Deck 16: Nuclear Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/89
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Nuclear Chemistry
1
An alpha particle may be represented by ________.
A)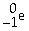
B)(1n)
C)(4He)
D)(1H)
A)
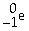
B)(1n)
C)(4He)
D)(1H)
(4He)
2
Which of the following does not carry neutrons?
A)(1n)
B)alpha rays
C)(1H)
D)deuterium
A)(1n)
B)alpha rays
C)(1H)
D)deuterium
(1H)
3
Isotopes have ________.
A)the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
B)the same number of neutrons but different number of protons
C)the same number protons and the same number of neutrons
D)different number protons and neutrons
A)the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
B)the same number of neutrons but different number of protons
C)the same number protons and the same number of neutrons
D)different number protons and neutrons
the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
4
Which of the following has a mass number of 1?
A)proton
B)neutron
C)helium
D)both A and B
A)proton
B)neutron
C)helium
D)both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How long will it take for a 5.0 g tritium sample to decay down to 0.313 g? The half-life of tritium is 12 years.
A)12 yrs
B)24 yrs
C)48 yrs
D)96 yrs
A)12 yrs
B)24 yrs
C)48 yrs
D)96 yrs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following has an atomic number of 0?
A)proton
B)neutron
C)positron
D)deuterium
A)proton
B)neutron
C)positron
D)deuterium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Binding energy is ________.
A)the amount of mass that is converted to energy during a nuclear reaction
B)the amount of mass produced during a nuclear reaction
C)the amount of energy released when an atom forms from its subatomic particles
D)the amount of energy absorbed when an atom forms from its subatomic particles
A)the amount of mass that is converted to energy during a nuclear reaction
B)the amount of mass produced during a nuclear reaction
C)the amount of energy released when an atom forms from its subatomic particles
D)the amount of energy absorbed when an atom forms from its subatomic particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If the half-life of a hypothetical isotope is 5 hr, the leftover amount of an original quantity of 20.0 g after 15 hr will be ________.
A)2.5 g
B)5.0 g
C)6.67 g
D)10.0 g
A)2.5 g
B)5.0 g
C)6.67 g
D)10.0 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Given the following half-lives, which of the following isotopes is the least stable?
A)0.001 s
B)0.92 s
C)56 s
D)72 s
A)0.001 s
B)0.92 s
C)56 s
D)72 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An beta particle may be represented by ________.
A)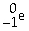
B)(1n)
C)(4He)
D)(1H)
A)
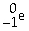
B)(1n)
C)(4He)
D)(1H)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The n/p ratio of stable isotopes becomes larger than 1, when the atomic number is larger than ________.
A)10
B)18
C)20
D)24
A)10
B)18
C)20
D)24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is the heaviest particle?
A)deuterium
B)neutron
C)alpha particle
D)beta particle
A)deuterium
B)neutron
C)alpha particle
D)beta particle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Mass defect is ________.
A)the amount of mass that is converted to energy during a nuclear reaction
B)the amount of mass produced during a nuclear reaction
C)the amount of energy released when an atom forms from its subatomic particles
D)the amount of energy absorbed when an atom forms from its subatomic particles
A)the amount of mass that is converted to energy during a nuclear reaction
B)the amount of mass produced during a nuclear reaction
C)the amount of energy released when an atom forms from its subatomic particles
D)the amount of energy absorbed when an atom forms from its subatomic particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The relationship between 16O, 17O and 18O is ________.
A)isotopes
B)isomers
C)isobars
D)none of the above
A)isotopes
B)isomers
C)isobars
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which is the lightest among the following particles?
A)proton
B)neutron
C)alpha particle
D)beta particle
A)proton
B)neutron
C)alpha particle
D)beta particle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following does not carry proton(s)?
A)(1H)
B)alpha rays
C)deuterium
D)gamma-rays
A)(1H)
B)alpha rays
C)deuterium
D)gamma-rays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Heavy water is ________.
A)water that contains cations such as magnesium, ferric and calcium
B)water whose hydrogens are deuterium
C)water whose hydrogens carry one neutron
D)both B and C
A)water that contains cations such as magnesium, ferric and calcium
B)water whose hydrogens are deuterium
C)water whose hydrogens carry one neutron
D)both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The only element whose most stable isotope has n/p < 1 is ________.
A)hydrogen
B)carbon
C)oxygen
D)helium
A)hydrogen
B)carbon
C)oxygen
D)helium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is able to penetrate the easiest through human tissue?
A)alpha rays
B)beta rays
C)neutrons
D)gamma rays
A)alpha rays
B)beta rays
C)neutrons
D)gamma rays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a nucleon?
A)proton
B)electron
C)postiron
D)both A and B
A)proton
B)electron
C)postiron
D)both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify X in the reaction below. 238U + 12C → 244Cf + X
A)6 electrons
B)1 alpha particle
C)3 protons
D)6 neutrons
A)6 electrons
B)1 alpha particle
C)3 protons
D)6 neutrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Nuclear radiation is harmful because of ________.
A)the high energy particles produced
B)the electromagnetic radiation emitted by a nucleus during the nuclear change
C)the ionizing of biological molecules
D)all of the above
A)the high energy particles produced
B)the electromagnetic radiation emitted by a nucleus during the nuclear change
C)the ionizing of biological molecules
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When an unstable nucleus expels a positron ________.
A)its mass number is decreased by four units
B)its atomic number is decreased by one unit
C)its atomic number is increased by one unit
D)its mass number is decreased by one unit
A)its mass number is decreased by four units
B)its atomic number is decreased by one unit
C)its atomic number is increased by one unit
D)its mass number is decreased by one unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An electron is a nucleon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Identify X in the reaction below. 27Al + 4He → X + 1n
A)(31P)
B)(30P)
C)(30S)
D)(31Si)
A)(31P)
B)(30P)
C)(30S)
D)(31Si)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When nickel-63 is converted to copper-63 ________.
A)an electron is captured
B)an alpha particle is emitted
C)an electron is released
D)a neutron is released
A)an electron is captured
B)an alpha particle is emitted
C)an electron is released
D)a neutron is released

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The main problem nuclear reactors have when uranium-235 serves as the fuel is ________.
A)the production of more neutrons that the reaction consumes
B)the production of gamma rays
C)the consumption of more alpha particles than the available alpha particles
D)the immense amount of energy produced
A)the production of more neutrons that the reaction consumes
B)the production of gamma rays
C)the consumption of more alpha particles than the available alpha particles
D)the immense amount of energy produced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is the easiest to block from penetrating?
A)alpha emissions
B)beta emissions
C)neutrons
D)gamma rays
A)alpha emissions
B)beta emissions
C)neutrons
D)gamma rays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The reaction below is an example of ________. 12C + 12C → 24Mg
A)fission
B)fusion
C)isotope coupling
D)transmutation
A)fission
B)fusion
C)isotope coupling
D)transmutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The reaction below is an example of ________. 235U → 139Ba + 94Kr + 2 1n
A)fission
B)fusion
C)isotope
D)transmutation
A)fission
B)fusion
C)isotope
D)transmutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When a neutron is transformed into a proton what else is emitted?
A)a beta particle
B)an electron
C)an alpha particle
D)Either A or B; both of them represent the same particle.
A)a beta particle
B)an electron
C)an alpha particle
D)Either A or B; both of them represent the same particle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the missing particle in the reaction below? 1p + 0e → ?
A)(2p)
B)(1H)
C)(1n)
D)(4He)
A)(2p)
B)(1H)
C)(1n)
D)(4He)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Identify X in the reaction below. X + 1n → 142Ba + 91Kr + 3 1n
A)(235Th)
B)(238U)
C)(235U)
D)(234Pa)
A)(235Th)
B)(238U)
C)(235U)
D)(234Pa)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The mercury-197 to gold-197 conversion is accompanied by ________.
A)an electron capture
B)an electron release
C)an alpha emission
D)a neutron capture
A)an electron capture
B)an electron release
C)an alpha emission
D)a neutron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When carbon-14 is converted to nitrogen-14 ________.
A)an electron is captured
B)an alpha particle is emitted
C)an electron is released
D)a neutron is released
A)an electron is captured
B)an alpha particle is emitted
C)an electron is released
D)a neutron is released

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When an unstable nucleus emits a beta particle ________.
A)its mass number is decreased by four units
B)its atomic number is decreased by two units
C)its atomic number is increased by one unit
D)its mass number is decreased by one unit
A)its mass number is decreased by four units
B)its atomic number is decreased by two units
C)its atomic number is increased by one unit
D)its mass number is decreased by one unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following transformations is not an electron capture?
A)(201Hg → 201Au)
B)(81Rb → 81Kr)
C)(231Th → 231Pa)
D)p → n
A)(201Hg → 201Au)
B)(81Rb → 81Kr)
C)(231Th → 231Pa)
D)p → n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following transformations is not an alpha emission?
A)(14C → 14N)
B)(225Ac → 221Fr)
C)(241Am → 237Np)
D)(218Po → 214Pb)
A)(14C → 14N)
B)(225Ac → 221Fr)
C)(241Am → 237Np)
D)(218Po → 214Pb)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
12C is the most stable carbon isotope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When radium-226 is converted to radon-222 ________.
A)an electron is captured
B)an alpha particle is emitted
C)an electron is released
D)a neutron is released
A)an electron is captured
B)an alpha particle is emitted
C)an electron is released
D)a neutron is released

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
During the MRI procedure the human is placed in a magnetic field and radio waves are used to probe certain nuclei in the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A fusion reaction is more energetic than a fission reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Many radioactive nuclei release energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation, such as gamma rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The daughter isotope of 180Hg when it undergoes alpha-emission is 176Pt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A nuclear reaction involves much higher energies than a chemical reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The daughter isotope of 196Po when it undergoes alpha-emission is 200Pb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
35Cl and 37Cl are isotopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
13C is the carbon isotope used for carbon dating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The half-life of an isotope decreases as the initial concentration decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A fission reaction is always endothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The daughter isotope of 196Po when it undergoes beta-emission is 196At.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Isotopes with the lowest possible n/p ratio are the most stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The atomic number of a neutron is 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A beta particle has a -1 charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Both the proton and neutron have the same mass number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An alpha particle is neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The n/p > 1 ratio appears in elements whose atomic number is greater than 24.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The larger the half-life value, the more stable the isotope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Nuclear radiation can cause biological damage by the weakening or breaking of bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The half life of 14C is close to 6,000 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
______ → 226Rn + 4He

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Calculate the binding energy of oxygen-16 in J/mol. This isotope has an atomic mass of 15.9949 g/mol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
238U + ______ → 239Np + -1e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
135Nd → 24Mg + ______

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
3H + 2H → ______ + 1n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the mass defect of the lithium-9 isotope in g/mol? Lithium-9 has an atomic mass of 9.0273 g/mol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Nuclear fission is sometimes referred to as the "holy grail" for energy production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
16O + 4He → ______

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
37Ar + -1e → ______

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
22Na → ______ + +1e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The half-life of chlorine-34 is 1.52 seconds. How much time will pass before a given sample of chlorine-34 decays by 60%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Calculate the binding energy of neon-22 in J/mol. This isotope has an atomic mass of 21.9914 g/mol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
14N + 4He → ______ + 1H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Calculate the amount of energy released when this nuclear reaction occurs inside an atomic warhead:
1n + 235U → 137Te + 97Zr + 2 1n
(235U = 235.0439 g/mol; 137Te = 136.9254 g/mol; 97Zr = 96.9110 g/mol; 1n = 1.00866 g/mol)
1n + 235U → 137Te + 97Zr + 2 1n
(235U = 235.0439 g/mol; 137Te = 136.9254 g/mol; 97Zr = 96.9110 g/mol; 1n = 1.00866 g/mol)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is the mass defect of the carbon-14 isotope (in g/mol)? Carbon-14 has an atomic mass of 14.0032 g/mol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Uranium-238 can capture a neutron inside a nuclear reactor (a so-called breeder reactor), producing an isotope of plutonium and two beta particles. The plutonium can then itself be used as a nuclear fuel. Write a balanced equation for the breeder reactor's production of plutonium (include isotope number)from uranium-238.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Fusion reactors of the future hope to make use of the following reaction:
2H + 3H → 4He + 1n
How much energy is released in this process (in J/mol)?
(2H = 2.0141 g/mol; 3H = 3.0160 g/mol; 4He = 4.0026 g/mol; 1n = 1.00866 g/mol)
2H + 3H → 4He + 1n
How much energy is released in this process (in J/mol)?
(2H = 2.0141 g/mol; 3H = 3.0160 g/mol; 4He = 4.0026 g/mol; 1n = 1.00866 g/mol)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
1n + ______ → 141Ba + 92Kr + 3 1n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Match each of the transformations that appear in the questions with the process that appears in the list below. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



