Deck 21: Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/244
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
1
The dollar amount of sales needed to achieve a target income is computed by dividing the sum of fixed costs plus the target pretax income by the contribution margin ratio.
True
2
While the total amount of variable cost changes with the level of production, variable cost per unit
remains constant as volume changes.
remains constant as volume changes.
True
3
Curvilinear costs increase as volume of activity increases, but at a nonconstant rate.
True
4
Cost-volume-profit analysis requires management to classify all costs as either fixed or variable with respect to production or sales volume within the relevant range of operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
As the volume increases, fixed cost per unit of output remains constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Total variable costs change in proportion to changes in volume of activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Dividing a mixed cost into its separate fixed and variable cost components makes it more difficult to perform cost-volume-profit analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A step-wise variable cost can be separated into a fixed component and a variable component.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Total fixed costs change in proportion to changes in volume of activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Fixed costs per unit decrease proportionately with increases in volume of activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Cost-volume-profit analysis is a predictive tool for determining the profit consequences of future cost changes, price changes, and volume of activity changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Variable costs per unit increase proportionately with increases in volume of activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Cost-volume-profit analysis is used to predict future costs to be incurred, volumes of activity, sales to be made, and profit to be earned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
While the total amount of fixed cost remains constant with the level of production, fixed cost per
unit changes as volume changes.
unit changes as volume changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Cost-volume-profit analysis can be used to compute expected income from predicted sales and cost levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The relevant range of operations is a range of volume neither close to zero nor at maximum capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
As the level of volume of activity increases, the variable cost per unit remains constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The relevant range of operations includes extremely high and low levels of production that are unlikely to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The margin of safety is the amount that sales can drop before the company incurs a loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
While the total amount of fixed cost changes with the level of production, fixed cost per unit
remains constant as volume changes.
remains constant as volume changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Scatter diagrams plot volume (units) on the vertical axis and cost on the horizontal axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Degree of operating leverage (DOL) is defined as total contribution margin in dollars divided by pretax income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
To determine the slope of the variable cost from a scatter diagram, divide the change in cost by the change in units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
To determine the slope of the variable cost from a scatter diagram, divide the change in units by the change in cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The break-even point is the sales level at which a company neither earns a profit nor incurs a loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The method most likely to produce the most precise line of cost behavior and require the least amount of judgment is the scatter diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The high-low method is used to derive the variable cost per unit and total fixed costs using just the highest and lowest volume levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The contribution margin ratio is the percent of each sales dollar that remains after deducting the total unit variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
There are only two methods to derive an estimated line of cost behavior; the high-low method and the scatter diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A visual line fit to points in a scatter diagram may be used to identify the approximate relation between past cost and unit data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Contribution margin per unit is the amount by which a product's unit selling price exceeds its total variable cost per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Scatter diagrams plot volume (units) on the horizontal axis and cost on the vertical axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The margin of safety can be expressed in units of product, in dollars, or as a percent of sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A break-even point can be calculated either in units or in dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The contribution margin per unit is the price at which a unit must be sold in order for the company to break even.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The high-low method can be used to estimate the cost equation using just two points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The extent, or relative size, of fixed costs in the total cost structure is known as operating leverage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The basic form of cost-volume-profit analysis is often called break-even analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Least-squares regression is a statistical method for identifying cost behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The high-low method of deriving an estimated cost line uses all the data points available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A graphic depiction of the break-even point is known as a cost-volume-profit (CVP) chart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A cost-volume-profit (CVP) chart is a graph that plots number of units produced on the horizontal axis and dollars of costs and sales on the vertical axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A cost that changes as volume changes, but at a nonconstant rate, is called a:
A) Step-wise variable cost.
B) Curvilinear cost.
C) Variable cost.
D) Differential cost.
E) Fixed cost.
A) Step-wise variable cost.
B) Curvilinear cost.
C) Variable cost.
D) Differential cost.
E) Fixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An important assumption in multiproduct CVP analysis is a changing sales mix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The proportion of sales volumes for various products in a multiproduct company is known as the composite mix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Under variable costing, only costs that change in total with changes in production levels are included in product costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
On a typical cost-volume-profit graph, unit sales are shown on the horizontal axis and both dollars of sales and dollars of costs are represented on the vertical axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A cost with a flat cost line within a relevant range that shifts to another level when volume significantly changes is a(n):
A) Flat line cost.
B) Step-wise cost.
C) Curvilinear cost.
D) Incremental cost.
E) Fixed cost.
A) Flat line cost.
B) Step-wise cost.
C) Curvilinear cost.
D) Incremental cost.
E) Fixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An important assumption in multiproduct CVP analysis is a constant sales mix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The contribution margin ratio is the percent by which the margin of safety exceeds the break-even point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The absorption costing method is required for external financial reporting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A cost that remains unchanged in total despite variations in volume of activity within a relevant range is a:
A) Curvilinear cost.
B) Standard cost.
C) Variable cost.
D) Step-wise variable cost.
E) Fixed cost.
A) Curvilinear cost.
B) Standard cost.
C) Variable cost.
D) Step-wise variable cost.
E) Fixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Managers can use variable costing information for internal decision making, but they must use absorption costing for external reporting purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Under absorption costing, fixed overhead costs are excluded from product costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The variable costing method is required for external financial reporting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Cost-volume-profit analysis cannot be used when a firm produces and sells more than one product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The proportion of sales volumes for various products in a multiproduct company is known as the sales mix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
To calculate the break-even point in units, one must know unit fixed cost, unit variable cost, and sales price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A cost that changes in proportion to changes in volume of activity is a(n):
A) Incremental cost.
B) Product cost.
C) Fixed cost.
D) Variable cost.
E) Differential cost.
A) Incremental cost.
B) Product cost.
C) Fixed cost.
D) Variable cost.
E) Differential cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Under variable costing, fixed overhead costs are excluded from product costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A company's normal operating range, which excludes extremely high or low operating levels that are not likely to occur, is called the:
A) Relevant range.
B) High-low point.
C) Margin of safety.
D) Break-even point.
E) Contribution range.
A) Relevant range.
B) High-low point.
C) Margin of safety.
D) Break-even point.
E) Contribution range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Watson Company has monthly fixed costs of $83,000 and a 40% contribution margin ratio. If the company has set a target monthly income of $15,000, what dollar amount of sales must be made to produce the target income?
A) $207,500
B) $245,000
C) $37,300
D) $170,000
E) $39,200
A) $207,500
B) $245,000
C) $37,300
D) $170,000
E) $39,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A firm expects to sell 25,000 units of its product at $11 per unit and to incur variable costs per unit of $6. Total fixed costs are $70,000. The pretax net income is:
A) $90,000.
B) $55,000.
C) $380,000.
D) $125,000.
E) $150,000.
A) $90,000.
B) $55,000.
C) $380,000.
D) $125,000.
E) $150,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following costs are most likely to be classified as fixed?
A) Property taxes
B) Shipping costs
C) Sales commissions
D) Direct labor
E) Direct materials
A) Property taxes
B) Shipping costs
C) Sales commissions
D) Direct labor
E) Direct materials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The margin of safety is the excess of:
A) Break-even sales over expected sales.
B) Expected sales over variable costs.
C) Fixed costs over expected sales.
D) Expected sales over break-even sales.
E) Expected sales over fixed costs.
A) Break-even sales over expected sales.
B) Expected sales over variable costs.
C) Fixed costs over expected sales.
D) Expected sales over break-even sales.
E) Expected sales over fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following costs are most likely to be classified as variable?
A) Insurance
B) Straight-line depreciation
C) Manager salaries
D) Factory rent
E) Direct materials
A) Insurance
B) Straight-line depreciation
C) Manager salaries
D) Factory rent
E) Direct materials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
During March, a firm expects its total sales to be $160,000, its total variable costs to be $95,000, and its total fixed costs to be $25,000. The contribution margin for March is:
A) $25,000.
B) $120,000.
C) $65,000.
D) $40,000.
E) $90,000.
A) $25,000.
B) $120,000.
C) $65,000.
D) $40,000.
E) $90,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A term describing a firm's normal range of operating activities is:
A) Relevant operating analysis.
B) Break-even level of operations.
C) Margin of safety of operations.
D) Relevant range of operations.
E) High-low level of operations.
A) Relevant operating analysis.
B) Break-even level of operations.
C) Margin of safety of operations.
D) Relevant range of operations.
E) High-low level of operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Select cost information for Seacrest Enterprises is as follows: 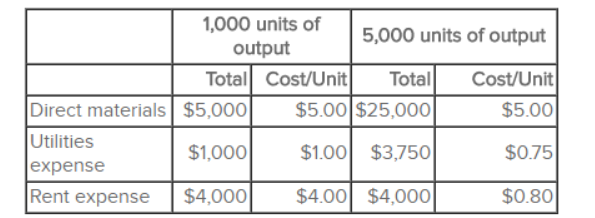
Based on this information:
A) Direct materials is a fixed cost and utilities expense is a mixed cost.
B) Utilities expense is a mixed cost and rent expense is a fixed cost.
C) Both direct materials and utilities expense are mixed costs.
D) Both direct materials and rent expense are variable costs.
E) Utilities expense is a mixed cost and rent expense is a variable cost.

Based on this information:
A) Direct materials is a fixed cost and utilities expense is a mixed cost.
B) Utilities expense is a mixed cost and rent expense is a fixed cost.
C) Both direct materials and utilities expense are mixed costs.
D) Both direct materials and rent expense are variable costs.
E) Utilities expense is a mixed cost and rent expense is a variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A firm expects to sell 25,000 units of its product at $11 per unit and to incur variable costs per unit of $6. Total fixed costs are $70,000. The total contribution margin is:
A) $380,000.
B) $125,000.
C) $150,000.
D) $55,000.
E) $90,000.
A) $380,000.
B) $125,000.
C) $150,000.
D) $55,000.
E) $90,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A cost that includes both fixed and variable cost components is called a:
A) Step-variable cost.
B) Mixed cost.
C) Curvilinear cost.
D) Differential cost.
E) Composite cost.
A) Step-variable cost.
B) Mixed cost.
C) Curvilinear cost.
D) Differential cost.
E) Composite cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Curvilinear costs always increase:
A) On a per unit basis when volume of activity goes down.
B) With decreases in volume.
C) When volume increases, but at a nonconstant rate.
D) When management performs break-even analysis.
E) In constant proportion to changes in production levels.
A) On a per unit basis when volume of activity goes down.
B) With decreases in volume.
C) When volume increases, but at a nonconstant rate.
D) When management performs break-even analysis.
E) In constant proportion to changes in production levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Cost-volume-profit analysis is based on necessary assumptions. Which of the following is not one of these assumptions?
A) Total fixed costs are held constant.
B) Costs can be classified as variable or fixed.
C) Relevant range includes all possible levels of activity that a company might experience.
D) A constant sales mix in a multiproduct company.
E) Sales price and variable costs per unit of output remain constant as volume changes.
A) Total fixed costs are held constant.
B) Costs can be classified as variable or fixed.
C) Relevant range includes all possible levels of activity that a company might experience.
D) A constant sales mix in a multiproduct company.
E) Sales price and variable costs per unit of output remain constant as volume changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Select cost information for Klondike Corporation is as follows:
Based on this information:
A) Both direct materials and rent expense are fixed costs.
B) Direct materials is a fixed cost and rent expense is a variable cost.
C) Both direct materials and rent expense are mixed costs.
D) Both direct materials and rent expense are variable costs.
E) Direct materials is a variable cost and rent expense is a fixed cost.
Based on this information:
A) Both direct materials and rent expense are fixed costs.
B) Direct materials is a fixed cost and rent expense is a variable cost.
C) Both direct materials and rent expense are mixed costs.
D) Both direct materials and rent expense are variable costs.
E) Direct materials is a variable cost and rent expense is a fixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A firm expects to sell 25,000 units of its product at $11 per unit. Pretax income is predicted to be $60,000. If the variable costs per unit are $5, total fixed costs must be:
A) $215,000.
B) $275,000.
C) $90,000.
D) $125,000.
E) $65,000.
A) $215,000.
B) $275,000.
C) $90,000.
D) $125,000.
E) $65,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An important tool in predicting the volume of activity, the costs to be incurred, the sales to be made, and the profit to be earned is:
A) Cost-volume-profit analysis.
B) Variance analysis.
C) Target income analysis.
D) Least-squares regression analysis.
E) Process costing.
A) Cost-volume-profit analysis.
B) Variance analysis.
C) Target income analysis.
D) Least-squares regression analysis.
E) Process costing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which one of the following statements is not true?
A) Total fixed costs remain the same regardless of volume within the relevant range.
B) Total variable costs change with volume.
C) Variable costs per unit remain the same regardless of the volume.
D) Total variable costs decrease as the volume increases.
E) Fixed costs per unit increase as the volume decreases.
A) Total fixed costs remain the same regardless of volume within the relevant range.
B) Total variable costs change with volume.
C) Variable costs per unit remain the same regardless of the volume.
D) Total variable costs decrease as the volume increases.
E) Fixed costs per unit increase as the volume decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If a firm's forecasted sales are $250,000 and its break-even sales are $190,000, the margin of safety in dollars is:
A) $60,000.
B) $250,000.
C) $440,000.
D) $24,000.
E) $190,000.
A) $60,000.
B) $250,000.
C) $440,000.
D) $24,000.
E) $190,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The excess of expected sales over the sales level at the break-even point is known as the:
A) Contribution margin.
B) Margin of safety.
C) Profit margin.
D) Relevant range.
E) Sales turnover.
A) Contribution margin.
B) Margin of safety.
C) Profit margin.
D) Relevant range.
E) Sales turnover.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A target income refers to:
A) Income planned for a future period.
B) Income at the break-even point.
C) Income only in a multiproduct environment.
D) Income at the minimum contribution margin.
E) Income from the most recent period.
A) Income planned for a future period.
B) Income at the break-even point.
C) Income only in a multiproduct environment.
D) Income at the minimum contribution margin.
E) Income from the most recent period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 244 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



