Deck 13: Tax Credits and Payment Procedures
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/120
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Tax Credits and Payment Procedures
1
The purpose of the tax credit for rehabilitation expenditures is to encourage the relocation of businesses from older, economically distressed areas (i.e., inner city) to newer locations.
False
2
The incremental research activities credit is 20% of the qualified research expenses that exceed the base amount.
True
3
Any unused general business credit must be carried back 3 years and then forward for 20 years.
False
4
The tax benefits resulting from tax credits and tax deductions are affected by the tax rate bracket of the taxpayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The credit for child and dependent care expenses is an example of a refundable credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A taxpayer who qualifies for the low-income housing credit claims the credit over a 20-year period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The purpose of the work opportunity tax credit is to encourage employers to hire individuals from specified target groups traditionally subject to high rates of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Employers are encouraged by the work opportunity tax credit to hire individuals who have been long-term recipients of family assistance welfare benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An employer's tax deduction for wages is affected by the work opportunity tax credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The tax credit for rehabilitation expenditures for certified historic structures differs from that for qualifying structures that are not certified historic structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If a taxpayer is required to recapture any tax credit for rehabilitation expenditures, the recapture amount need not be added to the adjusted basis of the rehabilitation expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The work opportunity tax credit is available only for wages paid to qualifying individuals during their first year of employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Nonrefundable credits are those that reduce the taxpayer's tax liability but are not paid when the amount of the credit (or credits) exceeds the taxpayer's tax liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A LIFO method is applied to general business credit carryovers, carrybacks, and utilization of credits earned during a particular year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Qualified research and experimentation expenditures are not only eligible for the 20% tax credit, but also can be expensed in the year incurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The tax benefit received from a tax credit is never affected by the tax rate of the taxpayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Some (or all) of the tax credit for rehabilitation expenditures will have to be recaptured if the rehabilitated property is disposed of prematurely or if it ceases to be qualifying property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Qualified rehabilitation expenditures include the cost of acquiring the building, but not the cost of acquiring the land.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
All taxpayers are eligible to take the basic research credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The low-income housing credit is available to low-income tenants who reside in qualifying low-income housing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The disabled access credit was enacted to encourage small businesses to make their businesses more accessible to disabled individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A small employer incurs $1,500 for consulting fees related to establishing a qualified retirement plan for its 75 employees. As a result, the employer may claim the credit for small employer pension plan startup costs for $750.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The earned income credit, a form of a negative income tax, is a refundable credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
BlueCo incurs $900,000 during the year to construct a facility that will be used exclusively for the care of its employees' pre-school age children during normal working hours. The credit for employer-provided child care available to BlueCo this year is $225,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Cardinal Company incurs $800,000 during the year to construct a facility that will be used exclusively for the care of its employees' pre-school age children during normal working hours. Assuming Cardinal claims the credit for employer-provided child care this year, its basis in the newly constructed facility is $640,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Because current U.S. corporate income tax rates are higher than many foreign corporate income tax rates only infrequently will the credit's, the overall limitation yield a lower foreign tax credit than the amount of foreign taxes actually paid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In computing the foreign tax credit, the greater of the foreign income taxes paid or the overall limitation is allowed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Unused foreign tax credits can be carried back three years and forward fifteen years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The earned income credit is available only if the taxpayer has at least one qualifying child in the household.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The maximum child tax credit under current law is $1,500 per qualifying child.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An individual generally may claim a credit for adoption expenses in the year in which the expenses are paid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The child tax credit is based on the number of the taxpayer's qualifying children under age 17.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Only married taxpayers with children are qualified to receive the earned income credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the cost of a building constructed and placed into service by an eligible small business in the current year includes the cost of a wheelchair ramp, the cost of the ramp qualifies for the disabled access credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The disabled access credit is computed at the rate of 50% of all access expenditures incurred by the taxpayer during the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A taxpayer's earned income credit is dependent on the number of his or her qualifying children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A taxpayer who meets the age requirement and receives no Social Security benefits will be entitled to the full tax credit for the elderly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If a taxpayer chooses to claim a foreign tax credit, those foreign income taxes paid can also be claimed as a deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Unless a taxpayer is disabled, the tax credit for the elderly or disabled is available only if the taxpayer is at least 59 1/2 years old.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
All foreign taxes qualify for the foreign tax credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Child and dependent care expenses include amounts paid for general household services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An employee with outside income may be able to avoid the penalty for underpayment of estimated tax by having his employer increase income tax withholdings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The additional Medicare taxes assessed on high-income individuals carry differing tax rates depending on the tax base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Child care payments to a relative are not eligible for the credit for child and dependent care expenses if the relative is a child (under age 19) of the taxpayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
On October 2, Ross quits his job with Blue Corporation. If requested by Ross, Blue Corporation must furnish a Form W-2 to Ross within 45 days after the date of the request or the final wage payment, whichever is later.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A taxpayer may qualify for the credit for child and dependent care expenses if the taxpayer's dependent is under age 17.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
John owns and operates a real estate agency as a sole proprietor. On a full-time basis, he employs his 17-year old daughter as a receptionist and his 22-year old son as a bookkeeper. Both children are subject to FICA withholding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
For purposes of computing the credit for child and dependent care expenses, the qualifying employment-related expenses are limited to an individual's actual or deemed earned income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the event that overwithholding of FICA tax occurs because the taxpayer has more than one employer, the excess amount should be claimed as a credit on the Federal income tax return of the employee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Certain high-income individuals are subject to three additional Medicare taxes-on wages, unearned income, and tax credits claimed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Expenses that are reimbursed by a taxpayer's employer under a dependent care assistance program can also qualify for the credit for child and dependent care expenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If an employee holds two jobs during the year, an overwithholding of FICA tax will result.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The maximum credit for child and dependent care expenses is $2,100 if only one spouse is employed and the other spouse is a full-time student.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Both education tax credits are available for qualified tuition expenses, and in certain instances, also may be available for room and board.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Juan refuses to give the bank where he maintains a savings account his Social Security number. Juan is subject to backup withholding for the interest earned on the savings account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Only self-employed individuals are required to make estimated tax payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The education tax credits (i.e., the American Opportunity credit and the lifetime learning credit) are available to help defray the cost of higher education regardless of the income level of the taxpayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The base amount for the Social Security portion (old age, survivors, and disability insurance) is different from that for the Medicare portion of FICA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Qualifying tuition expenses paid from the proceeds of a tax-exempt scholarship do not give rise to an education tax credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
An expatriate who works in a country with an income tax rate higher than the U.S. rate probably will find the foreign earned income exclusion preferable to the foreign tax credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Several years ago, Sarah purchased a structure for $150,000 that was placed in service in 1929. In the current year, she incurred qualifying rehabilitation expenditures of $200,000. The amount of the tax credit for rehabilitation expenditures, and the amount by which the building's basis for cost recovery would increase as a result of the rehabilitation expenditures are the following amounts.
A)$20,000 credit, $180,000 basis.
B)$20,000 credit, $200,000 basis.
C)$20,000 credit, $350,000 basis.
D)$40,000 credit, $160,000 basis.
A)$20,000 credit, $180,000 basis.
B)$20,000 credit, $200,000 basis.
C)$20,000 credit, $350,000 basis.
D)$40,000 credit, $160,000 basis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following correctly describes the tax credit for rehabilitation expenditures?
A)The cost of enlarging any existing business building is a qualifying expenditure.
B)The cost of facilities related to the building (e.g., a parking lot) is a qualifying expenditure.
C)No recapture provisions apply.
D)No credit is allowed for the rehabilitation of personal use property.
E)None of the above.
A)The cost of enlarging any existing business building is a qualifying expenditure.
B)The cost of facilities related to the building (e.g., a parking lot) is a qualifying expenditure.
C)No recapture provisions apply.
D)No credit is allowed for the rehabilitation of personal use property.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The components of the general business credit include all of the following except:
A)Credit for employer-provided child care.
B)Disabled access credit.
C)Research activities credit.
D)Tax credit for rehabilitation expenditures.
E)All of the above are components of the general business credit.
A)Credit for employer-provided child care.
B)Disabled access credit.
C)Research activities credit.
D)Tax credit for rehabilitation expenditures.
E)All of the above are components of the general business credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Several years ago, Tom purchased a structure for $300,000 that was placed in service in 1929. Three and one-half years ago he incurred qualifying rehabilitation expenditures of $600,000. In the current year, Tom sold the property in a taxable transaction. Calculate the amount of the recapture of the tax credit for rehabilitation expenditures.
A)$0
B)$24,000
C)$36,000
D)$48,000
E)None of the above
A)$0
B)$24,000
C)$36,000
D)$48,000
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Cheryl is single, has one child (age 6), and files as head of household during 2016. Her salary for the year is $19,500. She qualifies for an earned income credit of the following amount.
A)$0.
B)$3,115.
C)$3,215.
D)$3,400.
A)$0.
B)$3,115.
C)$3,215.
D)$3,400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
During the year, Green, Inc., incurs the following research expenditures:
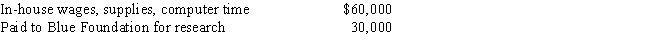 Green's qualifying research expenditures for the year are:
Green's qualifying research expenditures for the year are:
A)$60,000.
B)$75,000.
C)$79,500.
D)$90,000.
E)None of the above.
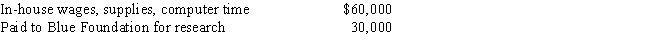 Green's qualifying research expenditures for the year are:
Green's qualifying research expenditures for the year are:A)$60,000.
B)$75,000.
C)$79,500.
D)$90,000.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Green Company, in the renovation of its building, incurs $9,000 of expenditures that qualify for the disabled access credit. The disabled access credit is:
A)$8,750.
B)$4,500.
C)$4,375.
D)$4,250.
E)None of the above.
A)$8,750.
B)$4,500.
C)$4,375.
D)$4,250.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Molly has generated general business credits over the years that have not been utilized. The amounts generated and not utilized follow:
 In the current year, 2017, her business generates an additional $15,000 general business credit. In 2017, based on her tax liability before credits, she can utilize a general business credit of up to $20,000. After utilizing the carryforwards and the current year credits, how much of the general business credit generated in 2017 is available for future years?
In the current year, 2017, her business generates an additional $15,000 general business credit. In 2017, based on her tax liability before credits, she can utilize a general business credit of up to $20,000. After utilizing the carryforwards and the current year credits, how much of the general business credit generated in 2017 is available for future years?
A)$0.
B)$1,000.
C)$14,000.
D)$15,000.
E)None of the above.
 In the current year, 2017, her business generates an additional $15,000 general business credit. In 2017, based on her tax liability before credits, she can utilize a general business credit of up to $20,000. After utilizing the carryforwards and the current year credits, how much of the general business credit generated in 2017 is available for future years?
In the current year, 2017, her business generates an additional $15,000 general business credit. In 2017, based on her tax liability before credits, she can utilize a general business credit of up to $20,000. After utilizing the carryforwards and the current year credits, how much of the general business credit generated in 2017 is available for future years?A)$0.
B)$1,000.
C)$14,000.
D)$15,000.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Cardinal Corporation hires two persons certified to be eligible employees for the work opportunity tax credit under the general rules (e.g., food stamp recipients), each of whom is paid $9,000 during the year. As a result of this event, Cardinal Corporation may claim a work opportunity credit of:
A)$1,440.
B)$2,880.
C)$4,800.
D)$7,200.
E)None of the above.
A)$1,440.
B)$2,880.
C)$4,800.
D)$7,200.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Amber is in the process this year of renovating the office building (placed in service in 1976) used by her business. Because of current Federal Regulations that require the structure to be accessible to handicapped individuals, she incurs an additional $11,000 for various features, such as ramps and widened doorways, to make her office building more accessible. The $11,000 incurred will produce a disabled access credit of what amount?
A)$0
B)$5,000
C)$5,125
D)$5,500
A)$0
B)$5,000
C)$5,125
D)$5,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which, if any, of the following correctly describes the earned income credit?
A)Would be available regardless of the amount of the taxpayer's adjusted gross income.
B)Not available to a surviving spouse.
C)A taxpayer must have a qualifying child to take advantage of the credit.
D)Is a refundable credit.
A)Would be available regardless of the amount of the taxpayer's adjusted gross income.
B)Not available to a surviving spouse.
C)A taxpayer must have a qualifying child to take advantage of the credit.
D)Is a refundable credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Roger is considering making a $6,000 investment in a venture that its promoter promises will generate immediate tax benefits for him. Roger, who does not anticipate itemizing his deductions, is in the 30% marginal income tax bracket. If the investment is of a type that produces a tax credit of 40% of the amount of the expenditure, by how much will Roger's tax liability decline because of the investment?
A)$0
B)$1,800
C)$2,200
D)$2,400
E)None of the above
A)$0
B)$1,800
C)$2,200
D)$2,400
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following best describes the treatment applicable to unused business credits?
A)Unused amounts are carried forward indefinitely.
B)Unused amounts are first carried back one year and then forward for 20 years.
C)Unused amounts are first carried back one year and then forward for 10 years.
D)Unused amounts are first carried back three years and then carried forward for 15 years.
E)None of the above.
A)Unused amounts are carried forward indefinitely.
B)Unused amounts are first carried back one year and then forward for 20 years.
C)Unused amounts are first carried back one year and then forward for 10 years.
D)Unused amounts are first carried back three years and then carried forward for 15 years.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
During 2017, Barry (who is single and has no children) earned a salary of $13,000. He is age 30. His earned income credit for the year is:
A)$0.
B)$151.
C)$359.
D)$510.
A)$0.
B)$151.
C)$359.
D)$510.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Black Company paid wages of $180,000, of which $40,000 was qualified wages for the work opportunity tax credit under the general rules. Black Company's deduction for wages for the year is:
A)$140,000.
B)$164,000.
C)$166,000.
D)$180,000.
E)None of the above.
A)$140,000.
B)$164,000.
C)$166,000.
D)$180,000.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Ahmad is considering making a $10,000 investment in a venture which its promoter promises will generate immediate tax benefits for him. Ahmad, who normally itemizes his deductions, is in the 28% marginal tax bracket. If the investment is of a type where the taxpayer may claim either a tax credit of 25% of the amount of the expenditure or an itemized deduction for the amount of the investment, what treatment normally would be most beneficial to Ahmad and by how much will Ahmad's tax liability decline because of the investment?
A)$0, take neither the itemized deduction nor the tax credit.
B)$2,500, take the tax credit.
C)$2,800, take the itemized deduction.
D)Both options produce the same benefit.
E)None of the above.
A)$0, take neither the itemized deduction nor the tax credit.
B)$2,500, take the tax credit.
C)$2,800, take the itemized deduction.
D)Both options produce the same benefit.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In March 2017, Gray Corporation hired two individuals, both of whom were certified as long-term recipients of family assistance benefits. Each employee was paid $11,000 during 2017. Gray Corporation's work opportunity tax credit amounts for 2016 is:
A)$4,000.
B)$8,000.
C)$10,000.
D)$11,000.
A)$4,000.
B)$8,000.
C)$10,000.
D)$11,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which, if any, of the following correctly describes the research activities credit?
A)The research activities credit is the greater of the incremental research credit, the basic research credit, or the energy research credit.
B)If the research activities credit is claimed, no deduction is allowed for research and experimentation expenditures.
C)The credit is not available for research conducted outside the United States.
D)All corporations qualify for the basic research credit.
E)None of the above.
A)The research activities credit is the greater of the incremental research credit, the basic research credit, or the energy research credit.
B)If the research activities credit is claimed, no deduction is allowed for research and experimentation expenditures.
C)The credit is not available for research conducted outside the United States.
D)All corporations qualify for the basic research credit.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Refundable tax credits include the:
A)Foreign tax credit.
B)Tax credit for rehabilitation expenses.
C)Credit for certain retirement plan contributions.
D)Earned income credit.
E)None of the above.
A)Foreign tax credit.
B)Tax credit for rehabilitation expenses.
C)Credit for certain retirement plan contributions.
D)Earned income credit.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Rex and Dena are married and have two children, Michelle (age 7) and Nancy (age 5). During 2017, Rex earned a salary of $24,500, received interest income of $300, and filed a joint income tax return with Dena. Dena had $0 gross income. Their earned income credit for the year is:
A)$0.
B)$5,316.
C)$5,433.
D)$5,616.
A)$0.
B)$5,316.
C)$5,433.
D)$5,616.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



