Deck 25: Electromagnetic Waves
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/79
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Electromagnetic Waves
1
An electromagnetic wave travels in a vacuum in the +y direction,as shown in the figure.If the 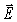 field at the origin is along the +z direction,what is the direction of the
field at the origin is along the +z direction,what is the direction of the  field?
field? 
A)+z
B)-z
C)+y
D)+x
E)-x
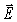 field at the origin is along the +z direction,what is the direction of the
field at the origin is along the +z direction,what is the direction of the 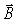 field?
field? 
A)+z
B)-z
C)+y
D)+x
E)-x
D
2
Which one of the following lists gives the correct order of the electromagnetic spectrum from low to high frequencies?
A)radio waves, infrared, microwaves, ultraviolet, visible, x-rays, gamma rays
B)radio waves, ultraviolet, x-rays, microwaves, infrared, visible, gamma rays
C)radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays
D)radio waves, microwaves, visible, x-rays, infrared, ultraviolet, gamma rays
E)radio waves, infrared, x-rays, microwaves, ultraviolet, visible, gamma rays
A)radio waves, infrared, microwaves, ultraviolet, visible, x-rays, gamma rays
B)radio waves, ultraviolet, x-rays, microwaves, infrared, visible, gamma rays
C)radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays
D)radio waves, microwaves, visible, x-rays, infrared, ultraviolet, gamma rays
E)radio waves, infrared, x-rays, microwaves, ultraviolet, visible, gamma rays
C
3
An FM radio station broadcasts at 96.7 MHz.What is the wavelength of the radio wave used for this broadcast? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
3.1 m
4
The frequency of a microwave signal is 9.76 GHz.What is its wavelength? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
A)3.07 cm
B)2.07 cm
C)1.07 cm
D)5.07 cm
E)4.07 cm
A)3.07 cm
B)2.07 cm
C)1.07 cm
D)5.07 cm
E)4.07 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which one of the following lists gives the correct order of the electromagnetic waves from longer wavelength to shorter wavelength?
A)radio waves, infrared, microwaves, ultraviolet, visible, x-rays, gamma rays
B)radio waves, ultraviolet, x-rays, microwaves, infrared, visible, gamma rays
C)radio waves, microwaves, visible, x-rays, infrared, ultraviolet, gamma rays
D)radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays
E)radio waves, infrared, x-rays, microwaves, ultraviolet, visible, gamma rays
A)radio waves, infrared, microwaves, ultraviolet, visible, x-rays, gamma rays
B)radio waves, ultraviolet, x-rays, microwaves, infrared, visible, gamma rays
C)radio waves, microwaves, visible, x-rays, infrared, ultraviolet, gamma rays
D)radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays
E)radio waves, infrared, x-rays, microwaves, ultraviolet, visible, gamma rays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In an electromagnetic wave in free space,the 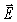 field and
field and 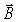 fields are
fields are
A)parallel to one another and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
B)parallel to one another and parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
C)perpendicular to one another and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
D)perpendicular to one another and parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
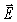 field and
field and 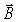 fields are
fields areA)parallel to one another and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
B)parallel to one another and parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
C)perpendicular to one another and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
D)perpendicular to one another and parallel to the direction of wave propagation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which one of the following expressions is the correct representation for the speed of light in vacuum?
A)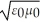
B)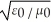
C)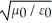
D)1 /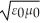
E)1 / ε0μ0
A)
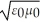
B)
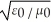
C)
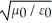
D)1 /
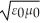
E)1 / ε0μ0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which one of the following types of electromagnetic wave travels through space the fastest?
A)radio waves
B)infrared
C)ultraviolet
D)microwaves
E)They all travel through space at the same speed.
A)radio waves
B)infrared
C)ultraviolet
D)microwaves
E)They all travel through space at the same speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements about electromagnetic waves in a vacuum are true? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
A)The electric field carries more energy than the magnetic field.
B)The electric and magnetic fields have equal amplitudes.
C)The electric field carries the same mount of energy as the magnetic field.
D)The frequency of the magnetic field is the same as the frequency of the electric field.
E)The frequency of the electric field is higher than the frequency of the magnetic field.
A)The electric field carries more energy than the magnetic field.
B)The electric and magnetic fields have equal amplitudes.
C)The electric field carries the same mount of energy as the magnetic field.
D)The frequency of the magnetic field is the same as the frequency of the electric field.
E)The frequency of the electric field is higher than the frequency of the magnetic field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
At a certain instant in time,the 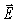 field of an electromagnetic wave in a vacuum points in the -z direction,and the
field of an electromagnetic wave in a vacuum points in the -z direction,and the 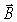 field points in the +y direction.In what direction is this wave traveling?
field points in the +y direction.In what direction is this wave traveling?
A)+x direction
B)-x direction
C)+y direction
D)-z direction
E)+z direction
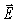 field of an electromagnetic wave in a vacuum points in the -z direction,and the
field of an electromagnetic wave in a vacuum points in the -z direction,and the 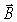 field points in the +y direction.In what direction is this wave traveling?
field points in the +y direction.In what direction is this wave traveling?A)+x direction
B)-x direction
C)+y direction
D)-z direction
E)+z direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which one of the following is not an electromagnetic wave?
A)ultraviolet
B)infrared
C)radio waves
D)sound waves
E)gamma rays
A)ultraviolet
B)infrared
C)radio waves
D)sound waves
E)gamma rays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For a certain electromagnetic wave in a vacuum,at one instant the 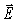 field vector points in the +z direction while the
field vector points in the +z direction while the 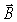 field vector points in the +x direction,as shown in the figure.In what direction is this wave traveling?
field vector points in the +x direction,as shown in the figure.In what direction is this wave traveling? 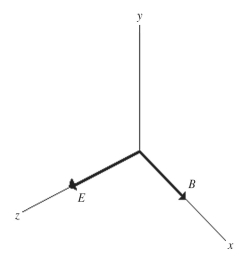
A)+x
B)-x
C)+y
D)-y
E)+z
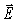 field vector points in the +z direction while the
field vector points in the +z direction while the 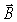 field vector points in the +x direction,as shown in the figure.In what direction is this wave traveling?
field vector points in the +x direction,as shown in the figure.In what direction is this wave traveling? 
A)+x
B)-x
C)+y
D)-y
E)+z

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A cordless phone operates at 900 MHz.What is the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave used by this phone? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An electromagnetic wave is propagating towards the west in a vacuum.At a certain moment the direction of the 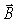 field vector associated with this wave points vertically upward.What is the direction of the
field vector associated with this wave points vertically upward.What is the direction of the 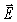 field vector?
field vector?
A)horizontal and pointing south
B)vertical and pointing down
C)horizontal and pointing north
D)vertical and pointing upward
E)horizontal and pointing east
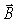 field vector associated with this wave points vertically upward.What is the direction of the
field vector associated with this wave points vertically upward.What is the direction of the 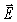 field vector?
field vector?A)horizontal and pointing south
B)vertical and pointing down
C)horizontal and pointing north
D)vertical and pointing upward
E)horizontal and pointing east

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements about electromagnetic waves in a vacuum are true? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
A)The higher-frequency travel faster than the lower-frequency waves.
B)The higher-frequency waves have shorter wavelengths than the lower-frequency waves.
C)The wavelengths of the visible waves are some of the longest electromagnetic waves.
D)The wavelengths of the visible waves are some of the shortest electromagnetic waves.
E)The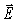 field vector is always at right angles to the
field vector is always at right angles to the 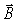 field vector.
field vector.
A)The higher-frequency travel faster than the lower-frequency waves.
B)The higher-frequency waves have shorter wavelengths than the lower-frequency waves.
C)The wavelengths of the visible waves are some of the longest electromagnetic waves.
D)The wavelengths of the visible waves are some of the shortest electromagnetic waves.
E)The
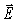 field vector is always at right angles to the
field vector is always at right angles to the 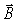 field vector.
field vector.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the wavelength used by a radio station that broadcasts at a frequency of 920 kHz? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
A)22.6 m
B)226 m
C)326 m
D)175 m
E)276 m
A)22.6 m
B)226 m
C)326 m
D)175 m
E)276 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If unpolarized light of intensity I0 passes through an ideal polarizer,what is the intensity of the emerging light?
A)I0
B)I0/2
C)I0/4
D)I0/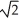
E)I0/16
A)I0
B)I0/2
C)I0/4
D)I0/
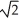
E)I0/16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
For an electromagnetic wave in free space having an 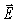 field of amplitude E1 and a
field of amplitude E1 and a 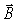 field of amplitude B1,the ratio of B1 /E1 is equal to
field of amplitude B1,the ratio of B1 /E1 is equal to
A)c
B)c2
C)1/c
D)1/c2
E)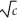
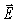 field of amplitude E1 and a
field of amplitude E1 and a 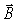 field of amplitude B1,the ratio of B1 /E1 is equal to
field of amplitude B1,the ratio of B1 /E1 is equal toA)c
B)c2
C)1/c
D)1/c2
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The energy density of an electromagnetic wave in free space is
A)entirely in the electric field.
B)entirely in the magnetic field.
C)1/4 in the electric field and 3/4 in the magnetic field.
D)1/4 in the magnetic field and 3/4 in the electric field.
E)equally divided between the magnetic and the electric fields.
A)entirely in the electric field.
B)entirely in the magnetic field.
C)1/4 in the electric field and 3/4 in the magnetic field.
D)1/4 in the magnetic field and 3/4 in the electric field.
E)equally divided between the magnetic and the electric fields.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For a beam of light,the direction of polarization is defined as
A)the beam's direction of travel.
B)the direction of the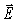 field's vibration.
field's vibration.
C)the direction of the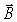 field's vibration.
field's vibration.
D)the direction that is perpendicular to both the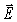 field and
field and 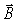 field vectors.
field vectors.
A)the beam's direction of travel.
B)the direction of the
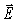 field's vibration.
field's vibration.C)the direction of the
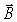 field's vibration.
field's vibration.D)the direction that is perpendicular to both the
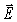 field and
field and 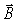 field vectors.
field vectors.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
At a particular point and instant,the 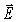 field component of an electromagnetic wave is 15.0 μT.What is the magnetic energy density of this wave at that point and instant? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
field component of an electromagnetic wave is 15.0 μT.What is the magnetic energy density of this wave at that point and instant? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A)2.26 × 10-4 J/m3
B)8.95 × 10-5 J/m3
C)1.79 × 10-4 J/m3
D)4.47 × 10-4 J/m3
E)9.72 × 10-5 J/m3
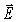 field component of an electromagnetic wave is 15.0 μT.What is the magnetic energy density of this wave at that point and instant? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
field component of an electromagnetic wave is 15.0 μT.What is the magnetic energy density of this wave at that point and instant? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)A)2.26 × 10-4 J/m3
B)8.95 × 10-5 J/m3
C)1.79 × 10-4 J/m3
D)4.47 × 10-4 J/m3
E)9.72 × 10-5 J/m3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How far does light travel in 1.0 μs? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)3.0 × 1014 m
B)0.30 km
C)3.0 m
D)30 cm
A)3.0 × 1014 m
B)0.30 km
C)3.0 m
D)30 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 2.4 x 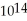 Hz laser emits a 3.5-μs pulse that is 5.0 mm in diameter.The average energy density in the beam is
Hz laser emits a 3.5-μs pulse that is 5.0 mm in diameter.The average energy density in the beam is 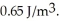 What average power is emitted by this laser? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
What average power is emitted by this laser? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A)3.8 kW
B)7.7 kW
C)12 kW
D)15 kW
E)19 kW
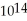 Hz laser emits a 3.5-μs pulse that is 5.0 mm in diameter.The average energy density in the beam is
Hz laser emits a 3.5-μs pulse that is 5.0 mm in diameter.The average energy density in the beam is 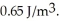 What average power is emitted by this laser? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
What average power is emitted by this laser? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)A)3.8 kW
B)7.7 kW
C)12 kW
D)15 kW
E)19 kW

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How much time does it take a beam of light to travel 2.9 km through space.(c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)9.7 s
B)9.7 ms
C)9.7 μs
D)9.7 ns
E)9.7 ps
A)9.7 s
B)9.7 ms
C)9.7 μs
D)9.7 ns
E)9.7 ps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the frequency of 20-mm microwaves? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)100 MHz
B)400 MHz
C)15 GHz
D)73 GHz
A)100 MHz
B)400 MHz
C)15 GHz
D)73 GHz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The maximum magnetic energy density of a sinusoidal electromagnetic wave is 8.95 × 10-5 J/m3.What is the amplitude of the 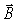 field component of this wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
field component of this wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A)12.0 μT
B)13.0 μT
C)14.0 μT
D)15.0 μT
E)16.0 μT
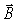 field component of this wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
field component of this wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)A)12.0 μT
B)13.0 μT
C)14.0 μT
D)15.0 μT
E)16.0 μT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How far does a beam of light travel in 2.0 ms? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)6.0 × 105 m
B)0.66 × 105 m
C)90 m
D)70 m
E)60 m
A)6.0 × 105 m
B)0.66 × 105 m
C)90 m
D)70 m
E)60 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The distance between two asteroids is 1600 km.How much time does it take for a light signal to go from one asteroid to the other? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)19 ms
B)4.5 ms
C)5.3 ms
D)13 ms
E)19 µs
A)19 ms
B)4.5 ms
C)5.3 ms
D)13 ms
E)19 µs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A laser beam takes 24 ms to travel from a rocket to the reflective surface of a planet and back to the rocket.How far is the rocket from this planet's surface? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)2400 km
B)1200 km
C)1800 km
D)3600 km
E)4800 km
A)2400 km
B)1200 km
C)1800 km
D)3600 km
E)4800 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An 800-kHz radio signal is detected at a point 9.5 km distant from a transmitter tower.The 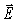 field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.23 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the average electromagnetic energy density at that point? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.23 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the average electromagnetic energy density at that point? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A)2.3 × 10-13 J/m3
B)3.3 × 10-13 J/m3
C)4.7 × 10-13 J/m3
D)6.6 × 10-13 J/m3
E)9.4 × 10-13 J/m3
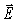 field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.23 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the average electromagnetic energy density at that point? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.23 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the average electromagnetic energy density at that point? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)A)2.3 × 10-13 J/m3
B)3.3 × 10-13 J/m3
C)4.7 × 10-13 J/m3
D)6.6 × 10-13 J/m3
E)9.4 × 10-13 J/m3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A 4.4 × 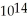 Hz laser emits a 2.1 μs pulse that is 5.0 mm in diameter.The energy density in the beam is
Hz laser emits a 2.1 μs pulse that is 5.0 mm in diameter.The energy density in the beam is 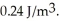 How many wavelengths are there in the length of the beam? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
How many wavelengths are there in the length of the beam? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A)9.2 × 108
B)2.8 × 109
C)2.8 × 108
D)9.2 × 109
E)2.8 × 1010
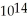 Hz laser emits a 2.1 μs pulse that is 5.0 mm in diameter.The energy density in the beam is
Hz laser emits a 2.1 μs pulse that is 5.0 mm in diameter.The energy density in the beam is 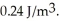 How many wavelengths are there in the length of the beam? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
How many wavelengths are there in the length of the beam? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)A)9.2 × 108
B)2.8 × 109
C)2.8 × 108
D)9.2 × 109
E)2.8 × 1010

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How far does a beam of light travel through space in one 365-day year? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)80 × 1012 m
B)95 × 1014 m
C)30 × 108 m
D)20 × 1015 m
E)36 × 1016 m
A)80 × 1012 m
B)95 × 1014 m
C)30 × 108 m
D)20 × 1015 m
E)36 × 1016 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is 600 nm.What is its frequency? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)200 × 1012 Hz
B)300 × 1012 Hz
C)400 × 1012 Hz
D)500 × 1012 Hz
E)600 × 1012 Hz
A)200 × 1012 Hz
B)300 × 1012 Hz
C)400 × 1012 Hz
D)500 × 1012 Hz
E)600 × 1012 Hz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A 7.55 × 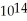 Hz electromagnetic wave travels in carbon tetrachloride with a speed of 2.05 ×108 m/s.What is the wavelength of the wave in this material?
Hz electromagnetic wave travels in carbon tetrachloride with a speed of 2.05 ×108 m/s.What is the wavelength of the wave in this material?
A)272 nm
B)301 nm
C)338 nm
D)361 nm
E)397 nm
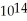 Hz electromagnetic wave travels in carbon tetrachloride with a speed of 2.05 ×108 m/s.What is the wavelength of the wave in this material?
Hz electromagnetic wave travels in carbon tetrachloride with a speed of 2.05 ×108 m/s.What is the wavelength of the wave in this material?A)272 nm
B)301 nm
C)338 nm
D)361 nm
E)397 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A radio station broadcasts at 80 MHz.How long does it take for this radio signal to travel a distance of 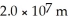 through space? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
through space? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)0.15 × 10-2 s
B)15 ms
C)6.7 × 10-2 s
D)20 ms
E)25 ms
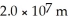 through space? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
through space? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)A)0.15 × 10-2 s
B)15 ms
C)6.7 × 10-2 s
D)20 ms
E)25 ms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How long does it take light to travel 1.0 m? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)3.3 ns
B)3.3 μs
C)3.3 ms
D)3.3 s
A)3.3 ns
B)3.3 μs
C)3.3 ms
D)3.3 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A certain part of the electromagnetic spectrum ranges from 200 nm to 400 nm.What is the lowest frequency associated with this portion of the spectrum? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
A)1.50 × 1014 Hz
B)7.50 × 1013 Hz
C)7.50 × 1014 Hz
D)7.50 × 1015 Hz
E)1.50 × 1015 Hz
A)1.50 × 1014 Hz
B)7.50 × 1013 Hz
C)7.50 × 1014 Hz
D)7.50 × 1015 Hz
E)1.50 × 1015 Hz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A certain part of the electromagnetic spectrum ranges from 200 nm to 400 nm.What is the highest frequency associated with this portion of the spectrum? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
A)1.50 × 1014 Hz
B)7.50 × 1013 Hz
C)7.50 × 1014 Hz
D)7.50 × 1015 Hz
E)1.50 × 1015 Hz
A)1.50 × 1014 Hz
B)7.50 × 1013 Hz
C)7.50 × 1014 Hz
D)7.50 × 1015 Hz
E)1.50 × 1015 Hz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A radar receiver indicates that a pulse return as an echo in 20 μs after it was sent.How far away is the reflecting object? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)1.5 km
B)3.0 km
C)6.0 km
D)9.0 km
A)1.5 km
B)3.0 km
C)6.0 km
D)9.0 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A radio station broadcasts at a frequency of 80 MHz.How far from the transmitter will this signal travel in 67 ms? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)60 × 106 m
B)67 m
C)40 km
D)80 km
E)20 × 106 m
A)60 × 106 m
B)67 m
C)40 km
D)80 km
E)20 × 106 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A sinusoidal electromagnetic wave is propagating in vacuum.At a given point and at a particular time the 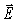 field is in the +x direction and the
field is in the +x direction and the 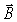 field is in the -y direction,and at that point the intensity of the wave is
field is in the -y direction,and at that point the intensity of the wave is 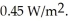
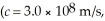
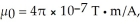
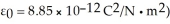 (a)What is the direction of propagation of the wave?
(a)What is the direction of propagation of the wave?
(b)What is the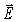 field amplitude at the given point?
field amplitude at the given point?
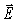 field is in the +x direction and the
field is in the +x direction and the 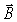 field is in the -y direction,and at that point the intensity of the wave is
field is in the -y direction,and at that point the intensity of the wave is 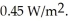
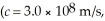
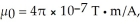
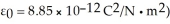 (a)What is the direction of propagation of the wave?
(a)What is the direction of propagation of the wave?(b)What is the
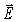 field amplitude at the given point?
field amplitude at the given point?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A sinusoidal electromagnetic wave has a peak electric field of 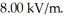 What is the intensity of the wave?
What is the intensity of the wave? 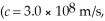
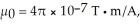
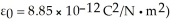
A)170 kW/m2
B)85 kW/m2
C)21 kW/m2
D)11 kW/m2
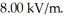 What is the intensity of the wave?
What is the intensity of the wave? 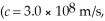
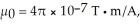
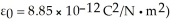
A)170 kW/m2
B)85 kW/m2
C)21 kW/m2
D)11 kW/m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A radio transmitter is operating at an average power of 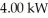 and is radiating uniformly in all directions.What is the average intensity of the signal
and is radiating uniformly in all directions.What is the average intensity of the signal 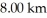 from the transmitter?
from the transmitter?
A)4.97 μW/m2
B)2.49 μW/m2
C)0.00497 W/m2
D)0.00249 W/m2
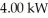 and is radiating uniformly in all directions.What is the average intensity of the signal
and is radiating uniformly in all directions.What is the average intensity of the signal 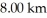 from the transmitter?
from the transmitter?A)4.97 μW/m2
B)2.49 μW/m2
C)0.00497 W/m2
D)0.00249 W/m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A radiometer has two square vanes (1.0 cm by 1.0 cm),attached to a light horizontal cross arm,and pivoted about a vertical axis through the center,as shown in the figure.The center of each vane is 6.0 cm from the axis.One vane is silvered and it reflects all radiant energy that falls upon it.The other vane is blackened and it absorbs all incident radiant energy.Radiant energy,having an intensity of 300 W/m2,is incident normally upon the front surfaces of both vanes.What is the radiant power absorbed by the blackened vane? 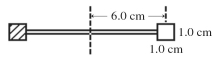
A)0.030 W
B)0.040 W
C)0.050 W
D)0.060 W
E)0.090 W

A)0.030 W
B)0.040 W
C)0.050 W
D)0.060 W
E)0.090 W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An 800-kHz sinusoidal radio signal is detected at a point 2.1 km distant from a transmitter tower.The 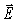 field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.80 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the intensity of the radio signal at that point? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.80 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the intensity of the radio signal at that point? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)8.5 × 10-4 W/m2
B)1.2 × 10-3 W/m2
C)1.7 × 10-3 W/m2
D)6.0 × 10-4 W/m2
E)4.2 × 10-4 W/m2
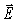 field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.80 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the intensity of the radio signal at that point? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.80 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the intensity of the radio signal at that point? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)A)8.5 × 10-4 W/m2
B)1.2 × 10-3 W/m2
C)1.7 × 10-3 W/m2
D)6.0 × 10-4 W/m2
E)4.2 × 10-4 W/m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How much energy is transported across a 1.00-cm2 area per hour by a sinusoidal electromagnetic wave whose 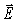 field has the amplitude of 30.4 V/m? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field has the amplitude of 30.4 V/m? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)0.44 nJ
B)0.44 μJ
C)0.44 mJ
D)0.44 J
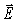 field has the amplitude of 30.4 V/m? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field has the amplitude of 30.4 V/m? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)A)0.44 nJ
B)0.44 μJ
C)0.44 mJ
D)0.44 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A light source radiates 60.0 W of single-wavelength sinusoidal light uniformly in all directions.What is the amplitude of the electric field of this light at a distance of 0.400 m from the bulb? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
A)162 N/C
B)212 N/C
C)82.1 N/C
D)150 N/C
E)52.9 N/C
A)162 N/C
B)212 N/C
C)82.1 N/C
D)150 N/C
E)52.9 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An 800-kHz sinusoidal radio signal is detected at a point 6.6 km from the transmitter tower.The 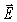 field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.780 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the amplitude of the
field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.780 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the amplitude of the 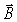 field of the signal at that point? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A)
field of the signal at that point? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A)
A)2.6 nT
B)2.1 nT
C)1.6 nT
D)3.1 nT
E)3.6 nT
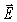 field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.780 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the amplitude of the
field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.780 V/m.Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed.What is the amplitude of the 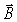 field of the signal at that point? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A)
field of the signal at that point? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A)A)2.6 nT
B)2.1 nT
C)1.6 nT
D)3.1 nT
E)3.6 nT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If the magnetic field in a traveling electromagnetic wave has a maximum value of 16.5 nT,what is the maximum value of the 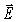 field associated with this wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
field associated with this wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
A)5.5 × 10-17 V/m
B)4.95 V/m
C)0.495 V/m
D)55.0 × 10-16 V/m
E)55.0 × 10-15 V/m
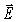 field associated with this wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
field associated with this wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)A)5.5 × 10-17 V/m
B)4.95 V/m
C)0.495 V/m
D)55.0 × 10-16 V/m
E)55.0 × 10-15 V/m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The maximum value of the electric field in an electromagnetic wave is 2.0 V/m.What is the maximum value of the 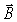 field in that wave? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field in that wave? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)6.7 pT
B)6.7 mT
C)6.7 nT
D)6.7 μT
E)6.7 T
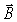 field in that wave? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field in that wave? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)A)6.7 pT
B)6.7 mT
C)6.7 nT
D)6.7 μT
E)6.7 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the maximum value of the 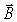 field at a distance of 2.5 m from a light bulb that radiates 100 W of single-frequency sinusoidal electromagnetic waves uniformly in all directions? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field at a distance of 2.5 m from a light bulb that radiates 100 W of single-frequency sinusoidal electromagnetic waves uniformly in all directions? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)0.10 μT
B)0.40 μT
C)0.50 μT
D)0.60 μT
E)0.80 μT
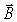 field at a distance of 2.5 m from a light bulb that radiates 100 W of single-frequency sinusoidal electromagnetic waves uniformly in all directions? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field at a distance of 2.5 m from a light bulb that radiates 100 W of single-frequency sinusoidal electromagnetic waves uniformly in all directions? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)A)0.10 μT
B)0.40 μT
C)0.50 μT
D)0.60 μT
E)0.80 μT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
About 1350 W/m2 of electromagnetic energy reaches the upper atmosphere of the earth from the sun,which is 1.5 × 1011 m away.Use this information to estimate the average power output of the sun.
A)1 × 1026 W
B)2 × 1026 W
C)3 × 1026 W
D)4 × 1026 W
A)1 × 1026 W
B)2 × 1026 W
C)3 × 1026 W
D)4 × 1026 W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The rate of energy flow per unit area of a sinusoidal electromagnetic wave has an average value of 0.601 W/m2.What is the maximum value of the 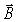 field in the wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
field in the wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A)7.09 × 10-8 T
B)5.02 × 10-8 T
C)3.55 × 10-8 T
D)9.81 × 10-8 T
E)1.42 × 10-7 T
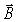 field in the wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
field in the wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)A)7.09 × 10-8 T
B)5.02 × 10-8 T
C)3.55 × 10-8 T
D)9.81 × 10-8 T
E)1.42 × 10-7 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A certain electromagnetic field traveling in vacuum has a maximum electric field of 1200 V/m.What is the maximum 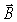 field of this wave? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field of this wave? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)3.4 × 10-4 T
B)4.0 × 10-6 T
C)2.2 × 10-5 T
D)9.6 × 10-6 T
E)8.7 × 10-6 T
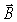 field of this wave? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field of this wave? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)A)3.4 × 10-4 T
B)4.0 × 10-6 T
C)2.2 × 10-5 T
D)9.6 × 10-6 T
E)8.7 × 10-6 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A light source radiates 60.0 W of single-wavelength sinusoidal light uniformly in all directions.What is the amplitude of the 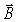 field of this light at a distance of 0.700 m from the bulb?(ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field of this light at a distance of 0.700 m from the bulb?(ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)1.76 × 10-7 T
B)2.02 × 10-7 T
C)2.22 × 10-7 T
D)2.86 × 10-7 T
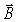 field of this light at a distance of 0.700 m from the bulb?(ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field of this light at a distance of 0.700 m from the bulb?(ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)A)1.76 × 10-7 T
B)2.02 × 10-7 T
C)2.22 × 10-7 T
D)2.86 × 10-7 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The amplitude of the electric field for a certain type of electromagnetic wave is 570 N/C.What is the amplitude of the 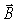 field for that wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
field for that wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
A)2.91 µT
B)1.90 µT
C)1.10 µT
D)1.41 µT
E)2.41 µT
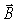 field for that wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
field for that wave? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)A)2.91 µT
B)1.90 µT
C)1.10 µT
D)1.41 µT
E)2.41 µT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An 8.00-mW laser beam emits a cylindrical beam of single-wavelength sinusoidal light 0.600 mm in diameter.What is the maximum value of the 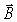 field in the laser beam? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field in the laser beam? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)9.24 µT
B)17.2 µT
C)12.4 µT
D)20.5 µT
E)15.4 µT
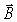 field in the laser beam? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
field in the laser beam? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)A)9.24 µT
B)17.2 µT
C)12.4 µT
D)20.5 µT
E)15.4 µT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A light source radiates 60.0 W of single-wavelength sinusoidal light uniformly in all directions.What is the average intensity of the light from this bulb at a distance of 0.400 m from the bulb?
A)14.9 W/m2
B)37.2 W/m2
C)27.4 W/m2
D)11.9 W/m2
E)29.8 W/m2
A)14.9 W/m2
B)37.2 W/m2
C)27.4 W/m2
D)11.9 W/m2
E)29.8 W/m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The rate of energy flow per unit area of an electromagnetic wave has an average value of 0.695 W/m2.The wave is incident at right angles upon a rectangular area measuring 1.5 m by 2.0 m.How much total energy falls upon this rectangle each minute? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)
A)130 J
B)160 J
C)190 J
D)220 J
E)250 J
A)130 J
B)160 J
C)190 J
D)220 J
E)250 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Radiation of a single frequency reaches the upper atmosphere of the earth with an intensity of 1350 W/m2.What is the maximum value of the 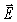 field associated with this radiation? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
field associated with this radiation? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A)675.0 V/m
B)1604 V/m
C)1400 V/m
D)1350 V/m
E)1010 V/m
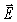 field associated with this radiation? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
field associated with this radiation? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A,ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)A)675.0 V/m
B)1604 V/m
C)1400 V/m
D)1350 V/m
E)1010 V/m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A ray of light traveling in water hits a glass surface.The index of refraction of the water is 1.33,and that of the glass is 1.50.At what angle with the plane of the surface must the incident ray strike the glass in order that the polarization of the reflected ray is the greatest?
A)36.9°
B)33.7°
C)41.6°
D)48.4°
E)53.1°
A)36.9°
B)33.7°
C)41.6°
D)48.4°
E)53.1°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Unpolarized light is incident upon two ideal polarizing filters that do not have their transmission axes aligned.If 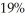 of the light passes through this combination,what is the angle between the transmission axes of the two filters?
of the light passes through this combination,what is the angle between the transmission axes of the two filters?
A)52°
B)72°
C)0°
D)0°
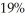 of the light passes through this combination,what is the angle between the transmission axes of the two filters?
of the light passes through this combination,what is the angle between the transmission axes of the two filters?A)52°
B)72°
C)0°
D)0°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Unpolarized light of intensity I0 passes through four ideal polarizing sheets.The polarizing angle of each sheet is rotated 30° from the one before it,so that the last sheet is aligned at 90° to the first sheet.What is the intensity of the light emerging from the fourth sheet in terms of I0?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A beam of light is polarized in a vertical plane and has an intensity I0.The beam passes through an ideal polarizer and then through an ideal analyzer whose axis is set horizontally.If the axis of the polarizer is set at 60° with the vertical,what is the ratio of the intensity of the final beam to I0?
A)0.19
B)0.25
C)0.31
D)0.37
E)0.43
A)0.19
B)0.25
C)0.31
D)0.37
E)0.43

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The critical angle for an air-glass interface is 42.6°.A light ray in air hits the interface,and the reflected ray is 100% polarized.What is the angle of refraction for that ray?
A)47.4°
B)55.9°
C)24.3°
D)65.7°
E)34.1°
A)47.4°
B)55.9°
C)24.3°
D)65.7°
E)34.1°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An ideal polarizer with its transmission axis rotated 30° to the vertical is placed in a beam of unpolarized light of intensity 10 W/m2.After passing through the polarizer,what is intensity of the beam?
A)2.5 W/m2
B)5.0 W/m2
C)8.7 W/m2
D)7.5 W/m2
E)10 W/m2
A)2.5 W/m2
B)5.0 W/m2
C)8.7 W/m2
D)7.5 W/m2
E)10 W/m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When light in air strikes the flat surface of a certain glass at 31.2° with the normal,the reflected ray is 100 percent polarized.What is the critical angle for the air-glass interface of this glass?
A)52.7°
B)58.8°
C)21.4°
D)37.3°
E)68.6°
A)52.7°
B)58.8°
C)21.4°
D)37.3°
E)68.6°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Unpolarized light passes through three ideal polarizing filters.The first filter is oriented with a horizontal transmission axis,the second one has its transmission axis at 30° from the horizontal,and the third filter has a vertical transmission axis.What percent of the light gets through this combination?
A)9.4%
B)91%
C)50%
D)0%
E)33%
A)9.4%
B)91%
C)50%
D)0%
E)33%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Unpolarized light passes through a combination of two ideal polarizers.The transmission axes of the first polarizer and the second polarizer are at 30.0° to each other.What percentage of the original light gets through the combination?
A)37.5%
B)50%
C)75%
D)100%
A)37.5%
B)50%
C)75%
D)100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Polarized light of intensity S0 passes through an ideal polarizer.If the E vector of the polarized light is horizontal what,in terms of the initial intensity S0,is the intensity of the light that passes through a polarizer if that polarizer is tilted 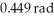 from the horizontal?
from the horizontal?
A)0.812 S0
B)0.188 S0
C)0.217 S0
D)0.284 S0
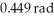 from the horizontal?
from the horizontal?A)0.812 S0
B)0.188 S0
C)0.217 S0
D)0.284 S0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When unpolarized light from air (with refractive index 1.00)strikes a piece of glass with index of refraction 1.80,the reflected light is found to be completely polarized when the angle of incidence is equal to Brewster's angle.What is the angle of refraction in this case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Find Brewster's angle for light in air that is reflected from the top of a water surface.The index of refraction of the water is 1.33.
A)53.1°
B)36.9°
C)56.3°
D)60.2°
E)90.0°
A)53.1°
B)36.9°
C)56.3°
D)60.2°
E)90.0°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Unpolarized light of intensity I0 passed through an ideal polarizing sheet with its polarizing axis at the 12 o'clock position and then through a second ideal sheet with its polarizing axis at the 1 o'clock position.What is the intensity of the emerging light in terms of I0?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The following items are positioned in sequence: A source of a beam of natural light of intensity I0,three ideal polarizers A,B,and C; and an observer.Polarizer axis angles are measured clockwise from the vertical,as viewed by the observer.The axis angle of polarizer A is set at 0° (vertical),and the axis angle of polarizer C is set at 50°.The axis angle of polarizer B is set at 120°.What is ratio of the intensity of the beam at the observer to the intensity I0 of the source?
A)0.015
B)0.020
C)0.025
D)0.030
E)0.035
A)0.015
B)0.020
C)0.025
D)0.030
E)0.035

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Three ideal polarizers are oriented as follows: The axis of the second polarizer is at an angle of 59.0° relative to the first one.The axis of the third polarizer is at an angle of 31.0° relative to the second one,so the axis of the axis of the third polarizer is perpendicular to the axis of the first one.Unpolarized light of intensity 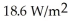 is incident on the first polarizer.
is incident on the first polarizer.
(a)What is the intensity of the light after it passes through all three polarizers?
(b)What is the intensity of the transmitted light if the second polarizer is removed?
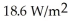 is incident on the first polarizer.
is incident on the first polarizer.(a)What is the intensity of the light after it passes through all three polarizers?
(b)What is the intensity of the transmitted light if the second polarizer is removed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
As shown in the figure,the orientation of the transmission axis for each of three ideal polarizing sheets is labeled relative to the vertical direction.A beam of light,polarized in the vertical direction,is incident on the first polarizer with an intensity of 1.00 kW/m2.What is the intensity of the beam after it has passed through the three polarizing sheets when θ1 = 30°,θ2 = 30°,and θ3= 60°? 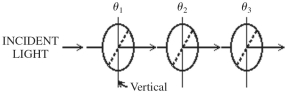
A)141 W/m2
B)316 W/m2
C)433 W/m2
D)563 W/m2
E)188 W/m2

A)141 W/m2
B)316 W/m2
C)433 W/m2
D)563 W/m2
E)188 W/m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A vertically polarized beam of light of intensity 100 W/m2 passes through two ideal polarizers.The transmission axis of the first polarizer makes an angle of 20.0° with the vertical,and the transmission axis of the second one makes an angle of 40.0° with the vertical.What is the intensity of the light after it has passes through both polarizers?
A)22.2 W/m2
B)44.4 W/m2
C)66.6 W/m2
D)78.0 W/m2
E)11.7 W/m2
A)22.2 W/m2
B)44.4 W/m2
C)66.6 W/m2
D)78.0 W/m2
E)11.7 W/m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is Brewster's angle for light traveling in vacuum and reflecting off a piece of glass having a refractive index of 1.52?
A)48.9°
B)33.3°
C)48.1°
D)56.7°
E)41.1°
A)48.9°
B)33.3°
C)48.1°
D)56.7°
E)41.1°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Light passes through three ideal polarizing sheets.Unpolarized light enters the first sheet and the resultant vertically polarized beam continues through the second sheet and third sheet.The second sheet has its transmission axis at 50° with respect to the first sheet,and the third sheet is at 70° with respect to the first sheet.
(a)What percent of the original intensity emerges from filter #1?
(b)What percent of the original intensity emerges from filter #2?
(c)What percent of the original intensity emerges from filter #3?
(a)What percent of the original intensity emerges from filter #1?
(b)What percent of the original intensity emerges from filter #2?
(c)What percent of the original intensity emerges from filter #3?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



