Deck 6: Merchandise Inventory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/199
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Merchandise Inventory
1
A company changes its inventory costing method each period in order to maximize net income. This is a violation of the consistency principle.
True
2
Changing the method of valuing inventory ignores the principle of ________.
A) conservatism
B) consistency
C) disclosure
D) materiality
A) conservatism
B) consistency
C) disclosure
D) materiality
B
3
Which of the following states that a company must perform strictly proper accounting only for items that are significant to the business's financial statements?
A) conservatism
B) materiality concept
C) disclosure principle
D) consistency principle
A) conservatism
B) materiality concept
C) disclosure principle
D) consistency principle
B
4
The disclosure principle states that a company should disclose all major accounting methods and procedures in the ________.
A) balance sheet
B) income statement
C) footnotes to the financial statements
D) internal accounting documents
A) balance sheet
B) income statement
C) footnotes to the financial statements
D) internal accounting documents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The consistency principle states that businesses should report the same amount of ending merchandise inventory from period to period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following principles states that a business's financial statements must report enough information for outsiders to make knowledgeable decisions about the company?
A) conservatism
B) materiality concept
C) disclosure principle
D) consistency principle
A) conservatism
B) materiality concept
C) disclosure principle
D) consistency principle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A company reports in its financial statements that it uses the FIFO method of inventory costing. This is an example of the disclosure principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is an application of conservatism?
A) reporting inventory at the lower of cost or market
B) reporting only material amounts in the financial statements
C) reporting all relevant information in the financial statements
D) using the same depreciation method from period to period
A) reporting inventory at the lower of cost or market
B) reporting only material amounts in the financial statements
C) reporting all relevant information in the financial statements
D) using the same depreciation method from period to period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The accounting principles followed for a $5,000 cost in a small company must be the same as the accounting principles followed for a $5,000 cost in a large company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A company decides to ignore a very small error in its inventory balance. This is an example of the application of the ________.
A) conservatism
B) materiality concept
C) disclosure principle
D) consistency principle
A) conservatism
B) materiality concept
C) disclosure principle
D) consistency principle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following states that the business should use the same accounting methods from period to period?
A) materiality concept
B) consistency principle
C) conservatism
D) disclosure principle
A) materiality concept
B) consistency principle
C) conservatism
D) disclosure principle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The disclosure principle states that a company should report enough information for outsiders to make knowledgeable decisions about the company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A company is uncertain whether a complex transaction should be recorded as a gain or loss. Under the conservatism principle, it should choose to treat it as a loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A company is uncertain whether a complex transaction should result in an asset being recorded at $100,000 or at $150,000. Under the conservatism principle, it should choose to show it at $100,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following principles states that a business should NOT report anticipated gains?
A) conservatism
B) materiality concept
C) disclosure
D) consistency
A) conservatism
B) materiality concept
C) disclosure
D) consistency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A company should not change the inventory costing method each period in order to maximize net income. This is an example of the disclosure principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A company discovers that its cost of goods sold is understated by an insignificant amount. It does not need to correct the error because of the conservatism principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The goal of reporting realistic figures and never overstating assets or net income applies to the ________.
A) conservatism principle
B) materiality concept
C) disclosure principle
D) consistency principle
A) conservatism principle
B) materiality concept
C) disclosure principle
D) consistency principle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The consistency principle states that a business should use the same accounting methods and procedures from period to period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A company is uncertain whether a complex transaction should be recorded as an asset or an expense. Under the conservatism principle, it should choose to treat it as an asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The tracking of inventory shrinkage due to theft, damage, or errors is done with the help of a(n) ________ of inventory.
A) authorization
B) sale
C) physical count
D) delivery
A) authorization
B) sale
C) physical count
D) delivery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Provide a definition for each of the following accounting principles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The materiality concept states that a company must ________.
A) report only such information that enhances the financial position of the company
B) perform strictly proper accounting only for significant items
C) report enough information for outsiders to make knowledgeable decisions about the company
D) use the same accounting methods and procedures from period to period
A) report only such information that enhances the financial position of the company
B) perform strictly proper accounting only for significant items
C) report enough information for outsiders to make knowledgeable decisions about the company
D) use the same accounting methods and procedures from period to period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Classic Autos specializes in selling gently used specialty sports cars and uses the specific identification method of determining ending inventory and cost of goods sold. Item 507K was sold for $90,000. Classic purchased the sports car for $50,000 and paid $1,800 for freight in and $1,000 for freight out. What is the cost of goods sold?
A) $38,200
B) $51,800
C) $51,000
D) $50,000
A) $38,200
B) $51,800
C) $51,000
D) $50,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
List and briefly discuss three measures that can be taken to maintain good controls over merchandise inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Provide a definition for each of the following accounting principles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The specific identification method of inventory requires businesses to keep detailed records of inventory sales and purchases and to also be able to carefully identify the inventory that is sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Maintaining good controls over merchandise inventory ensures that inventory purchases and sales are properly authorized and accounted for by the accounting system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Each inventory costing method matches the flow of inventory costs in a business and is used to determine ending inventory and cost of goods sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is NOT an inventory costing method?
A) specific identification
B) lower of cost or market
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out
A) specific identification
B) lower of cost or market
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A company that uses the perpetual inventory system purchased 500 pallets of industrial soap for $9,000 and paid $790 for the freight-in. The company sold the whole lot to a supermarket chain for $13,000 on account. The company uses the specific-identification method of inventory costing. Which of the following entries correctly records the cost of goods sold?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Ending inventory equals the cost of goods available for sale less beginning inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The specific identification method of inventory costing is required to be used by businesses that sell unique, easily identified inventory items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Companies determine the number of units on hand from perpetual inventory records backed up by a physical count.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following inventory valuation methods should be used for unique items?
A) first-in, first-out
B) last-in, first-out
C) weighted-average
D) specific identification
A) first-in, first-out
B) last-in, first-out
C) weighted-average
D) specific identification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following inventory costing methods is based on the actual cost of each particular unit of inventory?
A) specific identification
B) weighted-average
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out
A) specific identification
B) weighted-average
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Ending inventory is calculated by multiplying the number of units on hand by the unit cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements is true of a good merchandise inventory control system?
A) It eliminates the need for authorization of merchandise purchases.
B) It ensures that a physical count of inventory is not required.
C) It often prevents the company from a stockout.
D) It eliminates the need to examine inventory purchases for damage.
A) It eliminates the need for authorization of merchandise purchases.
B) It ensures that a physical count of inventory is not required.
C) It often prevents the company from a stockout.
D) It eliminates the need to examine inventory purchases for damage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Properly recording inventory when sold and removing the units sold from the inventory count will prevent a company from running out of inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is NOT included in a perpetual inventory record?
A) identification of the inventory item
B) cost per unit
C) unit selling price
D) quantity on hand
A) identification of the inventory item
B) cost per unit
C) unit selling price
D) quantity on hand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The total cost spent on inventory that was available to be sold during a period is called the cost of goods sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements regarding FIFO is incorrect?
A) Ending inventory is based on the costs of the most recent purchases.
B) FIFO is consistent with the physical movement of inventory for most companies.
C) The first units to come in are assumed to be the first units sold.
D) FIFO is a specific identification costing method because companies sell their oldest inventory first.
A) Ending inventory is based on the costs of the most recent purchases.
B) FIFO is consistent with the physical movement of inventory for most companies.
C) The first units to come in are assumed to be the first units sold.
D) FIFO is a specific identification costing method because companies sell their oldest inventory first.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When a company uses the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, the cost of goods sold represents the cost of the most recently purchased goods and the value of ending inventory represents the cost of the oldest goods in stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A company purchased 90 units for $20 each on January 31. It purchased 180 units for $25 each on February 28. It sold 180 units for $60 each from March 1 through December 31. If the company uses the first-in, first-out inventory costing method, what is the amount of Cost of Goods Sold on the income statement for the year ending December 31? (Assume that the company uses a perpetual inventory system.)
A) $1,800
B) $4,500
C) $4,050
D) $6,300
A) $1,800
B) $4,500
C) $4,050
D) $6,300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following inventory costing methods uses the cost of the oldest purchases to compute the cost of goods sold?
A) specific identification
B) weighted-average
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out
A) specific identification
B) weighted-average
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Countrywide Sales sold 400 units of product to a customer on account. The selling price was $28 per unit, and the cost, according to the company's inventory records, was $14 per unit. Prepare the journal entry to record the cost of goods sold. (Assume a perpetual inventory system and the FIFO inventory costing method.) Omit explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Modern Lifestyle Furniture began June with merchandise inventory of 45 sofas that cost a total of $31,500. During the month, Modern purchased and sold merchandise on account as follows:
Prepare a perpetual inventory record, using the FIFO inventory costing method, and determine the company's cost of goods sold, ending merchandise inventory, and gross profit.
| Purchases | Cost of Goods Sold | Inventory on Hand |

Prepare a perpetual inventory record, using the FIFO inventory costing method, and determine the company's cost of goods sold, ending merchandise inventory, and gross profit.
| Purchases | Cost of Goods Sold | Inventory on Hand |


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A company that uses the perpetual inventory system purchased 500 pallets of industrial soap for $10,000 and paid $950 for the freight-in. The company sold the whole lot to a supermarket chain for $13,000 on account. Which of the following entries correctly records the sale?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
First Street Merchandisers has total cost of goods sold of $54,500, total beginning inventory of $18,500, and total ending inventory of $22,100. Cost of goods available for sale is $73,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
James Sales sold 450 units of product to a customer on account. The company uses the perpetual inventory system and the FIFO inventory costing method. The selling price was $28 per unit, and the cost, according to the company's inventory records, was $12 per unit. Prepare the journal entries to record the sale. Omit explanations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Under which of the following inventory costing methods is the ending inventory based on the costs of the most recent purchases?
A) specific identification
B) weighted-average
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out
A) specific identification
B) weighted-average
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A company that uses the perpetual inventory system sold goods to a customer for cash for $4,200. The cost of the goods sold was $1,000. Which of the following journal entries correctly records this transaction?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Meadows, Inc. sold 500 units of inventory at $25 per unit on account. The company uses the perpetual inventory system and the FIFO inventory costing method. The beginning inventory included 400 units at $15 per unit. The most recent purchases include 600 units at $18 per unit. Prepare the journal entries to record the sale. Omit explanations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A company purchased 500 units for $30 each on January 31. It purchased 550 units for $33 each on February 28. It sold a total of 650 units for $45 each from March 1 through December 31. What is the cost of ending inventory on December 31 if the company uses the first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory costing method? (Assume that the company uses a perpetual inventory system.)
A) $13,200
B) $10,200
C) $12,000
D) $1,800
A) $13,200
B) $10,200
C) $12,000
D) $1,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Nichols, Inc. had the following balances and transactions during 2018: What would be reported for Ending Merchandise Inventory on the balance sheet at December 31, 2018 if the perpetual inventory system and the first-in, first-out inventory costing method are used?
A) $6,400
B) $51,000
C) $37,400
D) $24,000
A) $6,400
B) $51,000
C) $37,400
D) $24,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Baldwin, Inc. had the following balances and transactions during 2019: What would be reported as Cost of Goods Sold on the income statement for the year ending December 31, 2019 if the perpetual inventory system and the first-in, first-out inventory costing method are used?
A) $10,125
B) $14,675
C) $29,475
D) $18,725
A) $10,125
B) $14,675
C) $29,475
D) $18,725

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A company that uses the perpetual inventory system sold goods for $2,600 to a customer on account. The company had purchased the inventory for $500. Which of the following journal entries correctly records the cost of goods sold?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Western Sky, Inc. sold 500 units of inventory at $25 per unit for cash. The company uses the perpetual inventory system and the FIFO inventory costing method. The beginning inventory included 550 units at a cost of $15 per unit. The cost of the most recent purchases is $10 per unit. Prepare the journal entries to record the sale. Omit explanations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A company that uses the perpetual inventory system sold goods to a customer on account for $4,000. The cost of the goods sold was $2,000. Which of the following journal entries correctly records this transaction?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Costas, Inc. purchased inventory on account for $6,500. Prepare the journal entry to record the purchase of inventory on account. (Assume a perpetual inventory system.) Omit explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The last-in, first-out (LIFO) costing system is permitted under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A company purchased 300 units for $20 each on January 31. It purchased 200 units for $40 each on February 28. It sold a total of 250 units for $110 each from March 1 through December 31. If the company uses the last-in, first-out inventory costing method, calculate the cost of ending inventory on December 31. (Assume that the company uses a perpetual inventory system.)
A) $10,000
B) $22,500
C) $5,000
D) $250
A) $10,000
B) $22,500
C) $5,000
D) $250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Designer Furniture began June with merchandise inventory of 45 sofas that cost a total of $31,500. During the month, Designer Furniture purchased and sold merchandise on account as follows:
Prepare a perpetual inventory record, using the LIFO inventory costing method, and determine the company's cost of goods sold, ending merchandise inventory, and gross profit.
| Purchases | Cost of Goods Sold | Inventory on Hand |
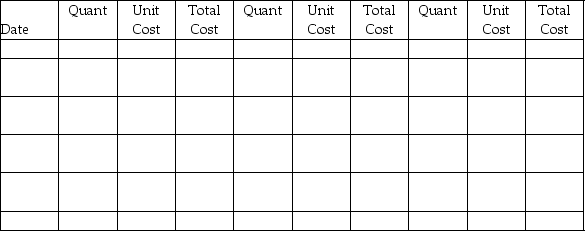
Prepare a perpetual inventory record, using the LIFO inventory costing method, and determine the company's cost of goods sold, ending merchandise inventory, and gross profit.
| Purchases | Cost of Goods Sold | Inventory on Hand |


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A company purchased 400 units for $30 each on January 31. It purchased 135 units for $40 each on February 28. It sold 200 units for $55 each from March 1 through December 31. If the company uses the last-in, first-out inventory costing method, what is the amount of Cost of Goods Sold on the income statement for the year ending December 31? (Assume that the company uses a perpetual inventory system.)
A) $7,350
B) $5,400
C) $12,000
D) $17,400
A) $7,350
B) $5,400
C) $12,000
D) $17,400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Rally Wheels, Inc. had the following balances and transactions during 2018: What would the company's ending merchandise inventory cost be on December 31, 2018 if the perpetual inventory system and the last-in, first-out inventory costing method are used?
A) $16,850
B) $75,000
C) $58,150
D) $60,800
A) $16,850
B) $75,000
C) $58,150
D) $60,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), companies may only use the specific identification, FIFO, and weighted-average methods to cost inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following statements regarding LIFO is incorrect?
A) The last units in are assumed to be the first units sold.
B) Ending inventory comes from the most recent purchases.
C) This method leaves the oldest costs in ending inventory.
D) LIFO is an assumption about how costs flow.
A) The last units in are assumed to be the first units sold.
B) Ending inventory comes from the most recent purchases.
C) This method leaves the oldest costs in ending inventory.
D) LIFO is an assumption about how costs flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following inventory costing methods requires the calculation of a new average cost after each purchase?
A) specific identification
B) weighted-average
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out
A) specific identification
B) weighted-average
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When a company uses the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, the cost of goods sold represents the costs of most recently purchased goods, and the ending inventory represents the oldest costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following inventory costing methods uses the costs of the oldest purchases to calculate the value of the ending inventory?
A) specific identification
B) weighted-average
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out
A) specific identification
B) weighted-average
C) last-in, first-out
D) first-in, first-out

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When using the weighted-average inventory costing method in a perpetual inventory system, a new weighted average cost per unit is computed at the end of each quarter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The last-in, first-out (LIFO) costing system may or may not match the physical flow of goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Centennial, Inc. sold 600 units of inventory at $20 per unit on account. The company uses the perpetual inventory system and the last-in, first-out (LIFO) inventory costing system. The beginning inventory included 200 units at $9 per unit. The most recent purchases include 700 units at $12 per unit. The sale occurred after the last purchase.
a. Prepare the journal entries to record the sale. Omit explanations.
b. Compute the cost of the ending inventory. Label your work.
a. Prepare the journal entries to record the sale. Omit explanations.
b. Compute the cost of the ending inventory. Label your work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A company purchased 400 units for $50 each on January 31. It purchased 200 units for $35 each on February 28. It sold a total of 250 units for $50 each from March 1 through December 31. If the company uses the weighted-average inventory costing method, calculate the cost of ending inventory on December 31. (Assume that the company uses a perpetual inventory system. Round any intermediate calculations two decimal places, and your final answer to the nearest dollar.)
A) $27,000
B) $15,750
C) $11,250
D) $14,875
A) $27,000
B) $15,750
C) $11,250
D) $14,875

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Under the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, the cost of goods sold is based on the oldest purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Weighted average cost per unit is determined by dividing the cost of goods available for sale by the number of units available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The Organizer Store uses the weighted-average inventory costing method in a perpetual inventory system. The unit cost of the beginning inventory for inventory item X500 was $10 per unit and the first purchase of the period has a unit cost of $12 per unit. The weighted average cost per unit is $11. Assume multiple units were purchased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
State the accounting term that applies to each of the following definitions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Jameson, Inc. had the following balances and transactions during 2019: What would be reported for Cost of Goods Sold on the income statement for the year ending December 31, 2019 if the perpetual inventory system and the last-in, first-out inventory costing method are used?
A) $18,145
B) $13,825
C) $4,320
D) $16,920
A) $18,145
B) $13,825
C) $4,320
D) $16,920

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
State the accounting term that applies to each of the following definitions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 199 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



