Deck 6: Trade Regulations and Industrial Policies
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/129
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Trade Regulations and Industrial Policies
1
The World Trade Organization was established by the ____ of multilateral trade negotiations:
A) Kennedy Round
B) Tokyo Round
C) Uruguay Round
D) Clinton Round
A) Kennedy Round
B) Tokyo Round
C) Uruguay Round
D) Clinton Round
C
2
Trade theory suggests that the United States would gain from a subsidy provided by Japan to its calculator producers if the gains to American consumers of calculators more than offset the losses to American calculator producers.This occurs as long as the United States:
A) Is a net importer of calculators
B) Is a net exporter of calculators
C) Has an absolute advantage in calculator production
D) Has a comparative advantage in calculator production
A) Is a net importer of calculators
B) Is a net exporter of calculators
C) Has an absolute advantage in calculator production
D) Has a comparative advantage in calculator production
A
3
The high point of U.S.protection culminated with the passage of the:
A) Smoot-Hawley Act of 1930
B) General Agreements on Tariffs and Trade in 1947
C) Trade Reduction Act of 1962
D) Adjustment Assistance Act of 1970
A) Smoot-Hawley Act of 1930
B) General Agreements on Tariffs and Trade in 1947
C) Trade Reduction Act of 1962
D) Adjustment Assistance Act of 1970
A
4
Under the original provisions of the Reciprocal Trade Agreements Act,the president of the United States was authorized to cut tariffs up to:
A) 10 percent
B) 50 percent
C) 75 percent
D) 100 percent
A) 10 percent
B) 50 percent
C) 75 percent
D) 100 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade and its successor,the World Trade Organization,have resulted in:
A) Termination of export subsidies applied to manufactured goods
B) Termination of import tariffs applied to manufactured goods
C) Encouragement of beggar-thy-neighbor policies
D) Reductions in trade barriers via multilateral negotiations
A) Termination of export subsidies applied to manufactured goods
B) Termination of import tariffs applied to manufactured goods
C) Encouragement of beggar-thy-neighbor policies
D) Reductions in trade barriers via multilateral negotiations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Export-Import Bank of the United States encourages American firms to sell overseas by providing direct loans and loan guarantees to foreign purchasers of American goods.To American firms,this represents a:
A) Specific subsidy
B) Ad valorem subsidy
C) Domestic subsidy
D) Export subsidy
A) Specific subsidy
B) Ad valorem subsidy
C) Domestic subsidy
D) Export subsidy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The principle of normal trade relations (most-favored-nation)treatment was established with the passage of the:
A) Fordney-McCumber Act of 1922
B) Smoot-Hawley Act of 1930
C) Reciprocal Trade Agreements Act of 1934
D) Trade Act of 1974
A) Fordney-McCumber Act of 1922
B) Smoot-Hawley Act of 1930
C) Reciprocal Trade Agreements Act of 1934
D) Trade Act of 1974

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Adjustment assistance is sometimes used to assist:
A) In retraining workers displaced by imports
B) In retraining workers displaced by exports
C) Foreign firms injured by our quotas
D) Foreign firms injured by our tariffs
A) In retraining workers displaced by imports
B) In retraining workers displaced by exports
C) Foreign firms injured by our quotas
D) Foreign firms injured by our tariffs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Under U.S.commercial policy,which clause permits the modification of a trade liberalization agreement on a temporary basis if serious injury occurs to domestic producers as a result of the agreement?
A) Adjustment assistance clause
B) Escape clause
C) Most-favored-nation clause
D) Reciprocal-trade clause
A) Adjustment assistance clause
B) Escape clause
C) Most-favored-nation clause
D) Reciprocal-trade clause

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
____ attempt to produce a fair and free-trading environment in which there exists a level playing field.
A) Trade-remedy laws
B) Industrial policies
C) Strategic trade policies
D) Economic sanctions
A) Trade-remedy laws
B) Industrial policies
C) Strategic trade policies
D) Economic sanctions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930 has generally been associated with:
A) Falling tariffs
B) Increases in the volume of trade
C) Intensifying the worldwide depression
D) Efforts to liberalize nontariff trade barriers
A) Falling tariffs
B) Increases in the volume of trade
C) Intensifying the worldwide depression
D) Efforts to liberalize nontariff trade barriers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Countervailing duties are intended to neutralize any unfair advantage that foreign exporters might gain over domestic producers because of foreign:
A) Tariffs
B) Subsidies
C) Quotas
D) Buy-national policies
A) Tariffs
B) Subsidies
C) Quotas
D) Buy-national policies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For the United States,which organization makes loans to foreign buyers of U.S.manufactured goods?
A) Export-Import Bank
B) Domestic International Sales Corporation
C) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
D) Commodity Credit Corporation
A) Export-Import Bank
B) Domestic International Sales Corporation
C) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
D) Commodity Credit Corporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Throughout the post-World War II era,the importance of tariffs as a trade barrier has:
A) Increased
B) Decreased
C) Remained the same
D) None of the above
A) Increased
B) Decreased
C) Remained the same
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A trade policy designed to alleviate some domestic economic problem by exporting it to foreign countries is known as a (an):
A) International dumping policy
B) Trade adjustment assistance policy
C) Most-favored-nation policy
D) Beggar-thy-neighbor policy
A) International dumping policy
B) Trade adjustment assistance policy
C) Most-favored-nation policy
D) Beggar-thy-neighbor policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Under U.S.commercial policy,the escape clause results in:
A) Temporary quotas granted to firms injured by import competition
B) Tariffs that offset export subsidies granted to foreign producers
C) Tax advantages extended to minority-owned exporting firms
D) Duties which offset commercial dumping on the part of foreign firms
A) Temporary quotas granted to firms injured by import competition
B) Tariffs that offset export subsidies granted to foreign producers
C) Tax advantages extended to minority-owned exporting firms
D) Duties which offset commercial dumping on the part of foreign firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The Uruguay Round of Multilateral Trade Negotiations accomplished all of the following except:
A) Placed primary emphasis on nontariff trade barriers
B) Is estimated to yield modest gains in world output and employment
C) Achieved cuts in tariffs but not in nontariff trade barriers
D) Abolished all barriers to trade in agricultural products
A) Placed primary emphasis on nontariff trade barriers
B) Is estimated to yield modest gains in world output and employment
C) Achieved cuts in tariffs but not in nontariff trade barriers
D) Abolished all barriers to trade in agricultural products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which policy reflects the notion that if society enjoys gains due to increased efficiency stemming from trade liberalization,some sort of compensation should be provided to those who are temporarily hurt by import competition?
A) Countervailing duties
B) Trade adjustment assistance
C) Domestic subsidies
D) Most-favored-nation standard
A) Countervailing duties
B) Trade adjustment assistance
C) Domestic subsidies
D) Most-favored-nation standard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The U.S."trade-remedy laws" could establish all of the following except:
A) Import tariffs to protect U.S.firms seriously injured by foreign competition
B) Countervailing duties which neutralize foreign export subsidies
C) Antidumping duties which protect U.S.firms from imports sold at less-than-fair-value
D) Economic sanctions levied against hostile nations
A) Import tariffs to protect U.S.firms seriously injured by foreign competition
B) Countervailing duties which neutralize foreign export subsidies
C) Antidumping duties which protect U.S.firms from imports sold at less-than-fair-value
D) Economic sanctions levied against hostile nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
As a way of helping American firms trade in the world market,U.S.trade law provides antitrust exemptions for horizontal combinations of American firms engaged solely in export trade.Such firms are permitted to form:
A) Export trade associations
B) Domestic international sales corporations
C) Export-import banks
D) Commodity sales corporations
A) Export trade associations
B) Domestic international sales corporations
C) Export-import banks
D) Commodity sales corporations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In 1990 the United States and its allies imposed trade embargoes on exports/imports to/from Iraq in response to its invasion of Kuwait.The embargoes would induce smaller losses in Iraq's consumer surplus the:
A) Lesser its initial dependence on foreign products
B) Less elastic Iraq's demand schedule
C) Lesser the available output from alternative suppliers
D) More inelastic Iraq's supply schedule
A) Lesser its initial dependence on foreign products
B) Less elastic Iraq's demand schedule
C) Lesser the available output from alternative suppliers
D) More inelastic Iraq's supply schedule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Referring to Figure 6.1,assume that Boeing is the first to enter the Canadian market.Without a governmental subsidy,the firm maximizes profits by selling ____ aircraft at a price of $____,and realizes profits totaling $____.
A) 4,$12 million,$16 million
B) 4,$16 million,$12 million
C) 8,$12 million,$16 million
D) 8,$16 million,$12 million
A) 4,$12 million,$16 million
B) 4,$16 million,$12 million
C) 8,$12 million,$16 million
D) 8,$16 million,$12 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Countervailing duties may be imposed:
A) In response to a foreign export subsidy
B) In response to a foreign antidumping tariff
C) To promote exports of domestic companies
D) To promote imports of domestic consumers
A) In response to a foreign export subsidy
B) In response to a foreign antidumping tariff
C) To promote exports of domestic companies
D) To promote imports of domestic consumers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Uruguay Round of trade negotiations lowered:
A) Trade sanctions levied against South Africa
B) Trade sanctions levied against the Soviet Union
C) Tariffs,but not nontariff trade barriers
D) Tariffs as well as nontariff trade barriers
A) Trade sanctions levied against South Africa
B) Trade sanctions levied against the Soviet Union
C) Tariffs,but not nontariff trade barriers
D) Tariffs as well as nontariff trade barriers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The World Trade Organization provides for all of the following except:
A) The usage of the normal-trade-relation (most-favored-nation)clause
B) Assistance in the settlement of trade disagreements
C) Multilateral tariff reductions
D) Bilateral tariff reductions
A) The usage of the normal-trade-relation (most-favored-nation)clause
B) Assistance in the settlement of trade disagreements
C) Multilateral tariff reductions
D) Bilateral tariff reductions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose the United States imposes trade sanctions (export quotas)on grain sold to the Russians.Assuming other nations do not increase grain exports to the Russians,all of the following would occur except:
A) Grain prices would rise in Russia
B) Consumer surplus would decrease for the Russians
C) Grain prices would rise in the United States
D) Export revenues would decrease for U.S.producers
A) Grain prices would rise in Russia
B) Consumer surplus would decrease for the Russians
C) Grain prices would rise in the United States
D) Export revenues would decrease for U.S.producers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Export embargoes induce greater losses in consumer surplus for the target country:
A) The lesser its initial dependence on foreign produced goods
B) The more elastic the target country's demand schedule
C) The greater the available output from alternative suppliers
D) The more inelastic the target country's supply schedule
A) The lesser its initial dependence on foreign produced goods
B) The more elastic the target country's demand schedule
C) The greater the available output from alternative suppliers
D) The more inelastic the target country's supply schedule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In U.S.trade law,Section 301 cases involve accusations of:
A) International dumping by U.S.companies
B) Full-cost pricing by U.S.companies
C) Unfair trade practices by foreign nations
D) Trade embargoes by foreign nations
A) International dumping by U.S.companies
B) Full-cost pricing by U.S.companies
C) Unfair trade practices by foreign nations
D) Trade embargoes by foreign nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The strongest political pressure for a trade policy that results in higher protectionism comes from:
A) Domestic workers lobbying for import restrictions
B) Domestic workers lobbying for export restrictions
C) Domestic consumers lobbying for export restrictions
D) Domestic consumers lobbying for import restrictions
A) Domestic workers lobbying for import restrictions
B) Domestic workers lobbying for export restrictions
C) Domestic consumers lobbying for export restrictions
D) Domestic consumers lobbying for import restrictions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In 1980 the United States announced an embargo on grain exports to the Soviet Union in response to the Soviet armed invasion of Afghanistan.The embargo was mainly resisted by:
A) U.S.grain consumers and producers of bread
B) U.S.farmers and grain companies
C) Grain producers in foreign countries
D) Grain consumers in foreign countries
A) U.S.grain consumers and producers of bread
B) U.S.farmers and grain companies
C) Grain producers in foreign countries
D) Grain consumers in foreign countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Uruguay Round of trade negotiations was primarily concerned with:
A) Import tariffs
B) Export tariffs
C) Economic sanctions
D) Nontariff trade barriers
A) Import tariffs
B) Export tariffs
C) Economic sanctions
D) Nontariff trade barriers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The average tariff rate today on dutiable imports in the United States is approximately:
A) 5 percent of the value of imports
B) 15 percent of the value of imports
C) 20 percent of the value of imports
D) 25 percent of the value of imports
A) 5 percent of the value of imports
B) 15 percent of the value of imports
C) 20 percent of the value of imports
D) 25 percent of the value of imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Those who argue in favor of import protection generally give the impression that such restricted trade will:
A) Decrease the level of national security
B) Provide benefits to some particular industry
C) Provide benefits to the entire nation
D) Not yield welfare losses for the nation
A) Decrease the level of national security
B) Provide benefits to some particular industry
C) Provide benefits to the entire nation
D) Not yield welfare losses for the nation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In U.S.trade law,which measure permits the levying of restrictions on fairly traded imports that harm or threaten to harm American manufacturers?
A) Antidumping duty
B) Countervailing duty
C) National security clause
D) Escape clause
A) Antidumping duty
B) Countervailing duty
C) National security clause
D) Escape clause

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
During the past four decades:
A) Nontariff barriers (NTBs)and tariffs have increased in importance
B) NTBs and tariffs have decreased in importance
C) NTBs have increased and tariffs have decreased in importance
D) NTBs have decreased and tariffs have increased in importance
A) Nontariff barriers (NTBs)and tariffs have increased in importance
B) NTBs and tariffs have decreased in importance
C) NTBs have increased and tariffs have decreased in importance
D) NTBs have decreased and tariffs have increased in importance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Consider Figure 6.1.At the monopoly price as established by Boeing,Canadian consumers realize $____ of consumer surplus from the availability of aircraft.
A) $4 million
B) $8 million
C) $12 million
D) $16 million
A) $4 million
B) $8 million
C) $12 million
D) $16 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The most recent round of multilateral trade negotiations is the:
A) Kennedy Round
B) Tokyo Round
C) Doha Round
D) Geneva Round
A) Kennedy Round
B) Tokyo Round
C) Doha Round
D) Geneva Round

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose the president lowers tariffs on radios as the result of negotiations under the trade agreements program.Radio producers in the United States can appeal under the:
A) Escape clause if rising imports substantially injure the U.S.radio industry
B) Escape clause if rising unemployment occurs even though imports remain unchanged
C) Infant industry clause if rising imports cause unemployment to rise among U.S.radio workers
D) Infant industry clause if rising imports result in losses for U.S.radio companies
A) Escape clause if rising imports substantially injure the U.S.radio industry
B) Escape clause if rising unemployment occurs even though imports remain unchanged
C) Infant industry clause if rising imports cause unemployment to rise among U.S.radio workers
D) Infant industry clause if rising imports result in losses for U.S.radio companies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Industrial policy attempts to fulfill all of the following objectives except:
A) Improving the infrastructure for an industry
B) Easing transitions for workers in declining industries
C) Supporting troubled industries if the difficulty is temporary
D) Fostering industries which offer long-run comparative disadvantage
A) Improving the infrastructure for an industry
B) Easing transitions for workers in declining industries
C) Supporting troubled industries if the difficulty is temporary
D) Fostering industries which offer long-run comparative disadvantage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which international organization stipulates procedures for the settlement of international trade disputes?
A) World Trade Organization
B) World Bank
C) International Monetary Fund
D) Organization of Economic Development
A) World Trade Organization
B) World Bank
C) International Monetary Fund
D) Organization of Economic Development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure 6.3 Iraqi Computer Market and Economic Sanctions 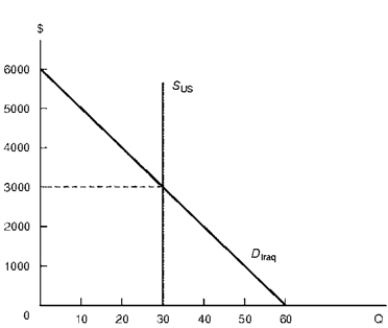
Consider Figure 6.3.With free trade,Iraq purchases ____ computers at a price of $____,and realizes $____ of consumer surplus from the availability of computers.
A) 30,$3,000,$25,000
B) 30,$3,000,$35,000
C) 30,$3,000,$45,000
D) 30,$3,000,$55,000

Consider Figure 6.3.With free trade,Iraq purchases ____ computers at a price of $____,and realizes $____ of consumer surplus from the availability of computers.
A) 30,$3,000,$25,000
B) 30,$3,000,$35,000
C) 30,$3,000,$45,000
D) 30,$3,000,$55,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 6.3 Iraqi Computer Market and Economic Sanctions 
Consider Figure 6.3.Of the quota-induced change in Iraqi consumer surplus,$____ is not transferred to other sectors of Iraq's economy and represents deadweight loss.
A) $5000
B) $10,000
C) $15,000
D) $20,000

Consider Figure 6.3.Of the quota-induced change in Iraqi consumer surplus,$____ is not transferred to other sectors of Iraq's economy and represents deadweight loss.
A) $5000
B) $10,000
C) $15,000
D) $20,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In 1995 the ____ was established to administer the new global trade rules agreed in the Uruguay Round of multilateral trade negotiations.
A) World Trade Organization
B) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
C) General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
D) United Nations
A) World Trade Organization
B) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
C) General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
D) United Nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Figure 6.3 Iraqi Computer Market and Economic Sanctions 
Consider Figure 6.3.Of the quota-induced change in Iraqi consumer surplus,the amount of the change in Iraq's consumer surplus that is transferred to other sectors of Iraq's economy is captured by the United States as:
A) Tax revenue
B) Export revenue
C) Producer surplus
D) Consumer surplus

Consider Figure 6.3.Of the quota-induced change in Iraqi consumer surplus,the amount of the change in Iraq's consumer surplus that is transferred to other sectors of Iraq's economy is captured by the United States as:
A) Tax revenue
B) Export revenue
C) Producer surplus
D) Consumer surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 6.3 Iraqi Computer Market and Economic Sanctions 
Consider Figure 6.3.In response to Iraq's armed invasion of neighboring countries,suppose the United States imposes a partial embargo that limits exports to Iraq to 10 computers.The export quota leads to an increase/decrease in the price of computers equal to $____,and an increase/decrease in consumer surplus equal to $____.
A) Increase,$2000,decrease,$40,000
B) Increase,$4000,decrease,$60,000
C) Decrease,$2000,increase,$40,000
D) Decrease,$4000,increase,$60,000

Consider Figure 6.3.In response to Iraq's armed invasion of neighboring countries,suppose the United States imposes a partial embargo that limits exports to Iraq to 10 computers.The export quota leads to an increase/decrease in the price of computers equal to $____,and an increase/decrease in consumer surplus equal to $____.
A) Increase,$2000,decrease,$40,000
B) Increase,$4000,decrease,$60,000
C) Decrease,$2000,increase,$40,000
D) Decrease,$4000,increase,$60,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The implicit industrial policies of the U.S.government have included:
A) Formulating industry-specific economic policies designed to promote national champions
B) Nationalizing basic industries such as steel and autos
C) Encouraging cartelization of aircraft and aluminum manufacturers
D) Improving the setting for industry such as communications and infrastructure
A) Formulating industry-specific economic policies designed to promote national champions
B) Nationalizing basic industries such as steel and autos
C) Encouraging cartelization of aircraft and aluminum manufacturers
D) Improving the setting for industry such as communications and infrastructure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Figure 6.3 Iraqi Computer Market and Economic Sanctions 
Consider Figure 6.3.For the United States,the export quota results in a (an):
A) Improvement in its terms of trade with Iraq
B) Increase in its export revenue
C) Increase in domestic computer prices
D) Decrease in domestic consumer surplus

Consider Figure 6.3.For the United States,the export quota results in a (an):
A) Improvement in its terms of trade with Iraq
B) Increase in its export revenue
C) Increase in domestic computer prices
D) Decrease in domestic consumer surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Figure 6.2.Effects of an Export Subsidy 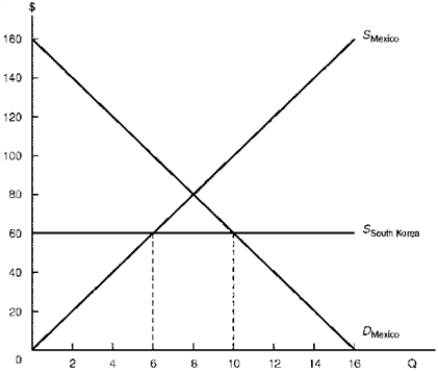
Consider Figure 6.2.With free trade,Mexican consumers purchase ____ calculators,Mexican firms produce ____ calculators,and ____ calculators are imported.
A) 10,4,6
B) 10,6,4
C) 10,8,2
D) 10,2,8

Consider Figure 6.2.With free trade,Mexican consumers purchase ____ calculators,Mexican firms produce ____ calculators,and ____ calculators are imported.
A) 10,4,6
B) 10,6,4
C) 10,8,2
D) 10,2,8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Economic sanctions are most effective in causing the target nation to modify its behavior when the:
A) Target nation had negligible economic relationships with the imposing nation prior to the sanctions
B) People of the target nation have weak cultural ties to the people of the imposing nation
C) Sanctions are levied by a large number of nations
D) Target government is supported by the majority of its people
A) Target nation had negligible economic relationships with the imposing nation prior to the sanctions
B) People of the target nation have weak cultural ties to the people of the imposing nation
C) Sanctions are levied by a large number of nations
D) Target government is supported by the majority of its people

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Figure 6.2.Effects of an Export Subsidy 
Consider Figure 6.2.With free trade,Mexicans attain $____ of consumer surplus from the availability of calculators,while Mexican producer surplus equals $____.
A) $400,$200
B) $200,$400
C) $500,$180
D) $500,$240

Consider Figure 6.2.With free trade,Mexicans attain $____ of consumer surplus from the availability of calculators,while Mexican producer surplus equals $____.
A) $400,$200
B) $200,$400
C) $500,$180
D) $500,$240

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In 1995 the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade was replaced by the ____.
A) Agency for International Development
B) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
C) United Nations Center for Trade and Development
D) World Trade Organization
A) Agency for International Development
B) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
C) United Nations Center for Trade and Development
D) World Trade Organization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Figure 6.2.Effects of an Export Subsidy 
Consider Figure 6.2.To help its firms further penetrate export markets,suppose the South Korean government provides them a production subsidy of $20 per calculator.With the subsidy,South Korean firms charge a price of $____ and export ____ calculators to Mexico.
A) $40,8
B) $40,10
C) $20,8
D) $20,10

Consider Figure 6.2.To help its firms further penetrate export markets,suppose the South Korean government provides them a production subsidy of $20 per calculator.With the subsidy,South Korean firms charge a price of $____ and export ____ calculators to Mexico.
A) $40,8
B) $40,10
C) $20,8
D) $20,10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 6.2.Effects of an Export Subsidy 
Consider Figure 6.2.The South Korean subsidy helps/hurts Mexican manufacturers,since their producer surplus rises/falls by $____.
A) Helps,rises,$60
B) Helps,rises,$100
C) Hurts,falls,$60
D) Hurts,falls,$100

Consider Figure 6.2.The South Korean subsidy helps/hurts Mexican manufacturers,since their producer surplus rises/falls by $____.
A) Helps,rises,$60
B) Helps,rises,$100
C) Hurts,falls,$60
D) Hurts,falls,$100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Consider Figure 6.1.Suppose the European government provides Airbus a subsidy of $4 million on each aircraft manufactured,and that the subsidy convinces Boeing to exit the Canadian market.As the monopoly seller,Airbus maximizes profit by selling ____ aircraft at a price of $____,and realizes profits totaling $____.
A) 6,$10 million,$36 million
B) 6,$12 million,$24 million
C) 12,$10 million,$36 million
D) 12,$12 million,$24 million
A) 6,$10 million,$36 million
B) 6,$12 million,$24 million
C) 12,$10 million,$36 million
D) 12,$12 million,$24 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Referring to Figure 6.1,the total cost of the Airbus subsidy to the European taxpayer equals:
A) $16 million
B) $20 million
C) $24 million
D) $28 million
A) $16 million
B) $20 million
C) $24 million
D) $28 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The most important determinants of sanctions include
A) Cultural factors including nationalistic attitudes
B) Strength of political opposition in the targeting nation
C) The number of nations imposing sanctions
D) All of the above
A) Cultural factors including nationalistic attitudes
B) Strength of political opposition in the targeting nation
C) The number of nations imposing sanctions
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure 6.2.Effects of an Export Subsidy 
Consider Figure 6.2.As a result of the South Korean subsidy,Mexicans find their consumer surplus:
A) Rising by $160
B) Rising by $220
C) Falling by $160
D) Falling by $220

Consider Figure 6.2.As a result of the South Korean subsidy,Mexicans find their consumer surplus:
A) Rising by $160
B) Rising by $220
C) Falling by $160
D) Falling by $220

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Referring to Figure 6.1,the Airbus subsidy leads to a (an)increase/decrease in Canadian consumer surplus of $____,as compared to the consumer surplus that existed in the absence of a subsidy.
A) Increase of $8 million
B) Increase of $10 million
C) Decrease of $8 million
D) Decrease of $10 million
A) Increase of $8 million
B) Increase of $10 million
C) Decrease of $8 million
D) Decrease of $10 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Figure 6.2.Effects of an Export Subsidy 
Consider Figure 6.2.For Mexico's producers and consumers as a whole,the South Korean subsidy leads to a:
A) $120 welfare gain
B) $320 welfare gain
C) $120 welfare loss
D) $320 welfare loss

Consider Figure 6.2.For Mexico's producers and consumers as a whole,the South Korean subsidy leads to a:
A) $120 welfare gain
B) $320 welfare gain
C) $120 welfare loss
D) $320 welfare loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider Figure 6.1.For Europe as a whole (Airbus and European taxpayers),the subsidy leads to a (an)increase/decrease in net revenues of $____.
A) Increase of $12 million
B) Increase of $16 million
C) Decrease of $12 million
D) Decrease of $16 million
A) Increase of $12 million
B) Increase of $16 million
C) Decrease of $12 million
D) Decrease of $16 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Trade adjustment assistance policies
A) Can resolve all workers' challenges to free trade
B) Attempt to share gains from free trade with disadvantaged workers
C) Have never been used to sustain a losing business concern
D) Are financed by state and local tax revenues
A) Can resolve all workers' challenges to free trade
B) Attempt to share gains from free trade with disadvantaged workers
C) Have never been used to sustain a losing business concern
D) Are financed by state and local tax revenues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Figure 6.5 Japanese Market for Jetliners 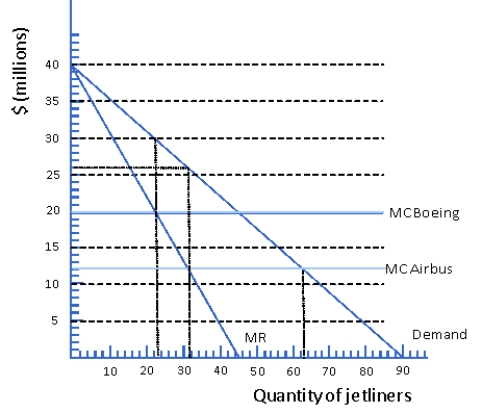
Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.5.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner but now a European manufacturer,Airbus,begins production.Airbus faces the same marginal cost as Boeing but the European government provides Airbus with a subsidy of $8 million per jetliner produced.As a result of the competition,Boeing leaves the Japanese market leaving Airbus as a monopoly.How much profit will Airbus earn?
A) $230 million
B) $350 million
C) $416 million
D) $450 million

Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.5.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner but now a European manufacturer,Airbus,begins production.Airbus faces the same marginal cost as Boeing but the European government provides Airbus with a subsidy of $8 million per jetliner produced.As a result of the competition,Boeing leaves the Japanese market leaving Airbus as a monopoly.How much profit will Airbus earn?
A) $230 million
B) $350 million
C) $416 million
D) $450 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
With the passage of the Smoot-Hawley Act in 1930,U.S.average tariffs were raised to over 50 percent on protected imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Figure 6.4 Japanese Market for Jetliners 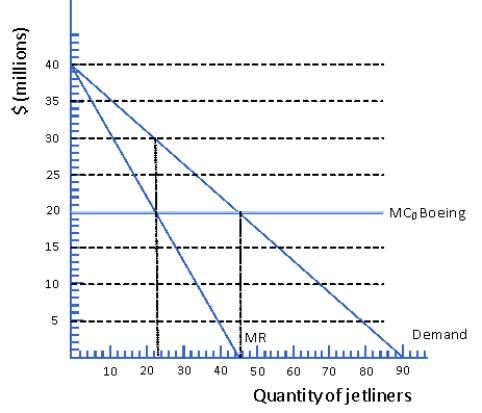
Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.4.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner.How much consumer surplus will the Japanese airlines who purchase the jetliners earn from their transactions with Boeing?
A) 0
B) $115 million
C) $230 million
D) $250 million

Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.4.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner.How much consumer surplus will the Japanese airlines who purchase the jetliners earn from their transactions with Boeing?
A) 0
B) $115 million
C) $230 million
D) $250 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
It is generally agreed that the Smoot-Hawley Act of 1930 led to improvements in U.S.exports and an overall increase in U.S.output and employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Figure 6.5 Japanese Market for Jetliners 
Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.5.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner but now a European manufacturer,Airbus,begins production.Airbus faces the same marginal cost as Boeing but the European government provides Airbus with a subsidy of $8 million per jetliner produced.As a result of the competition,Boeing leaves the Japanese market leaving Airbus as a monopoly.As a result of the entery of the subsidized producer what will happen to the consumer surplus gained by Japanese airlines from buying jetliners?
A) decrease by $109 million
B) nothing
C) increase by $50 million
D) increase by $109 million

Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.5.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner but now a European manufacturer,Airbus,begins production.Airbus faces the same marginal cost as Boeing but the European government provides Airbus with a subsidy of $8 million per jetliner produced.As a result of the competition,Boeing leaves the Japanese market leaving Airbus as a monopoly.As a result of the entery of the subsidized producer what will happen to the consumer surplus gained by Japanese airlines from buying jetliners?
A) decrease by $109 million
B) nothing
C) increase by $50 million
D) increase by $109 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
U.S.tariffs on imports from countries issued normal-trade-relations (most-favored-nation)status are often three or four times as high as those on comparable imports from nations not receiving that status.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
According to the normal-trade-relations (most-favored-nation)principle,if the United States extends MFN treatment to China and then grants a low tariff on imports of shirts from South Korea,the United States is obligated to provide the identical low-tariff on imports of shirts from China.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The high point of U.S.protectionism occurred with the passage of the Kennedy Act in the 1960s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The United States
A) Has been a heavy user of antidumping laws to protect domestic producers
B) Has rarely used antidumping laws to protect domestic producers
C) Has targeted antidumping action against China,Japan,Canada,Italy,and Germany
D) Both a and c
A) Has been a heavy user of antidumping laws to protect domestic producers
B) Has rarely used antidumping laws to protect domestic producers
C) Has targeted antidumping action against China,Japan,Canada,Italy,and Germany
D) Both a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Under the normal-trade-relations (most-favored-nation)principle,two nations agree to apply tariffs to each other at rates as low as those applied to any other nation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Figure 6.4 Japanese Market for Jetliners 
Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.4.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner.How much profit will boeing make?
A) 0
B) $150 million
C) $230 million
D) $250 million

Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.4.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner.How much profit will boeing make?
A) 0
B) $150 million
C) $230 million
D) $250 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Members of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade and its successor,the World Trade Organization,agree to the principle of nondiscrimination in trade and the reduction of trade barriers by multilateral negotiations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
According to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade and its successor,the World Trade Organization,only bilateral trade negotiations can take place between a country and its trading partners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Proponents of the Smoot-Hawley Act of 1930 viewed it as a means of combating domestic unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
According to the Reciprocal Trade Agreements Act of 1934,the President could lower tariffs by up to 10 percent of the existing level without congressional approval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Figure 6.4 Japanese Market for Jetliners 
Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.4.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner.What price will Boeing charge for jetliners in the Japanese market and how many will they sell?
A) $20 million,23
B) $20 million,46
C) $30 million,46
D) $30 million,23

Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.4.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner.What price will Boeing charge for jetliners in the Japanese market and how many will they sell?
A) $20 million,23
B) $20 million,46
C) $30 million,46
D) $30 million,23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Industrial policies
A) Require formal explicit efforts by governments
B) May be implicit
C) Have never been used by the U.S.government
D) Both a and b
A) Require formal explicit efforts by governments
B) May be implicit
C) Have never been used by the U.S.government
D) Both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure 6.5 Japanese Market for Jetliners 
Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.5.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner but now a European manufacturer,Airbus,begins production.Airbus faces the same marginal cost as Boeing but the European government provides Airbus with a subsidy of $8 million per jetliner produced.As a result of the competition,Boeing leaves the Japanese market leaving Airbus as a monopoly.How many jetlines will airbus produce and what price will they sell them for?
A) 23,$30 million
B) 32,$26 million
C) 23,$26 million
D) 32,$30 million

Consider the Japanese market for jetliners as depicted in Figure 6.5.Suppose lone producer of jetliners in the world is Boeing and Boeing faces a constant marginal cost of $20 million per jetliner but now a European manufacturer,Airbus,begins production.Airbus faces the same marginal cost as Boeing but the European government provides Airbus with a subsidy of $8 million per jetliner produced.As a result of the competition,Boeing leaves the Japanese market leaving Airbus as a monopoly.How many jetlines will airbus produce and what price will they sell them for?
A) 23,$30 million
B) 32,$26 million
C) 23,$26 million
D) 32,$30 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The Uruguay Round of trade negotiations resulted in the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade being succeeded by the World Trade Organization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



