be identified before decision criteria are established.
B)are limited to quantitative solutions
C)are evaluated as a part of the problem definition stage.
D)are best generated by brain-storming.
A)should be identified before decision criteria are established.
B)are limited to quantitative solutions
C)are evaluated as a part of the problem definition stage.
D)are best generated by brain-storming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Decision criteria
A)are the choices faced by the decision maker.
B)are the problems faced by the decision maker.
C)are the ways to evaluate the choices faced by the decision maker.
D)must be unique for a problem.
A)are the choices faced by the decision maker.
B)are the problems faced by the decision maker.
C)are the ways to evaluate the choices faced by the decision maker.
D)must be unique for a problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The decision making process includes implementation and evaluation of the decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A university schedules summer school courses based on anticipated enrollment.The cost for faculty compensation,laboratories,student services,and allocated overhead for a computer class is $8500.If students pay $420 to enroll in the course,how large would enrollment have to be for the university to break even?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
All uncontrollable inputs or data must be specified before we can analyze the model and recommend a decision or solution for the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
To find the choice that provides the highest profit and the fewest employees,apply a single-criterion decision process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If you are deciding to buy either machine A,B,or C with the objective of minimizing the sum of labor,material and utility costs,you are dealing with a single-criterion decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A toy train layout designed to represent an actual railyard is an example of an analog model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The relationship d = 5000 - 25p describes what happens to demand (d)as price (p)varies.Here,price can vary between $10 and $50.
a.How many units can be sold at the $10 price? How many can be sold at the $50 price?
b.Model the expression for total revenue.
c.Consider prices of $20,$30,and $40.Which price alternative will maximize total revenue? What are the values for demand and revenue at this price?
a.How many units can be sold at the $10 price? How many can be sold at the $50 price?
b.Model the expression for total revenue.
c.Consider prices of $20,$30,and $40.Which price alternative will maximize total revenue? What are the values for demand and revenue at this price?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Model development should be left to quantitative analysts;the model user's involvement should begin at the implementation stage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In quantitative analysis,the optimal solution is the mathematically-best solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The most successful quantitative analysis will separate the analyst from the managerial team until after the problem is fully structured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The most critical component in determining the success or failure of any quantitative approach to decision making is problem definition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An author has received an advance against royalties of $10,000.The royalty rate is $1.00 for every book sold in the United States,and $1.35 for every book sold outside the United States.Define variables for this problem and write an expression that could be used to calculate the number of books to be sold to cover the advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A feasible solution is one that satisfies at least one of the constraints in the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A snack food manufacturer buys corn for tortilla chips from two cooperatives,one in Iowa and one in Illinois.The price per unit of the Iowa corn is $6.00 and the price per unit of the Illinois corn is $5.50.
a.Define variables that would tell how many units to purchase from each source.
b.Develop an objective function that would minimize the total cost.
c.The manufacturer needs at least 12000 units of corn.The Iowa cooperative can supply up to 8000 units,and the Illinois cooperative can supply at least 6000 units.Develop constraints for these conditions.
a.Define variables that would tell how many units to purchase from each source.
b.Develop an objective function that would minimize the total cost.
c.The manufacturer needs at least 12000 units of corn.The Iowa cooperative can supply up to 8000 units,and the Illinois cooperative can supply at least 6000 units.Develop constraints for these conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Uncontrollable inputs are the decision variables for a model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The feasible solution is the best solution possible for a mathematical model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The first step in the decision making process is to identify the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Frederick Taylor is credited with forming the first MS/OR interdisciplinary teams in the 1940's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The value of any model is that it enables the user to make inferences about the real situation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
There is a fixed cost of $50,000 to start a production process.Once the process has begun,the variable cost per unit is $25.The revenue per unit is projected to be $45.
a.Write an expression for total cost.
b.Write an expression for total revenue.
c.Write an expression for total profit.
d.Find the break-even point.
a.Write an expression for total cost.
b.Write an expression for total revenue.
c.Write an expression for total profit.
d.Find the break-even point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A company seeks to maximize profit subject to limited availability of man-hours.Man-hours is a controllable input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A small firm builds television antennas.The investment in plan and equipment is $200,000.The variable cost per television antenna is $500.The price of the television antenna is $1000.How many television antennas would be needed for the firm to break even?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider a department store that must make weekly shipments of a certain product from two different warehouses to four different stores.
a.How could a quantitative approach to decision making be used to solve this problem?
b.What would be the uncontrollable inputs for which data must be gathered?
c.What would be the decision variables of the mathematical model? the objective function? the constraints?
d.Is the model deterministic or stochastic?
e.Suggest assumptions that could be made to simplify the model.
a.How could a quantitative approach to decision making be used to solve this problem?
b.What would be the uncontrollable inputs for which data must be gathered?
c.What would be the decision variables of the mathematical model? the objective function? the constraints?
d.Is the model deterministic or stochastic?
e.Suggest assumptions that could be made to simplify the model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
As part of their application for a loan to buy Lakeside Farm,a property they hope to develop as a bed-and-breakfast operation,the prospective owners have projected:
Monthly fixed cost (loan payment,taxes,insurance,maintenance)$6000
Variable cost per occupied room per night $ 20
Revenue per occupied room per night $ 75
a.Write the expression for total cost per month.Assume 30 days per month.
b.Write the expression for total revenue per month.
c.If there are 12 guest rooms available,can they break even? What percentage of rooms would need to be occupied,on average,to break even?
Monthly fixed cost (loan payment,taxes,insurance,maintenance)$6000
Variable cost per occupied room per night $ 20
Revenue per occupied room per night $ 75
a.Write the expression for total cost per month.Assume 30 days per month.
b.Write the expression for total revenue per month.
c.If there are 12 guest rooms available,can they break even? What percentage of rooms would need to be occupied,on average,to break even?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A furniture store has set aside 800 square feet to display its sofas and chairs.Each sofa utilizes 50 sq.ft.and each chair utilizes 30 sq.ft.At least five sofas and at least five chairs are to be displayed.
a.Write a mathematical model representing the store's constraints.
b.Suppose the profit on sofas is $200 and on chairs is $100.On a given day,the probability that a displayed sofa will be sold is .03 and that a displayed chair will be sold is .05.Mathematically model each of the following objectives:
1. Maximize the total pieces of furniture displayed.
2. Maximize the total expected number of daily sales.
3. Maximize the total expected daily profit.
a.Write a mathematical model representing the store's constraints.
b.Suppose the profit on sofas is $200 and on chairs is $100.On a given day,the probability that a displayed sofa will be sold is .03 and that a displayed chair will be sold is .05.Mathematically model each of the following objectives:
1. Maximize the total pieces of furniture displayed.
2. Maximize the total expected number of daily sales.
3. Maximize the total expected daily profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Zipco Printing operates a shop that has five printing machines.The machines differ in their capacities to perform various printing operations due to differences in the machines' designs and operator skill levels.At the start of the workday there are five printing jobs to schedule.The manager must decide what the job-machine assignments should be.
a.How could a quantitative approach to decision making be used to solve this problem?
b.What would be the uncontrollable inputs for which data must be collected?
c.Define the decision variables,objective function,and constraints to appear in the mathematical model.
d.Is the model deterministic or stochastic?
e.Suggest some simplifying assumptions for this problem.
a.How could a quantitative approach to decision making be used to solve this problem?
b.What would be the uncontrollable inputs for which data must be collected?
c.Define the decision variables,objective function,and constraints to appear in the mathematical model.
d.Is the model deterministic or stochastic?
e.Suggest some simplifying assumptions for this problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
To establish a driver education school,organizers must decide how many cars,instructors,and students to have.Costs are estimated as follows.Annual fixed costs to operate the school are $30,000.The annual cost per car is $3000.The cost per instructor is $11,000 and one instructor is needed for each car.Tuition for each student is $350.Let x be the number of cars and y be the number of students.
a.Write an expression for total cost.
b.Write an expression for total revenue.
c.Write an expression for total profit.
d.The school offers the course eight times each year.Each time the course is offered,there are two sessions.If they decide to operate five cars,and if four students can be assigned to each car,will they break even?
a.Write an expression for total cost.
b.Write an expression for total revenue.
c.Write an expression for total profit.
d.The school offers the course eight times each year.Each time the course is offered,there are two sessions.If they decide to operate five cars,and if four students can be assigned to each car,will they break even?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A manufacturer makes two products,doors and windows.Each must be processed through two work areas.Work area #1 has 60 hours of available production time.Work area #2 has 48 hours of available production time.Manufacturing of a door requires 4 hours in work area #1 and 2 hours in work area #2.Manufacturing of a window requires 2 hours in work area #1 and 4 hours in work area #2.Profit is $8 per door and $6 per window.
a.Define decision variables that will tell how many units to build (doors and windows).
b.Develop an objective function that will maximize profits.
c.Develop production constraints for work area #1 and #2.
a.Define decision variables that will tell how many units to build (doors and windows).
b.Develop an objective function that will maximize profits.
c.Develop production constraints for work area #1 and #2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In this portion of an Excel spreadsheet,the user has given values for selling price,the costs,and a sample volume.Give the cell formula for
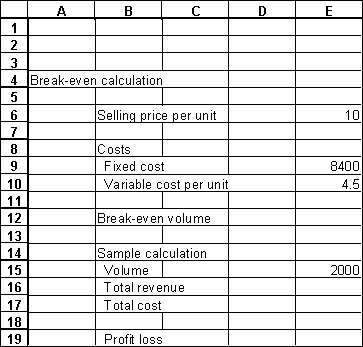
a.cell E12,break-even volume.
b.cell E16,total revenue.
c.cell E17,total cost.
d.cell E19,profit/loss.

a.cell E12,break-even volume.
b.cell E16,total revenue.
c.cell E17,total cost.
d.cell E19,profit/loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
As computer service center has the capacity to do 400 jobs per day.The expected level of jobs demanded per day is 250 per day.The fixed cost of renting the computer process is $200 per day.Space rents for $100 per day.The cost of material is $15 per unit of work and $.35 cents of labor per unit.What is the break-even level of work?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Organizers of an Internet training session will charge participants $150 to attend.It costs $3000 to reserve the room,hire the instructor,bring in the equipment,and advertise.Assume it costs $25 per student for the organizers to provide the course materials.
a.How many students would have to attend for the company to break even?
b.If the trainers think,realistically,that 20 people will attend,then what price should be charged per person for the organization to break even?
a.How many students would have to attend for the company to break even?
b.If the trainers think,realistically,that 20 people will attend,then what price should be charged per person for the organization to break even?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



